
List of Gaue of Nazi Germany
Encyclopedia
Following the suppression of the individual Länder
(states) of Weimar Germany in 1934, the Gaue
(Singular: Gau) were the de facto administrative sub-divisions of Nazi Germany
.
The Nazi Gaue were formed in 1926 as Nazi party districts of the respective German states and Prussian provinces
as shaped in the aftermath of World War I. Each Gau had an administrative leader, the Gauleiter
(Gau leader). Though Länder and Prussian provinces continued to exist after the Enabling Act of 1933, their administration was reduced to a rudimentary body attached to the respective Nazi Gau administration in the Gleichschaltung
process. In total, Germany consisted of 32 Gaue in 1934, and 42 Gaue at its collapse in 1945.
The regions occupied in 1938 (Anschluss
of Austria
, Sudetenland
from Czechoslovakia
by the Munich Agreement
) and early 1939 (Klaipėda Region
or Memelland from Lithuania
) as well as the areas conquered during the Second World War were either incorporated into existing Gaue or organised in Reichsgau
e, similar to the Gaue in all but name. In the Reichsgaue, the Gauleiter also carried the position of Reichsstatthalter
., thereby formally combining the spheres of both party and state offices.
Eventually, in the aftermath of its defeat in the war, and the Yalta Conference
, Germany would lose not only the newly annexed territories but some of the territories it held before the Nazi government assumed power; it would also spend most of the following second half of the 20th century divided into two separate states.
was left in place. The plan to abolish the Länder was ultimately given up because Hitler shrank away from structural reforms, a so-called Reichsreform, fearing it would upset local party leaders. For the same reason, the borders of the Gaue remained unchanged within Germany throughout this time. The Gaue were only enlarged through the adding of occupied territories after 1938. While the Länder continued to exist, the real power on local level did lay with the Gauleiters, not the Minister Presidents of the German states. The Gauleiters were directly appointed by Hitler and only answerable to him. In practice, interference from above was rare and their power almost absolute.
e were established after the Anschluss
of Austria
and the incorporation of Sudetenland
following the Munich Agreement
. Southern parts of Czechoslovakia
also gained by the Munich Agreement were not made part of Reichsgau Sudetenland, but incorporated into the northern Reichsgaue of former Austria
.
and the Free City of Danzig
in 1939, Reichsgau Wartheland
and Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia
were created. Annexed territories of pre-war Poland
not within these two Reichsgau
e was incorporated into the neighboring Gaue East Prussia
and Silesia
. The Grand Duchy of Luxembourg as well as Alsace-Lorraine
, annexed from pre-war France
in 1940, were attached to the bordering Southwestern Gaue of Nazi Germany
. Two further Reichsgaue in Belgium
were established in 1944, and also annexed de jure to Germany.
for party members overseas. Its headquarters were in Berlin. This Auslandsgau was considered to be the 43rd Gau of Nazi Germany.
, the Italian government secretly began negotiations with the Allies about Italy switching sides to the Allied camp. In retaliation the Germans occupied large parts
of Italy, freed Mussolini, and re-installed him as the puppet ruler
of a new fascist state
in those parts that were occupied by the German army
. While officially in control over all the areas held by erstwhile Fascist Italy, large parts in the northeast located between Switzerland
and the Adriatic were re-organized as Operational Zones (Operationszonen). These were informally annexed by Germany, and attached to adjacent Gaue of the Reich. There were two such Operational Zones:
In a supplementary OKW order dated 10 September 1943, Hitler decrees on the establishment of further Operational Zones in Northern Italy, which were the stretch all the way to the French border. Unlike Alpenvorland and Küstenland, these zones did not immediately receive high commissioners (oberster kommissar) as civilian advisors, but were military regions where the commander was to exercise power on behalf of Army Group B
. Operation zone Nordwest-Alpen or Schweizer Grenze was located between the Stelvio Pass
and Monte Rosa
and was to contain wholly the Italian provinces of Sondrio
and Como
and parts of the provinces of Brescia
, Varese
, Novara
and Vercelli
. The zone of Französische Grenze was to encompass areas west of Monte Rosa and was to incorporate the province of Aosta and a part of the province of Turin
, and presumably also the provinces of Cuneo
and Imperia
.
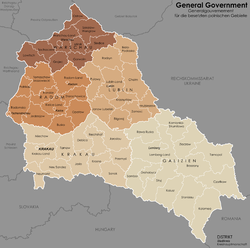 In those parts of Poland that were not directly annexed into the German Reich a separate civil administration was set up called the General Government
In those parts of Poland that were not directly annexed into the German Reich a separate civil administration was set up called the General Government
(of the Occupied Polish Territories). While theoretically outside the boundaries of the Reich proper, it was considered part of Greater Germany by Nazi officials as an "autonomous" region (i.e. not directly subordinated to the Berlin government).
It was in turn sub-divided into four distrikten (districts).
After the invasion
of the Soviet Union
in 1941, a fifth district was added, created out of former territories of Austrian
Galicia, the Distrikt Galizien.
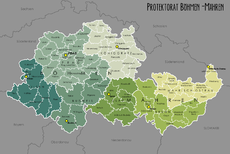 After the resulting agreement at the Munich Conference had granted Germany control over considerable parts of interwar Czechoslovakia
After the resulting agreement at the Munich Conference had granted Germany control over considerable parts of interwar Czechoslovakia
, the remainder was formally subordinated to German rule in March 1939. While Slovakia became a separate satellite state
of Germany, the remaining Czech lands
were turned into a Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia
under German dominion.
Two separate structures for its territorial administration existed within the protectorate. The Protectorate was officially divided into two Länder (lands): Bohemia
and Moravia
, which were in turn sub-divided into a number of smaller units. The Nazi party implemented a completely different form of organization by setting up four separate party districts in the area, and subordinating these organizationally to the surrounding Gaue and Reichsgaue: Sudetenland
, Bayreuth
(Bayerische Ostmark), Lower Danube, and Upper Danube. These two methods continued to co-exist in the protectorate for the entire duration of its existence.
, intending to further extend the already greatly increased territorial base of the German state. In anticipation of these expected future territorial enlargements, potential new districts were theorized upon at length by Nazi ideologists, government officials, and territorial planning departments. These expansions were intended to take place in two distinct ways:
of the German people the Slavic populations of Eastern Europe
were intended to be wiped out through a combined process of extermination
, expulsion, starvation
, and enslavement
that would effectively Germanize these territories in the long run. Nazi racial offices planned that the colonization with Germanic peoples
of these conquered eastern territories was to proceed most intensively in the three so-called Siedlungsmarken (Settlement marches) or Reichsmarken of Ingermannland (Ingria
), the Memel-Narew
area, and the Southern Ukraine
and the Crimean peninsula. The latter of these was intended to be newly re-organized as a Gotengau (Gau of the Goths
), in honor of the Crimean Goths
who had at one point dwelled there. Of the Baltic countries
, Peipusland
was proposed as a replacement-name for Estonia
, and Dünaland for Latvia
.
In a conference on July 16 1941 discussing the future organization of the conquered Soviet territories Hitler stated his intention to turn not only the above-mentioned areas, but also the entire Baltic region (Reichskommissariat Ostland
), the Volga German colony, and the Baku
district into future Reichsgebieten (Reich territories). On 3 November 1941 he also elaborated on the toponymic aspect of Germanizing the east:
The central and upper Vistula valley within the General Government
were variously discussed as having to become either a single Vandalengau (Gau of the Vandals
) or 3-5 other new Reichsgaue. An earlier proposal from 1939 also advocated for the creation of a Reichsgau Beskidenland
, which was to stretch from the area to the west of Cracow to the San river in the east. In Axis-occupied Yugoslavia, Sepp Janko
, Nazi representative of Danube Swabian interests, pushed for the establishment of a Reichsgau Banat or Prinz-Eugen
-Gau, which would have encompassed the Yugoslavian territories of Bačka
, Banat, parts of Transylvania
(Siebenbürgen) and Baranya
.
of the ethnic groups of Europe classified the Northern Europeans
, especially those closely related to the Germans
(itself considered to be a single nationality of which Swiss and Austrians
were nothing but sub-regional identities at best) such as the Dutch
, the Flemings, the Danish, Norwegians
, Swedish, and English
as part of a superior Aryan
-Nordic master race
(Herrenrasse). Following the highly successful integration
of Austria
into a Greater Germany (Großdeutschland), Hitler decided that he would follow the same policy in the future for all other countries that he regarded by virtue of their perceived racial qualifications as "belonging" to the Reich. This meant that the Low Countries
and the Scandinavia
n states were eventually to be annexed into a much larger Greater Germanic Reich
(Großgermanisches Reich) by being broken up into smaller state and party administrative units, such as Denmark into a Gau Nordmark, and the Netherlands into a Gau Westland.
Afterwards the very notion of these countries ever having been independent or separate from the rest of the Reich was to be suppressed indefinitely. The objective called for the inauguration of a new period of rapidly enforced Gleichschaltung
, the end result of which would be that aside from their local "language dialects" these countries were to become perfect duplicates of National Socialist Germany in all political and social respects.
In addition it was intended to revert the western borders of Germany with France
to those of the late-medieval Holy Roman Empire
. A strip of eastern France from the mouth of the Somme
to Lake Geneva
(the so-called "closed" or "forbidden" zone of German-occupied France was prepared to be annexed to the German Reich as Reichsgau Burgund, with Nancy (Nanzig) as the capital.
States of Germany
Germany is made up of sixteen which are partly sovereign constituent states of the Federal Republic of Germany. Land literally translates as "country", and constitutionally speaking, they are constituent countries...
(states) of Weimar Germany in 1934, the Gaue
Gau (German)
Gau is a German term for a region within a country, often a former or actual province. It was used in medieval times, when it can be seen as roughly corresponding to an English shire...
(Singular: Gau) were the de facto administrative sub-divisions of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
.
The Nazi Gaue were formed in 1926 as Nazi party districts of the respective German states and Prussian provinces
Provinces of Prussia
The Provinces of Prussia constituted the main administrative divisions of Prussia. Following the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806 and the Congress of Vienna in 1815 the various princely states in Germany gained their nominal sovereignty, but the reunification process that culminated in...
as shaped in the aftermath of World War I. Each Gau had an administrative leader, the Gauleiter
Gauleiter
A Gauleiter was the party leader of a regional branch of the NSDAP or the head of a Gau or of a Reichsgau.-Creation and Early Usage:...
(Gau leader). Though Länder and Prussian provinces continued to exist after the Enabling Act of 1933, their administration was reduced to a rudimentary body attached to the respective Nazi Gau administration in the Gleichschaltung
Gleichschaltung
Gleichschaltung , meaning "coordination", "making the same", "bringing into line", is a Nazi term for the process by which the Nazi regime successively established a system of totalitarian control and tight coordination over all aspects of society. The historian Richard J...
process. In total, Germany consisted of 32 Gaue in 1934, and 42 Gaue at its collapse in 1945.
The regions occupied in 1938 (Anschluss
Anschluss
The Anschluss , also known as the ', was the occupation and annexation of Austria into Nazi Germany in 1938....
of Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
, Sudetenland
Sudetenland
Sudetenland is the German name used in English in the first half of the 20th century for the northern, southwest and western regions of Czechoslovakia inhabited mostly by ethnic Germans, specifically the border areas of Bohemia, Moravia, and those parts of Silesia being within Czechoslovakia.The...
from Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia or Czecho-Slovakia was a sovereign state in Central Europe which existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until 1992...
by the Munich Agreement
Munich Agreement
The Munich Pact was an agreement permitting the Nazi German annexation of Czechoslovakia's Sudetenland. The Sudetenland were areas along Czech borders, mainly inhabited by ethnic Germans. The agreement was negotiated at a conference held in Munich, Germany, among the major powers of Europe without...
) and early 1939 (Klaipėda Region
Klaipėda Region
The Klaipėda Region or Memel Territory was defined by the Treaty of Versailles in 1920 when it was put under the administration of the Council of Ambassadors...
or Memelland from Lithuania
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
) as well as the areas conquered during the Second World War were either incorporated into existing Gaue or organised in Reichsgau
Reichsgau
A Reichsgau was an administrative subdivision created in a number of the areas annexed to Nazi Germany between 1938 and 1945...
e, similar to the Gaue in all but name. In the Reichsgaue, the Gauleiter also carried the position of Reichsstatthalter
Reichsstatthalter
The term Reichsstatthalter was used twice for different offices, in the imperial Hohenzollern dynasty's German Empire and the single-party Nazi Third Reich.- "Statthalter des Reiches" 1879-1918 in Alsace-Lorraine :...
., thereby formally combining the spheres of both party and state offices.
Eventually, in the aftermath of its defeat in the war, and the Yalta Conference
Yalta Conference
The Yalta Conference, sometimes called the Crimea Conference and codenamed the Argonaut Conference, held February 4–11, 1945, was the wartime meeting of the heads of government of the United States, the United Kingdom, and the Soviet Union, represented by President Franklin D...
, Germany would lose not only the newly annexed territories but some of the territories it held before the Nazi government assumed power; it would also spend most of the following second half of the 20th century divided into two separate states.
Gaue, Reichsgaue and Länder
The Gaue existed parallel to the German states, the Länder, and Prussian provinces throughout the Nazi period. Pro forma, the Administrative division of Weimar GermanyAdministrative division of Weimar Germany
Prior to World War I, the constituent states of the German Empire were 22 smaller monarchies, three city-states and the Imperial territory of Alsace-Lorraine. After the territorial losses of the Treaty of Versailles and the revolution of 1918, the remaining states continued as republics...
was left in place. The plan to abolish the Länder was ultimately given up because Hitler shrank away from structural reforms, a so-called Reichsreform, fearing it would upset local party leaders. For the same reason, the borders of the Gaue remained unchanged within Germany throughout this time. The Gaue were only enlarged through the adding of occupied territories after 1938. While the Länder continued to exist, the real power on local level did lay with the Gauleiters, not the Minister Presidents of the German states. The Gauleiters were directly appointed by Hitler and only answerable to him. In practice, interference from above was rare and their power almost absolute.
Gaue established in 1934
| English name | German name | Headquarters | Established | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baden | Baden | Karlsruhe Karlsruhe The City of Karlsruhe is a city in the southwest of Germany, in the state of Baden-Württemberg, located near the French-German border.Karlsruhe was founded in 1715 as Karlsruhe Palace, when Germany was a series of principalities and city states... |
1934 | Formed from the state of Baden Baden Baden is a historical state on the east bank of the Rhine in the southwest of Germany, now the western part of the Baden-Württemberg of Germany.... ; in 1940-45 the Gau included the former French France The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France... départements Départements of France The departments of France are French administrative divisions. The 101 departments form one of the three levels of local government, together with the 22 metropolitan and 5 overseas regions above them and more than 36 000 communes beneath them... of Bas-Rhin Bas-Rhin Bas-Rhin is a department of France. The name means "Lower Rhine". It is the more populous and densely populated of the two departments of the Alsace region, with 1,079,013 inhabitants in 2006.- History :... and Haut-Rhin Haut-Rhin Haut-Rhin is a département of the Alsace region of France, named after the Rhine river. Its name means Upper Rhine. Haut-Rhin is the smaller and less populated of the two departements of Alsace, although is still densely populated compared to the rest of France.-Subdivisions:The department... as Baden-Elsaß |
| Bayreuth Gau Bayreuth The Gau Bayreuth, until 1942 named Gau Bayerische Ostmark , was an administrative division of Nazi Germany in Lower Bavaria, Upper Palatinate and Upper Franconia, Bavaria from 1933 to 1945... |
Bayreuth | Bayreuth | 1934 | Formed from part of the state of Bavaria Bavaria Bavaria, formally the Free State of Bavaria is a state of Germany, located in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest state by area, forming almost 20% of the total land area of Germany... ; originally named Bayrische Ostmark, re-named Gau Bayreuth Gau Bayreuth The Gau Bayreuth, until 1942 named Gau Bayerische Ostmark , was an administrative division of Nazi Germany in Lower Bavaria, Upper Palatinate and Upper Franconia, Bavaria from 1933 to 1945... in 1942; also incooperated parts of Czechoslovakia from 1938 |
| Düsseldorf | Düsseldorf | Düsseldorf Düsseldorf Düsseldorf is the capital city of the German state of North Rhine-Westphalia and centre of the Rhine-Ruhr metropolitan region.Düsseldorf is an important international business and financial centre and renowned for its fashion and trade fairs. Located centrally within the European Megalopolis, the... |
1934 | Formed from the northern half of the Prussian province of the Rhine Rhine Province The Rhine Province , also known as Rhenish Prussia or synonymous to the Rhineland , was the westernmost province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia, within the German Reich, from 1822-1946. It was created from the provinces of the Lower Rhine and Jülich-Cleves-Berg... |
| East Prussia Gau East Prussia Gau East Prussia was formed in 1933 in Nazi Germany initially as a district within the Free State of Prussia. In 1935, Germany's constituent states were dissolved and the gaus replaced the states and their responsibilities.... |
Ostpreußen | Königsberg Königsberg Königsberg was the capital of East Prussia from the Late Middle Ages until 1945 as well as the northernmost and easternmost German city with 286,666 inhabitants . Due to the multicultural society in and around the city, there are several local names for it... |
1934 | Formed from the Prussian Province of East Prussia Province of East Prussia The Province of East Prussia was a province of Prussia from 1773–1829 and 1878-1945. Composed of the historical region East Prussia, the province's capital was Königsberg .... ; from 1939 also included territories annexed from Poland Poland Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north... |
| Eastern Hanover Gau Eastern Hanover Gau Eastern Hanover was a regional district of the NSDAP established in 1925 in the north eastern part of the Prussian Province of Hanover, comprising the governorates of Stade and Lunenburg in their then boundaries... |
Ost-Hannover | Lüneburg Lüneburg Lüneburg is a town in the German state of Lower Saxony. It is located about southeast of fellow Hanseatic city Hamburg. It is part of the Hamburg Metropolitan Region, and one of Hamburg's inner suburbs... |
1934 | Formed from the northern, central, and eastern parts of the Prussian Province of Hanover Province of Hanover The Province of Hanover was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia from 1868 to 1946.During the Austro-Prussian War, the Kingdom of Hanover had attempted to maintain a neutral position, along with some other member states of the German Confederation... |
| Electoral Hesse | Kurhessen | Kassel Kassel Kassel is a town located on the Fulda River in northern Hesse, Germany. It is the administrative seat of the Kassel Regierungsbezirk and the Kreis of the same name and has approximately 195,000 inhabitants.- History :... |
1934 | Formed from the northern half of the Prussian province of Hesse-Nassau |
| Cologne-Aix-la-Chapelle | Köln-Aachen | Cologne Cologne Cologne is Germany's fourth-largest city , and is the largest city both in the Germany Federal State of North Rhine-Westphalia and within the Rhine-Ruhr Metropolitan Area, one of the major European metropolitan areas with more than ten million inhabitants.Cologne is located on both sides of the... |
1934 | Formed from the north-central part of the Prussian province of the Rhine Rhine Province The Rhine Province , also known as Rhenish Prussia or synonymous to the Rhineland , was the westernmost province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia, within the German Reich, from 1822-1946. It was created from the provinces of the Lower Rhine and Jülich-Cleves-Berg... |
| Essen | Essen | Essen Essen - Origin of the name :In German-speaking countries, the name of the city Essen often causes confusion as to its origins, because it is commonly known as the German infinitive of the verb for the act of eating, and/or the German noun for food. Although scholars still dispute the interpretation of... |
1934 | Formed from the northern tip of the Prussian province of the Rhine Rhine Province The Rhine Province , also known as Rhenish Prussia or synonymous to the Rhineland , was the westernmost province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia, within the German Reich, from 1822-1946. It was created from the provinces of the Lower Rhine and Jülich-Cleves-Berg... |
| Franconia Gau Franconia Gau Franconia , was an administrative division of Nazi Germany in Middle Franconia, Bavaria from 1933 to 1945. Previous to that, since 1926, it was the regional subdivision of the Nazi Party in this region.-History:... |
Franken | Nuremberg Nuremberg Nuremberg[p] is a city in the German state of Bavaria, in the administrative region of Middle Franconia. Situated on the Pegnitz river and the Rhine–Main–Danube Canal, it is located about north of Munich and is Franconia's largest city. The population is 505,664... |
1934 | Formed from part of the state of Bavaria Bavaria Bavaria, formally the Free State of Bavaria is a state of Germany, located in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest state by area, forming almost 20% of the total land area of Germany... |
| Greater Berlin | Groß-Berlin | Berlin Berlin Berlin is the capital city of Germany and is one of the 16 states of Germany. With a population of 3.45 million people, Berlin is Germany's largest city. It is the second most populous city proper and the seventh most populous urban area in the European Union... |
1934 | Formed from the Prussian province of Greater Berlin |
| Halle-Merseburg | Halle-Merseburg | Halle | 1934 | Formed from the southern half of the Prussian Province of Saxony Province of Saxony The Province of Saxony was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and later the Free State of Prussia from 1816 until 1945. Its capital was Magdeburg.-History:The province was created in 1816 out of the following territories:... |
| Hamburg | Hamburg | Hamburg Hamburg -History:The first historic name for the city was, according to Claudius Ptolemy's reports, Treva.But the city takes its modern name, Hamburg, from the first permanent building on the site, a castle whose construction was ordered by the Emperor Charlemagne in AD 808... |
1934 | Formed from the state of Hamburg Hamburg -History:The first historic name for the city was, according to Claudius Ptolemy's reports, Treva.But the city takes its modern name, Hamburg, from the first permanent building on the site, a castle whose construction was ordered by the Emperor Charlemagne in AD 808... |
| Hesse-Nassau | Hessen-Nassau | Frankfurt am Main | 1934 | Formed from the state of Hesse Volksstaat Hessen The People's State of Hesse was the name of the German state of Hesse-Darmstadt from 1918 until 1945.After the end of World War I the Grand Duchy of Hesse became a republic and changed its name to People's State . Its capital was Darmstadt... and the southern half of the Prussian province of Hesse-Nassau |
| Koblenz-Trier | Koblenz-Trier | Koblenz Koblenz Koblenz is a German city situated on both banks of the Rhine at its confluence with the Moselle, where the Deutsches Eck and its monument are situated.As Koblenz was one of the military posts established by Drusus about 8 BC, the... |
1934 | Formed from the southern half of the Prussian province of the Rhine Rhine Province The Rhine Province , also known as Rhenish Prussia or synonymous to the Rhineland , was the westernmost province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia, within the German Reich, from 1822-1946. It was created from the provinces of the Lower Rhine and Jülich-Cleves-Berg... ; re-named Gau Moselland in 1942, following the incorporation of the formerly independent country of Luxembourg Luxembourg Luxembourg , officially the Grand Duchy of Luxembourg , is a landlocked country in western Europe, bordered by Belgium, France, and Germany. It has two principal regions: the Oesling in the North as part of the Ardennes massif, and the Gutland in the south... |
| Lower Silesia | Niederschlesien | Breslau | 1934 | Formed in the Prussian Province of Lower Silesia Province of Lower Silesia The Province of Lower Silesia was a province of the Free State of Prussia from 1919 to 1945. Between 1938 and 1941 it was reunited with Upper Silesia as the Silesia Province. The capital of Lower Silesia was Breslau... |
| Magdeburg-Anhalt | Magdeburg-Anhalt | Dessau Dessau Dessau is a town in Germany on the junction of the rivers Mulde and Elbe, in the Bundesland of Saxony-Anhalt. Since 1 July 2007, it is part of the merged town Dessau-Roßlau. Population of Dessau proper: 77,973 .-Geography:... |
1934 | Formed from the Free State of Anhalt Free State of Anhalt The Free State of Anhalt was formed after Joachim Ernst, Duke of Anhalt abdicated on 12 November 1918, ending the Duchy of Anhalt. It was a state of Germany during the time of the Weimar Republic... and the northern half of the Prussian Province of Saxony Province of Saxony The Province of Saxony was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and later the Free State of Prussia from 1816 until 1945. Its capital was Magdeburg.-History:The province was created in 1816 out of the following territories:... |
| Main-Franconia Gau Mainfranken The Gau Mainfranken , was an administrative division of Nazi Germany in Lower Franconia, Bavaria, from 1933 to 1945... |
Mainfranken | Würzburg Würzburg Würzburg is a city in the region of Franconia which lies in the northern tip of Bavaria, Germany. Located at the Main River, it is the capital of the Regierungsbezirk Lower Franconia. The regional dialect is Franconian.... |
1934 | Formed from part of the state of Bavaria Bavaria Bavaria, formally the Free State of Bavaria is a state of Germany, located in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest state by area, forming almost 20% of the total land area of Germany... |
| March of Brandenburg Gau March of Brandenburg The Gau March of Brandenburg was formed in 1933 initially under the name Gau Kurmark in Nazi Germany initially as a district within the Free State of Prussia. In 1935, Germany's constituent states were dissolved and the gaus replaced the states and their responsibilities. In 1940, Kurmark was... |
Mark Brandenburg | Berlin Berlin Berlin is the capital city of Germany and is one of the 16 states of Germany. With a population of 3.45 million people, Berlin is Germany's largest city. It is the second most populous city proper and the seventh most populous urban area in the European Union... |
1934 | Formed from the Prussian province of Province of Brandenburg Province of Brandenburg The Province of Brandenburg was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia from 1815 to 1946.-History:The first people who are known to have inhabited Brandenburg were the Suevi. They were succeeded by the Slavonians, whom Henry II conquered and converted to Christianity in... |
| Mecklenburg | Mecklenburg | Schwerin Schwerin Schwerin is the capital and second-largest city of the northern German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. The population, as of end of 2009, was 95,041.-History:... |
1934 | Formed from the state of Mecklenburg-Strelitz Mecklenburg-Strelitz Mecklenburg-Strelitz was a duchy and later grand duchy in northern Germany, consisting of the eastern fifth of the historic Mecklenburg region, roughly corresponding with the present-day Mecklenburg-Strelitz district , and the western exclave of the former Bishopric of Ratzeburg in modern... and the Free State of Mecklenburg-Schwerin Free State of Mecklenburg-Schwerin The Free State of Mecklenburg-Schwerin was a state in the Weimar Republic that was established in 1918 following the abdication of the Grand Duke of Mecklenburg-Schwerin following the German Revolution... |
| Munich-Upper Bavaria Gau München-Oberbayern The Gau München-Oberbayern was an administrative division of Nazi Germany in Upper Bavaria, Bavaria from 1933 to 1945... |
München-Oberbayern | Munich Munich Munich The city's motto is "" . Before 2006, it was "Weltstadt mit Herz" . Its native name, , is derived from the Old High German Munichen, meaning "by the monks' place". The city's name derives from the monks of the Benedictine order who founded the city; hence the monk depicted on the city's coat... |
1934 | Formed from part of the state of Bavaria Bavaria Bavaria, formally the Free State of Bavaria is a state of Germany, located in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest state by area, forming almost 20% of the total land area of Germany... |
| Pomerania | Pommern | Stettin | 1934 | Formed from the Prussian Province of Pomerania |
| Saar-Palatinate | Saarpfalz | Neustadt an der Weinstraße Neustadt an der Weinstraße Neustadt an der Weinstraße is a town located in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. With 53,892 inhabitants as of 2002, it is the largest town called Neustadt.-Etymology:... |
1934 | Formed from the Bavarian Palatinate and the Prussian Saarland Saarland Saarland is one of the sixteen states of Germany. The capital is Saarbrücken. It has an area of 2570 km² and 1,045,000 inhabitants. In both area and population, it is the smallest state in Germany other than the city-states... ; renamed Gau Westmark Gau Westmark The Gau Westmark was an administrative division of Nazi Germany from 1933 to 1945. Previous to that, since 1926, it was the regional subdivision of the Nazi Party.-History:... in 1940 after the incooperation of parts of Lorraine Lorraine (province) The Duchy of Upper Lorraine was an historical duchy roughly corresponding with the present-day northeastern Lorraine region of France, including parts of modern Luxembourg and Germany. The main cities were Metz, Verdun, and the historic capital Nancy.... |
| Saxony | Sachsen | Dresden Dresden Dresden is the capital city of the Free State of Saxony in Germany. It is situated in a valley on the River Elbe, near the Czech border. The Dresden conurbation is part of the Saxon Triangle metropolitan area.... |
1934 | Formed from the state of Saxony Saxony The Free State of Saxony is a landlocked state of Germany, contingent with Brandenburg, Saxony Anhalt, Thuringia, Bavaria, the Czech Republic and Poland. It is the tenth-largest German state in area, with of Germany's sixteen states.... |
| Schleswig-Holstein | Schleswig-Holstein | Kiel Kiel Kiel is the capital and most populous city in the northern German state of Schleswig-Holstein, with a population of 238,049 .Kiel is approximately north of Hamburg. Due to its geographic location in the north of Germany, the southeast of the Jutland peninsula, and the southwestern shore of the... |
1934 | Formed from the Prussian Province of Schleswig-Holstein Province of Schleswig-Holstein The Province of Schleswig-Holstein was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia from 1868 to 1946. It was created from the Duchies of Schleswig and Holstein, which had been conquered by Prussia and the Austrian Empire from Denmark in the Second War of Schleswig in 1864... , the Free City of Lübeck and territory belonging to the Free State of Oldenburg Free State of Oldenburg The Free State of Oldenburg was a state of the Weimar Republic. It was established in 1918 following the abdication of the Grand Duke Frederick Augustus II following the German Revolution.... |
| Southern Hanover-Brunswick | Südhannover-Braunschweig | Hanover Hanover Hanover or Hannover, on the river Leine, is the capital of the federal state of Lower Saxony , Germany and was once by personal union the family seat of the Hanoverian Kings of Great Britain, under their title as the dukes of Brunswick-Lüneburg... |
1934 | Formed from the Free State of Brunswick Free State of Brunswick The Free State of Brunswick was the republic formed after the abolition of the Duchy of Brunswick in the course of the German Revolution of 1918–19. It was a state of the German Reich in the time of the Weimar Republic and Nazi Germany.-History:... and the southern and western parts of the Province of Hanover Province of Hanover The Province of Hanover was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia from 1868 to 1946.During the Austro-Prussian War, the Kingdom of Hanover had attempted to maintain a neutral position, along with some other member states of the German Confederation... |
| Swabia Gau Swabia Gau Swabia was an administrative division of Nazi Germany in Swabia, Bavaria from 1933 to 1945. Previous to that, since 1926, it was the regional subdivision of the Nazi Party in Swabia.... |
Schwaben | Augsburg Augsburg Augsburg is a city in the south-west of Bavaria, Germany. It is a university town and home of the Regierungsbezirk Schwaben and the Bezirk Schwaben. Augsburg is an urban district and home to the institutions of the Landkreis Augsburg. It is, as of 2008, the third-largest city in Bavaria with a... |
1934 | Formed from part of the state of Bavaria Bavaria Bavaria, formally the Free State of Bavaria is a state of Germany, located in the southeast of Germany. With an area of , it is the largest state by area, forming almost 20% of the total land area of Germany... |
| Thuringia Gau Thüringen The Gau Thuringia , was an administrative division of Nazi Germany in Thuringia from 1933 to 1945. Previous to that, since 1926, it was the regional subdivision of the Nazi Party in this region.-Sources:*... |
Thüringen | Weimar Weimar Weimar is a city in Germany famous for its cultural heritage. It is located in the federal state of Thuringia , north of the Thüringer Wald, east of Erfurt, and southwest of Halle and Leipzig. Its current population is approximately 65,000. The oldest record of the city dates from the year 899... |
1934 | Formed from the state of Thuringia Thuringia The Free State of Thuringia is a state of Germany, located in the central part of the country.It has an area of and 2.29 million inhabitants, making it the sixth smallest by area and the fifth smallest by population of Germany's sixteen states.... and adjacent Prussian Province of Saxony Province of Saxony The Province of Saxony was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and later the Free State of Prussia from 1816 until 1945. Its capital was Magdeburg.-History:The province was created in 1816 out of the following territories:... |
| Upper Silesia | Oberschlesien | Kattowitz (from 1939) | 1934 | Formed in the Prussian Province of Upper Silesia Province of Upper Silesia The Province of Upper Silesia was a province of the Free State of Prussia created in the aftermath of World War I. It comprised much of the region of Upper Silesia and was eventually divided into two administrative regions , Kattowitz and Oppeln... , also incooperated parts of Poland from 1939 |
| Weser-Ems | Weser-Ems | Oldenburg Oldenburg Oldenburg is an independent city in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated in the western part of the state between the cities of Bremen and Groningen, Netherlands, at the Hunte river. It has a population of 160,279 which makes it the fourth biggest city in Lower Saxony after Hanover, Braunschweig... |
1934 | Formed from the Free State of Oldenburg Free State of Oldenburg The Free State of Oldenburg was a state of the Weimar Republic. It was established in 1918 following the abdication of the Grand Duke Frederick Augustus II following the German Revolution.... (excluding outlying territories), the state of Bremen Bremen (state) The Free Hanseatic City of Bremen is the smallest of Germany's 16 states. A more informal name, but used in some official contexts, is Land Bremen .-Geography:... and the far western part of the Prussian Province of Hanover Province of Hanover The Province of Hanover was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia from 1868 to 1946.During the Austro-Prussian War, the Kingdom of Hanover had attempted to maintain a neutral position, along with some other member states of the German Confederation... |
| Westphalia-North Gau Westfalen-Nord The Gau Westphalia-North , was an administrative division of Nazi Germany in Free State of Lippe, Free State of Schaumburg-Lippe and the northern half of the Prussian Province of Westphalia from 1933 to 1945... |
Westfalen-Nord | Münster Münster Münster is an independent city in North Rhine-Westphalia, Germany. It is located in the northern part of the state and is considered to be the cultural centre of the Westphalia region. It is also capital of the local government region Münsterland... |
1934 | Formed from the Free State of Lippe Free State of Lippe The Free State of Lippe was a German state formed after the Principality of Lippe was abolished following the German Revolution of 1918.After the end of World War II, Lippe was restored from Nazi rule. This autonomy ended in January 1947 when British forces incorporated Lippe into the new German... and the northern half of the Prussian Province of Westphalia Province of Westphalia The Province of Westphalia was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia from 1815 to 1946.-History:Napoleon Bonaparte founded the Kingdom of Westphalia, which was a client state of the First French Empire from 1807 to 1813... |
| Westphalia-South | Westfalen-Süd | Dortmund Dortmund Dortmund is a city in Germany. It is located in the Bundesland of North Rhine-Westphalia, in the Ruhr area. Its population of 585,045 makes it the 7th largest city in Germany and the 34th largest in the European Union.... |
1934 | Formed from the southern half of the Prussian Province of Westphalia Province of Westphalia The Province of Westphalia was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia and the Free State of Prussia from 1815 to 1946.-History:Napoleon Bonaparte founded the Kingdom of Westphalia, which was a client state of the First French Empire from 1807 to 1813... |
| Württemberg-Hohenzollern | Württemberg-Hohenzollern | Stuttgart Stuttgart Stuttgart is the capital of the state of Baden-Württemberg in southern Germany. The sixth-largest city in Germany, Stuttgart has a population of 600,038 while the metropolitan area has a population of 5.3 million .... |
1934 | Formed from the Free People's State of Württemberg Free People's State of Württemberg The Free People's State of Württemberg was a state of Germany during the Weimar Republic in Württemberg.-1918 revolution:As Germany underwent violent revolution near the end of World War I, the Kingdom of Württemberg was transformed from a monarchy to a democratic republic without bloodshed; its... and the Prussian Province of Hohenzollern Province of Hohenzollern Hohenzollern was a de facto province of the Kingdom of Prussia. It was created in 1850 by joining the principalities of Hohenzollern-Sigmaringen and Hohenzollern-Hechingen after both formerly independently ruling Catholic princely lines of the House of Hohenzollern had handed over their... |
Reichsgaue established in the 1930s
New ReichsgauReichsgau
A Reichsgau was an administrative subdivision created in a number of the areas annexed to Nazi Germany between 1938 and 1945...
e were established after the Anschluss
Anschluss
The Anschluss , also known as the ', was the occupation and annexation of Austria into Nazi Germany in 1938....
of Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
and the incorporation of Sudetenland
Sudetenland
Sudetenland is the German name used in English in the first half of the 20th century for the northern, southwest and western regions of Czechoslovakia inhabited mostly by ethnic Germans, specifically the border areas of Bohemia, Moravia, and those parts of Silesia being within Czechoslovakia.The...
following the Munich Agreement
Munich Agreement
The Munich Pact was an agreement permitting the Nazi German annexation of Czechoslovakia's Sudetenland. The Sudetenland were areas along Czech borders, mainly inhabited by ethnic Germans. The agreement was negotiated at a conference held in Munich, Germany, among the major powers of Europe without...
. Southern parts of Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia or Czecho-Slovakia was a sovereign state in Central Europe which existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until 1992...
also gained by the Munich Agreement were not made part of Reichsgau Sudetenland, but incorporated into the northern Reichsgaue of former Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
.
| English name | German name | Headquarters | Established | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carinthia Reichsgau Kärnten The Reichsgau Kärnten , was an administrative division of Nazi Germany in Carinthia and East Tyrol and Upper Carniola, Slovenia from 1938 to 1945.-Sources:* * Deutsches Historisches Museum website*... |
Kärnten | Klagenfurt Klagenfurt -Name:Carinthia's eminent linguists Primus Lessiak and Eberhard Kranzmayer assumed that the city's name, which literally translates as "ford of lament" or "ford of complaints", had something to do with the superstitious thought that fateful fairies or demons tend to live around treacherous waters... |
1938 | Formed from the former Austrian federal state of Carinthia Carinthia (state) Carinthia is the southernmost Austrian state or Land. Situated within the Eastern Alps it is chiefly noted for its mountains and lakes.The main language is German. Its regional dialects belong to the Southern Austro-Bavarian group... and Eastern Tyrol East Tyrol East Tyrol, or East Tirol , is an exclave of the Austrian state of Tyrol, sharing no border with the main North Tyrol part of the state. It corresponds with the administrative district of Lienz.... , included from 1941 were parts of Slovenia Slovenia Slovenia , officially the Republic of Slovenia , is a country in Central and Southeastern Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean. Slovenia borders Italy to the west, Croatia to the south and east, Hungary to the northeast, and Austria to the north, and also has a small portion of... |
| Lower Danube Reichsgau Niederdonau The Reichsgau Niederdonau , was an administrative division of Nazi Germany in Lower Austria and northern parts of Burgenland and parts of Southern Moravia, Czech Republic from 1938 to 1945.-Sources:*... |
Niederdonau | Krems an der Donau *However, in 1943 Hitler toured the Gau and assured Gauleiter Hugo Jury Hugo Jury Hugo Jury was an Austrian Nazi.... that the capital will be Brünn (Brno Brno Brno by population and area is the second largest city in the Czech Republic, the largest Moravian city, and the historical capital city of the Margraviate of Moravia. Brno is the administrative centre of the South Moravian Region where it forms a separate district Brno-City District... ) in the near future. |
1938 | Formed from the former Austrian federal state of Niederösterreich Lower Austria Lower Austria is the northeasternmost state of the nine states in Austria. The capital of Lower Austria since 1986 is Sankt Pölten, the most recently designated capital town in Austria. The capital of Lower Austria had formerly been Vienna, even though Vienna is not officially part of Lower Austria... and northern Burgenland Burgenland Burgenland is the easternmost and least populous state or Land of Austria. It consists of two Statutarstädte and seven districts with in total 171 municipalities. It is 166 km long from north to south but much narrower from west to east... ; included from 1939 were parts of southern Moravia Moravia Moravia is a historical region in Central Europe in the east of the Czech Republic, and one of the former Czech lands, together with Bohemia and Silesia. It takes its name from the Morava River which rises in the northwest of the region... |
| Upper Danube Reichsgau Oberdonau The Reichsgau Oberdonau , was an administrative division of Nazi Germany in Upper Austria, Austria and parts of Southern Bohemia, Czech Republic from 1938 to 1945. Parts of the Salzkammergut were annexed from Styria.... |
Oberdonau | Linz Linz Linz is the third-largest city of Austria and capital of the state of Upper Austria . It is located in the north centre of Austria, approximately south of the Czech border, on both sides of the river Danube. The population of the city is , and that of the Greater Linz conurbation is about... |
1938 | Formed from the former Austrian federal state of Oberösterreich Upper Austria Upper Austria is one of the nine states or Bundesländer of Austria. Its capital is Linz. Upper Austria borders on Germany and the Czech Republic, as well as on the other Austrian states of Lower Austria, Styria, and Salzburg... and Ausseerland, a part of Styria; included from 1939 were parts of southern Bohemia Bohemia Bohemia is a historical region in central Europe, occupying the western two-thirds of the traditional Czech Lands. It is located in the contemporary Czech Republic with its capital in Prague... |
| Salzburg Reichsgau Salzburg The Reichsgau Salzburg , was an administrative division of Nazi Germany in Salzburg, Austria from 1938 to 1945.-Sources:* * Deutsches Historisches Museum website*... |
Salzburg | Salzburg Salzburg -Population development:In 1935, the population significantly increased when Salzburg absorbed adjacent municipalities. After World War II, numerous refugees found a new home in the city. New residential space was created for American soldiers of the postwar Occupation, and could be used for... |
1938 | Formed from the former Austrian federal state of Salzburg Salzburg (state) Salzburg is a state or Land of Austria with an area of 7,156 km2, located adjacent to the German border. It is also known as Salzburgerland, to distinguish it from its capital city, also named Salzburg... |
| Sudetenland | Sudetenland | Reichenberg Liberec Liberec is a city in the Czech Republic. Located on the Lusatian Neisse and surrounded by the Jizera Mountains and Ještěd-Kozákov Ridge, it is the fifth-largest city in the Czech Republic.... |
1938 | Formed from the predominantly German speaking parts of Czechoslovakia Czechoslovakia Czechoslovakia or Czecho-Slovakia was a sovereign state in Central Europe which existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until 1992... which were ceded to Germany after the Munich Agreement Munich Agreement The Munich Pact was an agreement permitting the Nazi German annexation of Czechoslovakia's Sudetenland. The Sudetenland were areas along Czech borders, mainly inhabited by ethnic Germans. The agreement was negotiated at a conference held in Munich, Germany, among the major powers of Europe without... |
| Styria Reichsgau Steiermark The Reichsgau Steiermark , was an administrative division of Nazi Germany in Styria, southern parts of Burgenland and Lower Styria, Slovenia from 1938 to 1945.-Sources:* * Deutsches Historisches Museum website*... |
Steiermark | Graz Graz The more recent population figures do not give the whole picture as only people with principal residence status are counted and people with secondary residence status are not. Most of the people with secondary residence status in Graz are students... |
1938 | Formed from the former Austrian federal state of Styria and southern part of Burgenland Burgenland Burgenland is the easternmost and least populous state or Land of Austria. It consists of two Statutarstädte and seven districts with in total 171 municipalities. It is 166 km long from north to south but much narrower from west to east... ; included from 1941 were parts of Slovenia Slovenia Slovenia , officially the Republic of Slovenia , is a country in Central and Southeastern Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean. Slovenia borders Italy to the west, Croatia to the south and east, Hungary to the northeast, and Austria to the north, and also has a small portion of... |
| Tyrol-Vorarlberg Reichsgau Tirol-Vorarlberg The Reichsgau Tirol-Vorarlberg , was an administrative division of Nazi Germany in Vorarlberg and North Tyrol from 1938 to 1945.-Sources:* * Deutsches Historisches Museum website*... |
Tirol-Vorarlberg | Innsbruck Innsbruck - Main sights :- Buildings :*Golden Roof*Kaiserliche Hofburg *Hofkirche with the cenotaph of Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor*Altes Landhaus... |
1938 | Formed from the former Austrian federal state of Vorarlberg Vorarlberg Vorarlberg is the westernmost federal-state of Austria. Although it is the second smallest in terms of area and population , it borders three countries: Germany , Switzerland and Liechtenstein... and the northern part of Tyrol Tyrol (state) Tyrol is a state or Bundesland, located in the west of Austria. It comprises the Austrian part of the historical region of Tyrol.The state is split into two parts–called North Tyrol and East Tyrol–by a -wide strip of land where the state of Salzburg borders directly on the Italian province of... |
| Vienna Reichsgau Wien The Reichsgau Wien , was an administrative division of Nazi Germany in Vienna, Austria from 1938 to 1945. Parts of Lower Austria were annexed in 1938 to establish Greater Vienna, which then became the biggest city of Nazi Germany by area.-Sources:* * Deutsches Historisches Museum website*... |
Wien | Vienna Vienna Vienna is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Austria and one of the nine states of Austria. Vienna is Austria's primary city, with a population of about 1.723 million , and is by far the largest city in Austria, as well as its cultural, economic, and political centre... |
1938 | Formed from the former Austrian federal state of Vienna Vienna Vienna is the capital and largest city of the Republic of Austria and one of the nine states of Austria. Vienna is Austria's primary city, with a population of about 1.723 million , and is by far the largest city in Austria, as well as its cultural, economic, and political centre... and surrounding parts of former Niederösterreich |
Reichsgaue established during the Second World War
Of the territories annexed from PolandPolish areas annexed by Nazi Germany
At the beginning of World War II, nearly a quarter of the pre-war Polish areas were annexed by Nazi Germany and placed directly under German civil administration, while the rest of Nazi occupied Poland was named as General Government...
and the Free City of Danzig
Free City of Danzig
The Free City of Danzig was a semi-autonomous city-state that existed between 1920 and 1939, consisting of the Baltic Sea port of Danzig and surrounding areas....
in 1939, Reichsgau Wartheland
Reichsgau Wartheland
Reichsgau Wartheland was a Nazi German Reichsgau formed from Polish territory annexed in 1939. It comprised the Greater Poland and adjacent areas, and only in part matched the area of the similarly named pre-Versailles Prussian province of Posen...
and Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia
Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia
The Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia was a Nazi German province created on 8 October 1939 from the territory of the annexed Free City of Danzig, the annexed Polish province Greater Pomeranian Voivodship , and the Nazi German Regierungsbezirk West Prussia of Gau East Prussia. Before 2 November 1939,...
were created. Annexed territories of pre-war Poland
Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, Second Commonwealth of Poland or interwar Poland refers to Poland between the two world wars; a period in Polish history in which Poland was restored as an independent state. Officially known as the Republic of Poland or the Commonwealth of Poland , the Polish state was...
not within these two Reichsgau
Reichsgau
A Reichsgau was an administrative subdivision created in a number of the areas annexed to Nazi Germany between 1938 and 1945...
e was incorporated into the neighboring Gaue East Prussia
East Prussia
East Prussia is the main part of the region of Prussia along the southeastern Baltic Coast from the 13th century to the end of World War II in May 1945. From 1772–1829 and 1878–1945, the Province of East Prussia was part of the German state of Prussia. The capital city was Königsberg.East Prussia...
and Silesia
Province of Silesia
The Province of Silesia was a province of the Kingdom of Prussia from 1815 to 1919.-Geography:The territory comprised the bulk of the former Bohemian crown land of Silesia and the County of Kladsko, which King Frederick the Great had conquered from the Austrian Habsburg Monarchy in the 18th...
. The Grand Duchy of Luxembourg as well as Alsace-Lorraine
Alsace-Lorraine
The Imperial Territory of Alsace-Lorraine was a territory created by the German Empire in 1871 after it annexed most of Alsace and the Moselle region of Lorraine following its victory in the Franco-Prussian War. The Alsatian part lay in the Rhine Valley on the west bank of the Rhine River and east...
, annexed from pre-war France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
in 1940, were attached to the bordering Southwestern Gaue of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany , also known as the Third Reich , but officially called German Reich from 1933 to 1943 and Greater German Reich from 26 June 1943 onward, is the name commonly used to refer to the state of Germany from 1933 to 1945, when it was a totalitarian dictatorship ruled by...
. Two further Reichsgaue in Belgium
Belgium
Belgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
were established in 1944, and also annexed de jure to Germany.
| English name | German name | Headquarters | Established | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Danzig–West Prussia Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia The Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia was a Nazi German province created on 8 October 1939 from the territory of the annexed Free City of Danzig, the annexed Polish province Greater Pomeranian Voivodship , and the Nazi German Regierungsbezirk West Prussia of Gau East Prussia. Before 2 November 1939,... |
Danzig–Westpreußen | Danzig | 1939 | Formed in the Free City of Danzig Free City of Danzig The Free City of Danzig was a semi-autonomous city-state that existed between 1920 and 1939, consisting of the Baltic Sea port of Danzig and surrounding areas.... and the Polish region of the Pomeranian Voivodeship Pomeranian Voivodeship (1919-1939) Pomeranian Voivodeship or Pomorskie Voivodeship was an administrative unit of inter-war Poland . It ceased to exist in September 1939, following German and Soviet aggression on Poland... , which were both occupied by Germany in 1939, as well as the pre-1939 German Governorate of West Prussia within then East Prussia |
| Flanders Reichsgau Flandern The Reichsgau Flanders was a short-lived Reichsgau of Nazi Germany established in 1944. It encompassed the present-day Flemish Region in its old provincial borders, so including Comines-Warneton but excluding Voeren... |
Flandern | Antwerp | 1944 | Formed in the Flemish Region Flemish Region The Flemish Region is one of the three official regions of the Kingdom of Belgium—alongside the Walloon Region and the Brussels-Capital Region. Colloquially, it is usually simply referred to as Flanders, of which it is the institutional iteration within the context of the Belgian political system... of Belgium Belgium Belgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many... , comprising the Dutch Dutch language Dutch is a West Germanic language and the native language of the majority of the population of the Netherlands, Belgium, and Suriname, the three member states of the Dutch Language Union. Most speakers live in the European Union, where it is a first language for about 23 million and a second... -speaking province Province A province is a territorial unit, almost always an administrative division, within a country or state.-Etymology:The English word "province" is attested since about 1330 and derives from the 13th-century Old French "province," which itself comes from the Latin word "provincia," which referred to... s of Antwerp Antwerp (province) Antwerp is the northernmost province both of the Flemish Region, also called Flanders, and of Belgium. It borders on the Netherlands and the Belgian provinces of Limburg, Flemish Brabant and East Flanders. Its capital is Antwerp which comprises the Port of Antwerp... , Limburg Limburg (Belgium) Limburg is the easternmost province of modern Flanders, which is one of the three main political and cultural sub-divisions of modern Belgium. It is located west of the river Meuse . It borders on the Dutch provinces of North Brabant and Limburg and the Belgian provinces of Liège, Flemish Brabant... , East Flanders East Flanders East Flanders is a province of Flanders, one of the three regions of Belgium. It borders on the Netherlands and in Belgium on the provinces of Antwerp, Flemish Brabant , of Hainaut and of West Flanders... , West Flanders, the arrondissement Arrondissement Arrondissement is any of various administrative divisions of France, certain other Francophone countries, and the Netherlands.-France:The 101 French departments are divided into 342 arrondissements, which may be translated into English as districts. The capital of an arrondissement is called a... of Brussels Brussels Brussels , officially the Brussels Region or Brussels-Capital Region , is the capital of Belgium and the de facto capital of the European Union... (except the city of Brussels Brussels Brussels , officially the Brussels Region or Brussels-Capital Region , is the capital of Belgium and the de facto capital of the European Union... itself), and the arrondissement Arrondissement Arrondissement is any of various administrative divisions of France, certain other Francophone countries, and the Netherlands.-France:The 101 French departments are divided into 342 arrondissements, which may be translated into English as districts. The capital of an arrondissement is called a... of Leuven Leuven Leuven is the capital of the province of Flemish Brabant in the Flemish Region, Belgium... in the then-province Province A province is a territorial unit, almost always an administrative division, within a country or state.-Etymology:The English word "province" is attested since about 1330 and derives from the 13th-century Old French "province," which itself comes from the Latin word "provincia," which referred to... of Brabant (the present-day province of Flemish Brabant Flemish Brabant Flemish Brabant is a province of Flanders, one of the three regions of Belgium. It borders on the Belgian provinces of Antwerp, Limburg, Liège, Walloon Brabant, Hainaut and East Flanders. Flemish Brabant also completely surrounds the Brussels-Capital Region. Its capital is Leuven... ). |
| Wallonia Reichsgau Wallonien The Reichsgau Wallonia was a short-lived Reichsgau of Nazi Germany established in 1944. It encompassed present-day Wallonia in its old provincial borders, so excluding Comines-Warneton but including Voeren... |
Wallonien | Namur Namur (city) Namur is a city and municipality in Wallonia, in southern Belgium. It is both the capital of the province of Namur and of Wallonia.... |
1944 | Formed in the Walloon Region Walloon Region The Walloon Region, commonly called Wallonia, is one of the three federal Regions of Belgium, and its capital is Namur. It comprises, as defined by Article 5 of the Constitution of Belgium, the provinces of Walloon Brabant, Hainaut, Liège, Luxembourg and Namur... of Belgium Belgium Belgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many... , comprising the Francophone French language French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts... provinces of Hainaut, Liège Liège (province) Liège is the easternmost province of Belgium and belongs to the Walloon Region. It is an area of French and German ethnicity. It borders on the Netherlands, Germany, Luxembourg, and in Belgium the provinces of Luxembourg, Namur, Walloon Brabant , and those of Flemish Brabant and Limburg . Its... but the cantons of Eupen Eupen Eupen is a municipality in the Belgian province of Liège, from the German border , from the Dutch border and from the "High Fens" nature reserve... , Malmedy Malmedy Malmedy is a municipality of Belgium. It lies in the country's Walloon Region, Province of Liège. It belongs to the French Community of Belgium, within which it is French-speaking with facilities for German-speakers. On January 1, 2006 Malmedy had a total population of 11,829... and Sankt Vith Sankt Vith St. Vith is a municipality located in the Belgian province of Liège, and in the German speaking community in Belgium. It was named after Saint Vitus.... , Luxembourg, Namur Namur (province) Namur is a province of Wallonia, one of the three regions of Belgium. It borders on the Walloon provinces of Hainaut, Walloon Brabant, Liège and Luxembourg in Belgium, and on France. Its capital is the city of Namur... , and the arrondissement Arrondissement Arrondissement is any of various administrative divisions of France, certain other Francophone countries, and the Netherlands.-France:The 101 French departments are divided into 342 arrondissements, which may be translated into English as districts. The capital of an arrondissement is called a... of Nivelles Nivelles Nivelles is a Walloon city and municipality located in the Belgian province of Walloon Brabant. The Nivelles municipality includes the old communes of Baulers, Bornival, Thines, and Monstreux.... in the contemporary province of Brabant (now part of the separate province of Walloon Brabant Walloon Brabant Walloon Brabant is a province of Wallonia in Belgium. It borders on the province of Flemish Brabant and the provinces of Liège, Namur and Hainaut . Its capital is Wavre... ). |
| Wartheland Reichsgau Wartheland Reichsgau Wartheland was a Nazi German Reichsgau formed from Polish territory annexed in 1939. It comprised the Greater Poland and adjacent areas, and only in part matched the area of the similarly named pre-Versailles Prussian province of Posen... |
Wartheland | Posen | 1939 | Formed primarily in the Polish region of the Poznań Voivodeship Poznan Voivodeship (1921-1939) Poznań Voivodeship was a unit of administrative division and local government in Poland in the years 1921–1939, created after World War I from the Prussian-German province of Poznań... and incooperated areas of surrounding Voivodeships after the German occupation of Poland |
Auslandsgau
There was also an extraterritorial Gau named AuslandsorganisationNSDAP/AO
The NSDAP/AO was the Foreign Organization branch of the National Socialist German Workers Party . AO is the abbreviation of the German compound word Auslands-Organisation...
for party members overseas. Its headquarters were in Berlin. This Auslandsgau was considered to be the 43rd Gau of Nazi Germany.
Operational Zones
After the overthrow of Benito MussoliniBenito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini was an Italian politician who led the National Fascist Party and is credited with being one of the key figures in the creation of Fascism....
, the Italian government secretly began negotiations with the Allies about Italy switching sides to the Allied camp. In retaliation the Germans occupied large parts
Operation Achse
Operation Achse , also called Operation Alaric, were the codenames of the German plans to forcibly disarm the Italian armed forces after their expected armistice with the Allied forces...
of Italy, freed Mussolini, and re-installed him as the puppet ruler
Puppet state
A puppet state is a nominal sovereign of a state who is de facto controlled by a foreign power. The term refers to a government controlled by the government of another country like a puppeteer controls the strings of a marionette...
of a new fascist state
Italian Social Republic
The Italian Social Republic was a puppet state of Nazi Germany led by the "Duce of the Nation" and "Minister of Foreign Affairs" Benito Mussolini and his Republican Fascist Party. The RSI exercised nominal sovereignty in northern Italy but was largely dependent on the Wehrmacht to maintain control...
in those parts that were occupied by the German army
German Army
The German Army is the land component of the armed forces of the Federal Republic of Germany. Following the disbanding of the Wehrmacht after World War II, it was re-established in 1955 as the Bundesheer, part of the newly formed West German Bundeswehr along with the Navy and the Air Force...
. While officially in control over all the areas held by erstwhile Fascist Italy, large parts in the northeast located between Switzerland
Switzerland
Switzerland name of one of the Swiss cantons. ; ; ; or ), in its full name the Swiss Confederation , is a federal republic consisting of 26 cantons, with Bern as the seat of the federal authorities. The country is situated in Western Europe,Or Central Europe depending on the definition....
and the Adriatic were re-organized as Operational Zones (Operationszonen). These were informally annexed by Germany, and attached to adjacent Gaue of the Reich. There were two such Operational Zones:
| English name | German name | Headquarters | Established | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operational Zone of the Adriatic Littoral | Operationszone Adriatisches Küstenland (OZAK) | Triest | 1943 | Formed out of the Italian-occupied areas Province of Ljubljana The Province of Ljubljana was a province of the Kingdom of Italy and of the Nazi German Adriatic Littoral during World War II. It was created on May 3, 1941 from territory occupied and annexed to Italy after the Axis invasion and dissolution of Yugoslavia, and it was abolished on May 9, 1945, when... of Yugoslav Kingdom of Yugoslavia The Kingdom of Yugoslavia was a state stretching from the Western Balkans to Central Europe which existed during the often-tumultuous interwar era of 1918–1941... Slovenia Slovenia Slovenia , officially the Republic of Slovenia , is a country in Central and Southeastern Europe touching the Alps and bordering the Mediterranean. Slovenia borders Italy to the west, Croatia to the south and east, Hungary to the northeast, and Austria to the north, and also has a small portion of... , the Istrian peninsula Istria Istria , formerly Histria , is the largest peninsula in the Adriatic Sea. The peninsula is located at the head of the Adriatic between the Gulf of Trieste and the Bay of Kvarner... , and Friuli Friuli Friuli is an area of northeastern Italy with its own particular cultural and historical identity. It comprises the major part of the autonomous region Friuli-Venezia Giulia, i.e. the province of Udine, Pordenone, Gorizia, excluding Trieste... and Gorizia Gorizia Gorizia is a town and comune in northeastern Italy, in the autonomous region of Friuli Venezia Giulia. It is located at the foot of the Julian Alps, bordering Slovenia. It is the capital of the Province of Gorizia, and it is a local center of tourism, industry, and commerce. Since 1947, a twin... provinces. Attached (not incorporated) to Reichsgau of Carinthia. |
| Operational Zone of the Alpine Foothills | Operationszone Alpenvorland (OZAV) | Bozen Bozen Bozen may refer to:*Bolzano, a bi-lingual northern Italian provincial capital city of which Bozen is the official German name*Bözen, a Swiss municipality*Bożeń, a village in Poland*Bozen Green, a village in Hertfordshire, England... |
1943 | Formed out of former South Tyrol South Tyrol South Tyrol , also known by its Italian name Alto Adige, is an autonomous province in northern Italy. It is one of the two autonomous provinces that make up the autonomous region of Trentino-Alto Adige/Südtirol. The province has an area of and a total population of more than 500,000 inhabitants... , Italian Trentino, and adjacent smaller parts of northeastern Italy. Attached (not incorporated) to Reichsgau of Tirol-Voralberg. |
In a supplementary OKW order dated 10 September 1943, Hitler decrees on the establishment of further Operational Zones in Northern Italy, which were the stretch all the way to the French border. Unlike Alpenvorland and Küstenland, these zones did not immediately receive high commissioners (oberster kommissar) as civilian advisors, but were military regions where the commander was to exercise power on behalf of Army Group B
Army Group B
Army Group B was the name of three different German Army Groups that saw action during World War II.-Battle for France:The first was involved in the Western Campaign in 1940 in Belgium and the Netherlands which was to be aimed to conquer the Maas bridges after the German airborne actions in Rotterdam...
. Operation zone Nordwest-Alpen or Schweizer Grenze was located between the Stelvio Pass
Stelvio Pass
The Stelvio Pass , located in Italy, at 2757 m is the highest paved mountain pass in the Eastern Alps, and the second highest in the Alps, slightly below the Col de l'Iseran .-Location:...
and Monte Rosa
Monte Rosa
The Monte Rosa Massif is a mountain massif located in the eastern part of the Pennine Alps. It is located between Switzerland and Italy...
and was to contain wholly the Italian provinces of Sondrio
Province of Sondrio
The Province of Sondrio is in the Lombardy region of Italy. Its capital is the town of Sondrio.It has an area of 3,212 km², and a total population of 176,856...
and Como
Province of Como
The Province of Como is a province in the north of the Lombardy region of Italy and borders the Swiss cantons of Ticino and Grigioni to the North, the Italian provinces of Sondrio and Lecco to the East, the Province of Milan to the south and the Province of Varese to the West...
and parts of the provinces of Brescia
Province of Brescia
The Province of Brescia is a Province in Lombardy, Italy. It borders with the province of Sondrio in the N and NW, the province of Bergamo in the W, province of Cremona in the SW and S, the province of Mantova to the S, and to the east, the province of Verona and Trentino .Source for statistical...
, Varese
Province of Varese
The Province of Varese is a province in the Lombardy region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Varese but its largest city is Busto Arsizio....
, Novara
Province of Novara
Novara is a province in the Piedmont region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Novara.It has an area of 1,339 km², and a total population of 365.156 . There are 88 communes in the province.-External links:*...
and Vercelli
Province of Vercelli
Vercelli is a province in the Piedmont region of northern Italy. Its capital is Vercelli., it has an area of 2,088 km², and a total population of 176,829...
. The zone of Französische Grenze was to encompass areas west of Monte Rosa and was to incorporate the province of Aosta and a part of the province of Turin
Province of Turin
The Province of Turin is a province in the Piedmont region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Turin.It has an area of 6,830 km², and a total population of 2,277,686 . There are 315 comuni in the province – the most of any province in Italy...
, and presumably also the provinces of Cuneo
Province of Cuneo
ayr is a province in the southwest of the Piedmont region of Italy. To the west it borders on the French region of Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur ....
and Imperia
Province of Imperia
The Province of Imperia is a mountainous and hilly province, in the Liguria region of Italy, situated between the Maritime Alps to the north and the Ligurian Sea, an arm of the Mediterranean Sea to the south...
.
General Government

General Government
The General Government was an area of Second Republic of Poland under Nazi German rule during World War II; designated as a separate region of the Third Reich between 1939–1945...
(of the Occupied Polish Territories). While theoretically outside the boundaries of the Reich proper, it was considered part of Greater Germany by Nazi officials as an "autonomous" region (i.e. not directly subordinated to the Berlin government).
It was in turn sub-divided into four distrikten (districts).
- Distrikt Krakau;
- Distrikt WarsawWarsawWarsaw is the capital and largest city of Poland. It is located on the Vistula River, roughly from the Baltic Sea and from the Carpathian Mountains. Its population in 2010 was estimated at 1,716,855 residents with a greater metropolitan area of 2,631,902 residents, making Warsaw the 10th most...
; - Distrikt LublinLublinLublin is the ninth largest city in Poland. It is the capital of Lublin Voivodeship with a population of 350,392 . Lublin is also the largest Polish city east of the Vistula river...
; - Distrikt RadomRadomRadom is a city in central Poland with 223,397 inhabitants . It is located on the Mleczna River in the Masovian Voivodeship , having previously been the capital of Radom Voivodeship ; 100 km south of Poland's capital, Warsaw.It is home to the biennial Radom Air Show, the largest and...
.
After the invasion
Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa was the code name for Germany's invasion of the Soviet Union during World War II that began on 22 June 1941. Over 4.5 million troops of the Axis powers invaded the USSR along a front., the largest invasion in the history of warfare...
of the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
in 1941, a fifth district was added, created out of former territories of Austrian
Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire was a modern era successor empire, which was centered on what is today's Austria and which officially lasted from 1804 to 1867. It was followed by the Empire of Austria-Hungary, whose proclamation was a diplomatic move that elevated Hungary's status within the Austrian Empire...
Galicia, the Distrikt Galizien.
Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia

Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia or Czecho-Slovakia was a sovereign state in Central Europe which existed from October 1918, when it declared its independence from the Austro-Hungarian Empire, until 1992...
, the remainder was formally subordinated to German rule in March 1939. While Slovakia became a separate satellite state
Satellite state
A satellite state is a political term that refers to a country that is formally independent, but under heavy political and economic influence or control by another country...
of Germany, the remaining Czech lands
Czech lands
Czech lands is an auxiliary term used mainly to describe the combination of Bohemia, Moravia and Czech Silesia. Today, those three historic provinces compose the Czech Republic. The Czech lands had been settled by the Celts , then later by various Germanic tribes until the beginning of 7th...
were turned into a Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia
Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia
The Protectorate of Bohemia and Moravia was the majority ethnic-Czech protectorate which Nazi Germany established in the central parts of Bohemia, Moravia and Czech Silesia in what is today the Czech Republic...
under German dominion.
Two separate structures for its territorial administration existed within the protectorate. The Protectorate was officially divided into two Länder (lands): Bohemia
Bohemia
Bohemia is a historical region in central Europe, occupying the western two-thirds of the traditional Czech Lands. It is located in the contemporary Czech Republic with its capital in Prague...
and Moravia
Moravia
Moravia is a historical region in Central Europe in the east of the Czech Republic, and one of the former Czech lands, together with Bohemia and Silesia. It takes its name from the Morava River which rises in the northwest of the region...
, which were in turn sub-divided into a number of smaller units. The Nazi party implemented a completely different form of organization by setting up four separate party districts in the area, and subordinating these organizationally to the surrounding Gaue and Reichsgaue: Sudetenland
Sudetenland
Sudetenland is the German name used in English in the first half of the 20th century for the northern, southwest and western regions of Czechoslovakia inhabited mostly by ethnic Germans, specifically the border areas of Bohemia, Moravia, and those parts of Silesia being within Czechoslovakia.The...
, Bayreuth
Gau Bayreuth
The Gau Bayreuth, until 1942 named Gau Bayerische Ostmark , was an administrative division of Nazi Germany in Lower Bavaria, Upper Palatinate and Upper Franconia, Bavaria from 1933 to 1945...
(Bayerische Ostmark), Lower Danube, and Upper Danube. These two methods continued to co-exist in the protectorate for the entire duration of its existence.
Planned future districts
The Nazi government openly pursued and practiced aggressive territorial expansionismExpansionism
In general, expansionism consists of expansionist policies of governments and states. While some have linked the term to promoting economic growth , more commonly expansionism refers to the doctrine of a state expanding its territorial base usually, though not necessarily, by means of military...
, intending to further extend the already greatly increased territorial base of the German state. In anticipation of these expected future territorial enlargements, potential new districts were theorized upon at length by Nazi ideologists, government officials, and territorial planning departments. These expansions were intended to take place in two distinct ways:
Territorial expansion into Eastern Europe
In order to expand the LebensraumLebensraum
was one of the major political ideas of Adolf Hitler, and an important component of Nazi ideology. It served as the motivation for the expansionist policies of Nazi Germany, aiming to provide extra space for the growth of the German population, for a Greater Germany...
of the German people the Slavic populations of Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
were intended to be wiped out through a combined process of extermination
Genocide
Genocide is defined as "the deliberate and systematic destruction, in whole or in part, of an ethnic, racial, religious, or national group", though what constitutes enough of a "part" to qualify as genocide has been subject to much debate by legal scholars...
, expulsion, starvation
Hunger Plan
The Hunger Plan was an economic management scheme that was put in place to ensure that Germans were given priority over food supplies, at the expense of everyone else. This plan was featured as part of the planning phase of the Wehrmacht invasion of the Soviet Union in 1941...
, and enslavement
Slavery
Slavery is a system under which people are treated as property to be bought and sold, and are forced to work. Slaves can be held against their will from the time of their capture, purchase or birth, and deprived of the right to leave, to refuse to work, or to demand compensation...
that would effectively Germanize these territories in the long run. Nazi racial offices planned that the colonization with Germanic peoples
Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples are an Indo-European ethno-linguistic group of Northern European origin, identified by their use of the Indo-European Germanic languages which diversified out of Proto-Germanic during the Pre-Roman Iron Age.Originating about 1800 BCE from the Corded Ware Culture on the North...
of these conquered eastern territories was to proceed most intensively in the three so-called Siedlungsmarken (Settlement marches) or Reichsmarken of Ingermannland (Ingria
Ingria
Ingria is a historical region in the eastern Baltic, now part of Russia, comprising the southern bank of the river Neva, between the Gulf of Finland, the Narva River, Lake Peipus in the west, and Lake Ladoga and the western bank of the Volkhov river in the east...
), the Memel-Narew
Narew
The Narew River , in western Belarus and north-eastern Poland, is a left tributary of the Vistula river...
area, and the Southern Ukraine
Ukraine
Ukraine is a country in Eastern Europe. It has an area of 603,628 km², making it the second largest contiguous country on the European continent, after Russia...
and the Crimean peninsula. The latter of these was intended to be newly re-organized as a Gotengau (Gau of the Goths
Goths
The Goths were an East Germanic tribe of Scandinavian origin whose two branches, the Visigoths and the Ostrogoths, played an important role in the fall of the Roman Empire and the emergence of Medieval Europe....
), in honor of the Crimean Goths
Crimean Goths
Crimean Goths were those Gothic tribes who remained in the lands around the Black Sea, especially in Crimea. They were the least-powerful, least-known, and almost paradoxically, the longest-lasting of the Gothic communities...
who had at one point dwelled there. Of the Baltic countries
Baltic countries
The term Baltic states refers to the Baltic territories which gained independence from the Russian Empire in the wake of World War I: primarily the contiguous trio of Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania ; Finland also fell within the scope of the term after initially gaining independence in the 1920s.The...
, Peipusland
Lake Peipus
Lake Peipus, ) is the biggest transboundary lake in Europe on the border between Estonia and Russia.The lake is the fifth largest in Europe after Lake Ladoga and Lake Onega in Russia north of St...
was proposed as a replacement-name for Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
, and Dünaland for Latvia
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
.
In a conference on July 16 1941 discussing the future organization of the conquered Soviet territories Hitler stated his intention to turn not only the above-mentioned areas, but also the entire Baltic region (Reichskommissariat Ostland
Reichskommissariat Ostland
Reichskommissariat Ostland, literally "Reich Commissariat Eastland", was the civilian occupation regime established by Nazi Germany in the Baltic states and much of Belarus during World War II. It was also known as Reichskommissariat Baltenland initially...
), the Volga German colony, and the Baku
Baku
Baku , sometimes spelled as Baki or Bakou, is the capital and largest city of Azerbaijan, as well as the largest city on the Caspian Sea and of the Caucasus region. It is located on the southern shore of the Absheron Peninsula, which projects into the Caspian Sea. The city consists of two principal...
district into future Reichsgebieten (Reich territories). On 3 November 1941 he also elaborated on the toponymic aspect of Germanizing the east:
The central and upper Vistula valley within the General Government
General Government
The General Government was an area of Second Republic of Poland under Nazi German rule during World War II; designated as a separate region of the Third Reich between 1939–1945...
were variously discussed as having to become either a single Vandalengau (Gau of the Vandals
Vandals
The Vandals were an East Germanic tribe that entered the late Roman Empire during the 5th century. The Vandals under king Genseric entered Africa in 429 and by 439 established a kingdom which included the Roman Africa province, besides the islands of Sicily, Corsica, Sardinia and the Balearics....
) or 3-5 other new Reichsgaue. An earlier proposal from 1939 also advocated for the creation of a Reichsgau Beskidenland
Beskids
The Beskids , ) is a traditional name for a series of Eastern European mountain ranges.- Definition :The Beskids are approximately 600 km in length and 50–70 km in width...
, which was to stretch from the area to the west of Cracow to the San river in the east. In Axis-occupied Yugoslavia, Sepp Janko
Sepp Janko
Dr. Sepp Janko Dr. Sepp (Josef) Janko Dr. Sepp (Josef) Janko (born November 9, 1905 Ernsthausen (Banatski Despotovac) in the Banat, now Serbia, † 25 September 2001 in Belgrano (Buenos Aires) was Chairman of the Danube Swabian German Cultural Association (Schwäbisch-Deutschen Kulturbundes) in...
, Nazi representative of Danube Swabian interests, pushed for the establishment of a Reichsgau Banat or Prinz-Eugen
Prince Eugene of Savoy
Prince Eugene of Savoy , was one of the most successful military commanders in modern European history, rising to the highest offices of state at the Imperial court in Vienna. Born in Paris to aristocratic Italian parents, Eugene grew up around the French court of King Louis XIV...
-Gau, which would have encompassed the Yugoslavian territories of Bačka
Backa
Bačka is a geographical area within the Pannonian plain bordered by the river Danube to the west and south, and by the river Tisza to the east of which confluence is located near Titel...
, Banat, parts of Transylvania
Transylvania
Transylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
(Siebenbürgen) and Baranya
Baranya
Baranya may refer to:*Baranya , a geographical region in Hungary and Croatia*Baranya , a county in Hungary*Baranya , a county in the historic Kingdom of Hungary...
.
Annexation of the Germanic countries
The Nazi racial categorizationRacial policy of Nazi Germany
The racial policy of Nazi Germany was a set of policies and laws implemented by Nazi Germany, asserting the superiority of the "Aryan race", and based on a specific racist doctrine which claimed scientific legitimacy...
of the ethnic groups of Europe classified the Northern Europeans
Northern Europe
Northern Europe is the northern part or region of Europe. Northern Europe typically refers to the seven countries in the northern part of the European subcontinent which includes Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Finland and Sweden...
, especially those closely related to the Germans
Germans
The Germans are a Germanic ethnic group native to Central Europe. The English term Germans has referred to the German-speaking population of the Holy Roman Empire since the Late Middle Ages....
(itself considered to be a single nationality of which Swiss and Austrians
Austrians
Austrians are a nation and ethnic group, consisting of the population of the Republic of Austria and its historical predecessor states who share a common Austrian culture and Austrian descent....
were nothing but sub-regional identities at best) such as the Dutch
Dutch people
The Dutch people are an ethnic group native to the Netherlands. They share a common culture and speak the Dutch language. Dutch people and their descendants are found in migrant communities worldwide, notably in Suriname, Chile, Brazil, Canada, Australia, South Africa, New Zealand, and the United...
, the Flemings, the Danish, Norwegians
Norwegians
Norwegians constitute both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway. They share a common culture and speak the Norwegian language. Norwegian people and their descendants are found in migrant communities worldwide, notably in United States, Canada and Brazil.-History:Towards the end of the 3rd...
, Swedish, and English
English people
The English are a nation and ethnic group native to England, who speak English. The English identity is of early mediaeval origin, when they were known in Old English as the Anglecynn. England is now a country of the United Kingdom, and the majority of English people in England are British Citizens...
as part of a superior Aryan
Aryan race
The Aryan race is a concept historically influential in Western culture in the period of the late 19th century and early 20th century. It derives from the idea that the original speakers of the Indo-European languages and their descendants up to the present day constitute a distinctive race or...
-Nordic master race
Master race
Master race was a phrase and concept originating in the slave-holding Southern US. The later phrase Herrenvolk , interpreted as 'master race', was a concept in Nazi ideology in which the Nordic peoples, one of the branches of what in the late-19th and early-20th century was called the Aryan race,...
(Herrenrasse). Following the highly successful integration
Anschluss
The Anschluss , also known as the ', was the occupation and annexation of Austria into Nazi Germany in 1938....
of Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
into a Greater Germany (Großdeutschland), Hitler decided that he would follow the same policy in the future for all other countries that he regarded by virtue of their perceived racial qualifications as "belonging" to the Reich. This meant that the Low Countries
Low Countries
The Low Countries are the historical lands around the low-lying delta of the Rhine, Scheldt, and Meuse rivers, including the modern countries of Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg and parts of northern France and western Germany....
and the Scandinavia
Scandinavia
Scandinavia is a cultural, historical and ethno-linguistic region in northern Europe that includes the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden, characterized by their common ethno-cultural heritage and language. Modern Norway and Sweden proper are situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula,...
n states were eventually to be annexed into a much larger Greater Germanic Reich
Greater Germanic Reich
The Greater Germanic Reich , fully styled the Greater Germanic Reich of the German Nation is the official state name of the political entity that Nazi Germany tried to establish in Europe during World War II...
(Großgermanisches Reich) by being broken up into smaller state and party administrative units, such as Denmark into a Gau Nordmark, and the Netherlands into a Gau Westland.
Afterwards the very notion of these countries ever having been independent or separate from the rest of the Reich was to be suppressed indefinitely. The objective called for the inauguration of a new period of rapidly enforced Gleichschaltung
Gleichschaltung
Gleichschaltung , meaning "coordination", "making the same", "bringing into line", is a Nazi term for the process by which the Nazi regime successively established a system of totalitarian control and tight coordination over all aspects of society. The historian Richard J...
, the end result of which would be that aside from their local "language dialects" these countries were to become perfect duplicates of National Socialist Germany in all political and social respects.
In addition it was intended to revert the western borders of Germany with France
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
to those of the late-medieval Holy Roman Empire
Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a realm that existed from 962 to 1806 in Central Europe.It was ruled by the Holy Roman Emperor. Its character changed during the Middle Ages and the Early Modern period, when the power of the emperor gradually weakened in favour of the princes...
. A strip of eastern France from the mouth of the Somme
Somme
Somme is a department of France, located in the north of the country and named after the Somme river. It is part of the Picardy region of France....
to Lake Geneva
Lake Geneva
Lake Geneva or Lake Léman is a lake in Switzerland and France. It is one of the largest lakes in Western Europe. 59.53 % of it comes under the jurisdiction of Switzerland , and 40.47 % under France...
(the so-called "closed" or "forbidden" zone of German-occupied France was prepared to be annexed to the German Reich as Reichsgau Burgund, with Nancy (Nanzig) as the capital.
See also
- Administrative division of Weimar GermanyAdministrative division of Weimar GermanyPrior to World War I, the constituent states of the German Empire were 22 smaller monarchies, three city-states and the Imperial territory of Alsace-Lorraine. After the territorial losses of the Treaty of Versailles and the revolution of 1918, the remaining states continued as republics...
- Administrative divisions of the German Democratic RepublicAdministrative divisions of the German Democratic RepublicThe Administrative divisions of the German Democratic Republic were constituted in two different forms during the country's 41-year-long history. The Republic first retained the traditional German division into federated states called Länder, but in 1952 replaced them with arbitrarily-drawn...
- Administrative divisions of GermanyAdministrative divisions of GermanySubdivisions of Germany - overview....
- Polish areas annexed by Nazi GermanyPolish areas annexed by Nazi GermanyAt the beginning of World War II, nearly a quarter of the pre-war Polish areas were annexed by Nazi Germany and placed directly under German civil administration, while the rest of Nazi occupied Poland was named as General Government...
- States of the German Empire
Sources
- Der große Atlas der Weltgeschichte (in German), Historical map book, published: 1990, publisher: Orbis Verlag, Munich, ISBN 3-572-04755-2
External links
- Shoa.de - List of Gaue and Gauleiter (in German)

