
Al-Andalus
Encyclopedia

Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar...
and Septimania
Septimania
Septimania was the western region of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed under the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septimania was ceded to their king, Theodoric II. Under the Visigoths it was known as simply Gallia or Narbonensis. It corresponded roughly with the modern...
governed by Muslims (given the generic name of Moors
Moors
The description Moors has referred to several historic and modern populations of the Maghreb region who are predominately of Berber and Arab descent. They came to conquer and rule the Iberian Peninsula for nearly 800 years. At that time they were Muslim, although earlier the people had followed...
), at various times in the period between 711 and 1492, although the territorial boundaries underwent constant changes due to wars with the Christian Kingdoms.
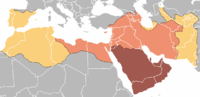
Following the Muslim conquest of Hispania
Umayyad conquest of Hispania
The Umayyad conquest of Hispania is the initial Islamic Ummayad Caliphate's conquest, between 711 and 718, of the Christian Visigothic Kingdom of Hispania, centered in the Iberian Peninsula, which was known to them under the Arabic name al-Andalus....
, Al-Andalus was divided into five administrative areas roughly corresponding to Andalusia
Andalusia
Andalusia is the most populous and the second largest in area of the autonomous communities of Spain. The Andalusian autonomous community is officially recognised as a nationality of Spain. The territory is divided into eight provinces: Huelva, Seville, Cádiz, Córdoba, Málaga, Jaén, Granada and...
, Galicia and Portugal
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
, Castile
Castile (historical region)
A former kingdom, Castile gradually merged with its neighbours to become the Crown of Castile and later the Kingdom of Spain when united with the Crown of Aragon and the Kingdom of Navarre...
and León
Kingdom of León
The Kingdom of León was an independent kingdom situated in the northwest region of the Iberian Peninsula. It was founded in AD 910 when the Christian princes of Asturias along the northern coast of the peninsula shifted their capital from Oviedo to the city of León...
, Aragon
Aragon
Aragon is a modern autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. Located in northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces : Huesca, Zaragoza, and Teruel. Its capital is Zaragoza...
and Catalonia
Catalonia
Catalonia is an autonomous community in northeastern Spain, with the official status of a "nationality" of Spain. Catalonia comprises four provinces: Barcelona, Girona, Lleida, and Tarragona. Its capital and largest city is Barcelona. Catalonia covers an area of 32,114 km² and has an...
, and Septimania
Septimania
Septimania was the western region of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed under the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septimania was ceded to their king, Theodoric II. Under the Visigoths it was known as simply Gallia or Narbonensis. It corresponded roughly with the modern...
. As a political domain or domains, it successively constituted a province of the Umayyad Caliphate, initiated by the Caliph Al-Walid I (711–750); the Emirate of Córdoba (c. 750–929); the Caliphate of Córdoba
Caliphate of Córdoba
The Caliphate of Córdoba ruled the Iberian peninsula and part of North Africa, from the city of Córdoba, from 929 to 1031. This period was characterized by remarkable success in trade and culture; many of the masterpieces of Islamic Iberia were constructed in this period, including the famous...
(929–1031); and the Caliphate of Córdoba's taifa
Taifa
In the history of the Iberian Peninsula, a taifa was an independent Muslim-ruled principality, usually an emirate or petty kingdom, though there was one oligarchy, of which a number formed in the Al-Andalus after the final collapse of the Umayyad Caliphate of Córdoba in 1031.-Rise:The origins of...
(successor) kingdoms. Rule under these kingdoms saw the rise in cultural exchange and cooperation between Christians, Muslims, and Jews. Under the Caliphate of Córdoba, al-Andalus was a beacon of learning, and the city of Córdoba
Córdoba, Spain
-History:The first trace of human presence in the area are remains of a Neanderthal Man, dating to c. 32,000 BC. In the 8th century BC, during the ancient Tartessos period, a pre-urban settlement existed. The population gradually learned copper and silver metallurgy...
became one of the leading cultural and economic centres in both the Mediterranean Basin
Mediterranean Basin
In biogeography, the Mediterranean Basin refers to the lands around the Mediterranean Sea that have a Mediterranean climate, with mild, rainy winters and hot, dry summers, which supports characteristic Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub vegetation...
and the Islamic world.
In succeeding centuries, Al-Andalus became a province of the Berber
Berber people
Berbers are the indigenous peoples of North Africa west of the Nile Valley. They are continuously distributed from the Atlantic to the Siwa oasis, in Egypt, and from the Mediterranean to the Niger River. Historically they spoke the Berber language or varieties of it, which together form a branch...
Muslim
Muslim
A Muslim, also spelled Moslem, is an adherent of Islam, a monotheistic, Abrahamic religion based on the Quran, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God as revealed to prophet Muhammad. "Muslim" is the Arabic term for "submitter" .Muslims believe that God is one and incomparable...
dynasties of the Almoravids
Almoravids
The Almoravids were a Berber dynasty of Morocco, who formed an empire in the 11th-century that stretched over the western Maghreb and Al-Andalus. Their capital was Marrakesh, a city which they founded in 1062 C.E...
and Almohads, subsequently fragmenting into a number of minor states, most notably the Emirate of Granada
Emirate of Granada
The Emirate of Granada , also known as the Nasrid Kingdom of Granada , was an emirate established in 1238 following the defeat of Muhammad an-Nasir of the Almohad dynasty by an alliance of Christian kingdoms at the Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa in 1212...
. With the support of local inhabitants of the Iberian Peninsula the Almoravids deposed of the taifa Muslim princes, after helping to repel Christian attacks on the region by Alfonso VI. Rule under the Almoravids and Almohads saw a decline in cultural and social exchange and increased persecution of religious minorities, with a return to more fundamentalist forms of Islam.
For much of its history, Al-Andalus existed in conflict with Christian
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
kingdoms to the north, which at first were forced into subservience but eventually overpowered their Muslim neighbors to the South. In 1085, Alfonso VI of León and Castile captured Toledo
Toledo, Spain
Toledo's Alcázar became renowned in the 19th and 20th centuries as a military academy. At the outbreak of the Spanish Civil War in 1936 its garrison was famously besieged by Republican forces.-Economy:...
, precipitating a gradual decline until, by 1236, with the fall of Córdoba, the Emirate of Granada remained the only Muslim-ruled territory in what is now Spain
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
. The Portuguese
Portugal
Portugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
Reconquista
Reconquista
The Reconquista was a period of almost 800 years in the Middle Ages during which several Christian kingdoms succeeded in retaking the Muslim-controlled areas of the Iberian Peninsula broadly known as Al-Andalus...
culminated in 1249 with the conquest of the Algarve by Afonso III
Afonso III of Portugal
Afonso III , or Affonso , Alfonso or Alphonso or Alphonsus , the Bolognian , the fifth King of Portugal and the first to use the title King of Portugal and the Algarve, from 1249...
. In 1238, the Emirate of Granada
Emirate of Granada
The Emirate of Granada , also known as the Nasrid Kingdom of Granada , was an emirate established in 1238 following the defeat of Muhammad an-Nasir of the Almohad dynasty by an alliance of Christian kingdoms at the Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa in 1212...
officially became a tributary state
Tributary state
The term tributary state refers to one of the two main ways in which a pre-modern state might be subordinate to a more powerful neighbour. The heart of the relationship was that the tributary would send a regular token of submission to the superior power...
to the Kingdom of Castile
Crown of Castile
The Crown of Castile was a medieval and modern state in the Iberian Peninsula that formed in 1230 as a result of the third and definitive union of the crowns and parliaments of the kingdoms of Castile and León upon the accession of the then King Ferdinand III of Castile to the vacant Leonese throne...
, then ruled by King Ferdinand III
Ferdinand III of Castile
Saint Ferdinand III, T.O.S.F., was the King of Castile from 1217 and León from 1230. He was the son of Alfonso IX of León and Berenguela of Castile. Through his second marriage he was also Count of Aumale. He finished the work done by his maternal grandfather Alfonso VIII and consolidated the...
. On January 2, 1492, Emir Muhammad XII surrendered the Emirate of Granada to Queen Isabella I of Castile
Isabella I of Castile
Isabella I was Queen of Castile and León. She and her husband Ferdinand II of Aragon brought stability to both kingdoms that became the basis for the unification of Spain. Later the two laid the foundations for the political unification of Spain under their grandson, Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor...
, who along with her husband King Ferdinand II of Aragon
Ferdinand II of Aragon
Ferdinand the Catholic was King of Aragon , Sicily , Naples , Valencia, Sardinia, and Navarre, Count of Barcelona, jure uxoris King of Castile and then regent of that country also from 1508 to his death, in the name of...
were the "Catholic Monarchs
Catholic Monarchs
The Catholic Monarchs is the collective title used in history for Queen Isabella I of Castile and King Ferdinand II of Aragon. They were both from the House of Trastámara and were second cousins, being both descended from John I of Castile; they were given a papal dispensation to deal with...
". The surrender concluded Al-Andalus as a political entity, but the cultural and social contributions under Muslim rule still persist in the region.
Etymology of Al-Andalus
The etymologyEtymology
Etymology is the study of the history of words, their origins, and how their form and meaning have changed over time.For languages with a long written history, etymologists make use of texts in these languages and texts about the languages to gather knowledge about how words were used during...
of the word "Al-Andalus" is disputed. Furthermore, the extent of Iberian territory encompassed by the name changed over the centuries. As a designation for Iberia
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar...
or its southern portion, the name is first attested by inscriptions on coins minted by the new Muslim government in Iberia circa 715 (the uncertainty in the year is due to the fact that the coins were bilingual in Latin and Arabic and the two inscriptions differ as to the year of minting).
At least three specific etymologies have been proposed in Western scholarship, all presuming that the name arose after the Roman period
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
in the Iberian Peninsula's history. Their originators or defenders have been historians. Recently, linguistics expertise has been brought to bear on the issue. Arguments from toponymy
Toponymy
Toponymy is the scientific study of place names , their origins, meanings, use and typology. The word "toponymy" is derived from the Greek words tópos and ónoma . Toponymy is itself a branch of onomastics, the study of names of all kinds...
(the study of place names), history, and language structure demonstrate the lack of substance in all preceding proposals, and evidence has been presented that the name predates, rather than postdates, the Roman occupation.
A major objection to all earlier proposals is that the very name Andaluz (the equivalent of Andalus in Spanish spelling) exists in several places in mountainous areas of Castile. Furthermore, the fragment and- is common in Spanish place names, and the fragment -luz also occurs several times across Spain.
Older proposals
The name Andalusia or Vandalusia was traditionally believed to be derived from Vandal (the Germanic tribe that colonized parts of Iberia from 407 to 429). However, there is no historical reference to support this. The proposal is sometimes associated with the 19th century historian Reinhart DozyReinhart Dozy
Reinhart Pieter Anne Dozy was a Dutch scholar of French origin, who was born in Leiden...
, but it predates him and he recognized some of its shortcomings. Although he accepted that Al-Andalus derived from Vandal, he believed that geographically it referred only to the harbor from which the Vandals departed Iberia for Africa—the location of which harbour was unknown.
Another proposal is that Andalus is an Arabic language version of the name Atlantis
Atlantis
Atlantis is a legendary island first mentioned in Plato's dialogues Timaeus and Critias, written about 360 BC....
. This idea has recently been defended by the Spanish historian Vallvé, but purely on the grounds that it is allegedly plausible phonetically and would explain several toponymic facts (no historical evidence was offered).
Vallvé writes:
Arabic texts offering the first mentions of the island of Al-Andalus and the sea of al-Andalus become extraordinarily clear if we substitute this expressions with "Atlantis" or "Atlantic". The same can be said with reference to HerculesHerculesHercules is the Roman name for Greek demigod Heracles, son of Zeus , and the mortal Alcmene...
and the AmazonsAmazonsThe Amazons are a nation of all-female warriors in Greek mythology and Classical antiquity. Herodotus placed them in a region bordering Scythia in Sarmatia...
whose island, according to Arabic commentaries of these GreekGreek mythologyGreek mythology is the body of myths and legends belonging to the ancient Greeks, concerning their gods and heroes, the nature of the world, and the origins and significance of their own cult and ritual practices. They were a part of religion in ancient Greece...
and LatinLatinLatin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
legends, was located in jauf Al-Andalus—that is, to the north or interior of the Atlantic OceanAtlantic OceanThe Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
.
The Island of Al-Andalus is mentioned in an anonymous Arabic chronicle of the conquest of Iberia composed two to three centuries after the fact. It is identified as the location of the landfall of the advance guard of the Moorish conquest of Iberia. The chronicle also says that "Island of al-Andalus" was subsequently renamed "Island of Tarifa". The preliminary conquest force of a few hundred, led by the Berber chief, Tarif abu Zura, seized the first bit of land that is encountered after crossing the Strait of Gibraltar in 710. The main conquest force led by Tariq ibn Ziyad followed them a year later. The landfall, now known in Spain as either Punta Marroquí or Punta de Tarifa, is in fact the southern tip of an islet, presently known as Isla de Tarifa or Isla de las Palomas, just offshore of the Iberian mainland.
This testimony of the Arab chronicle, the modern name Isla de Tarifa, and the above mentioned toponymic evidence that Andaluz is a name of pre-Roman origin taken together lead to the supposition that the Island of Andalus is the present day Isla de Tarifa, which lies just offshore from the modern day Spanish city of Tarifa. The extension of the scope of the designation "Al-Andalus" from a single islet to all of Iberia has several historical precedents.
In the 1980s, the historian Halm, also rejecting the Vandal proposal, originated an innovative alternative. Halm took as his points of departure ancient reports that Germanic tribes in general were reported to have distributed conquered lands by having members draw lots, and that Iberia during the period of Visigothic rule was sometimes known to outsiders by a Latin name, Gothica Sors, whose meaning is 'Gothic lot'. Halm thereupon speculated that the Visigoths themselves might have called their new lands "lot lands" and done so in their own language. However, the Gothic language version of the term Gothica Sors is not attested. Halm claimed to have been able to reconstruct it, proposing that it was *landahlauts (the asterisk is the standard symbol among linguists for a linguistic form that is proposed but has not been attested). Halm then suggested that the hypothetical Gothic language term gave rise to both the attested Latin term, Gothica Sors (by translating the meaning) and the Arabic name, Al-Andalus (by phonetic imitation). However, Halm did not offer evidence (historical or linguistic) that any of the language developments in his argument had in fact occurred.
Province of the Caliphate
Tariq ibn-Ziyad
Tariq ibn Ziyad was a Muslim Berber general who led the Islamic conquest of Visigothic Hispania in 711 A.D. He is considered to be one of the most important military commanders in Iberian history. Under the orders of the Umayyad Caliph Al-Walid I he led a large army from the north coast of...
led a small force that landed at Gibraltar
Gibraltar
Gibraltar is a British overseas territory located on the southern end of the Iberian Peninsula at the entrance of the Mediterranean. A peninsula with an area of , it has a northern border with Andalusia, Spain. The Rock of Gibraltar is the major landmark of the region...
on April 30, 711, ostensibly to intervene in a Visigothic civil war. After a decisive victory over King Roderic
Roderic
Ruderic was the Visigothic King of Hispania for a brief period between 710 and 712. He is famous in legend as "the last king of the Goths"...
at the Battle of Guadalete
Battle of Guadalete
The Battle of Guadalete was fought in 711 or 712 at an unidentified location between the Christian Visigoths of Hispania under their king, Roderic, and an invading force of Muslim Arabs and Berbers under Ṭāriq ibn Ziyad. The battle was significant as the culmination of a series of Arab-Berber...
on July 19, 711, Tariq ibn-Ziyad, joined by Arab governor Musa ibn Nusayr of Ifriqiya
Ifriqiya
In medieval history, Ifriqiya or Ifriqiyah was the area comprising the coastal regions of what are today western Libya, Tunisia, and eastern Algeria. This area included what had been the Roman province of Africa, whose name it inherited....
, brought most of the Visigothic Kingdom
Visigothic Kingdom
The Visigothic Kingdom was a kingdom which occupied southwestern France and the Iberian Peninsula from the 5th to 8th century AD. One of the Germanic successor states to the Western Roman Empire, it was originally created by the settlement of the Visigoths under King Wallia in the province of...
under Muslim occupation in a seven-year campaign. They crossed the Pyrenees
Pyrenees
The Pyrenees is a range of mountains in southwest Europe that forms a natural border between France and Spain...
and occupied Visigothic Septimania
Septimania
Septimania was the western region of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed under the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septimania was ceded to their king, Theodoric II. Under the Visigoths it was known as simply Gallia or Narbonensis. It corresponded roughly with the modern...
in southern France.
Most of the Iberian peninsula became part of the expanding Umayyad empire
Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate was the second of the four major Arab caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. It was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty, whose name derives from Umayya ibn Abd Shams, the great-grandfather of the first Umayyad caliph. Although the Umayyad family originally came from the...
, under the name of Al-Andalus. It was organized as a province subordinate to Ifriqiya
Ifriqiya
In medieval history, Ifriqiya or Ifriqiyah was the area comprising the coastal regions of what are today western Libya, Tunisia, and eastern Algeria. This area included what had been the Roman province of Africa, whose name it inherited....
, so, for the first few decades, the governors of al-Andalus were appointed by the emir of Kairouan
Kairouan
Kairouan , also known as Kirwan or al-Qayrawan , is the capital of the Kairouan Governorate in Tunisia. Referred to as the Islamic Cultural Capital, it is a UNESCO World Heritage site. The city was founded by the Arabs around 670...
, rather than the Caliph in Damascus. The regional capital was set at Cordoba, and the initial influx of Muslim colonists were widely distributed - Arab
Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
colonists were assigned to the south and east, while Berber
Berber people
Berbers are the indigenous peoples of North Africa west of the Nile Valley. They are continuously distributed from the Atlantic to the Siwa oasis, in Egypt, and from the Mediterranean to the Niger River. Historically they spoke the Berber language or varieties of it, which together form a branch...
colonists were scattered across the west and center. Visigothic lords who agreed to recognize Muslim suzerainity were allowed to retain their fiefs (notably, in Murcia, Galicia and the Ebro valley). Resistant Visigoths took refuge in the Cantabria
Cantabria
Cantabria is a Spanish historical region and autonomous community with Santander as its capital city. It is bordered on the east by the Basque Autonomous Community , on the south by Castile and León , on the west by the Principality of Asturias, and on the north by the Cantabrian Sea.Cantabria...
n highlands, where they carved out a rump state, the Kingdom of Asturias
Kingdom of Asturias
The Kingdom of Asturias was a Kingdom in the Iberian peninsula founded in 718 by Visigothic nobles under the leadership of Pelagius of Asturias. It was the first Christian political entity established following the collapse of the Visigothic kingdom after Islamic conquest of Hispania...
.
In the 720s, the Andalusian governors launched several sa'ifa raids into Aquitaine
Aquitaine
Aquitaine , archaic Guyenne/Guienne , is one of the 27 regions of France, in the south-western part of metropolitan France, along the Atlantic Ocean and the Pyrenees mountain range on the border with Spain. It comprises the 5 departments of Dordogne, :Lot et Garonne, :Pyrénées-Atlantiques, Landes...
. Duke Odo the Great of Aquitaine appealed to the Frankish
Franks
The Franks were a confederation of Germanic tribes first attested in the third century AD as living north and east of the Lower Rhine River. From the third to fifth centuries some Franks raided Roman territory while other Franks joined the Roman troops in Gaul. Only the Salian Franks formed a...
mayor Charles Martel
Charles Martel
Charles Martel , also known as Charles the Hammer, was a Frankish military and political leader, who served as Mayor of the Palace under the Merovingian kings and ruled de facto during an interregnum at the end of his life, using the title Duke and Prince of the Franks. In 739 he was offered the...
for assistance, offering to place himself under Carolingian sovereignty. At the Battle of Poitiers
Battle of Tours
The Battle of Tours , also called the Battle of Poitiers and in Battle of the Court of the Martyrs, was fought in an area between the cities of Poitiers and Tours, located in north-central France, near the village of Moussais-la-Bataille, about northeast of Poitiers...
in 732, an Andalusian raiding army was defeated by Charles Martel. In 734, the Andalusians launched raids to the east, capturing Avignon
Avignon
Avignon is a French commune in southeastern France in the départment of the Vaucluse bordered by the left bank of the Rhône river. Of the 94,787 inhabitants of the city on 1 January 2010, 12 000 live in the ancient town centre surrounded by its medieval ramparts.Often referred to as the...
and Arles
Arles
Arles is a city and commune in the south of France, in the Bouches-du-Rhône department, of which it is a subprefecture, in the former province of Provence....
and overran much of Provence
Provence
Provence ; Provençal: Provença in classical norm or Prouvènço in Mistralian norm) is a region of south eastern France on the Mediterranean adjacent to Italy. It is part of the administrative région of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur...
. In 737, they climbed up the Rhône
Rhône
Rhone can refer to:* Rhone, one of the major rivers of Europe, running through Switzerland and France* Rhône Glacier, the source of the Rhone River and one of the primary contributors to Lake Geneva in the far eastern end of the canton of Valais in Switzerland...
valley, reached as far as Burgundy. Charles Martel of the Franks, with the assistance of Liutprand
Liutprand, King of the Lombards
Liutprand was the King of the Lombards from 712 to 744 and is chiefly remembered for his Donation of Sutri, in 728, and his long reign, which brought him into a series of conflicts, mostly successful, with most of Italy. He profited by Byzantine weakness to enlarge his domains in Emilia and the...
of the Lombards
Lombards
The Lombards , also referred to as Longobards, were a Germanic tribe of Scandinavian origin, who from 568 to 774 ruled a Kingdom in Italy...
, invaded Burgundy and Provence and expelled the raiders by 739.
Relations between Arab
Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
s and Berber
Berber people
Berbers are the indigenous peoples of North Africa west of the Nile Valley. They are continuously distributed from the Atlantic to the Siwa oasis, in Egypt, and from the Mediterranean to the Niger River. Historically they spoke the Berber language or varieties of it, which together form a branch...
s in al-Andalus had been tense in the years after the conquest. Berbers heavily outnumbered the Arabs in the province, and had done the bulk of the fighting, but they had been given the lesser plums of the conquest and were assigned the harsher duties (e.g. garrisoning the more troubled areas). Although some Arab governors had cultivated their Berber lieutenants, others had grievously mistreated them. Mutinies by Berber soldiers were frequent, e.g. in 729, the Berber commander Munnus revolted and managed to carve out a rebel state in Cerdanya
Cerdanya
Cerdanya is a natural comarca and historical region of the eastern Pyrenees divided between France and Spain. Historically it has been one of the counties of Catalonia....
for a spell. In 740, a great Berber Revolt
Berber Revolt
The Great Berber Revolt of 739/740-743 AD took place during the reign of the Umayyad Caliph Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik and marked the first successful secession from the Arab caliphate...
erupted in the Maghreb
Maghreb
The Maghreb is the region of Northwest Africa, west of Egypt. It includes five countries: Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and Mauritania and the disputed territory of Western Sahara...
(North Africa). To put down the rebellion, the Umayyad Caliph Hisham
Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik
Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik 10th Umayyad caliph who ruled from 723 until his death in 743. When he was born in 691 his mother named him after her father....
dispatched a large Arab army, composed of regiments (junds) of Greater Syria
Greater Syria
Greater Syria , also known simply as Syria, is a term that denotes a region in the Near East bordering the Eastern Mediterranean Sea or the Levant....
to North Africa. But the great Syrian army was crushed by the Berber rebels at the Battle of Bagdoura
Battle of Bagdoura
The Battle of Bagdoura was a decisive confrontation in the Berber Revolt in late 741 CE. It was a follow-up to the Battle of the Nobles the previous year, and resulted in a major Berber victory over the Arabs by the Sebou river...
(in Morocco). Heartened by the victories of their North African brethren, the Berbers of al-Andalus quickly raised their own revolt. Berber garrisons in northern Spain mutinied, deposed their Arab commanders and organized a large rebel army to march against the strongholds of Toledo, Cordoba and Algeciras. The Andalusian Arab governor, joined by the remnant of the Syrian army (some 10,000) which had fled across the straits
Strait of Gibraltar
The Strait of Gibraltar is a narrow strait that connects the Atlantic Ocean to the Mediterranean Sea and separates Spain in Europe from Morocco in Africa. The name comes from Gibraltar, which in turn originates from the Arabic Jebel Tariq , albeit the Arab name for the Strait is Bab el-Zakat or...
, crushed the Berber rebels in a series of ferocious battles in 742. However, a quarrel immediately erupted between the Syrian commanders and the older Andalusian Arabs. The Syrians defeated the Andalusians at the hard-fought Battle of Aqua Portora in August 742, but were too few to impose themselves on the province. The quarrel was settled in 743, with the distribution of the Syrians in regimental fiefs across al-Andalus - the Damascus jund was established in Elvira (Granada
Granada
Granada is a city and the capital of the province of Granada, in the autonomous community of Andalusia, Spain. Granada is located at the foot of the Sierra Nevada mountains, at the confluence of three rivers, the Beiro, the Darro and the Genil. It sits at an elevation of 738 metres above sea...
), the Jordan jund in Rayyu (Málaga
Málaga
Málaga is a city and a municipality in the Autonomous Community of Andalusia, Spain. With a population of 568,507 in 2010, it is the second most populous city of Andalusia and the sixth largest in Spain. This is the southernmost large city in Europe...
and Archidona
Archidona
Archidona is a town and municipality in the province of Málaga, part of the autonomous community of Andalusia in southern Spain. The municipality is situated approximately 50 kilometres from the city of Málaga and 20 from Antequera. It has a population of approximately 8,500 residents. The natives...
), the Palestine jund in Medina-Sidonia
Medina-Sidonia
Medina-Sidonia is a city and municipality in the province of Cádiz in the autonomous community of Andalusia, southern Spain. It is considered by some to be the oldest city in Europe, used as a military defense location due to its elevated location. Locals are known as Asidonenses...
and Jerez, the Emesa (Hims) jund in Seville
Seville
Seville is the artistic, historic, cultural, and financial capital of southern Spain. It is the capital of the autonomous community of Andalusia and of the province of Seville. It is situated on the plain of the River Guadalquivir, with an average elevation of above sea level...
and Niebla
Niebla
-Places:* Niebla, Chile, a coastal town in the municipality of Valdivia* Niebla, Huelva, a municipality in Huelva province, Spain* Taifa of Niebla, a medieval taifa kingdom of the Iberian peninsula-People:* Mr...
and the Qinnasrin jund in Jaén
Jaén, Spain
Jaén is a city in south-central Spain, the name is derived from the Arabic word Jayyan, . It is the capital of the province of Jaén. It is located in the autonomous community of Andalusia....
. The Egypt jund was divided between Beja
Beja (Portugal)
Beja is a city in the Beja Municipality in the Alentejo region, Portugal. The municipality has a total area of 1,147.1 km² and a total population of 34,970 inhabitants. The city proper has a population of 21,658....
(Algarve) in the west and Tudmir (Murcia
Murcia
-History:It is widely believed that Murcia's name is derived from the Latin words of Myrtea or Murtea, meaning land of Myrtle , although it may also be a derivation of the word Murtia, which would mean Murtius Village...
) in the east. The arrival of the Syrians increased substantially the Arab element in the Iberian peninsula and helped deepen the Muslim hold on the south. However, at the same time, unwilling to be governed, the Syrian junds carried on an existence of autonomous feudal anarchy, severely destabilizing the authority of the governor of al-Andalus.
A second significant consequence of the revolt was the expansion of Kingdom of the Asturias, hitherto confined to enclaves in the Cantabrian highlands. After the rebellious Berber garrisons evacuted the northern frontier fortresses, the Christian king Alfonso I of Asturias
Alfonso I of Asturias
Alfonso I , called the Catholic , was the King of Asturias from 739 to his death in 757.He was son of Duke Peter of Cantabria and held many lands in that region. He may have been the hereditary chief of the Basques, but this is uncertain...
set about immediately seizing the empty forts for himself, quickly adding the northwestern provinces of Galicia and León
León (province)
León is a province of northwestern Spain, in the northwestern part of the autonomous community of Castile and León.About one quarter of its population of 500,200 lives in the capital, León. The weather is cold and dry during the winter....
to his fledgling kingdom. The Asturians evacuated the Christian populations from the towns and villages of the Galician-Leonese lowlands, creating an empty buffer zone in the Douro River valley (the "Desert of the Duero"). This new emptied frontier would remain roughly in place for the next few centuries as the boundary between the Christian north and the Islamic south. Between this frontier and the Andalusian heartland in the south, the Andalusian state organized three large march territories (thughur) - the lower march (capital initially at Merida
Mérida, Spain
Mérida is the capital of the autonomous community of Extremadura, western central Spain. It has a population of 57,127 . The Archaeological Ensemble of Mérida is a UNESCO World Heritage site since 1993.- Climate :...
, later Badajoz
Badajoz
Badajoz is the capital of the Province of Badajoz in the autonomous community of Extremadura, Spain, situated close to the Portuguese border, on the left bank of the river Guadiana, and the Madrid–Lisbon railway. The population in 2007 was 145,257....
), the middle march (centered at Toledo
Toledo
- Places :Belize:*Toledo District*Toledo SettlementBrazil:*Pedro de Toledo, São Paulo*Toledo, ParanáColombia:*Toledo, Norte de SantanderPhilippines:*Toledo City, CebuSpain:*Toledo, Spain *Kingdom of Toledo...
) and the upper march (centered at Zaragoza
Zaragoza
Zaragoza , also called Saragossa in English, is the capital city of the Zaragoza Province and of the autonomous community of Aragon, Spain...
)
The disturbances and disorders also allowed the Franks, now under mayor Pepin the Short, to invade the strategic strip of Septimania
Septimania
Septimania was the western region of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed under the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septimania was ceded to their king, Theodoric II. Under the Visigoths it was known as simply Gallia or Narbonensis. It corresponded roughly with the modern...
in 752, hoping to deprive Andalusians of their easy launching pad for raids into Francia. After a lengthy siege, the last Arab stronghold, the citadel of Narbonne
Narbonne
Narbonne is a commune in southern France in the Languedoc-Roussillon region. It lies from Paris in the Aude department, of which it is a sub-prefecture. Once a prosperous port, it is now located about from the shores of the Mediterranean Sea...
, finally fell to the Franks in 759. Al-Andalus was sealed off at the Pyrenees.
The third consequence of the Berber revolt was the collapse of the authority of the Damascus
Damascus
Damascus , commonly known in Syria as Al Sham , and as the City of Jasmine , is the capital and the second largest city of Syria after Aleppo, both are part of the country's 14 governorates. In addition to being one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, Damascus is a major...
Caliphate over the western provinces. With the Umayyad Caliphs distracted by the challenge of the Abbasid
Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate or, more simply, the Abbasids , was the third of the Islamic caliphates. It was ruled by the Abbasid dynasty of caliphs, who built their capital in Baghdad after overthrowing the Umayyad caliphate from all but the al-Andalus region....
s in the east, the western provinces of the Maghreb and al-Andalus spun out of their control. From around 745, the Fihrids
Fihrids
The Fihrids were an illustrious Arab family and clan, prominent in North Africa and Muslim Iberia during the 8th century.The al-Fihri were originally an Arabian clan Banu Fihr attached to the Quraysh, the tribe of the Prophet...
, an illustrious local Arab clan descended from Oqba ibn Nafi al-Fihri
Uqba ibn Nafi
Uqba ibn Nafi was an Arab hero and general who was serving the Umayyad dynasty, in Amir Muavia and Yazid periods, who began the Islamic conquest of the Maghreb, including present-day Algeria, Tunisia, Libya and Morocco in North Africa. He was the nephew of 'Amr ibn al-'As. Uqba is often surnamed...
, seized power in the western provinces, and ruled them almost as a private family empire of their own - Abd al-Rahman ibn Habib al-Fihri in Ifriqiya and Yūsuf al-Fihri
Yusuf ibn 'Abd al-Rahman al-Fihri
Yusuf ibn 'Abd al-Rahman al-Fihri was Umayyad governor of Narbonne in Septimania and then from 747 to 756 governor of al-Andalus, ruling independently following the collapse of the Umayyad Caliphate in 750...
in al-Andalus. The Fihrids welcomed the fall of the Umayyads in the east in 750, and sought to reach an understanding with the Abbasids, hoping they might be allowed to continue their autonomous existence. But when the Abbassids rejected the offer and demanded submission, the Fihrids declared independence and, probably out of spite, invited the deposed remnants of the Umayyad clan to take refuge in their dominions. It was a fateful decision they soon regretted, for the Umayyads, the sons and grandsons of caliphs, had a more legitimate claim to rule than the Fihrids themselves. Rebellious-minded local lords, disenchanted with the autocratic rule of the Fihrids, intrigued with the arriving Umayyad exiles.
Umayyad Emirate and Caliphate of Córdoba

Emir
Emir , meaning "commander", "general", or "prince"; also transliterated as Amir, Aamir or Ameer) is a title of high office, used throughout the Muslim world...
of Córdoba
Córdoba, Spain
-History:The first trace of human presence in the area are remains of a Neanderthal Man, dating to c. 32,000 BC. In the 8th century BC, during the ancient Tartessos period, a pre-urban settlement existed. The population gradually learned copper and silver metallurgy...
. He refused to submit to the Abbasid caliph, as Abbasid forces had killed most of his family. Over a thirty year reign, he established a tenuous rule over much of al-Andalus, overcoming partisans of both the al-Fihri family and of the Abbasid caliph.
For the next century and a half, his descendants continued as emirs of Córdoba, with nominal control over the rest of al-Andalus and sometimes even parts of western North Africa
North Africa
North Africa or Northern Africa is the northernmost region of the African continent, linked by the Sahara to Sub-Saharan Africa. Geopolitically, the United Nations definition of Northern Africa includes eight countries or territories; Algeria, Egypt, Libya, Morocco, South Sudan, Sudan, Tunisia, and...
, but with real control, particularly over the marches along the Christian border, vacillating depending on the competence of the individual emir. Indeed, the power of emir Abdallah ibn Muhammad (circa 900) did not extend beyond Córdoba itself.
But his grandson Abd-al-Rahman III, who succeeded him in 912, not only rapidly restored Umayyad power throughout al-Andalus but extended it into western North Africa as well. In 929 he proclaimed himself Caliph, elevating the emirate to a position competing in prestige not only with the Abbasid
Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate or, more simply, the Abbasids , was the third of the Islamic caliphates. It was ruled by the Abbasid dynasty of caliphs, who built their capital in Baghdad after overthrowing the Umayyad caliphate from all but the al-Andalus region....
caliph in Baghdad
Baghdad
Baghdad is the capital of Iraq, as well as the coterminous Baghdad Governorate. The population of Baghdad in 2011 is approximately 7,216,040...
but also the Shi'ite
Shi'a Islam
Shia Islam is the second largest denomination of Islam. The followers of Shia Islam are called Shi'ites or Shias. "Shia" is the short form of the historic phrase Shīʻatu ʻAlī , meaning "followers of Ali", "faction of Ali", or "party of Ali".Like other schools of thought in Islam, Shia Islam is...
caliph in Tunis
Tunis
Tunis is the capital of both the Tunisian Republic and the Tunis Governorate. It is Tunisia's largest city, with a population of 728,453 as of 2004; the greater metropolitan area holds some 2,412,500 inhabitants....
—with whom he was competing for control of North Africa.

Islamic Golden Age
During the Islamic Golden Age philosophers, scientists and engineers of the Islamic world contributed enormously to technology and culture, both by preserving earlier traditions and by adding their own inventions and innovations...
of al-Andalus. Crops produced using irrigation, along with food imported from the Middle East, provided the area around Córdoba and some other Andalusī cities with an agricultural economic sector by far the most advanced in Europe. Among European cities, Córdoba under the Caliphate, with a population of perhaps 500,000, eventually overtook Constantinople
Constantinople
Constantinople was the capital of the Roman, Eastern Roman, Byzantine, Latin, and Ottoman Empires. Throughout most of the Middle Ages, Constantinople was Europe's largest and wealthiest city.-Names:...
as the largest and most prosperous city in Europe. Within the Islamic world, Córdoba was one of the leading cultural centres. The work of its most important philosophers and scientists (notably Abulcasis
Abu al-Qasim
Abu al-Qasim Khalaf ibn al-Abbas Al-Zahrawi , also known in the West as Abulcasis, was an Arab physician who lived in Al-Andalus. He is considered the greatest medieval surgeon to have appeared from the Islamic World, and has been described by some as the father of modern surgery...
and Averroes
Averroes
' , better known just as Ibn Rushd , and in European literature as Averroes , was a Muslim polymath; a master of Aristotelian philosophy, Islamic philosophy, Islamic theology, Maliki law and jurisprudence, logic, psychology, politics, Arabic music theory, and the sciences of medicine, astronomy,...
) had a major influence on the intellectual life of medieval Europe.
Muslims and non-Muslims often came from abroad to study in the famous libraries and universities of al-Andalus after the reconquest of Toledo in 1085. The most noted of these was Michael Scot
Michael Scot
Michael Scot was a medieval mathematician and scholar.- Early life and education :He was born in Scotland, and studied first at the cathedral school of Durham and then at Oxford and Paris, devoting himself to philosophy, mathematics, and astrology...
(c. 1175 to c. 1235), who took the works of Ibn Rushd ("Averroes") and Ibn Sina ("Avicenna") to Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
. This transmission was to have a significant impact on the formation of the European Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
.
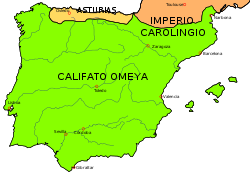
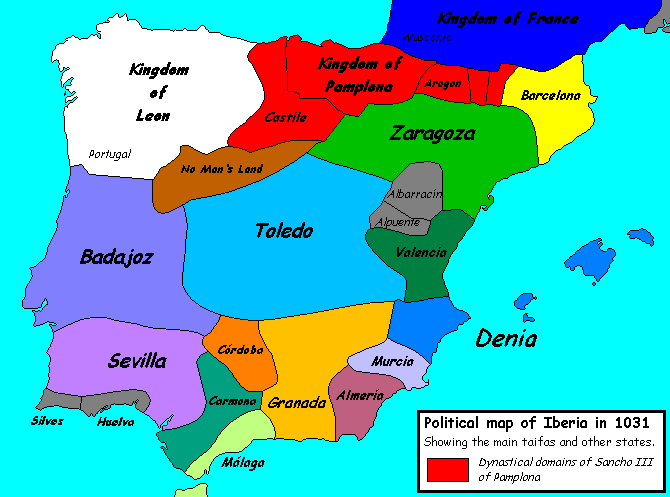
First Taifa period
The Córdoba Caliphate effectively collapsed during a ruinous civil war between 1009 and 1013, although it was not finally abolished until 1031. Al-Andalus then broke up into a number of mostly independent states called taifaTaifa
In the history of the Iberian Peninsula, a taifa was an independent Muslim-ruled principality, usually an emirate or petty kingdom, though there was one oligarchy, of which a number formed in the Al-Andalus after the final collapse of the Umayyad Caliphate of Córdoba in 1031.-Rise:The origins of...
s. These were generally too weak to defend themselves against repeated raids and demands for tribute from the Christian states to the north and west, which were known to the Muslims as "the Galician nations", and which had spread from their initial strongholds in Galicia
Kingdom of Galicia
The Kingdom of Galicia was a political entity located in southwestern Europe, which at its territorial zenith occupied the entire northwest of the Iberian Peninsula. Founded by Suebic king Hermeric in the year 409, the Galician capital was established in Braga, being the first kingdom which...
, Asturias
Kingdom of Asturias
The Kingdom of Asturias was a Kingdom in the Iberian peninsula founded in 718 by Visigothic nobles under the leadership of Pelagius of Asturias. It was the first Christian political entity established following the collapse of the Visigothic kingdom after Islamic conquest of Hispania...
, Cantabria
Cantabria
Cantabria is a Spanish historical region and autonomous community with Santander as its capital city. It is bordered on the east by the Basque Autonomous Community , on the south by Castile and León , on the west by the Principality of Asturias, and on the north by the Cantabrian Sea.Cantabria...
, the Basque country and the Carolingian
Carolingian Empire
Carolingian Empire is a historiographical term which has been used to refer to the realm of the Franks under the Carolingian dynasty in the Early Middle Ages. This dynasty is seen as the founders of France and Germany, and its beginning date is based on the crowning of Charlemagne, or Charles the...
Marca Hispanica
Marca Hispanica
The Marca Hispanica , also known as Spanish March or March of Barcelona was a buffer zone beyond the province of Septimania, created by Charlemagne in 795 as a defensive barrier between the Umayyad Moors of Al-Andalus and the Frankish Kingdom....
to become the Kingdoms of Navarre
Kingdom of Navarre
The Kingdom of Navarre , originally the Kingdom of Pamplona, was a European kingdom which occupied lands on either side of the Pyrenees alongside the Atlantic Ocean....
, León
Kingdom of León
The Kingdom of León was an independent kingdom situated in the northwest region of the Iberian Peninsula. It was founded in AD 910 when the Christian princes of Asturias along the northern coast of the peninsula shifted their capital from Oviedo to the city of León...
, Portugal
Kingdom of Portugal
The Kingdom of Portugal was Portugal's general designation under the monarchy. The kingdom was located in the west of the Iberian Peninsula, Europe and existed from 1139 to 1910...
, Castile
Kingdom of Castile
Kingdom of Castile was one of the medieval kingdoms of the Iberian Peninsula. It emerged as a political autonomous entity in the 9th century. It was called County of Castile and was held in vassalage from the Kingdom of León. Its name comes from the host of castles constructed in the region...
and Aragon
Kingdom of Aragon
The Kingdom of Aragon was a medieval and early modern kingdom in the Iberian Peninsula, corresponding to the modern-day autonomous community of Aragon, in Spain...
and the County of Barcelona. Eventually raids turned into conquests, and in response the taifa kings were forced to request help from the Almoravids, Islamic rulers of the Maghreb
Maghreb
The Maghreb is the region of Northwest Africa, west of Egypt. It includes five countries: Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, and Mauritania and the disputed territory of Western Sahara...
. Their desperate maneuver would eventually fall to their disadvantage, however, as the Moravids they had summoned from the south went on to conquer many of the taifa kingdoms.
Almoravids, Almohads and Marinids
Almoravids
The Almoravids were a Berber dynasty of Morocco, who formed an empire in the 11th-century that stretched over the western Maghreb and Al-Andalus. Their capital was Marrakesh, a city which they founded in 1062 C.E...
ruler of Morocco Yusuf ibn Tashfin
Yusuf ibn Tashfin
Yusef ibn Tashfin also, Tashafin, or Teshufin; or Yusuf; was a king of the Almoravid empire, he founded the city of Marrakech and led the Muslim forces in the Battle of Zallaqa....
was invited by the Muslim princes in Iberia to defend them against Alfonso VI
Alfonso VI of Castile
Alfonso VI , nicknamed the Brave or the Valiant, was King of León from 1065, King of Castile and de facto King of Galicia from 1072, and self-proclaimed "Emperor of all Spain". After the conquest of Toledo he was also self-proclaimed victoriosissimo rege in Toleto, et in Hispania et Gallecia...
, King of Castile
Kingdom of Castile
Kingdom of Castile was one of the medieval kingdoms of the Iberian Peninsula. It emerged as a political autonomous entity in the 9th century. It was called County of Castile and was held in vassalage from the Kingdom of León. Its name comes from the host of castles constructed in the region...
and León
Kingdom of León
The Kingdom of León was an independent kingdom situated in the northwest region of the Iberian Peninsula. It was founded in AD 910 when the Christian princes of Asturias along the northern coast of the peninsula shifted their capital from Oviedo to the city of León...
. In that year, Yusuf ibn Tashfin
Yusuf ibn Tashfin
Yusef ibn Tashfin also, Tashafin, or Teshufin; or Yusuf; was a king of the Almoravid empire, he founded the city of Marrakech and led the Muslim forces in the Battle of Zallaqa....
crossed the straits to Algeciras
Algeciras
Algeciras is a port city in the south of Spain, and is the largest city on the Bay of Gibraltar . Port of Algeciras is one of the largest ports in Europe and in the world in three categories: container,...
and inflicted a severe defeat on the Christians at the az-Zallaqah. By 1094, Yusuf ibn Tashfin
Yusuf ibn Tashfin
Yusef ibn Tashfin also, Tashafin, or Teshufin; or Yusuf; was a king of the Almoravid empire, he founded the city of Marrakech and led the Muslim forces in the Battle of Zallaqa....
had removed all Muslim princes in Iberia and annexed their states, except for the one at Zaragoza
Zaragoza
Zaragoza , also called Saragossa in English, is the capital city of the Zaragoza Province and of the autonomous community of Aragon, Spain...
. He regained Valencia from the Christians.
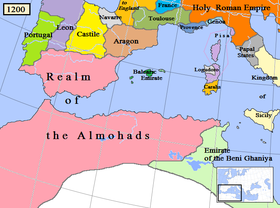
The Almoravids
Almoravids
The Almoravids were a Berber dynasty of Morocco, who formed an empire in the 11th-century that stretched over the western Maghreb and Al-Andalus. Their capital was Marrakesh, a city which they founded in 1062 C.E...
were succeeded in the 12th century by the Almohad
Almohad
The Almohad Dynasty , was a Moroccan Berber-Muslim dynasty founded in the 12th century that established a Berber state in Tinmel in the Atlas Mountains in roughly 1120.The movement was started by Ibn Tumart in the Masmuda tribe, followed by Abd al-Mu'min al-Gumi between 1130 and his...
s, another Berber dynasty, after the victory of Abu Yusuf Ya'qub al-Mansur
Yaqub, Almohad Caliph
Abu Yusuf Ya'qub al-Mansur , also known as Moulay Yacoub, was the third Almohad AmirSucceeding his father, Abu Ya'qub Yusuf, Yaqub al-Mansur reigned from 1184 to 1199 with distinction. During his tenure, trade, architecture, philosophy and the sciences flourished, to say nothing of military...
over the Castilian Alfonso VIII
Alfonso VIII of Castile
Alfonso VIII , called the Noble or el de las Navas, was the King of Castile from 1158 to his death and King of Toledo. He is most remembered for his part in the Reconquista and the downfall of the Almohad Caliphate...
at the Battle of Alarcos
Battle of Alarcos
Battle of Alarcos , was a battle between the Almohads led by Abu Yusuf Ya'qub al-Mansur and King Alfonso VIII of Castile. It resulted in the defeat of the Castilian forces and their subsequent retreat to Toledo whereas the Almohads conquered back Trujillo, Montánchez and Talavera.-Background:In...
. In 1212 a coalition of Christian kings under the leadership of the Castilian Alfonso VIII
Alfonso VIII of Castile
Alfonso VIII , called the Noble or el de las Navas, was the King of Castile from 1158 to his death and King of Toledo. He is most remembered for his part in the Reconquista and the downfall of the Almohad Caliphate...
defeated the Almohads at the Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa
Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa
The Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa, known in Arab history as the Battle of Al-Uqab , took place on 16 July 1212 and was an important turning point in the Reconquista and in the medieval history of Spain...
. The Almohads continued to rule Al Andalus for another decade, but with much reduced power and prestige; and the civil wars following the death of Abu Ya'qub Yusuf II
Yusuf II, Almohad Caliph
Yusuf II was Caliph of Morocco from 1213 until his death. Son of the previous caliph, Muhammad an-Nasir, Yusuf assumed the throne following his father's death, at the age of only sixteen years....
rapidly led to the re-establishment of taifas. The taifas, newly independent but now weakened, were quickly conquered by Portugal, Castile and Aragon. After the fall of Murcia
Murcia
-History:It is widely believed that Murcia's name is derived from the Latin words of Myrtea or Murtea, meaning land of Myrtle , although it may also be a derivation of the word Murtia, which would mean Murtius Village...
(1243) and the Algarve (1249), only the Emirate of Granada
Emirate of Granada
The Emirate of Granada , also known as the Nasrid Kingdom of Granada , was an emirate established in 1238 following the defeat of Muhammad an-Nasir of the Almohad dynasty by an alliance of Christian kingdoms at the Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa in 1212...
survived as a Muslim state, but only as a tributary of Castile. Most of its tribute was paid in gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
from present-day Mali
Mali
Mali , officially the Republic of Mali , is a landlocked country in Western Africa. Mali borders Algeria on the north, Niger on the east, Burkina Faso and the Côte d'Ivoire on the south, Guinea on the south-west, and Senegal and Mauritania on the west. Its size is just over 1,240,000 km² with...
and Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso – also known by its short-form name Burkina – is a landlocked country in west Africa. It is surrounded by six countries: Mali to the north, Niger to the east, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana to the south, and Côte d'Ivoire to the southwest.Its size is with an estimated...
that was carried to Iberia through the merchant routes of the Sahara
Sahara
The Sahara is the world's second largest desert, after Antarctica. At over , it covers most of Northern Africa, making it almost as large as Europe or the United States. The Sahara stretches from the Red Sea, including parts of the Mediterranean coasts, to the outskirts of the Atlantic Ocean...
.
The last Muslim threat to the Christian kingdoms was the rise of the Marinids in Morocco during the 14th century, who took Granada into their sphere of influence and occupied some of its cities, like Algeciras
Algeciras
Algeciras is a port city in the south of Spain, and is the largest city on the Bay of Gibraltar . Port of Algeciras is one of the largest ports in Europe and in the world in three categories: container,...
. However, they were unable to take Tarifa
Tarifa
Tarifa is a small town in the province of Cádiz, Andalusia, on the southernmost coast of Spain. The town is located on the Costa de la Luz and across the Straits of Gibraltar facing Morocco. The municipality includes Punta de Tarifa, the southernmost point in continental Europe. There are five...
, which held out until the arrival of the Castilian Army led by Alfonso XI. The Castilian king, helped by Afonso IV of Portugal
Afonso IV of Portugal
Afonso IV , called the Brave , was the seventh king of Portugal and the Algarve from 1325 until his death. He was the only legitimate son of King Denis of Portugal by his wife Elizabeth of Aragon.-Biography:...
and Peter IV of Aragon
Peter IV of Aragon
Peter IV, , called el Cerimoniós or el del punyalet , was the King of Aragon, King of Sardinia and Corsica , King of Valencia , and Count of Barcelona Peter IV, (Balaguer, September 5, 1319 – Barcelona, January 6, 1387), called el Cerimoniós ("the Ceremonious") or el del punyalet ("the one...
, decisively defeated the Marinids at the Battle of Salado in 1340 and took Algeciras in 1344. Gibraltar
Gibraltar
Gibraltar is a British overseas territory located on the southern end of the Iberian Peninsula at the entrance of the Mediterranean. A peninsula with an area of , it has a northern border with Andalusia, Spain. The Rock of Gibraltar is the major landmark of the region...
, then under Granadian rule, was besieged in 1349–1350, Alfonso XI along with most of his army perished by the Black Death
Black Death
The Black Death was one of the most devastating pandemics in human history, peaking in Europe between 1348 and 1350. Of several competing theories, the dominant explanation for the Black Death is the plague theory, which attributes the outbreak to the bacterium Yersinia pestis. Thought to have...
. His successor, Peter of Castile, made peace with the Muslims and turned his attention to Christian lands, starting a period of almost 150 years of rebellions and wars between the Christian states that secured the survival of Granada.
In 1469 the marriage of Ferdinand of Aragon and Isabella of Castile signaled the launching of the final assault on the Emirate of Granada (Gharnatah). The King and Queen convinced the Pope to declare their war a crusade. The Christians crushed one center of resistance after another and finally, in January 1492, after a long siege, the Moorish sultan, Muhammad XII, surrendered the fortress palace, the renowned Alhambra
Alhambra
The Alhambra , the complete form of which was Calat Alhambra , is a palace and fortress complex located in the Granada, Andalusia, Spain...
, itself.
Society

Berber people
Berbers are the indigenous peoples of North Africa west of the Nile Valley. They are continuously distributed from the Atlantic to the Siwa oasis, in Egypt, and from the Mediterranean to the Niger River. Historically they spoke the Berber language or varieties of it, which together form a branch...
and the Arab
Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
s. Mozarab
Mozarab
The Mozarabs were Iberian Christians who lived under Arab Islamic rule in Al-Andalus. Their descendants remained unconverted to Islam, but did however adopt elements of Arabic language and culture...
s were Christians that had long lived under Muslim rule and so had adopted many Arabic customs, art and words, while still maintaining their Christian rituals and their own Romance languages. Each of these communities inhabited distinct neighborhoods in the cities. In the 10th century a massive conversion of Christians took place, and muladi
Muladi
The Muladi were Muslims of ethnic Iberian descent or of mixed Arab, Berber and European origin, who lived in Al-Andalus during the Middle Ages. They were also called "Musalima" .-Etymology:...
es (Muslims of ethnic Iberian
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar...
origin) plus Arabs and Berbers comprised eighty percent of the population of Al-Andalus by around 1100.

Trade
Trade is the transfer of ownership of goods and services from one person or entity to another. Trade is sometimes loosely called commerce or financial transaction or barter. A network that allows trade is called a market. The original form of trade was barter, the direct exchange of goods and...
, or as doctors or ambassadors. At the end of the fifteenth century there were about 50,000 Jews
Jews
The Jews , also known as the Jewish people, are a nation and ethnoreligious group originating in the Israelites or Hebrews of the Ancient Near East. The Jewish ethnicity, nationality, and religion are strongly interrelated, as Judaism is the traditional faith of the Jewish nation...
in Granada and roughly 100,000 in the whole of Islamic Iberia.
Non-Muslims under the Caliphate
Treatment of non-Muslims
The non-Muslims were given the status of ahl al-dhimmaDhimmi
A , is a non-Muslim subject of a state governed in accordance with sharia law. Linguistically, the word means "one whose responsibility has been taken". This has to be understood in the context of the definition of state in Islam...
(the people under protection), adults paying a "Jizya
Jizya
Under Islamic law, jizya or jizyah is a per capita tax levied on a section of an Islamic state's non-Muslim citizens, who meet certain criteria...
" tax, equal to one Dinar per year with exemptions for old people, women, children and the disabled, whenever there was a Christian authority in the community. When there was no Christian authority, the non-Muslims were given the status of majus
Majus
Majūs was originally a term meaning Zoroastrians . It was a technical term, meaning magus, and like its synonym gabr originally had no pejorative implications.In al-Andalus the pagan non-Christian population were called majus and could either have the status of mozarab or of...
.
The treatment of non-Muslims in the Caliphate
Caliphate
The term caliphate, "dominion of a caliph " , refers to the first system of government established in Islam and represented the political unity of the Muslim Ummah...
has been a subject of considerable debate among scholars and commentators, especially those interested in drawing parallels to the coexistence of Muslims and non-Muslims in the modern world. María Rosa Menocal
María Rosa Menocal
María Rosa Menocal is a Cuban-born scholar of medieval culture and history. Menocal earned a B.A., M.A., and Ph.D. from the University of Pennsylvania...
, a specialist in Iberian literature, has argued that "tolerance was an inherent aspect of Andalusian society". In her view, the Jewish and Christian dhimmi
Dhimmi
A , is a non-Muslim subject of a state governed in accordance with sharia law. Linguistically, the word means "one whose responsibility has been taken". This has to be understood in the context of the definition of state in Islam...
s living under the Caliphate, while allowed fewer rights than Muslims, were much better off than minorities in Christian parts of Europe.
Jews
History of the Jews in Spain
Spanish Jews once constituted one of the largest and most prosperous Jewish communities under Muslim and Christian rule in Spain, before the majority, together with resident Muslims, were forced to convert to Catholicism, be expelled or be killed when Spain became united under the Catholic Monarchs...
constituted more than 5% of the population. Al-Andalus was a key center of Jewish life during the early Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
, producing important scholars and one of the most stable and wealthy Jewish communities. Bernard Lewis
Bernard Lewis
Bernard Lewis, FBA is a British-American historian, scholar in Oriental studies, and political commentator. He is the Cleveland E. Dodge Professor Emeritus of Near Eastern Studies at Princeton University...
takes issue with this view, arguing its modern use is ahistorical and apologetic. He argues that Islam traditionally did not offer equality nor even pretended that it did, arguing that it would have been both a "theological as well as a logical absurdity." However, even Bernard Lewis states:

Abd-ar-Rahman III
Abd-ar-Rahman III was the Emir and Caliph of Córdoba of the Ummayad dynasty in al-Andalus. Called al-Nasir li-Din Allah , he ascended the throne in his early 20s, and reigned for half a century as the most powerful prince of Iberia...
and his son, Al-Hakam II
Al-Hakam II
Al-Hakam II was the second Caliph of Cordoba, in Al-Andalus , and son of Abd-ar-rahman III . He ruled from 961 to 976....
where the Jews of Al-Andalus prospered, devoting themselves to the service of the Caliphate of Córdoba
Caliphate of Córdoba
The Caliphate of Córdoba ruled the Iberian peninsula and part of North Africa, from the city of Córdoba, from 929 to 1031. This period was characterized by remarkable success in trade and culture; many of the masterpieces of Islamic Iberia were constructed in this period, including the famous...
, to the study of the sciences, and to commerce and industry, especially to trading in silk
Silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The best-known type of silk is obtained from the cocoons of the larvae of the mulberry silkworm Bombyx mori reared in captivity...
and slaves
Slavery
Slavery is a system under which people are treated as property to be bought and sold, and are forced to work. Slaves can be held against their will from the time of their capture, purchase or birth, and deprived of the right to leave, to refuse to work, or to demand compensation...
, in this way promoting the prosperity of the country. Southern Iberia became an asylum for the oppressed Jews of other countries.
Under the Almoravids
Almoravids
The Almoravids were a Berber dynasty of Morocco, who formed an empire in the 11th-century that stretched over the western Maghreb and Al-Andalus. Their capital was Marrakesh, a city which they founded in 1062 C.E...
and the Almohads there may have been intermittent persecution of Jews, but sources are extremely scarce and do not give a clear picture, though the situation appears to have deteriorated after 1160.
The 11th century saw Muslim pogroms against Jews in Al-Andalus; those occurred in Córdoba in 1011 and in Granada in 1066
1066 Granada massacre
The 1066 Granada massacre took place on 30 December 1066 when a Muslim mob stormed the royal palace in Granada, which was at that time in Muslim-ruled al-Andalus, assassinated the Jewish vizier Joseph ibn Naghrela and massacred many of the Jewish population of the city.-Joseph ibn Naghrela:Joseph...
. However, such massacres are of rare occurrence in Islamic history.
The Almohad
Almohad
The Almohad Dynasty , was a Moroccan Berber-Muslim dynasty founded in the 12th century that established a Berber state in Tinmel in the Atlas Mountains in roughly 1120.The movement was started by Ibn Tumart in the Masmuda tribe, followed by Abd al-Mu'min al-Gumi between 1130 and his...
s, who had taken control of the Almoravids' Maghribi and Andalusian territories by 1147, far surpassed the Almoravides in fundamentalist outlook, and they treated the non-muslims harshly. Faced with the choice of either death or conversion, many Jews and Christians emigrated. Some, such as the family of Maimonides
Maimonides
Moses ben-Maimon, called Maimonides and also known as Mūsā ibn Maymūn in Arabic, or Rambam , was a preeminent medieval Jewish philosopher and one of the greatest Torah scholars and physicians of the Middle Ages...
, fled east to more tolerant Muslim lands, while others went northward to settle in the growing Christian kingdoms.
Rise and fall of Muslim power
Medieval SpainSpain in the Middle Ages
After the disorders of the passage of the Vandals and Alans down the Mediterranean coast of Hispania from 408, the history of Medieval Spain begins with the Iberian kingdom of the Arianist Visigoths , who were converted to Catholicism with their king Reccared in 587...
and Portugal
History of Portugal (1112-1279)
The history of Portugal, in most of the 12th and 13th centuries, is chiefly that of its origin as a separate state, in the process of the Christian reconquest of the Iberian Peninsula.-Background:...
was the scene of almost constant warfare between Muslims and Christians. The last Muslim bastion, Nasrid Granada
Granada
Granada is a city and the capital of the province of Granada, in the autonomous community of Andalusia, Spain. Granada is located at the foot of the Sierra Nevada mountains, at the confluence of three rivers, the Beiro, the Darro and the Genil. It sits at an elevation of 738 metres above sea...
fell around 1492. By this time the Moors in Castile
Crown of Castile
The Crown of Castile was a medieval and modern state in the Iberian Peninsula that formed in 1230 as a result of the third and definitive union of the crowns and parliaments of the kingdoms of Castile and León upon the accession of the then King Ferdinand III of Castile to the vacant Leonese throne...
numbered "half a million within the realm, 100,000 had died or been enslaved, 200,000 emigrated, and 200,000 remained as the residual population. Many of the Muslim elite, including Muhammad XII, who had been given the area of the Alpujarra mountain as a principality, found life under Christian rule intolerable and passed over into North Africa"
Culture

From the earliest days, the Umayyads wanted to be seen as intellectual rivals to the Abbasids, and for Córdoba to have libraries and educational institutions to rival Baghdad's. Although there was a clear rivalry between the two powers, freedom to travel between the two Caliphates was allowed, which helped spread new ideas and innovations over time.
Andalusian philosophy

Said Al-Andalusi
Said al-Andalusí was an Andalusi Muslim Qadi. He was born at Almería and died at Toledo. Said Al-Andalusi was a historian, philosopher of science and thought, and mathematical scientist with an especial interest in astronomy. He was highly interested in the science of Astronomy his claim to the...
wrote that Caliph Abd-ar-Rahman III
Abd-ar-Rahman III
Abd-ar-Rahman III was the Emir and Caliph of Córdoba of the Ummayad dynasty in al-Andalus. Called al-Nasir li-Din Allah , he ascended the throne in his early 20s, and reigned for half a century as the most powerful prince of Iberia...
had collected libraries of books and granted patronage to scholars of medicine
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
and "ancient sciences". Later, al-Mustansir (Al-Hakam II
Al-Hakam II
Al-Hakam II was the second Caliph of Cordoba, in Al-Andalus , and son of Abd-ar-rahman III . He ruled from 961 to 976....
) went yet further, building a university and libraries in Córdoba. Córdoba became one of the world's leading centres of medicine and philosophical debate.
However, when Al-Hakam's son Hisham II
Hisham II
Hisham II was the third Caliph of Cordoba, of the Umayyad dynasty. He ruled 976–1009, and 1010–1013 in the Al-Andalus ....
took over, real power was ceded to the hajib, al-Mansur Ibn Abi Aamir
Al-Mansur Ibn Abi Aamir
Abu Aamir Muhammad Ibn Abdullah Ibn Abi Aamir, Al-Hajib Al-Mansur , better known as Almanzor, was the de facto ruler of Muslim Al-Andalus in the late 10th to early 11th centuries. His rule marked the peak of power for Moorish Iberia.-Origins:He was born Muhammad Ibn Abi Aamir, into a noble Arab...
. Al-Mansur was a distinctly religious man and disapproved of the sciences of astronomy
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that deals with the study of celestial objects and phenomena that originate outside the atmosphere of Earth...
, logic
Logic
In philosophy, Logic is the formal systematic study of the principles of valid inference and correct reasoning. Logic is used in most intellectual activities, but is studied primarily in the disciplines of philosophy, mathematics, semantics, and computer science...
and especially astrology
Astrology
Astrology consists of a number of belief systems which hold that there is a relationship between astronomical phenomena and events in the human world...
, so much so that many books on these subjects, which had been preserved and collected at great expense by Al-Hakam II
Al-Hakam II
Al-Hakam II was the second Caliph of Cordoba, in Al-Andalus , and son of Abd-ar-rahman III . He ruled from 961 to 976....
, were burned publicly
Book burning
Book burning, biblioclasm or libricide is the practice of destroying, often ceremoniously, books or other written material and media. In modern times, other forms of media, such as phonograph records, video tapes, and CDs have also been ceremoniously burned, torched, or shredded...
. However, with Al-Mansur's death in 1002 interest in philosophy revived. Numerous scholars emerged, including Abu Uthman Ibn Fathun, whose masterwork was the philosophical treatise "Tree of Wisdom". An outstanding scholar in astronomy and astrology was Maslamah Ibn Ahmad al-Majriti
Maslamah Ibn Ahmad al-Majriti
Maslama al-Majriti or Abu al-Qasim al-Qurtubi al-Majriti was a Muslim astronomer, chemist, mathematician, economist and Scholar in Islamic Spain...
(died 1008), an intrepid traveller who journeyed all over the Islamic world and beyond, and who kept in touch with the Brethren of Purity
Brethren of Purity
The Brethren of Purity were a secret society of Muslim philosophers in Basra, Iraq, in the 10th century CE....
. Indeed, it is said to have been he who brought the 51 "Epistles of the Brethren of Purity" to al-Andalus and who added the compendium to this work, although it is quite possible that it was added later by another scholar of the name al-Majriti. Another book attributed to al-Majriti is the Ghayat al-Hakim "The Aim of the Sage", a book which explored a synthesis of Platonism
Platonism
Platonism is the philosophy of Plato or the name of other philosophical systems considered closely derived from it. In a narrower sense the term might indicate the doctrine of Platonic realism...
with Hermetic philosophy
Hermes Trismegistus
Hermes Trismegistus is the eponymous author of the Hermetic Corpus, a sacred text belonging to the genre of divine revelation.-Origin and identity:...
. Its use of incantations led the book to be widely dismissed in later years, although the Sufi communities kept studies of it.
A prominent follower of al-Majriti was the philosopher and geometer Abu al-Hakam al-Kirmani
Abu al-Hakam al-Kirmani
Abu al-Hakam al-Kirmani was a prominent philosopher and scholar from the Muslim al-Andalus. A student of Maslamah Ibn Ahmad al-Majriti, he was a Neoplatonic advocate, and seen as an influence on Ibn 'Arabi, but he also wrote extensively on geometry and logic. His exact date of death is not known as...
. A follower of his in turn was the great Abu Bakr Ibn al-Sayigh, usually known in the Arab world as Ibn Bajjah
Ibn Bajjah
Abū-Bakr Muhammad ibn Yahya ibn al-Sāyigh , known as Ibn Bājjah , was an Andalusian polymath: an astronomer, logician, musician, philosopher, physician, physicist, psychologist, botanist, poet and scientist. He was known in the West by his Latinized name, Avempace...
, "Avempace"
The Andalusian philosopher Averroes
Averroes
' , better known just as Ibn Rushd , and in European literature as Averroes , was a Muslim polymath; a master of Aristotelian philosophy, Islamic philosophy, Islamic theology, Maliki law and jurisprudence, logic, psychology, politics, Arabic music theory, and the sciences of medicine, astronomy,...
(1126–1198) was the founder of the Averroism
Averroism
Averroism is the term applied to either of two philosophical trends among scholastics in the late 13th century: the Arab philosopher Averroës or Ibn Rushd's interpretations of Aristotle and his reconciliation of Aristotelianism with Islamic faith; and the application of these ideas in the Latin...
school of philosophy, and his works and commentaries had an impact on the rise of secular thought
Secularism
Secularism is the principle of separation between government institutions and the persons mandated to represent the State from religious institutions and religious dignitaries...
in Western Europe
Western Europe
Western Europe is a loose term for the collection of countries in the western most region of the European continents, though this definition is context-dependent and carries cultural and political connotations. One definition describes Western Europe as a geographic entity—the region lying in the...
. He also developed the concept of "existence precedes essence
Existence precedes essence
The proposition that existence precedes essence is a central claim of existentialism, which reverses the traditional philosophical view that the essence or nature of a thing is more fundamental and immutable than its existence...
".
Another influential Andalusian philosopher who had a significant influence on modern philosophy
Modern philosophy
Modern philosophy is a type of philosophy that originated in Western Europe in the 17th century, and is now common worldwide. It is not a specific doctrine or school , although there are certain assumptions common to much of it, which helps to distinguish it from earlier philosophy.The 17th and...
was Ibn Tufail
Ibn Tufail
Ibn Tufail was an Andalusian Muslim polymath: an Arabic writer, novelist, Islamic philosopher, Islamic theologian, physician, vizier,...
. His philosophical novel
Philosophical novel
Philosophical fiction refers to works of fiction in which a significant proportion of the work is devoted to a discussion of the sort of questions normally addressed in discursive philosophy. These might include the function and role of society, the purpose of life, ethics or morals, the role of...
, Hayy ibn Yaqdhan
Hayy ibn Yaqdhan
Ḥayy ibn Yaqẓān is an Arabic philosophical novel and allegorical tale written by Ibn Tufail in the early 12th century.- Translations :* from Wikisource* English translations of Hayy bin Yaqzan...
, translated into Latin as Philosophus Autodidactus in 1671, developed the themes of empiricism, tabula rasa, nature versus nurture
Nature versus nurture
The nature versus nurture debate concerns the relative importance of an individual's innate qualities versus personal experiences The nature versus nurture debate concerns the relative importance of an individual's innate qualities ("nature," i.e. nativism, or innatism) versus personal experiences...
, condition of possibility
Condition of possibility
Condition of possibility is a philosophical concept made popular by Immanuel Kant.A condition of possibility is a necessary framework for the possible appearance of a given list of entities. It is often used in contrast to the unilateral causality concept, or even to the notion of interaction. For...
, materialism
Materialism
In philosophy, the theory of materialism holds that the only thing that exists is matter; that all things are composed of material and all phenomena are the result of material interactions. In other words, matter is the only substance...
, and Molyneux's Problem
Molyneux's Problem
Molyneux's problem is a thought experiment in philosophy concerning immediate recovery from blindness.It was first formulated by William Molyneux, and notably referenced in John Locke's An Essay Concerning Human Understanding....
. European scholars and writers influenced by this novel include John Locke
John Locke
John Locke FRS , widely known as the Father of Liberalism, was an English philosopher and physician regarded as one of the most influential of Enlightenment thinkers. Considered one of the first of the British empiricists, following the tradition of Francis Bacon, he is equally important to social...
, Gottfried Leibniz
Gottfried Leibniz
Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz was a German philosopher and mathematician. He wrote in different languages, primarily in Latin , French and German ....
, Melchisédech Thévenot
Melchisédech Thévenot
Melchisédech Thévenot was a French author, scientist, traveler, cartographer, orientalist, inventor, and diplomat...
, John Wallis, Christiaan Huygens, George Keith
George Keith
George Keith was a Scottish missionary.-Life:Born in Peterhead, Aberdeenshire, Scotland, to a Presbyterian family, he received an M.A. from the University of Aberdeen...
, Robert Barclay
Robert Barclay
Robert Barclay was a Scottish Quaker, one of the most eminent writers belonging to the Religious Society of Friends and a member of the Clan Barclay. He was also governor of the East Jersey colony in North America through most of the 1680s, although he himself never resided in the...
, the Quakers
Religious Society of Friends
The Religious Society of Friends, or Friends Church, is a Christian movement which stresses the doctrine of the priesthood of all believers. Members are known as Friends, or popularly as Quakers. It is made of independent organisations, which have split from one another due to doctrinal differences...
, and Samuel Hartlib
Samuel Hartlib
Samuel Hartlib was a German-British polymath. An active promoter and expert writer in many fields, he was interested in science, medicine, agriculture, politics, and education. He settled in England, where he married and died...
.
Jewish philosophy and culture
With the relative tolerance of al-Andalus and the decline of the previous centre of Jewish thought in Babylonia, al-Andalus became the centre of Jewish intellectual endeavours. Poets and commentators like Judah Halevi (1086–1145) and Dunash ben LabratDunash ben Labrat
Dunash ha-Levi ben Labrat was a medieval Jewish commentator, poet, and grammarian of the Golden age of Jewish culture in Spain. He was, according to Moses ibn Ezra, born in Fes. In his youth he travelled to Bagdad to study with Saadia Gaon.Dunash is called the founder of Spanish Hebrew poetry...
(920–990) contributed to the cultural life of al-Andalus, but the area was even more important to the development of Jewish philosophy. A stream of Jewish philosophers, cross-fertilizing with Muslim philosophers, (see joint Jewish and Islamic philosophies
Joint Jewish and Islamic philosophies
This article covers the influence of Jewish and Islamic philosophy on each other, focusing especially on the period from 800–1400 CE.- Early philosophy :...
) culminated in a widely celebrated Jewish thinker of the Middle Ages, Maimonides
Maimonides
Moses ben-Maimon, called Maimonides and also known as Mūsā ibn Maymūn in Arabic, or Rambam , was a preeminent medieval Jewish philosopher and one of the greatest Torah scholars and physicians of the Middle Ages...
(1135–1205), though he did not actually do any of his work in al-Andalus, as, when he was 13, his family fled persecution by the Almohads.
Astronomy
In the 11th–12th centuries, astronomers in Al-Andalus took up the challenge earlier posed by Ibn al-Haytham, namely to develop an alternate non-Ptolemaic configuration that evaded the errors found in the Ptolemaic modelGeocentric model
In astronomy, the geocentric model , is the superseded theory that the Earth is the center of the universe, and that all other objects orbit around it. This geocentric model served as the predominant cosmological system in many ancient civilizations such as ancient Greece...
. Like Ibn al-Haytham's critique, the anonymous Andalusian work, al-Istidrak ala Batlamyus (Recapitulation regarding Ptolemy), included a list of objections to Ptolemic astronomy. This marked the beginning of the Andalusian school's revolt against Ptolemaic astronomy, otherwise known as the "Andalusian Revolt".
In the late 11th century, al-Zarqali
Arzachel
', Al-Zarqali, Ibn Zarqala , Latinized as Arzachel, was an instrument maker and one of the leading theoretical and practical astronomers of his time. Although his name is conventionally given as al-Zarqālī, it is probable that the correct form was al-Zarqālluh. He lived in Toledo in Castile,...
(Latinized as Arzachel) discovered that the orbits of the planet
Planet
A planet is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science,...
s are elliptic orbit
Elliptic orbit
In astrodynamics or celestial mechanics an elliptic orbit is a Kepler orbit with the eccentricity less than 1; this includes the special case of a circular orbit, with eccentricity equal to zero. In a stricter sense, it is a Kepler orbit with the eccentricity greater than 0 and less than 1 . In a...
s and not circular orbits, though he still followed the Ptolemaic model.
In the 12th century, Averroes
Averroes
' , better known just as Ibn Rushd , and in European literature as Averroes , was a Muslim polymath; a master of Aristotelian philosophy, Islamic philosophy, Islamic theology, Maliki law and jurisprudence, logic, psychology, politics, Arabic music theory, and the sciences of medicine, astronomy,...
rejected the eccentric deferents
Deferent and epicycle
In the Ptolemaic system of astronomy, the epicycle was a geometric model used to explain the variations in speed and direction of the apparent motion of the Moon, Sun, and planets...
introduced by Ptolemy
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy , was a Roman citizen of Egypt who wrote in Greek. He was a mathematician, astronomer, geographer, astrologer, and poet of a single epigram in the Greek Anthology. He lived in Egypt under Roman rule, and is believed to have been born in the town of Ptolemais Hermiou in the...
. He rejected the Ptolemaic model and instead argued for a strictly concentric
Concentric
Concentric objects share the same center, axis or origin with one inside the other. Circles, tubes, cylindrical shafts, disks, and spheres may be concentric to one another...
model of the universe. He wrote the following criticism on the Ptolemaic model of planetary motion:
Averroes' Jewish contemporary, Maimonides
Maimonides
Moses ben-Maimon, called Maimonides and also known as Mūsā ibn Maymūn in Arabic, or Rambam , was a preeminent medieval Jewish philosopher and one of the greatest Torah scholars and physicians of the Middle Ages...
, wrote the following on the planetary model proposed by Ibn Bajjah
Ibn Bajjah
Abū-Bakr Muhammad ibn Yahya ibn al-Sāyigh , known as Ibn Bājjah , was an Andalusian polymath: an astronomer, logician, musician, philosopher, physician, physicist, psychologist, botanist, poet and scientist. He was known in the West by his Latinized name, Avempace...
(Avempace):
Ibn Bajjah also proposed the Milky Way
Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that contains the Solar System. This name derives from its appearance as a dim un-resolved "milky" glowing band arching across the night sky...
galaxy
Galaxy
A galaxy is a massive, gravitationally bound system that consists of stars and stellar remnants, an interstellar medium of gas and dust, and an important but poorly understood component tentatively dubbed dark matter. The word galaxy is derived from the Greek galaxias , literally "milky", a...
to be made up of many stars but that it appears to be a continuous image due to the effect of refraction
Refraction
Refraction is the change in direction of a wave due to a change in its speed. It is essentially a surface phenomenon . The phenomenon is mainly in governance to the law of conservation of energy. The proper explanation would be that due to change of medium, the phase velocity of the wave is changed...
in the Earth's atmosphere
Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention , and reducing temperature extremes between day and night...
. Later in the 12th century, his successors Ibn Tufail
Ibn Tufail
Ibn Tufail was an Andalusian Muslim polymath: an Arabic writer, novelist, Islamic philosopher, Islamic theologian, physician, vizier,...
and Nur Ed-Din Al Betrugi
Nur Ed-Din Al Betrugi
Nur ad-Din al-Bitruji was an astronomer and a Qadi from Al-Andalus...
(Alpetragius) were the first to propose planetary models without any equant
Equant
Equant is a mathematical concept developed by Claudius Ptolemy in the 2nd century AD to account for the observed motion of heavenly bodies....
, epicycles or eccentrics
Deferent and epicycle
In the Ptolemaic system of astronomy, the epicycle was a geometric model used to explain the variations in speed and direction of the apparent motion of the Moon, Sun, and planets...
. Al-Betrugi was also the first to discover that the planets are self-luminous
Luminosity
Luminosity is a measurement of brightness.-In photometry and color imaging:In photometry, luminosity is sometimes incorrectly used to refer to luminance, which is the density of luminous intensity in a given direction. The SI unit for luminance is candela per square metre.The luminosity function...
. Their configurations, however, were not accepted due to the numerical predictions of the planetary positions in their models being less accurate than that of the Ptolemaic model, mainly because they followed Aristotle
Aristotle
Aristotle was a Greek philosopher and polymath, a student of Plato and teacher of Alexander the Great. His writings cover many subjects, including physics, metaphysics, poetry, theater, music, logic, rhetoric, linguistics, politics, government, ethics, biology, and zoology...
's notion of perfect circular motion.
Earth sciences
In the late 11th century, Abu 'Abd Allah Muhammad ibn Ma'udh, who lived in Al-Andalus, wrote a work on opticsOptics
Optics is the branch of physics which involves the behavior and properties of light, including its interactions with matter and the construction of instruments that use or detect it. Optics usually describes the behavior of visible, ultraviolet, and infrared light...
later translated into Latin as Liber de crepisculis, which was mistakenly attributed to Alhazen. This was a short work containing an estimation of the angle of depression of the sun at the beginning of the morning twilight
Twilight
Twilight is the time between dawn and sunrise or between sunset and dusk, during which sunlight scattering in the upper atmosphere illuminates the lower atmosphere, and the surface of the earth is neither completely lit nor completely dark. The sun itself is not directly visible because it is below...
and at the end of the evening twilight, and an attempt to calculate on the basis of this and other data the height of the atmospheric moisture responsible for the refraction of the sun's rays. Through his experiments, he obtained the accurate value of 18°, which comes close to the modern value.
In the early 13th century, the Andalusian-Arab
Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
ian biologist Abu al-Abbas al-Nabati developed an early scientific method
Scientific method
Scientific method refers to a body of techniques for investigating phenomena, acquiring new knowledge, or correcting and integrating previous knowledge. To be termed scientific, a method of inquiry must be based on gathering empirical and measurable evidence subject to specific principles of...
for botany
Botany
Botany, plant science, or plant biology is a branch of biology that involves the scientific study of plant life. Traditionally, botany also included the study of fungi, algae and viruses...
, introducing empirical
Empirical
The word empirical denotes information gained by means of observation or experimentation. Empirical data are data produced by an experiment or observation....
and experiment
Experiment
An experiment is a methodical procedure carried out with the goal of verifying, falsifying, or establishing the validity of a hypothesis. Experiments vary greatly in their goal and scale, but always rely on repeatable procedure and logical analysis of the results...
al techniques in the testing, description and identification of numerous materia medica
Materia medica
Materia medica is a Latin medical term for the body of collected knowledge about the therapeutic properties of any substance used for healing . The term 'materia medica' derived from the title of a work by the Ancient Greek physician Pedanius Dioscorides in the 1st century AD, De materia medica libre...
, and separating unverified reports from those supported by actual tests and observation
Observation
Observation is either an activity of a living being, such as a human, consisting of receiving knowledge of the outside world through the senses, or the recording of data using scientific instruments. The term may also refer to any data collected during this activity...
s. His student Ibn al-Baitar published the Kitab al-Jami fi al-Adwiya al-Mufrada, which is considered one of the greatest botanical compilations in history, and was a botanical authority for centuries. It contains details on at least 1,400 different plant
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
s, food
Food
Food is any substance consumed to provide nutritional support for the body. It is usually of plant or animal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals...
s, and drug
Drug
A drug, broadly speaking, is any substance that, when absorbed into the body of a living organism, alters normal bodily function. There is no single, precise definition, as there are different meanings in drug control law, government regulations, medicine, and colloquial usage.In pharmacology, a...
s, 300 of which were his own original discoveries. The Kitab al-Jami fi al-Adwiya al-Mufrada was also influential in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
after it was translated into Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
in 1758.
Geography and exploration
Long distance travel created a need for mapping, and travelers often provided the information to achieve the task. While such travel during the medieval period was hazardous, Muslims nonetheless undertook long journeys. One motive for these was the HajjHajj
The Hajj is the pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia. It is one of the largest pilgrimages in the world, and is the fifth pillar of Islam, a religious duty that must be carried out at least once in their lifetime by every able-bodied Muslim who can afford to do so...
or the Muslim pilgrimage. Annually, Muslims came to Mecca
Mecca
Mecca is a city in the Hijaz and the capital of Makkah province in Saudi Arabia. The city is located inland from Jeddah in a narrow valley at a height of above sea level...
in Arabia from Islamic Iberia, Persia, Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
, and India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
. Another motive for travels was commerce. Muslims were involved in trade with Europeans, Indians and the Chinese, and Muslim merchants travelled long distances to conduct commercial activities.
The origins of the caravel
Caravel
A caravel is a small, highly maneuverable sailing ship developed in the 15th century by the Portuguese to explore along the West African coast and into the Atlantic Ocean. The lateen sails gave her speed and the capacity for sailing to windward...
ship, used for long distance travel by the Portuguese after the beginning of their overseas expansion in the 15th century, date back to the designs of the Cog
Cog (ship)
A cog is a type of ship that first appeared in the 10th century, and was widely used from around the 12th century on. Cogs were generally built of oak, which was an abundant timber in the Baltic region of Prussia. This vessel was fitted with a single mast and a square-rigged single sail...
, the Holk
Hulk (ship)
A hulk is a ship that is afloat, but incapable of going to sea. Although sometimes used to describe a ship that has been launched but not completed, the term most often refers to an old ship that has had its rigging or internal equipment removed, retaining only its flotational qualities...
and the Dromon
Dromon
The dromon was a type of galley and the most important warship of the Byzantine navy from the 6th to 12th centuries AD...
, but also possibly to the qarib used by explorers from Islamic Iberia in the 13th century.
Medicine
Muslim physicianPhysician
A physician is a health care provider who practices the profession of medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring human health through the study, diagnosis, and treatment of disease, injury and other physical and mental impairments...
s from Al-Andalus contributed significantly to the field of medicine
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
, including the subjects of anatomy
Anatomy
Anatomy is a branch of biology and medicine that is the consideration of the structure of living things. It is a general term that includes human anatomy, animal anatomy , and plant anatomy...
and physiology
Physiology
Physiology is the science of the function of living systems. This includes how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells, and bio-molecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system. The highest honor awarded in physiology is the Nobel Prize in Physiology or...
. Major figures of this period included Abu al-Qasim al-Zahrawi (Abulcasis), author of the Kitab al-Tasrif
Al-Tasrif
The Kitab al-Tasrif was an Arabic encyclopedia on medicine and surgery, written near the year 1000 by Abu al-Qasim al-Zahrawi...
("Book of Concessions"), a 30-volume medical encyclopedia
Encyclopedia
An encyclopedia is a type of reference work, a compendium holding a summary of information from either all branches of knowledge or a particular branch of knowledge....
, and Ibn Zuhr
Ibn Zuhr
Abū Merwān ’Abdal-Malik ibn Zuhr was a Muslim physician, surgeon and teacher in Al-Andalus.He was born at Seville...
(Avenzoar), who made advances in surgery.
Psychology and sociology
Abu al-QasimAbu al-Qasim
Abu al-Qasim Khalaf ibn al-Abbas Al-Zahrawi , also known in the West as Abulcasis, was an Arab physician who lived in Al-Andalus. He is considered the greatest medieval surgeon to have appeared from the Islamic World, and has been described by some as the father of modern surgery...
(Abulcasis), the father of modern surgery
Surgery
Surgery is an ancient medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a patient to investigate and/or treat a pathological condition such as disease or injury, or to help improve bodily function or appearance.An act of performing surgery may be called a surgical...
, developed material and technical designs which are still used in neurosurgery
Neurosurgery
Neurosurgery is the medical specialty concerned with the prevention, diagnosis, treatment, and rehabilitation of disorders which affect any portion of the nervous system including the brain, spine, spinal cord, peripheral nerves, and extra-cranial cerebrovascular system.-In the United States:In...
. Ibn Zuhr
Ibn Zuhr
Abū Merwān ’Abdal-Malik ibn Zuhr was a Muslim physician, surgeon and teacher in Al-Andalus.He was born at Seville...
(Avenzoar) gave the first accurate descriptions on neurological disorders, including meningitis
Meningitis
Meningitis is inflammation of the protective membranes covering the brain and spinal cord, known collectively as the meninges. The inflammation may be caused by infection with viruses, bacteria, or other microorganisms, and less commonly by certain drugs...
, intracranial thrombophlebitis
Thrombophlebitis
Thrombophlebitis is phlebitis related to a thrombus . When it occurs repeatedly in different locations, it is known as "Thrombophlebitis migrans" or "migrating thrombophlebitis".-Signs and symptoms:...
, and mediastinal germ cell tumor
Mediastinal germ cell tumor
Malignant mediastinal germ cell tumors of various histologies were first described as a clinical entity approximately 50 years ago. Mediastinal and other extragonadal germ cell tumors were initially thought to represent isolated metastases from an inapparent gonadal primary site.-Etiology:Some...
s, and made contributions to modern neuropharmacology
Neuropharmacology
Neuropharmacology is the study of how drugs affect cellular function in the nervous system. There are two main branches of neuropharmacology: behavioral and molecular. Behavioral neuropharmacology focuses on the study of how drugs affect human behavior , including the study of how drug dependence...
. Averroes
Averroes
' , better known just as Ibn Rushd , and in European literature as Averroes , was a Muslim polymath; a master of Aristotelian philosophy, Islamic philosophy, Islamic theology, Maliki law and jurisprudence, logic, psychology, politics, Arabic music theory, and the sciences of medicine, astronomy,...
suggested the existence of Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease
Parkinson's disease is a degenerative disorder of the central nervous system...
and attributed photoreceptor properties to the retina
Retina
The vertebrate retina is a light-sensitive tissue lining the inner surface of the eye. The optics of the eye create an image of the visual world on the retina, which serves much the same function as the film in a camera. Light striking the retina initiates a cascade of chemical and electrical...
. Maimonides
Maimonides
Moses ben-Maimon, called Maimonides and also known as Mūsā ibn Maymūn in Arabic, or Rambam , was a preeminent medieval Jewish philosopher and one of the greatest Torah scholars and physicians of the Middle Ages...
wrote about neuropsychiatric disorders and described rabies
Rabies
Rabies is a viral disease that causes acute encephalitis in warm-blooded animals. It is zoonotic , most commonly by a bite from an infected animal. For a human, rabies is almost invariably fatal if post-exposure prophylaxis is not administered prior to the onset of severe symptoms...
and belladonna
Deadly nightshade
Atropa belladonna or Atropa bella-donna, commonly known as Belladonna, Devil's Berries, Death Cherries or Deadly Nightshade, is a perennial herbaceous plant in the family Solanaceae, native to Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia. The foliage and berries are extremely toxic, containing tropane...
intoxication.
Said Al-Andalusi
Said Al-Andalusi
Said al-Andalusí was an Andalusi Muslim Qadi. He was born at Almería and died at Toledo. Said Al-Andalusi was a historian, philosopher of science and thought, and mathematical scientist with an especial interest in astronomy. He was highly interested in the science of Astronomy his claim to the...
(1029–1070) stated that people in all corners of the world have a common origin but differ in certain aspects: "ethics
Islamic ethics
Islamic ethics , defined as "good character," historically took shape gradually from the 7th century and was finally established by the 11th century...
, appearance, landscape and language". He treated the history of Egypt
History of Egypt
Egyptian history can be roughly divided into the following periods:*Prehistoric Egypt*Ancient Egypt**Early Dynastic Period of Egypt: 31st to 27th centuries BC**Old Kingdom of Egypt: 27th to 22nd centuries BC...
as part of the universal history
Universal history
Universal history is basic to the Western tradition of historiography, especially the Abrahamic wellspring of that tradition. Simply stated, universal history is the presentation of the history of humankind as a whole, as a coherent unit.-Ancient authors:...
of all humanity, and he linked Egypt and Sudan
Sudan
Sudan , officially the Republic of the Sudan , is a country in North Africa, sometimes considered part of the Middle East politically. It is bordered by Egypt to the north, the Red Sea to the northeast, Eritrea and Ethiopia to the east, South Sudan to the south, the Central African Republic to the...
to the history of the Arab
Arab
Arab people, also known as Arabs , are a panethnicity primarily living in the Arab world, which is located in Western Asia and North Africa. They are identified as such on one or more of genealogical, linguistic, or cultural grounds, with tribal affiliations, and intra-tribal relationships playing...
s through a common ancestry. They linked ancient Egypt to Muslim history
Muslim history
Muslim history is the history of Muslim people. In the history of Islam the followers of the religion of Islam have impacted political history, economic history, and military history...
through Hajar
Hagar (Bible)
Hagar , according to the Abrahamic faiths, was the second wife of Abraham, and the mother of his first son, Ishmael. Her story is recorded in the Book of Genesis, mentioned in Hadith, and alluded to in the Qur'an...
(Hagar), the wife of Ibrahim (Abraham) and mother of Ismail (Ishmael), the patriarch of the Arabs, thus making Hajar the mother of the Arabs.
Agriculture
As early as the 9th century, an essentially modern agricultural system became central to economic life and organization in the Arab caliphates, replacing the largely export-driven Roman model. It started with Zakat, an Islamic tax on large land holdings, which slowly broke the land monopoly of the nobility that had smothered the rural economy for centuries. Cities of the Near East, North Africa, and Moorish Spain were supported by elaborate agricultural systems which included extensive irrigation based on knowledge of hydraulic and hydrostatic principles, some of which were continued from Roman times.{Glick, Thomas (1996) Irrigation and Hydraulic Systems pp. 10}The introduction of new crops transforming private farming into a new global industry exported everywhere, including Europe, where farming was mostly restricted to wheat strains obtained much earlier via central Asia. Spain received what she in turn transmitted to the rest of Europe; many agricultural and fruit-growing processes, together with many new plants, fruit and vegetables. These new crops included sugar cane, rice, citrus fruit, apricots, cotton, artichokes, aubergines, and saffron. Others, previously known, were further developed. Several were later exported from Spanish coastal areas to the Spanish colonies in the New World. Also transmitted via Muslim influence, a silk industry flourished, flax was cultivated and linen exported, and esparto
Esparto
Esparto, or esparto grass, also known as "halfah grass" or "needle grass", Macrochloa tenacissima and Stipa tenacissima, is a perennial grass grown in northwest Africa and the southern part of the Iberian Peninsula employed for crafts .-Esparto paper:It is also used for fiber production for paper...
grass, which grew wild in the more arid parts, was collected and turned into various articles.
The process of getting all of these new crops was not as easy as some might assume it was. It was difficult to take these new plants and fruits to the Iberian Peninsula and in some cases it was done illegally. Bringing them was difficult in many cases because there were specific varieties of plants that were not allowed to be removed from Muslim territories that people had to smuggle out; however, in the end this process proved very helpful to the Iberian peninsula. The economic implications were enormous. By having so many new crops people began to become more healthy and due to this there was a great economic upturn in this time.
Architecture
Muslim rulers introduced a characteristically Arabic architectural style, which by the end of their rule in Iberia included elements of Arabic, Byzantine, and Visigothic architecture. These features remained influential in the Iberian Peninsula after the Reconquista. Some examples of the lasting architectural contributions under the taifa include the Great Mosque of Córdoba and the Cordoban palace estate al-Rustafa. Christians and Jews adopted Arabic architectural elements into their own churches and synagogues. This became known as the Mozarabic style. Mozarabic architecture included the absence of exterior decoration, diversity of floor plans, the use of the horseshoe arch in the Islamic style, and the use of the column as support, with a capital decorated with vegetable elements.Cuisine
RestaurantRestaurant
A restaurant is an establishment which prepares and serves food and drink to customers in return for money. Meals are generally served and eaten on premises, but many restaurants also offer take-out and food delivery services...
s in medieval Islamic Spain served three-course meals, which were introduced in the 9th century by Ziryab
Ziryab
Abu l-Hasan ‘Ali Ibn Nafi‘ , nicknamed Ziryab , was a Black African or Persian or Kurdish polymath: a poet, musician, singer, chemist, cosmetologist, fashion designer, trendsetter, strategist, astronomer, botanist and...
, who insisted that meals should be served in three separate courses consisting of soup
Soup
Soup is a generally warm food that is made by combining ingredients such as meat and vegetables with stock, juice, water, or another liquid. Hot soups are additionally characterized by boiling solid ingredients in liquids in a pot until the flavors are extracted, forming a broth.Traditionally,...
, the main course
Main course
A main dish is the featured or primary dish in a meal consisting of several courses. It usually follows the entrée course, and the salad course. In North American usage it may in fact be called the "entree"....
, and dessert
Dessert
In cultures around the world, dessert is a course that typically comes at the end of a meal, usually consisting of sweet food. The word comes from the French language as dessert and this from Old French desservir, "to clear the table" and "to serve." Common Western desserts include cakes, biscuits,...
.
Linguistics and literature
In the 12th century, the Andalusian-Arabian philosopherEarly Islamic philosophy
Early Islamic philosophy or classical Islamic philosophy is a period of intense philosophical development beginning in the 2nd century AH of the Islamic calendar and lasting until the 6th century AH...
and novelist Ibn Tufail
Ibn Tufail
Ibn Tufail was an Andalusian Muslim polymath: an Arabic writer, novelist, Islamic philosopher, Islamic theologian, physician, vizier,...
(known as "Abubacer" or "Ebn Tophail" in the West) first demonstrated Avicenna
Avicenna
Abū ʿAlī al-Ḥusayn ibn ʿAbd Allāh ibn Sīnā , commonly known as Ibn Sīnā or by his Latinized name Avicenna, was a Persian polymath, who wrote almost 450 treatises on a wide range of subjects, of which around 240 have survived...
's theory of tabula rasa
Tabula rasa
Tabula rasa is the epistemological theory that individuals are born without built-in mental content and that their knowledge comes from experience and perception. Generally proponents of the tabula rasa thesis favour the "nurture" side of the nature versus nurture debate, when it comes to aspects...
as a thought experiment
Thought experiment
A thought experiment or Gedankenexperiment considers some hypothesis, theory, or principle for the purpose of thinking through its consequences...
in his Arabic novel
Arabic literature
Arabic literature is the writing produced, both prose and poetry, by writers in the Arabic language. The Arabic word used for literature is adab which is derived from a meaning of etiquette, and implies politeness, culture and enrichment....
, Hayy ibn Yaqzan, in which he depicted the development of the mind of a feral child
Feral child
A feral child is a human child who has lived isolated from human contact from a very young age, and has no experience of human care, loving or social behavior, and, crucially, of human language...
"from a tabula rasa to that of an adult, in complete isolation from society" on a desert island
Desert island
A desert island or uninhabited island is an island that has yet to be populated by humans. Uninhabited islands are often used in movies or stories about shipwrecked people, and are also used as stereotypes for the idea of "paradise". Some uninhabited islands are protected as nature reserves and...
. The Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
translation of his work, titled Philosophus Autodidactus, published by Edward Pococke
Edward Pococke
Edward Pococke was an English Orientalist and biblical scholar.-Early life:He was the son of clergyman from Chieveley in Berkshire, and was educated at Lord Williams's School of Thame in Oxfordshire and at Corpus Christi College, Oxford...
the Younger in 1671, had an influence on John Locke
John Locke
John Locke FRS , widely known as the Father of Liberalism, was an English philosopher and physician regarded as one of the most influential of Enlightenment thinkers. Considered one of the first of the British empiricists, following the tradition of Francis Bacon, he is equally important to social...
's formulation of tabula rasa in An Essay Concerning Human Understanding
An Essay Concerning Human Understanding
First appearing in 1690 with the printed title An Essay Concerning Humane Understanding, An Essay Concerning Human Understanding by John Locke concerns the foundation of human knowledge and understanding. He describes the mind at birth as a blank slate filled later through experience...
, which went on to become one of the principal sources of empiricism
Empiricism
Empiricism is a theory of knowledge that asserts that knowledge comes only or primarily via sensory experience. One of several views of epistemology, the study of human knowledge, along with rationalism, idealism and historicism, empiricism emphasizes the role of experience and evidence,...
in modern Western philosophy, and influenced many Enlightenment philosophers, such as David Hume
David Hume
David Hume was a Scottish philosopher, historian, economist, and essayist, known especially for his philosophical empiricism and skepticism. He was one of the most important figures in the history of Western philosophy and the Scottish Enlightenment...
and George Berkeley
George Berkeley
George Berkeley , also known as Bishop Berkeley , was an Irish philosopher whose primary achievement was the advancement of a theory he called "immaterialism"...
.
Hadith Bayad wa Riyad
Hadith Bayad wa Riyad
Hadith Bayāḍ wa Riyāḍ or Qissat Bayad wa Riyad is a 13th-century Arabic love story...
(The Story of Bayad and Riyad) was a 13th century Arabic love story written in Al-Andalus. The main characters of the tale are Bayad, a merchant's son and a foreigner from Damascus
Damascus
Damascus , commonly known in Syria as Al Sham , and as the City of Jasmine , is the capital and the second largest city of Syria after Aleppo, both are part of the country's 14 governorates. In addition to being one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, Damascus is a major...
, and Riyad, a well educated girl in the court of an unnamed Hajib
Hajib
The term "hajib" is not to be confused with the word "hijab", which is a headscarf for Muslim women.A hajib was a government official in Al-Andalus and Egypt. They began as treasurers or Chamberlains but by 756, the position had evolved to be equivalent to a vizier or higher....
(vizier or minister) of Al-Andalus who is referred to as the lady. The Hadith Bayad wa Riyad manuscript is believed to be the only illustrated manuscript known to have survived from more than eight centuries of Muslim and Arab presence in Spain.
Translations
Thanks to the Toledo School of TranslatorsToledo School of Translators
The Toledo School of Translators is the name that commonly describes the group of scholars who worked together in the city of Toledo during the 12th and 13th centuries, to translate many of the philosophical and scientific works from classical Arabic, classical Greek, and ancient Hebrew.The School...
, established after Toledo was reconquered by the Christian forces in 1085, the work of many Islamic scholars, that previously could have only be accessed by Muslims, especially in Al-Andalus and Islamic Sicily
History of Islam in southern Italy
The history of Islam in southern Italy begins with the Islamic conquest and subsequent rule of Sicily and Malta, a process that started in the 9th century. Islamic rule over Sicily was effective from 902, and the complete rule of the island lasted from 965 until 1061...
, finally found its way into European science. These scholars most translated new scientific and philosophical texts from Arabic
Arabic language
Arabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book...
into Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
.
One of the most productive translators in Castile was Gerard of Cremona
Gerard of Cremona
Gerard of Cremona was an Italian translator of Arabic scientific works found in the abandoned Arab libraries of Toledo, Spain....
, who translated 87 books from Arabic to Latin,
including Muhammad ibn Mūsā al-Khwārizmī
Muhammad ibn Musa al-Khwarizmi
'There is some confusion in the literature on whether al-Khwārizmī's full name is ' or '. Ibn Khaldun notes in his encyclopedic work: "The first who wrote upon this branch was Abu ʿAbdallah al-Khowarizmi, after whom came Abu Kamil Shojaʿ ibn Aslam." . 'There is some confusion in the literature on...
's On Algebra and Almucabala
The Compendious Book on Calculation by Completion and Balancing
, also known under a shorter name spelled as Hisab al-jabr w’al-muqabala, Kitab al-Jabr wa-l-Muqabala and other transliterations) is a mathematical book written in Arabic in approximately AD 820 by the Persian (Arabic for "The Compendious Book on Calculation by Completion and Balancing", in...
, Jabir ibn Aflah
Jabir ibn Aflah
Abū Muḥammad Jābir ibn Aflaḥ was a Muslim astronomer and mathematician from Seville, who was active in 12th century Andalusia. His work Iṣlāḥ al-Majisṭi influenced Islamic, Jewish and Christian astronomers....
's Elementa astronomica,
al-Kindi
Al-Kindi
' , known as "the Philosopher of the Arabs", was a Muslim Arab philosopher, mathematician, physician, and musician. Al-Kindi was the first of the Muslim peripatetic philosophers, and is unanimously hailed as the "father of Islamic or Arabic philosophy" for his synthesis, adaptation and promotion...
's On Optics, Ahmad ibn Muhammad ibn Kathīr al-Farghānī's On Elements of Astronomy on the Celestial Motions, al-Farabi
Al-Farabi
' known in the West as Alpharabius , was a scientist and philosopher of the Islamic world...
's On the Classification of the Sciences,
the chemical and medical
Islamic medicine
In the history of medicine, Islamic medicine, Arabic medicine or Arabian medicine refers to medicine developed in the Islamic Golden Age, and written in Arabic, the lingua franca of Islamic civilization....
works of Razi,
the works of Thabit ibn Qurra
Thabit ibn Qurra
' was a mathematician, physician, astronomer and translator of the Islamic Golden Age.Ibn Qurra made important discoveries in algebra, geometry and astronomy...
and Hunayn ibn Ishaq
Hunayn ibn Ishaq
Hunayn ibn Ishaq was a famous and influential Assyrian Nestorian Christian scholar, physician, and scientist, known for his work in translating Greek scientific and medical works into Arabic and Syriac during the heyday of the Islamic Abbasid Caliphate.Ḥunayn ibn Isḥaq was the most productive...
,
and the works of Arzachel
Arzachel
', Al-Zarqali, Ibn Zarqala , Latinized as Arzachel, was an instrument maker and one of the leading theoretical and practical astronomers of his time. Although his name is conventionally given as al-Zarqālī, it is probable that the correct form was al-Zarqālluh. He lived in Toledo in Castile,...
, Jabir ibn Aflah
Jabir ibn Aflah
Abū Muḥammad Jābir ibn Aflaḥ was a Muslim astronomer and mathematician from Seville, who was active in 12th century Andalusia. His work Iṣlāḥ al-Majisṭi influenced Islamic, Jewish and Christian astronomers....
, the Banū Mūsā
Banu Musa
The Banū Mūsā brothers , namely Abū Jaʿfar Muḥammad ibn Mūsā ibn Shākir , Abū al‐Qāsim Aḥmad ibn Mūsā ibn Shākir and Al-Ḥasan ibn Mūsā ibn Shākir , were three 9th-century Persian scholars of Baghdad who are known for their Book of Ingenious Devices on automata and mechanical devices...
, Abū Kāmil Shujā ibn Aslam, Abu al-Qasim
Abu al-Qasim
Abu al-Qasim Khalaf ibn al-Abbas Al-Zahrawi , also known in the West as Abulcasis, was an Arab physician who lived in Al-Andalus. He is considered the greatest medieval surgeon to have appeared from the Islamic World, and has been described by some as the father of modern surgery...
, and Ibn al-Haytham (including the Book of Optics
Book of Optics
The Book of Optics ; ; Latin: De Aspectibus or Opticae Thesaurus: Alhazeni Arabis; Italian: Deli Aspecti) is a seven-volume treatise on optics and other fields of study composed by the medieval Muslim scholar Alhazen .-See also:* Science in medieval Islam...
).
With the fall of the Emirate of Granada
Emirate of Granada
The Emirate of Granada , also known as the Nasrid Kingdom of Granada , was an emirate established in 1238 following the defeat of Muhammad an-Nasir of the Almohad dynasty by an alliance of Christian kingdoms at the Battle of Las Navas de Tolosa in 1212...
in 1492, the scientific and technological initiative of the Islamic world was inherited by Europeans and laid the foundations for Europe's Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
and Scientific Revolution
Scientific revolution
The Scientific Revolution is an era associated primarily with the 16th and 17th centuries during which new ideas and knowledge in physics, astronomy, biology, medicine and chemistry transformed medieval and ancient views of nature and laid the foundations for modern science...
.
Music

Musical instrument
A musical instrument is a device created or adapted for the purpose of making musical sounds. In principle, any object that produces sound can serve as a musical instrument—it is through purpose that the object becomes a musical instrument. The history of musical instruments dates back to the...
s are believed to have been derived from Arabic musical instruments used in Al-Andalus: the naker
Naker
A naker or nakir is a small drum, of Arabic origin, and the forebear of the European timpani .The nakers were imported into Europe during the Crusades of the 13th century....
from naqareh
Naqareh
The naqqāra is a drum with a rounded back and a hide head. It is thus a membranophone.The term naqqāra , also naqqarat, naqqarah, naqqåre, nakkare, nagora comes from the Arabic verb naqr- that means "to strike, beat".-Construction:The rounded section of a naqqara is made of baked clay, while the...
, adufe
Adufe
The adufe is a traditional square tambourine of Moorish origin, which is used in Portugal.-History:A Portuguese percussion instrument, it was traditionally used in the Beira and Trás-os-Montes regions. It was also used in many other regions across the Iberian Peninsula, and similar instruments are...
from al-duff
Daf
A daf is a frame drum used as a musical instrument in popular and classical music. The term daf is used in Iran / Kurdistan for a large drum that has a series of four interlinked rings in the frame. Daf is mostly used in Middle East, Iran, Armenia, Pakistan, Turkey, Tajikistan, Azerbaijan and ...
, alboka
Alboka
The alboka is a double hornpipe or clarinet native to the Basque Country.Although the alboka is a woodwind instrument, its name is derived from the Arabic "al-bûq"...
from al-buq, anafil
Naffir
Naffīr is an Arabic word used in parts of Sudan to describe particular types of communal work undertakings. Naffīr has been described as including a group recruited through family networks, in-laws and village neighbors for some particular purpose, which then disbands when that purpose is...
from al-nafir, exabeba from al-shabbaba (flute
Flute
The flute is a musical instrument of the woodwind family. Unlike woodwind instruments with reeds, a flute is an aerophone or reedless wind instrument that produces its sound from the flow of air across an opening...
), atabal (bass drum
Bass drum
Bass drums are percussion instruments that can vary in size and are used in several musical genres. Three major types of bass drums can be distinguished. The type usually seen or heard in orchestral, ensemble or concert band music is the orchestral, or concert bass drum . It is the largest drum of...
) from al-tabl, atambal from al-tinbal,
the balaban, the castanet
Castanet
Castanets are a percussion instrument , used in Moorish, Ottoman, ancient Roman, Italian, Spanish, Sephardic Music, and Portuguese music. The instrument consists of a pair of concave shells joined on one edge by a string. They are held in the hand and used to produce clicks for rhythmic accents or...
from kasatan, sonajas de azófar
Tuna (music)
A University Tuna is a musical group in Spain, Portugal, The Netherlands, Central America or South America, made up of university students. It is also known as a Tuna or Tunas if it is in plural...
from sunuj al-sufr, the conical bore
Bore (wind instruments)
The bore of a wind instrument is its interior chamber that defines a flow path through which air travels and is set into vibration to produce sounds. The shape of the bore has a strong influence on the instruments' timbre.-Bore shapes:...
wind instrument
Wind instrument
A wind instrument is a musical instrument that contains some type of resonator , in which a column of air is set into vibration by the player blowing into a mouthpiece set at the end of the resonator. The pitch of the vibration is determined by the length of the tube and by manual modifications of...
s, the xelami from the sulami or fistula
Fistula
In medicine, a fistula is an abnormal connection or passageway between two epithelium-lined organs or vessels that normally do not connect. It is generally a disease condition, but a fistula may be surgically created for therapeutic reasons.-Locations:Fistulas can develop in various parts of the...
(flute or musical pipe
Organ pipe
An organ pipe is a sound-producing element of the pipe organ that resonates at a specific pitch when pressurized air is driven through it. Each pipe is tuned to a specific note of the musical scale...
),
the shawm
Shawm
The shawm was a medieval and Renaissance musical instrument of the woodwind family made in Europe from the 12th century until the 17th century. It was developed from the oriental zurna and is the predecessor of the modern oboe. The body of the shawm was usually turned from a single piece of wood,...
and dulzaina
Dulzaina
The dulzaina or dolçaina is a Spanish double reed instrument in the oboe family. It has a conical shape and is the equivalent of the Breton bombarde....
from the reed instruments
Reed (instrument)
A reed is a thin strip of material which vibrates to produce a sound on a musical instrument. The reeds of most Woodwind instruments are made from Arundo donax or synthetic material; tuned reeds are made of metal or synthetics.-Single reeds:Single reeds are used on the mouthpieces of clarinets...
zamr and al-zurna
Zurna
The zurna , is a multinational outdoor wind instrument, usually accompanied by a davul in Anatolian folk music. The name is from Turkish zurna, itself derived from Persian سرنای surnāy, composed of sūr “banquet, feast” and nāy “reed, pipe”...
,
the gaita
Galician gaita
The gaita or gaita de foles is a traditional bagpipe of Galicia, Asturias and northern Portugal.The name gaita is used in Galician and Spanishlanguages as a generic term for "bagpipe"...
from the ghaita
Rhaita
The rhaita or ghaita is a double reed instrument from Northern Africa. It is nearly identical in construction to the Arabic mizmar and the Turkish zurna....
, rackett
Rackett
The rackett is a Renaissance-era double reed wind instrument.There are several sizes of rackett, in a family ranging from soprano to great bass. Relative to their pitch, racketts are quite small . This is achieved through its ingenious construction...
from iraqya or iraqiyya,
the harp
Harp
The harp is a multi-stringed instrument which has the plane of its strings positioned perpendicularly to the soundboard. Organologically, it is in the general category of chordophones and has its own sub category . All harps have a neck, resonator and strings...
and zither
Zither
The zither is a musical string instrument, most commonly found in Slovenia, Austria, Hungary citera, northwestern Croatia, the southern regions of Germany, alpine Europe and East Asian cultures, including China...
from the qanun
Kanun (Instrument)
The Qanun is a string instrument found in the 10th century in Farab in Turkestan...
,
canon
Canon (music)
In music, a canon is a contrapuntal composition that employs a melody with one or more imitations of the melody played after a given duration . The initial melody is called the leader , while the imitative melody, which is played in a different voice, is called the follower...
from qanun, geige
Violin
The violin is a string instrument, usually with four strings tuned in perfect fifths. It is the smallest, highest-pitched member of the violin family of string instruments, which includes the viola and cello....
(violin) from ghichak,
and the theorbo
Theorbo
A theorbo is a plucked string instrument. As a name, theorbo signifies a number of long-necked lutes with second pegboxes, such as the liuto attiorbato, the French théorbe des pièces, the English theorbo, the archlute, the German baroque lute, the angélique or angelica. The etymology of the name...
from the tarab. It is also commonly acknowledged by flamenco performers that the vocal, instrumental, and dance elements of modern flamenco were greatly influenced by the Arab performing arts.
Pottery

Pottery
Pottery is the material from which the potteryware is made, of which major types include earthenware, stoneware and porcelain. The place where such wares are made is also called a pottery . Pottery also refers to the art or craft of the potter or the manufacture of pottery...
created in Al-Andalus, after the Moors
Moors
The description Moors has referred to several historic and modern populations of the Maghreb region who are predominately of Berber and Arab descent. They came to conquer and rule the Iberian Peninsula for nearly 800 years. At that time they were Muslim, although earlier the people had followed...
had introduced two ceramic
Ceramic
A ceramic is an inorganic, nonmetallic solid prepared by the action of heat and subsequent cooling. Ceramic materials may have a crystalline or partly crystalline structure, or may be amorphous...
techniques to Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
: glazing
Ceramic glaze
Glaze is a layer or coating of a vitreous substance which has been fired to fuse to a ceramic object to color, decorate, strengthen or waterproof it.-Use:...
with an opaque
Opacity (optics)
Opacity is the measure of impenetrability to electromagnetic or other kinds of radiation, especially visible light. In radiative transfer, it describes the absorption and scattering of radiation in a medium, such as a plasma, dielectric, shielding material, glass, etc...
white tin-glaze
Tin-glazing
Tin-glazing is the process of giving ceramic items a tin-based glaze which is white, glossy and opaque, normally applied to red or buff earthenware. The opacity and whiteness of tin glaze make it valued by its ability to decorate with colour....
, and painting in metallic lusters. Hispano-Moresque ware was distinguished from the pottery of Christendom
Christendom
Christendom, or the Christian world, has several meanings. In a cultural sense it refers to the worldwide community of Christians, adherents of Christianity...
by the Islamic character of its decoration.
The tin-glazing
Tin-glazing
Tin-glazing is the process of giving ceramic items a tin-based glaze which is white, glossy and opaque, normally applied to red or buff earthenware. The opacity and whiteness of tin glaze make it valued by its ability to decorate with colour....
of ceramic
Ceramic
A ceramic is an inorganic, nonmetallic solid prepared by the action of heat and subsequent cooling. Ceramic materials may have a crystalline or partly crystalline structure, or may be amorphous...
s was invented by Muslim potters in 8th century Basra
Basra
Basra is the capital of Basra Governorate, in southern Iraq near Kuwait and Iran. It had an estimated population of two million as of 2009...
, Iraq
Iraq
Iraq ; officially the Republic of Iraq is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert....
. The earliest tin-glazed pottery
Tin-glazed pottery
Tin-glazed pottery is a majolica pottery covered in glaze containing tin oxide which is white, shiny and opaque. The pottery body is usually made of red or buff colored earthenware and the white glaze was often used to imitate Chinese porcelain...
thus appears to have been made in Iraq
Iraq
Iraq ; officially the Republic of Iraq is a country in Western Asia spanning most of the northwestern end of the Zagros mountain range, the eastern part of the Syrian Desert and the northern part of the Arabian Desert....
in the 9th century. From there, it spread to Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
, Persia and Iberian Peninsula, before reaching Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
in the Renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
, Holland in the 16th century, and England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
, France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
and other European countries shortly after.
Lusterware
Lusterware
Lusterware or Lustreware is a type of pottery or porcelain with a metallic glaze that gives the effect of iridescence, produced by metallic oxides in an overglaze finish, which is given a second firing at a lower temperature in a "muffle kiln", reduction kiln, which excludes oxygen.The first use...
was invented by Jābir ibn Hayyān, who applied it to ceramic glazes in the 8th century. After the production of lusterware became popular in the Middle East
Middle East
The Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
, it spread to Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
—first to Al-Andalus, notably at Málaga
Málaga
Málaga is a city and a municipality in the Autonomous Community of Andalusia, Spain. With a population of 568,507 in 2010, it is the second most populous city of Andalusia and the sixth largest in Spain. This is the southernmost large city in Europe...
, and then to Italy
History of Islam in southern Italy
The history of Islam in southern Italy begins with the Islamic conquest and subsequent rule of Sicily and Malta, a process that started in the 9th century. Islamic rule over Sicily was effective from 902, and the complete rule of the island lasted from 965 until 1061...
, where it was used to enhance maiolica
Maiolica
Maiolica is Italian tin-glazed pottery dating from the Renaissance. It is decorated in bright colours on a white background, frequently depicting historical and legendary scenes.-Name:...
.
An albarello
Albarello
An albarello is a type of maiolica earthenware jar, originally a medicinal jar designed to hold apothecaries' ointments and dry drugs. The development of this type of pharmacy jar had its roots in the Middle East during the time of the Islamic conquests....
is a type of maiolica
Maiolica
Maiolica is Italian tin-glazed pottery dating from the Renaissance. It is decorated in bright colours on a white background, frequently depicting historical and legendary scenes.-Name:...
earthenware jar originally designed to hold apothecaries'
Apothecary
Apothecary is a historical name for a medical professional who formulates and dispenses materia medica to physicians, surgeons and patients — a role now served by a pharmacist and some caregivers....
ointments and dry drugs. The development of this type of pharmacy
Pharmacy
Pharmacy is the health profession that links the health sciences with the chemical sciences and it is charged with ensuring the safe and effective use of pharmaceutical drugs...
jar had its roots in the Islamic Middle East. It was brought to Italy by Hispano-Moresque
Hispano-Moresque
Hispano-Moresque ware is a style of initially Islamic pottery created in Al Andalus or Muslim Spain, which continued to be produced under Christian rule in styles blending Islamic and European elements...
traders by the 15th century.
Technology legacy

Infrastructure
Industrial water mills were built in Al-Andalus between the 11th and 13th centuries. FullingFulling
Fulling or tucking or walking is a step in woolen clothmaking which involves the cleansing of cloth to eliminate oils, dirt, and other impurities, and making it thicker. The worker who does the job is a fuller, tucker, or walker...
mills, steel mill
Steel mill
A steel mill or steelworks is an industrial plant for the manufacture of steel.Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon. It is produced in a two-stage process. First, iron ore is reduced or smelted with coke and limestone in a blast furnace, producing molten iron which is either cast into pig iron or...
s, and other mills, spread from Al-Andalus to Christian Iberia by the 12th century. The first windmill
Windmill
A windmill is a machine which converts the energy of wind into rotational energy by means of vanes called sails or blades. Originally windmills were developed for milling grain for food production. In the course of history the windmill was adapted to many other industrial uses. An important...
s were built in Sistan
Sistan
Sīstān is a border region in eastern Iran , southwestern Afghanistan and northern tip of Southwestern Pakistan .-Etymology:...
, Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
, sometime between the 7th century and 9th century, as described by Muslim
Muslim
A Muslim, also spelled Moslem, is an adherent of Islam, a monotheistic, Abrahamic religion based on the Quran, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God as revealed to prophet Muhammad. "Muslim" is the Arabic term for "submitter" .Muslims believe that God is one and incomparable...
geographers. These were horizontal axis windmills with rectangle shaped blade
Blade
A blade is that portion of a tool, weapon, or machine with a cutting edge and/or a pointed tip that is designed to cut and/or puncture, stab, slash, chop, slice, thrust, or scrape animate or inanimate surfaces or materials...
s, geared to long vertical driveshaft
Driveshaft
A drive shaft, driveshaft, driving shaft, propeller shaft, or Cardan shaft is a mechanical component for transmitting torque and rotation, usually used to connect other components of a drive train that cannot be connected directly because of distance or the need to allow for relative movement...
s. These were introduced to Europe through Spain. The bridge mill was a unique type of water mill that was built as part of the superstructure
Superstructure
A superstructure is an upward extension of an existing structure above a baseline. This term is applied to various kinds of physical structures such as buildings, bridges, or ships...
of a bridge
Bridge
A bridge is a structure built to span physical obstacles such as a body of water, valley, or road, for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle...
. The earliest record of a bridge mill is from Córdoba in the 12th century. The first forge
Forge
A forge is a hearth used for forging. The term "forge" can also refer to the workplace of a smith or a blacksmith, although the term smithy is then more commonly used.The basic smithy contains a forge, also known as a hearth, for heating metals...
to be driven by a hydropower
Hydropower
Hydropower, hydraulic power, hydrokinetic power or water power is power that is derived from the force or energy of falling water, which may be harnessed for useful purposes. Since ancient times, hydropower has been used for irrigation and the operation of various mechanical devices, such as...
ed water mill rather than manual labour
Manual labour
Manual labour , manual or manual work is physical work done by people, most especially in contrast to that done by machines, and also to that done by working animals...
, also known as a finery forge
Finery forge
Iron tapped from the blast furnace is pig iron, and contains significant amounts of carbon and silicon. To produce malleable wrought iron, it needs to undergo a further process. In the early modern period, this was carried out in a finery forge....
, was invented in 12th century Al-Andalus. Stamp mill
Stamp mill
A stamp mill is a type of mill machine that crushes material by pounding rather than grinding, either for further processing or for extraction of metallic ores. Breaking material down is a type of unit operation....
s were used by miners in Samarkand
Samarkand
Although a Persian-speaking region, it was not united politically with Iran most of the times between the disintegration of the Seleucid Empire and the Arab conquest . In the 6th century it was within the domain of the Turkic kingdom of the Göktürks.At the start of the 8th century Samarkand came...
from as early as 973. They were used in medieval Persia for the purpose of crushing ore
Ore
An ore is a type of rock that contains minerals with important elements including metals. The ores are extracted through mining; these are then refined to extract the valuable element....
. By the 11th century, stamp mills were in widespread use throughout the Islamic world, including Al-Andalus.
Many Damdams (or dams
DAMS
Driot-Arnoux Motorsport is a racing team from France, involved in many areas of motorsports. DAMS was founded in 1988 by Jean-Paul Driot and former Formula One driver René Arnoux. It is headquartered near Le Mans, only 2 km from the Bugatti Circuit.- History :The year after its foundation,...
), acequia
Acequia
An acequia or séquia is a community-operated waterway used in Spain and former Spanish colonies in the Americas for irrigation. Particularly in Spain, the Andes, northern Mexico, and the modern-day American Southwest, acequias are usually historically engineered canals that carry snow runoff or...
s, and qanat
Qanat
A qanāt is a water management system used to provide a reliable supply of water for human settlements and irrigation in hot, arid and semi-arid climates...
water supply
Water supply
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavours or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes...
systems, and "Tribunal of Waters" irrigation
Irrigation
Irrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
systems, were built during the Islamic Golden Age and are still in use today in Islamic countries and in formerly Islamic Provinces in Europe such as Sicily
Sicily
Sicily is a region of Italy, and is the largest island in the Mediterranean Sea. Along with the surrounding minor islands, it constitutes an autonomous region of Italy, the Regione Autonoma Siciliana Sicily has a rich and unique culture, especially with regard to the arts, music, literature,...
and the Iberian Peninsula
Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula , sometimes called Iberia, is located in the extreme southwest of Europe and includes the modern-day sovereign states of Spain, Portugal and Andorra, as well as the British Overseas Territory of Gibraltar...
, particularly in the Andalusia, Aragon
Aragon
Aragon is a modern autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. Located in northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces : Huesca, Zaragoza, and Teruel. Its capital is Zaragoza...
and Valencia
Valencia (province)
Valencia or València is a province of Spain, in the central part of the Valencian Community.It is bordered by the provinces of Alicante, Albacete, Cuenca, Teruel, Castellón, and the Mediterranean Sea...
Provinces of Spain. The Arabic systems of irrigation and water distribution were later adopted in the Canary Islands
Canary Islands
The Canary Islands , also known as the Canaries , is a Spanish archipelago located just off the northwest coast of mainland Africa, 100 km west of the border between Morocco and the Western Sahara. The Canaries are a Spanish autonomous community and an outermost region of the European Union...
and Americas
Americas
The Americas, or America , are lands in the Western hemisphere, also known as the New World. In English, the plural form the Americas is often used to refer to the landmasses of North America and South America with their associated islands and regions, while the singular form America is primarily...
due to the Spanish
Spain
Spain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
and are still used including in Texas
Texas
Texas is the second largest U.S. state by both area and population, and the largest state by area in the contiguous United States.The name, based on the Caddo word "Tejas" meaning "friends" or "allies", was applied by the Spanish to the Caddo themselves and to the region of their settlement in...
, New Mexico
New Mexico
New Mexico is a state located in the southwest and western regions of the United States. New Mexico is also usually considered one of the Mountain States. With a population density of 16 per square mile, New Mexico is the sixth-most sparsely inhabited U.S...
, Mexico
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
, Peru
Peru
Peru , officially the Republic of Peru , is a country in western South America. It is bordered on the north by Ecuador and Colombia, on the east by Brazil, on the southeast by Bolivia, on the south by Chile, and on the west by the Pacific Ocean....
, and Chile
Chile
Chile ,officially the Republic of Chile , is a country in South America occupying a long, narrow coastal strip between the Andes mountains to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. It borders Peru to the north, Bolivia to the northeast, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far...
.
Muslim cities such as Córdoba had advanced domestic water systems with sanitary sewer
Sanitary sewer
A sanitary sewer is a separate underground carriage system specifically for transporting sewage from houses and commercial buildings to treatment or disposal. Sanitary sewers serving industrial areas also carry industrial wastewater...
s, public baths, drinking fountain
Fountain
A fountain is a piece of architecture which pours water into a basin or jets it into the air either to supply drinking water or for decorative or dramatic effect....
s, piped
Water pipe
Water pipes are pipes or tubes, frequently made of polyvinyl chloride , ductile iron, steel, cast iron, polypropylene, polyethylene, or copper, that carry pressurized and treated fresh water to buildings , as well as inside the building.-History:For many centuries, lead was the favoured material...
drinking water
Drinking water
Drinking water or potable water is water pure enough to be consumed or used with low risk of immediate or long term harm. In most developed countries, the water supplied to households, commerce and industry is all of drinking water standard, even though only a very small proportion is actually...
supplies, and widespread private and public toilet and bathing
Bathing
Bathing is the washing or cleansing of the body in a fluid, usually water or an aqueous solution. It may be practised for personal hygiene, religious ritual or therapeutic purposes or as a recreational activity....
facilities. The first street lamps
Street light
A street light, lamppost, street lamp, light standard, or lamp standard is a raised source of light on the edge of a road or walkway, which is turned on or lit at a certain time every night. Modern lamps may also have light-sensitive photocells to turn them on at dusk, off at dawn, or activate...
were built in the Arab Empire
Caliphate of Córdoba
The Caliphate of Córdoba ruled the Iberian peninsula and part of North Africa, from the city of Córdoba, from 929 to 1031. This period was characterized by remarkable success in trade and culture; many of the masterpieces of Islamic Iberia were constructed in this period, including the famous...
, especially in Córdoba, which also had the first facilities and waste container
Waste container
A waste container is a container for temporarily storing refuse and waste. Different terms are in use, depending on the language area, the design and material and the respective site .The most general terms are waste receptacle and container bin.Common terms include dustbin ,...
s for litter collection.
Aviation
In 9th century Al-Andalus, Abbas Ibn FirnasAbbas Ibn Firnas
Abbas Ibn Firnas , also known as Abbas Qasim Ibn Firnas and عباس بن فرناس , was a Muslim Andalusian polymath: an inventor, engineer, aviator, physician, Arabic poet, and Andalusian musician. Of Berber descent, he was born in Izn-Rand Onda, Al-Andalus , and lived in the Emirate of Córdoba...
(Armen Firnas) invented a primitive version of the parachute
Parachute
A parachute is a device used to slow the motion of an object through an atmosphere by creating drag, or in the case of ram-air parachutes, aerodynamic lift. Parachutes are usually made out of light, strong cloth, originally silk, now most commonly nylon...
. John H. Lienhard described it in The Engines of Our Ingenuity as follows:
Ibn Firnas was also the first to make an attempt at controlled flight
Flight
Flight is the process by which an object moves either through an atmosphere or beyond it by generating lift or propulsive thrust, or aerostatically using buoyancy, or by simple ballistic movement....
, as opposed to earlier gliding
Gliding
Gliding is a recreational activity and competitive air sport in which pilots fly unpowered aircraft known as gliders or sailplanes using naturally occurring currents of rising air in the atmosphere to remain airborne. The word soaring is also used for the sport.Gliding as a sport began in the 1920s...
attempts in ancient China which were not controllable. Ibn Firnas manipulated the flight controls
Aircraft flight control systems
A conventional fixed-wing aircraft flight control system consists of flight control surfaces, the respective cockpit controls, connecting linkages, and the necessary operating mechanisms to control an aircraft's direction in flight...
of his hang glider using two sets of artificial wing
Wing
A wing is an appendage with a surface that produces lift for flight or propulsion through the atmosphere, or through another gaseous or liquid fluid...
s to adjust his altitude
Altitude
Altitude or height is defined based on the context in which it is used . As a general definition, altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The reference datum also often varies according to the context...
and to change his direction. He successfully returned to where he had lifted off from, but his landing
Landing
thumb|A [[Mute Swan]] alighting. Note the ruffled feathers on top of the wings indicate that the swan is flying at the [[Stall |stall]]ing speed...
was unsuccessful. According to Philip Hitti in History of the Arabs:
Ibn Firnas' glider was possibly the first hang glider
Hang gliding
Hang gliding is an air sport in which a pilot flies a light and unmotorized foot-launchable aircraft called a hang glider ....
, though there were earlier instances of manned kite
Kite
A kite is a tethered aircraft. The necessary lift that makes the kite wing fly is generated when air flows over and under the kite's wing, producing low pressure above the wing and high pressure below it. This deflection also generates horizontal drag along the direction of the wind...
s being used in ancient China. Knowledge of Firman and Firnas' flying machines spread to other parts of Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
from Arabic
Arabic language
Arabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book...
references. Ibn Firnas' hang glider was also the first to have artificial wing
Wing
A wing is an appendage with a surface that produces lift for flight or propulsion through the atmosphere, or through another gaseous or liquid fluid...
s, though the flight was ultimately unsuccessful.
Genetic legacy of Muslim rule
A number of studies have tried to find out the genetic impact of non-European Muslim populations on the modern Spanish and Portuguese populations, through comparison of genetic markers in Spain and Portugal with North Africa and the Near East. The most recent and thorough study about Moorish influence in the Iberian Peninsula by Capelli et al. 2009 reported that North African male haplogroups, especially E1b1b1b (E-M81), E1b1b1a-b (M78 derived chromosomes showing the rare DYS439 allele 10, or E-V65) and a subset of J1 (M267 derived), represented, on average, 7-8% of the current Iberian male lineages.Historically introduced NW African types in Iberia (Capelli et al. (2009))
| Sample | N | E1b1b1b (M81) Haplogroup E1b1b1b (Y-DNA) In human genetics, E1b1b1b , is the name of a major Y chromosome haplogroup mainly found in North Africa and to a lesser extent in Western Asia and Europe. E1b1b1b is dominated by its dominant sub-clade E1b1b1b1 , formerly known as E1b1b1b, E3b1b, and E3b2, which was discovered first, and has... |
E1b1b1a-b (V65) | J1 Haplogroup J1 (Y-DNA) In human genetics, Y DNA haplogroup J1, also known as J-M267, is a sub-haplogroup of Y DNA haplogroup J, along with its sibling clade Y DNA haplogroup J2. Men with this type of Y DNA share a common paternal ancestry, which is demonstrated and defined by the presence of the SNP mutation referred to... (subset) |
Total % |
| Spain | 717 | 5.2 | 1 | 1.5 | 7.7 |
| Portugal | 659 | 5 | 0.3 | 1.8 | 7.1 |
| Iberia | 1376 | 5.1 | 0.7 | 1.7 | 7.4 |
See also
- Al-Andalus
- Social and cultural exchange in Al-AndalusSocial and cultural exchange in Al-AndalusMuslims, Christians, and Jews co-existed for over seven centuries in the geographic area known as Al-Andalus or Moorish Spain. The degree to which the Christians and the Jews were tolerated by their Muslim, and predominantly Arab rulers, is a subject widely contested among historians...
- Timeline of the Muslim presence in the Iberian peninsulaTimeline of the Muslim presence in the Iberian peninsulaThis is a timeline of notable events in the Muslim presence in Iberia, which started with the Umayyad conquest in the 8th century.-Conquest :...
- Muslim conquestsMuslim conquestsMuslim conquests also referred to as the Islamic conquests or Arab conquests, began with the Islamic prophet Muhammad. He established a new unified polity in the Arabian Peninsula which under the subsequent Rashidun and Umayyad Caliphates saw a century of rapid expansion of Muslim power.They...
- Caliph of Córdoba
- Al'Garb Al'AndalusAl'Garb Al'AndalusThe Al-Gharb Al-Andalus , or just Al-Gharb , was the name given by the Moors of Iberia to the modern region of Algarve and, by extension, to most of Portugal.-See also:*Timeline of Portuguese history...
- AlmoravidsAlmoravidsThe Almoravids were a Berber dynasty of Morocco, who formed an empire in the 11th-century that stretched over the western Maghreb and Al-Andalus. Their capital was Marrakesh, a city which they founded in 1062 C.E...
- Almohad dynasty
- La ConvivenciaLa ConvivenciaLa Convivencia is a term used to describe a postulated situation in Spanish history when Jews, Muslims, and Catholics in Spain lived in relative peace together within the different kingdoms. It lasted from the Muslim Umayyad conquest of Hispania in 711 until 1492, concurrent with the Reconquista...
- Islamic Golden AgeIslamic Golden AgeDuring the Islamic Golden Age philosophers, scientists and engineers of the Islamic world contributed enormously to technology and culture, both by preserving earlier traditions and by adding their own inventions and innovations...
- Islam in SpainIslam in SpainIslam in Spain has had a fundamental presence in the culture and history of the nation. The religion was present in modern Spanish soil from 711 until 1492 under the rule of the Arabs and Moors of al-Andalus. For key historical dates, see Timeline of the Muslim presence in the Iberian peninsula...
- History of Islam
- History of the Jews under Muslim rule
- Golden age of Jewish culture in the Iberian PeninsulaGolden age of Jewish culture in the Iberian PeninsulaThe golden age of Jewish culture in Spain coincided with the Middle Ages in Europe, a period of Muslim rule throughout much of the Iberian Peninsula. During that time, Jews were generally accepted in society and Jewish religious, cultural, and economic life blossomed.The nature and length of this...
- Islam and antisemitism#Iberian peninsula
- Arab diasporaArab diasporaArab diaspora refers to Arab immigrants, and their descendants who, voluntarily or as refugees, emigrated from their native lands and now reside in non-Arab countries, primarily in Latin America, and Europe, as well as North America and South Asia, parts of Southeast Asia, the Caribbean, and West...
- Spanish peopleSpanish peopleThe Spanish are citizens of the Kingdom of Spain. Within Spain, there are also a number of vigorous nationalisms and regionalisms, reflecting the country's complex history....
- DhimmiDhimmiA , is a non-Muslim subject of a state governed in accordance with sharia law. Linguistically, the word means "one whose responsibility has been taken". This has to be understood in the context of the definition of state in Islam...
- MoriscoMoriscoMoriscos or Mouriscos , meaning "Moorish", were the converted Christian inhabitants of Spain and Portugal of Muslim heritage. Over time the term was used in a pejorative sense applied to those nominal Catholics who were suspected of secretly practicing Islam.-Demographics:By the beginning of the...
- MozarabMozarabThe Mozarabs were Iberian Christians who lived under Arab Islamic rule in Al-Andalus. Their descendants remained unconverted to Islam, but did however adopt elements of Arabic language and culture...
- MuladiMuladiThe Muladi were Muslims of ethnic Iberian descent or of mixed Arab, Berber and European origin, who lived in Al-Andalus during the Middle Ages. They were also called "Musalima" .-Etymology:...
- Kemal ReisKemal ReisKemal Reis was a Turkish privateer and admiral of the Ottoman Empire. He was also the paternal uncle of the famous Ottoman admiral and cartographer Piri Reis who accompanied him in most of his important naval expeditions....
- List of Moroccan writers#List of Moorish writers
External links
- Paper by Georg Bossong evaluating proposals for the etymology of "al-Andalus". In German.
- Photocopy of the Ajbar Machmu'a, translated by Lafuente 1867
- The routes of al-Andalus (from the UNESCOUNESCOThe United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations...
web site) - History and influences of Andalusian music
- The Library of Iberian Resources Online
- Al-Andalus Chronology and Photos
- Christian Martyrs in Muslim Spain by Kenneth Baxter Wolf
- The Musical Legacy of Al-Andalus – historical maps, photos, and music showing the Great Mosque of Córdoba and related movements of people and culture over time
- Patricia, Countess Jellicoe, 1992, The Art of Islamic Spain, Saudi Aramco World
- "Cities of Light: The Rise and Fall of Islamic Spain" (documentary film)

