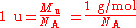Atomic mass
Encyclopedia

Mass
Mass can be defined as a quantitive measure of the resistance an object has to change in its velocity.In physics, mass commonly refers to any of the following three properties of matter, which have been shown experimentally to be equivalent:...
of a specific isotope
Isotope
Isotopes are variants of atoms of a particular chemical element, which have differing numbers of neutrons. Atoms of a particular element by definition must contain the same number of protons but may have a distinct number of neutrons which differs from atom to atom, without changing the designation...
, most often expressed in unified atomic mass units
Atomic mass unit
The unified atomic mass unit or dalton is a unit that is used for indicating mass on an atomic or molecular scale. It is defined as one twelfth of the rest mass of an unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state, and has a value of...
. The atomic mass is the total mass of protons, neutrons and electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s in a single atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
.
The atomic mass is sometimes incorrectly used as a synonym of relative atomic mass, average atomic mass and atomic weight; these differ subtly from the atomic mass. The atomic mass is defined as the mass of an atom, which can only be one isotope
Isotope
Isotopes are variants of atoms of a particular chemical element, which have differing numbers of neutrons. Atoms of a particular element by definition must contain the same number of protons but may have a distinct number of neutrons which differs from atom to atom, without changing the designation...
at a time and is not an abundance-weighted average as in the case of atomic weight
Atomic weight
Atomic weight is a dimensionless physical quantity, the ratio of the average mass of atoms of an element to 1/12 of the mass of an atom of carbon-12...
. In the case of many elements that have one dominant isotope the actual numerical similarity/difference between the atomic mass of the most common isotope and the relative atomic mass or standard atomic weights can be very small such that it does not affect most bulk calculations—but such an error can be critical when considering individual atoms. For elements with more than one common isotope the difference even to the most common atomic mass can be half a mass unit or more (e.g. chlorine
Chlorine
Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine...
). The atomic mass of an uncommon isotope can differ from the relative atomic mass or standard atomic weight by several mass units.
Standard atomic weight refers to the mean relative atomic mass of an element in the local environment of the Earth's crust and atmosphere
Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention , and reducing temperature extremes between day and night...
as determined by the IUPAC Commission on Atomic Weights and Isotopic Abundances. These are what are included in a standard periodic table
Periodic table
The periodic table of the chemical elements is a tabular display of the 118 known chemical elements organized by selected properties of their atomic structures. Elements are presented by increasing atomic number, the number of protons in an atom's atomic nucleus...
and is what is used in most bulk calculations. An uncertainty in brackets is included which often reflects natural variability in isotopic distribution rather than uncertainty in measurement. For synthetic element
Synthetic element
In chemistry, a synthetic element is a chemical element that is too unstable to occur naturally on Earth, and therefore has to be created artificially. So far 30 synthetic elements have been discovered—that is, synthesized...
s the isotope formed depends on the means of synthesis, so the concept of natural isotope abundance has no meaning. Therefore, for synthetic elements the total nucleon count of the most stable isotope (i.e., the isotope with the longest half-life) is listed in brackets in place of the standard atomic weight. Lithium
Lithium
Lithium is a soft, silver-white metal that belongs to the alkali metal group of chemical elements. It is represented by the symbol Li, and it has the atomic number 3. Under standard conditions it is the lightest metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly...
represents a unique case where the natural abundances of the isotopes have been perturbed by human activities to the point of affecting the uncertainty in its standard atomic weight, even in samples obtained from natural sources, such as rivers.
Relative atomic mass is a synonym for atomic weight
Atomic weight
Atomic weight is a dimensionless physical quantity, the ratio of the average mass of atoms of an element to 1/12 of the mass of an atom of carbon-12...
and closely related to average atomic mass (but not a synonym for atomic mass), the weighted mean
Weighted mean
The weighted mean is similar to an arithmetic mean , where instead of each of the data points contributing equally to the final average, some data points contribute more than others...
of the atomic masses of all the atoms of a chemical element found in a particular sample, weighted by isotopic abundance. This is frequently used as a synonym for the standard atomic weight and it is correct to do so since the standard atomic weights are relative atomic masses, although it is less specific to do so. Relative atomic mass also refers to non-terrestrial environments and highly specific terrestrial environments that deviate from the average or have different certainties (number of significant figures) than the standard atomic weights.
Relative isotopic mass is the relative mass of a given isotope (more specifically, any single nuclide
Nuclide
A nuclide is an atomic species characterized by the specific constitution of its nucleus, i.e., by its number of protons Z, its number of neutrons N, and its nuclear energy state....
), scaled with carbon-12
Carbon-12
Carbon-12 is the more abundant of the two stable isotopes of the element carbon, accounting for 98.89% of carbon; it contains 6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 6 electrons....
as exactly 12. No other nuclides other than carbon-12 have exactly whole-number masses in this scale. This is due to two factors: [1] the different mass of neutrons and protons acting to change the total mass in nuclides with proton/neutron ratios other than the 1:1 ratio of carbon-12; and [2] an exact whole-number will not be located if there exists a loss/gain of mass to difference in mean binding energy
Binding energy
Binding energy is the mechanical energy required to disassemble a whole into separate parts. A bound system typically has a lower potential energy than its constituent parts; this is what keeps the system together—often this means that energy is released upon the creation of a bound state...
relative to the mean binding energy for carbon-12. However, since any mass defect due to binding energy is a small fraction (less than 1%) compared to the mass of a nucleon, and even less compared to the average mass per nucleon in carbon-12, which is moderately strongly bound. Since protons and neutrons differ in mass from each by an even smaller fraction (about 0.0014 u
Atomic mass unit
The unified atomic mass unit or dalton is a unit that is used for indicating mass on an atomic or molecular scale. It is defined as one twelfth of the rest mass of an unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state, and has a value of...
), the practice of rounding the atomic mass of any given nuclide or isotope to the nearest whole number, always gives the simple whole number total nucleon count. Neutron count can then be derived by subtracting the atomic number
Atomic number
In chemistry and physics, the atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom and therefore identical to the charge number of the nucleus. It is conventionally represented by the symbol Z. The atomic number uniquely identifies a chemical element...
.
The mass number
Mass number
The mass number , also called atomic mass number or nucleon number, is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atomic nucleus. Because protons and neutrons both are baryons, the mass number A is identical with the baryon number B as of the nucleus as of the whole atom or ion...
of a nuclide is simply the total number of nucleons in the nucleus. It is equal to the number of protons (atomic number) plus the number of neutrons. This number is always a simple whole number. It has units of "nucleons" not atomic mass units. An example is oxygen-16, which has 16 nucleons (8 protons and 8 neutrons).
Mass defects in atomic masses
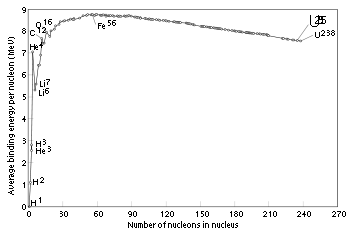
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
-1, becomes negative until a minimum is reached at iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
-56, iron-58 and nickel
Nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with the chemical symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel belongs to the transition metals and is hard and ductile...
-62, then increases to positive values in the heavy isotopes, with increasing atomic number. This corresponds to the following: nuclear fission
Nuclear fission
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, nuclear fission is a nuclear reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into smaller parts , often producing free neutrons and photons , and releasing a tremendous amount of energy...
in an element heavier than iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
produces energy, and fission in any element lighter than iron requires energy. The opposite is true of nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion is the process by which two or more atomic nuclei join together, or "fuse", to form a single heavier nucleus. This is usually accompanied by the release or absorption of large quantities of energy...
reactions: fusion in elements lighter than iron produces energy, and fusion in elements heavier than iron requires energy.
Measurement of atomic masses
Direct comparison and measurement of the masses of atoms is achieved with mass spectrometryMass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of charged particles.It is used for determining masses of particles, for determining the elemental composition of a sample or molecule, and for elucidating the chemical structures of molecules, such as peptides and...
.
Conversion factor between atomic mass units and grams
The standard scientific unit for dealing with atoms in macroscopic quantities is the moleMole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
(mol), which is defined arbitrarily as the amount of a substance with as many atoms or other units as there are in 12 grams of the carbon isotope C-12. The number of atoms in a mole is called Avogadro's number
Avogadro's number
In chemistry and physics, the Avogadro constant is defined as the ratio of the number of constituent particles N in a sample to the amount of substance n through the relationship NA = N/n. Thus, it is the proportionality factor that relates the molar mass of an entity, i.e...
, the value of which is approximately 6.022 × 10 mol−1. One mole of a substance always contains almost exactly the relative atomic mass or molar mass
Molar mass
Molar mass, symbol M, is a physical property of a given substance , namely its mass per amount of substance. The base SI unit for mass is the kilogram and that for amount of substance is the mole. Thus, the derived unit for molar mass is kg/mol...
of that substance (which is the concept of molar mass
Molar mass
Molar mass, symbol M, is a physical property of a given substance , namely its mass per amount of substance. The base SI unit for mass is the kilogram and that for amount of substance is the mole. Thus, the derived unit for molar mass is kg/mol...
), expressed in grams; however, this is almost never true for the atomic mass. For example, the standard atomic weight of iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
is 55.847 g/mol, and therefore one mole of iron as commonly found on earth has a mass of 55.847 grams. The atomic mass of an 56Fe isotope is 55.935 u and one mole of 56Fe will in theory weigh 55.935g, but such amounts of pure 56Fe have never been found on Earth.
The formulaic conversion between atomic mass unit
Atomic mass unit
The unified atomic mass unit or dalton is a unit that is used for indicating mass on an atomic or molecular scale. It is defined as one twelfth of the rest mass of an unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state, and has a value of...
s and SI
Si
Si, si, or SI may refer to :- Measurement, mathematics and science :* International System of Units , the modern international standard version of the metric system...
mass in grams for a single atom is:
where
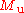 is the Molar mass constant
is the Molar mass constantMolar mass constant
The molar mass constant, symbol Mu, is a physical constant which relates atomic weight and molar mass. Its value is defined to be 1 g/mol in SI units....
and
 is the Avogadro constant.
is the Avogadro constant.Relationship between atomic and molecular masses
Similar definitions apply to moleculeMolecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
s. One can compute the molecular mass
Molecular mass
The molecular mass of a substance is the mass of one molecule of that substance, in unified atomic mass unit u...
of a compound by adding the atomic masses of its constituent atoms (nuclides). One can compute the molar mass
Molar mass
Molar mass, symbol M, is a physical property of a given substance , namely its mass per amount of substance. The base SI unit for mass is the kilogram and that for amount of substance is the mole. Thus, the derived unit for molar mass is kg/mol...
of a compound by adding the relative atomic masses of the elements given in the chemical formula
Chemical formula
A chemical formula or molecular formula is a way of expressing information about the atoms that constitute a particular chemical compound....
. In both cases the multiplicity of the atoms (the number of times it occurs) must be taken into account, usually by multiplication of each unique mass by its multiplicity.
History
The first scientists to determine atomic weights were John DaltonJohn Dalton
John Dalton FRS was an English chemist, meteorologist and physicist. He is best known for his pioneering work in the development of modern atomic theory, and his research into colour blindness .-Early life:John Dalton was born into a Quaker family at Eaglesfield, near Cockermouth, Cumberland,...
and Thomas Thomson between 1803 and 1805 and Jöns Jakob Berzelius
Jöns Jakob Berzelius
Jöns Jacob Berzelius was a Swedish chemist. He worked out the modern technique of chemical formula notation, and is together with John Dalton, Antoine Lavoisier, and Robert Boyle considered a father of modern chemistry...
between 1808 and 1826. Atomic weight was originally defined relative to that of the lightest element hydrogen taken as 1.00, and in the 1820s Prout's hypothesis
Prout's hypothesis
Prout's hypothesis was an early 19th century attempt to explain the existence of the various chemical elements through a hypothesis regarding the internal structure of the atom...
stated that atomic masses of all elements would prove via a whole number rule
Whole number rule
The whole number rule states that the masses of the elements are whole number multiples of the mass of the hydrogen atom. The rule can be formulated from Prout's hypothesis put forth in 1815. In 1920, Francis W...
to be exact multiples of this hydrogen weight. Berzelius, however, soon proved that this hypothesis did not always hold even approximately, and in some elements, such as chlorine, atomic weight falls almost exactly between two multiples of the hydrogen weight. Still later, as noted, this was shown to be an isotope effect, and that the atomic masses of pure isotopes, or nuclide
Nuclide
A nuclide is an atomic species characterized by the specific constitution of its nucleus, i.e., by its number of protons Z, its number of neutrons N, and its nuclear energy state....
s, are multiples of the hydrogen mass, to within about 1%.
In the 1860s Stanislao Cannizzaro
Stanislao Cannizzaro
Stanislao Cannizzaro, FRS was an Italian chemist. He is remembered today largely for the Cannizzaro reaction and for his influential role in the atomic-weight deliberations of the Karlsruhe Congress in 1860.-Biography:...
refined atomic weights by applying Avogadro's law
Avogadro's law
Avogadro's law is a gas law named after Amedeo Avogadro who, in 1811, hypothesized that two given samples of an ideal gas, at the same temperature, pressure and volume, contain the same number of molecules...
(notably at the Karlsruhe Congress
Karlsruhe Congress
The Karlsruhe Congress was an international meeting of chemists held in Karlsruhe, Germany from 3 to 5 September, 1860. It was the first international conference of chemistry worldwide.- The meeting :...
of 1860). He formulated a law to determine atomic weights of elements: the different quantities of the same element contained in different molecules are all whole multiples of the atomic weight and determined atomic weights and molecular weights by comparing the vapor density of a collection of gases with molecules containing one or more of the chemical element in question.
In the early twentieth century, up until the 1960s chemists
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
and physicists
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
used two different atomic mass scales. The chemists used a scale such that the natural mixture of oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
isotopes had an atomic mass 16, while the physicists assigned the same number 16 to the atomic mass of the most common oxygen isotope (containing eight protons and eight neutrons). However, because oxygen-17
Oxygen-17
Oxygen-17 is a low abundant isotope of oxygen . Being the only stable isotope of oxygen possessing a nuclear spin and the unique characteristic of field-independent relaxation it enables NMR studies of metabolic pathways of compounds incorporating oxygen at high magnetic fields Oxygen-17 is a low...
and oxygen-18
Oxygen-18
Oxygen-18 is a natural, stable isotope of oxygen and one of the environmental isotopes.18O is an important precursor for the production of fluorodeoxyglucose used in positron emission tomography...
are also present in natural oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
this led to 2 different tables of atomic mass. The unified scale based on carbon-12, 12C, met the physicists' need to base the scale on a pure isotope, while being numerically close to the chemists' scale.
The term atomic weight is being phased out slowly and being replaced by relative atomic mass, in most current usage. The history of this shift in nomenclature reaches back to the 1960s and has been the source of much debate in the scientific community. The debate was largely created by the adoption of the unified atomic mass unit and the realization that weight was in some ways an inappropriate term. The argument for keeping the term "atomic weight" was primarily that it was a well understood term to those in the field, that the term "atomic mass" was already in use (as it is currently defined) and that the term "relative atomic mass" was in some ways redundant. In 1979, in a compromise move, the definition was refined and the term "relative atomic mass" was introduced as a secondary synonym. Twenty years later the primacy of these synonyms was reversed and the term "relative atomic mass" is now the preferred term; however the "standard atomic weights" have maintained the same name.
See also
- Atomic numberAtomic numberIn chemistry and physics, the atomic number is the number of protons found in the nucleus of an atom and therefore identical to the charge number of the nucleus. It is conventionally represented by the symbol Z. The atomic number uniquely identifies a chemical element...
- Atomic mass unitAtomic mass unitThe unified atomic mass unit or dalton is a unit that is used for indicating mass on an atomic or molecular scale. It is defined as one twelfth of the rest mass of an unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state, and has a value of...
- IsotopeIsotopeIsotopes are variants of atoms of a particular chemical element, which have differing numbers of neutrons. Atoms of a particular element by definition must contain the same number of protons but may have a distinct number of neutrons which differs from atom to atom, without changing the designation...
- Molecular massMolecular massThe molecular mass of a substance is the mass of one molecule of that substance, in unified atomic mass unit u...
- Jean StasJean StasJean Servais Stas was a Belgian analytical chemist.- Life and work :Stas was born in Leuven and trained initially as a physician. He later switched to chemistry and worked at the École Polytechnique in Paris under the direction of Jean-Baptiste Dumas...
External links
- NIST relative atomic masses of all isotopes and the standard atomic weights of the elements
- Tutorial on the concept and measurement of atomic mass
- AME2003 Atomic Mass Evaluation from the National Nuclear Data CenterNational Nuclear Data CenterThe National Nuclear Data Center is an organization based in the Brookhaven National Laboratory that acts as a repository for data regarding nuclear chemistry, such as nuclear structure, decay, and reaction data, as well as historical information regarding previous experiments and literature...