
Ontario
Encyclopedia
Ontario ɒ is a province of Canada
, located in east-central Canada
. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto
, and the nation's capital, Ottawa
.
Ontario is bordered by Manitoba on its west, Hudson Bay
on its north, Quebec
on its east, and by three states of the United States to its south (from west to east): Minnesota
, Michigan
, and New York
. Ohio
and Pennsylvania
are across Lake Erie
. All but a small portion of Ontario's 2,700 km (1,677 mi) border with the United States follow inland waterways: from the west at Lake of the Woods
, eastward along the major rivers and lakes of the Great Lakes
/St. Lawrence River drainage system. These are the Rainy River
, the Pigeon River, Lake Superior
, the St. Mary's River
, Lake Huron
, the St. Clair River
, Lake St. Clair
, the Detroit River
, Lake Erie
, the Niagara River
, Lake Ontario
, and along the St. Lawrence River from Kingston, Ontario
to the Quebec boundary just east of Cornwall, Ontario
.
Ontario is sometimes conceptually divided into two regions, Northern Ontario
and Southern Ontario
. The great majority of Ontario's population and its arable land
is located in the south. In contrast, the northern three-quarters of Ontario is sparsely populated.
The province is named after Lake Ontario, which is thought to have been derived from Ontarí:io, a Huron
(Wyandot) word meaning "great lake", or possibly skanadario which means "beautiful water" in the Iroquoian languages
. Ontario contains about 250,000 freshwater lakes.
 The province consists of three main geographical regions:
The province consists of three main geographical regions:
Despite the absence of any mountainous terrain in the province, there are large areas of uplands, particularly within the Canadian Shield which traverses the province from northwest to southeast and also above the Niagara Escarpment
which crosses the south. The highest point is Ishpatina Ridge
at 693 metres (2,273.6 ft) above sea level
located in Temagami, Northeastern Ontario
. In the south, elevations of over 500 m (1,640.42 ft) are surpassed near Collingwood, above the Blue Mountains in the Dundalk Highlands and in hilltops near the Madawaska River
in Renfrew County.
The Carolinian forest
zone covers most of the southwestern region of the province. The temperate and fertile Great Lakes-Saint Lawrence Valley in the south is part of the Eastern Great Lakes lowland forests
ecoregion
where the forest has now been largely replaced by agriculture, industrial and urban development. A well-known geographic feature is Niagara Falls
, part of the Niagara Escarpment
. The Saint Lawrence Seaway
allows navigation to and from the Atlantic Ocean
as far inland as Thunder Bay
in Northwestern Ontario. Northern Ontario
occupies roughly 87% of the surface area of the province; conversely Southern Ontario contains 94% of the population.
Point Pelee
is a peninsula of Lake Erie in southwestern Ontario (near Windsor
and Detroit, Michigan) that is the southernmost extent of Canada's mainland. Pelee Island
and Middle Island in Lake Erie extend slightly farther. All are south of 42°N
– slightly farther south than the northern border of California
.

 Ontario has three main climatic regions. Parts of Southwestern Ontario have a moderate humid continental climate
Ontario has three main climatic regions. Parts of Southwestern Ontario have a moderate humid continental climate
(Köppen climate classification
Dfa), similar to that of the inland Mid-Atlantic States
and the Great Lakes portion of the Midwestern United States
. The region has warm, humid summers and cold winters. Annual precipitation ranges from 750–1000 mm (29.5–39.4 in) and is well distributed throughout the year with a usual summer peak. Most of this region lies in the lee of the Great Lakes making for abundant snow in some areas. Under the Köppen climate parameters, Point Pelee and Middle Island, the southernmost parts of Canada located close to the lake boundary with Ohio, are at the dividing line of a humid continental climate
and a humid subtropical climate
(Dfa/Cfa).
Central and Eastern Ontario have a more severe humid continental climate (Köppen Dfb). This region is ontaro has warm and sometimes hot summers with colder, longer winters, ample snowfall and annual precipitation similar to the rest of Southern Ontario. Along the eastern shores of Lake Superior and Lake Huron, frequent heavy lake-effect snow squalls increase seasonal snowfall totals upwards of 3 m (9.8 ft) in some places.
The northernmost parts of Ontario — primarily north of 50°N have a subarctic climate
(Köppen Dfc) with long, severely cold winters and short, cool to warm summers with dramatic temperature changes possible in all seasons. With no major mountain ranges blocking sinking Arctic
air mass
es, temperatures of -40 C are not uncommon, snowfall remains on the ground for sometimes over half the year. Precipitation is generally less than 70 cm (27.6 in).
Severe and non-severe thunderstorm
s peak in summer. London
, situated in Southern
(Southwestern)
Ontario, has the most lightning strikes per year in Canada, averaging 34 days of thunderstorm activity per year. In a typical year, Ontario averages 15 confirmed tornado
touchdowns, though seldom they are destructive (the majority between F0 to F2 on the Fujita scale
). Tropical depression
remnants occasionally bring heavy rains and winds in the south, but are rarely deadly. A notable exception was Hurricane Hazel
which struck Toronto, in October 1954.
Winter storms can disrupt power supply and transportation, severe ice storms can also occur, especially in the east.
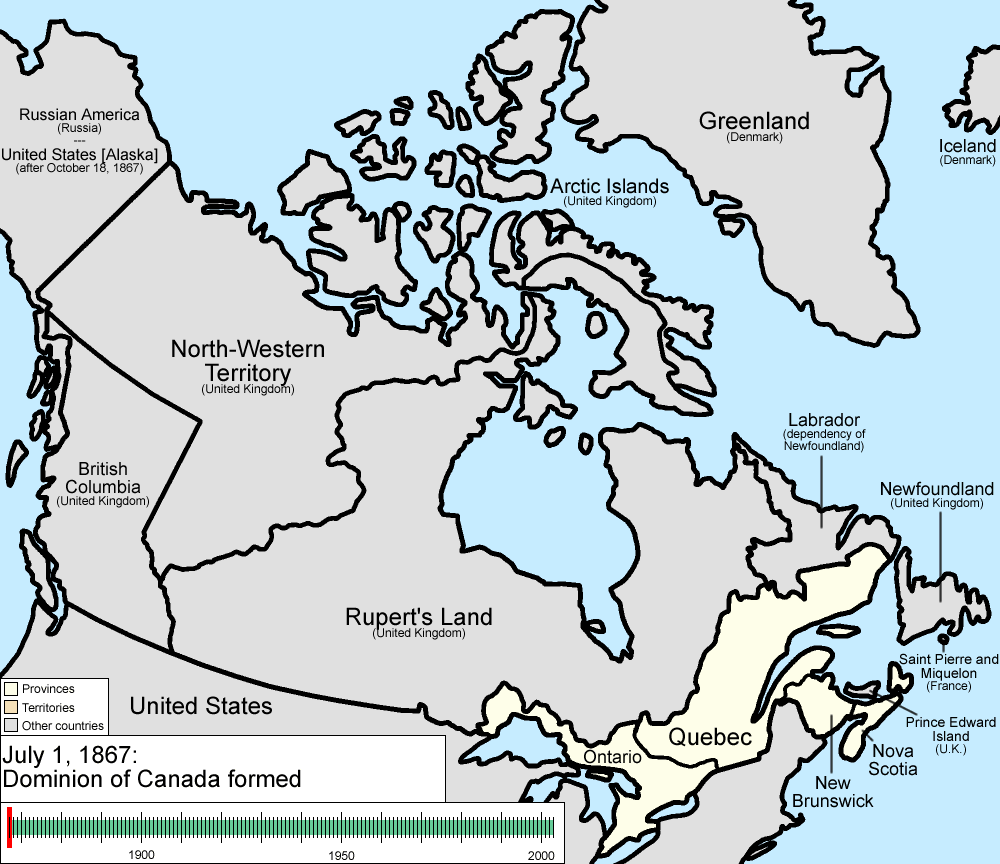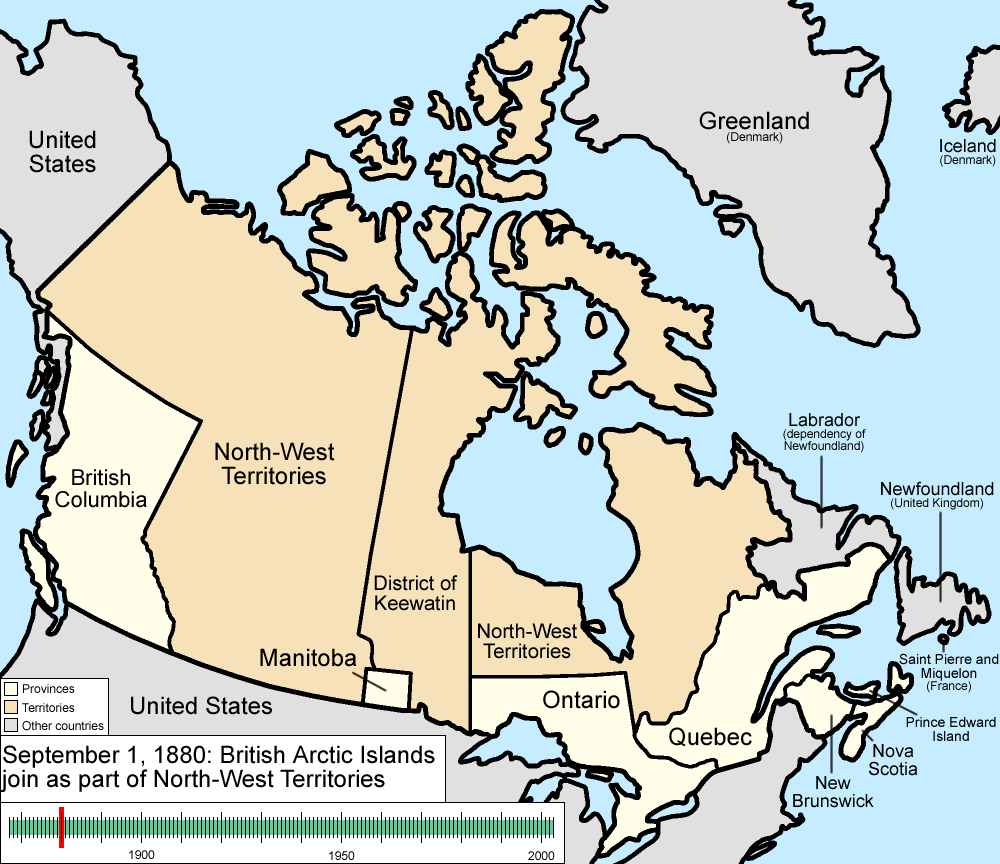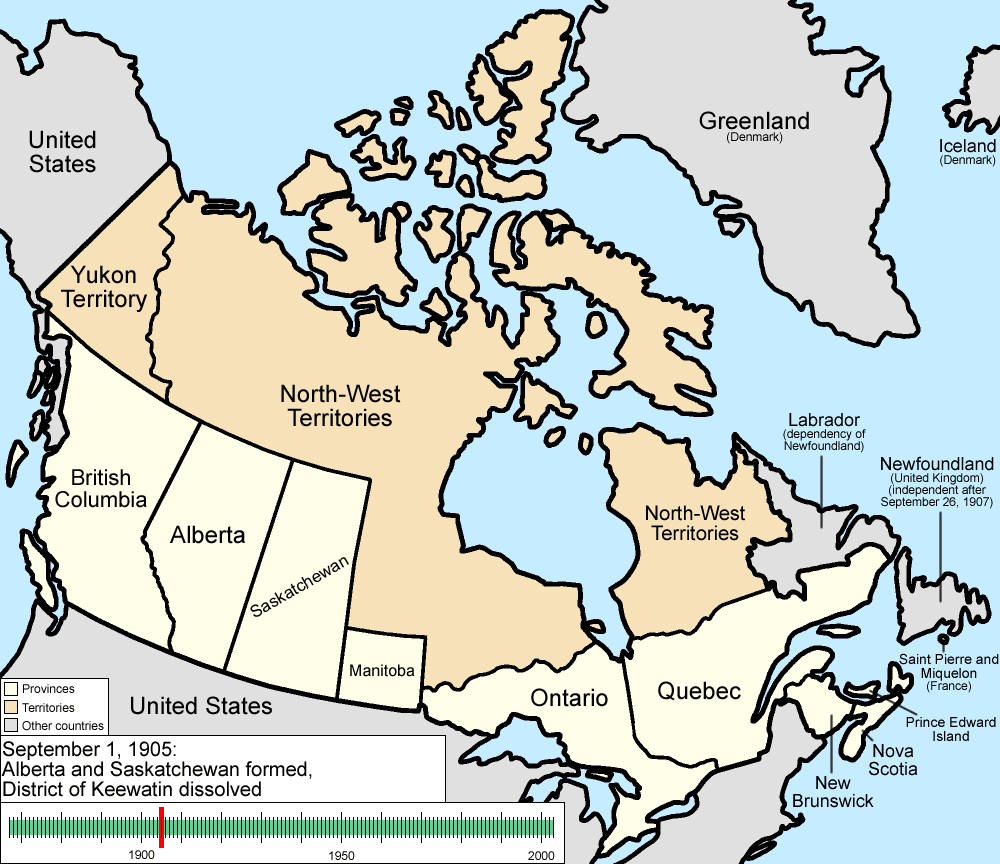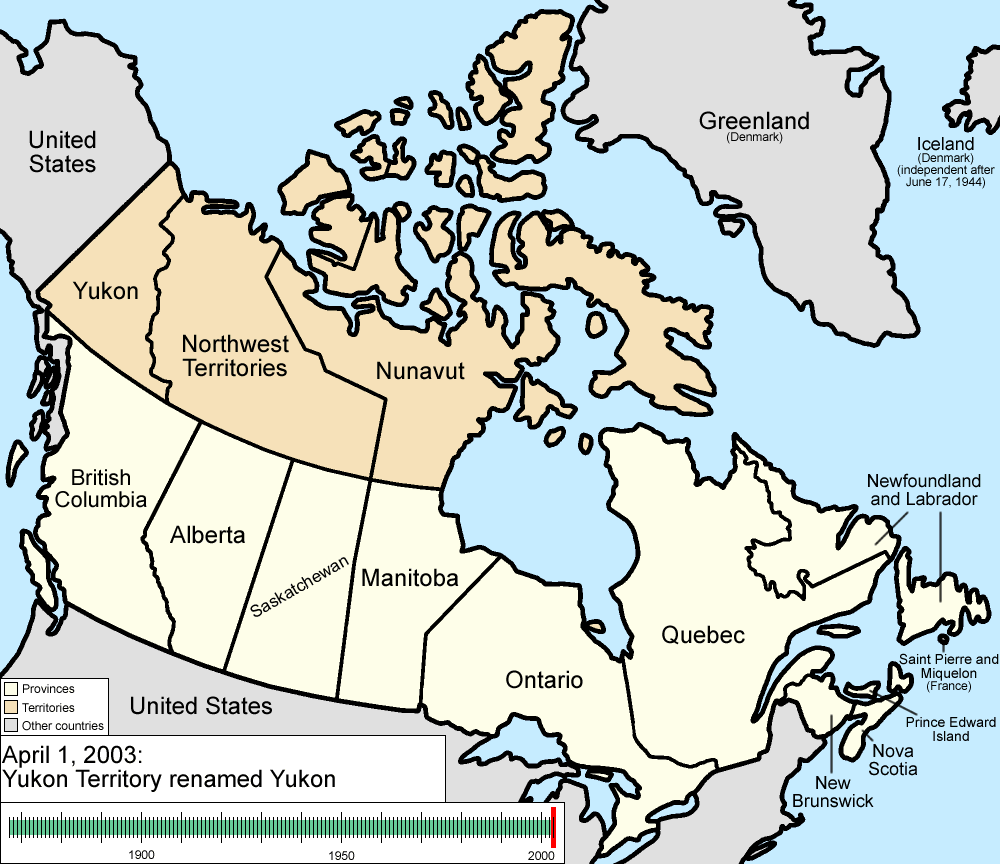 Land was not legally subdivided into administrative units until a treaty had been concluded with the native peoples ceding the land
Land was not legally subdivided into administrative units until a treaty had been concluded with the native peoples ceding the land
. In 1788, while part of the Province of Quebec (1763–1791), southern Ontario was divided into four districts: Hesse
, Lunenburg
, Mecklenburg
, and Nassau
.
In 1792, the four districts were renamed: Hesse became the Western District, Lunenburg became the Eastern District, Mecklenburg became the Midland District, and Nassau became the Home District. Counties were created within the districts.
By 1798, there were eight districts: Eastern, Home, Johnstown, London, Midland, Newcastle, Niagara, and Western.
By 1826, there were eleven districts: Bathurst, Eastern, Gore, Home, Johnstown, London, Midland, Newcastle, Niagara, Ottawa, and Western.
By 1838, there were twenty districts: Bathurst, Brock, Colbourne, Dalhousie, Eastern, Gore, Home, Huron, Johnstown, London, Midland, Newcastle, Niagara, Ottawa, Prince Edward, Simcoe
, Talbot, Victoria, Wellington, and Western.
In 1849, the districts of southern Ontario were abolished by the Province of Canada
, and county
governments took over certain municipal responsibilities. The Province of Canada also began creating districts in sparsely populated Northern Ontario with the establishment of Algoma District
and Nipissing District
in 1858.
The borders of Ontario, its new name in 1867, were provisionally expanded north and west. When the Province of Canada was formed, its borders were not entirely clear, and Ontario claimed to eventually reach all the way to the Rocky Mountains
and Arctic Ocean
. With Canada's acquisition of Rupert's Land
, Ontario was interested in clearly defining its borders, especially since some of the new areas it was interested in were rapidly growing. After the federal government asked Ontario to pay for construction in the new disputed area, the province asked for an elaboration on its limits, and its boundary was moved north to the 51st parallel north
.
The northern and western boundaries of Ontario were in dispute after Confederation
. Ontario's right to Northwestern Ontario was determined by the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council
in 1884 and confirmed by the Canada (Ontario Boundary) Act, 1889 of the Parliament of the United Kingdom
. By 1899, there were seven northern districts: Algoma, Manitoulin, Muskoka, Nipissing, Parry Sound, Rainy River, and Thunder Bay. Four more northern districts were created between 1907 and 1912: Cochrane, Kenora, Sudbury and Timiskaming.
 Before the arrival of the Europeans, the region was inhabited both by Algonquian
Before the arrival of the Europeans, the region was inhabited both by Algonquian
(Ojibwa
, Cree
and Algonquin) in the northern/western portions and Iroquois
and Wyandot (Huron) tribes more in the south/east. During the 17th century, the Algonquians and Hurons fought a bitter war against the Iroquois. The French explorer Étienne Brûlé
explored part of the area in 1610-12. The English explorer Henry Hudson
sailed into Hudson Bay
in 1611 and claimed the area for England
.
Samuel de Champlain
reached Lake Huron in 1615, and French
missionaries began to establish posts along the Great Lakes. French settlement was hampered by their hostilities with the Iroquois, who allied themselves with the British. From 1634 to 1640, Hurons were devastated by European infectious diseases, such as measles
and smallpox
, to which they had no immunity.
The British established trading post
s on Hudson Bay in the late 17th century and began a struggle for domination of Ontario. The 1763 Treaty of Paris
ended the Seven Years' War
by awarding nearly all of France's North American possessions
(New France
) to Britain. The region was annexed to Quebec in 1774. From 1783 to 1796, the Kingdom of Great Britain
granted United Empire Loyalists leaving the United States following the American Revolution
200 acre (80.9 ha) of land and other items with which to rebuild their lives.
This measure substantially increased the population of Canada west of the St. Lawrence-Ottawa River confluence during this period, a fact recognized by the Constitutional Act of 1791
, which split Quebec into the Canadas
: Upper Canada
southwest of the St. Lawrence-Ottawa River confluence, and Lower Canada
east of it. John Graves Simcoe
was appointed Upper Canada's first Lieutenant-Governor in 1793.
invaded Upper Canada across the Niagara River
and the Detroit River
, but were defeated and pushed back by British regulars, Canadian fencibles
and militias, and First Nations
warriors. The Americans gained control of Lake Erie and Lake Ontario, however. During the Battle of York
they occupied the Town of York
(later named Toronto) in 1813. The Americans looted the town and burned the Parliament Buildings but were soon forced to leave.
After the War of 1812, relative stability allowed for increasing numbers of immigrants to arrive from Europe rather than from the United States. As was the case in the previous decades, this deliberate immigration shift was encouraged by the colonial leaders. Despite affordable and often free land, many arriving newcomers, mostly from Britain and Ireland, found frontier life with the harsh climate difficult, and some of those with the means eventually returned home or went south. However, population growth far exceeded emigration in the decades that followed. It was a mostly agrarian-based society, but canal projects and a new network of plank roads spurred greater trade within the colony and with the United States, thereby improving previously damaged relations over time.
 Meanwhile, Ontario's numerous waterways aided travel and transportation into the interior and supplied water power
Meanwhile, Ontario's numerous waterways aided travel and transportation into the interior and supplied water power
for development. As the population increased, so did the industries and transportation networks, which in turn led to further development. By the end of the century, Ontario vied with Quebec as the nation's leader in terms of growth in population, industry, arts and communications.
Many in the colony however, began to chafe against the aristocratic Family Compact
who governed while benefiting economically from the region's resources, and who did not allow elected bodies the power to effect change (much as the Château Clique
ruled Lower Canada). This resentment spurred republican ideals and sowed the seeds for early Canadian nationalism
. Accordingly, rebellion in favour of responsible government
rose in both regions; Louis-Joseph Papineau
led the Lower Canada Rebellion
and William Lyon Mackenzie
led the Upper Canada Rebellion
.
sent Lord Durham
to investigate the causes of the unrest. He recommended that self-government be granted and that Lower and Upper Canada be re-joined in an attempt to assimilate the French Canadian
s. Accordingly, the two colonies were merged into the Province of Canada by the Act of Union 1840
, with the capital at Kingston
, and Upper Canada becoming known as Canada West. Parliament
ary self-government
was granted in 1848. There were heavy waves of immigration in the 1840s, and the population of Canada West more than doubled by 1851 over the previous decade. As a result, for the first time the English-speaking population of Canada West surpassed the French-speaking population of Canada East
, tilting the representative balance of power.
An economic boom in the 1850s coincided with railway expansion across the province, further increasing the economic strength of Central Canada. With the repeal of the Corn Laws
and a reciprocity agreement in place with United States, various industries such as timber, mining, farming and alcohol distilling benefited tremendously.
A political stalemate between the French
- and English
-speaking legislators, as well as fear of aggression from the United States during and immediately after the American Civil War
, led the political elite to hold a series of conferences in the 1860s to effect a broader federal union of all British North America
n colonies. The British North America Act took effect on July 1, 1867, establishing the Dominion of Canada, initially with four provinces: Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Quebec and Ontario. The Province of Canada was divided into Ontario and Quebec so that each linguistic group would have its own province. Both Quebec and Ontario were required by section 93 of the British North America Act
to safeguard existing educational rights and privileges of Protestant and the Catholic minority. Thus, separate Catholic schools and school boards
were permitted in Ontario. However, neither province had a constitutional requirement to protect its French- or English-speaking minority. Toronto was formally established as Ontario's provincial capital.
became Premier of Ontario
and remained as premier until 1896. He fought for provincial rights, weakening the power of the federal government
in provincial matters, usually through well-argued appeals to the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council. His battles with the federal government greatly decentralized
Canada, giving the provinces far more power than John A. Macdonald
had intended. He consolidated and expanded Ontario's educational and provincial institutions, created districts in Northern Ontario, and fought to ensure that those parts of Northwestern Ontario not historically part of Upper Canada (the vast areas north and west of the Lake Superior-Hudson Bay watershed, known as the District of Keewatin
) would become part of Ontario, a victory embodied in the Canada (Ontario Boundary) Act, 1889. He also presided over the emergence of the province into the economic powerhouse of Canada. Mowat was the creator of what is often called Empire Ontario.
Beginning with Sir John A. Macdonald's National Policy
(1879) and the construction of the Canadian Pacific Railway
(1875–1885) through Northern Ontario and the Canadian Prairies
to British Columbia
, Ontario manufacturing and industry flourished. However, population increase slowed after a large recession hit the province in 1893, thus slowing growth drastically but only for a few short years. Many newly arrived immigrants and others moved west along the railway to the Prairie Provinces and British Columbia, sparsely settling Northern Ontario.
Mineral
exploitation accelerated in the late 19th century, leading to the rise of important mining centres in the northeast like Sudbury, Cobalt
and Timmins
. The province harnessed its water power to generate hydro-electric power and created the state-controlled Hydro-Electric Power Commission of Ontario, later Ontario Hydro
. The availability of cheap electric power further facilitated the development of industry. The Ford Motor Company of Canada
was established in 1904. General Motors Canada
was formed in 1918. The motor vehicle industry would go on to become the most lucrative industry for the Ontario economy during the 20th century.
In July 1912, the Conservative
government of Sir James Whitney
issued Regulation 17
which severely limited the availability of French-language schooling to the province's French-speaking minority. French Canadians reacted with outrage, journalist Henri Bourassa
denouncing the "Prussians of Ontario". It was eventually repealed in 1927.
Influenced by events in the United States, the government of Sir William Hearst introduced prohibition
of alcoholic drinks in 1916 with the passing of the Ontario Temperance Act
. However, residents could distil and retain their own personal supply, and liquor producers could continue distillation and export for sale, which allowed this already sizable industry to strengthen further. Ontario became a hotbed for the illegal smuggling of liquor and the biggest supplier into the United States, which was under complete prohibition. Prohibition in Ontario came to an end in 1927 with the establishment of the Liquor Control Board of Ontario
under the government of Howard Ferguson
. The sale and consumption of liquor, wine, and beer are still controlled by some of the most extreme laws in North America to ensure that strict community standards and revenue generation from the alcohol retail monopoly are upheld. In April 2007, Ontario Member of Provincial Parliament Kim Craitor
suggested that local brewers should be able to sell their beer in local corner stores; however, the motion was quickly rejected by Premier Dalton McGuinty
.
The post-World War II
period was one of exceptional prosperity and growth. Ontario, and the Greater Toronto Area in particular, have been the recipients of most immigration to Canada, largely immigrants from war-torn Europe in the 1950s and 1960s and after changes in federal immigration law
, a massive influx of non-Europeans since the 1970s. From a largely ethnically
British province, Ontario has rapidly become very culturally diverse.
The nationalist movement in Quebec, particularly after the election of the Parti Québécois
in 1976, contributed to driving many businesses and English-speaking people out of Quebec to Ontario, and as a result Toronto surpassed Montreal
as the largest city and economic centre of Canada. Depressed economic conditions in the Maritime Provinces
have also resulted in de-population of those provinces in the 20th century, with heavy migration into Ontario.
Ontario has no official language, but English
is considered the de facto language. Numerous French language
services are available under the French Language Services Act
of 1990 in designated areas where sizable francophone
populations exist.
" and the category "Canadian"). Groups with greater than 200,000 responses are included.
The majority of Ontarians are of English
or other European descent. Slightly less than 5% of the population of Ontario is Franco-Ontarian
, that is those whose native tongue is French, although those with French ancestry account for 11% of the population. In relation to natural increase or inter-provincial migration, immigration
is a huge population growth force in Ontario, as it has been over the last two centuries. More recent sources of immigrants
with large or growing communities in Ontario include Caribbean
s, Asia
ns, Latin America
ns, Europe
ans, and Africa
ns. Most populations have settled in the larger urban centres.
Ontario is the second most diverse province in terms of visible minorities after British Columbia
, with 22.8% of the population consisting of visible minorities. The Greater Toronto Area
, Ottawa
, Windsor
, Hamilton
and Waterloo Region are quite diverse metropolitan areas. Aboriginal peoples make up 2% of the population, with two-thirds of that consisting of North American Indians and the other third consisting of Métis
. The number of Aboriginal people has been increasing at rates greater than the general population of Ontario.
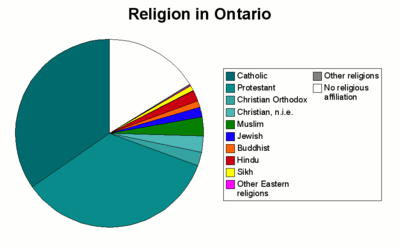
a 2006 Census
with 3,866,350 (34%); the United Church of Canada
with 1,334,570 (12%); and the Anglican Church of Canada
with 985,110 (9%).
The major religious groups in Ontario, as of 2001, are:

 Ontario is Canada's leading manufacturing
Ontario is Canada's leading manufacturing
province accounting for 52% of the total national manufacturing shipments in 2004. Ontario's largest trading partner is the American state of Michigan
. The government of Ontario posted a record C$21.3 billion ($20.7 billion) deficit for the 2009-10 fiscal year. The province’s net debt will rise to C$220 billion in 2010-11, or a record 37% of gross domestic product.
Ontario's rivers, including its share of the Niagara River, make it rich in hydroelectric energy. In 2009 Ontario Power Generation
generated 70% of the electricity of the province, of which 51% is nuclear
, 39% is hydroelectric
and 10% is fossil fuel
derived. Much of the newer power generation coming online in the last few years is natural gas or combined cycle natural gas plants. OPG is not however responsible for the transmission of power, which is under the control of Hydro One
. Despite its diverse range of power options, problems related to increasing consumption, lack of energy efficiency and aging nuclear reactors, Ontario has been forced in recent years to purchase power from its neighbours Quebec and Michigan to supplement its power needs during peak consumption periods.
An abundance of natural resource
s, excellent transportation links to the American heartland and the inland Great Lakes making ocean access possible via container ship
s, have all contributed to making manufacturing
the principal industry
, found mainly in the Golden Horseshoe region, which is the largest industrialized area in Canada, the southern end of the region being part of the North American Rust Belt
. Important products include motor vehicle
s, iron
, steel
, food, electrical appliances, machinery, chemical
s, and paper
. Ontario surpassed Michigan in car
production, assembling 2.696 million vehicles in 2004. Ontario has Chrysler
plants in Windsor
and Bramalea, two GM
plants in Oshawa and one in Ingersoll, a Honda
assembly plant in Alliston, Ford plants in Oakville and St. Thomas and Toyota assembly plants in Cambridge and Woodstock.
However, as a result of steeply declining sales, in 2005, General Motors
announced massive layoffs at production facilities across North America including two large GM plants in Oshawa
and a drive train
facility in St. Catharines resulting in 8,000 job losses in Ontario alone. In 2006, Ford Motor Company
announced between 25,000 and 30,000 layoffs phased until 2012; Ontario was spared the worst, but job losses were announced for the St. Thomas
facility and the Windsor Casting
plant. However, these losses will be offset by Ford's recent announcement of a hybrid vehicle
facility slated to begin production in 2007 at its Oakville
plant and GM's re-introduction of the Camaro
which will be produced in Oshawa. On December 4, 2008 Toyota announced the grand opening of the RAV4
plant in Woodstock
, and Honda
also has plans to add an engine plant at its facility in Alliston
. Despite these new plants coming online, Ontario has not yet fully recovered following massive layoffs caused by the global recession; its unemployment rate was 8.1% (as of October 2011), compared to 8.7% in Jan. 2010 and roughly 6% in 2007.
Toronto, the capital of Ontario, is the centre of Canada's financial services
and banking industry. Neighbouring cities forming part of the Greater Toronto Area
, such as Brampton
, Mississauga and Vaughan
, are large product distribution and IT centres, in addition to having various manufacturing industries. The information technology
sector is also important, particularly in the Silicon Valley North section of Ottawa
, as well as the Waterloo Region
, where the world headquarters of Research in Motion
(the developers of the BlackBerry
smartphone) is located. Providing more than 19% of the local jobs and employing more than 13% of the entire local population, Canada's Federal Government is by far the largest single employer in the National Capital Region
, which centres on the border cities of Ontario's Ottawa and Quebec's Gatineau. Hamilton
is the largest steel manufacturing city in Canada, and Sarnia
is the centre for petrochemical
production. Construction
continues to employ more than 6½% of the province's work force as of June 2011.
Mining
and the forest products
industry, notably pulp and paper
, are vital to the economy of Northern Ontario. More than any other region, tourism contributes heavily to the economy of Central Ontario, peaking during the summer months owing to the abundance of fresh water
recreation and wilderness found there in reasonable proximity to the major urban centres. At other times of the year, hunting
, skiing
and snowmobiling
are popular. This region has some of the most vibrant fall colour displays anywhere on the continent, and tours directed at overseas visitors are organized to see them. Tourism also plays a key role in border cities with large casinos, among them Windsor, Cornwall
, Sarnia and Niagara Falls
, which attract many U.S. visitors.
occupies a small percentage of the population but still a large part of Southern Ontario's land area. As the following table shows, while the number of individual farms has steadily decreased and their overall size has shrunk at a lower rate, greater mechanization has supported increased supply to satisfy the ever increasing demands of a growing population base; this has also meant a gradual increase in the total amount of land used for growing crops.
Cattle, small grains and dairy
were the common types of farms in the 2001 census. The fruit, grape and vegetable growing industry is located primarily on the Niagara Peninsula
and along Lake Erie, where tobacco
farms are also situated.
The Corn Belt
covers much of the southwestern area of the province extending as far north as close to Goderich. Apple orchards are a common sight along the southern shore of Georgian Bay near Collingwood and along the northern shore of Lake Ontario near Cobourg. Tobacco production, centred in Norfolk County
has decreased leading to an increase in some other new crop alternatives gaining popularity, such as hazelnuts
and ginseng
. The Ontario origins of Massey Ferguson
, once one of the largest farm implement
manufacturers in the world, indicate the importance agriculture once had to the Canadian economy.
Southern Ontario
's limited supply of agricultural land is going out of production at an increasing rate. Urban sprawl
and farmland severances contribute to the loss of thousands of acres of productive agricultural land in Ontario each year. Over 2,000 farms and 150000 acre (60,702.9 ha) of farmland in the GTA alone were lost to production in the two decades between 1976 and 1996. This loss represented approximately 18% of Ontario's Class 1 farmland being converted to urban purposes. In addition, increasing rural severances provide ever-greater interference with agricultural production.
The 500,000, or so, acres (200,000 ha) comprising the black peat soil Holland Marsh
, located just south of Lake Simcoe
and near the town of Bradford West Gwillimbury
(35 mi (56.3 km) north of Toronto) continues to be Canada's premier vegetable production center.
 The Green Energy and Green Economy Act, 2009 (GEA), takes a two-pronged approach to creating a renewable-energy economy. The first is to bring more renewable energy sources
The Green Energy and Green Economy Act, 2009 (GEA), takes a two-pronged approach to creating a renewable-energy economy. The first is to bring more renewable energy sources
to the province and the second is the creation of more energy efficiency
measures to help conserve energy
. The bill would also appoint a Renewable Energy Facilitator to provide "one-window" assistance and support to project developers in order to facilitate project approvals.
The approvals process for transmission projects would also be streamlined and for the first time in Ontario, the bill would enact standards for renewable energy projects. Homeowners would have access to incentives to develop small-scale renewables such as low- or no-interest loan
s to finance the capital cost of renewable energy generating facilities like solar panels.
Ontario is home to Niagara Falls
, which supplies a large amount of clean, hydroelectric energy for the province. The Bruce Nuclear Generating Station
, the second largest nuclear power
plant in the world, is also in Ontario and uses 8 CANDU reactors to power the province with clean, reliable energy.
rs, travels northwest from Montreal along the Ottawa River
, then continues westward towards Manitoba. Major cities on or near the route include Ottawa, North Bay, Sudbury, Sault Ste. Marie
, and Thunder Bay. The much more heavily travelled southerly route, which was driven by growth in predominantly English-speaking settlements originated by the United Empire Loyalists and later other European immigrants, travels southwest from Montreal along the St. Lawrence River, Lake Ontario, and Lake Erie before entering the United States in Michigan. Major cities on or near the route include Kingston, Oshawa, Toronto, Mississauga, Kitchener-Waterloo
, Hamilton, London, Sarnia, and Windsor. This route was also heavily used by immigrants to the Midwestern US particularly in the late 19th century. Most of Ontario's major transportation infrastructure is oriented east-west and roughly follows one of these two original routes.
make up the primary vehicular network in the south of province, and they connect to numerous border crossings with the U.S., the busiest being the Detroit–Windsor Tunnel
and Ambassador Bridge
(via Highway 401) and the Blue Water Bridge
(via Highway 402). The primary highway along the southern route is Highway 401/Highway of Heroes, the busiest highway in North America and the backbone of Ontario's road network, tourism, and economy, while the primary highways across the north are Highway 417/Highway 17 and Highway 11, both part of the Trans-Canada Highway
. Highway 400/Highway 69
connects Toronto to Northern Ontario. Other provincial highways and regional roads inter-connect the remainder of the province.
, which extends across most of the southern portion of the province and connects to the Atlantic Ocean, is the primary water transportation
route for cargo, particularly iron ore and grain. In the past, the Great Lakes and St. Lawrence River were also a major passenger transportation route, but over the past half century passenger travel has been reduced to ferry services and sightseeing cruises.
operates the inter-regional passenger train service on the Quebec City – Windsor Corridor, along with The Canadian
, a transcontinental rail service from Toronto to Vancouver
, and the Sudbury – White River train. Additionally, Amtrak
rail connects Ontario with key New York cities including Buffalo
, Albany
, and New York City
. Ontario Northland
provides rail service to destinations as far north as Moosonee
near James Bay
, connecting them with the south.
Freight rail
is dominated by the founding cross-country Canadian National Railway
and CP Rail
companies, which during the 1990s sold many short rail lines from their vast network to private companies operating mostly in the south.
Regional commuter rail is limited to the provincially owned GO Transit
, and serves a trainbus network spanning the Golden Horseshoe region, with its hub in Toronto.
The Toronto Transit Commission
operates the province's only subway
and streetcar
system, one of the busiest in North America. OC Transpo
operates, in addition to bus service, the O-Train
Light rail
line in Ottawa.
 Toronto Pearson International Airport
Toronto Pearson International Airport
is the nation's busiest and the world's 29th busiest, handling over 30 million passengers per year. Other important airports include Ottawa Macdonald-Cartier International Airport
and Hamilton's John C. Munro Hamilton International Airport, which is an important courier and freight aviation centre. Toronto/Pearson and Ottawa/Macdonald-Cartier form two of the three points in Canada's busiest set of air routes (the third point is Montréal-Pierre Elliott Trudeau International Airport
).
Most Ontario cities have regional airports, many of which have scheduled commuter flights from Air Canada Jazz
or smaller airlines and charter companies — flights from the larger cities such as Thunder Bay, Sault Ste. Marie, Sudbury, North Bay, Timmins, Windsor, London, and Kingston feed directly into Toronto Pearson. Bearskin Airlines
also runs flights along the northerly east-west route, connecting Ottawa, North Bay, Sudbury, Sault Ste. Marie, and Thunder Bay directly without requiring connections at Toronto Pearson.
Isolated towns and settlements in the northern areas of the province rely partly or entirely on air service
for travel, goods, and even ambulance
services (MEDIVAC), since much of the far northern area of the province cannot be reached by road or rail.

 The British North America Act 1867 section 69 stipulated "There shall be a Legislature for Ontario consisting of the Lieutenant Governor and of One House, styled the Legislative Assembly of Ontario
The British North America Act 1867 section 69 stipulated "There shall be a Legislature for Ontario consisting of the Lieutenant Governor and of One House, styled the Legislative Assembly of Ontario
." The assembly has 107 seats representing riding
s elected in a first-past-the-post
system across the province.
The legislative buildings at Queen's Park in Toronto are the seat of government. Following the Westminster system
, the leader of the party holding the most seats in the assembly is known as the "Premier and President of the Council" (Executive Council Act R.S.O. 1990). The Premier chooses the cabinet
or Executive Council
whose members are deemed "ministers of the Crown."
Although the Legislative Assembly Act (R.S.O. 1990) refers to members of the assembly", the legislators are now commonly called MPPs (Members of the Provincial Parliament) in English and députés de l'Assemblée législative in French, but they have also been called MLAs (Members of the Legislative Assembly
), and both are acceptable. The title of Prime Minister of Ontario, correct in French (le Premier ministre), is permissible in English but now generally avoided in favour of the title "Premier" to avoid confusion with the Prime Minister of Canada.
, conservative Progressive Conservative Party of Ontario
, and social-democratic Ontario New Democratic Party
have all ruled the province at different times.
Ontario is currently under a Liberal government headed by Premier Dalton McGuinty
. The present government, first elected in 2003, was re-elected
on October 10, 2007. On October 6, 2011, the Ontario Liberal Party won a third mandate, although it lost seats and was reduced to a minority government capturing only 53 seats (as opposed to the 71 it won in 2007), with the Progressive Conservatives and NDP winning 37 seats and 17 seats, respectively.
In the 2011 Canadian federal election in Ontario the Conservatives
were elected in 73 ridings, 22 went to the NDP, and 11 to the Liberals. The Green Party
did not get a candidate elected in Ontario.
* Parts of Quebec (including Gatineau
) are included in the Ottawa CMA. The entire population of the Ottawa CMA, in both provinces, is shown.
Ten largest municipalities by population
government of the 1960s, the slogan "Is There Any Other Place You'd Rather Be?" was in use to promote tourism. During a blizzard
early in 1971, highway travellers who were stranded at a Highway 401 service centre with Premier Robarts (already in his last months of office) asked him the slogan in an ironic twist.
In 1967, in conjunction with the celebration of Canada's centennial
, the song "A Place to Stand
" was introduced at the inauguration of Ontario's pavilion at the Expo 67
World's Fair, and became the background for the province's advertising for decades.
In 1973 the first slogan to appear on licence plates in Ontario
was "Keep It Beautiful". This was replaced by "Yours to Discover" in 1982, apparently inspired by a tourism slogan, "Discover Ontario," dating back to 1927. Plates with the French equivalent, "Tant à découvrir", were made available to the public beginning in May 2008. (From 1988 to 1990, "Ontario Incredible" gave "Yours to Discover" a brief respite.)
In 2007, a new song replaced "A Place to Stand" after four decades. "There's No Place Like This" is featured in current television advertising
, performed by Ontario artists including Molly Johnson
, Brian Byrne
, Keshia Chanté
, as well as Tomi Swick
and Arkells
. The new song is featured on the Ontario Tourism website.
Provinces and territories of Canada
The provinces and territories of Canada combine to make up the world's second-largest country by area. There are ten provinces and three territories...
, located in east-central Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
. It is Canada's most populous province and second largest in total area. It is home to the nation's most populous city, Toronto
Toronto
Toronto is the provincial capital of Ontario and the largest city in Canada. It is located in Southern Ontario on the northwestern shore of Lake Ontario. A relatively modern city, Toronto's history dates back to the late-18th century, when its land was first purchased by the British monarchy from...
, and the nation's capital, Ottawa
Ottawa
Ottawa is the capital of Canada, the second largest city in the Province of Ontario, and the fourth largest city in the country. The city is located on the south bank of the Ottawa River in the eastern portion of Southern Ontario...
.
Ontario is bordered by Manitoba on its west, Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay , sometimes called Hudson's Bay, is a large body of saltwater in northeastern Canada. It drains a very large area, about , that includes parts of Ontario, Quebec, Saskatchewan, Alberta, most of Manitoba, southeastern Nunavut, as well as parts of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota,...
on its north, Quebec
Quebec
Quebec or is a province in east-central Canada. It is the only Canadian province with a predominantly French-speaking population and the only one whose sole official language is French at the provincial level....
on its east, and by three states of the United States to its south (from west to east): Minnesota
Minnesota
Minnesota is a U.S. state located in the Midwestern United States. The twelfth largest state of the U.S., it is the twenty-first most populous, with 5.3 million residents. Minnesota was carved out of the eastern half of the Minnesota Territory and admitted to the Union as the thirty-second state...
, Michigan
Michigan
Michigan is a U.S. state located in the Great Lakes Region of the United States of America. The name Michigan is the French form of the Ojibwa word mishigamaa, meaning "large water" or "large lake"....
, and New York
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
. Ohio
Ohio
Ohio is a Midwestern state in the United States. The 34th largest state by area in the U.S.,it is the 7th‑most populous with over 11.5 million residents, containing several major American cities and seven metropolitan areas with populations of 500,000 or more.The state's capital is Columbus...
and Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania
The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to...
are across Lake Erie
Lake Erie
Lake Erie is the fourth largest lake of the five Great Lakes in North America, and the tenth largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has the shortest average water residence time. It is bounded on the north by the...
. All but a small portion of Ontario's 2,700 km (1,677 mi) border with the United States follow inland waterways: from the west at Lake of the Woods
Lake of the Woods
Lake of the Woods is a lake occupying parts of the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Manitoba and the U.S. state of Minnesota. It separates a small land area of Minnesota from the rest of the United States. The Northwest Angle and the town of Angle Township can only be reached from the rest of...
, eastward along the major rivers and lakes of the Great Lakes
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes are a collection of freshwater lakes located in northeastern North America, on the Canada – United States border. Consisting of Lakes Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario, they form the largest group of freshwater lakes on Earth by total surface, coming in second by volume...
/St. Lawrence River drainage system. These are the Rainy River
Rainy River, Ontario
The Canadian town of Rainy River is situated on the Ontario-Minnesota border, along the Rainy River opposite Baudette, Minnesota, USA, and southeast of the Lake of the Woods...
, the Pigeon River, Lake Superior
Lake Superior
Lake Superior is the largest of the five traditionally-demarcated Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded to the north by the Canadian province of Ontario and the U.S. state of Minnesota, and to the south by the U.S. states of Wisconsin and Michigan. It is the largest freshwater lake in the...
, the St. Mary's River
St. Marys River (Michigan-Ontario)
The St. Marys River , sometimes written as the St. Mary's River, drains Lake Superior, starting at the end of Whitefish Bay and flowing 74.5 miles southeast into Lake Huron, with a fall of ....
, Lake Huron
Lake Huron
Lake Huron is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. Hydrologically, it comprises the larger portion of Lake Michigan-Huron. It is bounded on the east by the Canadian province of Ontario and on the west by the state of Michigan in the United States...
, the St. Clair River
St. Clair River
The St. Clair River is a river in central North America which drains Lake Huron into Lake St Clair, forming part of the international boundary between the Canadian province of Ontario and the U.S. state of Michigan...
, Lake St. Clair
Lake Saint Clair (North America)
Lake St. Clair is a fresh-water lake named after Clare of Assisi that lies between the Province of Ontario and the State of Michigan, and its midline also forms the boundary between Canada and the United States of America. Lake St. Clair includes the Anchor Bay along the Metro Detroit coastline...
, the Detroit River
Detroit River
The Detroit River is a strait in the Great Lakes system. The name comes from the French Rivière du Détroit, which translates literally as "River of the Strait". The Detroit River has served an important role in the history of Detroit and is one of the busiest waterways in the world. The river...
, Lake Erie
Lake Erie
Lake Erie is the fourth largest lake of the five Great Lakes in North America, and the tenth largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has the shortest average water residence time. It is bounded on the north by the...
, the Niagara River
Niagara River
The Niagara River flows north from Lake Erie to Lake Ontario. It forms part of the border between the Province of Ontario in Canada and New York State in the United States. There are differing theories as to the origin of the name of the river...
, Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario
Lake Ontario is one of the five Great Lakes of North America. It is bounded on the north and southwest by the Canadian province of Ontario, and on the south by the American state of New York. Ontario, Canada's most populous province, was named for the lake. In the Wyandot language, ontarío means...
, and along the St. Lawrence River from Kingston, Ontario
Kingston, Ontario
Kingston, Ontario is a Canadian city located in Eastern Ontario where the St. Lawrence River flows out of Lake Ontario. Originally a First Nations settlement called "Katarowki," , growing European exploration in the 17th Century made it an important trading post...
to the Quebec boundary just east of Cornwall, Ontario
Cornwall, Ontario
Cornwall is a city in Eastern Ontario, Canada and the seat of the United Counties of Stormont, Dundas and Glengarry, Ontario. Cornwall is Ontario's easternmost city, located on the St...
.
Ontario is sometimes conceptually divided into two regions, Northern Ontario
Northern Ontario
Northern Ontario is a region of the Canadian province of Ontario which lies north of Lake Huron , the French River and Lake Nipissing. The region has a land area of 802,000 km2 and constitutes 87% of the land area of Ontario, although it contains only about 6% of the population...
and Southern Ontario
Southern Ontario
Southern Ontario is a region of the province of Ontario, Canada that lies south of the French River and Algonquin Park. Depending on the inclusion of the Parry Sound and Muskoka districts, its surface area would cover between 14 to 15% of the province. It is the southernmost region of...
. The great majority of Ontario's population and its arable land
Arable land
In geography and agriculture, arable land is land that can be used for growing crops. It includes all land under temporary crops , temporary meadows for mowing or pasture, land under market and kitchen gardens and land temporarily fallow...
is located in the south. In contrast, the northern three-quarters of Ontario is sparsely populated.
The province is named after Lake Ontario, which is thought to have been derived from Ontarí:io, a Huron
Wyandot language
Wyandot is the Iroquoian language traditionally spoken by the people known variously as Wyandot, Wyandotte, Wendat, or Huron. It was last spoken primarily in Oklahoma and Quebec...
(Wyandot) word meaning "great lake", or possibly skanadario which means "beautiful water" in the Iroquoian languages
Iroquoian languages
The Iroquoian languages are a First Nation and Native American language family.-Family division:*Ruttenber, Edward Manning. 1992 [1872]. History of the Indian tribes of Hudson's River. Hope Farm Press....
. Ontario contains about 250,000 freshwater lakes.
Geography
- See also List of parks and protected areas of Ontario

- The thinly populated Canadian ShieldCanadian ShieldThe Canadian Shield, also called the Laurentian Plateau, or Bouclier Canadien , is a vast geological shield covered by a thin layer of soil that forms the nucleus of the North American or Laurentia craton. It is an area mostly composed of igneous rock which relates to its long volcanic history...
in the northwestern and central portions, which comprises over half the land area of Ontario; though this area mostly does not support agriculture it is rich in mineralMineralA mineral is a naturally occurring solid chemical substance formed through biogeochemical processes, having characteristic chemical composition, highly ordered atomic structure, and specific physical properties. By comparison, a rock is an aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids and does not...
s and in part covered by the CentralCentral Canadian Shield forestsThe Central Canadian Shield forests are a taiga ecoregion of Canada.-Setting:This ecoregion consists of rolling hills, lakes, bogs and rocky outcrops covering a large curved swathe on the Canadian Shield from eastern Manitoba and Northern Ontario running southeastwards through Thunder Bay District...
and Midwestern Canadian Shield forestsMidwestern Canadian Shield forestsThe Midwestern Canadian Shield forests ecoregion, in the Taiga and Boreal forests Biome, are of northern Canada.-Setting:This is an area of rolling hills with lakes both small and large, wetlands, and rocky outcrops on the Canadian Shield in northern Saskatchewan, north-central Manitoba and...
, studded with lakes and rivers. Northern OntarioNorthern OntarioNorthern Ontario is a region of the Canadian province of Ontario which lies north of Lake Huron , the French River and Lake Nipissing. The region has a land area of 802,000 km2 and constitutes 87% of the land area of Ontario, although it contains only about 6% of the population...
is subdivided into two sub-regions: Northwestern OntarioNorthwestern OntarioNorthwestern Ontario is the region within the Canadian province of Ontario which lies north and west of Lake Superior, and west of Hudson Bay and James Bay. It includes most of subarctic Ontario. Its western boundary is the Canadian province of Manitoba, which disputed Ontario's claim to the...
and Northeastern OntarioNortheastern OntarioNortheastern Ontario is the region within the Canadian province of Ontario which lies north and east of Lakes Superior and Huron.Northeastern Ontario consists of the districts of Algoma, Sudbury, Cochrane, Timiskaming, Nipissing and Manitoulin; and the single-tier municipality of Greater...
.
- The virtually unpopulated Hudson Bay LowlandsHudson Bay LowlandsThe Hudson Bay Lowlands is a large, poorly drained piece of wetlands wedged between the Canadian Shield and southern shores of Hudson Bay and James Bay. Many wide and slow-moving rivers flow through this area toward the salt water of Hudson Bay. Mosquitoes and black flies thrive here. This is a...
in the extreme north and northeast, mainly swampy and sparsely forested.
- Southern OntarioSouthern OntarioSouthern Ontario is a region of the province of Ontario, Canada that lies south of the French River and Algonquin Park. Depending on the inclusion of the Parry Sound and Muskoka districts, its surface area would cover between 14 to 15% of the province. It is the southernmost region of...
which is further sub-divided into four regions; Central Ontario (although not actually the province's geographic centre), Eastern OntarioEastern OntarioEastern Ontario is a subregion of Southern Ontario in the Canadian province of Ontario which lies in a wedge-shaped area between the Ottawa River and St. Lawrence River...
, Golden HorseshoeGolden HorseshoeThe Golden Horseshoe is a densely populated and industrialized region centred around the Greater Toronto Area at the western end of Lake Ontario in Southern Ontario, Canada, with outer boundaries stretching south to Lake Erie and north to Georgian Bay. Most of it is also part of the Quebec City...
and Southwestern OntarioSouthwestern OntarioSouthwestern Ontario is a subregion of Southern Ontario in the Canadian province of Ontario, centred on the city of London. It extends north to south from the Bruce Peninsula on Lake Huron to the Lake Erie shoreline, and east to south-west roughly from Guelph to Windsor. The region had a population...
(parts of which were formerly referred to as Western Ontario).
Despite the absence of any mountainous terrain in the province, there are large areas of uplands, particularly within the Canadian Shield which traverses the province from northwest to southeast and also above the Niagara Escarpment
Niagara Escarpment
The Niagara Escarpment is a long escarpment, or cuesta, in the United States and Canada that runs westward from New York State, through Ontario, Michigan, Wisconsin and Illinois...
which crosses the south. The highest point is Ishpatina Ridge
Ishpatina Ridge
The Ishpatina Ridge is the highest point of land in the Canadian province of Ontario. At an estimated above sea level, it is a rather low mountain and not that steep, as the surrounding land in the area is already quite elevated. Ishpatina Ridge rises approximately above the immediate area. To...
at 693 metres (2,273.6 ft) above sea level
Above mean sea level
The term above mean sea level refers to the elevation or altitude of any object, relative to the average sea level datum. AMSL is used extensively in radio by engineers to determine the coverage area a station will be able to reach...
located in Temagami, Northeastern Ontario
Temagami, Ontario
Temagami, formerly spelt as Timagami, is a region and a municipality in northeastern Ontario, Canada, in the District of Nipissing with Lake Temagami at its heart....
. In the south, elevations of over 500 m (1,640.42 ft) are surpassed near Collingwood, above the Blue Mountains in the Dundalk Highlands and in hilltops near the Madawaska River
Madawaska River (Ontario)
The Madawaska River is a river in Ontario, Canada. The river is long and drains an area of . It originates at Source Lake in the highlands of Algonquin Park at an elevation of and flows east, dropping before emptying into the Ottawa River at Arnprior....
in Renfrew County.
The Carolinian forest
Carolinian forest
The Carolinian forest is a life zone in eastern North America characterized primarily by a predominance of deciduous, or broad-leaf trees. The term "Carolinian forest" is used primarily in Canada...
zone covers most of the southwestern region of the province. The temperate and fertile Great Lakes-Saint Lawrence Valley in the south is part of the Eastern Great Lakes lowland forests
Eastern Great Lakes lowland forests
The Eastern Great Lakes lowland forests is a Temperate Broadleaf and Mixed Forests ecoregion of North America, mostly in eastern Canada.-Setting:...
ecoregion
Ecoregion
An ecoregion , sometimes called a bioregion, is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than an ecozone and larger than an ecosystem. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and contain characteristic, geographically distinct assemblages of natural...
where the forest has now been largely replaced by agriculture, industrial and urban development. A well-known geographic feature is Niagara Falls
Niagara Falls
The Niagara Falls, located on the Niagara River draining Lake Erie into Lake Ontario, is the collective name for the Horseshoe Falls and the adjacent American Falls along with the comparatively small Bridal Veil Falls, which combined form the highest flow rate of any waterfalls in the world and has...
, part of the Niagara Escarpment
Niagara Escarpment
The Niagara Escarpment is a long escarpment, or cuesta, in the United States and Canada that runs westward from New York State, through Ontario, Michigan, Wisconsin and Illinois...
. The Saint Lawrence Seaway
Saint Lawrence Seaway
The Saint Lawrence Seaway , , is the common name for a system of locks, canals and channels that permits ocean-going vessels to travel from the Atlantic Ocean to the North American Great Lakes, as far as Lake Superior. Legally it extends from Montreal to Lake Erie, including the Welland Canal...
allows navigation to and from the Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
as far inland as Thunder Bay
Thunder Bay
-In Canada:Thunder Bay is the name of three places in the province of Ontario, Canada along Lake Superior:*Thunder Bay District, Ontario, a district in Northwestern Ontario*Thunder Bay, a city in Thunder Bay District*Thunder Bay, Unorganized, Ontario...
in Northwestern Ontario. Northern Ontario
Northern Ontario
Northern Ontario is a region of the Canadian province of Ontario which lies north of Lake Huron , the French River and Lake Nipissing. The region has a land area of 802,000 km2 and constitutes 87% of the land area of Ontario, although it contains only about 6% of the population...
occupies roughly 87% of the surface area of the province; conversely Southern Ontario contains 94% of the population.
Point Pelee
Point Pelee National Park
-See also:*National Parks of Canada*List of National Parks of Canada*Long Point-External links:**...
is a peninsula of Lake Erie in southwestern Ontario (near Windsor
Windsor, Ontario
Windsor is the southernmost city in Canada and is located in Southwestern Ontario at the western end of the heavily populated Quebec City – Windsor Corridor. It is within Essex County, Ontario, although administratively separated from the county government. Separated by the Detroit River, Windsor...
and Detroit, Michigan) that is the southernmost extent of Canada's mainland. Pelee Island
Pelee, Ontario
Pelee Island, Ontario, Canada , is an island in the western half of Lake Erie. Pelee Island is connected to the Canadian and United States mainland by ferry service. At 42 km2, Pelee Island is the largest island in Lake Erie and the southernmost populated point in Canada...
and Middle Island in Lake Erie extend slightly farther. All are south of 42°N
42nd parallel north
The 42nd parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 42 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, the Mediterranean Sea, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean....
– slightly farther south than the northern border of California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
.
Climate


Humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region typified by large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot summers and cold winters....
(Köppen climate classification
Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by Crimea German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen himself, notably in 1918 and 1936...
Dfa), similar to that of the inland Mid-Atlantic States
Mid-Atlantic States
The Mid-Atlantic states, also called middle Atlantic states or simply the mid Atlantic, form a region of the United States generally located between New England and the South...
and the Great Lakes portion of the Midwestern United States
Midwestern United States
The Midwestern United States is one of the four U.S. geographic regions defined by the United States Census Bureau, providing an official definition of the American Midwest....
. The region has warm, humid summers and cold winters. Annual precipitation ranges from 750–1000 mm (29.5–39.4 in) and is well distributed throughout the year with a usual summer peak. Most of this region lies in the lee of the Great Lakes making for abundant snow in some areas. Under the Köppen climate parameters, Point Pelee and Middle Island, the southernmost parts of Canada located close to the lake boundary with Ohio, are at the dividing line of a humid continental climate
Humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region typified by large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot summers and cold winters....
and a humid subtropical climate
Humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a climate zone characterized by hot, humid summers and mild to cool winters...
(Dfa/Cfa).
Central and Eastern Ontario have a more severe humid continental climate (Köppen Dfb). This region is ontaro has warm and sometimes hot summers with colder, longer winters, ample snowfall and annual precipitation similar to the rest of Southern Ontario. Along the eastern shores of Lake Superior and Lake Huron, frequent heavy lake-effect snow squalls increase seasonal snowfall totals upwards of 3 m (9.8 ft) in some places.
The northernmost parts of Ontario — primarily north of 50°N have a subarctic climate
Subarctic climate
The subarctic climate is a climate characterized by long, usually very cold winters, and short, cool to mild summers. It is found on large landmasses, away from the moderating effects of an ocean, generally at latitudes from 50° to 70°N poleward of the humid continental climates...
(Köppen Dfc) with long, severely cold winters and short, cool to warm summers with dramatic temperature changes possible in all seasons. With no major mountain ranges blocking sinking Arctic
Arctic
The Arctic is a region located at the northern-most part of the Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean and parts of Canada, Russia, Greenland, the United States, Norway, Sweden, Finland, and Iceland. The Arctic region consists of a vast, ice-covered ocean, surrounded by treeless permafrost...
air mass
Air mass
In meteorology, an air mass is a volume of air defined by its temperature and water vapor content. Air masses cover many hundreds or thousands of square miles, and adopt the characteristics of the surface below them. They are classified according to latitude and their continental or maritime...
es, temperatures of -40 C are not uncommon, snowfall remains on the ground for sometimes over half the year. Precipitation is generally less than 70 cm (27.6 in).
Severe and non-severe thunderstorm
Thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm, a lightning storm, thundershower or simply a storm is a form of weather characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere known as thunder. The meteorologically assigned cloud type associated with the...
s peak in summer. London
London, Ontario
London is a city in Southwestern Ontario, Canada, situated along the Quebec City – Windsor Corridor. The city has a population of 352,395, and the metropolitan area has a population of 457,720, according to the 2006 Canadian census; the metro population in 2009 was estimated at 489,274. The city...
, situated in Southern
Southern Ontario
Southern Ontario is a region of the province of Ontario, Canada that lies south of the French River and Algonquin Park. Depending on the inclusion of the Parry Sound and Muskoka districts, its surface area would cover between 14 to 15% of the province. It is the southernmost region of...
(Southwestern)
Southwestern Ontario
Southwestern Ontario is a subregion of Southern Ontario in the Canadian province of Ontario, centred on the city of London. It extends north to south from the Bruce Peninsula on Lake Huron to the Lake Erie shoreline, and east to south-west roughly from Guelph to Windsor. The region had a population...
Ontario, has the most lightning strikes per year in Canada, averaging 34 days of thunderstorm activity per year. In a typical year, Ontario averages 15 confirmed tornado
Tornado
A tornado is a violent, dangerous, rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. They are often referred to as a twister or a cyclone, although the word cyclone is used in meteorology in a wider...
touchdowns, though seldom they are destructive (the majority between F0 to F2 on the Fujita scale
Fujita scale
The Fujita scale , or Fujita-Pearson scale, is a scale for rating tornado intensity, based primarily on the damage tornadoes inflict on human-built structures and vegetation...
). Tropical depression
Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Tropical cyclones strengthen when water evaporated from the ocean is released as the saturated air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor...
remnants occasionally bring heavy rains and winds in the south, but are rarely deadly. A notable exception was Hurricane Hazel
Hurricane Hazel
Hurricane Hazel was the deadliest and costliest hurricane of the 1954 Atlantic hurricane season. The storm killed as many as 1,000 people in Haiti before striking the United States near the border between North and South Carolina, as a Category 4 hurricane...
which struck Toronto, in October 1954.
Winter storms can disrupt power supply and transportation, severe ice storms can also occur, especially in the east.
Territorial evolution

Royal Proclamation of 1763
The Royal Proclamation of 1763 was issued October 7, 1763, by King George III following Great Britain's acquisition of French territory in North America after the end of the French and Indian War/Seven Years' War...
. In 1788, while part of the Province of Quebec (1763–1791), southern Ontario was divided into four districts: Hesse
Western District, Upper Canada
Western District was one of four districts of the Province of Quebec created in 1788 in the western reaches of the Montreal District and partitioned in 1791 to create the new colony of Upper Canada. Known as Hesse District until 1792, it was abolished in 1849...
, Lunenburg
Eastern District, Upper Canada
Eastern District was one of four districts of the Province of Quebec created in 1788 in the western reaches of the Montreal District and partitioned in 1791 to create the new colony of Upper Canada. Known as Lunenburg District until 1792, it was abolished in 1849...
, Mecklenburg
Midland District, Upper Canada
Midland District was one of four districts of the Province of Quebec created in 1788 in the western reaches of the Montreal District and partitioned in 1791 to create the new colony of Upper Canada. Known as Mecklenburg District until 1792, it was abolished in 1849...
, and Nassau
Home District
The Home District was one of four districts of the Province of Quebec created in 1788 in the western reaches of the Montreal District and partitioned in 1791 to create the new colony of Upper Canada. Known as Nassau District until 1792, it was composed of the areas along western Lake Ontario and...
.
In 1792, the four districts were renamed: Hesse became the Western District, Lunenburg became the Eastern District, Mecklenburg became the Midland District, and Nassau became the Home District. Counties were created within the districts.
By 1798, there were eight districts: Eastern, Home, Johnstown, London, Midland, Newcastle, Niagara, and Western.
By 1826, there were eleven districts: Bathurst, Eastern, Gore, Home, Johnstown, London, Midland, Newcastle, Niagara, Ottawa, and Western.
By 1838, there were twenty districts: Bathurst, Brock, Colbourne, Dalhousie, Eastern, Gore, Home, Huron, Johnstown, London, Midland, Newcastle, Niagara, Ottawa, Prince Edward, Simcoe
Simcoe County, Ontario
Simcoe County is located in central portion of Southern Ontario. The County is situated just north of the Greater Toronto Area stretching from the shores of Lake Simcoe in the east to Georgian Bay in the west...
, Talbot, Victoria, Wellington, and Western.
In 1849, the districts of southern Ontario were abolished by the Province of Canada
Province of Canada
The Province of Canada, United Province of Canada, or the United Canadas was a British colony in North America from 1841 to 1867. Its formation reflected recommendations made by John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham in the Report on the Affairs of British North America following the Rebellions of...
, and county
County
A county is a jurisdiction of local government in certain modern nations. Historically in mainland Europe, the original French term, comté, and its equivalents in other languages denoted a jurisdiction under the sovereignty of a count A county is a jurisdiction of local government in certain...
governments took over certain municipal responsibilities. The Province of Canada also began creating districts in sparsely populated Northern Ontario with the establishment of Algoma District
Algoma District, Ontario
Algoma District is a district and census division in Northeastern Ontario in the Canadian province of Ontario. It was created in 1858 comprising territory as far west as Minnesota...
and Nipissing District
Nipissing District, Ontario
Nipissing District, Ontario is a district in Northeastern Ontario in the Canadian province of Ontario. It was created in 1858. The district seat is North Bay.In 2006, the population was 84,688...
in 1858.
The borders of Ontario, its new name in 1867, were provisionally expanded north and west. When the Province of Canada was formed, its borders were not entirely clear, and Ontario claimed to eventually reach all the way to the Rocky Mountains
Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains are a major mountain range in western North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch more than from the northernmost part of British Columbia, in western Canada, to New Mexico, in the southwestern United States...
and Arctic Ocean
Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean, located in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Arctic north polar region, is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceanic divisions...
. With Canada's acquisition of Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land, or Prince Rupert's Land, was a territory in British North America, consisting of the Hudson Bay drainage basin that was nominally owned by the Hudson's Bay Company for 200 years from 1670 to 1870, although numerous aboriginal groups lived in the same territory and disputed the...
, Ontario was interested in clearly defining its borders, especially since some of the new areas it was interested in were rapidly growing. After the federal government asked Ontario to pay for construction in the new disputed area, the province asked for an elaboration on its limits, and its boundary was moved north to the 51st parallel north
51st parallel north
The 51st parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 51 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean....
.
The northern and western boundaries of Ontario were in dispute after Confederation
Confederation
A confederation in modern political terms is a permanent union of political units for common action in relation to other units. Usually created by treaty but often later adopting a common constitution, confederations tend to be established for dealing with critical issues such as defense, foreign...
. Ontario's right to Northwestern Ontario was determined by the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council
Judicial Committee of the Privy Council
The Judicial Committee of the Privy Council is one of the highest courts in the United Kingdom. Established by the Judicial Committee Act 1833 to hear appeals formerly heard by the King in Council The Judicial Committee of the Privy Council (JCPC) is one of the highest courts in the United...
in 1884 and confirmed by the Canada (Ontario Boundary) Act, 1889 of the Parliament of the United Kingdom
Parliament of the United Kingdom
The Parliament of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland is the supreme legislative body in the United Kingdom, British Crown dependencies and British overseas territories, located in London...
. By 1899, there were seven northern districts: Algoma, Manitoulin, Muskoka, Nipissing, Parry Sound, Rainy River, and Thunder Bay. Four more northern districts were created between 1907 and 1912: Cochrane, Kenora, Sudbury and Timiskaming.
European contact

Algonquian peoples
The Algonquian are one of the most populous and widespread North American native language groups, with tribes originally numbering in the hundreds. Today hundreds of thousands of individuals identify with various Algonquian peoples...
(Ojibwa
Ojibwa
The Ojibwe or Chippewa are among the largest groups of Native Americans–First Nations north of Mexico. They are divided between Canada and the United States. In Canada, they are the third-largest population among First Nations, surpassed only by Cree and Inuit...
, Cree
Cree
The Cree are one of the largest groups of First Nations / Native Americans in North America, with 200,000 members living in Canada. In Canada, the major proportion of Cree live north and west of Lake Superior, in Ontario, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta and the Northwest Territories, although...
and Algonquin) in the northern/western portions and Iroquois
Iroquois
The Iroquois , also known as the Haudenosaunee or the "People of the Longhouse", are an association of several tribes of indigenous people of North America...
and Wyandot (Huron) tribes more in the south/east. During the 17th century, the Algonquians and Hurons fought a bitter war against the Iroquois. The French explorer Étienne Brûlé
Étienne Brûlé
Étienne Brûlé , was the first of European French explorers to journey along the St. Lawrence River with the Native Americans and to view Georgian Bay and Lake Huron Canada in the 17th century. A rugged outdoorsman, he took to the lifestyle of the First Nations and had a unique contribution to the...
explored part of the area in 1610-12. The English explorer Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson was an English sea explorer and navigator in the early 17th century. Hudson made two attempts on behalf of English merchants to find a prospective Northeast Passage to Cathay via a route above the Arctic Circle...
sailed into Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay , sometimes called Hudson's Bay, is a large body of saltwater in northeastern Canada. It drains a very large area, about , that includes parts of Ontario, Quebec, Saskatchewan, Alberta, most of Manitoba, southeastern Nunavut, as well as parts of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota,...
in 1611 and claimed the area for England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
.
Samuel de Champlain
Samuel de Champlain
Samuel de Champlain , "The Father of New France", was a French navigator, cartographer, draughtsman, soldier, explorer, geographer, ethnologist, diplomat, and chronicler. He founded New France and Quebec City on July 3, 1608....
reached Lake Huron in 1615, and French
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
missionaries began to establish posts along the Great Lakes. French settlement was hampered by their hostilities with the Iroquois, who allied themselves with the British. From 1634 to 1640, Hurons were devastated by European infectious diseases, such as measles
Measles
Measles, also known as rubeola or morbilli, is an infection of the respiratory system caused by a virus, specifically a paramyxovirus of the genus Morbillivirus. Morbilliviruses, like other paramyxoviruses, are enveloped, single-stranded, negative-sense RNA viruses...
and smallpox
Smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease unique to humans, caused by either of two virus variants, Variola major and Variola minor. The disease is also known by the Latin names Variola or Variola vera, which is a derivative of the Latin varius, meaning "spotted", or varus, meaning "pimple"...
, to which they had no immunity.
The British established trading post
Trading post
A trading post was a place or establishment in historic Northern America where the trading of goods took place. The preferred travel route to a trading post or between trading posts, was known as a trade route....
s on Hudson Bay in the late 17th century and began a struggle for domination of Ontario. The 1763 Treaty of Paris
Treaty of Paris (1763)
The Treaty of Paris, often called the Peace of Paris, or the Treaty of 1763, was signed on 10 February 1763, by the kingdoms of Great Britain, France and Spain, with Portugal in agreement. It ended the French and Indian War/Seven Years' War...
ended the Seven Years' War
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War was a global military war between 1756 and 1763, involving most of the great powers of the time and affecting Europe, North America, Central America, the West African coast, India, and the Philippines...
by awarding nearly all of France's North American possessions
French colonization of the Americas
The French colonization of the Americas began in the 16th century, and continued in the following centuries as France established a colonial empire in the Western Hemisphere. France founded colonies in much of eastern North America, on a number of Caribbean islands, and in South America...
(New France
New France
New France was the area colonized by France in North America during a period beginning with the exploration of the Saint Lawrence River by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Spain and Great Britain in 1763...
) to Britain. The region was annexed to Quebec in 1774. From 1783 to 1796, the Kingdom of Great Britain
Kingdom of Great Britain
The former Kingdom of Great Britain, sometimes described as the 'United Kingdom of Great Britain', That the Two Kingdoms of Scotland and England, shall upon the 1st May next ensuing the date hereof, and forever after, be United into One Kingdom by the Name of GREAT BRITAIN. was a sovereign...
granted United Empire Loyalists leaving the United States following the American Revolution
American Revolution
The American Revolution was the political upheaval during the last half of the 18th century in which thirteen colonies in North America joined together to break free from the British Empire, combining to become the United States of America...
200 acre (80.9 ha) of land and other items with which to rebuild their lives.
This measure substantially increased the population of Canada west of the St. Lawrence-Ottawa River confluence during this period, a fact recognized by the Constitutional Act of 1791
Constitutional Act of 1791
The Constitutional Act of 1791, formally The Clergy Endowments Act, 1791 , is an Act of the Parliament of Great Britain...
, which split Quebec into the Canadas
The Canadas
The Canadas is the collective name for Upper Canada and Lower Canada, two British colonies in Canada. They were both created by the Constitutional Act of 1791 and abolished in 1841 with the union of Upper and Lower Canada....
: Upper Canada
Upper Canada
The Province of Upper Canada was a political division in British Canada established in 1791 by the British Empire to govern the central third of the lands in British North America and to accommodate Loyalist refugees from the United States of America after the American Revolution...
southwest of the St. Lawrence-Ottawa River confluence, and Lower Canada
Lower Canada
The Province of Lower Canada was a British colony on the lower Saint Lawrence River and the shores of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence...
east of it. John Graves Simcoe
John Graves Simcoe
John Graves Simcoe was a British army officer and the first Lieutenant Governor of Upper Canada from 1791–1796. Then frontier, this was modern-day southern Ontario and the watersheds of Georgian Bay and Lake Superior...
was appointed Upper Canada's first Lieutenant-Governor in 1793.
Upper Canada
American troops in the War of 1812War of 1812
The War of 1812 was a military conflict fought between the forces of the United States of America and those of the British Empire. The Americans declared war in 1812 for several reasons, including trade restrictions because of Britain's ongoing war with France, impressment of American merchant...
invaded Upper Canada across the Niagara River
Niagara River
The Niagara River flows north from Lake Erie to Lake Ontario. It forms part of the border between the Province of Ontario in Canada and New York State in the United States. There are differing theories as to the origin of the name of the river...
and the Detroit River
Detroit River
The Detroit River is a strait in the Great Lakes system. The name comes from the French Rivière du Détroit, which translates literally as "River of the Strait". The Detroit River has served an important role in the history of Detroit and is one of the busiest waterways in the world. The river...
, but were defeated and pushed back by British regulars, Canadian fencibles
Fencibles
The Fencibles were army regiments raised in the United Kingdom and in the colonies for defence against the threat of invasion during the American War of Independence and French Revolutionary Wars in the late 18th century...
and militias, and First Nations
First Nations
First Nations is a term that collectively refers to various Aboriginal peoples in Canada who are neither Inuit nor Métis. There are currently over 630 recognised First Nations governments or bands spread across Canada, roughly half of which are in the provinces of Ontario and British Columbia. The...
warriors. The Americans gained control of Lake Erie and Lake Ontario, however. During the Battle of York
Battle of York
The Battle of York was a battle of the War of 1812 fought on 27 April 1813, at York, Upper Canada . An American force supported by a naval flotilla landed on the lake shore to the west, defeated the defending British force and captured the town and dockyard...
they occupied the Town of York
York, Upper Canada
York was the name of Old Toronto between 1793 and 1834. It was the second capital of Upper Canada.- History :The town was established in 1793 by Governor John Graves Simcoe, with a new 'Fort York' on the site of the last French 'Fort Toronto'...
(later named Toronto) in 1813. The Americans looted the town and burned the Parliament Buildings but were soon forced to leave.
After the War of 1812, relative stability allowed for increasing numbers of immigrants to arrive from Europe rather than from the United States. As was the case in the previous decades, this deliberate immigration shift was encouraged by the colonial leaders. Despite affordable and often free land, many arriving newcomers, mostly from Britain and Ireland, found frontier life with the harsh climate difficult, and some of those with the means eventually returned home or went south. However, population growth far exceeded emigration in the decades that followed. It was a mostly agrarian-based society, but canal projects and a new network of plank roads spurred greater trade within the colony and with the United States, thereby improving previously damaged relations over time.

Hydropower
Hydropower, hydraulic power, hydrokinetic power or water power is power that is derived from the force or energy of falling water, which may be harnessed for useful purposes. Since ancient times, hydropower has been used for irrigation and the operation of various mechanical devices, such as...
for development. As the population increased, so did the industries and transportation networks, which in turn led to further development. By the end of the century, Ontario vied with Quebec as the nation's leader in terms of growth in population, industry, arts and communications.
Many in the colony however, began to chafe against the aristocratic Family Compact
Family Compact
Fully developed after the War of 1812, the Compact lasted until Upper and Lower Canada were united in 1841. In Lower Canada, its equivalent was the Château Clique. The influence of the Family Compact on the government administration at different levels lasted to the 1880s...
who governed while benefiting economically from the region's resources, and who did not allow elected bodies the power to effect change (much as the Château Clique
Château Clique
The Clique du Château or Château Clique was a group of wealthy families in Lower Canada in the early 19th century. They were the Lower Canadian equivalent of the Family Compact in Upper Canada...
ruled Lower Canada). This resentment spurred republican ideals and sowed the seeds for early Canadian nationalism
Canadian nationalism
Canadian nationalism is a term which has been applied to ideologies of several different types which highlight and promote specifically Canadian interests over those of other countries, notably the United States...
. Accordingly, rebellion in favour of responsible government
Responsible government
Responsible government is a conception of a system of government that embodies the principle of parliamentary accountability which is the foundation of the Westminster system of parliamentary democracy...
rose in both regions; Louis-Joseph Papineau
Louis-Joseph Papineau
Louis-Joseph Papineau , born in Montreal, Quebec, was a politician, lawyer, and the landlord of the seigneurie de la Petite-Nation. He was the leader of the reformist Patriote movement before the Lower Canada Rebellion of 1837–1838. His father was Joseph Papineau, also a famous politician in Quebec...
led the Lower Canada Rebellion
Lower Canada Rebellion
The Lower Canada Rebellion , commonly referred to as the Patriots' War by Quebeckers, is the name given to the armed conflict between the rebels of Lower Canada and the British colonial power of that province...
and William Lyon Mackenzie
William Lyon Mackenzie
William Lyon Mackenzie was a Scottish born American and Canadian journalist, politician, and rebellion leader. He served as the first mayor of Toronto, Upper Canada and was an important leader during the 1837 Upper Canada Rebellion.-Background and early years in Scotland, 1795–1820:Mackenzie was...
led the Upper Canada Rebellion
Upper Canada Rebellion
The Upper Canada Rebellion was, along with the Lower Canada Rebellion in Lower Canada, a rebellion against the British colonial government in 1837 and 1838. Collectively they are also known as the Rebellions of 1837.-Issues:...
.
Canada West
Although both rebellions were put down in short order, the British governmentGovernment
Government refers to the legislators, administrators, and arbitrators in the administrative bureaucracy who control a state at a given time, and to the system of government by which they are organized...
sent Lord Durham
John Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham
John George Lambton, 1st Earl of Durham GCB, PC , also known as "Radical Jack" and commonly referred to in history texts simply as Lord Durham, was a British Whig statesman, colonial administrator, Governor General and high commissioner of British North America...
to investigate the causes of the unrest. He recommended that self-government be granted and that Lower and Upper Canada be re-joined in an attempt to assimilate the French Canadian
French Canadian
French Canadian or Francophone Canadian, , generally refers to the descendents of French colonists who arrived in New France in the 17th and 18th centuries...
s. Accordingly, the two colonies were merged into the Province of Canada by the Act of Union 1840
Act of Union 1840
The Act of Union, formally the The British North America Act, 1840 , was enacted in July 1840 and proclaimed 10 February 1841. It abolished the legislatures of Lower Canada and Upper Canada and established a new political entity, the Province of Canada to replace them...
, with the capital at Kingston
Kingston, Ontario
Kingston, Ontario is a Canadian city located in Eastern Ontario where the St. Lawrence River flows out of Lake Ontario. Originally a First Nations settlement called "Katarowki," , growing European exploration in the 17th Century made it an important trading post...
, and Upper Canada becoming known as Canada West. Parliament
Parliament
A parliament is a legislature, especially in those countries whose system of government is based on the Westminster system modeled after that of the United Kingdom. The name is derived from the French , the action of parler : a parlement is a discussion. The term came to mean a meeting at which...
ary self-government
Self-governance
Self-governance is an abstract concept that refers to several scales of organization.It may refer to personal conduct or family units but more commonly refers to larger scale activities, i.e., professions, industry bodies, religions and political units , up to and including autonomous regions and...
was granted in 1848. There were heavy waves of immigration in the 1840s, and the population of Canada West more than doubled by 1851 over the previous decade. As a result, for the first time the English-speaking population of Canada West surpassed the French-speaking population of Canada East
Canada East
Canada East was the eastern portion of the United Province of Canada. It consisted of the southern portion of the modern-day Canadian Province of Quebec, and was primarily a French-speaking region....
, tilting the representative balance of power.
An economic boom in the 1850s coincided with railway expansion across the province, further increasing the economic strength of Central Canada. With the repeal of the Corn Laws
Corn Laws
The Corn Laws were trade barriers designed to protect cereal producers in the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland against competition from less expensive foreign imports between 1815 and 1846. The barriers were introduced by the Importation Act 1815 and repealed by the Importation Act 1846...
and a reciprocity agreement in place with United States, various industries such as timber, mining, farming and alcohol distilling benefited tremendously.
A political stalemate between the French
Canadian French
Canadian French is an umbrella term referring to the varieties of French spoken in Canada. French is the mother tongue of nearly seven million Canadians, a figure constituting roughly 22% of the national population. At the federal level it has co-official status alongside English...
- and English
Canadian English
Canadian English is the variety of English spoken in Canada. English is the first language, or "mother tongue", of approximately 24 million Canadians , and more than 28 million are fluent in the language...
-speaking legislators, as well as fear of aggression from the United States during and immediately after the American Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
, led the political elite to hold a series of conferences in the 1860s to effect a broader federal union of all British North America
British North America
British North America is a historical term. It consisted of the colonies and territories of the British Empire in continental North America after the end of the American Revolutionary War and the recognition of American independence in 1783.At the start of the Revolutionary War in 1775 the British...
n colonies. The British North America Act took effect on July 1, 1867, establishing the Dominion of Canada, initially with four provinces: Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Quebec and Ontario. The Province of Canada was divided into Ontario and Quebec so that each linguistic group would have its own province. Both Quebec and Ontario were required by section 93 of the British North America Act
Constitution Act, 1867
The Constitution Act, 1867 , is a major part of Canada's Constitution. The Act created a federal dominion and defines much of the operation of the Government of Canada, including its federal structure, the House of Commons, the Senate, the justice system, and the taxation system...
to safeguard existing educational rights and privileges of Protestant and the Catholic minority. Thus, separate Catholic schools and school boards
Board of education
A board of education or a school board or school committee is the title of the board of directors or board of trustees of a school, local school district or higher administrative level....
were permitted in Ontario. However, neither province had a constitutional requirement to protect its French- or English-speaking minority. Toronto was formally established as Ontario's provincial capital.
Provincehood
Once constituted as a province, Ontario proceeded to assert its economic and legislative power. In 1872, the lawyer Oliver MowatOliver Mowat
Sir Oliver Mowat, was a Canadian politician, and the third Premier of Ontario from 1872 to 1896, making him the longest serving premier of that province and the 3rd longest in all of Canadian history...
became Premier of Ontario
Premier of Ontario
The Premier of Ontario is the first Minister of the Crown for the Canadian province of Ontario. The Premier is appointed as the province's head of government by the Lieutenant Governor of Ontario, and presides over the Executive council, or Cabinet. The Executive Council Act The Premier of Ontario...
and remained as premier until 1896. He fought for provincial rights, weakening the power of the federal government
Government of Canada
The Government of Canada, formally Her Majesty's Government, is the system whereby the federation of Canada is administered by a common authority; in Canadian English, the term can mean either the collective set of institutions or specifically the Queen-in-Council...
in provincial matters, usually through well-argued appeals to the Judicial Committee of the Privy Council. His battles with the federal government greatly decentralized
Decentralization
__FORCETOC__Decentralization or decentralisation is the process of dispersing decision-making governance closer to the people and/or citizens. It includes the dispersal of administration or governance in sectors or areas like engineering, management science, political science, political economy,...
Canada, giving the provinces far more power than John A. Macdonald
John A. Macdonald
Sir John Alexander Macdonald, GCB, KCMG, PC, PC , QC was the first Prime Minister of Canada. The dominant figure of Canadian Confederation, his political career spanned almost half a century...
had intended. He consolidated and expanded Ontario's educational and provincial institutions, created districts in Northern Ontario, and fought to ensure that those parts of Northwestern Ontario not historically part of Upper Canada (the vast areas north and west of the Lake Superior-Hudson Bay watershed, known as the District of Keewatin
District of Keewatin
The District of Keewatin was a territory of Canada and later an administrative district of the Northwest Territories.The name "Keewatin" comes from Algonquian roots—either kīwēhtin in Cree or giiwedin in Ojibwe—both of which mean north wind in their respective languages...
) would become part of Ontario, a victory embodied in the Canada (Ontario Boundary) Act, 1889. He also presided over the emergence of the province into the economic powerhouse of Canada. Mowat was the creator of what is often called Empire Ontario.
Beginning with Sir John A. Macdonald's National Policy
National Policy
The National Policy was a Canadian economic program introduced by John A. Macdonald's Conservative Party in 1876 and put into action in 1879. It called for high tariffs on imported manufactured items to protect the manufacturing industry...
(1879) and the construction of the Canadian Pacific Railway
Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway , formerly also known as CP Rail between 1968 and 1996, is a historic Canadian Class I railway founded in 1881 and now operated by Canadian Pacific Railway Limited, which began operations as legal owner in a corporate restructuring in 2001...
(1875–1885) through Northern Ontario and the Canadian Prairies
Canadian Prairies
The Canadian Prairies is a region of Canada, specifically in western Canada, which may correspond to several different definitions, natural or political. Notably, the Prairie provinces or simply the Prairies comprise the provinces of Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba, as they are largely covered...
to British Columbia
British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost of Canada's provinces and is known for its natural beauty, as reflected in its Latin motto, Splendor sine occasu . Its name was chosen by Queen Victoria in 1858...
, Ontario manufacturing and industry flourished. However, population increase slowed after a large recession hit the province in 1893, thus slowing growth drastically but only for a few short years. Many newly arrived immigrants and others moved west along the railway to the Prairie Provinces and British Columbia, sparsely settling Northern Ontario.
Mineral
Mineral
A mineral is a naturally occurring solid chemical substance formed through biogeochemical processes, having characteristic chemical composition, highly ordered atomic structure, and specific physical properties. By comparison, a rock is an aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids and does not...
exploitation accelerated in the late 19th century, leading to the rise of important mining centres in the northeast like Sudbury, Cobalt
Cobalt, Ontario
Cobalt is a town in the district of Timiskaming, province of Ontario, Canada, with a population of 1,223 In 2001 Cobalt was named "Ontario's Most Historic Town" by a panel of judges on the TV Ontario program Studio 2, and in 2002 the area was designated a National Historic Site.-History:Silver was...
and Timmins
Timmins
Timmins is a city in northeastern Ontario, Canada on the Mattagami River. At the time of the Canada 2006 Census, Timmins' population was 42,997...
. The province harnessed its water power to generate hydro-electric power and created the state-controlled Hydro-Electric Power Commission of Ontario, later Ontario Hydro
Ontario Hydro
Ontario Hydro was the official name from 1974 of the Hydro-Electric Power Commission of Ontario which was established in 1906 by the provincial Power Commission Act to build transmission lines to supply municipal utilities with electricity generated by private companies already operating at Niagara...
. The availability of cheap electric power further facilitated the development of industry. The Ford Motor Company of Canada
Ford Motor Company of Canada
Ford Motor Company of Canada, Limited was founded in 1904 for the purpose of manufacturing and selling Ford automobiles in Canada and the British Empire. The Ford Motor Company in Detroit transferred the patent and selling rights to the Walkerville Wagon Company, in order to avoid the tariff rates...
was established in 1904. General Motors Canada
General Motors Canada
General Motors of Canada Limited is General Motors' Canadian division. Its national headquarters office, Canadian Regional Engineering Centre, and main manufacturing plants are located in Oshawa, Ontario. GM Canada is 100% owned by GM.As of Apr...
was formed in 1918. The motor vehicle industry would go on to become the most lucrative industry for the Ontario economy during the 20th century.
In July 1912, the Conservative
Progressive Conservative Party of Ontario
The Progressive Conservative Party of Ontario , is a right-of-centre political party in Ontario, Canada. The party was known for many years as "Ontario's natural governing party." It has ruled the province for 80 of the years since Confederation, including an uninterrupted run from 1943 to 1985...
government of Sir James Whitney
James Whitney
Sir James Pliny Whitney, KCMG was a politician in the Canadian province of Ontario. Whitney was a lawyer in eastern Ontario, Conservative member for Dundas from 1888 to 1914, and the sixth Premier of Ontario from 1905 to 1914.- Early life :Whitney was born in Williamsburgh Township in 1843 and...
issued Regulation 17
Regulation 17
Regulation 17 was a regulation of the Ontario Ministry of Education, issued in July 1912 by the Conservative government of premier Sir James P. Whitney. It restricted the use of French as a language of instruction to the first two years of schooling. It was amended in 1913, and it is that version...
which severely limited the availability of French-language schooling to the province's French-speaking minority. French Canadians reacted with outrage, journalist Henri Bourassa
Henri Bourassa
Joseph-Napoléon-Henri Bourassa was a French Canadian political leader and publisher. He is seen by many as an ideological father of Canadian nationalism....
denouncing the "Prussians of Ontario". It was eventually repealed in 1927.
Influenced by events in the United States, the government of Sir William Hearst introduced prohibition
Prohibition in Canada
The temperance movement reached its height in Canada in the 1920s, when outside imports were cut off by provincial referendums. As legislation prohibiting consumption of alcohol was repealed, it was typically replaced with regulation restricting the sale of alcohol to minors and imposing excise...
of alcoholic drinks in 1916 with the passing of the Ontario Temperance Act
Ontario Temperance Act
Ontario Temperance Act was a law passed in Ontario in 1916 to prohibit the sale of alcohol, a period known as Prohibition. This meant the province remained dry in legal terms, but smugglers continued to import alcohol into the province. The cause was the demand of religious elements led by women...
. However, residents could distil and retain their own personal supply, and liquor producers could continue distillation and export for sale, which allowed this already sizable industry to strengthen further. Ontario became a hotbed for the illegal smuggling of liquor and the biggest supplier into the United States, which was under complete prohibition. Prohibition in Ontario came to an end in 1927 with the establishment of the Liquor Control Board of Ontario
Liquor Control Board of Ontario
The Liquor Control Board of Ontario is a provincial Crown corporation in Ontario, Canada established in 1927 by Lieutenant Governor William Donald Ross, on the advice of his Premier, Howard Ferguson, to sell liquor, wine, and beer through a chain of retail stores...
under the government of Howard Ferguson
Howard Ferguson
George Howard Ferguson, PC was a Conservative politician and the ninth Premier of Ontario, Canada, from 1923 to 1930.-Background:He was the son of Charles Frederick Ferguson who served in the Canadian House of Commons...
. The sale and consumption of liquor, wine, and beer are still controlled by some of the most extreme laws in North America to ensure that strict community standards and revenue generation from the alcohol retail monopoly are upheld. In April 2007, Ontario Member of Provincial Parliament Kim Craitor
Kim Craitor
Kim Craitor is a politician in Ontario, Canada. He is a member of the Legislative Assembly of Ontario, representing the constituency of Niagara Falls for the Ontario Liberal Party.-Early life:...
suggested that local brewers should be able to sell their beer in local corner stores; however, the motion was quickly rejected by Premier Dalton McGuinty
Dalton McGuinty
Dalton James Patrick McGuinty, Jr., MPP is a Canadian lawyer, politician and, since October 23, 2003, the 24th and current Premier of the Canadian province of Ontario....
.
The post-World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
period was one of exceptional prosperity and growth. Ontario, and the Greater Toronto Area in particular, have been the recipients of most immigration to Canada, largely immigrants from war-torn Europe in the 1950s and 1960s and after changes in federal immigration law
Immigration law
Immigration law refers to national government policies which control the phenomenon of immigration to their country.Immigraton law, regarding foreign citizens, is related to nationality law, which governs the legal status of people, in matters such as citizenship...
, a massive influx of non-Europeans since the 1970s. From a largely ethnically
Ethnic group
An ethnic group is a group of people whose members identify with each other, through a common heritage, often consisting of a common language, a common culture and/or an ideology that stresses common ancestry or endogamy...
British province, Ontario has rapidly become very culturally diverse.
The nationalist movement in Quebec, particularly after the election of the Parti Québécois
Parti Québécois
The Parti Québécois is a centre-left political party that advocates national sovereignty for the province of Quebec and secession from Canada. The Party traditionally has support from the labour movement. Unlike many other social-democratic parties, its ties with the labour movement are informal...
in 1976, contributed to driving many businesses and English-speaking people out of Quebec to Ontario, and as a result Toronto surpassed Montreal
Montreal
Montreal is a city in Canada. It is the largest city in the province of Quebec, the second-largest city in Canada and the seventh largest in North America...
as the largest city and economic centre of Canada. Depressed economic conditions in the Maritime Provinces
Atlantic Canada
Atlantic Canada is the region of Canada comprising the four provinces located on the Atlantic coast, excluding Quebec: the three Maritime provinces – New Brunswick, Prince Edward Island, and Nova Scotia – and Newfoundland and Labrador...
have also resulted in de-population of those provinces in the 20th century, with heavy migration into Ontario.
Ontario has no official language, but English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
is considered the de facto language. Numerous French language
French language
French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
services are available under the French Language Services Act
French Language Services Act
The French Language Services Act is a law in the province of Ontario, Canada which is intended to protect the rights of Franco-Ontarians, or French-speaking people, in the province....
of 1990 in designated areas where sizable francophone
Francophone
The adjective francophone means French-speaking, typically as primary language, whether referring to individuals, groups, or places. Often, the word is used as a noun to describe a natively French-speaking person....
populations exist.
Demographics
The percentages add to more than 100% because of dual responses (e.g. "French and Canadian" response generates an entry in both the category "French CanadianFrench Canadian
French Canadian or Francophone Canadian, , generally refers to the descendents of French colonists who arrived in New France in the 17th and 18th centuries...
" and the category "Canadian"). Groups with greater than 200,000 responses are included.
The majority of Ontarians are of English
English Canadian
An English Canadian is a Canadian of English ancestry; it is used primarily in contrast with French Canadian. Canada is an officially bilingual state, with English and French official language communities. Immigrant cultural groups ostensibly integrate into one or both of these communities, but...
or other European descent. Slightly less than 5% of the population of Ontario is Franco-Ontarian
Franco-Ontarian
Franco-Ontarians are French Canadian or francophone residents of the Canadian province of Ontario. They are sometimes known as "Ontarois"....
, that is those whose native tongue is French, although those with French ancestry account for 11% of the population. In relation to natural increase or inter-provincial migration, immigration
Immigration to Canada
Immigration to Canada is the process by which people migrate to Canada to reside permanently in the country. The majority of these individuals become Canadian citizens. After 1947, domestic immigration law and policy went through major changes, most notably with the Immigration Act, 1976, and the...
is a huge population growth force in Ontario, as it has been over the last two centuries. More recent sources of immigrants
Immigration
Immigration is the act of foreigners passing or coming into a country for the purpose of permanent residence...
with large or growing communities in Ontario include Caribbean
Caribbean
The Caribbean is a crescent-shaped group of islands more than 2,000 miles long separating the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean Sea, to the west and south, from the Atlantic Ocean, to the east and north...
s, Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
ns, Latin America
Latin America
Latin America is a region of the Americas where Romance languages – particularly Spanish and Portuguese, and variably French – are primarily spoken. Latin America has an area of approximately 21,069,500 km² , almost 3.9% of the Earth's surface or 14.1% of its land surface area...
ns, Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
ans, and Africa
Africa
Africa is the world's second largest and second most populous continent, after Asia. At about 30.2 million km² including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of the Earth's total surface area and 20.4% of the total land area...
ns. Most populations have settled in the larger urban centres.
Ontario is the second most diverse province in terms of visible minorities after British Columbia
British Columbia
British Columbia is the westernmost of Canada's provinces and is known for its natural beauty, as reflected in its Latin motto, Splendor sine occasu . Its name was chosen by Queen Victoria in 1858...
, with 22.8% of the population consisting of visible minorities. The Greater Toronto Area
Greater Toronto Area
The Greater Toronto Area is the largest metropolitan area in Canada, with a 2006 census population of 5.5 million. The Greater Toronto Area is usually defined as the central city of Toronto, along with four regional municipalities surrounding it: Durham, Halton, Peel, and York...
, Ottawa
Ottawa
Ottawa is the capital of Canada, the second largest city in the Province of Ontario, and the fourth largest city in the country. The city is located on the south bank of the Ottawa River in the eastern portion of Southern Ontario...
, Windsor
Windsor, Ontario
Windsor is the southernmost city in Canada and is located in Southwestern Ontario at the western end of the heavily populated Quebec City – Windsor Corridor. It is within Essex County, Ontario, although administratively separated from the county government. Separated by the Detroit River, Windsor...
, Hamilton
Hamilton, Ontario
Hamilton is a port city in the Canadian province of Ontario. Conceived by George Hamilton when he purchased the Durand farm shortly after the War of 1812, Hamilton has become the centre of a densely populated and industrialized region at the west end of Lake Ontario known as the Golden Horseshoe...
and Waterloo Region are quite diverse metropolitan areas. Aboriginal peoples make up 2% of the population, with two-thirds of that consisting of North American Indians and the other third consisting of Métis
Métis people (Canada)
The Métis are one of the Aboriginal peoples in Canada who trace their descent to mixed First Nations parentage. The term was historically a catch-all describing the offspring of any such union, but within generations the culture syncretised into what is today a distinct aboriginal group, with...
. The number of Aboriginal people has been increasing at rates greater than the general population of Ontario.
| Ethnicity | ||
|---|---|---|
| Ethnic origins | Responses | % |
| Total population | 12,028,895 | 100 |
| English English Canadian An English Canadian is a Canadian of English ancestry; it is used primarily in contrast with French Canadian. Canada is an officially bilingual state, with English and French official language communities. Immigrant cultural groups ostensibly integrate into one or both of these communities, but... |
2,971,360 | 24.7 |
| Canadian | 2,768,870 | 23.0 |
| Scottish Scottish Canadian Scottish Canadians are people of Scottish descent or heritage living in Canada. As the third-largest ethnic group in Canada and among the first to settle in Canada, Scottish people have made a large impact on Canadian culture since colonial times... |
2,101,100 | 17.5 |
| Irish Irish Canadian Irish Canadian are immigrants and descendants of immigrants who originated in Ireland. 1.2 million Irish immigrants arrived, 1825 to 1970, at least half of those in the period from 1831-1850. By 1867, they were the second largest ethnic group , and comprised 24% of Canada's population... |
1,988,940 | 16.5 |
| French French Canadian French Canadian or Francophone Canadian, , generally refers to the descendents of French colonists who arrived in New France in the 17th and 18th centuries... |
1,351,600 | 11.2 |
| German | 1,144,560 | 9.5 |
| Italian | 867,980 | 7.2 |
| Chinese Chinese Canadian Chinese Canadians are Canadians of Chinese descent. They constitute the second-largest visible minority group in Canada, after South Asian Canadians... |
644,465 | 5.4 |
| East Indian Indo-Canadians Indo-Canadians are Canadians whose origins trace back to India. The terms East Indian and South Asian are used to distinguish people of ancestral origin from India, from the First Nations peoples of Canada who are often referred to as Indian, and from the people of the Caribbean, who are sometimes... |
573,250 | 4.8 |
| Dutch (Netherlands) | 490,995 | 4.1 |
| Polish Polish Canadians Polish Canadians are Citizens of Canada with Polish ancestry, and Poles who immigrated to Canada from abroad. According to the 2001 census by Statistics Canada, 984,585 Canadians claim full or partial Polish ancestry.-History:... |
465,560 | 3.9 |
| Ukrainian Ukrainian Canadian A Ukrainian Canadian is a person of Ukrainian descent or origin who was born in or immigrated to Canada. In 2006, there were an estimated 1,209,085 persons residing in Canada of Ukrainian origin, making them Canada's ninth largest ethnic group; and giving Canada the world's third-largest... |
336,355 | 2.8 |
| North American Indian First Nations First Nations is a term that collectively refers to various Aboriginal peoples in Canada who are neither Inuit nor Métis. There are currently over 630 recognised First Nations governments or bands spread across Canada, roughly half of which are in the provinces of Ontario and British Columbia. The... |
317,890 | 2.6 |
| Portuguese Portuguese Canadians Portuguese Canadians are both Canadians born with Portuguese descent or citizenship or Portuguese born with Canadian descent or citizenship . According to StatCan, in 2006, there were 410,850 persons of Portuguese descent living in Canada, or 1.3% of the nation's total population... |
282,870 | 2.4 |
| Filipino Filipino Canadian Filipino Canadians are Canadians of Filipino ancestry. Filipino-Canadians are the fourth-largest subgroup of the Overseas Filipinos.Canada only had a small population of Filipinos until the late 20th century. To date, there are currently around 400,000 Filipino Canadians in Canada, most of them... |
215,750 | 1.8 |
| British British people The British are citizens of the United Kingdom, of the Isle of Man, any of the Channel Islands, or of any of the British overseas territories, and their descendants... , |
205,755 | 1.7 |
| Jamaican Jamaican Canadian Jamaican Canadians are Canadians of Jamaican descent, or Jamaican-born people with Canadian citizenship. The population, according to Canada's 2006 Census, is 231,110. Jamaican Canadians comprise about 30% of the entire black Canadian population.-History:... |
197,540 | 1.6 |
| Welsh | 182,825 | 1.5 |
| Jewish | 177,255 | 1.5 |
| Russian | 167,365 | 1.4 |
| Hungarian (Magyar) | 151,750 | 1.3 |
| Spanish | 149,160 | 1.2 |
| Greek Greek Canadians Greek Canadians are Canadian citizens of Greek origin, also known as Hellenic origin. According to the 2006 Canadian census, there were 242,685 Canadians who claimed Greek ethnicity.- Authors :... |
132,440 | 1.1 |
| American (USA) Canadians of American origin American-Canadians are people of Canadian citizenship who were born in the United States of America. They account for a significant portion of Canada's population. Canada and the United States share much culturally but are separate geopolitical entities in North America.According to the Canada 2006... |
113,050 | 0.9 |
| Pakistani | 91,160 | 0.8 |
| Métis Métis people (Canada) The Métis are one of the Aboriginal peoples in Canada who trace their descent to mixed First Nations parentage. The term was historically a catch-all describing the offspring of any such union, but within generations the culture syncretised into what is today a distinct aboriginal group, with... |
87,090 | 0.7 |
| Sri Lankan | 85,935 | 0.7 |
| Vietnamese Vietnamese Canadian Mainstream Vietnamese communities began arriving in Canada in the mid 1970s and early 1980s as refugees or boat people following the end of the Vietnam War in 1975, though a couple thousand were already living in Quebec before then, most of whom were students... |
83,330 | 0.7 |
| Romanian | 80,710 | 0.7 |
| African African people African people refers to natives, inhabitants, or citizen of Africa and to people of African descent.-Etymology:Many etymological hypotheses that have been postulated for the ancient name "Africa":... , |
75,500 | 0.6 |
| Finnish | 72,990 | 0.6 |
| Korean | 72,065 | 0.6 |
| Croatian | 71,380 | 0.6 |
| Iranian Iranian-Canadian Iranian Canadians or Persian Canadians are Canadians of Iranian/Persian national background or descent. Their numbers are estimated as 121,510 from the 2006 Canadian census and the main communities can be found in Southern Ontario, British Columbia, and Quebec; the vast majority, however, live in... |
70,590 | 0.6 |
| Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | Census Figures | Five-year % change |
Ten-year % change |
Rank among provinces |
| 1851 | 952,004 | n/a | 208.8 | 1 |
| 1861 | 1,396,091 | n/a | 46.6 | 1 |
| 1871 | 1,620,851 | n/a | 16.1 | 1 |
| 1881 | 1,926,922 | n/a | 18.9 | 1 |
| 1891 | 2,114,321 | n/a | 9.7 | 1 |
| 1901 | 2,182,947 | n/a | 3.2 | 1 |
| 1911 | 2,527,292 | n/a | 15.8 | 1 |
| 1921 | 2,933,662 | n/a | 16.1 | 1 |
| 1931 | 3,431,683 | n/a | 17.0 | 1 |
| 1941 | 3,787,655 | n/a | 10.3 | 1 |
| 1951 | 4,597,542 | n/a | 21.4 | 1 |
| 1956 | 5,404,933 | 17.6 | n/a | 1 |
| 1961 | 6,236,092 | 15.4 | 35.6 | 1 |
| 1966 | 6,960,870 | 11.6 | 28.8 | 1 |
| 1971 | 7,703,105 | 10.7 | 23.5 | 1 |
| 1976 | 8,264,465 | 7.3 | 18.7 | 1 |
| 1981 | 8,625,107 | 4.4 | 12.0 | 1 |
| 1986 | 9,101,695 | 5.5 | 10.1 | 1 |
| 1991 | 10,084,885 | 10.8 | 16.9 | 1 |
| 1996 | 10,753,573 | 6.6 | 18.1 | 1 |
| 2001 | 11,410,046 | 6.1 | 13.1 | 1 |
| 2006a | 12,160,282 | 6.6 | 11.6 | 1 |
a 2006 Census
Religion
The largest denominations by number of adherents according to the 2001 census were the Roman Catholic ChurchRoman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the world's largest Christian church, with over a billion members. Led by the Pope, it defines its mission as spreading the gospel of Jesus Christ, administering the sacraments and exercising charity...
with 3,866,350 (34%); the United Church of Canada
United Church of Canada
The United Church of Canada is a Protestant Christian denomination in Canada. It is the largest Protestant church and, after the Roman Catholic Church, the second-largest Christian church in Canada...
with 1,334,570 (12%); and the Anglican Church of Canada
Anglican Church of Canada
The Anglican Church of Canada is the Province of the Anglican Communion in Canada. The official French name is l'Église Anglicane du Canada. The ACC is the third largest church in Canada after the Roman Catholic Church and the United Church of Canada, consisting of 800,000 registered members...
with 985,110 (9%).
The major religious groups in Ontario, as of 2001, are:

| Religion | People | % |
|---|---|---|
| Total | 11,285,545 | 100 |
| Protestant Protestantism Protestantism is one of the three major groupings within Christianity. It is a movement that began in Germany in the early 16th century as a reaction against medieval Roman Catholic doctrines and practices, especially in regards to salvation, justification, and ecclesiology.The doctrines of the... |
3,935,745 | 34.9 |
| Catholic Catholicism Catholicism is a broad term for the body of the Catholic faith, its theologies and doctrines, its liturgical, ethical, spiritual, and behavioral characteristics, as well as a religious people as a whole.... |
3,911,760 | 34.7 |
| No Religion Irreligion Irreligion is defined as an absence of religion or an indifference towards religion. Sometimes it may also be defined more narrowly as hostility towards religion. When characterized as hostility to religion, it includes antitheism, anticlericalism and antireligion. When characterized as... |
1,841,290 | 16.3 |
| Muslim Islam Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~... |
352,530 | 3.1 |
| Other Christian Christian A Christian is a person who adheres to Christianity, an Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as recorded in the Canonical gospels and the letters of the New Testament... s |
301,935 | 2.7 |
| Christian Orthodox Orthodox Christianity The term Orthodox Christianity may refer to:* the Eastern Orthodox Church and its various geographical subdivisions... |
264,055 | 2.3 |
| Hindu Hinduism Hinduism is the predominant and indigenous religious tradition of the Indian Subcontinent. Hinduism is known to its followers as , amongst many other expressions... |
217,555 | 1.9 |
| Jewish Judaism Judaism ) is the "religion, philosophy, and way of life" of the Jewish people... |
190,795 | 1.7 |
| Buddhist Buddhism Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th... |
128,320 | 1.1 |
| Sikh Sikhism Sikhism is a monotheistic religion founded during the 15th century in the Punjab region, by Guru Nanak Dev and continued to progress with ten successive Sikh Gurus . It is the fifth-largest organized religion in the world and one of the fastest-growing... |
104,785 | 0.9 |
| Eastern Religions Eastern religion This article is about far east and Indian religions. For other eastern religions see: Eastern_world#Eastern_cultureEastern religions refers to religions originating in the Eastern world —India, China, Japan and Southeast Asia —and thus having dissimilarities with Western religions... |
17,780 | 0.2 |
| Other Religions | 18,985 | 0.2 |
Economy


Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the use of machines, tools and labor to produce goods for use or sale. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high tech, but is most commonly applied to industrial production, in which raw materials are transformed into finished goods on a large scale...
province accounting for 52% of the total national manufacturing shipments in 2004. Ontario's largest trading partner is the American state of Michigan
Michigan
Michigan is a U.S. state located in the Great Lakes Region of the United States of America. The name Michigan is the French form of the Ojibwa word mishigamaa, meaning "large water" or "large lake"....
. The government of Ontario posted a record C$21.3 billion ($20.7 billion) deficit for the 2009-10 fiscal year. The province’s net debt will rise to C$220 billion in 2010-11, or a record 37% of gross domestic product.
Ontario's rivers, including its share of the Niagara River, make it rich in hydroelectric energy. In 2009 Ontario Power Generation
Ontario Power Generation
Ontario Power Generation is a public company wholly owned by the Government of Ontario. OPG is responsible for approximately 70% of the electricity generation in the Province of Ontario, Canada. Sources of electricity include nuclear, hydroelectric, solar, wind, and fossil fuel...
generated 70% of the electricity of the province, of which 51% is nuclear
Nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity...
, 39% is hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity
Hydroelectricity is the term referring to electricity generated by hydropower; the production of electrical power through the use of the gravitational force of falling or flowing water. It is the most widely used form of renewable energy...
and 10% is fossil fuel
Fossil fuel
Fossil fuels are fuels formed by natural processes such as anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms. The age of the organisms and their resulting fossil fuels is typically millions of years, and sometimes exceeds 650 million years...
derived. Much of the newer power generation coming online in the last few years is natural gas or combined cycle natural gas plants. OPG is not however responsible for the transmission of power, which is under the control of Hydro One
Hydro One
Hydro One Incorporated delivers electricity across the Canadian province of Ontario. It is a Corporation established under the Business Corporations Act with a single shareholder, the Government of Ontario....
. Despite its diverse range of power options, problems related to increasing consumption, lack of energy efficiency and aging nuclear reactors, Ontario has been forced in recent years to purchase power from its neighbours Quebec and Michigan to supplement its power needs during peak consumption periods.
An abundance of natural resource
Natural resource
Natural resources occur naturally within environments that exist relatively undisturbed by mankind, in a natural form. A natural resource is often characterized by amounts of biodiversity and geodiversity existent in various ecosystems....
s, excellent transportation links to the American heartland and the inland Great Lakes making ocean access possible via container ship
Container ship
Container ships are cargo ships that carry all of their load in truck-size intermodal containers, in a technique called containerization. They form a common means of commercial intermodal freight transport.-History:...
s, have all contributed to making manufacturing
Manufacturing
Manufacturing is the use of machines, tools and labor to produce goods for use or sale. The term may refer to a range of human activity, from handicraft to high tech, but is most commonly applied to industrial production, in which raw materials are transformed into finished goods on a large scale...
the principal industry
Industry
Industry refers to the production of an economic good or service within an economy.-Industrial sectors:There are four key industrial economic sectors: the primary sector, largely raw material extraction industries such as mining and farming; the secondary sector, involving refining, construction,...
, found mainly in the Golden Horseshoe region, which is the largest industrialized area in Canada, the southern end of the region being part of the North American Rust Belt
Rust Belt
The Rust Belt is a term that gained currency in the 1980s as the informal description of an area straddling the Midwestern and Northeastern United States, in which local economies traditionally garnered an increased manufacturing sector to add jobs and corporate profits...
. Important products include motor vehicle
Motor vehicle
A motor vehicle or road vehicle is a self-propelled wheeled vehicle that does not operate on rails, such as trains or trolleys. The vehicle propulsion is provided by an engine or motor, usually by an internal combustion engine, or an electric motor, or some combination of the two, such as hybrid...
s, iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
, steel
Steel
Steel is an alloy that consists mostly of iron and has a carbon content between 0.2% and 2.1% by weight, depending on the grade. Carbon is the most common alloying material for iron, but various other alloying elements are used, such as manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten...
, food, electrical appliances, machinery, chemical
Chemical substance
In chemistry, a chemical substance is a form of matter that has constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. It cannot be separated into components by physical separation methods, i.e. without breaking chemical bonds. They can be solids, liquids or gases.Chemical substances are...
s, and paper
Paper
Paper is a thin material mainly used for writing upon, printing upon, drawing or for packaging. It is produced by pressing together moist fibers, typically cellulose pulp derived from wood, rags or grasses, and drying them into flexible sheets....
. Ontario surpassed Michigan in car
Automobile
An automobile, autocar, motor car or car is a wheeled motor vehicle used for transporting passengers, which also carries its own engine or motor...
production, assembling 2.696 million vehicles in 2004. Ontario has Chrysler
Chrysler
Chrysler Group LLC is a multinational automaker headquartered in Auburn Hills, Michigan, USA. Chrysler was first organized as the Chrysler Corporation in 1925....
plants in Windsor
Windsor, Ontario
Windsor is the southernmost city in Canada and is located in Southwestern Ontario at the western end of the heavily populated Quebec City – Windsor Corridor. It is within Essex County, Ontario, although administratively separated from the county government. Separated by the Detroit River, Windsor...
and Bramalea, two GM
General Motors
General Motors Company , commonly known as GM, formerly incorporated as General Motors Corporation, is an American multinational automotive corporation headquartered in Detroit, Michigan and the world's second-largest automaker in 2010...
plants in Oshawa and one in Ingersoll, a Honda
Honda
is a Japanese public multinational corporation primarily known as a manufacturer of automobiles and motorcycles.Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, as well as the world's largest manufacturer of internal combustion engines measured by volume, producing more than...
assembly plant in Alliston, Ford plants in Oakville and St. Thomas and Toyota assembly plants in Cambridge and Woodstock.
However, as a result of steeply declining sales, in 2005, General Motors
General Motors
General Motors Company , commonly known as GM, formerly incorporated as General Motors Corporation, is an American multinational automotive corporation headquartered in Detroit, Michigan and the world's second-largest automaker in 2010...
announced massive layoffs at production facilities across North America including two large GM plants in Oshawa
Oshawa
Oshawa is a city in Ontario, Canada, on the Lake Ontario shoreline. It lies in Southern Ontario approximately 60 kilometres east of downtown Toronto. It is commonly viewed as the eastern anchor of both the Greater Toronto Area and the Golden Horseshoe. It is now commonly referred to as the most...
and a drive train
Powertrain
In a motor vehicle, the term powertrain or powerplant refers to the group of components that generate power and deliver it to the road surface, water, or air. This includes the engine, transmission, drive shafts, differentials, and the final drive...
facility in St. Catharines resulting in 8,000 job losses in Ontario alone. In 2006, Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company
Ford Motor Company is an American multinational automaker based in Dearborn, Michigan, a suburb of Detroit. The automaker was founded by Henry Ford and incorporated on June 16, 1903. In addition to the Ford and Lincoln brands, Ford also owns a small stake in Mazda in Japan and Aston Martin in the UK...
announced between 25,000 and 30,000 layoffs phased until 2012; Ontario was spared the worst, but job losses were announced for the St. Thomas
St. Thomas, Ontario
St. Thomas is a city in southern , Ontario, Canada. It is the seat for Elgin County and gained its city charter on March 4, 1881.-History:...
facility and the Windsor Casting
Windsor Casting
Windsor Casting Plant was an Iron Foundry owned by Ford Motor Company in Windsor, Ontario, Canada. The plant first opened November 9, 1934 and was located next to Ford Windsor engine plant in downtown Windsor. It was known to area residents as the "Foundry"...
plant. However, these losses will be offset by Ford's recent announcement of a hybrid vehicle
Hybrid vehicle
A hybrid vehicle is a vehicle that uses two or more distinct power sources to move the vehicle. The term most commonly refers to hybrid electric vehicles , which combine an internal combustion engine and one or more electric motors.-Power:...
facility slated to begin production in 2007 at its Oakville
Oakville, Ontario
Oakville is a town in Halton Region, on Lake Ontario in Southern Ontario, Canada, and is part of the Greater Toronto Area. As of the 2006 census the population was 165,613.-History:In 1793, Dundas Street was surveyed for a military road...
plant and GM's re-introduction of the Camaro
Chevrolet Camaro
The Chevrolet Camaro is an automobile manufactured by General Motors under the Chevrolet brand, classified as a pony car and some versions also as a muscle car. It went on sale on September 29, 1966, for the 1967 model year and was designed as a competing model to the Ford Mustang...
which will be produced in Oshawa. On December 4, 2008 Toyota announced the grand opening of the RAV4
Toyota RAV4
The Toyota RAV4 is a compact crossover SUV from Toyota. It was the first compact crossover SUV, introduced in Japan and Europe in 1994 and beginning sales in North America in 1996...
plant in Woodstock
Woodstock, Ontario
Woodstock is a city and the county seat of Oxford County in Southern Ontario, Canada. Woodstock is located 128 km southwest of Toronto, north of Highway 401 along the historic Thames River...
, and Honda
Honda
is a Japanese public multinational corporation primarily known as a manufacturer of automobiles and motorcycles.Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, as well as the world's largest manufacturer of internal combustion engines measured by volume, producing more than...
also has plans to add an engine plant at its facility in Alliston
Alliston, Ontario
Alliston is a settlement in Simcoe County in the Canadian province of Ontario. It is part of the Town of New Tecumseth since the 1991 amalgamation of Alliston and nearby villages of Beeton, Tottenham, and the Township of Tecumseth...
. Despite these new plants coming online, Ontario has not yet fully recovered following massive layoffs caused by the global recession; its unemployment rate was 8.1% (as of October 2011), compared to 8.7% in Jan. 2010 and roughly 6% in 2007.
Toronto, the capital of Ontario, is the centre of Canada's financial services
Financial services
Financial services refer to services provided by the finance industry. The finance industry encompasses a broad range of organizations that deal with the management of money. Among these organizations are credit unions, banks, credit card companies, insurance companies, consumer finance companies,...
and banking industry. Neighbouring cities forming part of the Greater Toronto Area
Greater Toronto Area
The Greater Toronto Area is the largest metropolitan area in Canada, with a 2006 census population of 5.5 million. The Greater Toronto Area is usually defined as the central city of Toronto, along with four regional municipalities surrounding it: Durham, Halton, Peel, and York...
, such as Brampton
Brampton
Brampton is the third-largest city in the Greater Toronto Area of Ontario, Canada.Brampton may also refer to:- Canada :* Brampton, a city in Ontario** Brampton GO Station, a station in the GO Transit network located in the city- United Kingdom :...
, Mississauga and Vaughan
Vaughan
Vaughan is a city in York Region north of Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Vaughan is the fastest growing municipality in Canada achieving a population growth rate of 80.2% between 1996–2006, according to Statistics Canada having nearly doubled in population since 1991. Vaughan is located in Southern...
, are large product distribution and IT centres, in addition to having various manufacturing industries. The information technology
Information technology
Information technology is the acquisition, processing, storage and dissemination of vocal, pictorial, textual and numerical information by a microelectronics-based combination of computing and telecommunications...
sector is also important, particularly in the Silicon Valley North section of Ottawa
Ottawa
Ottawa is the capital of Canada, the second largest city in the Province of Ontario, and the fourth largest city in the country. The city is located on the south bank of the Ottawa River in the eastern portion of Southern Ontario...
, as well as the Waterloo Region
Regional Municipality of Waterloo
The Regional Municipality of Waterloo is a regional municipality located in Southern Ontario, Canada. It consists of the cities of Kitchener, Cambridge, and Waterloo, and the townships of Wellesley, Woolwich, Wilmot, and North Dumfries. It is often referred to as the Region of Waterloo or just...
, where the world headquarters of Research in Motion
Research In Motion
Research In Motion Limited or RIM is a Canadian multinational telecommunications company headquartered in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada that designs, manufactures and markets wireless solutions for the worldwide mobile communications market...
(the developers of the BlackBerry
BlackBerry
BlackBerry is a line of mobile email and smartphone devices developed and designed by Canadian company Research In Motion since 1999.BlackBerry devices are smartphones, designed to function as personal digital assistants, portable media players, internet browsers, gaming devices, and much more...
smartphone) is located. Providing more than 19% of the local jobs and employing more than 13% of the entire local population, Canada's Federal Government is by far the largest single employer in the National Capital Region
National Capital Region (Canada)
The National Capital Region, also referred to as Canada's Capital Region, is an official federal designation for the Canadian capital of Ottawa, Ontario, the neighbouring city of Gatineau, Quebec, and surrounding urban and rural communities....
, which centres on the border cities of Ontario's Ottawa and Quebec's Gatineau. Hamilton
Hamilton, Ontario
Hamilton is a port city in the Canadian province of Ontario. Conceived by George Hamilton when he purchased the Durand farm shortly after the War of 1812, Hamilton has become the centre of a densely populated and industrialized region at the west end of Lake Ontario known as the Golden Horseshoe...
is the largest steel manufacturing city in Canada, and Sarnia
Sarnia, Ontario
Sarnia is a city in Southern Ontario, Canada . It is the largest city on Lake Huron and is located where the upper Great Lakes empty into the St. Clair River....
is the centre for petrochemical
Petrochemical
Petrochemicals are chemical products derived from petroleum. Some chemical compounds made from petroleum are also obtained from other fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, or renewable sources such as corn or sugar cane....
production. Construction
Construction
In the fields of architecture and civil engineering, construction is a process that consists of the building or assembling of infrastructure. Far from being a single activity, large scale construction is a feat of human multitasking...
continues to employ more than 6½% of the province's work force as of June 2011.
Mining
Mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the earth, from an ore body, vein or seam. The term also includes the removal of soil. Materials recovered by mining include base metals, precious metals, iron, uranium, coal, diamonds, limestone, oil shale, rock...
and the forest products
Forestry
Forestry is the interdisciplinary profession embracing the science, art, and craft of creating, managing, using, and conserving forests and associated resources in a sustainable manner to meet desired goals, needs, and values for human benefit. Forestry is practiced in plantations and natural stands...
industry, notably pulp and paper
Pulp and paper industry in Canada
The pulp and paper industry in Canada is one of the country's most important and profitable industries. It is especially concentrated in Ontario and Quebec but plays an important role in many other provinces.- Leading companies :...
, are vital to the economy of Northern Ontario. More than any other region, tourism contributes heavily to the economy of Central Ontario, peaking during the summer months owing to the abundance of fresh water
Fresh Water
Fresh Water is the debut album by Australian rock and blues singer Alison McCallum, released in 1972. Rare for an Australian artist at the time, it came in a gatefold sleeve...
recreation and wilderness found there in reasonable proximity to the major urban centres. At other times of the year, hunting
Hunting
Hunting is the practice of pursuing any living thing, usually wildlife, for food, recreation, or trade. In present-day use, the term refers to lawful hunting, as distinguished from poaching, which is the killing, trapping or capture of the hunted species contrary to applicable law...
, skiing
Skiing
Skiing is a recreational activity using skis as equipment for traveling over snow. Skis are used in conjunction with boots that connect to the ski with use of a binding....
and snowmobiling
Snowmobile
A snowmobile, also known in some places as a snowmachine, or sled,is a land vehicle for winter travel on snow. Designed to be operated on snow and ice, they require no road or trail. Design variations enable some machines to operate in deep snow or forests; most are used on open terrain, including...
are popular. This region has some of the most vibrant fall colour displays anywhere on the continent, and tours directed at overseas visitors are organized to see them. Tourism also plays a key role in border cities with large casinos, among them Windsor, Cornwall
Cornwall, Ontario
Cornwall is a city in Eastern Ontario, Canada and the seat of the United Counties of Stormont, Dundas and Glengarry, Ontario. Cornwall is Ontario's easternmost city, located on the St...
, Sarnia and Niagara Falls
Niagara Falls, Ontario
Niagara Falls is a Canadian city on the Niagara River in the Golden Horseshoe region of Southern Ontario. The municipality was incorporated on June 12, 1903...
, which attract many U.S. visitors.
Agriculture
Once the dominant industry, agricultureAgriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
occupies a small percentage of the population but still a large part of Southern Ontario's land area. As the following table shows, while the number of individual farms has steadily decreased and their overall size has shrunk at a lower rate, greater mechanization has supported increased supply to satisfy the ever increasing demands of a growing population base; this has also meant a gradual increase in the total amount of land used for growing crops.
Cattle, small grains and dairy
Dairy
A dairy is a business enterprise established for the harvesting of animal milk—mostly from cows or goats, but also from buffalo, sheep, horses or camels —for human consumption. A dairy is typically located on a dedicated dairy farm or section of a multi-purpose farm that is concerned...
were the common types of farms in the 2001 census. The fruit, grape and vegetable growing industry is located primarily on the Niagara Peninsula
Niagara Peninsula
The Niagara Peninsula is the portion of Southern Ontario, Canada lying between the south shore of Lake Ontario and the north shore of Lake Erie. It stretches from the Niagara River in the east to Hamilton, Ontario in the west. The population of the peninsula is roughly 1,000,000 people...
and along Lake Erie, where tobacco
Tobacco
Tobacco is an agricultural product processed from the leaves of plants in the genus Nicotiana. It can be consumed, used as a pesticide and, in the form of nicotine tartrate, used in some medicines...
farms are also situated.
The Corn Belt
Corn Belt
The Corn Belt is a region of the Midwestern United States where corn has, since the 1850s, been the predominant crop, replacing the native tall grasses. By 1950, 99% of the corn was grown from hybrids. Most corn is fed to livestock, especially hogs and poultry. In recent decades soybeans have...
covers much of the southwestern area of the province extending as far north as close to Goderich. Apple orchards are a common sight along the southern shore of Georgian Bay near Collingwood and along the northern shore of Lake Ontario near Cobourg. Tobacco production, centred in Norfolk County
Norfolk County, Ontario
Norfolk County is a rural city-status single-tier municipality on the north shore of Lake Erie in Southwestern Ontario, Canada. Bloomsburg is a small town located in Norfolk County and is the hometown of David Slater. The county seat and largest community is Simcoe...
has decreased leading to an increase in some other new crop alternatives gaining popularity, such as hazelnuts
Corylus avellana
Corylus avellana, the Common Hazel, is a species of hazel native to Europe and western Asia, from the British Isles south to Iberia, Greece, Turkey and Cyprus, north to central Scandinavia, and east to the central Ural Mountains, the Caucasus, and northwestern Iran. It is an important component of...
and ginseng
Ginseng
Ginseng is any one of eleven species of slow-growing perennial plants with fleshy roots, belonging to the genus Panax of the family Araliaceae....
. The Ontario origins of Massey Ferguson
Massey Ferguson
Massey Ferguson Limited was a major agricultural equipment manufacturer which was based in Canada before its purchase by AGCO. The company was formed by a merger between Massey Harris and the Ferguson tractor company in 1953, creating the company Massey Harris Ferguson. However in 1958 the name was...
, once one of the largest farm implement
Agricultural machinery
Agricultural machinery is machinery used in the operation of an agricultural area or farm.-Hand tools:The first person to turn from the hunting and gathering lifestyle to farming probably did so by using his bare hands, and perhaps some sticks or stones. Tools such as knives, scythes, and wooden...
manufacturers in the world, indicate the importance agriculture once had to the Canadian economy.
Southern Ontario
Southern Ontario
Southern Ontario is a region of the province of Ontario, Canada that lies south of the French River and Algonquin Park. Depending on the inclusion of the Parry Sound and Muskoka districts, its surface area would cover between 14 to 15% of the province. It is the southernmost region of...
's limited supply of agricultural land is going out of production at an increasing rate. Urban sprawl
Urban sprawl
Urban sprawl, also known as suburban sprawl, is a multifaceted concept, which includes the spreading outwards of a city and its suburbs to its outskirts to low-density and auto-dependent development on rural land, high segregation of uses Urban sprawl, also known as suburban sprawl, is a...
and farmland severances contribute to the loss of thousands of acres of productive agricultural land in Ontario each year. Over 2,000 farms and 150000 acre (60,702.9 ha) of farmland in the GTA alone were lost to production in the two decades between 1976 and 1996. This loss represented approximately 18% of Ontario's Class 1 farmland being converted to urban purposes. In addition, increasing rural severances provide ever-greater interference with agricultural production.
The 500,000, or so, acres (200,000 ha) comprising the black peat soil Holland Marsh
Holland Marsh
The Holland Marsh is a wetland and agricultural area north of Toronto, Ontario. It lies entirely within the valley of the Holland River, stretching from the northern edge of the Oak Ridges Moraine near Schomberg to the river mouth at Cook's Bay, Lake Simcoe. In its entirety it comprises about or...
, located just south of Lake Simcoe
Lake Simcoe
Lake Simcoe is a lake in Southern Ontario, Canada, the fourth-largest lake wholly in the province, after Lake Nipigon, Lac Seul, and Lake Nipissing. At the time of the first European contact in the 17th century the lake was called Ouentironk by the Huron natives...
and near the town of Bradford West Gwillimbury
Bradford West Gwillimbury, Ontario
Bradford West Gwillimbury, a town in south-central Ontario, in the County of Simcoe in the Greater Toronto Area on the Holland River. West Gwillimbury takes its name from the family of Elizabeth Simcoe, née Gwillim....
(35 mi (56.3 km) north of Toronto) continues to be Canada's premier vegetable production center.
Energy

Renewable resource
A renewable resource is a natural resource with the ability of being replaced through biological or other natural processes and replenished with the passage of time...
to the province and the second is the creation of more energy efficiency
Efficient energy use
Efficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the goal of efforts to reduce the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a home allows a building to use less heating and cooling energy to achieve and maintain a comfortable temperature...
measures to help conserve energy
Energy conservation
Energy conservation refers to efforts made to reduce energy consumption. Energy conservation can be achieved through increased efficient energy use, in conjunction with decreased energy consumption and/or reduced consumption from conventional energy sources...
. The bill would also appoint a Renewable Energy Facilitator to provide "one-window" assistance and support to project developers in order to facilitate project approvals.
The approvals process for transmission projects would also be streamlined and for the first time in Ontario, the bill would enact standards for renewable energy projects. Homeowners would have access to incentives to develop small-scale renewables such as low- or no-interest loan
Loan
A loan is a type of debt. Like all debt instruments, a loan entails the redistribution of financial assets over time, between the lender and the borrower....
s to finance the capital cost of renewable energy generating facilities like solar panels.
Ontario is home to Niagara Falls
Niagara Falls
The Niagara Falls, located on the Niagara River draining Lake Erie into Lake Ontario, is the collective name for the Horseshoe Falls and the adjacent American Falls along with the comparatively small Bridal Veil Falls, which combined form the highest flow rate of any waterfalls in the world and has...
, which supplies a large amount of clean, hydroelectric energy for the province. The Bruce Nuclear Generating Station
Bruce Nuclear Generating Station
Bruce Nuclear Generating Station is a Canadian nuclear power station located on the eastern shore of Lake Huron, in the communities of Inverhuron and Tiverton, Ontario. It occupies 932 ha of land. The facility derives its name from Bruce County in which it is located, in the former Bruce Township...
, the second largest nuclear power
Nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity...
plant in the world, is also in Ontario and uses 8 CANDU reactors to power the province with clean, reliable energy.
Transportation
Historically, the province has used two major east-west routes, both starting from Montreal in the neighbouring province of Quebec. The northerly route, which was pioneered by early French-speaking fur tradeFur trade
The fur trade is a worldwide industry dealing in the acquisition and sale of animal fur. Since the establishment of world market for in the early modern period furs of boreal, polar and cold temperate mammalian animals have been the most valued...
rs, travels northwest from Montreal along the Ottawa River
Ottawa River
The Ottawa River is a river in the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. For most of its length, it now defines the border between these two provinces.-Geography:...
, then continues westward towards Manitoba. Major cities on or near the route include Ottawa, North Bay, Sudbury, Sault Ste. Marie
Sault Ste. Marie, Ontario
Sault Ste. Marie is a city on the St. Marys River in Algoma District, Ontario, Canada. It is the third largest city in Northern Ontario, after Sudbury and Thunder Bay, with a population of 74,948. The community was founded as a French religious mission: Sault either means "jump" or "rapids" in...
, and Thunder Bay. The much more heavily travelled southerly route, which was driven by growth in predominantly English-speaking settlements originated by the United Empire Loyalists and later other European immigrants, travels southwest from Montreal along the St. Lawrence River, Lake Ontario, and Lake Erie before entering the United States in Michigan. Major cities on or near the route include Kingston, Oshawa, Toronto, Mississauga, Kitchener-Waterloo
Regional Municipality of Waterloo
The Regional Municipality of Waterloo is a regional municipality located in Southern Ontario, Canada. It consists of the cities of Kitchener, Cambridge, and Waterloo, and the townships of Wellesley, Woolwich, Wilmot, and North Dumfries. It is often referred to as the Region of Waterloo or just...
, Hamilton, London, Sarnia, and Windsor. This route was also heavily used by immigrants to the Midwestern US particularly in the late 19th century. Most of Ontario's major transportation infrastructure is oriented east-west and roughly follows one of these two original routes.
Roads
400-Series Highways400-series highways (Ontario)
The 400-series highways are a network of controlled-access highways throughout the southern portion of the Canadian province of Ontario, forming a special subset of the provincial highway system. They are analogous to the Interstate Highway System in the United States or the British Motorway...
make up the primary vehicular network in the south of province, and they connect to numerous border crossings with the U.S., the busiest being the Detroit–Windsor Tunnel
Detroit–Windsor Tunnel
The Detroit–Windsor Tunnel is an underwater highway tunnel connecting Detroit, Michigan in the United States, with Windsor, Ontario in Canada. It was completed in 1930....
and Ambassador Bridge
Ambassador Bridge
The Ambassador Bridge is a suspension bridge that connects Detroit, Michigan, in the United States, with Windsor, Ontario, in Canada. It is the busiest international border crossing in North America in terms of trade volume: more than 25 percent of all merchandise trade between the United States...
(via Highway 401) and the Blue Water Bridge
Blue Water Bridge
The Blue Water Bridge is a twin-span international bridge across the St. Clair River that links Port Huron, Michigan, USA and Sarnia, Ontario, Canada...
(via Highway 402). The primary highway along the southern route is Highway 401/Highway of Heroes, the busiest highway in North America and the backbone of Ontario's road network, tourism, and economy, while the primary highways across the north are Highway 417/Highway 17 and Highway 11, both part of the Trans-Canada Highway
Trans-Canada Highway
The Trans-Canada Highway is a federal-provincial highway system that joins the ten provinces of Canada. It is, along with the Trans-Siberian Highway and Australia's Highway 1, one of the world's longest national highways, with the main route spanning 8,030 km...
. Highway 400/Highway 69
Ontario Highway 69
King's Highway 69, commonly referred to as Highway 69, is a major north–south highway in the central area of the Canadian province of Ontario, linking Highway 400 north of Parry Sound with Sudbury...
connects Toronto to Northern Ontario. Other provincial highways and regional roads inter-connect the remainder of the province.
Waterways
The Saint Lawrence SeawaySaint Lawrence Seaway
The Saint Lawrence Seaway , , is the common name for a system of locks, canals and channels that permits ocean-going vessels to travel from the Atlantic Ocean to the North American Great Lakes, as far as Lake Superior. Legally it extends from Montreal to Lake Erie, including the Welland Canal...
, which extends across most of the southern portion of the province and connects to the Atlantic Ocean, is the primary water transportation
Water transportation
Water transportation is the intentional movement of water over large distances. Methods of transportation fall into three categories:* Aqueducts, which include pipelines, canals, and tunnels,...
route for cargo, particularly iron ore and grain. In the past, the Great Lakes and St. Lawrence River were also a major passenger transportation route, but over the past half century passenger travel has been reduced to ferry services and sightseeing cruises.
Railways
Via RailVIA Rail
Via Rail Canada is an independent crown corporation offering intercity passenger rail services in Canada. It is headquartered near Montreal Central Station at 3 Place Ville-Marie in Montreal, Quebec....
operates the inter-regional passenger train service on the Quebec City – Windsor Corridor, along with The Canadian
The Canadian
The Canadian is a Canadian transcontinental passenger train originally operated by the Canadian Pacific Railway between 1955 and 1978. It is currently operated as an Inter-city rail service by Via Rail Canada with service between Union Station in Toronto, Ontario and Pacific Central Station in...
, a transcontinental rail service from Toronto to Vancouver
Vancouver
Vancouver is a coastal seaport city on the mainland of British Columbia, Canada. It is the hub of Greater Vancouver, which, with over 2.3 million residents, is the third most populous metropolitan area in the country,...
, and the Sudbury – White River train. Additionally, Amtrak
Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, doing business as Amtrak , is a government-owned corporation that was organized on May 1, 1971, to provide intercity passenger train service in the United States. "Amtrak" is a portmanteau of the words "America" and "track". It is headquartered at Union...
rail connects Ontario with key New York cities including Buffalo
Buffalo, New York
Buffalo is the second most populous city in the state of New York, after New York City. Located in Western New York on the eastern shores of Lake Erie and at the head of the Niagara River across from Fort Erie, Ontario, Buffalo is the seat of Erie County and the principal city of the...
, Albany
Albany, New York
Albany is the capital city of the U.S. state of New York, the seat of Albany County, and the central city of New York's Capital District. Roughly north of New York City, Albany sits on the west bank of the Hudson River, about south of its confluence with the Mohawk River...
, and New York City
New York City
New York is the most populous city in the United States and the center of the New York Metropolitan Area, one of the most populous metropolitan areas in the world. New York exerts a significant impact upon global commerce, finance, media, art, fashion, research, technology, education, and...
. Ontario Northland
Ontario Northland Railway
The Ontario Northland Railway is a Canadian railway operated by the Ontario Northland Transportation Commission, a provincial Crown agency of the government of Ontario....
provides rail service to destinations as far north as Moosonee
Moosonee, Ontario
Moosonee is a town in northern Ontario, Canada, on the Moose River approximately south of James Bay. It is considered as "the Gateway to the Arctic" and has Ontario's only saltwater port...
near James Bay
James Bay
James Bay is a large body of water on the southern end of Hudson Bay in Canada. Both bodies of water extend from the Arctic Ocean. James Bay borders the provinces of Quebec and Ontario; islands within the bay are part of Nunavut...
, connecting them with the south.
Freight rail
Freight train
A freight train or goods train is a group of freight cars or goods wagons hauled by one or more locomotives on a railway, ultimately transporting cargo between two points as part of the logistics chain...
is dominated by the founding cross-country Canadian National Railway
Canadian National Railway
The Canadian National Railway Company is a Canadian Class I railway headquartered in Montreal, Quebec. CN's slogan is "North America's Railroad"....
and CP Rail
Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway , formerly also known as CP Rail between 1968 and 1996, is a historic Canadian Class I railway founded in 1881 and now operated by Canadian Pacific Railway Limited, which began operations as legal owner in a corporate restructuring in 2001...
companies, which during the 1990s sold many short rail lines from their vast network to private companies operating mostly in the south.
Regional commuter rail is limited to the provincially owned GO Transit
GO Transit
GO Transit is an inter-regional public transit system in Southern Ontario, Canada. It primarily serves the Greater Toronto and Hamilton Area conurbation, with operations extending to several communities beyond the GTHA proper in the Greater Golden Horseshoe...
, and serves a trainbus network spanning the Golden Horseshoe region, with its hub in Toronto.
The Toronto Transit Commission
Toronto Transit Commission
-Island Ferry:The ferry service to the Toronto Islands was operated by the TTC from 1927 until 1962, when it was transferred to the Metro Parks and Culture department. Since 1998, the ferry service is run by Toronto Parks and Recreation.-Gray Coach:...
operates the province's only subway
Toronto subway and RT
The Toronto subway and RT is a rapid transit system in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, consisting of both underground and elevated railway lines, operated by the Toronto Transit Commission . It was Canada's first completed subway system, with the first line being built under Yonge Street, which opened in...
and streetcar
Toronto streetcar system
The Toronto streetcar system comprises eleven streetcar routes in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, operated by the Toronto Transit Commission , and is the largest such system in the Americas in terms of ridership, number of cars, and track length. The network is concentrated primarily in downtown and in...
system, one of the busiest in North America. OC Transpo
OC Transpo
OC Transpo is the urban transit service of the City of Ottawa, Ontario, Canada. An integrated hub-and-spoke system of services is available consisting of: regular buses travelling on fixed routes in mixed traffic, typical of most urban transit systems; a bus rapid transit system — a high...
operates, in addition to bus service, the O-Train
Ottawa O-Train
The O-Train is a light-rail transit service in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada operated by OC Transpo. The present line runs north-south on a railway line, from Bayview to Greenboro, a distance of approximately...
Light rail
Light rail
Light rail or light rail transit is a form of urban rail public transportation that generally has a lower capacity and lower speed than heavy rail and metro systems, but higher capacity and higher speed than traditional street-running tram systems...
line in Ottawa.
Air travel

Toronto Pearson International Airport
Toronto Pearson International Airport is an international airport serving Toronto, Ontario, Canada; its metropolitan area; and the Golden Horseshoe, an urban agglomeration that is home to 8.1 million people – approximately 25% of Canada's population...
is the nation's busiest and the world's 29th busiest, handling over 30 million passengers per year. Other important airports include Ottawa Macdonald-Cartier International Airport
Ottawa Macdonald-Cartier International Airport
Ottawa/Macdonald-Cartier International Airport or Macdonald-Cartier International Airport , in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada is named after Sirs John A. Macdonald and George-Étienne Cartier...
and Hamilton's John C. Munro Hamilton International Airport, which is an important courier and freight aviation centre. Toronto/Pearson and Ottawa/Macdonald-Cartier form two of the three points in Canada's busiest set of air routes (the third point is Montréal-Pierre Elliott Trudeau International Airport
Montréal-Pierre Elliott Trudeau International Airport
Montréal-Pierre Elliott Trudeau International Airport or Montréal-Trudeau, formerly known as Montréal-Dorval International Airport, is located on the Island of Montreal, from Montreal's downtown core. The airport terminals are located entirely in Dorval, while the Air Canada headquarters complex...
).
Most Ontario cities have regional airports, many of which have scheduled commuter flights from Air Canada Jazz
Air Canada Jazz
Jazz Aviation LP is a Canadian regional airline based at Halifax Stanfield International Airport in Enfield and Halifax Regional Municipality, Nova Scotia, and is a wholly owned subsidiary of Chorus Aviation....
or smaller airlines and charter companies — flights from the larger cities such as Thunder Bay, Sault Ste. Marie, Sudbury, North Bay, Timmins, Windsor, London, and Kingston feed directly into Toronto Pearson. Bearskin Airlines
Bearskin Airlines
Bearskin Lake Air Services Ltd., trading as Bearskin Airlines, is a regional airline based in Sioux Lookout, Ontario, Canada. It operates services in northern Ontario and Manitoba...
also runs flights along the northerly east-west route, connecting Ottawa, North Bay, Sudbury, Sault Ste. Marie, and Thunder Bay directly without requiring connections at Toronto Pearson.
Isolated towns and settlements in the northern areas of the province rely partly or entirely on air service
Airline
An airline provides air transport services for traveling passengers and freight. Airlines lease or own their aircraft with which to supply these services and may form partnerships or alliances with other airlines for mutual benefit...
for travel, goods, and even ambulance
Air ambulance
An air ambulance is an aircraft used for emergency medical assistance in situations where either a traditional ambulance cannot reach the scene easily or quickly enough, or the patient needs to be transported over a distance or terrain that makes air transportation the most practical transport....
services (MEDIVAC), since much of the far northern area of the province cannot be reached by road or rail.
Government


Legislative Assembly of Ontario
The Legislative Assembly of Ontario , is the legislature of the Canadian province of Ontario, and is the second largest provincial legislature of Canada...
." The assembly has 107 seats representing riding
Electoral district (Canada)
An electoral district in Canada, also known as a constituency or a riding, is a geographical constituency upon which Canada's representative democracy is based...
s elected in a first-past-the-post
Plurality voting system
The plurality voting system is a single-winner voting system often used to elect executive officers or to elect members of a legislative assembly which is based on single-member constituencies...
system across the province.
The legislative buildings at Queen's Park in Toronto are the seat of government. Following the Westminster system
Westminster System
The Westminster system is a democratic parliamentary system of government modelled after the politics of the United Kingdom. This term comes from the Palace of Westminster, the seat of the Parliament of the United Kingdom....
, the leader of the party holding the most seats in the assembly is known as the "Premier and President of the Council" (Executive Council Act R.S.O. 1990). The Premier chooses the cabinet
Cabinet (government)
A Cabinet is a body of high ranking government officials, typically representing the executive branch. It can also sometimes be referred to as the Council of Ministers, an Executive Council, or an Executive Committee.- Overview :...
or Executive Council
Executive Council of Ontario
The Executive Council of Ontario plays an important role in theGovernment of Ontario, in accordance with the Westminster system....
whose members are deemed "ministers of the Crown."
Although the Legislative Assembly Act (R.S.O. 1990) refers to members of the assembly", the legislators are now commonly called MPPs (Members of the Provincial Parliament) in English and députés de l'Assemblée législative in French, but they have also been called MLAs (Members of the Legislative Assembly
Member of the Legislative Assembly
A Member of the Legislative Assembly or a Member of the Legislature , is a representative elected by the voters of a constituency to the legislature or legislative assembly of a sub-national jurisdiction....
), and both are acceptable. The title of Prime Minister of Ontario, correct in French (le Premier ministre), is permissible in English but now generally avoided in favour of the title "Premier" to avoid confusion with the Prime Minister of Canada.
Politics
Ontario has numerous political parties which run for election. Three political parties dominate election results: the Conservatives,Liberals,and NDP. In the last few decades the liberal Ontario Liberal PartyOntario Liberal Party
The Ontario Liberal Party is a provincial political party in the province of Ontario, Canada. It has formed the Government of Ontario since the provincial election of 2003. The party is ideologically aligned with the Liberal Party of Canada but the two parties are organizationally independent and...
, conservative Progressive Conservative Party of Ontario
Progressive Conservative Party of Ontario
The Progressive Conservative Party of Ontario , is a right-of-centre political party in Ontario, Canada. The party was known for many years as "Ontario's natural governing party." It has ruled the province for 80 of the years since Confederation, including an uninterrupted run from 1943 to 1985...
, and social-democratic Ontario New Democratic Party
Ontario New Democratic Party
The Ontario New Democratic Party or , formally known as New Democratic Party of Ontario, is a social democratic political party in Ontario, Canada. It is a provincial section of the federal New Democratic Party. It was formed in October 1961, a few months after the federal party. The ONDP had its...
have all ruled the province at different times.
Ontario is currently under a Liberal government headed by Premier Dalton McGuinty
Dalton McGuinty
Dalton James Patrick McGuinty, Jr., MPP is a Canadian lawyer, politician and, since October 23, 2003, the 24th and current Premier of the Canadian province of Ontario....
. The present government, first elected in 2003, was re-elected
Ontario general election, 2007
The Ontario general election of 2007 was held on October 10, 2007 to elect members of the 39th Legislative Assembly of the Province of Ontario, Canada. The Liberals under Dalton McGuinty won the election with a majority government, winning 71 out of a possible 107 seats with 42.2% of the popular...
on October 10, 2007. On October 6, 2011, the Ontario Liberal Party won a third mandate, although it lost seats and was reduced to a minority government capturing only 53 seats (as opposed to the 71 it won in 2007), with the Progressive Conservatives and NDP winning 37 seats and 17 seats, respectively.
In the 2011 Canadian federal election in Ontario the Conservatives
Conservative Party of Canada
The Conservative Party of Canada , is a political party in Canada which was formed by the merger of the Canadian Alliance and the Progressive Conservative Party of Canada in 2003. It is positioned on the right of the Canadian political spectrum...
were elected in 73 ridings, 22 went to the NDP, and 11 to the Liberals. The Green Party
Green Party of Ontario
The Green Party of Ontario is a political party in Ontario, Canada. The party is led by Mike Schreiner. It has never held any seats in the Ontario Legislative Assembly; however, the party did see significant gains in the 2007 provincial election, earning 8% of the popular vote with some candidates...
did not get a candidate elected in Ontario.
Urban areas
Statistics Canada's measure of a "metro area", the Census Metropolitan Area (CMA), roughly bundles together population figures from the core municipality with those from "commuter" municipalities.| CMA (largest other included municipalities in brackets) | 2001 | 2006 | % Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Toronto Greater Toronto Area The Greater Toronto Area is the largest metropolitan area in Canada, with a 2006 census population of 5.5 million. The Greater Toronto Area is usually defined as the central city of Toronto, along with four regional municipalities surrounding it: Durham, Halton, Peel, and York... CMA (Mississauga, Brampton Brampton Brampton is the third-largest city in the Greater Toronto Area of Ontario, Canada.Brampton may also refer to:- Canada :* Brampton, a city in Ontario** Brampton GO Station, a station in the GO Transit network located in the city- United Kingdom :... , Pickering Pickering, Ontario Pickering is a city located in Southern Ontario, Canada immediately east of Toronto in Durham Region. It is part of the Greater Toronto Area, the largest metropolitan area in Canada.- Early Period :... ) |
4,682,897 | 5,113,149 | 9.2% |
| Ottawa National Capital Region (Canada) The National Capital Region, also referred to as Canada's Capital Region, is an official federal designation for the Canadian capital of Ottawa, Ontario, the neighbouring city of Gatineau, Quebec, and surrounding urban and rural communities.... CMA (Gatineau Gatineau Gatineau is a city in western Quebec, Canada. It is the fourth largest city in the province. It is located on the northern banks of the Ottawa River, immediately across from Ottawa, Ontario, and together they form Canada's National Capital Region. Ottawa and Gatineau comprise a single Census... , Clarence-Rockland Clarence-Rockland, Ontario Clarence-Rockland is a city in Eastern Ontario, Canada, in the United Counties of Prescott and Russell on the Ottawa River. Clarence-Rockland is located immediately to the east of Ottawa and is considered part of Canada's National Capital Region in the census.... ) |
1,067,800 |
1,130,761 |
5.9% |
| Hamilton Hamilton, Ontario Hamilton is a port city in the Canadian province of Ontario. Conceived by George Hamilton when he purchased the Durand farm shortly after the War of 1812, Hamilton has become the centre of a densely populated and industrialized region at the west end of Lake Ontario known as the Golden Horseshoe... CMA (Burlington Burlington, Ontario Burlington , is a city located in Halton Region at the western end of Lake Ontario. Burlington is part of the Greater Toronto Area, and is also included in the Hamilton Census Metropolitan Area. Physically, Burlington lies between the north shore of Lake Ontario and the Niagara Escarpment... , Grimsby Grimsby, Ontario Grimsby is a town on Lake Ontario in the Niagara Region, Ontario, Canada. Grimsby is a part of the Hamilton Census Metropolitan Area. The majority of residents reside in the area bounded by Lake Ontario and the Niagara escarpment... ) |
662,401 | 692,911 | 4.6% |
| London London, Ontario London is a city in Southwestern Ontario, Canada, situated along the Quebec City – Windsor Corridor. The city has a population of 352,395, and the metropolitan area has a population of 457,720, according to the 2006 Canadian census; the metro population in 2009 was estimated at 489,274. The city... CMA (St. Thomas St. Thomas, Ontario St. Thomas is a city in southern , Ontario, Canada. It is the seat for Elgin County and gained its city charter on March 4, 1881.-History:... , Strathroy-Caradoc Strathroy-Caradoc, Ontario Strathroy-Caradoc is a municipality located just west of London, Ontario, Canada. It was created through the merger of the former township of Caradoc and the town of Strathroy in 2001. Its two largest settlements are Strathroy and Mount Brydges.... ) |
435,600 | 457,720 | 5.1% |
| Kitchener Kitchener, Ontario The City of Kitchener is a city in Southern Ontario, Canada. It was the Town of Berlin from 1854 until 1912 and the City of Berlin from 1912 until 1916. The city had a population of 204,668 in the Canada 2006 Census... CMA (Cambridge Cambridge, Ontario Cambridge is a city located in Southern Ontario at the confluence of the Grand and Speed rivers in the Regional Municipality of Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. It is an amalgamation of the City of Galt, the towns of Preston and Hespeler, and the hamlet of Blair.Galt covers the largest portion of... , Waterloo Waterloo, Ontario Waterloo is a city in Southern Ontario, Canada. It is the smallest of the three cities in the Regional Municipality of Waterloo, and is adjacent to the city of Kitchener.... ) |
414,284 | 451,235 | 8.9% |
| St. Catharines CMA (Niagara Falls Niagara Falls, Ontario Niagara Falls is a Canadian city on the Niagara River in the Golden Horseshoe region of Southern Ontario. The municipality was incorporated on June 12, 1903... , Welland Welland, Ontario Welland is a city in the Regional Municipality of Niagara in Southern Ontario, Canada.The city has been traditionally known as the place where rails and water meet, referring to the railways from Buffalo to Toronto and Southwestern Ontario, and the waterways of Welland Canal and Welland River,... ) |
377,009 | 390,317 | 3.5% |
| Oshawa Oshawa Oshawa is a city in Ontario, Canada, on the Lake Ontario shoreline. It lies in Southern Ontario approximately 60 kilometres east of downtown Toronto. It is commonly viewed as the eastern anchor of both the Greater Toronto Area and the Golden Horseshoe. It is now commonly referred to as the most... CMA (Whitby Whitby, Ontario Whitby is a town in Durham Region. Whitby is located in Southern Ontario east of Toronto on the north shore of Lake Ontario, and is home to the headquarters of Durham Region... , Clarington Clarington, Ontario Clarington is a municipality in Ontario, Canada in the Regional Municipality of Durham. It took its present name in 1994 after having been known as the Town of Newcastle from 1974-93. The name change was made to alleviate long-standing confusion between the municipality as a whole and the included... ) |
296,298 | 330,594 | 11.6% |
| Windsor Windsor, Ontario Windsor is the southernmost city in Canada and is located in Southwestern Ontario at the western end of the heavily populated Quebec City – Windsor Corridor. It is within Essex County, Ontario, although administratively separated from the county government. Separated by the Detroit River, Windsor... CMA (Lakeshore Lakeshore, Ontario Lakeshore is a town in southwestern Ontario, Canada, on Lake St. Clair. Its nearest city is Windsor, located in Essex County. The town was incorporated in 1999 by amalgamating the Town of Belle River with the townships of Maidstone, Rochester, Tilbury North, and Tilbury West.Lakeshore has a... , LaSalle LaSalle, Ontario LaSalle is a town in Essex County, Ontario, Canada, on the Detroit River. It is a bedroom community of the City of Windsor and part of the Windsor Census Metropolitan Area, and is located south of that city. LaSalle, along with Windsor, is the oldest French settlement area in Southwestern Ontario,... ) |
307,877 | 323,342 | 5.0% |
| Barrie Barrie Barrie may refer to:* Barrie, city in Ontario, Canada* Barrie , Canadian federal electoral district* Barrie , provincial electoral district* Barrie—Simcoe—Bradford, former Canadian electoral district... CMA (Innisfil Innisfil, Ontario Innisfil is a town in Ontario, Canada, located on the western shore of Lake Simcoe in Simcoe County, immediately south of Barrie and 80 kilometres north of Toronto... , Springwater Springwater, Ontario Springwater is a township in central Ontario, Canada, in Simcoe County near Barrie. It includes the former townships of Flos and Vespra. Springwater is the County seat of Simcoe.-Communities:... ) |
148,480 | 177,061 | 19.2% |
| Sudbury CMA (Whitefish Lake Whitefish Lake 6, Ontario Whitefish Lake 6 is a reserve in Ontario, Canada. It is inhabited by the Ojibwa Whitefish Lake First Nation.It is immediately south of the community of Naughton in Greater Sudbury, and is considered part of Greater Sudbury's Census Metropolitan Area... , Wanapitei Reserve Wahnapitae First Nation The Wahnapitae First Nation is an Ojibwa First Nation in the Canadian province of Ontario, who primarily reside on the Wahnapitae 11 reserve on the northwestern shore of Lake Wanapitei. The First Nation is a signatory to the Robinson-Huron Treaty of 1850 as the Tahgaiwenene's Band... ) |
155,601 | 158,258 | 1.7% |
| Kingston Kingston, Ontario Kingston, Ontario is a Canadian city located in Eastern Ontario where the St. Lawrence River flows out of Lake Ontario. Originally a First Nations settlement called "Katarowki," , growing European exploration in the 17th Century made it an important trading post... CMA |
146,838 | 152,358 | 3.8% |
Gatineau
Gatineau is a city in western Quebec, Canada. It is the fourth largest city in the province. It is located on the northern banks of the Ottawa River, immediately across from Ottawa, Ontario, and together they form Canada's National Capital Region. Ottawa and Gatineau comprise a single Census...
) are included in the Ottawa CMA. The entire population of the Ottawa CMA, in both provinces, is shown.
Ten largest municipalities by population
| Municipality | 1996 | 2001 | 2006 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Toronto Toronto Toronto is the provincial capital of Ontario and the largest city in Canada. It is located in Southern Ontario on the northwestern shore of Lake Ontario. A relatively modern city, Toronto's history dates back to the late-18th century, when its land was first purchased by the British monarchy from... (Provincial capital) |
2,385,421 | 2,481,494 | 2,503,281 |
| Ottawa Ottawa Ottawa is the capital of Canada, the second largest city in the Province of Ontario, and the fourth largest city in the country. The city is located on the south bank of the Ottawa River in the eastern portion of Southern Ontario... (National capital) |
721,136 | 774,072 | 812,129 |
| Mississauga | 544,382 | 612,925 | 668,549 |
| Hamilton Hamilton, Ontario Hamilton is a port city in the Canadian province of Ontario. Conceived by George Hamilton when he purchased the Durand farm shortly after the War of 1812, Hamilton has become the centre of a densely populated and industrialized region at the west end of Lake Ontario known as the Golden Horseshoe... |
467,799 | 490,268 | 504,559 |
| Brampton Brampton Brampton is the third-largest city in the Greater Toronto Area of Ontario, Canada.Brampton may also refer to:- Canada :* Brampton, a city in Ontario** Brampton GO Station, a station in the GO Transit network located in the city- United Kingdom :... |
268,251 | 325,428 | 433,806 |
| London London, Ontario London is a city in Southwestern Ontario, Canada, situated along the Quebec City – Windsor Corridor. The city has a population of 352,395, and the metropolitan area has a population of 457,720, according to the 2006 Canadian census; the metro population in 2009 was estimated at 489,274. The city... |
325,669 | 336,539 | 352,395 |
| Markham Markham, Ontario Markham is a town in the Regional Municipality of York, located within the Greater Toronto Area of Southern Ontario, Canada. The population was 261,573 at the 2006 Canadian census... |
173,383 | 208,615 | 261,573 |
| Vaughan Vaughan Vaughan is a city in York Region north of Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Vaughan is the fastest growing municipality in Canada achieving a population growth rate of 80.2% between 1996–2006, according to Statistics Canada having nearly doubled in population since 1991. Vaughan is located in Southern... |
132,549 | 182,022 | 238,866 |
| Windsor Windsor, Ontario Windsor is the southernmost city in Canada and is located in Southwestern Ontario at the western end of the heavily populated Quebec City – Windsor Corridor. It is within Essex County, Ontario, although administratively separated from the county government. Separated by the Detroit River, Windsor... |
197,694 | 209,218 | 216,473 |
| Kitchener Kitchener, Ontario The City of Kitchener is a city in Southern Ontario, Canada. It was the Town of Berlin from 1854 until 1912 and the City of Berlin from 1912 until 1916. The city had a population of 204,668 in the Canada 2006 Census... |
178,420 | 190,399 | 204,668 |
Higher education
Songs and slogans
During the John RobartsJohn Robarts
John Parmenter Robarts, PC, CC, QC was a Canadian lawyer and statesman, and the 17th Premier of Ontario.-Early life:...
government of the 1960s, the slogan "Is There Any Other Place You'd Rather Be?" was in use to promote tourism. During a blizzard
Blizzard
A blizzard is a severe snowstorm characterized by strong winds. By definition, the difference between blizzard and a snowstorm is the strength of the wind. To be a blizzard, a snow storm must have winds in excess of with blowing or drifting snow which reduces visibility to 400 meters or ¼ mile or...
early in 1971, highway travellers who were stranded at a Highway 401 service centre with Premier Robarts (already in his last months of office) asked him the slogan in an ironic twist.
In 1967, in conjunction with the celebration of Canada's centennial
Canadian Centennial
The Canadian Centennial was a year long celebration held in 1967 when Canada celebrated the 100th anniversary of the Canadian Confederation. Celebrations occurred throughout the year but culminated on Dominion Day, July 1. 1967 coins were different from previous years' issues, with animals on each...
, the song "A Place to Stand
A Place to Stand, A Place to Grow
A Place to Stand, A Place to Grow was an unofficial anthem of the Canadian province of Ontario. The song was written as the signature tune for a movie of the same name that was featured at the Expo 67 Ontario pavilion....
" was introduced at the inauguration of Ontario's pavilion at the Expo 67
Expo 67
The 1967 International and Universal Exposition or Expo 67, as it was commonly known, was the general exhibition, Category One World's Fair held in Montreal, Quebec, Canada, from April 27 to October 29, 1967. It is considered to be the most successful World's Fair of the 20th century, with the...
World's Fair, and became the background for the province's advertising for decades.
In 1973 the first slogan to appear on licence plates in Ontario
Vehicle registration plates of Ontario
The province of Ontario first required its residents to register their vehicles and display licence plates in 1903. Along with regular series plates, the province also offers graphic plates and vanity plates with a maximum of 8 digits...
was "Keep It Beautiful". This was replaced by "Yours to Discover" in 1982, apparently inspired by a tourism slogan, "Discover Ontario," dating back to 1927. Plates with the French equivalent, "Tant à découvrir", were made available to the public beginning in May 2008. (From 1988 to 1990, "Ontario Incredible" gave "Yours to Discover" a brief respite.)
In 2007, a new song replaced "A Place to Stand" after four decades. "There's No Place Like This" is featured in current television advertising
Television advertisement
A television advertisement or television commercial, often just commercial, advert, ad, or ad-film – is a span of television programming produced and paid for by an organization that conveys a message, typically one intended to market a product...
, performed by Ontario artists including Molly Johnson
Molly Johnson
Molly Johnson, OC is a Canadian Juno Award-winning singer-songwriter of pop and jazz.-Biography:Johnson began as a child performer, receiving formal training from the National Ballet School and the Banff School of Fine Arts...
, Brian Byrne
Brian Byrne
Brian Byrne is a Canadian singer-songwriter and musician, best recognized as the second vocalist for I Mother Earth.-Biography:...
, Keshia Chanté
Keshia Chanté
Keshia Chanté is a Canadian Juno Award-winning critically acclaimed singer-songwriter, model, and actress...
, as well as Tomi Swick
Tomi Swick
Tomi Swick is a Canadian singer-songwriter from Hamilton, Ontario signed to Warner Music Canada.By age 13, Swick had learned to play several instruments, including the bagpipes, military drums, piano and guitar. At 19 he began playing in a Hamilton band but soon pursued a solo career. He is a...
and Arkells
Arkells
Arkells are a Canadian rock band, formed in Hamilton, Ontario. In 2006, they signed with Dine Alone Records, the label for other Canadian acts such as City and Colour, Attack In Black, Alexisonfire, and Tokyo Police Club.-Band history:...
. The new song is featured on the Ontario Tourism website.
See also
|
|
|
Geography
|
||
|---|---|---|
| Lists
|
|
|
Further reading
- Celebrating One Thousand Years of Ontario's History: Proceedings of the Celebrating One Thousand Years of Ontario's History Symposium, April 14, 15, and 16, 2000. Ontario Historical Society, 2000. 343 pp.
- Baskerville, Peter A. Sites of Power: A Concise History of Ontario. Oxford U. Press., 2005. 296 pp. (first edition was Ontario: Image, Identity and Power, 2002). online review
- Chambers, Lori, and Edgar-Andre Montigny, eds. Ontario Since Confederation: A Reader (2000), articles by scholars
External links
- Canadian Government Atlas - Official Map of Ontario.
- CBC Digital Archives - Ontario Elections: Twenty Tumultuous Years
- Government of Ontario - Official website of the Provincial government.
- Ontario Visual Heritage Project - Non-profit documentary project about Ontario's history
- Tourism Ontario - Official tourism website of the Province of Ontario

