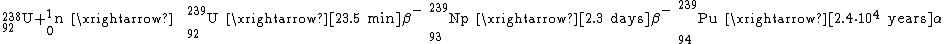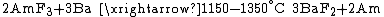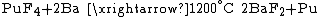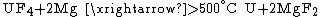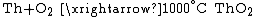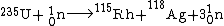Actinide
Encyclopedia

IUPAC nomenclature
A chemical nomenclature is a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compounds. The nomenclature used most frequently worldwide is the one created and developed by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry ....
) series encompasses the 15 metal
Metal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
lic chemical element
Chemical element
A chemical element is a pure chemical substance consisting of one type of atom distinguished by its atomic number, which is the number of protons in its nucleus. Familiar examples of elements include carbon, oxygen, aluminum, iron, copper, gold, mercury, and lead.As of November 2011, 118 elements...
s with atomic number
Atomic number
In chemistry and physics, the atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom and therefore identical to the charge number of the nucleus. It is conventionally represented by the symbol Z. The atomic number uniquely identifies a chemical element...
s from 89 to 103, actinium
Actinium
Actinium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Ac and atomic number 89, which was discovered in 1899. It was the first non-primordial radioactive element to be isolated. Polonium, radium and radon were observed before actinium, but they were not isolated until 1902...
through lawrencium
Lawrencium
Lawrencium is a radioactive synthetic chemical element with the symbol Lr and atomic number 103. In the periodic table of the elements, it is a period 7 d-block element and the last element of actinide series...
.
The actinide series derives its name from the group 3 element
Group 3 element
The group 3 elements are a group of chemical elements in the periodic table. This group, like other d-block groups, should contain four elements, but it is not agreed what elements belong in the group...
actinium. All but one of the actinides are f-block
F-block
The f-block of the periodic table of the elements consists of those elements whose atoms or ions have valence electrons in f-orbitals. Actual electronic configurations may be slightly different from what is predicted by the Aufbau principle...
elements, corresponding to the filling of the 5f electron shell
Electron shell
An electron shell may be thought of as an orbit followed by electrons around an atom's nucleus. The closest shell to the nucleus is called the "1 shell" , followed by the "2 shell" , then the "3 shell" , and so on further and further from the nucleus. The shell letters K,L,M,.....
; lawrencium, a d-block
D-block
The d-block is the portion of the periodic table that contains the element groups 3-12. These groups correspond to the filling of the atomic d-orbital subshell, with electron configurations ranging from s2d1 to s2d10...
element, is also generally considered an actinide. In comparison with the lanthanides, also mostly f-block
F-block
The f-block of the periodic table of the elements consists of those elements whose atoms or ions have valence electrons in f-orbitals. Actual electronic configurations may be slightly different from what is predicted by the Aufbau principle...
elements, the actinides show much more variable valence
Valence (chemistry)
In chemistry, valence, also known as valency or valence number, is a measure of the number of bonds formed by an atom of a given element. "Valence" can be defined as the number of valence bonds...
.
| 89Ac Actinium Actinium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Ac and atomic number 89, which was discovered in 1899. It was the first non-primordial radioactive element to be isolated. Polonium, radium and radon were observed before actinium, but they were not isolated until 1902... |
90Th Thorium Thorium is a natural radioactive chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. It was discovered in 1828 and named after Thor, the Norse god of thunder.... |
91Pa Protactinium Protactinium is a chemical element with the symbol Pa and atomic number 91. It is a dense, silvery-gray metal which readily reacts with oxygen, water vapor and inorganic acids. It forms various chemical compounds where protactinium is usually present in the oxidation state +5, but can also assume... |
92U Uranium Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons... |
93Np Neptunium Neptunium is a chemical element with the symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element and belongs to the actinide series. Its most stable isotope, 237Np, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and plutonium production and it can be used as a... |
94Pu Plutonium Plutonium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the chemical symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, forming a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation... |
95Am Americium Americium is a synthetic element that has the symbol Am and atomic number 95. This transuranic element of the actinide series is located in the periodic table below the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was named after another continent, America.Americium was first produced in 1944... |
96Cm Curium Curium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This radioactive transuranic element of the actinide series was named after Marie Skłodowska-Curie and her husband Pierre Curie. Curium was first intentionally produced and identified in summer 1944 by the group of... |
97Bk Berkelium Berkelium , is a synthetic element with the symbol Bk and atomic number 97, a member of the actinide and transuranium element series. It is named after the city of Berkeley, California, the location of the University of California Radiation Laboratory where it was discovered in December 1949... |
98Cf Californium Californium is a radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Cf and atomic number 98. The element was first made in the laboratory in 1950 by bombarding curium with alpha particles at the University of California, Berkeley. It is the ninth member of the actinide series and was the... |
99Es Einsteinium Einsteinium is a synthetic element with the symbol Es and atomic number 99. It is the seventh transuranic element, and an actinide.Einsteinium was discovered in the debris of the first hydrogen bomb explosion in 1952, and named after Albert Einstein... |
100Fm Fermium Fermium is a synthetic element with the symbol Fm. It is the 100th element in the periodic table and a member of the actinide series. It is the heaviest element that can be formed by neutron bombardment of lighter elements, and hence the last element that can be prepared in macroscopic quantities,... |
101Md Mendelevium Mendelevium is a synthetic element with the symbol Md and the atomic number 101. A metallic radioactive transuranic element in the actinide series, mendelevium is usually synthesized by bombarding einsteinium with alpha particles. It was named after Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev, who created the... |
102No Nobelium Nobelium is a synthetic element with the symbol No and atomic number 102. It was first correctly identified in 1966 by scientists at the Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions in Dubna, Soviet Union... |
103Lr Lawrencium Lawrencium is a radioactive synthetic chemical element with the symbol Lr and atomic number 103. In the periodic table of the elements, it is a period 7 d-block element and the last element of actinide series... |
Of the actinides, thorium
Thorium
Thorium is a natural radioactive chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. It was discovered in 1828 and named after Thor, the Norse god of thunder....
and uranium
Uranium
Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons...
occur naturally in substantial, primordial
Primordial nuclide
In geochemistry and geonuclear physics, primordial nuclides or primordial isotopes are nuclides found on the earth that have existed in their current form since before Earth was formed. Only 288 such nuclides are known...
, quantities and small amounts of persisting natural plutonium
Plutonium
Plutonium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the chemical symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, forming a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation...
have also been identified. The radioactive decay of uranium produces transient amounts of protactinium
Protactinium
Protactinium is a chemical element with the symbol Pa and atomic number 91. It is a dense, silvery-gray metal which readily reacts with oxygen, water vapor and inorganic acids. It forms various chemical compounds where protactinium is usually present in the oxidation state +5, but can also assume...
, and atoms of neptunium
Neptunium
Neptunium is a chemical element with the symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element and belongs to the actinide series. Its most stable isotope, 237Np, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and plutonium production and it can be used as a...
are occasionally produced from transmutation
Nuclear transmutation
Nuclear transmutation is the conversion of one chemical element or isotope into another. In other words, atoms of one element can be changed into atoms of other element by 'transmutation'...
reactions in uranium ores. The other actinides are purely synthetic elements. Nuclear weapons tests have released at least six of these synthetic actinides into the environment
Natural environment
The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species....
; analysis of debris from a 1952 hydrogen bomb explosion showed the presence of americium
Americium
Americium is a synthetic element that has the symbol Am and atomic number 95. This transuranic element of the actinide series is located in the periodic table below the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was named after another continent, America.Americium was first produced in 1944...
, curium
Curium
Curium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This radioactive transuranic element of the actinide series was named after Marie Skłodowska-Curie and her husband Pierre Curie. Curium was first intentionally produced and identified in summer 1944 by the group of...
, berkelium
Berkelium
Berkelium , is a synthetic element with the symbol Bk and atomic number 97, a member of the actinide and transuranium element series. It is named after the city of Berkeley, California, the location of the University of California Radiation Laboratory where it was discovered in December 1949...
, californium
Californium
Californium is a radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Cf and atomic number 98. The element was first made in the laboratory in 1950 by bombarding curium with alpha particles at the University of California, Berkeley. It is the ninth member of the actinide series and was the...
, einsteinium
Einsteinium
Einsteinium is a synthetic element with the symbol Es and atomic number 99. It is the seventh transuranic element, and an actinide.Einsteinium was discovered in the debris of the first hydrogen bomb explosion in 1952, and named after Albert Einstein...
and fermium
Fermium
Fermium is a synthetic element with the symbol Fm. It is the 100th element in the periodic table and a member of the actinide series. It is the heaviest element that can be formed by neutron bombardment of lighter elements, and hence the last element that can be prepared in macroscopic quantities,...
.
All actinides are radioactive and release energy upon radioactive decay; naturally occurring uranium and thorium, and synthetically produced plutonium are the most abundant actinides on Earth. These are used in nuclear reactor
Nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device to initiate and control a sustained nuclear chain reaction. Most commonly they are used for generating electricity and for the propulsion of ships. Usually heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid , which runs through turbines that power either ship's...
s and nuclear weapons. Uranium and thorium also have diverse current or historical uses, and americium is used in the ionization chamber
Ionization chamber
The ionization chamber is the simplest of all gas-filled radiation detectors, and is used for the detection or measurement of ionizing radiation...
s of most modern smoke detector
Smoke detector
A smoke detector is a device that detects smoke, typically as an indicator of fire. Commercial, industrial, and mass residential devices issue a signal to a fire alarm system, while household detectors, known as smoke alarms, generally issue a local audible and/or visual alarm from the detector...
s.
In presentations of the periodic table
Periodic table
The periodic table of the chemical elements is a tabular display of the 118 known chemical elements organized by selected properties of their atomic structures. Elements are presented by increasing atomic number, the number of protons in an atom's atomic nucleus...
, the lanthanides and the actinides are customarily shown as two additional rows below the main body of the table, with placeholders or else a selected single element of each series (either lanthanum
Lanthanum
Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57.Lanthanum is a silvery white metallic element that belongs to group 3 of the periodic table and is the first element of the lanthanide series. It is found in some rare-earth minerals, usually in combination with cerium and...
or lutetium, and either actinium
Actinium
Actinium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Ac and atomic number 89, which was discovered in 1899. It was the first non-primordial radioactive element to be isolated. Polonium, radium and radon were observed before actinium, but they were not isolated until 1902...
or lawrencium
Lawrencium
Lawrencium is a radioactive synthetic chemical element with the symbol Lr and atomic number 103. In the periodic table of the elements, it is a period 7 d-block element and the last element of actinide series...
, respectively) shown in a single cell of the main table, between barium
Barium
Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in Group 2, a soft silvery metallic alkaline earth metal. Barium is never found in nature in its pure form due to its reactivity with air. Its oxide is historically known as baryta but it reacts with...
and hafnium
Hafnium
Hafnium is a chemical element with the symbol Hf and atomic number 72. A lustrous, silvery gray, tetravalent transition metal, hafnium chemically resembles zirconium and is found in zirconium minerals. Its existence was predicted by Dmitri Mendeleev in 1869. Hafnium was the penultimate stable...
, and radium
Radium
Radium is a chemical element with atomic number 88, represented by the symbol Ra. Radium is an almost pure-white alkaline earth metal, but it readily oxidizes on exposure to air, becoming black in color. All isotopes of radium are highly radioactive, with the most stable isotope being radium-226,...
and rutherfordium
Rutherfordium
Rutherfordium is a chemical element with symbol Rf and atomic number 104, named in honor of New Zealand physicist Ernest Rutherford. It is a synthetic element and radioactive; the most stable known isotope, 267Rf, has a half-life of approximately 1.3 hours.In the periodic table of the elements,...
, respectively. This convention is entirely a matter of aesthetics
Aesthetics
Aesthetics is a branch of philosophy dealing with the nature of beauty, art, and taste, and with the creation and appreciation of beauty. It is more scientifically defined as the study of sensory or sensori-emotional values, sometimes called judgments of sentiment and taste...
and formatting practicality; a rarely used wide-formatted periodic table
Periodic table (wide)
This is a version of the periodic table of the elements that places all elements of one period in the same row. For more information on its contents and history, see the article Periodic table.----- See also :*Periodic table*Periodic table...
inserts the lanthanide and actinide series in their proper places, as parts of the table's sixth and seventh rows (periods).
Discovery, isolation and synthesis
| Element | Year | Method |
|---|---|---|
| Neptunium Neptunium Neptunium is a chemical element with the symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element and belongs to the actinide series. Its most stable isotope, 237Np, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and plutonium production and it can be used as a... |
1940 | Bombarding 238U by neutron Neutron The neutron is a subatomic hadron particle which has the symbol or , no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons. The number of... s |
| Plutonium Plutonium Plutonium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the chemical symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, forming a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation... |
1941 | Bombarding 238U by deuterons |
| Americium Americium Americium is a synthetic element that has the symbol Am and atomic number 95. This transuranic element of the actinide series is located in the periodic table below the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was named after another continent, America.Americium was first produced in 1944... |
1944 | Bombarding 239Pu by neutrons |
| Curium Curium Curium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This radioactive transuranic element of the actinide series was named after Marie Skłodowska-Curie and her husband Pierre Curie. Curium was first intentionally produced and identified in summer 1944 by the group of... |
1944 | Bombarding 239Pu by α-particles Alpha particle Alpha particles consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium nucleus, which is classically produced in the process of alpha decay, but may be produced also in other ways and given the same name... |
| Berkelium Berkelium Berkelium , is a synthetic element with the symbol Bk and atomic number 97, a member of the actinide and transuranium element series. It is named after the city of Berkeley, California, the location of the University of California Radiation Laboratory where it was discovered in December 1949... |
1949 | Bombarding 241Am by α-particles |
| Californium Californium Californium is a radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Cf and atomic number 98. The element was first made in the laboratory in 1950 by bombarding curium with alpha particles at the University of California, Berkeley. It is the ninth member of the actinide series and was the... |
1950 | Bombarding 242Cm by α-particles |
| Einsteinium Einsteinium Einsteinium is a synthetic element with the symbol Es and atomic number 99. It is the seventh transuranic element, and an actinide.Einsteinium was discovered in the debris of the first hydrogen bomb explosion in 1952, and named after Albert Einstein... |
1952 | As a product of nuclear explosion Nuclear explosion A nuclear explosion occurs as a result of the rapid release of energy from an intentionally high-speed nuclear reaction. The driving reaction may be nuclear fission, nuclear fusion or a multistage cascading combination of the two, though to date all fusion based weapons have used a fission device... |
| Fermium Fermium Fermium is a synthetic element with the symbol Fm. It is the 100th element in the periodic table and a member of the actinide series. It is the heaviest element that can be formed by neutron bombardment of lighter elements, and hence the last element that can be prepared in macroscopic quantities,... |
1952 | As a product of nuclear explosion |
| Mendelevium Mendelevium Mendelevium is a synthetic element with the symbol Md and the atomic number 101. A metallic radioactive transuranic element in the actinide series, mendelevium is usually synthesized by bombarding einsteinium with alpha particles. It was named after Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev, who created the... |
1955 | Bombarding 253Es by α-particles |
| Nobelium Nobelium Nobelium is a synthetic element with the symbol No and atomic number 102. It was first correctly identified in 1966 by scientists at the Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions in Dubna, Soviet Union... |
1965 | Bombarding 243Am by 15N or 238U with α-particles |
| Lawrencium Lawrencium Lawrencium is a radioactive synthetic chemical element with the symbol Lr and atomic number 103. In the periodic table of the elements, it is a period 7 d-block element and the last element of actinide series... |
1961–1971 | Bombarding 252Cf by 10B or 11B and of 243Am with 18O |
Like the lanthanide
Lanthanide
The lanthanide or lanthanoid series comprises the fifteen metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57 through 71, from lanthanum through lutetium...
s, the actinides form a family of elements with similar properties. Within the actinides, there are two overlapping groups: transuranium elements, which follow uranium in the periodic table
Periodic table
The periodic table of the chemical elements is a tabular display of the 118 known chemical elements organized by selected properties of their atomic structures. Elements are presented by increasing atomic number, the number of protons in an atom's atomic nucleus...
—and transplutonium element
Transuranium element
In chemistry, transuranium elements are the chemical elements with atomic numbers greater than 92...
s, which follow plutonium. Compared to the lanthanides, which (except for promethium
Promethium
Promethium is a chemical element with the symbol Pm and atomic number 61. It is notable for being the only exclusively radioactive element besides technetium that is followed by chemical elements with stable isotopes.- Prediction :...
) are found in nature in appreciable quantities, most actinides are rare. The most abundant, or easy to synthesize actinides are uranium and thorium, followed by plutonium, americium, actinium, protactinium and neptunium.
The existence of transuranium elements was suggested by Enrico Fermi
Enrico Fermi
Enrico Fermi was an Italian-born, naturalized American physicist particularly known for his work on the development of the first nuclear reactor, Chicago Pile-1, and for his contributions to the development of quantum theory, nuclear and particle physics, and statistical mechanics...
based on his experiments in 1934. However, even though four actinides were known by that time, it was not yet understood that they formed a family similar to lanthanides. The prevailing view that dominated early research into transuranics was that they were regular elements in the 7th period, with thorium, protactinium and uranium corresponding to 6th-period hafnium, tantalum and tungsten, respectively. Synthesis of transuranics gradually undermined this point of view. By 1944 an observation that curium failed to exhibit oxidation states above 4 (whereas its supposed 6th period neighbor, platinum, can reach oxidation state of 7) prompted Glenn Seaborg to formulate a so-called "actinide hypothesis". Studies of known actinides and discoveries of further transuranic elements provided more data in support of this point of view, but the phrase "actinide hypothesis" (the implication being that "hypothesis" is something that's not been decisively proven) remained in active use by scientists through the late 1950s.
At present, there are two major methods of producing isotope
Isotope
Isotopes are variants of atoms of a particular chemical element, which have differing numbers of neutrons. Atoms of a particular element by definition must contain the same number of protons but may have a distinct number of neutrons which differs from atom to atom, without changing the designation...
s of transplutonium elements: irradiation of the lighter elements with either neutron
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic hadron particle which has the symbol or , no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons. The number of...
s or accelerated charged particles. The first method is most important for applications, as only neutron irradiation using nuclear reactors allows the production of sizeable amounts of synthetic actinides; however, it is limited to relatively light elements. The advantage of the second method is that elements heavier than plutonium, as well as neutron-deficient isotopes, can be obtained, which are not formed during neutron irradiation.
In 1962–1966, there were attempts in the United States to produce transplutonium isotopes using a series of six underground nuclear explosions
Underground nuclear testing
Underground nuclear testing refers to test detonations of nuclear weapons that are performed underground. When the device being tested is buried at sufficient depth, the explosion may be contained, with no release of radioactive materials to the atmosphere....
. Small samples of rock were extracted from the blast area immediately after the test to study the explosion products, but no isotopes with mass number
Mass number
The mass number , also called atomic mass number or nucleon number, is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atomic nucleus. Because protons and neutrons both are baryons, the mass number A is identical with the baryon number B as of the nucleus as of the whole atom or ion...
greater than 257 could be detected, despite predictions that such isotopes would have relatively long half-lives
Half-life
Half-life, abbreviated t½, is the period of time it takes for the amount of a substance undergoing decay to decrease by half. The name was originally used to describe a characteristic of unstable atoms , but it may apply to any quantity which follows a set-rate decay.The original term, dating to...
of α-decay. This inobservation was attributed to spontaneous fission
Spontaneous fission
Spontaneous fission is a form of radioactive decay characteristic of very heavy isotopes. Because the nuclear binding energy reaches a maximum at a nuclear mass greater than about 60 atomic mass units , spontaneous breakdown into smaller nuclei and single particles becomes possible at heavier masses...
owing to the large speed of the products and to other decay channels, such as neutron emission and nuclear fission
Nuclear fission
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, nuclear fission is a nuclear reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into smaller parts , often producing free neutrons and photons , and releasing a tremendous amount of energy...
.
From actinium to neptunium

Martin Heinrich Klaproth
Martin Heinrich Klaproth was a German chemist.Klaproth was born in Wernigerode. During a large portion of his life he followed the profession of an apothecary...
in pitchblende
Uraninite
Uraninite is a radioactive, uranium-rich mineral and ore with a chemical composition that is largely UO2, but also contains UO3 and oxides of lead, thorium, and rare earth elements...
ore. He named it after the planet Uranus, which had been discovered only eight years earlier. Klaproth was able to precipitate a yellow compound (likely sodium diuranate
Sodium diuranate
Sodium diuranate, Na2U2O7·6H2O, is a uranium salt also known as the yellow oxide of uranium. Along with ammonium diuranate it was a component in early yellowcakes, the ratio of the two species determined by process conditions; yellowcake is now largely a mix of uranium oxides...
) by dissolving pitchblende in nitric acid
Nitric acid
Nitric acid , also known as aqua fortis and spirit of nitre, is a highly corrosive and toxic strong acid.Colorless when pure, older samples tend to acquire a yellow cast due to the accumulation of oxides of nitrogen. If the solution contains more than 86% nitric acid, it is referred to as fuming...
and neutralizing the solution with sodium hydroxide. He then reduced the obtained yellow powder with charcoal, and extracted a black substance that he mistook for metal. Only 60 years later, the French scientist Eugène-Melchior Péligot
Eugène-Melchior Péligot
Eugène-Melchior Péligot , also known as Eugène Péligot, was a French chemist who isolated the first sample of uranium metal in 1841....
identified it with uranium oxide. He also isolated the first sample of uranium metal by heating uranium tetrachloride
Uranium tetrachloride
Uranium tetrachloride is compound of uranium in oxidation state +4. It was used in the electromagnetic isotope separation process of uranium enrichment. It is one of the main starting materials for organouranium chemistry.- Synthesis :...
with potassium
Potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K and atomic number 19. Elemental potassium is a soft silvery-white alkali metal that oxidizes rapidly in air and is very reactive with water, generating sufficient heat to ignite the hydrogen emitted in the reaction.Potassium and sodium are...
. The atomic mass
Atomic mass
The atomic mass is the mass of a specific isotope, most often expressed in unified atomic mass units. The atomic mass is the total mass of protons, neutrons and electrons in a single atom....
of uranium was then calculated as 120, but Dmitri Mendeleev
Dmitri Mendeleev
Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev , was a Russian chemist and inventor. He is credited as being the creator of the first version of the periodic table of elements...
in 1872 corrected it to 240 using his periodicity laws. This value was confirmed experimentally in 1882 by K. Zimmerman.
Thorium oxide was discovered by Friedrich Wöhler
Friedrich Wöhler
Friedrich Wöhler was a German chemist, best known for his synthesis of urea, but also the first to isolate several chemical elements.-Biography:He was born in Eschersheim, which belonged to aau...
in the mineral, which was found in Norway (1827). Jöns Jacob Berzelius characterized this material in more detail by in 1828. By reduction of thorium tetrachloride with potassium, he isolated the metal and named it thorium after the Norse god
Norse mythology
Norse mythology, a subset of Germanic mythology, is the overall term for the myths, legends and beliefs about supernatural beings of Norse pagans. It flourished prior to the Christianization of Scandinavia, during the Early Middle Ages, and passed into Nordic folklore, with some aspects surviving...
of thunder and lightning Thor
Thor
In Norse mythology, Thor is a hammer-wielding god associated with thunder, lightning, storms, oak trees, strength, the protection of mankind, and also hallowing, healing, and fertility...
. The same isolation method was later used by Péligot for uranium.
Actinium was discovered in 1899 by André-Louis Debierne
André-Louis Debierne
André-Louis Debierne was a French chemist and is considered the discoverer of the element actinium....
, an assistant of Marie Curie
Marie Curie
Marie Skłodowska-Curie was a physicist and chemist famous for her pioneering research on radioactivity. She was the first person honored with two Nobel Prizes—in physics and chemistry...
, in the pitchblende waste left after removal of radium and polonium. He described the substance (in 1899) as similar to titanium
Titanium
Titanium is a chemical element with the symbol Ti and atomic number 22. It has a low density and is a strong, lustrous, corrosion-resistant transition metal with a silver color....
and (in 1900) as similar to thorium. The discovery of actinium by Debierne was however questioned in 1971 and 2000, arguing that Debierne's publications in 1904 contradicted his earlier work of 1899–1900. The name for word actinium comes from the Greek aktis, aktinos (ακτίς, ακτίνος), meaning beam or ray. This metal was discovered not by its own radiation but by the radiation of the daughter products. Owing to the close similarity of actinium and lanthanum and low abundance, pure actinium could only be produced in 1950. The term actinide was probably introduced by Victor Goldschmidt
Victor Goldschmidt
Victor Moritz Goldschmidt was a mineralogist considered to be the founder of modern geochemistry and crystal chemistry, developer of the Goldschmidt Classification of elements.-Early life & career:Goldschmidt was born in Zürich...
in 1937.
Protactinium
Protactinium
Protactinium is a chemical element with the symbol Pa and atomic number 91. It is a dense, silvery-gray metal which readily reacts with oxygen, water vapor and inorganic acids. It forms various chemical compounds where protactinium is usually present in the oxidation state +5, but can also assume...
was possibly isolated in 1900 by William Crookes
William Crookes
Sir William Crookes, OM, FRS was a British chemist and physicist who attended the Royal College of Chemistry, London, and worked on spectroscopy...
. It was first identified in 1913, when Kasimir Fajans and Oswald Helmuth Göhring encountered the short-lived isotope 234mPa (half-life 1.17 minutes) during their studies of the 238U decay. They named the new element brevium (from Latin brevis meaning brief); the name was changed to protoactinium (from Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
πρῶτος + ἀκτίς meaning "first beam element") in 1918 when two groups of scientists, led by Otto Hahn
Otto Hahn
Otto Hahn FRS was a German chemist and Nobel laureate, a pioneer in the fields of radioactivity and radiochemistry. He is regarded as "the father of nuclear chemistry". Hahn was a courageous opposer of Jewish persecution by the Nazis and after World War II he became a passionate campaigner...
and Lise Meitner
Lise Meitner
Lise Meitner FRS was an Austrian-born, later Swedish, physicist who worked on radioactivity and nuclear physics. Meitner was part of the team that discovered nuclear fission, an achievement for which her colleague Otto Hahn was awarded the Nobel Prize...
of Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
and Frederick Soddy
Frederick Soddy
Frederick Soddy was an English radiochemist who explained, with Ernest Rutherford, that radioactivity is due to the transmutation of elements, now known to involve nuclear reactions. He also proved the existence of isotopes of certain radioactive elements...
and John Cranston of Great Britain
Great Britain
Great Britain or Britain is an island situated to the northwest of Continental Europe. It is the ninth largest island in the world, and the largest European island, as well as the largest of the British Isles...
, independently discovered 231Pa. The name was shortened to Protactinium in 1949. This element was little characterized until 1960, when A. G. Maddock and co-workers in UK produced 130 grams of protactinium from 60 tonnes of waste left after extraction of uranium from its ore.
Neptunium (named for the planet Neptune
Neptune
Neptune is the eighth and farthest planet from the Sun in the Solar System. Named for the Roman god of the sea, it is the fourth-largest planet by diameter and the third largest by mass. Neptune is 17 times the mass of Earth and is slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus, which is 15 times...
, the next planet
Planet
A planet is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science,...
out from Uranus, after which uranium was named) was discovered by Edwin McMillan
Edwin McMillan
Edwin Mattison McMillan was an American physicist and Nobel laureate credited with being the first ever to produce a transuranium element. He shared the Nobel Prize in Chemistry with Glenn Seaborg in 1951....
and Philip H. Abelson in 1940 in Berkeley, California. They produced the 239Np isotope (half-life 2.4 days) by bombarding uranium with slow neutrons. It was the first transuranium element
Transuranium element
In chemistry, transuranium elements are the chemical elements with atomic numbers greater than 92...
produced synthetically.
Plutonium and above

Nuclear reaction
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, a nuclear reaction is semantically considered to be the process in which two nuclei, or else a nucleus of an atom and a subatomic particle from outside the atom, collide to produce products different from the initial particles...
s conducted with nuclear reactors. For example, under irradiation with reactor neutrons, uranium-238
Uranium-238
Uranium-238 is the most common isotope of uranium found in nature. It is not fissile, but is a fertile material: it can capture a slow neutron and after two beta decays become fissile plutonium-239...
partially converts to plutonium-239
Plutonium-239
Plutonium-239 is an isotope of plutonium. Plutonium-239 is the primary fissile isotope used for the production of nuclear weapons, although uranium-235 has also been used and is currently the secondary isotope. Plutonium-239 is also one of the three main isotopes demonstrated usable as fuel in...
:
In this way, Enrico Fermi with collaborators, using the first nuclear reactor Chicago Pile-1
Chicago Pile-1
Chicago Pile-1 was the world's first man-made nuclear reactor. CP-1 was built on a rackets court, under the abandoned west stands of the original Alonzo Stagg Field stadium, at the University of Chicago. The first self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction was initiated in CP-1 on December 2, 1942...
, obtained significant amounts of plutonium-239, which were then used in nuclear weapons
Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development program, led by the United States with participation from the United Kingdom and Canada, that produced the first atomic bomb during World War II. From 1942 to 1946, the project was under the direction of Major General Leslie Groves of the US Army...
.
Actinides with the highest mass numbers are synthesized by bombarding uranium, plutonium, curium and californium with ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
s of nitrogen, oxygen, carbon, neon or boron in a particle accelerator
Particle accelerator
A particle accelerator is a device that uses electromagnetic fields to propel charged particles to high speeds and to contain them in well-defined beams. An ordinary CRT television set is a simple form of accelerator. There are two basic types: electrostatic and oscillating field accelerators.In...
. So, nobelium
Nobelium
Nobelium is a synthetic element with the symbol No and atomic number 102. It was first correctly identified in 1966 by scientists at the Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions in Dubna, Soviet Union...
was produced by bombarding uranium-238 with neon-22 as
-
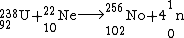 .
.
First isotopes of transplutonium elements, americium-241 and curium-242, were synthesized in 1944 by Glenn T. Seaborg, Ralph A. James and Albert Ghiorso
Albert Ghiorso
Albert Ghiorso was an American nuclear scientist and co-discoverer of a record 12 chemical elements on the periodic table. His research career spanned five decades, from the early 1940s to the late 1990s.-Early life:...
. Curium-242 was obtained by bombarding plutonium-239 with 32-MeV α-particles
-
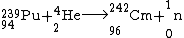 .
.
The americium-241 and curium-242 isotopes also were produced by irradiating plutonium in a nuclear reactor. The latter element was named after Marie Curie
Marie Curie
Marie Skłodowska-Curie was a physicist and chemist famous for her pioneering research on radioactivity. She was the first person honored with two Nobel Prizes—in physics and chemistry...
and her husband Pierre
Pierre Curie
Pierre Curie was a French physicist, a pioneer in crystallography, magnetism, piezoelectricity and radioactivity, and Nobel laureate. He was the son of Dr. Eugène Curie and Sophie-Claire Depouilly Curie ...
who are noted for discovering radium
Radium
Radium is a chemical element with atomic number 88, represented by the symbol Ra. Radium is an almost pure-white alkaline earth metal, but it readily oxidizes on exposure to air, becoming black in color. All isotopes of radium are highly radioactive, with the most stable isotope being radium-226,...
and for their work in radioactivity.
Bombarding curium-242 with α-particles resulted in an isotope of californium 245Cf (1950), and a similar procedure yielded in 1949 berkelium-243 from americium-241. The new elements were named after Berkeley, California
Berkeley, California
Berkeley is a city on the east shore of the San Francisco Bay in Northern California, United States. Its neighbors to the south are the cities of Oakland and Emeryville. To the north is the city of Albany and the unincorporated community of Kensington...
, by analogy with its lanthanide
Lanthanide
The lanthanide or lanthanoid series comprises the fifteen metallic chemical elements with atomic numbers 57 through 71, from lanthanum through lutetium...
homologue terbium
Terbium
Terbium is a chemical element with the symbol Tb and atomic number 65. It is a silvery-white rare earth metal that is malleable, ductile and soft enough to be cut with a knife...
, which was named after the village of Ytterby
Ytterby
Ytterby is a village on the Swedish island of Resarö, in Vaxholm Municipality in the Stockholm archipelago.The name of the village means "outer village", implying that its location is its most noteworthy feature....
in Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
.

Einsteinium and fermium were identified in 1952–1953 in the fallout from the "Ivy Mike
Ivy Mike
Ivy Mike was the codename given to the first United States test of a thermonuclear weapon, in which a major part of the explosive yield came from nuclear fusion. It was detonated on November 1, 1952 by the United States at on Enewetak, an atoll in the Pacific Ocean, as part of Operation Ivy...
" nuclear test (1 November 1952), the first successful test of a hydrogen bomb. Instantaneous exposure of uranium-238 to a large neutron flux resulting from the explosion produced heavy isotopes of uranium, including uranium-253 and uranium-255, and their β-decay
Beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle is emitted from an atom. There are two types of beta decay: beta minus and beta plus. In the case of beta decay that produces an electron emission, it is referred to as beta minus , while in the case of a...
yielded einsteinium-253 and fermium-255. The discovery of the new elements and the new data on neutron capture were initially kept secret on the orders of the U.S. military until 1955 due to Cold War
Cold War
The Cold War was the continuing state from roughly 1946 to 1991 of political conflict, military tension, proxy wars, and economic competition between the Communist World—primarily the Soviet Union and its satellite states and allies—and the powers of the Western world, primarily the United States...
tensions. Nevertheless, the Berkeley team were able to prepare einsteinium and fermium by civilian means, through the neutron bombardment of plutonium-239, and published this work in 1954 with the disclaimer that it was not the first studies that had been carried out on the elements. The "Ivy Mike" studies were declassified and published in 1955. The first significant (submicrograms) amounts of einsteinium were produced in 1961 by Cunningham and colleagues, but this has not been done for fermium yet.
The first isotope of mendelevium, 256Md (half-life 87 min), was synthesized by Albert Ghiorso, Glenn T. Seaborg, Gregory R. Choppin, Bernard G. Harvey and Stanley G. Thompson when they bombarded an 253Es target with alpha particle
Alpha particle
Alpha particles consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium nucleus, which is classically produced in the process of alpha decay, but may be produced also in other ways and given the same name...
s in the 60-inch cyclotron
Cyclotron
In technology, a cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator. In physics, the cyclotron frequency or gyrofrequency is the frequency of a charged particle moving perpendicularly to the direction of a uniform magnetic field, i.e. a magnetic field of constant magnitude and direction...
of Berkeley Radiation Laboratory; this was the first isotope of any element to be synthesized one atom at a time.
There were several attempts to obtain isotopes of nobelium by Swedish (1957) and American (1958) groups, but the first reliable results was the synthesis of 256No by the Russian group (Georgy Flyorov
Georgy Flyorov
Georgy Nikolayevich Flyorov was a prominent Soviet nuclear physicist.-Biography:Flyorov was born in Rostov-on-Don and attended the Leningrad Polytechnic Institute Georgy Nikolayevich Flyorov (March 2, 1913 – November 19, 1990) was a prominent Soviet nuclear physicist.-Biography:Flyorov was born...
et al.) in 1965, as acknowledges by the IUPAC in 1992. In their experiments, Flyorov et al. bombarded uranium-238 with neon-22.
In 1961, Ghiorso et al. obtained the first isotope of lawrencium by irradiating californium (mostly californium-252) with boron-10 and boron-11 ions. The mass number
Mass number
The mass number , also called atomic mass number or nucleon number, is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atomic nucleus. Because protons and neutrons both are baryons, the mass number A is identical with the baryon number B as of the nucleus as of the whole atom or ion...
of this isotope was not clearly established (possibly 258 or 259) at the time. In 1965, 256Lr were synthesized by Flyorov et al. from 243Am and 18O
Oxygen-18
Oxygen-18 is a natural, stable isotope of oxygen and one of the environmental isotopes.18O is an important precursor for the production of fluorodeoxyglucose used in positron emission tomography...
. Thus IUPAC recognized the nuclear physics teams at Dubna and Berkeley as the co-discoverers of lawrencium.
Isotopes
| Isotope | Half-life Half-life Half-life, abbreviated t½, is the period of time it takes for the amount of a substance undergoing decay to decrease by half. The name was originally used to describe a characteristic of unstable atoms , but it may apply to any quantity which follows a set-rate decay.The original term, dating to... |
Probability of spontaneous fission Spontaneous fission Spontaneous fission is a form of radioactive decay characteristic of very heavy isotopes. Because the nuclear binding energy reaches a maximum at a nuclear mass greater than about 60 atomic mass units , spontaneous breakdown into smaller nuclei and single particles becomes possible at heavier masses... , % |
Emission energy, MeV (yield in%) | Specific activity of | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | γ | α, β-particles, Bq/kg | fission, Bq/kg | |||
| 241Am | 432.2(7) years | 4.3(18) | 5.485 (84.8) 5.442 (13.1) 5.388 (1.66) |
0.059 (35.9) 0.026 (2.27) |
1.27 | 546.1 |
| 243Am | 7.37(4) years | 3.7(2) | 5.275 (87.1) 5.233 (11.2) 5.181 (1.36) |
0.074 (67.2) 0.043 (5.9) |
7.39 | 273.3 |
| 242Cm | 162.8(2) days | 6.2(3) | 6.069 (25.92) 6.112 (74.08) |
0.044 (0.04) 0.102 (4) |
1.23 | 7.6 |
| 244Cm | 18.10(2) years | 1.37(3) | 5.762 (23.6) 5.804 (76.4) |
0.043 (0.02) 0.100 (1.5) |
2.96 | 4.1 |
| 245Cm | 8.5(1) years | 6.1(9) | 5.529 (0.58) 5.488 (0.83) 5.361 (93.2) |
0.175 (9.88) 0.133 (2.83) |
6.35 | 3.9 |
| 246Cm | 4.76(4) years | 0.02615(7) | 5.343 (17.8) 5.386 (82.2) |
0.045 (19) | 1.13 | 2.95 |
| 247Cm | 1.56(5) years | — | 5.267 (13.8) 5.212 (5.7) 5.147 (1.2) |
0.402 (72) 0.278 (3.4) |
3.43 | — |
| 248Cm | 3.48(6) years | 8.39(16) | 5.034 (16.52) 5.078 (75) |
— | 1.40 | 1.29 |
| 249Bk | 330(4) days | 4.7(2) | 5.406 (1) 5.378 (2.6) |
0.32 (5.8) | 5.88 | 2.76 |
| 249Cf | 351(2) years | 5.0(4) | 6.193 (2.46) 6.139 (1.33) 5.946 (3.33) |
0.388 (66) 0.333 (14.6) |
1.51 | 7.57 |
| 250Cf | 13.08(9) years | 0.077(3) | 5.988 (14.99) 6.030 (84.6) |
0.043 | 4.04 | 3.11 |
| 251Cf | 900(40) years | ? | 6.078 (2.6) 5.567 (0.9) 5.569 (0.9) |
0.177 (17.3) 0.227 (6.8) |
5.86 | — |
| 252Cf | 2.645(8) years | 3.092(8) | 6.075 (15.2) 6.118 (81.6) |
0.042 (1.4) 0.100 (1.3) |
1.92 | 6.14 |
| 254Cf | 60.5(2) days | ≈100 | 5.834 (0.26) 5.792 (5.3) |
— | 9.75 | 3.13 |
| 253Es | 20.47(3) days | 8.7(3) | 6.540 (0.85) 6.552 (0.71) 6.590 (6.6) |
0.387 (0.05) 0.429 (8) |
9.33 | 8.12 |
| 254Es | 275.7(5) days | < 3 | 6.347 (0.75) 6.358 (2.6) 6.415 (1.8) |
0.042 (100) 0.034 (30) |
6.9 | — |
| 255Es | 39.8(12) days | 0.0041(2) | 6.267 (0.78) 6.401 (7) |
— | 4.38(β) 3.81(α) |
1.95 |
| 255Fm | 20.07(7) hours | 2.4(10) | 7.022 (93.4) 6.963 (5.04) 6.892 (0.62) |
0.00057 (19.1) 0.081 (1) |
2.27 | 5.44 |
| 256Fm | 157.6(13) min | 91.9(3) | 6.872 (1.2) 6.917 (6.9) |
— | 1.58 | 1.4 |
| 257Fm | 100.5(2) days | 0.210(4) | 6.752 (0.58) 6.695 (3.39) 6.622 (0.6) |
0.241 (11) 0.179 (8.7) |
1.87 | 3.93 |
| 256Md | 77(2) min | — | 7.142 (1.84) 7.206 (5.9) |
— | 3.53 | — |
| 257Md | 5.52(5) hours | — | 7.074 (14) | 0.371 (11.7) 0.325 (2.5) |
8.17 | — |
| 258Md | 51.5(3) days | — | 6.73 | — | 3.64 | — |
| 255No | 3.1(2) min | — | 8.312 (1.16) 8.266 (2.6) 8.121 (27.8) |
0.187 (3.4) | 8.78 | — |
| 259No | 58(5) min | — | 7.455 (9.8) 7.500 (29.3) 7.533 (17.3) |
— | 4.63 | — |
| 256Lr | 27(3) s | < 0.03 | 8.319 (5.4) 8.390 (16) 8.430 (33) |
— | 5.96 | — |
| 257Lr | 646(25) ms | — | 8.796 (18) 8.861 (82) |
— | 1.54 | — |
Isotopes of actinium
Actinium has no stable isotopes, thus a standard atomic mass cannot be given. There are 31 known isotopes, from 206Ac to 236Ac, and 2 isomers. Two isotopes are found in nature, 227Ac and 228Ac, as intermediate decay products of, respectively, 235U and 238U...
and eight excited isomeric states of some of its nuclide
Nuclide
A nuclide is an atomic species characterized by the specific constitution of its nucleus, i.e., by its number of protons Z, its number of neutrons N, and its nuclear energy state....
s were identified by 2010. Three isotopes, 225Ac, 227Ac and 228Ac, were found in nature and the others were produced in the laboratory; only the three natural isotopes are used in applications. Actinium-225 is a member of radioactive neptunium series; it was first discovered in 1947 as a fission product of uranium-233
Uranium-233
Uranium-233 is a fissile isotope of uranium, bred from Thorium as part of the thorium fuel cycle. It has been used in a few nuclear reactors and has been proposed for much wider use as a nuclear fuel. It has a half-life of 160,000 years....
, it is an α-emitter with a half-life of 10 days. Actinium-225 is less available than actinium-228, but is more promising in radiotracer applications. Actinium-227 (half-life 21.77 years) occurs in all uranium ores, but in small quantities. One gram of uranium (in radioactive equilibrium) contains only 2 gram of 227Ac. Actinium-228 is a member of radioactive thorium series formed by the decay of 228Ra; it is a β– emitter with a half-life of 6.15 hours. In one tonne of thorium there is 5 gram of 228Ac. It was discovered by Otto Hahn
Otto Hahn
Otto Hahn FRS was a German chemist and Nobel laureate, a pioneer in the fields of radioactivity and radiochemistry. He is regarded as "the father of nuclear chemistry". Hahn was a courageous opposer of Jewish persecution by the Nazis and after World War II he became a passionate campaigner...
in 1906.
Twenty nine isotopes of protactinium
Isotopes of protactinium
Protactinium has no stable isotopes. There are three naturally occurring isotopes, allowing a standard mass to be given.Standard atomic mass: 231.03588 u...
are known with mass numbers 212–240 as well as three excited isomeric states. Only 231Pa and 234Pa have been found in nature. All the isotopes have short lifetime, except for protactinium-231 (half-life 32,760 years). The most important isotopes are 231Pa and 233Pa, which is an intermediate product in obtaining uranium-233 and is the most affordable among artificial isotopes of protactinium. 233Pa has convenient half-life and energy of γ-radiation, and thus was used in most studies of protactinium chemistry. Protactinium-233 is a β-emitter with a half-life of 26.97 days.
Uranium has the highest number (25) of both natural and synthetic isotopes
Isotopes of uranium
Uranium is a naturally occurring radioactive element that has no stable isotopes but two primordial isotopes that have long half-life and are found in appreciable quantity in the Earth's crust, along with the decay product uranium-234. The average atomic mass of natural uranium is 238.02891 u...
. They have mass numbers of 217–242, and three of them, 234U, 235U and 238U, are present in appreciable quantities in nature. Among others, the most important is 233U, which is a final product of transformations of 232Th irradiated by slow neutrons. 233U has a very higher fission efficiency by low-energy (thermal) neutrons, compared e.g. with 235U. Most uranium chemistry studies were carried out on uranium-238 owing to its long half-life of 4.4 years.
There are 19 isotopes of neptunium
Isotopes of neptunium
Neptunium is an artificial element, and thus a standard atomic mass cannot be given. Like all artificial elements, it has no stable isotopes...
with mass numbers from 225 to 244; they are all highly radioactive. The most popular among scientists are long-lived 237Np (t½ = 2.20 years) and short-lived 239Np, 238Np (t½ ~ 2 days).
Sixteen isotopes of americium
Isotopes of americium
Americium is an artificial element, and thus a standard atomic mass cannot be given. Like all artificial elements, it has no stable isotopes. The first isotope to be synthesized was 241Am in 1944....
are known with mass numbers from 232 to 248. The most important are 241Am and 243Am, which are alpha-emitters and also emit soft, but intense γ-rays; both of them can be obtained in an isotopically pure form. Chemical properties of americium were first studied with 241Am, but later shifted to 243Am, which is almost 20 times less radioactive. The disadvantage of 243Am is production of the short-lived daughter isotope 239Np, which has to be considered in the data analysis.
Among 19 isotopes of curium
Isotopes of curium
Curium is an artificial element, and thus a standard atomic mass cannot be given. Like all artificial elements, it has no stable isotopes. The first isotope synthesized was 242Cm in 1944....
, the most accessible are 242Cm and 244Cm; they are α-emitters, but with much shorter lifetime than the americium isotopes. These isotopes emit almost no γ-radiation, but undergo spontaneous fission
Spontaneous fission
Spontaneous fission is a form of radioactive decay characteristic of very heavy isotopes. Because the nuclear binding energy reaches a maximum at a nuclear mass greater than about 60 atomic mass units , spontaneous breakdown into smaller nuclei and single particles becomes possible at heavier masses...
with the associated emission of neutrons. More long-lived isotopes of curium (245–248Cm, all α-emitters) are formed as a mixture during neutron irradiation of plutonium or americium. Upon short irradiation, this mixture is dominated by curium-246, and then curium-248 begins to accumulate. Both of these isotopes, especially 248Cm, have a longer half-life (3.48 years) and are much more convenient for carrying out chemical research than 242Cm and 244Cm, but they also have a rather high rate of spontaneous fission. 247Cm has the longest lifetime among isotopes of curium (1.56 years), but is not formed in large quantities because of the strong fission induced by thermal neutrons.
Fourteen isotopes of berkelium
Isotopes of berkelium
Berkelium is an artificial element, and thus a standard atomic mass cannot be given. Like all artificial elements, it has no stable isotopes. The first isotope to be synthesized was 243Bk in 1949. There are 20 known radioisotopes, from 235Bk to 254Bk, and 6 nuclear isomers...
were identified with mass numbers 238–252. Only 249Bk is available in large quantities; it has a relatively short half-life of 330 days and emits mostly soft β-particles
Beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle is emitted from an atom. There are two types of beta decay: beta minus and beta plus. In the case of beta decay that produces an electron emission, it is referred to as beta minus , while in the case of a...
, which are inconvenient for detection. Its alpha radiation is rather weak (1.45% with respect to β-radiation), but is sometimes used to detect this isotope. 247Bk is an alpha-emitter with a long half-life of 1,380 years, but it is hard to obtain in appreciable quantities; it is not formed upon neutron irradiation of plutonium because of the β-stability of isotopes of curium isotopes with mass number below 248.
Isotopes of californium
Isotopes of californium
Californium is an artificial element, and thus a standard atomic mass cannot be given. Like all artificial elements, it has no stable isotopes. The first isotope to be synthesized was 245Cf in 1950. There are 20 known radioisotopes ranging from 237Cf to 256Cf and one nuclear isomer, 249mCf...
with mass numbers 237–256 are formed in nuclear reactors; californium-253 is a β-emitter and the rest are α-emitters. The isotopes with even mass numbers (250Cf, 252Cf and 254Cf) have a high rate of spontaneous fission, especially 254Cf of which 99.7% decays by spontaneous fission. Californium-249 has a relatively long half-life (352 years), weak spontaneous fission and strong γ-emission that facilitates its identification. 249Cf is not formed in large quantities in a nuclear reactor because of the slow β-decay of the parent isotope 249Bk and a large cross section of interaction with neutrons, but it can be accumulated in the isotopically pure form as the β-decay product of (pre-selected) 249Bk. Californium produced by reactor-irradiation of plutonium mostly consists of 250Cf and 252Cf, the latter being predominant for large neutron fluences, and its study is hindered by the strong neutron radiation.
| Parent isotope |
t½ | Daughter isotope |
t½ | Time to establish radioactive equilibrium |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 243Am | 7370 years | 239Np | 2.35 days | 47.3 days |
| 245Cm | 8265 years | 241Pu | 14 years | 129 years |
| 247Cm | 1.64 years | 243Pu | 4.95 hours | 7.2 days |
| 254Es | 270 days | 250Bk | 3.2 hours | 35.2 hours |
| 255Es | 39.8 days | 255Fm | 22 hours | 5 days |
| 257Fm | 79 days | 253Cf | 17.6 days | 49 days |
Among the 16 known isotopes of einsteinium
Isotopes of einsteinium
Einsteinium is an artificial element, and thus a standard atomic mass cannot be given. Like all artificial elements, it has no stable isotopes. The first isotope to be discovered was 253Es in 1952...
with mass numbers from 241 to 257 the most affordable is 253Es. It is an α-emitter with a half-life of 20.47 days, a relatively weak γ-emission and small spontaneous fission rate as compared with the isotopes of californium. Prolonged neutron irradiation also produces a long-lived isotope 254Es (t½ = 275.5 days).
Nineteen isotopes of fermium
Isotopes of fermium
Fermium is an artificial element, and thus a standard atomic mass cannot be given. Like all artificial elements, it has no stable isotopes. The first isotope to be discovered was 255Fm in 1952. 250Fm was independently synthesized shortly after the discovery of 255Fm...
are known with mass numbers of 242–260. 254Fm, 255Fm and 256Fm are α-emitters with a short half-life (hours), which can be isolated in significant amounts. 257Fm (t½ = 100 days) can accumulate upon prolonged and strong irradiation. All these isotopes are characterized by high rates of spontaneous fission.
Among the 15 known isotopes of mendelevium
Isotopes of mendelevium
Mendelevium is an artificial element, and thus a standard atomic mass cannot be given. Like all artificial elements, it has no stable isotopes. The first isotope to be synthesized was 256Md in 1955. There are 18 known radioisotopes, ranging in atomic mass from 245Md to 262Md, and 5 isomers...
(mass numbers from 245 to 260), the most studied is 256Md, which mainly decays through the electron capture (α-radiation is ≈10%) with the half-life of 77 minutes. Another alpha emitter, 258Md, has a half-life of 53 days. Both these isotopes are produced from rare einsteinium (253Es and 255Es respectively), that limits their so their availability.
Long-lived isotopes of nobelium
Isotopes of nobelium
Nobelium is an artificial element, and thus a standard atomic mass cannot be given. Like all artificial elements, it has no stable isotopes. The first isotope to be synthesized was 254No in 1966. There are 16 known radioisotopes which are 248No and 250No to 264No, and 3 isomers, 251mNo, 253mNo,...
and isotopes of lawrencium
Isotopes of lawrencium
Lawrencium is an artificial element, and thus a standard atomic mass cannot be given. Like all artificial elements, it has no stable isotopes. The first isotope to be synthesized was 258Lr in 1961. There are eleven known radioisotopes from 252Lr to 262Lr, and 1 isomer . The longest-lived isotope...
(and of heavier elements) have relatively small half-lives. For nobelium 11 isotopes are known with mass numbers 250–260 and 262. Chemical properties of nobelium and lawrencium were studied with 255No (t½ = 3 min) and 256Lr (t½ = 35 s). The longest-lived nobelium isotope 259No has a half-life of 1.5 hours.
Distribution in nature
Thorium and uranium are the most abundant actinides in nature with the respective mass concentrations of 1.6% and 4%. Uranium mostly occurs in the Earth's crust as a mixture of its oxides in the minerals uraniniteUraninite
Uraninite is a radioactive, uranium-rich mineral and ore with a chemical composition that is largely UO2, but also contains UO3 and oxides of lead, thorium, and rare earth elements...
, which is also called pitchblende because of its black color. There are several dozens of other uranium minerals such as carnotite
Carnotite
Carnotite is a potassium uranium vanadate radioactive mineral with chemical formula: K222·3H2O. The water content can vary and small amounts of calcium, barium, magnesium, iron, and sodium are often present.-Occurrence:...
(KUO2VO4·3H2O) and autunite
Autunite
Autunite with formula: Ca22·10-12H2O is a yellow - greenish fluorescent mineral with a hardness of 2 - 2½. Autunite crystallizes in the tetragonal system and often occurs as tabular square crystals. Due to the moderate uranium content of 48.27% it is radioactive and also used as uranium ore...
(Ca(UO2)2(PO4)2·nH2O). The isotopic composition of natural uranium is 238U
Uranium-238
Uranium-238 is the most common isotope of uranium found in nature. It is not fissile, but is a fertile material: it can capture a slow neutron and after two beta decays become fissile plutonium-239...
(relative abundance 99.2742%), 235U
Uranium-235
- References :* .* DOE Fundamentals handbook: Nuclear Physics and Reactor theory , .* A piece of U-235 the size of a grain of rice can produce energy equal to that contained in three tons of coal or fourteen barrels of oil. -External links:* * * one of the earliest articles on U-235 for the...
(0.7204%) and 234U (0.0054%); of these 238U has the largest half-life of 4.51 years. The worldwide production of uranium in 2009 amounted to 50,572 tonne
Tonne
The tonne, known as the metric ton in the US , often put pleonastically as "metric tonne" to avoid confusion with ton, is a metric system unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. The tonne is not an International System of Units unit, but is accepted for use with the SI...
s, of which 27.3% was mined in Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan , officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country in Central Asia and Eastern Europe. Ranked as the ninth largest country in the world, it is also the world's largest landlocked country; its territory of is greater than Western Europe...
. Other important uranium mining countries are Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
(20.1%), Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
(15.7%), Namibia
Namibia
Namibia, officially the Republic of Namibia , is a country in southern Africa whose western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Angola and Zambia to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and east. It gained independence from South Africa on 21 March...
(9.1%), Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
(7.0%), and Niger
Niger
Niger , officially named the Republic of Niger, is a landlocked country in Western Africa, named after the Niger River. It borders Nigeria and Benin to the south, Burkina Faso and Mali to the west, Algeria and Libya to the north and Chad to the east...
(6.4%).
| Ore | Location | Uranium content, % |
Mass ratio 239Pu/ore |
239Pu/U |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Uraninite Uraninite Uraninite is a radioactive, uranium-rich mineral and ore with a chemical composition that is largely UO2, but also contains UO3 and oxides of lead, thorium, and rare earth elements... |
Canada | 13.5 | 9.1 | 7.1 |
| Uraninite | Congo | 38 | 4.8 | 12 |
| Uraninite | Colorado Colorado Colorado is a U.S. state that encompasses much of the Rocky Mountains as well as the northeastern portion of the Colorado Plateau and the western edge of the Great Plains... , US |
50 | 3.8 | 7.7 |
| Monazite Monazite Monazite is a reddish-brown phosphate mineral containing rare earth metals. It occurs usually in small isolated crystals. There are actually at least four different kinds of monazite, depending on relative elemental composition of the mineral:... |
Brazil | 0.24 | 2.1 | 8.3 |
| Monazite | North Carolina North Carolina North Carolina is a state located in the southeastern United States. The state borders South Carolina and Georgia to the south, Tennessee to the west and Virginia to the north. North Carolina contains 100 counties. Its capital is Raleigh, and its largest city is Charlotte... , US |
1.64 | 5.9 | 3.6 |
| Fergusonite Fergusonite Fergusonite is a mineral comprising a complex oxide of various rare earth elements. The chemical formula of fergusonite species is NbO4, where RE = rare-earth elements in solid solution with Y. Yttrium is usually dominant , but sometimes Ce or Nd may predominate in molar proportion... |
||||
| 0.25 | <1 | <4 | ||
| Carnotite Carnotite Carnotite is a potassium uranium vanadate radioactive mineral with chemical formula: K222·3H2O. The water content can vary and small amounts of calcium, barium, magnesium, iron, and sodium are often present.-Occurrence:... |
||||
| 10 | <4 | <0.4 |
The most abundant thorium minerals are thorianite
Thorianite
Thorianite is a rare mineral, originally discovered by Ananda Coomaraswamy in 1904 as uraninite, but recognized as a new species by Wyndham R. Dunstan. It was so named on account of its high percentage of thorium ; it also contains the oxides of uranium, lanthanum, cerium and didymium...
(ThO2), thorite
Thorite
Thorite, SiO4, is a rare nesosilicate of thorium that crystallizes in the tetragonal system and is isomorphous with zircon and hafnon. It is the most common mineral of thorium and is nearly always strongly radioactive. It was named in 1829 to reflect its thorium content...
(ThSiO4) and monazite
Monazite
Monazite is a reddish-brown phosphate mineral containing rare earth metals. It occurs usually in small isolated crystals. There are actually at least four different kinds of monazite, depending on relative elemental composition of the mineral:...
, ((Th,Ca,Ce)PO4). Most thorium minerals contain uranium and vice versa; and they all have significant fraction of lanthanides. Rich deposits of thorium minerals are located in the United States (440,000 tonnes), Australia and India (~300,000 tonnes each) and Canada (~100,000 tonnes).
The abundance of actinium in the Earth's crust is only about 5%. Actinium is mostly present in uranium-containing, but also in other minerals, though in much smaller quantities. The content of actinium in most natural objects corresponds to the isotopic equilibrium of parent isotope 235U, and it is not affected by the weak Ac migration. Protactinium is more abundant (10−12%) in the Earth's crust than actinium. It was discovered in the uranium ore in 1913 by Fajans and Göhring. As actinium, the distribution of protactinium follows that of 235U.
The half-life of the longest-lived isotope of neptunium, 237Np, is negligible compared to the age of the Earth. Thus neptunium is present in nature in negligible amounts produced as intermediate decay products of other isotopes. Traces of plutonium in uranium minerals were first found in 1942, and the more systematic results on 239Pu are summarized in the table (no other plutonium isotopes could be detected in those samples). The upper limit of abundance of the longest-living isotope of plutonium, 244Pu, is 3%. Plutonium could not be detected in samples of lunar soil. Owing to its scarcity in nature, most plutonium is produced synthetically.
Extraction

Fluoride
Fluoride is the anion F−, the reduced form of fluorine when as an ion and when bonded to another element. Both organofluorine compounds and inorganic fluorine containing compounds are called fluorides. Fluoride, like other halides, is a monovalent ion . Its compounds often have properties that are...
s of actinides are usually used because they are insoluble in water and can be easily separated with redox
Redox
Redox reactions describe all chemical reactions in which atoms have their oxidation state changed....
reactions. Fluorides are reduced with calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
, magnesium
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole...
or barium
Barium
Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in Group 2, a soft silvery metallic alkaline earth metal. Barium is never found in nature in its pure form due to its reactivity with air. Its oxide is historically known as baryta but it reacts with...
:
Among the actinides, thorium and uranium are the easiest to isolate. Thorium is extracted mostly from monazite
Monazite
Monazite is a reddish-brown phosphate mineral containing rare earth metals. It occurs usually in small isolated crystals. There are actually at least four different kinds of monazite, depending on relative elemental composition of the mineral:...
: thorium diphosphate (Th(PO4)2) is reacted with nitric acid
Nitric acid
Nitric acid , also known as aqua fortis and spirit of nitre, is a highly corrosive and toxic strong acid.Colorless when pure, older samples tend to acquire a yellow cast due to the accumulation of oxides of nitrogen. If the solution contains more than 86% nitric acid, it is referred to as fuming...
, and the produced thorium nitrate treated with tributyl phosphate
Tributyl phosphate
Tributyl phosphate, known commonly as TBP, is an organophosphorus compound with the formula 3PO. This colourless, odorless liquid finds some applications as an extractant and a plasticizer. It is an ester of orthophosphoric acid with n-butanol.- Production :Tributyl phosphate is manufactured by...
. Rare-earth
Rare earth element
As defined by IUPAC, rare earth elements or rare earth metals are a set of seventeen chemical elements in the periodic table, specifically the fifteen lanthanides plus scandium and yttrium...
impurities are separated by increasing the pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
in sulfate solution.
In another extraction method, monazite is decomposed with a 45% aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide at 140 °C. Mixed metal hydroxides are extracted first, filtered at 80 °C, washed with water and dissolved with concentrated hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid
Hydrochloric acid is a solution of hydrogen chloride in water, that is a highly corrosive, strong mineral acid with many industrial uses. It is found naturally in gastric acid....
. Next, the acidic solution is neutralized with hydroxides to pH = 5.8 that results in precipitation of thorium hydroxide (Th(OH)4) contaminated with ~3% of rare-earth hydroxides; the rest of rare-earth hydroxides remains in solution. Thorium hydroxide is dissolved in an inorganic acid and then purified from the rare earth element
Rare earth element
As defined by IUPAC, rare earth elements or rare earth metals are a set of seventeen chemical elements in the periodic table, specifically the fifteen lanthanides plus scandium and yttrium...
s. An efficient method is the dissolution of thorium hydroxide in nitric acid, because the resulting solution can be purified by extraction
Liquid-liquid extraction
Liquid–liquid extraction, also known as solvent extraction and partitioning, is a method to separate compounds based on their relative solubilities in two different immiscible liquids, usually water and an organic solvent. It is an extraction of a substance from one liquid phase into another liquid...
with organic solvents:
Th(OH)4 + 4 HNO3 → Th(NO3)4 + 4 H2O
Metallic thorium is separated from the anhydrous oxide, chloride or fluoride by reacting it with calcium in an inert atmosphere:
ThO2 + 2 Ca → 2 CaO + Th
Sometimes thorium is extracted by electrolysis
Electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a method of using a direct electric current to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction...
of a fluoride in a mixture of sodium and potassium chloride at 700–800 °C in a graphite
Graphite
The mineral graphite is one of the allotropes of carbon. It was named by Abraham Gottlob Werner in 1789 from the Ancient Greek γράφω , "to draw/write", for its use in pencils, where it is commonly called lead . Unlike diamond , graphite is an electrical conductor, a semimetal...
crucible. Highly pure thorium can be extracted from its iodide with the crystal bar process
Crystal bar process
The crystal bar process was developed by Anton Eduard van Arkel and Jan Hendrik de Boer in 1925. This process was the first industrial process for the commercial production of pure ductile metallic zirconium. It is used in the production of small quantities of ultra-pure titanium and zirconium...
.
Uranium is extracted from its ores in various ways. In one method, the ore is burned and then reacted with nitric acid to convert uranium into a dissolved state. Treating the solution with a solution of tributyl phosphate (TBP) in kerosene transforms uranium into an organic form UO2(NO3)2(TBP)2. The insoluble impurities are filtered and the uranium is extracted by reaction with hydroxides as (NH4)2U2O7 or with hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is the simplest peroxide and an oxidizer. Hydrogen peroxide is a clear liquid, slightly more viscous than water. In dilute solution, it appears colorless. With its oxidizing properties, hydrogen peroxide is often used as a bleach or cleaning agent...
as UO4·2H2O.
When the uranium ore is rich in such minerals as dolomite
Dolomite
Dolomite is a carbonate mineral composed of calcium magnesium carbonate CaMg2. The term is also used to describe the sedimentary carbonate rock dolostone....
, magnesite
Magnesite
Magnesite is magnesium carbonate, MgCO3. Iron substitutes for magnesium with a complete solution series with siderite, FeCO3. Calcium, manganese, cobalt, and nickel may also occur in small amounts...
, etc., those minerals consume much acid. In this case, the carbonate method is used for uranium extraction. Its main component is an aqueous solution of sodium carbonate
Sodium carbonate
Sodium carbonate , Na2CO3 is a sodium salt of carbonic acid. It most commonly occurs as a crystalline heptahydrate, which readily effloresces to form a white powder, the monohydrate. Sodium carbonate is domestically well-known for its everyday use as a water softener. It can be extracted from the...
, which converts uranium into a complex [UO2(CO3)3]4–, which is stable in aqueous solutions at low concentrations of hydroxide ions. The advantages of the sodium carbonate method are that the chemicals have low corrosivity
Corrosion
Corrosion is the disintegration of an engineered material into its constituent atoms due to chemical reactions with its surroundings. In the most common use of the word, this means electrochemical oxidation of metals in reaction with an oxidant such as oxygen...
(compared to nitrates) and that most non-uranium metals precipitate from the solution. The disadvantage is that tetravalent uranium compounds precipitate as well. Therefore, the uranium ore is treated with sodium carbonate at elevated temperature and under oxygen pressure:
- 2 UO2 + O2 + 6 CO32– → 2 [UO2(CO3)3]4–
This equation suggests that the best solvent for the uranium carbonate processing is a mixture of carbonate with bicarbonate. At high pH, this results in precipitation of diuranate, which is treated with hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
in the presence of nickel
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile...
yielding an insoluble uranium tetracarbonate.
Another separation method uses polymeric resins as a polyelectrolyte
Polyelectrolyte
Polyelectrolytes are polymers whose repeating units bear an electrolyte group. These groups will dissociate in aqueous solutions , making the polymers charged. Polyelectrolyte properties are thus similar to both electrolytes and polymers , and are sometimes called polysalts. Like salts, their...
. Ion exchange processes in the resins result in separation of uranium. Uranium from resins is washed with a solution of ammonium nitrate or nitric acid that yields uranyl
Uranyl
The uranyl ion is an oxycation of uranium in the oxidation state +6, with the chemical formula [UO2]2+. It has a linear structure with short U-O bonds, indicative of the presence of multiple bonds between uranium and oxygen. Four or more ligands are bound to the uranyl ion in an equatorial plane...
nitrate, UO2(NO3)2·6H2O. When heated, it turns into UO3, which is converted to UO2 with hydrogen:
- UO3 + H2 → UO2 + H2O
Reacting uranium dioxide with fluoric acid changes it to uranium tetrafluoride
Uranium tetrafluoride
Uranium tetrafluoride is a green crystalline solid compound of uranium with an insignificant vapor pressure and very slight solubility in water. Uranium in its tetravalent state is very important in different technological processes...
, which yields uranium metal upon reaction with magnesium metal:
- 4 HF + UO2 → UF4 + 2 H2O
To extract plutonium, neutron-irradiated uranium is dissolved in nitric acid, and a reducing agent (FeSO4
Iron(II) sulfate
Iron sulfate or ferrous sulfate is the chemical compound with the formula FeSO4. Known since ancient times as copperas and as green vitriol, the blue-green heptahydrate is the most common form of this material...
, or H2O2
Hydrogen peroxide
Hydrogen peroxide is the simplest peroxide and an oxidizer. Hydrogen peroxide is a clear liquid, slightly more viscous than water. In dilute solution, it appears colorless. With its oxidizing properties, hydrogen peroxide is often used as a bleach or cleaning agent...
) is added to the resulting solution. This addition changes the oxidation state of plutonium from +6 to +4, while uranium remains in the form of uranyl nitrate (UO2(NO3)2). The solution is treated with a reducing agent and neutralized with ammonium carbonate
Ammonium carbonate
Ammonium carbonate is a commercial salt with the chemical formula 2CO3. It is used when crushed as a smelling salt. It can be crushed when needed in order to revive someone who has fainted...
to pH = 8 that results in precipitation of Pu4+ compounds.
In another method, Pu4+and UO22+ are first extracted with tributyl phosphate, then reacted with hydrazine
Hydrazine
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the formula N2H4. It is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odor. Hydrazine is highly toxic and dangerously unstable unless handled in solution. Approximately 260,000 tons are manufactured annually...
washing out the recovered plutonium.
The major difficulty in separation of actinium is the similarity of its properties with those of lanthanum. Thus actinium is either synthesized in nuclear reactions from isotopes of radium or separated using ion-exchange procedures.
Properties
Actinides have similar properties to lanthanides. The 6dD-block
The d-block is the portion of the periodic table that contains the element groups 3-12. These groups correspond to the filling of the atomic d-orbital subshell, with electron configurations ranging from s2d1 to s2d10...
and 7s
S-block
The s-block of the periodic table of elements consists of the first two groups: the alkali metals and alkaline earth metals, plus hydrogen and helium.Except in hydrogen and helium, these electrons are very easily lost to form positive ions...
electronic shells are completed in actinium and thorium, and the 5f shell
F-block
The f-block of the periodic table of the elements consists of those elements whose atoms or ions have valence electrons in f-orbitals. Actual electronic configurations may be slightly different from what is predicted by the Aufbau principle...
is being filled with further increase in atomic number; the 4f shell is filled in the lanthanides. The first experimental evidence for the filling of the 5f shell in actinides was obtained by McMillan and Abelson in 1940. As in lanthanides (see lanthanide contraction
Lanthanide contraction
Lanthanide contraction is a term used in chemistry to describe the decrease in ionic radii of the elements in the lanthanide series from atomic number 58, Cerium to 71, Lutetium, which results in smaller than otherwise expected ionic radii for the subsequent elements starting with 72, Hafnium...
), the ionic radius
Ionic radius
Ionic radius, rion, is the radius of an atom's ion. Although neither atoms nor ions have sharp boundaries, it is important to treat them as if they are hard spheres with radii such that the sum of ionic radii of the cation and anion gives the distance between the ions in a crystal lattice...
of actinides monotonically decreases with atomic number (see also Aufbau principle
Aufbau principle
The Aufbau principle is used to determine the electron configuration of an atom, molecule or ion. The principle postulates a hypothetical process in which an atom is "built up" by progressively adding electrons...
).
| Property | Ac | Th | Pa | U | Np | Pu | Am | Cm | Bk | Cf | Es | Fm | Md | No | Lr |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core charge | 89 | 90 | 91 | 92 | 93 | 94 | 95 | 96 | 97 | 98 | 99 | 100 | 101 | 102 | 103 |
| atomic mass | [227] | 232.0381 | 231.03588 | 238.02891 | [237] | [244] | [243] | [247] | [247] | [251] | [252] | [257] | [258] | [259] | [262] |
| Number of natural isotopes | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | — |
| Longest-lived isotope | 227 | 232 | 231 | 238 | 237 | 244 | 243 | 247 | 247 | 251 | 252 | 257 | 258 | 259 | 262 |
| Half-life Half-life Half-life, abbreviated t½, is the period of time it takes for the amount of a substance undergoing decay to decrease by half. The name was originally used to describe a characteristic of unstable atoms , but it may apply to any quantity which follows a set-rate decay.The original term, dating to... of the longest-lived isotope |
21.8 years | 14 billion years | 32,500 years | 4.47 billion years | 2.14 million years | 80.8 million years | 7,370 years | 15.6 million years | 1,400 years | 900 years | 1.29 years | 100.5 days | 52 days | 58 min | 261 min |
| Electronic configuration in the ground state | 6d17s2 | 6d27s2 | 5f26d17s2or 5f16d27s2 | 5f36d17s2 | 5f46d17s2or 5f57s2 | 5f67s2 | 5f77s2 | 5f76d17s2 | 5f97s2or 5f86d17s2 | 5f107s2 | 5f117s2 | 5f127s2 | 5f137s2 | 5f147s2 | 5f147s27p1 |
| Oxidation state | 3 | 3, 4 | 3, 4, 5 | 3, 4, 5, 6 | 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 | 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 | 2, 3, 4 | 3, 4 | 3, 4 | 2, 3 | 2, 3 | 2, 3 | 2, 3 | 2, 3 | 3 |
| Metallic radius, nm | 0.203 | 0.180 | 0.162 | 0.153 | 0.150 | 0.162 | 0.173 | 0.174 | 0.170 | 0.186 | 0.186 | — | — | — | — |
| Ionic radius, nm: An4+ An3+ |
— 0.126 |
0.114 — |
0.104 0.118 |
0.103 0.118 |
0.101 0.116 |
0.100 0.115 |
0.099 0.114 |
0.099 0.112 |
0.097 0.110 |
0.096 0.109 |
0.085 0.098 |
0.084 0.091 |
0.084 0.090 |
0.084 0.095 |
0.083 0.088 |
| Temperature, °C: melting boiling |
1050 3300 |
1750 4800 |
1572 4400 |
1130 3800 |
640 3900 |
640 3230 |
1176 2610 |
1340 — |
1050 — |
900 — |
860 — |
1530 — |
830 — |
830 — |
1630 — |
| Density, g/cm3 | 10.07 | 11.78 | 15.37 | 19.06 | 20.25 | 19.84 | 11.7 | 13.51 | 14.78 | ||||||
| Standard electrode potential, V: E° (An4+/An0) E° (An3+/An0) |
— −2.13 |
−1.83 — |
−1.47 — |
−1.38 −1.66 |
−1.30 −1.79 |
−1.25 −2.00 |
−0.90 −2.07 |
−0.75 −2.06 |
−0.55 −1.96 |
−0.59 −1.97 |
−0.36 −1.98 |
−0.29 −1.96 |
— −1.74 |
— −1.20 |
- −2.10 |
| Color [M(H2O)n]4+ [M(H2O)n]3+ |
— Colorless |
Colorless Blue |
Yellow Dark blue |
Green Purple |
Yellow-green Purple |
Brown Violet |
Red Rose |
Yellow Colorless |
Beige Beige Beige may be described as an off tan color or an extremely pale brown color.The term originates from beige cloth, a cotton fabric left undyed in its natural color... Yellow-green |
Green Green |
— Pink |
— — |
— — |
— — |
— — |
| Oxidation state | 89 | 90 | 91 | 92 | 93 | 94 | 95 | 96 | 97 | 98 | 99 |
| +3 | Ac3+ | Th3+ | Pa3+ | U3+ | Np3+ | Pu3+ | Am3+ | Cm3+ | Bk3+ | Cf3+ | Es3+ |
| +4 | Th4+ | Pa4+ | U4+ | Np4+ | Pu4+ | Am4+ | Cm4+ | Bk4+ | Cf4+ | ||
| +5 | PaO2+ | UO2+ | NpO2+ | PuO2+ | AmO2+ | ||||||
| +6 | UO22+ | NpO22+ | PuO22+ | AmO22+ | |||||||
| +7 | NpO23+ | PuO23+ | [AmO6]5- |
Physical properties
| Major crystal structures of some actinides vs. temperature | Metallic Metallic bond Metallic bonding is the electrostatic attractive forces between the delocalized electrons, called conduction electrons, gathered in an "electron sea", and the positively charged metal ions... and ionic Ionic radius Ionic radius, rion, is the radius of an atom's ion. Although neither atoms nor ions have sharp boundaries, it is important to treat them as if they are hard spheres with radii such that the sum of ionic radii of the cation and anion gives the distance between the ions in a crystal lattice... radii of actinides |

Metal
A metal , is an element, compound, or alloy that is a good conductor of both electricity and heat. Metals are usually malleable and shiny, that is they reflect most of incident light...
s. All of them are soft and have a silvery color (but tarnish in air), relatively high density
Density
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
and plasticity. Some of them can be cut with a knife. Their electrical resistivity varies between 15 and 150 µOhm·cm. The hardness of thorium is similar to that of soft steel
Steel
Steel is an alloy that consists mostly of iron and has a carbon content between 0.2% and 2.1% by weight, depending on the grade. Carbon is the most common alloying material for iron, but various other alloying elements are used, such as manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten...
, so heated pure thorium can be rolled in sheets and pulled into wire. Thorium is nearly half as dense as uranium and plutonium, but is harder than either of them. All actinides are radioactive, paramagnetic
Paramagnetism
Paramagnetism is a form of magnetism whereby the paramagnetic material is only attracted when in the presence of an externally applied magnetic field. In contrast with this, diamagnetic materials are repulsive when placed in a magnetic field...
, and, with the exception of actinium, have several crystalline phases: plutonium has seven, and uranium, neptunium and californium three. Crystal structure
Crystal structure
In mineralogy and crystallography, crystal structure is a unique arrangement of atoms or molecules in a crystalline liquid or solid. A crystal structure is composed of a pattern, a set of atoms arranged in a particular way, and a lattice exhibiting long-range order and symmetry...
s of protactinium, uranium, neptunium and plutonium do not have clear analogs among the lanthanide and are more similar to those of the 3d-transition metal
Transition metal
The term transition metal has two possible meanings:*The IUPAC definition states that a transition metal is "an element whose atom has an incomplete d sub-shell, or which can give rise to cations with an incomplete d sub-shell." Group 12 elements are not transition metals in this definition.*Some...
s.
All actinides are pyrophoric
Pyrophoricity
A pyrophoric substance is a substance that will ignite spontaneously in air. Examples are iron sulfide and many reactive metals including uranium, when powdered or sliced thin. Pyrophoric materials are often water-reactive as well and will ignite when they contact water or humid air...
, especially when finely divided, that is, they spontaneously ignite upon reaction with air. The melting point
Melting point
The melting point of a solid is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard atmospheric pressure...
of actinides does not have a clear dependence on the number of f-electrons. The unusually low melting point of neptunium and plutonium (~640 °C) is explained by hybridization of 5f and 6d orbitals and the formation of directional bonds in these metals.
| Lanthanides | Ln3+, Å | Actinides | An3+, Å | An4+, Å |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lanthanum Lanthanum Lanthanum is a chemical element with the symbol La and atomic number 57.Lanthanum is a silvery white metallic element that belongs to group 3 of the periodic table and is the first element of the lanthanide series. It is found in some rare-earth minerals, usually in combination with cerium and... |
1.061 | Actinium Actinium Actinium is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol Ac and atomic number 89, which was discovered in 1899. It was the first non-primordial radioactive element to be isolated. Polonium, radium and radon were observed before actinium, but they were not isolated until 1902... |
1.11 | – |
| Cerium Cerium Cerium is a chemical element with the symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a soft, silvery, ductile metal which easily oxidizes in air. Cerium was named after the dwarf planet . Cerium is the most abundant of the rare earth elements, making up about 0.0046% of the Earth's crust by weight... |
1.034 | Thorium Thorium Thorium is a natural radioactive chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. It was discovered in 1828 and named after Thor, the Norse god of thunder.... |
1.08 | 0.99 |
| Praseodymium Praseodymium Praseodymium is a chemical element that has the symbol Pr and atomic number 59. Praseodymium is a soft, silvery, malleable and ductile metal in the lanthanide group. It is too reactive to be found in native form, and when artificially prepared, it slowly develops a green oxide coating.The element... |
1.013 | Protactinium Protactinium Protactinium is a chemical element with the symbol Pa and atomic number 91. It is a dense, silvery-gray metal which readily reacts with oxygen, water vapor and inorganic acids. It forms various chemical compounds where protactinium is usually present in the oxidation state +5, but can also assume... |
1.05 | 0.93 |
| Neodymium Neodymium Neodymium is a chemical element with the symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is a soft silvery metal that tarnishes in air. Neodymium was discovered in 1885 by the Austrian chemist Carl Auer von Welsbach. It is present in significant quantities in the ore minerals monazite and bastnäsite... |
0.995 | Uranium Uranium Uranium is a silvery-white metallic chemical element in the actinide series of the periodic table, with atomic number 92. It is assigned the chemical symbol U. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons... |
1.03 | 0.93 |
| Promethium Promethium Promethium is a chemical element with the symbol Pm and atomic number 61. It is notable for being the only exclusively radioactive element besides technetium that is followed by chemical elements with stable isotopes.- Prediction :... |
0.979 | Neptunium Neptunium Neptunium is a chemical element with the symbol Np and atomic number 93. A radioactive metal, neptunium is the first transuranic element and belongs to the actinide series. Its most stable isotope, 237Np, is a by-product of nuclear reactors and plutonium production and it can be used as a... |
1.01 | 0.92 |
| Samarium Samarium Samarium is a chemical element with the symbol Sm, atomic number 62 and atomic weight 150.36. It is a moderately hard silvery metal which readily oxidizes in air. Being a typical member of the lanthanide series, samarium usually assumes the oxidation state +3... |
0.964 | Plutonium Plutonium Plutonium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the chemical symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, forming a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation... |
1.00 | 0.90 |
| Europium Europium Europium is a chemical element with the symbol Eu and atomic number 63. It is named after the continent of Europe. It is a moderately hard silvery metal which readily oxidizes in air and water... |
0.950 | Americium Americium Americium is a synthetic element that has the symbol Am and atomic number 95. This transuranic element of the actinide series is located in the periodic table below the lanthanide element europium, and thus by analogy was named after another continent, America.Americium was first produced in 1944... |
0.99 | 0.89 |
| Gadolinium Gadolinium Gadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. It is a silvery-white, malleable and ductile rare-earth metal. It is found in nature only in combined form. Gadolinium was first detected spectroscopically in 1880 by de Marignac who separated its oxide and is credited with... |
0.938 | Curium Curium Curium is a synthetic chemical element with the symbol Cm and atomic number 96. This radioactive transuranic element of the actinide series was named after Marie Skłodowska-Curie and her husband Pierre Curie. Curium was first intentionally produced and identified in summer 1944 by the group of... |
0.98 | 0.88 |
| Terbium Terbium Terbium is a chemical element with the symbol Tb and atomic number 65. It is a silvery-white rare earth metal that is malleable, ductile and soft enough to be cut with a knife... |
0.923 | Berkelium Berkelium Berkelium , is a synthetic element with the symbol Bk and atomic number 97, a member of the actinide and transuranium element series. It is named after the city of Berkeley, California, the location of the University of California Radiation Laboratory where it was discovered in December 1949... |
||
| Dysprosium Dysprosium Dysprosium is a chemical element with the symbol Dy and atomic number 66. It is a rare earth element with a metallic silver luster. Dysprosium is never found in nature as a free element, though it is found in various minerals, such as xenotime... |
0.908 | Californium Californium Californium is a radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Cf and atomic number 98. The element was first made in the laboratory in 1950 by bombarding curium with alpha particles at the University of California, Berkeley. It is the ninth member of the actinide series and was the... |
||
| Holmium Holmium Holmium is a chemical element with the symbol Ho and atomic number 67. Part of the lanthanide series, holmium is a rare earth element. Its oxide was first isolated from rare earth ores in 1878 and the element was named after the city of Stockholm.... |
0.894 | Einsteinium Einsteinium Einsteinium is a synthetic element with the symbol Es and atomic number 99. It is the seventh transuranic element, and an actinide.Einsteinium was discovered in the debris of the first hydrogen bomb explosion in 1952, and named after Albert Einstein... |
||
| Erbium Erbium Erbium is a chemical element in the lanthanide series, with the symbol Er and atomic number 68. A silvery-white solid metal when artificially isolated, natural erbium is always found in chemical combination with other elements on Earth... |
0.881 | Fermium Fermium Fermium is a synthetic element with the symbol Fm. It is the 100th element in the periodic table and a member of the actinide series. It is the heaviest element that can be formed by neutron bombardment of lighter elements, and hence the last element that can be prepared in macroscopic quantities,... |
||
| Thulium Thulium Thulium is a chemical element that has the symbol Tm and atomic number 69. Thulium is the second least abundant of the lanthanides . It is an easily workable metal with a bright silvery-gray luster... |
0.869 | Mendelevium Mendelevium Mendelevium is a synthetic element with the symbol Md and the atomic number 101. A metallic radioactive transuranic element in the actinide series, mendelevium is usually synthesized by bombarding einsteinium with alpha particles. It was named after Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev, who created the... |
||
| Ytterbium Ytterbium Ytterbium is a chemical element with the symbol Yb and atomic number 70. A soft silvery metallic element, ytterbium is a rare earth element of the lanthanide series and is found in the minerals gadolinite, monazite, and xenotime. The element is sometimes associated with yttrium or other related... |
0.858 | Nobelium Nobelium Nobelium is a synthetic element with the symbol No and atomic number 102. It was first correctly identified in 1966 by scientists at the Flerov Laboratory of Nuclear Reactions in Dubna, Soviet Union... |
||
| Lutetium | 0.848 | Lawrencium Lawrencium Lawrencium is a radioactive synthetic chemical element with the symbol Lr and atomic number 103. In the periodic table of the elements, it is a period 7 d-block element and the last element of actinide series... |
||
Chemical properties
Like the lanthanides, all actinides are highly reactive with halogenHalogen
The halogens or halogen elements are a series of nonmetal elements from Group 17 IUPAC Style of the periodic table, comprising fluorine , chlorine , bromine , iodine , and astatine...
s and chalcogen
Chalcogen
The chalcogens are the chemical elements in group 16 of the periodic table. This group is also known as the oxygen family...
s; however, actinides react more easily. Actinides, especially those with a small number of 5f-electrons, are prone to hybridization. This is explained by the similarity of the electron energies at the 5f, 7s and 6d shells. Most actinides exhibit a larger variety of valence states, and the most stable are +6 for uranium, +5 for protactinium and neptunium, +4 for thorium and plutonium and +3 for actinium and other actinides.
Chemically, actinium is similar to lanthanum, which is explained by their similar ionic radii and electronic structure. Like lanthanum, actinium has oxidation of +3, but it is less reactive and has more pronounced basic
Base (chemistry)
For the term in genetics, see base A base in chemistry is a substance that can accept hydrogen ions or more generally, donate electron pairs. A soluble base is referred to as an alkali if it contains and releases hydroxide ions quantitatively...
properties. Among other trivalent actinides Ac3+ is least acidic, i.e. has the weakest tendency to hydrolyze in aqueous solutions.
Thorium is rather active chemically. Owing to lack of electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s on 6d-and 4f-orbitals, the tetravalent thorium compounds are colorless. At pH < 3, the solutions of thorium salts are dominated by the cations [Th(H2O)8]4+. The Th4+ ion is relatively large, and depending on the coordination number
Coordination number
In chemistry and crystallography, the coordination number of a central atom in a molecule or crystal is the number of its nearest neighbours. This number is determined somewhat differently for molecules and for crystals....
can have a radius between 0.95 and 1.14 Å. As a result, thorium salts have a weak tendency to a hydrolysis. The distinctive ability of thorium salts is their high solubility, not only in water, but also in polar organic solvents.
Protactinium exhibits two valence states; the +5 is stable, and the +4 state easily oxidizes to protactinium(V). Thus tetravalent protactinium in solutions is obtained by the action of strong reducing agents in a hydrogen atmosphere. Tetravalent protactinium is chemically similar to uranium(IV) and thorium(IV). Fluorides, phosphates, hypophosphate, iodate and phenylarsonates of protactinium(IV) are insoluble in water and dilute acids. Protactinium forms soluble carbonates. The hydrolytic properties of pentavalent protactinium are close to those of tantalum
Tantalum
Tantalum is a chemical element with the symbol Ta and atomic number 73. Previously known as tantalium, the name comes from Tantalus, a character in Greek mythology. Tantalum is a rare, hard, blue-gray, lustrous transition metal that is highly corrosion resistant. It is part of the refractory...
(V) and niobium
Niobium
Niobium or columbium , is a chemical element with the symbol Nb and atomic number 41. It's a soft, grey, ductile transition metal, which is often found in the pyrochlore mineral, the main commercial source for niobium, and columbite...
(V). The complex chemical behavior of protactinium is a consequence of the start of the filling of the 5f shell in this element.
Uranium has a valence from 3 to 6, the last being most stable. In the hexavalent state, uranium is very similar to the sixth group elements. Many compounds of uranium(IV) and uranium(VI) are nonstoichiometric, i.e. have variable composition. For example, the actual chemical formula of uranium dioxide is UO2+x, where x varies between −0.4 and 0.32. Uranium(VI) compounds are weak oxidants
Oxidizing agent
An oxidizing agent can be defined as a substance that removes electrons from another reactant in a redox chemical reaction...
. Most of them contain the linear "uranyl
Uranyl
The uranyl ion is an oxycation of uranium in the oxidation state +6, with the chemical formula [UO2]2+. It has a linear structure with short U-O bonds, indicative of the presence of multiple bonds between uranium and oxygen. Four or more ligands are bound to the uranyl ion in an equatorial plane...
" group, UO22+. Between 4 to 6 ligands can be accommodated in an equatorial plane perpendicular to the uranyl group. The uranyl group acts as a hard acid and forms stronger complexes with oxygen-donor ligands than with nitrogen-donor ligands. NpO22+ and PuO22+ are also the common form of Np and Pu in the +6 oxidation state. Uranium(IV) compounds exhibit reducing properties, e.g., they are easily oxidized by atmospheric oxygen. Uranium(III) is a very strong reducing agent. Owing to the presence of d-shell, uranium (as well as many other actinides) forms organometallic compounds, such as UIII(C5H5)3 and UIV(C5H5)4.
Neptunium has valence states from 3 to 7, which can be simultaneously observed in solutions. The most stable state in solution is +5, but the valence +4 is preferred in solid neptunium compounds. Neptunium metal is very reactive. Ions of neptunium are prone to hydrolysis and formation of coordination compounds.
Plutonium also exhibits the valence between 3 and 7, and thus is chemically similar to neptunium and uranium. It is highly reactive, and quickly forms an oxide film in air. Plutonium reacts with hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
even at temperatures as low as 25–50 °C; it also easily forms halide
Halide
A halide is a binary compound, of which one part is a halogen atom and the other part is an element or radical that is less electronegative than the halogen, to make a fluoride, chloride, bromide, iodide, or astatide compound. Many salts are halides...
s and intermetallic compounds. Hydrolysis reactions of plutonium ions of different oxidation states are quite diverse. Plutonium(V) can enter polymerization
Polymerization
In polymer chemistry, polymerization is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form three-dimensional networks or polymer chains...
reactions.
The largest chemical diversity among actinides is observed in americium, which can have valence between 2 and 6. Divalent americium is obtained only in dry compounds and non-aqueous solutions (acetonitrile
Acetonitrile
Acetonitrile is the chemical compound with formula . This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile. It is produced mainly as a byproduct of acrylonitrile manufacture...
). Oxidation states +3, +5 and +6 are typical for aqueous solutions, but also in the solid state. Tetravalent americium forms stable solid compounds (dioxide, fluoride and hydroxide) as well as complexes in aqueous solutions. It was reported that in alkaline solution americium can be oxidized to the heptavalent state, but these data proved erroneous. The most stable valence of americium is 3 in the aqueous solutions and 3 or 4 in solid compounds.
Valence 3 is dominant in all subsequent elements up to lawrencium (with the possible exception of nobelium). Curium can be tetravalent in solids (fluoride, dioxide). Berkelium, along with a valence of +3, also shows the valence of +4, more stable than that of curium; the valence 4 is observed in solid fluoride and dioxide. The stability of Bk4+ in aqueous solution is close to that of Ce
Cerium
Cerium is a chemical element with the symbol Ce and atomic number 58. It is a soft, silvery, ductile metal which easily oxidizes in air. Cerium was named after the dwarf planet . Cerium is the most abundant of the rare earth elements, making up about 0.0046% of the Earth's crust by weight...
4+. Only valence 3 was observed for californium, einsteinium and fermium. The divalent state is proven for mendelevium and nobelium, and in nobelium it is more stable than the trivalent state. Lawrencium shows valence 3 both in solutions and solids.
The redox potential
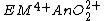 increases from −0.32 V in uranium, through 0.34 V (Np) and 1.04 V (Pu) to 1.34 V in americium revealing the increasing reduction ability of the An4+ ion from americium to uranium. All actinides form AnH3 hydrides of black color with salt-like properties. Actinides also produce carbide
increases from −0.32 V in uranium, through 0.34 V (Np) and 1.04 V (Pu) to 1.34 V in americium revealing the increasing reduction ability of the An4+ ion from americium to uranium. All actinides form AnH3 hydrides of black color with salt-like properties. Actinides also produce carbideCarbide
In chemistry, a carbide is a compound composed of carbon and a less electronegative element. Carbides can be generally classified by chemical bonding type as follows: salt-like, covalent compounds, interstitial compounds, and "intermediate" transition metal carbides...
s with the general formula of AnC or AnC2 (U2C3 for uranium) as well as sulfides An2S3 and AnS2.
Oxides and hydroxides
| Compound | Color | Crystal symmetry, type | Lattice constants, Å | Density, g/cm3 | Temperature, °C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | |||||
| Ac2O3 | White | Hexagonal, La2O3 | 4.07 | ||||
| 6.29 | 9.19 | – | |||||
| PaO2 | |||||||
| Cubic, CaF2 | 5.505 | ||||||
| Pa2O5 | White | cubic, CaF2 Cubic Tetragonal Hexagonal Rhombohedral Orthorhombic |
5.446 10.891 5.429 3.817 5.425 6.92 |
- - - - - 4.02 |
- 10.992 5.503 13.22 - 4. 18 |
||
| 700 700–1100 1000 1000–1200 1240–1400 – |
|||||||
| ThO2 | Colorless | Cubic | 5.59 | ||||
| 9.87 | – | ||||||
| UO2 | Black-brown | Cubic | 5.47 | ||||
| 10.9 | – | ||||||
| NpO2 | Greenish-brown | Cubic, CaF2 | 5.424 | ||||
| 11.1 | – | ||||||
| PuO | Black | Cubic, NaCl | 4.96 | ||||
| 13.9 | – | ||||||
| PuO2 | Olive green | Cubic | 5.39 | ||||
| 11.44 | – | ||||||
| Am2O3 | Red-brown Red-brown |
Cubic, Mn2O3 Hexagonal, La2O3 |
11.03 3.817 |
||||
| 10.57 11.7 |
– | ||||||
| AmO2 | Black | Cubic, CaF2 | 5.376 | ||||
| Cm2O3 | White - - |
Cubic, Mn2O2 Hexagonal, LaCl3 Monoclinic, Sm2O3 |
11.01 3.80 14.28 |
- - 3.65 |
- 6 8.9 |
11.7 | – |
| CmO2 | Black | Cubic, CaF2 | 5.37 | ||||
| Bk2O3 | Light brown | Cubic, Mn2O3 | 10.886 | ||||
| BkO2 | Red-brown | Cubic, CaF2 | 5.33 | ||||
| Cf2O3 | Colorless Yellowish - |
Cubic, Mn2O3 Monoclinic, Sm2O3 Hexagonal, La2O3 |
10.79 14.12 3.72 |
- 3.59 - |
- 8.80 5.96 |
||
| CfO2 | Black | Cubic | 5.31 | ||||
| Es2O3 | |||||||
| Cubic, Mn2O3 Monoclinic Hexagonal, La2O3 |
10.07 14.1 3.7 |
- 3.59 - |
- 8.80 6 |
||||
| Oxidation state | 89 | 90 | 91 | 92 | 93 | 94 | 95 | 96 | 97 | 98 | 99 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| +3 | Pu2O3 | Am2O3 | Cm2O3 | Bk2O3 | Cf2O3 | Es2O3 | |||||
| +4 | ThO2 | PaO2 | UO2 | NpO2 | PuO2 | AmO2 | CmO2 | BkO2 | CfO2 | ||
| +5 | PaO2+ | U2O5 | Np2O5 | ||||||||
| +6 | U3O8 | ||||||||||
| UO3 |
| Chemical formula Chemical formula A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound.... |
ThO2 | PaO2 | UO2 | NpO2 | PuO2 | AmO2 | CmO2 | BkO2 | CfO2 |
| CAS-number | 1314-20-1 | 12036-03-2 | 1344-57-6 | 12035-79-9 | 12059-95-9 | 12005-67-3 | 12016-67-0 | 12010-84-3 | 12015-10-0 |
| PubChem | 14808 | 10916 | |||||||
| Molar mass Molar mass Molar mass, symbol M, is a physical property of a given substance , namely its mass per amount of substance. The base SI unit for mass is the kilogram and that for amount of substance is the mole. Thus, the derived unit for molar mass is kg/mol... |
264.04 | 263.035 | 270.03 | 269.047 | 276.063 | 275.06 | 270–284** | 279.069 | 283.078 |
| Melting point Melting point The melting point of a solid is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard atmospheric pressure... |
3390 °C | 2878 °C | 2600 °C | 2400 °C | 2050 °C | ||||
| Boiling point Boiling point The boiling point of an element or a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the environmental pressure surrounding the liquid.... |
4400 °C | 2800 °C | |||||||
| structure | An4+: __ / O2−: __ |
||||||||
| Space group Space group In mathematics and geometry, a space group is a symmetry group, usually for three dimensions, that divides space into discrete repeatable domains.In three dimensions, there are 219 unique types, or counted as 230 if chiral copies are considered distinct... |
Fmm | ||||||||
| Coordination number Coordination number In chemistry and crystallography, the coordination number of a central atom in a molecule or crystal is the number of its nearest neighbours. This number is determined somewhat differently for molecules and for crystals.... |
An[8], O[4] | ||||||||
- An – actinide
**Depending on the isotopes
Some actinides can exists in various oxide forms: An2O3, AnO2, An2O5 and AnO3. For all actinides, oxides AnO3 are amphoteric
Amphoterism
In chemistry, an amphoteric species is a molecule or ion that can react as an acid as well as a base. The word is derived from the Greek word amphoteroi meaning "both"...
and An2O3, AnO2 and An2O5 are basic, they easily react with water, forming bases:
- An2O3 + 3 H2O → 2 An(OH)3.
These bases are poorly soluble in water and by their activity are close to the hydroxide
Hydroxide
Hydroxide is a diatomic anion with chemical formula OH−. It consists of an oxygen and a hydrogen atom held together by a covalent bond, and carrying a negative electric charge. It is an important but usually minor constituent of water. It functions as a base, as a ligand, a nucleophile, and a...
s of rare-earth metals. The strongest base is of actinium. All compounds of actinium are colorless, except for black actinium sulfide (Ac2S3). Dioxides of tetravalent actinides crystallize in the cubic system, same as in calcium fluoride
Calcium fluoride
Calcium fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula CaF2. This ionic compound of calcium and fluorine occurs naturally as the mineral fluorite . It is the source of most of the world's fluorine. This insoluble solid adopts a cubic structure wherein calcium is coordinated to eight fluoride...
.
Thorium reacting with oxygen exclusively forms dioxide:
Thorium dioxide is a refractory material with the highest melting point among any known oxide (3390 °C). Adding 0.8–1% ThO2 to tungsten stabilizes its structure, so the doped filaments have better mechanical stability to vibrations. To dissolve ThO2 in acids, it is heated to 500–600 °C; heating above 600 °C produces a very resistant to acids and other reagents form of ThO2. Small addition of fluoride ions catalyses dissolution of thorium dioxide in acids.
Two protactinium oxides were obtained: PaO2 (black) and Pa2O5(white); the former is isomorphic
Isomorphism
In abstract algebra, an isomorphism is a mapping between objects that shows a relationship between two properties or operations. If there exists an isomorphism between two structures, the two structures are said to be isomorphic. In a certain sense, isomorphic structures are...
with ThO2 and the latter is easier to obtain. Both oxides are basic, and Pa(OH)5 is a weak, poorly soluble base.
Decomposition of certain salts of uranium, for example UO2(NO3)·6H2O in air at 400 °C, yields orange or yellow UO3. This oxide is amphoteric and forms several hydroxides, the most stable being UO2(OH)2.
Reaction of uranium(VI) oxide with hydrogen results in uranium dioxide, which is similar in its properties with ThO2. This oxide is also basic and corresponds to the uranium hydroxide (U(OH)4).
Plutonium, neptunium and americium form two basic oxides: An2O3 and AnO2. Neptunium trioxide is unstable, thus only Np3O8 could be obtained so far. However, the oxides of plutonium and neptunium with the chemical formula AnO2 and An2O3 are well characterized.
Salts
| Chemical formula Chemical formula A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound.... |
AcCl3 | UCl3 | NpCl3 | PuCl3 | AmCl3 | CmCl3 | BkCl3 | CfCl3 |
| CAS-number | 22986-54-5 | 10025-93-1 | 20737-06-8 | 13569-62-5 | 13464-46-5 | 13537-20-7 | 13536-46-4 | 13536-90-8 |
| PubChem | | 167444 | |||||||
| Molar mass Molar mass Molar mass, symbol M, is a physical property of a given substance , namely its mass per amount of substance. The base SI unit for mass is the kilogram and that for amount of substance is the mole. Thus, the derived unit for molar mass is kg/mol... |
333.386 | 344.387 | 343.406 | 350.32 | 349.42 | 344–358** | 353.428 | 357.438 |
| Melting point Melting point The melting point of a solid is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends on pressure and is usually specified at standard atmospheric pressure... |
| 837 °C | 800 °C | 767 °C | 715 °C | 695 °C | 603 °C | 545 °C | |
| Boiling point Boiling point The boiling point of an element or a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the environmental pressure surrounding the liquid.... |
| 1657 °C | 1767 °C | 850 °C | |||||
| Crystal structure | An3+: __ / Cl−: __ |
|||||||
| Space group Space group In mathematics and geometry, a space group is a symmetry group, usually for three dimensions, that divides space into discrete repeatable domains.In three dimensions, there are 219 unique types, or counted as 230 if chiral copies are considered distinct... |
P63/m | |||||||
| Coordination number Coordination number In chemistry and crystallography, the coordination number of a central atom in a molecule or crystal is the number of its nearest neighbours. This number is determined somewhat differently for molecules and for crystals.... |
An*[9], Cl [3] | |||||||
| Lattice constants | a = 762 pm c = 455 pm |
a = 745.2 pm c = 432.8 pm |
a = 739.4 pm c = 424.3 pm |
a = 738.2 pm c = 421.4 pm |
a = 726 pm c = 414 pm |
a = 738.2 pm c = 412.7 pm |
a = 738 pm c = 409 pm |
|
- *An – actinide
**Depending on the isotopes
| Compound | Color | Crystal symmetry, type | Lattice constants, Å | Density, g/cm3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | b | c | ||||
| AcF3 | White | Hexagonal, LaF3 | 4.27 | |||
| 7.53 | 7.88 | |||||
| PaF4 | Dark brown | Monoclinic | 12.7 | 10.7 | 8.42 | – |
| PaF5 | Black | Tetragonal, β-UF5 | 11.53 | |||
| 5.19 | – | |||||
| ThF4 | Colorless | Monoclinic | 13 | 10.99 | 8.58 | 5.71 |
| UF3 | Reddish-purple | Hexagonal | 7.18 | |||
| 7.34 | 8.54 | |||||
| UF4 | Green | Monoclinic | 11.27 | 10.75 | 8.40 | 6.72 |
| α-UF5 | Bluish | Tetragonal | 6.52 | |||
| 4.47 | 5.81 | |||||
| β-UF5 | Bluish | Tetragonal | 11.47 | |||
| 5.20 | 6.45 | |||||
| UF6 | Yellowish | Orthorhombic | 9.92 | 8.95 | 5.19 | 5.06 |
| NpF3 | Black or purple | Hexagonal | 7.129 | |||
| 7.288 | 9.12 | |||||
| NpF4 | Light green | Monoclinic | 12.67 | 10.62 | 8.41 | 6.8 |
| NpF6 | Orange | Orthorhombic | 9.91 | 8.97 | 5.21 | 5 |
| PuF3 | Violet-blue | Trigonal | 7.09 | |||
| 7.25 | 9.32 | |||||
| PuF4 | Pale brown | Monoclinic | 12.59 | 10.57 | 8.28 | 6.96 |
| PuF6 | Red-brown | Orthorhombic | 9.95 | 9.02 | 3.26 | 4.86 |
| AmF3 | Pink or light beige Beige Beige may be described as an off tan color or an extremely pale brown color.The term originates from beige cloth, a cotton fabric left undyed in its natural color... |
hexagonal Hexagonal crystal system In crystallography, the hexagonal crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems, the hexagonal lattice system is one of the 7 lattice systems, and the hexagonal crystal family is one of the 6 crystal families... , LaF3 |
7.04 | |||
| 7.255 | 9.53 | |||||
| AmF4 | Orange-red | Monoclinic | 12.53 | 10.51 | 8.20 | – |
| CmF3 | From brown to white | Hexagonal | 4.041 | |||
| 7.179 | 9.7 | |||||
| CmF4 | Yellow | Monoclinic, UF4 | 12.51 | 10.51 | 8.20 | – |
| BkF3 | Yellow-green | Trigonal, LaF3 Orthorhombic, YF3 |
6.97 6.7 |
- 7.09 |
7.14 4.41 |
10.15 9.7 |
| BkF4 | ||||||
| Monoclinic, UF4 | 12.47 | 10.58 | 8.17 | – | ||
| CfF3 | - - |
Trigonal, LaF3 Orthorhombic, YF3 |
6. 94 6.65 |
- 7.04 |
7.10 4.39 |
– |
| CfF4 | - - |
Monoclinic, UF4 Monoclinic, UF4 |
1.242 1.233 |
1.047 1.040 |
8.126 8.113 |
– |
Actinides easily react with halogens forming salts with the formulas MX3 and MX4 (X = halogen
Halogen
The halogens or halogen elements are a series of nonmetal elements from Group 17 IUPAC Style of the periodic table, comprising fluorine , chlorine , bromine , iodine , and astatine...
). So the first berkelium compound, BkCl3, was synthesized in 1962 with an amount of 3 nanogram. Like the halogens of rare earth elements, actinide chloride
Chloride
The chloride ion is formed when the element chlorine, a halogen, picks up one electron to form an anion Cl−. The salts of hydrochloric acid HCl contain chloride ions and can also be called chlorides. The chloride ion, and its salts such as sodium chloride, are very soluble in water...
s, bromide
Bromide
A bromide is a chemical compound containing bromide ion, that is bromine atom with effective charge of −1. The class name can include ionic compounds such as caesium bromide or covalent compounds such as sulfur dibromide.-Natural occurrence:...
s, and iodide
Iodide
An iodide ion is the ion I−. Compounds with iodine in formal oxidation state −1 are called iodides. This page is for the iodide ion and its salts. For information on organoiodides, see organohalides. In everyday life, iodide is most commonly encountered as a component of iodized salt,...
s are water soluble, and fluoride
Fluoride
Fluoride is the anion F−, the reduced form of fluorine when as an ion and when bonded to another element. Both organofluorine compounds and inorganic fluorine containing compounds are called fluorides. Fluoride, like other halides, is a monovalent ion . Its compounds often have properties that are...
s are insoluble. Uranium easily yields a colorless hexafluoride, which sublimates at a temperature of 56.5 °C; because of its volatility, it is used in the separation of uranium isotopes with gas centrifuge
Gas centrifuge
A gas centrifuge is a device that performs isotope separation of gases. A centrifuge relies on the principles of centripetal force accelerating molecules so that particles of different masses are physically separated in a gradient along the radius of a rotating container.A prominent use of gas...
or gaseous diffusion
Gaseous diffusion
Gaseous diffusion is a technology used to produce enriched uranium by forcing gaseous uranium hexafluoride through semi-permeable membranes. This produces a slight separation between the molecules containing uranium-235 and uranium-238 . By use of a large cascade of many stages, high separations...
. Actinide hexafluorides have properties close to anhydrides. They are very sensitive to moisture and hydrolyze forming AnO2F2. Pentachloride and black hexachloride of uranium were synthesized, but they are both unstable.
Action of acids on actinides yields salts, and if the acids are non-oxidizing then the actinide in the salt is in low-valence state:
- U + 2 H2SO4 → U (SO4)2 + 2 H2
- 2 Pu + 6 HCl → 2 PuCl3 + 3 H2
However, in these reactions the regenerating hydrogen can react with the metal, forming the corresponding hydride. Uranium reacts with acids and water much easier than thorium.
Actinide salts can also be obtained by dissolving the corresponding hydroxides in acids. Nitrates, chlorides, sulfates and perchlorates of actinides are water soluble. When crystallizing from aqueous solutions, these salts forming a hydrates, such as Th(NO3)4·6H2O, Th(SO4)2·9H2O and Pu2(SO4)3·7H2O. Salts of high-valence actinides easily hydrolyze. So, colorless sulfate, chloride, perchlorate and nitrate of thorium transform into basic salts with formulas Th(OH)2SO4 and Th(OH)3NO3. The solubility and insolubility of trivalent and tetravalent actinides is like that of lanthanide salts. So phosphate
Phosphate
A phosphate, an inorganic chemical, is a salt of phosphoric acid. In organic chemistry, a phosphate, or organophosphate, is an ester of phosphoric acid. Organic phosphates are important in biochemistry and biogeochemistry or ecology. Inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in...
s, fluoride
Fluoride
Fluoride is the anion F−, the reduced form of fluorine when as an ion and when bonded to another element. Both organofluorine compounds and inorganic fluorine containing compounds are called fluorides. Fluoride, like other halides, is a monovalent ion . Its compounds often have properties that are...
s, oxalate
Oxalate
Oxalate , is the dianion with formula C2O42− also written 22−. Either name is often used for derivatives, such as disodium oxalate, 2C2O42−, or an ester of oxalic acid Oxalate (IUPAC: ethanedioate), is the dianion with formula C2O42− also written (COO)22−. Either...
s, iodate
Iodate
An iodate is a conjugate base of iodic acid. In the iodate anion, iodine is bonded to three oxygen atoms and the molecular formula is IO3−. The molecular geometry of iodate is trigonal pyramidal....
s and carbonates of actinides are weakly soluble in water; they precipitate as hydrates, such as ThF4·3H2O and Th(CrO4)2·3H2O.
Actinides with oxidation state +6, except for the AnO22+-type cations, form [AnO4]2–, [An2O7]2– and other complex anions. For example, uranium, neptunium and plutonium form salts of the Na2UO4 (uranate) and (NH4)2U2O7 (diuranate) types. In comparison with lanthanides, actinides easier form coordination compounds, and this ability increases with the actinide valence. Trivalent actinides do not form fluoride coordination compounds, whereas tetravalent thorium forms K2ThF6, KThF5, and even K5ThF9 complexes. Thorium also forms the corresponding sulfate
Sulfate
In inorganic chemistry, a sulfate is a salt of sulfuric acid.-Chemical properties:...
s (for example Na2SO4·Th (SO4)2·5H2O), nitrate
Nitrate
The nitrate ion is a polyatomic ion with the molecular formula NO and a molecular mass of 62.0049 g/mol. It is the conjugate base of nitric acid, consisting of one central nitrogen atom surrounded by three identically-bonded oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement. The nitrate ion carries a...
s and thiocyanates. Salts with the general formula An2Th(NO3)6·nH2O are of coordination nature, with the coordination number
Coordination number
In chemistry and crystallography, the coordination number of a central atom in a molecule or crystal is the number of its nearest neighbours. This number is determined somewhat differently for molecules and for crystals....
of thorium equal to 12. Even easier is to produce complex salts of pentavalent and hexavalent actinides. The most stable coordination compounds of actinides – tetravalent thorium and uranium – are obtained in reactions with diketones, e.g. acetylacetone
Acetylacetone
Acetylacetone is an organic compound that famously exists in two tautomeric forms that rapidly interconvert. The less stable tautomer is a diketone formally named pentane-2,4-dione. The more common tautomer is the enol form. The pair of tautomers rapidly interconvert and are treated as a single...
.
Applications
While actinides have some established daily-life applications, such as in smoke detectors (americium) and gas mantleGas mantle
An incandescent gas mantle, gas mantle, or Welsbach mantle is a device for generating bright white light when heated by a flame. The name refers to its original heat source, existing gas lights, which filled the streets of Europe and North America in the late 19th century, mantle referring to the...
s (thorium), they are mostly used in nuclear weapon
Nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission or a combination of fission and fusion. Both reactions release vast quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. The first fission bomb test released the same amount...
s and use as a fuel
Nuclear fuel
Nuclear fuel is a material that can be 'consumed' by fission or fusion to derive nuclear energy. Nuclear fuels are the most dense sources of energy available...
in nuclear reactors. The last two areas exploit the property of actinides to release enormous energy in nuclear reactions, which under certain conditions may become self-sustaining chain reaction
Nuclear chain reaction
A nuclear chain reaction occurs when one nuclear reaction causes an average of one or more nuclear reactions, thus leading to a self-propagating number of these reactions. The specific nuclear reaction may be the fission of heavy isotopes or the fusion of light isotopes...
.

Nuclear power
Nuclear power is the use of sustained nuclear fission to generate heat and electricity. Nuclear power plants provide about 6% of the world's energy and 13–14% of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for about 50% of nuclear generated electricity...
applications is uranium-235
Uranium-235
- References :* .* DOE Fundamentals handbook: Nuclear Physics and Reactor theory , .* A piece of U-235 the size of a grain of rice can produce energy equal to that contained in three tons of coal or fourteen barrels of oil. -External links:* * * one of the earliest articles on U-235 for the...
. It is used in the thermal reactor
Thermal reactor
A thermal reactor is a nuclear reactor that uses slow or thermal neutrons. Most power reactors are of this type. These type of reactors use a neutron moderator to slow neutrons until they approach the average kinetic energy of the surrounding particles, that is, to reduce the speed of the neutrons...
, and its concentration in natural uranium does not exceed 0.72%. This isotope strongly absorbs thermal neutrons releasing much energy. One fission act of 1 gram of 235U converts into about 1 MW·day. Of importance, is that 235U emits more neutrons than it absorbs; upon reaching the critical mass
Critical mass
A critical mass is the smallest amount of fissile material needed for a sustained nuclear chain reaction. The critical mass of a fissionable material depends upon its nuclear properties A critical mass is the smallest amount of fissile material needed for a sustained nuclear chain reaction. The...
, 235U enters into a self-sustaining chain reaction. Typically, uranium nucleus is divided into two fragments with the release of 2–3 neutrons, for example:
Other promising actinide isotopes for nuclear power are thorium-232 and its fission product, formed uranium-233
Uranium-233
Uranium-233 is a fissile isotope of uranium, bred from Thorium as part of the thorium fuel cycle. It has been used in a few nuclear reactors and has been proposed for much wider use as a nuclear fuel. It has a half-life of 160,000 years....
.
| Nuclear reactor Nuclear reactor A nuclear reactor is a device to initiate and control a sustained nuclear chain reaction. Most commonly they are used for generating electricity and for the propulsion of ships. Usually heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid , which runs through turbines that power either ship's... |
| The core of any nuclear reactor contains a set of hollow metal rods, usually made of zirconium Zirconium Zirconium is a chemical element with the symbol Zr and atomic number 40. The name of zirconium is taken from the mineral zircon. Its atomic mass is 91.224. It is a lustrous, grey-white, strong transition metal that resembles titanium... alloys, filled with nuclear fuel Nuclear fuel Nuclear fuel is a material that can be 'consumed' by fission or fusion to derive nuclear energy. Nuclear fuels are the most dense sources of energy available... cells – mostly oxide, carbide, nitride or monosulfide of uranium, plutonium or thorium, or their mixture (the so-called MOX fuel MOX fuel Mixed oxide fuel, commonly referred to as MOX fuel, is nuclear fuel that contains more than one oxide of fissile material. MOX fuel contains plutonium blended with natural uranium, reprocessed uranium, or depleted uranium. MOX fuel is an alternative to the low-enriched uranium fuel used in the... ). The most common fuel is oxide of uranium-235. Fast neutrons Neutron temperature The neutron detection temperature, also called the neutron energy, indicates a free neutron's kinetic energy, usually given in electron volts. The term temperature is used, since hot, thermal and cold neutrons are moderated in a medium with a certain temperature. The neutron energy distribution is... are slowed by moderators, which contain water, carbon Carbon Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds... , deuterium Deuterium Deuterium, also called heavy hydrogen, is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen. It has a natural abundance in Earth's oceans of about one atom in of hydrogen . Deuterium accounts for approximately 0.0156% of all naturally occurring hydrogen in Earth's oceans, while the most common isotope ... , or beryllium Beryllium Beryllium is the chemical element with the symbol Be and atomic number 4. It is a divalent element which occurs naturally only in combination with other elements in minerals. Notable gemstones which contain beryllium include beryl and chrysoberyl... , as thermal neutrons to increase the efficiency of their interaction with uranium-235. The rate of nuclear reaction is controlled by introducing additional rods made of boron Boron Boron is the chemical element with atomic number 5 and the chemical symbol B. Boron is a metalloid. Because boron is not produced by stellar nucleosynthesis, it is a low-abundance element in both the solar system and the Earth's crust. However, boron is concentrated on Earth by the... or cadmium Cadmium Cadmium is a chemical element with the symbol Cd and atomic number 48. This soft, bluish-white metal is chemically similar to the two other stable metals in group 12, zinc and mercury. Similar to zinc, it prefers oxidation state +2 in most of its compounds and similar to mercury it shows a low... or a liquid absorbent, usually boric acid Boric acid Boric acid, also called hydrogen borate or boracic acid or orthoboric acid or acidum boricum, is a weak acid of boron often used as an antiseptic, insecticide, flame retardant, as a neutron absorber, and as a precursor of other chemical compounds. It exists in the form of colorless crystals or a... . Reactors for plutonium production are called breeder reactor Breeder reactor A breeder reactor is a nuclear reactor capable of generating more fissile material than it consumes because its neutron economy is high enough to breed fissile from fertile material like uranium-238 or thorium-232. Breeders were at first considered superior because of their superior fuel economy... or breeders; they have a different design and use fast neutrons. |
Emission of neutrons during the fission of uranium is important not only for maintaining the nuclear chain reaction, but also for the synthesis of the heavier actinides. Uranium-239 converts via β-decay
Beta decay
In nuclear physics, beta decay is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle is emitted from an atom. There are two types of beta decay: beta minus and beta plus. In the case of beta decay that produces an electron emission, it is referred to as beta minus , while in the case of a...
into plutonium-239, which, like uranium-235, is capable of spontaneous fission. The world's first nuclear reactors were built not for energy, but for producing plutonium-239 for nuclear weapons.
About half of the produced thorium is used as the light-emitting material of gas mantles. Thorium is also added into multicomponent alloy
Alloy
An alloy is a mixture or metallic solid solution composed of two or more elements. Complete solid solution alloys give single solid phase microstructure, while partial solutions give two or more phases that may or may not be homogeneous in distribution, depending on thermal history...
s of magnesium
Magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg, atomic number 12, and common oxidation number +2. It is an alkaline earth metal and the eighth most abundant element in the Earth's crust and ninth in the known universe as a whole...
and zinc
Zinc
Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
. So the Mg-Th alloys are light and strong, but also have high melting point and ductility and thus are widely used in the aviation industry and in the production of missile
Missile
Though a missile may be any thrown or launched object, it colloquially almost always refers to a self-propelled guided weapon system.-Etymology:The word missile comes from the Latin verb mittere, meaning "to send"...
s. Thorium also has good electron emission properties, with long lifetime and low potential barrier for the emission. The relative content of thorium and uranium isotopes is widely used to estimate the age of various objects, including stars (see radiometric dating).
The major application of plutonium has been in nuclear weapon
Nuclear weapon
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission or a combination of fission and fusion. Both reactions release vast quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter. The first fission bomb test released the same amount...
s, where the isotope plutonium-239 was a key component due to its ease of fission and availability. Plutonium-based designs allow reducing the critical mass to about a third of that for uranium-235. The "Fat Man
Fat Man
"Fat Man" is the codename for the atomic bomb that was detonated over Nagasaki, Japan, by the United States on August 9, 1945. It was the second of the only two nuclear weapons to be used in warfare to date , and its detonation caused the third man-made nuclear explosion. The name also refers more...
"-type plutonium bombs produced during the Manhattan Project
Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development program, led by the United States with participation from the United Kingdom and Canada, that produced the first atomic bomb during World War II. From 1942 to 1946, the project was under the direction of Major General Leslie Groves of the US Army...
used explosive compression of plutonium to obtain significantly higher densities than normal, combined with a central neutron source to begin the reaction and increase efficiency. Thus only 6.2 kg of plutonium was needed for an explosive yield
Nuclear weapon yield
The explosive yield of a nuclear weapon is the amount of energy discharged when a nuclear weapon is detonated, expressed usually in the equivalent mass of trinitrotoluene , either in kilotons or megatons , but sometimes also in terajoules...
equivalent to 20 kilotons of TNT. (See also Nuclear weapon design
Nuclear weapon design
Nuclear weapon designs are physical, chemical, and engineering arrangements that cause the physics package of a nuclear weapon to detonate. There are three basic design types...
.) Hypothetically, as little as 4 kg of plutonium—and maybe even less—could be used to make a single atomic bomb using very sophisticated assembly designs.
Plutonium-238
Plutonium-238
-External links:**...
is potentially more efficient isotope for nuclear reactors, as it has smaller critical mass than uranium-235, but releases much more thermal energy (0.56 W/g). However, its application is limited by the high price (about 1000 USD/g). This isotope has been used in thermopile
Thermopile
A thermopile is an electronic device that converts thermal energy into electrical energy. It is composed of several thermocouples connected usually in series or, less commonly, in parallel....
s and water distillation
Distillation
Distillation is a method of separating mixtures based on differences in volatilities of components in a boiling liquid mixture. Distillation is a unit operation, or a physical separation process, and not a chemical reaction....
systems of some space satellites and stations. So Galileo and Apollo spacecrafts (e.g. Apollo 14
Apollo 14
Apollo 14 was the eighth manned mission in the American Apollo program, and the third to land on the Moon. It was the last of the "H missions", targeted landings with two-day stays on the Moon with two lunar EVAs, or moonwalks....
) had heaters powered by kilogram quantities of plutonium-238 oxide; this heat is also transformed into electricity with thermopiles. The decay of plutonium-238 is produced relatively harmless alpha particles and is not accompanied by gamma-irradiation. Therefore and this isotope (~160 mg) is used as the energy source in heart pacemakers where it lasts about 5 times longer than conventional batteries.
Actinium-227 is used as a neutron source. Its high specific energy (14.5 W/g) and the possibility of obtaining significant quantities of thermally stable compounds are attractive for use in long-lasting thermoelectric generators for remote use. 228Ac is used as an indicator of radioactivity in chemical research, as it emits high-energy electrons (2.18 MeV) that can be easily detected. 228Ac-228Ra mixtures are widely used as an intense gamma-source in industry and medicine.
Toxicity
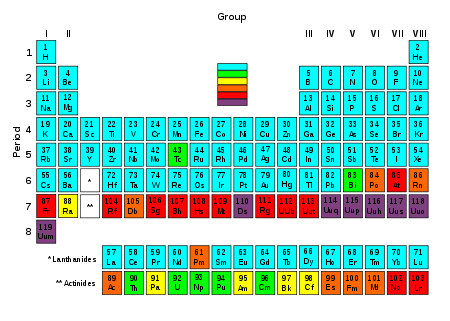
Beta particle
Beta particles are high-energy, high-speed electrons or positrons emitted by certain types of radioactive nuclei such as potassium-40. The beta particles emitted are a form of ionizing radiation also known as beta rays. The production of beta particles is termed beta decay...
and γ-radiation
Gamma ray
Gamma radiation, also known as gamma rays or hyphenated as gamma-rays and denoted as γ, is electromagnetic radiation of high frequency . Gamma rays are usually naturally produced on Earth by decay of high energy states in atomic nuclei...
. Together with radium and transuranium elements, actinium is one of the most dangerous radioactive poisons with high specific α-activity. The most important feature of actinium is its ability to accumulate and remain in the surface layer of skeleton
Skeleton
The skeleton is the body part that forms the supporting structure of an organism. There are two different skeletal types: the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, and the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside the body.In a figurative sense, skeleton can...
s. At the initial stage of poisoning, actinium accumulates in the liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
. Another danger of actinium is that it undergoes radioactive decay faster than being excreted. Adsorption
Adsorption
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions, biomolecules or molecules of gas, liquid, or dissolved solids to a surface. This process creates a film of the adsorbate on the surface of the adsorbent. It differs from absorption, in which a fluid permeates or is dissolved by a liquid or solid...
from the digestive tract is much smaller (~0.05%) for actinium than radium.
Protactinium in the body tends to accumulate in the kidneys and bones. The maximum safe dose of Pa in the human body is 0.03 µCi that corresponds to 0.5 micrograms of 231Pa. This isotope, which might be present in the air as aerosol
Aerosol
Technically, an aerosol is a suspension of fine solid particles or liquid droplets in a gas. Examples are clouds, and air pollution such as smog and smoke. In general conversation, aerosol usually refers to an aerosol spray can or the output of such a can...
, is 2.5 times more toxic than hydrocyanic acid.
Plutonium, when entering the body through air, food or blood (e.g. a wound), mostly settles in the lungs, liver and bones with only about 10% going to other organs, and remains there for decades. The long residence time of plutonium in the body is partly explained by its poor solubility in water. Some isotopes of plutonium emit ionizing α-radiation, which damages the surrounding cells. The median lethal dose (LD50) for 30 days in dogs after intravenous injection of plutonium is 0.32 milligram per kg of body mass, and thus the lethal dose for humans is approximately 22 mg for a person weighing 70 kg; the amount for respiratory exposure should be approximately four times greater. Another estimate assumes that plutonium is 50 times less toxic than radium
Radium
Radium is a chemical element with atomic number 88, represented by the symbol Ra. Radium is an almost pure-white alkaline earth metal, but it readily oxidizes on exposure to air, becoming black in color. All isotopes of radium are highly radioactive, with the most stable isotope being radium-226,...
, and thus permissible content of plutonium in the body should be 5 µg or 0.3 µCi. Such amount is nearly invisible in under microscope. After trials on animals, this maximum permissible dose was reduced to 0.65 µg or 0.04 µCi. Studies on animals also revealed that the most dangerous Pu exposure route is through inhalation, after which 5–25% of inhaled substances is retained in the body. Depending on the particle size and solubility of the plutonium compounds, Pu is localized either in the lungs or in the lymphatic system
Lymphatic system
The lymphoid system is the part of the immune system comprising a network of conduits called lymphatic vessels that carry a clear fluid called lymph unidirectionally toward the heart. Lymphoid tissue is found in many organs, particularly the lymph nodes, and in the lymphoid follicles associated...
, or is absorbed in the blood and then transported to the liver and bones. Contamination via food is the least likely way. In this case, only about 0.05% of soluble 0.01% insoluble compounds of plutonium absorbs into blood, and the rest is excreted. Exposure of damaged skin to plutonium would retain nearly 100% of it.