
List of planetary probes
Encyclopedia
This is a list of all space probe
s that have left Earth orbit (or were launched with that intention but failed), organised by their planned destination. It includes planetary probes, solar probes, and probes to asteroids and comets, but excludes lunar probes (listed separately at List of lunar probes). Flybys (such as gravity assists
) that were incidental to the main purpose of the mission are also included. Confirmed future probes are included, but missions that are still at the concept stage, or which never progressed beyond the concept stage, are not.
Solar
These are solar observation probes designed to operate in heliocentric orbit
or at one of the Earth–Sun Lagrangian point
s. The list excludes Earth-orbiting solar observatories.
Mercury
Earth
These are probes that incidentally performed Earth flybys during missions to other bodies, often as part of gravity-assist orbital manoeuvres. Earth-orbiting craft are not listed.
Phobos
Asteroid
Jupiter
Saturn
Titan
Uranus
Neptune
Pluto
Comet
Space probe
A robotic spacecraft is a spacecraft with no humans on board, that is usually under telerobotic control. A robotic spacecraft designed to make scientific research measurements is often called a space probe. Many space missions are more suited to telerobotic rather than crewed operation, due to...
s that have left Earth orbit (or were launched with that intention but failed), organised by their planned destination. It includes planetary probes, solar probes, and probes to asteroids and comets, but excludes lunar probes (listed separately at List of lunar probes). Flybys (such as gravity assists
Gravitational slingshot
In orbital mechanics and aerospace engineering, a gravitational slingshot, gravity assist maneuver, or swing-by is the use of the relative movement and gravity of a planet or other celestial body to alter the path and speed of a spacecraft, typically in order to save propellant, time, and expense...
) that were incidental to the main purpose of the mission are also included. Confirmed future probes are included, but missions that are still at the concept stage, or which never progressed beyond the concept stage, are not.
Key
Colour key:| – Mission or flyby completed successfully (or partially successfully) | – Failed or cancelled mission | ||
| – Mission en route or in progress (including mission extensions) | – Planned mission |
- † means "tentatively identified", as classified by NASA http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/planetary/tent_launch.html. These are Cold War-era Soviet missions, mostly failures, about which few or no details have been officially released. The information given may be speculative.
- Date is the date of:
- closest encounter (flybys)
- impact (impactors)
- orbital insertion to end of mission, whether planned or premature (orbiters)
- landing to end of mission, whether planned or premature (landers)
- launch (missions that never got underway due to failure at or soon after launch)
- In cases which do not fit any of the above, the event to which the date refers is stated. Note that as a result of this scheme missions are not always listed in order of launch.
- Under Status:
- success means that the mission fulfilled its primary goals. In the case of flybys (such as gravity assists) that are incidental to the main mission, "success" indicates the successful completion of the flyby, not necessarily that of the main mission.
- partial success means that the mission fulfilled some but not all of its primary goals
- failure means that the mission did not fulfil any of its primary goals
- Other entries are self-explanatory.
SolarSunThe Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
probes
These are solar observation probes designed to operate in heliocentric orbitHeliocentric orbit
A heliocentric orbit is an orbit around the Sun. All planets, comets, and asteroids in our Solar System are in such orbits, as are many artificial probes and pieces of debris. The moons of planets in the Solar System, by contrast, are not in heliocentric orbits as they orbit their respective planet...
or at one of the Earth–Sun Lagrangian point
Lagrangian point
The Lagrangian points are the five positions in an orbital configuration where a small object affected only by gravity can theoretically be stationary relative to two larger objects...
s. The list excludes Earth-orbiting solar observatories.
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pioneer 5 Pioneer 5 Pioneer 5 was a spin-stabilized space probe in the NASA Pioneer program used to investigate interplanetary space between the orbits of Earth and Venus. It was launched on March 11, 1960 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Launch Complex 17a at 13:00:00 UTC with an on-orbit dry mass of 43 kg... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... /  DOD DODUnited States Department of Defense The United States Department of Defense is the U.S... |
March–April 1960 | orbiter | success | measured magnetic field phenomena, solar flare particles, and ionization in the interplanetary region |  |
||
| Pioneer 6 Pioneer 6, 7, 8 and 9 Pioneer 6, 7, 8, and 9 were space probes in the Pioneer program. Together, they formed a series of solar-orbiting, spin-stabilized, solar-cell and battery-powered satellites designed to obtain measurements on a continuing basis of interplanetary phenomena from widely separated points in space. They... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
December 1965 – still contactable in 2000 | orbiter | success | network of solar-orbiting "space weather" monitors, observing solar wind, cosmic rays, and magnetic fields |  |
||
| Pioneer 7 Pioneer 6, 7, 8 and 9 Pioneer 6, 7, 8, and 9 were space probes in the Pioneer program. Together, they formed a series of solar-orbiting, spin-stabilized, solar-cell and battery-powered satellites designed to obtain measurements on a continuing basis of interplanetary phenomena from widely separated points in space. They... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
August 1966 – still contactable in 1995 | orbiter | success | ||||
| Pioneer 8 Pioneer 6, 7, 8 and 9 Pioneer 6, 7, 8, and 9 were space probes in the Pioneer program. Together, they formed a series of solar-orbiting, spin-stabilized, solar-cell and battery-powered satellites designed to obtain measurements on a continuing basis of interplanetary phenomena from widely separated points in space. They... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
December 1967 – still contactable in 2001 | orbiter | success | ||||
| Pioneer 9 Pioneer 6, 7, 8 and 9 Pioneer 6, 7, 8, and 9 were space probes in the Pioneer program. Together, they formed a series of solar-orbiting, spin-stabilized, solar-cell and battery-powered satellites designed to obtain measurements on a continuing basis of interplanetary phenomena from widely separated points in space. They... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
November 1968 – May 1983 | orbiter | success | ||||
| Pioneer-E Pioneer 6, 7, 8 and 9 Pioneer 6, 7, 8, and 9 were space probes in the Pioneer program. Together, they formed a series of solar-orbiting, spin-stabilized, solar-cell and battery-powered satellites designed to obtain measurements on a continuing basis of interplanetary phenomena from widely separated points in space. They... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
27 August 1969 | orbiter | failure | intended as part of the Pioneer network; failed to reach orbit |  |
||
| Helios A Helios probes Helios-A and Helios-B , were a pair of probes launched into heliocentric orbit for the purpose of studying solar processes. A joint venture of the Federal Republic of Germany and NASA, the probes were launched from the John F. Kennedy Space Center at Cape Canaveral, Florida, on Dec. 10, 1974,... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... /  BWF BWF |
November 1974 – 1982 | orbiter | success | observations of solar wind, magnetic and electric fields, cosmic rays and cosmic dust between Earth and Sun |  |
||
| Helios B |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... /  BWF BWF |
January 1976 – 1985? | orbiter | success | ||||
| ISEE-3 |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
1978–1982 | orbiter | success | observed solar phenomena in conjunction with earth-orbiting ISEE-1 and ISEE-2; later renamed International Cometary Explorer (ICE) and directed to Comet Giacobini-Zinner |  |
||
| Ulysses Ulysses probe Ulysses is a decommissioned robotic space probe that was designed to study the Sun as a joint venture of NASA and the European Space Agency . The spacecraft was originally named Odysseus, because of its lengthy and indirect trajectory to near Solar distance... (first pass) |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... /  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
1994 | orbiter | success | south polar observations |  |
||
| 1995 | north polar observations | |||||||
| WIND |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
November 1994 — still returning data (as of December 2010) | orbiter | success | solar wind measurements |  |
||
| SOHO Solar and Heliospheric Observatory The Solar and Heliospheric Observatory is a spacecraft built by a European industrial consortium led by Matra Marconi Space that was launched on a Lockheed Martin Atlas IIAS launch vehicle on December 2, 1995 to study the Sun, and has discovered over 2100 comets. It began normal operations in May... |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... /  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
May 1996 – mission extended until at least December 2012 | orbiter | success | investigation of Sun's core, corona, and solar wind; comet discoveries | |||
| ACE Advanced Composition Explorer Advanced Composition Explorer is a NASA space exploration mission being conducted as part of the Explorer program to study matter in situ, comprising energetic particles from the solar wind, the interplanetary medium, and other sources. Real-time data from ACE is used by the Space Weather... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
August 1997 – still returning data (as of December 2010) | orbiter | success | solar wind observations |  |
||
| Ulysses Ulysses probe Ulysses is a decommissioned robotic space probe that was designed to study the Sun as a joint venture of NASA and the European Space Agency . The spacecraft was originally named Odysseus, because of its lengthy and indirect trajectory to near Solar distance... (second pass) |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... /  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2000 | orbiter | success | south polar observations |  |
||
| 2001 | north polar observations | |||||||
| Genesis Genesis (spacecraft) The Genesis spacecraft was a NASA sample return probe which collected a sample of solar wind and returned it to Earth for analysis. It was the first NASA sample return mission to return material since the Apollo Program, and the first to return material from beyond the orbit of the Moon... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2001–2004 | orbiter/ sample return |
partial success | solar wind sample return; crash landed on return to Earth, some samples salvaged |  |
||
| STEREO A STEREO STEREO is a solar observation mission. Two nearly identical spacecraft were launched into orbits that cause them to respectively pull farther ahead of and fall gradually behind the Earth... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
December 2006 – still active (as of December 2010) | orbiter | success | stereoscopic imaging of coronal mass ejections and other solar phenomena | 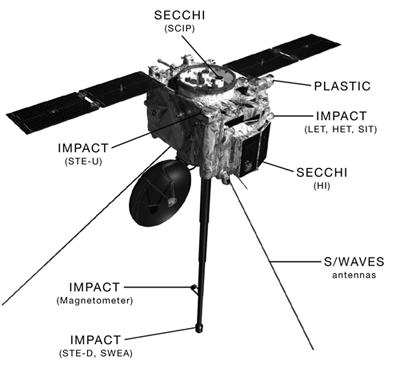 |
||
| STEREO B STEREO STEREO is a solar observation mission. Two nearly identical spacecraft were launched into orbits that cause them to respectively pull farther ahead of and fall gradually behind the Earth... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
December 2006 – still active (as of December 2010) | orbiter | success | ||||
| Ulysses Ulysses probe Ulysses is a decommissioned robotic space probe that was designed to study the Sun as a joint venture of NASA and the European Space Agency . The spacecraft was originally named Odysseus, because of its lengthy and indirect trajectory to near Solar distance... (third pass) |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... /  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2007 | orbiter | success | south polar observations |  |
||
| 2008 | partial success | north polar observations; some data returned despite failing power and reduced transmission capacity | ||||||
| Solar Sentinels Solar Sentinels The Solar Sentinels is a space mission to study the Sun during its solar maximum, the last before the beginning of the Orion program. Six spacecraft will be launched, which will separate into three groups... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2015 | multi-probe orbiter | planned | six probes watching the sun | |||
| Solar Probe Plus |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2015 | orbiter | under study | close-range coronal observations | |||
| Solar Orbiter Solar Orbiter Solar Orbiter is a planned Sun-observing satellite, under development by the European Space Agency . The main mission scenario is a launch by an Atlas V from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida in January 2017... |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
2017 | orbiter | proposed | close-range solar observations | |||
MercuryMercury (planet)Mercury is the innermost and smallest planet in the Solar System, orbiting the Sun once every 87.969 Earth days. The orbit of Mercury has the highest eccentricity of all the Solar System planets, and it has the smallest axial tilt. It completes three rotations about its axis for every two orbits...
probes
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mariner 10 Mariner 10 Mariner 10 was an American robotic space probe launched by NASA on November 3, 1973, to fly by the planets Mercury and Venus. It was launched approximately two years after Mariner 9 and was the last spacecraft in the Mariner program... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
29 March 1974 | flyby | success | minimum distance 704 km |  |
||
| 48,069 km | ||||||||
| 16 March 1975 | 327 km | |||||||
| MESSENGER MESSENGER The MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry and Ranging space probe is a robotic NASA spacecraft in orbit around the planet Mercury. The spacecraft was launched aboard a Delta II rocket in August 2004 to study the chemical composition, geology, and magnetic field of Mercury... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
14 January 2008 | flyby | success | minimum distance 200 km |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2004-030A | |
| 6 October 2008 | minimum distance 200 km | |||||||
| 29 September 2009 | minimum distance 200 km | |||||||
| 18 March 2011 – March 2012 |
orbiter | success | ||||||
| BepiColombo BepiColombo BepiColombo is a joint mission of the European Space Agency and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency to the planet Mercury, due to launch in 2014. The mission is still in the planning stages so changes to the current description are likely over the next few years... |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... /  JAXA JAXAJapan Aerospace Exploration Agency The , or JAXA, is Japan's national aerospace agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on October 1, 2003, as an Independent Administrative Institution administered by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology and the... |
2014 | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=BEPICLMBO | |||||
| Mercury Planetary Orbiter |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
orbiter | under construction | |||||
| Mercury Magnetospheric Orbiter |
 JAXA JAXAJapan Aerospace Exploration Agency The , or JAXA, is Japan's national aerospace agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on October 1, 2003, as an Independent Administrative Institution administered by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology and the... |
orbiter | under construction | |||||
1961–1965
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sputnik 7 Sputnik 7 Tyazhely Sputnik, , also known as Venera 1VA No.1, and in the West as Sputnik 7, was a Soviet spacecraft, which was intended to be the first spacecraft to explore Venus. Due to a problem with its upper stage it failed to leave low Earth orbit... |
 (USSR (USSRSoviet Union The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991.... ) |
4 February 1961 | lander | failure | failed to escape from Earth orbit | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1961-002A | ||
| Venera 1 Venera 1 On February 12, 1961, 00:34:36 UTC, was the first planetary probe launched to Venus by the Soviet Union. The Venus-1 Automatic Interplanetary Station, or Venera 1, was a 643.5 kg probe consisting of a cylindrical body 1.05 metres in diameter topped by a dome, totalling 2.035 metres... |
 (USSR (USSRSoviet Union The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991.... ) |
19 May 1961 – 20 May 1961 |
flyby | failure | contact lost 7 days after launch; first spacecraft to fly by another planet | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1961-003A | ||
| Mariner 1 Mariner 1 Mariner 1 was the first spacecraft of the American Mariner program. Launched on July 22, 1962 as a Venus flyby mission, a range safety officer ordered its destructive abort at 09:26:16 UT, 294.5 seconds after launch.... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
22 July 1962 | flyby | failure | guidance failure shortly after launch | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=MARIN1 | ||
| Sputnik 19 Sputnik 19 Venera 2MV-1 No.1, also known as Sputnik 19 in the West, was a Soviet spacecraft, which was launched in 1962 as part of the Venera programme, and was intended to become the first spacecraft to land on Venus. Due to a problem with its upper stage it failed to leave low Earth orbit, and reentered the... |
 (USSR (USSRSoviet Union The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991.... ) |
25 August 1962 | lander | failure | failed to escape Earth orbit | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1962-040A | ||
| Sputnik 20 Sputnik 20 Venera 2MV-1 No.2, also known as Sputnik 20 in the West, was a Soviet spacecraft, which was launched in 1962 as part of the Venera programme, and was intended to become the first spacecraft to land on Venus. Due to a problem with its upper stage it failed to leave low Earth orbit, and reentered the... |
 (USSR (USSRSoviet Union The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991.... ) |
1 September 1962 | lander | failure | failed to escape Earth orbit | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1962-043A | ||
| Sputnik 21 Sputnik 21 Venera 2MV-2 No.1, also known as Sputnik 21 in the West, was a Soviet spacecraft, which was launched in 1962 as part of the Venera programme, and was intended to make a flyby of Venus. Due to a problem with the rocket which launched it, it failed to leave low Earth orbit, and reentered the... |
 (USSR (USSRSoviet Union The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991.... ) |
12 September 1962 | flyby | failure | third stage exploded | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1962-045A | ||
| Mariner 2 Mariner 2 Mariner 2 , an American space probe to Venus, was the first space probe to conduct a successful planetary encounter . The first successful spacecraft in the NASA Mariner program, it was a simplified version of the Block I spacecraft of the Ranger program and an exact copy of Mariner 1... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
14 December 1962 | flyby | success | first successful Venus flyby; minimum distance 34,773 km |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1962-041A | |
| Cosmos 21 Cosmos 21 Kosmos 21 was a Soviet spacecraft with an unknown mission. This mission has been tentatively identified by NASA as a technology test of the Venera series space probes. It may have been an attempted Venus flyby, presumably similar to the later Kosmos 27 mission, or it may have been intended from... † |
 (USSR (USSRSoviet Union The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991.... ) |
11 November 1963 | flyby? | failure | failed to escape Earth orbit | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1963-044A | ||
| Venera 1964A† |  (USSR) (USSR) |
19 February 1964 | flyby | failure | failed to reach Earth orbit | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/planetary/tent_launch.html | ||
| Venera 1964B† |  (USSR) (USSR) |
1 March 1964 | flyby | failure | failed to reach Earth orbit | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/planetary/tent_launch.html | ||
| Cosmos 27 Cosmos 27 Kosmos 27 was a space mission intended as a Venus flyby. The SL-6/A-2-e launcher successfully achieved Earth orbit, but the spacecraft failed to escape orbit for its flight to Venus.... |
 (USSR (USSRSoviet Union The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991.... ) |
27 March 1964 | flyby | failure | failed to escape Earth orbit | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1964-014A | ||
| Zond 1 Zond 1 Zond 1 was a member of the Soviet Zond program. It was the second Soviet research spacecraft to successfully reach Venus, although communications had failed by that time... |
 (USSR) (USSR) |
1964 | flyby and possible lander | failure | contact lost en route | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1964-016D | ||
| Cosmos 96 |  (USSR) (USSR) |
23 November 1965 | lander | failure | exploded? | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1965-094A | ||
| Venera 1965A† |  (USSR) (USSR) |
26 November 1965 | flyby | failure | launch vehicle failure? | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/planetary/tent_launch.html | ||
1966–1970
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Venera 2 Venera 2 Venera 2 was a probe in the Soviet Venera program for the exploration of Venus.*Launch Date/Time: 1965 November 12 at 05:02:00 UTC*On-orbit Dry Mass: 963 kg... |
 (USSR) (USSR) |
27 February 1966 | flyby | failure | ceased to operate en route | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1965-091A | ||
| Venera 3 Venera 3 Venera 3 was a Venera program space probe that was built and launched by the Soviet Union to explore the surface of Venus. It was launched on November 16, 1965 at 04:19 UTC from Baikonur, Kazakhstan.... |
 (USSR) (USSR) |
1 March 1966 | lander | failure | contact lost before arrival; first spacecraft to impact on the surface of another planet | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1965-092A | ||
| Cosmos 167 |  (USSR) (USSR) |
17 June 1967 | lander | failure | failed to escape Earth orbit | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1967-063A | ||
| Venera 4 Venera 4 Venera 4 ) was a probe in the Soviet Venera program for the exploration of Venus. Venera-4 was the first successful probe to perform in-place analysis of the environment of another planet. It was also the first probe to land on another planet... |
 (USSR) (USSR) |
18 October 1967 | atmospheric probe | success | continued to transmit to an altitude of 25 km | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1967-058A | ||
| Mariner 5 Mariner 5 Mariner 5 was a spacecraft of the Mariner program that carried a complement of experiments to probe Venus' atmosphere by radio occultation, measure the hydrogen Lyman-alpha spectrum, and sample the solar particles and magnetic field fluctuations above the planet... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
19 October 1967 | flyby | success | minimum distance 5,000 km |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1967-060A | |
| Venera 5 Venera 5 Venera 5 was a probe in the Soviet space program Venera for the exploration of Venus.Venera 5 was launched from a Tyazheliy Sputnik towards Venus to obtain atmospheric data... |
 (USSR) (USSR) |
16 May 1969 | atmospheric probe | success | transmitted atmospheric data for 53 minutes, to an altitude of about 26 km | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1969-001A | ||
| Venera 6 Venera 6 Venera 6 was a Soviet spacecraft, launched from a Tyazheliy Sputnik on January 10, 1969 towards Venus to obtain atmospheric data. It had an on-orbit dry mass of 1130 kg.... |
 (USSR) (USSR) |
17 May 1969 | atmospheric probe | success | transmitted atmospheric data for 51 minutes, to an altitude of perhaps 10–12 km | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1969-002A | ||
| Cosmos 359 |  (USSR) (USSR) |
22 August 1970 | lander? | failure | failed to escape Earth orbit | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1970-065A | ||
| Venera 7 Venera 7 The Venera 7 was a Soviet spacecraft, part of the Venera series of probes to Venus. When it landed on the Venusian surface, it became the first man-made spacecraft to successfully land on another planet and to transmit data from there back to Earth.*Launch date/time: 1970 August 17 at 05:38... |
 (USSR) (USSR) |
15 December 1970 | lander | success | first successful landing on another planet; signals returned from surface for 23 minutes |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1970-060A | |
1971–1975
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cosmos 482 Cosmos 482 Kosmos 482 , launched March 31, 1972 at 04:02:33 UTC, was an attempted Venus probe which failed to escape low Earth orbit.Beginning in 1962, the name Kosmos was given to Soviet spacecraft which remained in Earth orbit, regardless of whether that was their intended final destination... |
 (USSR) (USSR) |
31 March 1972 | lander? | failure | failed to escape Earth orbit | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1972-023A | ||
| Venera 8 Venera 8 Venera 8 was a probe in the Soviet Venera program for the exploration of Venus.Venera 8 was a Venus atmospheric probe and lander. Its instrumentation included temperature, pressure, and light sensors as well as an altimeter, gamma ray spectrometer, gas analyzer, and radio transmitters... |
 (USSR) (USSR) |
22 July 1972 | lander | success | signals returned from surface for 50 minutes |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1972-021A | |
| Mariner 10 Mariner 10 Mariner 10 was an American robotic space probe launched by NASA on November 3, 1973, to fly by the planets Mercury and Venus. It was launched approximately two years after Mariner 9 and was the last spacecraft in the Mariner program... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
5 February 1974 | flyby | success | minimum distance 5768 km, en route to Mercury; first use of gravity assist Gravitational slingshot In orbital mechanics and aerospace engineering, a gravitational slingshot, gravity assist maneuver, or swing-by is the use of the relative movement and gravity of a planet or other celestial body to alter the path and speed of a spacecraft, typically in order to save propellant, time, and expense... by an interplanetary spacecraft |
 |
||
| Venera 9 Venera 9 Venera 9 was a USSR unmanned space mission to Venus. It consisted of an orbiter and a lander. It was launched on June 8, 1975 02:38:00 UTC and weighed 4,936 kg... |
 (USSR) (USSR) |
1975 | orbiter | success | first spacecraft to orbit Venus; communications relay for lander; atmospheric and magnetic studies |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1975-050A | |
| 22 October 1975 | lander | success | first images from the surface; operated on surface for 53 minutes | 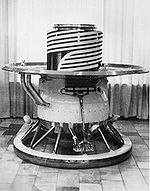 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1975-050D | |||
| Venera 10 Venera 10 Venera 10 was a USSR unmanned space mission to Venus. It consisted of an orbiter and a lander. It launched on June 14, 1975 03:00:31 UTC.-Orbiter:The orbiter entered Venus orbit on October 23, 1975... |
 (USSR) (USSR) |
1975 | orbiter | success | communications relay for lander; atmospheric and magnetic studies |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1975-054A | |
| 23 October 1975 | lander | success | transmitted from surface for 65 minutes | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1975-054D | ||||
1978
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pioneer Venus Orbiter Pioneer Venus project The Pioneer mission to Venus consisted of two components, launched separately. Pioneer Venus 1 or Pioneer Venus Orbiter was launched in 1978 and studied the planet for more than a decade after orbital insertion in 1978. Pioneer Venus 2 or Pioneer Venus Multiprobe sent four small probes into the... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
1992 |
orbiter | success | atmospheric and magnetic studies |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1978-051A | |
| Pioneer Venus Multiprobe Pioneer Venus project The Pioneer mission to Venus consisted of two components, launched separately. Pioneer Venus 1 or Pioneer Venus Orbiter was launched in 1978 and studied the planet for more than a decade after orbital insertion in 1978. Pioneer Venus 2 or Pioneer Venus Multiprobe sent four small probes into the... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
9 December 1978 |  |
|||||
| bus | probe transporter | success | deployed four atmospheric probes, then burnt up in Venusian atmosphere, continuing to transmit to 110 km altitude | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1978-078A | ||||
| large probe | atmospheric probe | success |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1978-078D | ||||
| north probe | atmospheric probe | success | 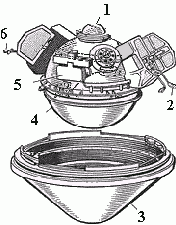 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1978-078E | ||||
| day probe | atmospheric probe | success | survived impact and continued to transmit from surface for over an hour | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1978-078G | ||||
| night probe | atmospheric probe | success | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1978-078F | |||||
| Venera 12 Venera 12 The Venera 12 was an USSR unmanned space mission to explore the planet Venus. Venera 12 was launched on 14 September 1978 at 02:25:13 UTC. Separating from its flight platform on December 19, 1978, the lander entered the Venus atmosphere two days later at 11.2 km/s. During the descent, it... |
 SAS SASRussian Academy of Sciences The Russian Academy of Sciences consists of the national academy of Russia and a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation as well as auxiliary scientific and social units like libraries, publishers and hospitals.... |
|||||||
| flight platform | 21 December 1978 | flyby | success | minimum distance 34,000 km; deployed lander and then acted as communications relay | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1978-086A | |||
| descent craft | 21 December 1978 | lander | partial success | soft landing; transmissions returned for 110 minutes; failure of some instruments |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1978-086C | ||
| Venera 11 Venera 11 The Venera 11 was a USSR unmanned space mission part of the Venera program to explore the planet Venus. Venera 11 was launched on 9 September 1978 at 3:25:39 UTC.... |
 SAS SASRussian Academy of Sciences The Russian Academy of Sciences consists of the national academy of Russia and a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation as well as auxiliary scientific and social units like libraries, publishers and hospitals.... |
identical to Venera 12 | ||||||
| flight platform | flyby | success | minimum distance 34,000 km; deployed lander and then acted as communications relay | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1978-084A | ||||
| descent craft | 25 December 1978 | lander | partial success | soft landing; transmissions returned for 95 minutes; failure of some instruments |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1978-084D | ||
1982–1994
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Venera 13 Venera 13 Venera 13 was a probe in the Soviet Venera program for the exploration of Venus.Venera 13 and 14 were identical spacecraft built to take advantage of the 1981 Venus launch opportunity and launched 5 days apart, Venera 13 on 1981-10-30 at 06:04:00 UTC and Venera 14 on 1981-11-04 at 05:31:00 UTC,... |
 SAS SASRussian Academy of Sciences The Russian Academy of Sciences consists of the national academy of Russia and a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation as well as auxiliary scientific and social units like libraries, publishers and hospitals.... |
|||||||
| bus | 1 March 1982 | flyby | success | deployed lander and then acted as communications relay | 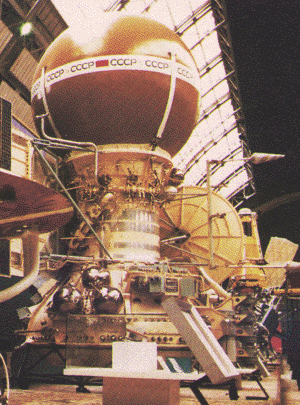 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1981-106A | ||
| descent craft | 1 March 1982 | lander | success | survived on surface for 127 minutes |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1981-106D | ||
| Venera 14 Venera 14 Venera 14 was a probe in the Soviet Venera program for the exploration of Venus.Venera 14 was identical to the Venera 13 spacecraft and built to take advantage of the 1981 Venus launch opportunity and launched 5 days apart... |
 SAS SASRussian Academy of Sciences The Russian Academy of Sciences consists of the national academy of Russia and a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation as well as auxiliary scientific and social units like libraries, publishers and hospitals.... |
identical to Venera 13 | ||||||
| bus | 5 March 1982 | flyby | success | deployed lander and then acted as communications relay |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1981-110A | ||
| descent craft | 5 March 1982 | lander | success | survived on surface for 57 minutes |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1981-110D | ||
| Venera 15 Venera 15 Venera 15 was a spacecraft sent to Venus by the Soviet Union. This unmanned orbiter was to map the surface of Venus using high resolution imaging systems... |
 SAS SASRussian Academy of Sciences The Russian Academy of Sciences consists of the national academy of Russia and a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation as well as auxiliary scientific and social units like libraries, publishers and hospitals.... |
1983–1984 | orbiter | success | radar mapping | 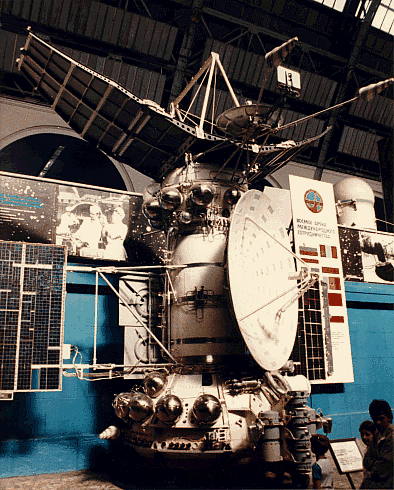 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1983-053A | |
| Venera 16 Venera 16 Venera 16 was a spacecraft sent to Venus by the Soviet Union. This unmanned orbiter was to map the surface of Venus using high resolution imaging systems... |
 SAS SASRussian Academy of Sciences The Russian Academy of Sciences consists of the national academy of Russia and a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation as well as auxiliary scientific and social units like libraries, publishers and hospitals.... |
1983–1984 | orbiter | success | radar mapping; identical to Venera 15 |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1983-054A | |
| Vega 1 Vega 1 Vega 1 is a Soviet space probe part of the Vega program. The spacecraft was a development of the earlier Venera craft... |
 SAS SASRussian Academy of Sciences The Russian Academy of Sciences consists of the national academy of Russia and a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation as well as auxiliary scientific and social units like libraries, publishers and hospitals.... |
11 June 1985 | flyby | success | went on to fly by Halley's comet | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1984-125A | ||
| lander | failure | instruments deployed prematurely | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1984-125E | |||||
| atmospheric balloon | success | floated at an altitude of about 54 km and transmitted for around 46 hours | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1984-125F | |||||
| Vega 2 Vega 2 Vega 2 is a Soviet space probe part of the Vega program. The spacecraft was a development of the earlier Venera craft. They were designed by Babakin Space Center and constructed as 5VK by Lavochkin at Khimki... |
 SAS SASRussian Academy of Sciences The Russian Academy of Sciences consists of the national academy of Russia and a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation as well as auxiliary scientific and social units like libraries, publishers and hospitals.... |
15 June 1985 | flyby | success | went on to fly by Halley's comet | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1984-128A | ||
| lander | success | transmitted from surface for 56 minutes | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1984-128E | |||||
| atmospheric balloon | success | floated at an altitude of about 54 km and transmitted for around 46 hours | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1984-128F | |||||
| Galileo |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
10 February 1990 | flyby | success | gravity assist en route to Jupiter; minimum distance 16,000 km |  |
http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/galileo/mission/journey-cruise.html | |
| Magellan Magellan probe The Magellan spacecraft, also referred to as the Venus Radar Mapper, was a 1,035-kilogram robotic space probe launched by NASA on May 4, 1989, to map the surface of Venus using Synthetic Aperture Radar and measure the planetary gravity... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
10 August 1990 – 12 October 1994 |
orbiter | success | global radar mapping |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/planetary/magellan.html | |
1998–present
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cassini |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... /  ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... /  ASI ASIItalian Space Agency The Italian Space Agency is a government agency established in 1988 to fund, regulate and coordinate space exploration activities in Italy... |
26 April 1998 | flyby | success | gravity assist en route to Saturn |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/tmp/1997-061A-traj.html | |
| 24 June 1999 | ||||||||
| Venus Express Venus Express Venus Express is the first Venus exploration mission of the European Space Agency. Launched in November 2005, it arrived at Venus in April 2006 and has been continuously sending back science data from its polar orbit around Venus. Equipped with seven science instruments, the main objective of the... |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
11 April 2006 – mission extended until at least December 2012 | orbiter | success | atmospheric studies; planetary imaging; magnetic observations |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2005-045A | |
| MESSENGER MESSENGER The MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry and Ranging space probe is a robotic NASA spacecraft in orbit around the planet Mercury. The spacecraft was launched aboard a Delta II rocket in August 2004 to study the chemical composition, geology, and magnetic field of Mercury... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
24 October 2006 | flyby | success | gravity assist only; minimum distance 2990 km |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2004-030A | |
| 6 June 2007 | success | minimum distance 300 km; en route to Mercury | ||||||
| Akatsuki (PLANET-C) |
 JAXA JAXAJapan Aerospace Exploration Agency The , or JAXA, is Japan's national aerospace agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on October 1, 2003, as an Independent Administrative Institution administered by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology and the... |
7 December 2010 | orbiter | failure | failed to attain Venus orbit. | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=PLANET-C | ||
| IKAROS IKAROS IKAROS is a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency experimental spacecraft. The spacecraft was launched on 21 May, 2010, aboard an H-IIA rocket, together with the Akatsuki probe and four other small spacecraft... |
 JAXA JAXAJapan Aerospace Exploration Agency The , or JAXA, is Japan's national aerospace agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on October 1, 2003, as an Independent Administrative Institution administered by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology and the... |
8 December 2010 | flyby | success | solar sail Solar sail Solar sails are a form of spacecraft propulsion using the radiation pressure of light from a star or laser to push enormous ultra-thin mirrors to high speeds.... technology development / interplanetary space exploration |
http://www.jspec.jaxa.jp/e/activity/ikaros.html | ||
| Shin'en Shin'en (spacecraft) Shin'en, known before launch as UNITEC-1 or UNISEC Technology Experiment Carrier 1, is a Japanese student spacecraft which was intended to make a flyby of Venus in order to study the effects of interplanetary spaceflight on spacecraft computers. In doing so, it was intended to become the first... (UNITEC-1) |
 UNISEC UNISEC |
December 2010? | flyby | failure | contact lost shortly after launch | http://www.unisec.jp/unitec-1/en/top.html | ||
| Akatsuki (PLANET-C) |
 JAXA JAXA |
Dec 2016 or Jan 2017 | orbiter | en route | planned second attempt at orbit insertion when craft next approaches Venus | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=PLANET-C | ||
Future
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Venera-D Venera-D The Venera-D probe is a proposed Russian space probe to Venus, to be launched around 2016. Venera-D's prime purpose is to make remote-sensing observations around the planet Venus in a manner similar to that of the U.S. Magellan spacecraft in the 1990s, but with the use of more powerful radar.... |
 RFSA RFSARussian Federal Space Agency The Russian Federal Space Agency , commonly called Roscosmos and abbreviated as FKA and RKA , is the government agency responsible for the Russian space science program and general aerospace research. It was previously the Russian Aviation and Space Agency .Headquarters of Roscosmos are located... |
2013 | orbiter | planned | http://www.esa.int/SPECIALS/ESA_Permanent_Mission_in_Russia/SEM0LFW4QWD_0.html | |||
| Venus In-Situ Explorer Venus In-Situ Explorer The Venus In-Situ Explorer is a mission that was proposed by the NASA planetary science Decadal Survey as a space probe designed to answer fundamental scientific questions by landing and performing experiments on Venus... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2013 | in-situ explorer | planned |  |
http://solarsystem.nasa.gov/missions/profile.cfm?MCode=VISE | ||
| Venus Surface Explorer |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2020 | in-situ explorer | planned | http://sse.jpl.nasa.gov/missions/profile.cfm?MCode=VenusSE | |||
EarthEarthEarth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
flybys
These are probes that incidentally performed Earth flybys during missions to other bodies, often as part of gravity-assist orbital manoeuvres. Earth-orbiting craft are not listed.| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Giotto Giotto mission Giotto was a European robotic spacecraft mission from the European Space Agency, intended to fly by and study Halley's Comet. On 13 March 1986, the mission succeeded in approaching Halley's nucleus at a distance of 596 kilometers.... (first pass) |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
2 July 1990 | flyby | success | first Earth flyby, en route to Comet Grigg-Skjellerup | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1985-056A | ||
| Galileo (first pass) |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
8 December 1990 | flyby | success | gravity assist en route to Jupiter; minimum distance 960 km |  |
http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/galileo/mission/journey-cruise.html | |
| Sakigake Sakigake Sakigake , pre-launch codename MS-T5, was Japan's first interplanetary spacecraft, and the first deep space probe to be launched by any country other than the USA or the Soviet Union... (first pass) |
 ISAS ISASInstitute of Space and Astronautical Science is a Japanese national research organization of astrophysics using rockets, astronomical satellites and interplanetary probes. It is a division of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency .- History :... |
8 January 1992 | flyby | previously visited Halley's comet | 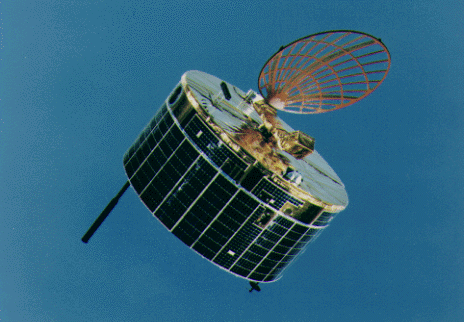 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1985-001A | ||
| Suisei Suisei probe Suisei , originally known as Planet-A, was an unmanned space probe developed by the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science .... |
 ISAS ISASInstitute of Space and Astronautical Science is a Japanese national research organization of astrophysics using rockets, astronomical satellites and interplanetary probes. It is a division of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency .- History :... |
20 August 1992 | flyby | failure | previously visited Halley's comet; hydrazine depleted, further planned comet flybys abandoned | 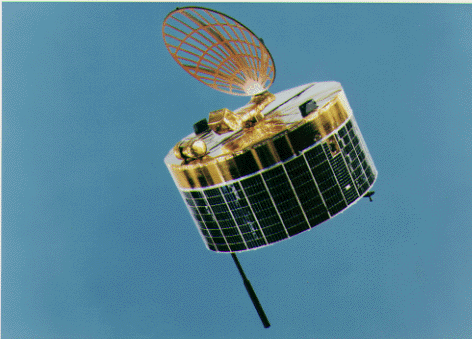 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1985-073A | |
| Galileo (second pass) |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
8 December 1992 | flyby | success | gravity assist en route to Jupiter; minimum distance 305 km |  |
http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/galileo/mission/journey-cruise.html | |
| Sakigake Sakigake Sakigake , pre-launch codename MS-T5, was Japan's first interplanetary spacecraft, and the first deep space probe to be launched by any country other than the USA or the Soviet Union... (second and third passes) |
 ISAS ISASInstitute of Space and Astronautical Science is a Japanese national research organization of astrophysics using rockets, astronomical satellites and interplanetary probes. It is a division of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency .- History :... |
14 June 1993 | flyby |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1985-001A | |||
| 28 October 1994 | flyby | out of fuel; telemetry contact lost November 1995 | ||||||
| NEAR Shoemaker NEAR Shoemaker The Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous - Shoemaker , renamed after its 1996 launch in honor of planetary scientist Eugene M. Shoemaker, was a robotic space probe designed by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory for NASA to study the near-Earth asteroid Eros from close orbit over a... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
23 January 1998 | flyby | success | gravity assist en route to Eros; closest approach 540 km |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1996-008A | |
| Nozomi (first pass) |
 ISAS ISASInstitute of Space and Astronautical Science is a Japanese national research organization of astrophysics using rockets, astronomical satellites and interplanetary probes. It is a division of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency .- History :... |
20 December 1998 | flyby | partial success | gravity assist on planned mission to Mars; valve malfunction during flyby required extra burn, which later forced alternate trajectory plan | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1998-041A | ||
| Giotto Giotto mission Giotto was a European robotic spacecraft mission from the European Space Agency, intended to fly by and study Halley's Comet. On 13 March 1986, the mission succeeded in approaching Halley's nucleus at a distance of 596 kilometers.... (second pass) |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
1 July 1999 | flyby | n/a | already defunct | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1985-056A | ||
| Cassini |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... /  ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... /  ASI ASIItalian Space Agency The Italian Space Agency is a government agency established in 1988 to fund, regulate and coordinate space exploration activities in Italy... |
August, 1999 | flyby | success | gravity assist en route to Saturn |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1997-061A | |
| Stardust Stardust (spacecraft) Stardust is a 300-kilogram robotic space probe launched by NASA on February 7, 1999 to study the asteroid 5535 Annefrank and collect samples from the coma of comet Wild 2. The primary mission was completed January 15, 2006, when the sample return capsule returned to Earth... (first pass) |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
15 January 2001 | flyby | success | gravity assist en route to comet 81P/Wild 81P/Wild Comet 81P/Wild, also known as Wild 2 , is a comet named after Swiss astronomer Paul Wild, who discovered it in 1978 using a 40-cm Schmidt telescope at Zimmerwald.... |
 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1999-003A | |
| Nozomi (second pass) |
 ISAS ISASInstitute of Space and Astronautical Science is a Japanese national research organization of astrophysics using rockets, astronomical satellites and interplanetary probes. It is a division of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency .- History :... |
December, 2002 | flyby | success | gravity assist en route to Mars | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1998-041A | ||
| Nozomi (third pass) |
 ISAS ISASInstitute of Space and Astronautical Science is a Japanese national research organization of astrophysics using rockets, astronomical satellites and interplanetary probes. It is a division of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency .- History :... |
19 June 2003 | flyby | success | gravity assist en route to Mars | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1998-041A | ||
| Hayabusa Hayabusa was an unmanned spacecraft developed by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency to return a sample of material from a small near-Earth asteroid named 25143 Itokawa to Earth for further analysis.... |
 ISAS ISASInstitute of Space and Astronautical Science is a Japanese national research organization of astrophysics using rockets, astronomical satellites and interplanetary probes. It is a division of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency .- History :... |
19 May 2004 | flyby | success | en route to Itokawa 25143 Itokawa 25143 Itokawa is an Apollo and Mars-crosser asteroid. It was the first asteroid to be the target of a sample return mission, the Japanese space probe Hayabusa.-Discovery and naming:... |
_sampling.jpg) |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2003-019A | |
| Rosetta Rosetta (spacecraft) Rosetta is a robotic spacecraft of the European Space Agency on a mission to study the comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. Rosetta consists of two main elements: the Rosetta space probe and the Philae lander. The spacecraft was launched on 2 March 2004 on an Ariane 5 rocket and will reach the comet by... (first pass) |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
4 March 2005 | flyby | success | gravity assist en route to asteroid and comet encounters |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2004-006A | |
| MESSENGER MESSENGER The MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry and Ranging space probe is a robotic NASA spacecraft in orbit around the planet Mercury. The spacecraft was launched aboard a Delta II rocket in August 2004 to study the chemical composition, geology, and magnetic field of Mercury... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2 August 2005 | flyby | success | en route to Venus and Mercury |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2004-030A | |
| Stardust Stardust (spacecraft) Stardust is a 300-kilogram robotic space probe launched by NASA on February 7, 1999 to study the asteroid 5535 Annefrank and collect samples from the coma of comet Wild 2. The primary mission was completed January 15, 2006, when the sample return capsule returned to Earth... (second pass) |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
15 January 2006 | flyby | success | drop-off of sample return capsule |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1999-003A | |
| Rosetta Rosetta (spacecraft) Rosetta is a robotic spacecraft of the European Space Agency on a mission to study the comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. Rosetta consists of two main elements: the Rosetta space probe and the Philae lander. The spacecraft was launched on 2 March 2004 on an Ariane 5 rocket and will reach the comet by... (second pass) |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
13 November 2007 | flyby | success | gravity assist en route to asteroid and comet encounters | |||
| Deep Impact (redesignated EPOXI EPOXI EPOXI is a NASA unmanned space mission led by the University of Maryland using the existing Deep Impact vehicle to begin a new series of observations. It first investigated extrasolar planets and, on November 4, 2010, it performed a close approach to the comet 103P/Hartley... ) (first pass) |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
31 December 2007 | flyby | success | previously visited Comet 9P/Tempel 9P/Tempel Tempel 1 , is a periodic comet discovered by Wilhelm Tempel in 1867. It currently completes an orbit of the Sun every 5.5 years. Tempel 1 was the target of the Deep Impact space mission, which photographed a deliberate high-speed impact upon the comet in 2005... ; gravity assist en route to encounter with Comet 103P/Hartley 103P/Hartley Comet Hartley 2, designated as 103P/Hartley by the Minor Planet Center, is a small periodic comet with an orbital period of 6.46 years. It was discovered by Malcolm Hartley in 1986 at the Schmidt Telescope Unit, Siding Spring Observatory, Australia... |
 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2005-001A | |
| Deep Impact (redesignated EPOXI EPOXI EPOXI is a NASA unmanned space mission led by the University of Maryland using the existing Deep Impact vehicle to begin a new series of observations. It first investigated extrasolar planets and, on November 4, 2010, it performed a close approach to the comet 103P/Hartley... ) (second pass) |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
December 2008 | flyby | success | gravity assist |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2005-001A | |
| Stardust Stardust (spacecraft) Stardust is a 300-kilogram robotic space probe launched by NASA on February 7, 1999 to study the asteroid 5535 Annefrank and collect samples from the coma of comet Wild 2. The primary mission was completed January 15, 2006, when the sample return capsule returned to Earth... (third pass) |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
14 January 2009 | flyby | success | mission extension to Comet 9P/Tempel 9P/Tempel Tempel 1 , is a periodic comet discovered by Wilhelm Tempel in 1867. It currently completes an orbit of the Sun every 5.5 years. Tempel 1 was the target of the Deep Impact space mission, which photographed a deliberate high-speed impact upon the comet in 2005... ; minimum distance 9200 km |
 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1999-003A | |
| Rosetta Rosetta (spacecraft) Rosetta is a robotic spacecraft of the European Space Agency on a mission to study the comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. Rosetta consists of two main elements: the Rosetta space probe and the Philae lander. The spacecraft was launched on 2 March 2004 on an Ariane 5 rocket and will reach the comet by... (third pass) |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
13 November 2009 | flyby | success | gravity assist en route to asteroid and comet encounters | |||
| Deep Impact (redesignated EPOXI EPOXI EPOXI is a NASA unmanned space mission led by the University of Maryland using the existing Deep Impact vehicle to begin a new series of observations. It first investigated extrasolar planets and, on November 4, 2010, it performed a close approach to the comet 103P/Hartley... ) (third pass) |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
June 2009 | distant flyby | success |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2005-001A | ||
| Deep Impact (redesignated EPOXI EPOXI EPOXI is a NASA unmanned space mission led by the University of Maryland using the existing Deep Impact vehicle to begin a new series of observations. It first investigated extrasolar planets and, on November 4, 2010, it performed a close approach to the comet 103P/Hartley... ) (fourth pass) |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
December 2009 | distant flyby | success |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2005-001A | ||
| Deep Impact (redesignated EPOXI EPOXI EPOXI is a NASA unmanned space mission led by the University of Maryland using the existing Deep Impact vehicle to begin a new series of observations. It first investigated extrasolar planets and, on November 4, 2010, it performed a close approach to the comet 103P/Hartley... ) (fifth pass) |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
June 2010 | flyby | success |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2005-001A | ||
1960s
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mars 1960A |  USSR USSR |
10 October 1960 | flyby | failure | failed to reach Earth orbit | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=MARSNK1 | ||
| Mars 1960B |  USSR USSR |
14 October 1960 | flyby | failure | failed to reach Earth orbit | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=MARSNK2 | ||
| Mars 1962A |  USSR USSR |
24 October 1962 | flyby | failure | exploded in or en route to Earth orbit | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1962-057A | ||
| Mars 1962B |  USSR USSR |
11 November 1962 (launch) | lander | failure | broke up during transfer to Mars trajectory | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1962-062A | ||
| Mars 1 Mars 1 Mars 1, also known as 1962 Beta Nu 1, Mars 2MV-4 and Sputnik 23, was an automatic interplanetary station launched in the direction of Mars on November 1, 1962, the first of the Soviet Mars probe program, with the intent of flying by the planet at a distance of about 11,000 km... |
 USSR USSR |
19 June 1963 | flyby | failure | contact lost en route; flew within approximately 193,000 km of Mars | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1962-061A | ||
| Mariner 3 Mariner 3 Mariner 3 and 4 were identical spacecraft of the Mariner program designed to carry out the first flybys of Mars and obtain photographs of the planet's surface. Mariner 3 was launched on November 5, 1964 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Launch Complex 13, but the shroud encasing the spacecraft... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
5 November 1964 | flyby | failure | protective shield failed to eject, preventing craft from attaining correct trajectory |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1964-073A | |
| Zond 2 Zond 2 Zond 2, a member of the Soviet Zond program, was the fifth Soviet spacecraft to attempt a flyby of Mars. Zond-2 carried a phototelevision camera of the same type later used to photograph the Moon on Zond 3. The camera system also included two ultraviolet spectrometers... |
 USSR USSR |
6 August 1965 | flyby | failure | contact lost en route; flew within 1,500 km of Mars | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1964-078C | ||
| Mariner 4 Mariner 4 Mariner 4 was the fourth in a series of spacecraft, launched on November 28, 1964, intended for planetary exploration in a flyby mode and performed the first successful flyby of the planet Mars, returning the first pictures of the Martian surface... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
15 July 1965 | flyby | success | first close-up images of Mars |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1964-077A | |
| Mariner 6 Mariner 6 and 7 As part of NASA's wider Mariner program, Mariner 6 and Mariner 7 completed the first dual mission to Mars in 1969. Mariner 6 was launched from Launch Complex 36B at Cape Kennedy and Mariner 7 from Launch Complex 36A at Cape Kennedy... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
31 July 1969 | flyby | success | 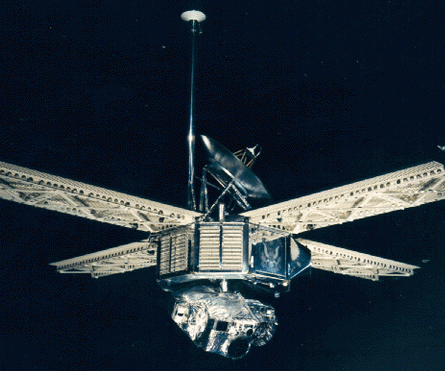 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1969-014A | ||
| Mariner 7 Mariner 6 and 7 As part of NASA's wider Mariner program, Mariner 6 and Mariner 7 completed the first dual mission to Mars in 1969. Mariner 6 was launched from Launch Complex 36B at Cape Kennedy and Mariner 7 from Launch Complex 36A at Cape Kennedy... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
5 August 1969 | flyby | success |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1969-030A | ||
| Mars 1969A Mars 1969A Mars 2M No.521, also known as Mars M-69 No.521 and sometimes identified by NASA as Mars 1969A, was a Soviet spacecraft which was lost in a launch failure in 1969. It consisted of an orbiter and a lander. The spacecraft was intended to image the surface of Mars using three cameras, with images being... |
 USSR USSR |
27 March 1969 | orbiter | failure | launch failure | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=MARS69A | ||
| Mars 1969B Mars 1969B Mars 2M No.522, also known as Mars M-69 No.522 and sometimes identified by NASA as Mars 1969B, was a Soviet spacecraft which was lost in a launch failure in 1969. It consisted of an orbiter and a lander. The spacecraft was intended to image the surface of Mars using three cameras, with images being... |
 USSR USSR |
2 April 1969 | orbiter | failure | launch failure | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=MARS69B | ||
1970s
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mariner 8 Mariner 8 Mariner-H, also commonly known as Mariner 8, was part of the Mariner Mars 71 project. It was intended to go into Mars orbit and return images and data.-Mission description:... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
9 May 1971 | orbiter | failure | launch vehicle failure |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=MARINH | |
| Mariner 9 Mariner 9 Mariner 9 was a NASA space orbiter that helped in the exploration of Mars and was part of the Mariner program. Mariner 9 was launched toward Mars on May 30, 1971 from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station and reached the planet on November 13 of the same year, becoming the first spacecraft to orbit... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
14 November 1971 | orbiter | success | first spacecraft to orbit another planet |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1971-051A | |
| Mars 2 Mars 2 The Mars program was a series of Mars unmanned landers and orbiters launched by the Soviet Union in the early 1970s.The Mars 2 and Mars 3 missions consisted of identical spacecraft, each with an orbiter and an attached lander; they were the first human artifacts to impact the surface of Mars... |
 USSR USSR |
November 1971 – August 1972 |
orbiter | success | first Russian spacecraft to orbit another planet | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1971-045A | ||
| Mars 2 Lander Mars 2 The Mars program was a series of Mars unmanned landers and orbiters launched by the Soviet Union in the early 1970s.The Mars 2 and Mars 3 missions consisted of identical spacecraft, each with an orbiter and an attached lander; they were the first human artifacts to impact the surface of Mars... |
 USSR USSR |
27 November 1971 | lander and short range rover | failure | crashed; first manmade object to reach surface of Mars | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1971-045D | ||
| Mars 3 Mars 3 The Mars 3 was an unmanned space probe of the Mars program, a series of unmanned Mars landers and orbiters launched by the Soviet Union in the early 1970s.... |
 USSR USSR |
December 1971 – August 1972 |
orbiter | partial success | attained a different orbit than intended due to insufficient fuel | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1971-049A | ||
| Mars 3 Lander Mars 3 The Mars 3 was an unmanned space probe of the Mars program, a series of unmanned Mars landers and orbiters launched by the Soviet Union in the early 1970s.... |
 USSR USSR |
2 December 1971 | lander and short range rover | failure | contact lost 110 sec after soft landing | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1971-049F | ||
| Cosmos 419 Cosmos 419 Kosmos 419 was launched by the Soviet Union on May 10, 1971. Mars was at its closest to Earth since 1956 and, in May that year, both the Soviet Union and the United States made new attempts to reach the Red Planet. The payload however failed to separate from the fourth stage of the launch vehicle,... |
 USSR USSR |
10 May 1971 | orbiter | failure | failed to escape Earth orbit | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1971-042A | ||
| Mars 4 |  USSR USSR |
10 February 1974 | orbiter | failure | orbit insertion failed, became flyby | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1973-047A | ||
| Mars 5 |  USSR USSR |
February 1974 | orbiter | success | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1973-049A | |||
| Mars 6 |  USSR USSR |
12 March 1974 | flyby | success | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1973-052A | |||
| Mars 6 Lander |  USSR USSR |
12 March 1974 | lander | failure | contact lost 148 sec after parachute deployment | |||
| Mars 7 |  USSR USSR |
9 March 1974 | flyby | success | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1973-053A | |||
| Mars 7 Lander |  USSR USSR |
9 March 1974 | lander | failure | missed Mars | |||
| Viking 1 Orbiter Viking 1 Viking 1 was the first of two spacecraft sent to Mars as part of NASA's Viking program. It was the first spacecraft to successfully land on Mars and perform its mission, and until May 19, 2010 held the record for the second longest Mars surface mission of 6 years and 116 days .- Mission :Following... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
June 1976 – August 1980 |
orbiter | success | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1975-075A | |||
| Viking 1 Lander Viking 1 Viking 1 was the first of two spacecraft sent to Mars as part of NASA's Viking program. It was the first spacecraft to successfully land on Mars and perform its mission, and until May 19, 2010 held the record for the second longest Mars surface mission of 6 years and 116 days .- Mission :Following... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
20 July 1976 – 13 November 1982 |
lander | success | first images from surface |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1975-075C | |
| Viking 2 Orbiter Viking 2 The Viking 2 mission was part of the American Viking program to Mars, and consisted of an orbiter and a lander essentially identical to that of the Viking 1 mission. The Viking 2 lander operated on the surface for 1,281 Mars days and was turned off on 11 April 1980 when its batteries failed... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
August 1976 – July 1978 |
orbiter | success | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1975-083A | |||
| Viking 2 Lander Viking 2 The Viking 2 mission was part of the American Viking program to Mars, and consisted of an orbiter and a lander essentially identical to that of the Viking 1 mission. The Viking 2 lander operated on the surface for 1,281 Mars days and was turned off on 11 April 1980 when its batteries failed... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
11 April 1980 |
lander | success |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1975-083C | ||
1980s
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phobos 1 |  USSR USSR |
7 July 1988 (launch) | orbiter | failure | contact lost en route to Mars |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1988-058A | |
| Phobos 2 |  USSR USSR |
29 January 1989 – 27 March 1989 |
orbiter | partial success | Mars orbit acquired, but contact lost shortly before Phobos approach phase and deployment of Phobos landers |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1988-059A | |
1990s
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mars Observer Mars Observer The Mars Observer spacecraft, also known as the Mars Geoscience/Climatology Orbiter, was a 1,018-kilogram robotic space probe launched by NASA on September 25, 1992 to study the Martian surface, atmosphere, climate and magnetic field... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
25 September 1992 (launch) | orbiter | failure | contact lost shortly before Mars orbit insertion | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1992-063A | ||
| Mars 96 Mars 96 Mars 96 was a failed Mars mission launched in 1996 to investigate Mars by the Russian Space Forces and not directly related to the Soviet Mars probe program of the same name. After failure of the second fourth-stage burn, the probe assembly re-entered the Earth's atmosphere, breaking up over a... |
 RFSA RFSARussian Federal Space Agency The Russian Federal Space Agency , commonly called Roscosmos and abbreviated as FKA and RKA , is the government agency responsible for the Russian space science program and general aerospace research. It was previously the Russian Aviation and Space Agency .Headquarters of Roscosmos are located... |
16 November 1996 (launch) | orbiter | failure | failed to escape Earth orbit | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1996-064A | ||
| lander |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=MARS96B | ||||||
| lander | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=MARS96C | |||||||
| penetrator |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=MARS96D | ||||||
| penetrator | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=MARS96E | |||||||
| Mars Pathfinder Mars Pathfinder Mars Pathfinder was an American spacecraft that landed a base station with roving probe on Mars in 1997. It consisted of a lander, renamed the Carl Sagan Memorial Station, and a lightweight wheeled robotic rover named Sojourner.Launched on December 4, 1996 by NASA aboard a Delta II booster a... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
4 July 1997 – 27 September 1997 |
lander | success | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1996-068A | |||
| Sojourner |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
6 July 1997 – 27 September 1997 |
rover | success | first Mars rover |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=MESURPR | |
| Mars Global Surveyor Mars Global Surveyor The Mars Global Surveyor was a US spacecraft developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and launched November 1996. It began the United States's return to Mars after a 10-year absence. It completed its primary mission in January 2001 and was in its third extended mission phase when, on 2... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2 November 2006 |
orbiter | success |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1996-062A | ||
| Mars Climate Orbiter Mars Climate Orbiter The Mars Climate Orbiter was a 338 kilogram robotic space probe launched by NASA on December 11, 1998 to study the Martian climate, atmosphere, surface changes and to act as the communications relay in the Mars Surveyor '98 program, for Mars Polar Lander... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
23 September 1999 | orbiter | failure | Mars orbit insertion failed due to navigation error |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1998-073A | |
| Mars Polar Lander Mars Polar Lander The Mars Polar Lander, also referred to as the Mars Surveyor '98 Lander, was a 290-kilogram robotic spacecraft lander, launched by NASA on January 3, 1999, to study the soil and climate of Planum Australe, a region near the south pole on Mars, as part of the Mars Surveyor '98 mission... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
3 December 1999 | lander | failure | contact lost just prior to entering Martian atmosphere |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1999-001A | |
| Deep Space 2 Deep Space 2 Deep Space 2 was a NASA probe which was part of the New Millennium Program. It included two highly advanced miniature space probes which were sent to Mars aboard the Mars Polar Lander in January 1999. The probes were named "Scott" and "Amundsen", in honor of Robert Falcon Scott and Roald Amundsen,... "Amundsen" |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
3 December 1999 | penetrator |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=DEEPSP2 | |||
| Deep Space 2 "Scott" |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
3 December 1999 | penetrator | |||||
2000s
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2001 Mars Odyssey |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
24 October 2001 – | orbiter | success | studying climate and geology; communications relay for Spirit and Opportunity rovers |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2001-014A | |
| Nozomi |  ISAS ISASInstitute of Space and Astronautical Science is a Japanese national research organization of astrophysics using rockets, astronomical satellites and interplanetary probes. It is a division of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency .- History :... |
14 December 2003 | orbiter | failure | failed to attain Mars orbit, became flyby | 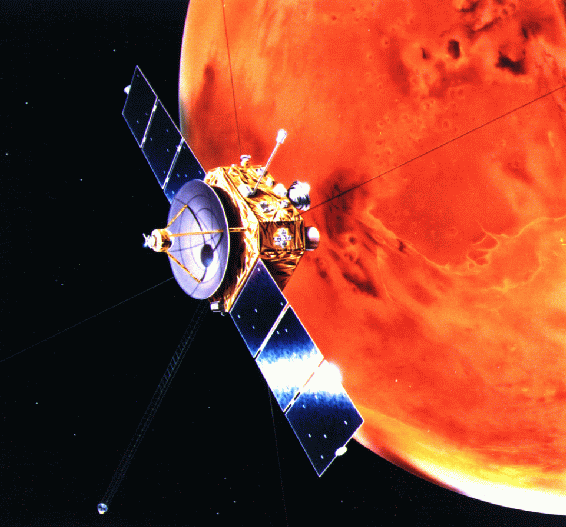 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1998-041A | |
| Mars Express Mars Express Mars Express is a space exploration mission being conducted by the European Space Agency . The Mars Express mission is exploring the planet Mars, and is the first planetary mission attempted by the agency. "Express" originally referred to the speed and efficiency with which the spacecraft was... |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
25 December 2003 – | orbiter | success | surface imaging and mapping; first European probe in Martian orbit |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2003-022A | |
| Beagle 2 Beagle 2 Beagle 2 was an unsuccessful British landing spacecraft that formed part of the European Space Agency's 2003 Mars Express mission. All contact with it was lost upon its separation from the Mars Express six days before its scheduled entry into the atmosphere... |
 UK UK |
25 December 2003 | lander | failure | no contact after release | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2003-022C | ||
| MER-A "Spirit Spirit rover Spirit, MER-A , is a robotic rover on Mars, active from 2004 to 2010. It was one of two rovers of NASA's ongoing Mars Exploration Rover Mission. It landed successfully on Mars at 04:35 Ground UTC on January 4, 2004, three weeks before its twin, Opportunity , landed on the other side of the planet... " |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
4 January 2004 – 22 March 2010 | rover | success | became stuck in May 2009; then operating as a static science station until contact lost in March 2010 |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2003-027A | |
| MER-B "Opportunity Opportunity rover Opportunity, MER-B , is a robotic rover on the planet Mars, active since 2004. It is the remaining rover in NASA's ongoing Mars Exploration Rover Mission... " |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
25 January 2004 – | rover | success |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2003-032A | ||
| Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter is a NASA multipurpose spacecraft designed to conduct reconnaissance and Exploration of Mars from orbit... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
10 March 2006 – | orbiter | success | surface imaging and surveying |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2005-029A | |
| Rosetta Rosetta (spacecraft) Rosetta is a robotic spacecraft of the European Space Agency on a mission to study the comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. Rosetta consists of two main elements: the Rosetta space probe and the Philae lander. The spacecraft was launched on 2 March 2004 on an Ariane 5 rocket and will reach the comet by... |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
25 February 2007 | flyby | success | gravity assist en route to asteroid and comet encounters |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2004-006A | |
| Phoenix Phoenix (spacecraft) Phoenix was a robotic spacecraft on a space exploration mission on Mars under the Mars Scout Program. The Phoenix lander descended on Mars on May 25, 2008... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
25 May 2008 – 10 November 2008 |
lander | success | collection of soil samples near the northern pole to search for water and investigate Mars' geological history and biological potential |  |
http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/phoenix/main/index.html | |
| Dawn Dawn Mission Dawn is a NASA spacecraft tasked with the exploration and study of the two largest members of the asteroid belt – Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The spacecraft was constructed with some European cooperation, with partners in Germany, Italy, and the Netherlands providing Dawns framing... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
17 February 2009 | flyby | success | gravity assist en route to Vesta and Ceres |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=DAWN | |
| Yinghuo-1 |  CNSA CNSAChina National Space Administration The China National Space Administration is the national space agency of the People's Republic of China responsible for the national space program. It is responsible for planning and development of space activities... |
8 November 2011 (launch) | orbiter | presently stuck in Earth orbit | launched with Phobos-Grunt Phobos lander | |||
| MSL Curiosity Mars Science Laboratory The Mars Science Laboratory is a National Aeronautics and Space Administration mission with the aim to land and operate a rover named Curiosity on the surface of Mars. The MSL was launched November 26, 2011, at 10:02 EST and is scheduled to land on Mars at Gale Crater between August 6 and 20, 2012... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
26 November 2011 | rover | En route to Mars. |  |
http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/msl/ | ||
Future
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAVEN Maven A maven is a trusted expert in a particular field, who seeks to pass knowledge on to others. The word maven comes from Hebrew, via Yiddish, and means one who understands, based on an accumulation of knowledge.-History:... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2013 | orbiter | planned | http://www.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news.cfm?release=2010-323 | |||
| ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter |  ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... /  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2016 | orbiter, lander | planned | http://exploration.esa.int/science-e/www/object/index.cfm?fobjectid=46124 | |||
| ExoMars rover ExoMars ExoMars is a European-led robotic mission to Mars currently under development by the European Space Agency with collaboration by NASA... |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... /  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2018 | rover | planned |  |
http://exploration.esa.int/science-e/www/object/index.cfm?fobjectid=45084 | ||
| Mars Sample Return Mission Mars Sample Return Mission A Mars sample return mission would be a spaceflight mission to collect rock and dust samples from Mars and to return them to Earth for analysis... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... /  ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
2024? | orbiter, lander, rover, and sample return | under study |  |
http://mars.jpl.nasa.gov/missions/future/futureMissions.htmlhttp://www.esa.int/SPECIALS/Aurora/SEM1PM808BE_0.html | ||
PhobosPhobos (moon)Phobos is the larger and closer of the two natural satellites of Mars. Both moons were discovered in 1877. With a mean radius of , Phobos is 7.24 times as massive as Deimos...
probes
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phobos 1 |  USSR USSR |
7 July 1988 (launch) | flyby | failure | contact lost en route to Mars |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1988-058A | |
| DAS |  USSR USSR |
2 September 1988 | fixed lander | failure | never deployed | |||
| Phobos 2 |  USSR USSR |
27 March 1989 (contact lost) | flyby | failure | attained Mars orbit; contact lost prior to deployment of lander |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1988-059A | |
| DAS |  USSR USSR |
27 March 1989 | fixed lander | failure | never deployed | |||
| "Frog" |  USSR USSR |
27 March 1989 | mobile lander | failure | never deployed | |||
| Phobos-Grunt Phobos-Grunt Fobos-Grunt or Phobos-Grunt was an attempted Russian sample return mission to Phobos, one of the moons of Mars. It was launched on 9 November 2011 at 02:16 local time from the Baikonur Cosmodrome, but subsequent rocket burns intended to set the craft on a course for Mars failed, leaving it... |
 RFSA RFSARussian Federal Space Agency The Russian Federal Space Agency , commonly called Roscosmos and abbreviated as FKA and RKA , is the government agency responsible for the Russian space science program and general aerospace research. It was previously the Russian Aviation and Space Agency .Headquarters of Roscosmos are located... |
8 November 2011 (launch) | sample return | presently stuck in Earth orbit | launched with Yinghuo-1 Mars orbiter | |||
Ceres probes
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dawn |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2015 | orbiter | en route | will orbit Vesta 4 Vesta Vesta, formally designated 4 Vesta, is one of the largest asteroids, with a mean diameter of about . It was discovered by Heinrich Wilhelm Olbers on March 29, 1807, and is named after the Roman virgin goddess of home and hearth, Vesta.... first |
 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=DAWN | |
AsteroidAsteroidAsteroids are a class of small Solar System bodies in orbit around the Sun. They have also been called planetoids, especially the larger ones...
probes
| Target | Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 951 Gaspra 951 Gaspra 951 Gaspra is an S-type asteroid that orbits very close to the inner edge of the asteroid belt. Gaspra was the first asteroid ever to be closely approached when it was visited by the Galileo spacecraft, which flew by on its way to Jupiter on 29 October 1991.-Characteristics:Apart from a multitude... |
Galileo |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
29 October 1991 | flyby | success | en route to Jupiter; minimum distance 1900 km |  |
http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/galileo/mission/journey-cruise.html | |
| 243 Ida 243 Ida 243 Ida is an asteroid in the Koronis family of the asteroid belt. It was discovered on 29 September 1884 by Johann Palisa and named after a nymph from Greek mythology. Later telescopic observations categorized Ida as an S-type asteroid, the most numerous type in the inner asteroid belt. On 28... |
Galileo |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
28 August 1993 | flyby | success | en route to Jupiter; minimum distance 2400 km; discovery of the first asteroid satellite Binary asteroid A binary asteroid is a system of two asteroids orbiting their common center of mass, in analogy with binary stars. 243 Ida was the first binary asteroid to be identified when the Galileo spacecraft did a flyby in 1993... Dactyl |
 |
http://www2.jpl.nasa.gov/galileo/mission/journey-cruise.html | |
| 1620 Geographos 1620 Geographos The asteroid 1620 Geographos was discovered on September 14, 1951 at the Palomar Observatory by Albert George Wilson and Rudolph Minkowski. It was originally given the provisional designation 1951 RA... |
Clementine Clementine mission Clementine was a joint space project between the Ballistic Missile Defense Organization and NASA... |
 BMDO BMDOBallistic Missile Defense Organization The Ballistic Missile Defense Organization was an agency of the United States Department of Defense that began on 20 May 1974 with the responsibility for all U.S. ballistic missile defense efforts. It evolved from the SAFEGUARD System Organization. The original mission of BMDO was comparable to... /  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
1994 | flyby | failure | flyby cancelled due to equipment malfunction | 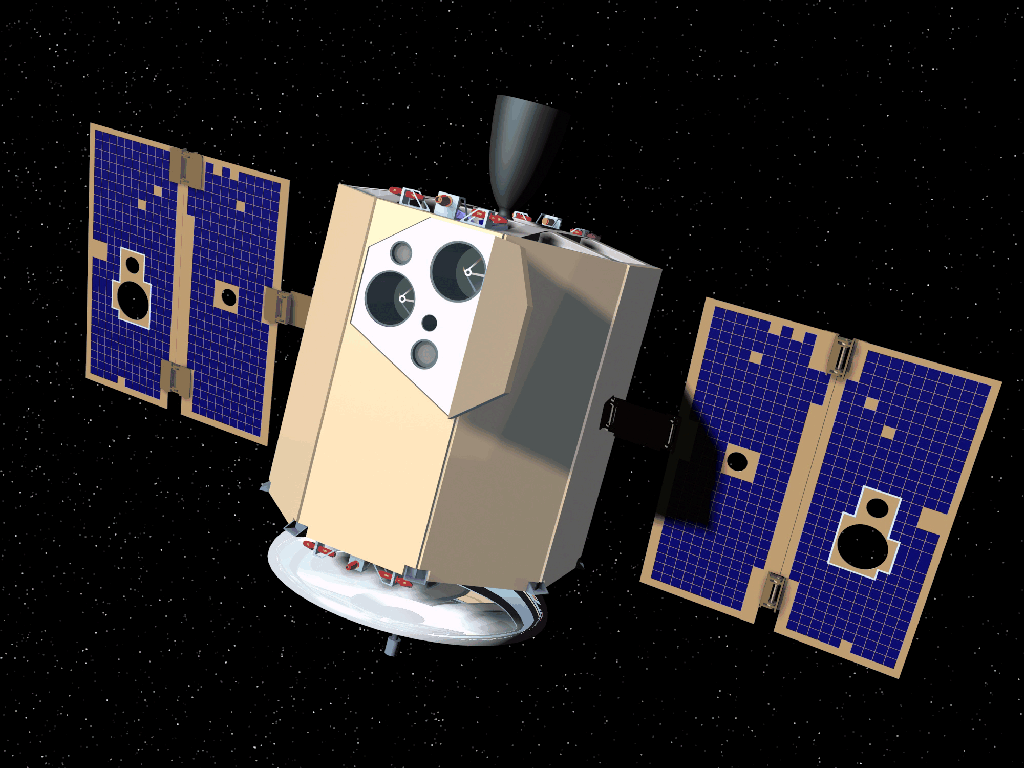 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1994-004A | |
| 253 Mathilde 253 Mathilde 253 Mathilde is a main-belt asteroid about 50 km in diameter that was discovered by Johann Palisa in 1885. It has a relatively elliptical orbit that requires more than four years to circle the Sun. This asteroid has an unusually slow rate of rotation, requiring 17.4 days to complete a... |
NEAR Shoemaker NEAR Shoemaker The Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous - Shoemaker , renamed after its 1996 launch in honor of planetary scientist Eugene M. Shoemaker, was a robotic space probe designed by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory for NASA to study the near-Earth asteroid Eros from close orbit over a... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
27 June 1997 | flyby | success | flew within 1200 km of 253 Mathilde 253 Mathilde 253 Mathilde is a main-belt asteroid about 50 km in diameter that was discovered by Johann Palisa in 1885. It has a relatively elliptical orbit that requires more than four years to circle the Sun. This asteroid has an unusually slow rate of rotation, requiring 17.4 days to complete a... en route to 433 Eros 433 Eros 433 Eros is a near-Earth asteroid discovered in 1898, and the first asteroid to be orbited by a probe . It is an S-type asteroid approximately 34.4×11.2×11.2 km in size, the second-largest NEA after 1036 Ganymed, and belongs to the Amor group.Eros is a Mars-crosser asteroid, the first known... |
 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1996-008A | |
| 433 Eros 433 Eros 433 Eros is a near-Earth asteroid discovered in 1898, and the first asteroid to be orbited by a probe . It is an S-type asteroid approximately 34.4×11.2×11.2 km in size, the second-largest NEA after 1036 Ganymed, and belongs to the Amor group.Eros is a Mars-crosser asteroid, the first known... |
NEAR Shoemaker NEAR Shoemaker The Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous - Shoemaker , renamed after its 1996 launch in honor of planetary scientist Eugene M. Shoemaker, was a robotic space probe designed by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory for NASA to study the near-Earth asteroid Eros from close orbit over a... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
January 1999 | orbiter | failure | became flyby due to software and communications problems (later attempt at orbit insertion succeeded; see below) |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1996-008A | |
| 9969 Braille 9969 Braille 9969 Braille is a small Mars-crossing asteroid that orbits the Sun once every 3.58 years. It was discovered in 1992 by astronomers at Palomar observatory and later named after Louis Braille, the inventor of the writing system for the blind... |
Deep Space 1 Deep Space 1 Deep Space 1 is a spacecraft of the NASA New Millennium Program dedicated to testing a payload of advanced, high risk technologies.... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
29 July 1999 | flyby | partial success | no close-up images due to camera pointing error; went on to visit comet 19P/Borrelly 19P/Borrelly Comet Borrelly or Borrelly's Comet is a periodic comet, which was visited by the spacecraft Deep Space 1 in 2001.- Discovery :... |
 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1998-061A | |
| 2685 Masursky 2685 Masursky The asteroid 2685 Masursky is a main-belt asteroid. It was discovered by Edward Bowell in 1981. It was named after Harold Masursky , a planetary geologist at the U.S. Geological Survey, Flagstaff, who worked on numerous space missions.... |
Cassini |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... /  ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... /  ASI ASIItalian Space Agency The Italian Space Agency is a government agency established in 1988 to fund, regulate and coordinate space exploration activities in Italy... |
23 January 2000 | distant flyby | success | en route to Saturn |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1997-061A | |
| 433 Eros 433 Eros 433 Eros is a near-Earth asteroid discovered in 1898, and the first asteroid to be orbited by a probe . It is an S-type asteroid approximately 34.4×11.2×11.2 km in size, the second-largest NEA after 1036 Ganymed, and belongs to the Amor group.Eros is a Mars-crosser asteroid, the first known... |
NEAR Shoemaker NEAR Shoemaker The Near Earth Asteroid Rendezvous - Shoemaker , renamed after its 1996 launch in honor of planetary scientist Eugene M. Shoemaker, was a robotic space probe designed by the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory for NASA to study the near-Earth asteroid Eros from close orbit over a... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
February 2001 |
orbiter, became lander | success | improvised landing by orbiter at end of mission |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1996-008A | |
| 5535 Annefrank 5535 Annefrank 5535 Annefrank is an inner main-belt asteroid, and member of the Augusta family. It was discovered by Karl Reinmuth in 1942. It is named after Anne Frank, the Dutch-Jewish diarist who died in a concentration camp... |
Stardust Stardust (spacecraft) Stardust is a 300-kilogram robotic space probe launched by NASA on February 7, 1999 to study the asteroid 5535 Annefrank and collect samples from the coma of comet Wild 2. The primary mission was completed January 15, 2006, when the sample return capsule returned to Earth... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
November 2, 2002 | distant flyby | success | went on to visit comet 81P/Wild 81P/Wild Comet 81P/Wild, also known as Wild 2 , is a comet named after Swiss astronomer Paul Wild, who discovered it in 1978 using a 40-cm Schmidt telescope at Zimmerwald.... |
 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1999-003A | |
| 25143 Itokawa 25143 Itokawa 25143 Itokawa is an Apollo and Mars-crosser asteroid. It was the first asteroid to be the target of a sample return mission, the Japanese space probe Hayabusa.-Discovery and naming:... |
Hayabusa Hayabusa was an unmanned spacecraft developed by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency to return a sample of material from a small near-Earth asteroid named 25143 Itokawa to Earth for further analysis.... |
 ISAS ISASInstitute of Space and Astronautical Science is a Japanese national research organization of astrophysics using rockets, astronomical satellites and interplanetary probes. It is a division of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency .- History :... |
2005–07 | sample return | success | landed on Itokawa in 2005 and returned to Earth in 2010 | _sampling.jpg) |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2003-019A | |
| MINERVA |  ISAS ISASInstitute of Space and Astronautical Science is a Japanese national research organization of astrophysics using rockets, astronomical satellites and interplanetary probes. It is a division of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency .- History :... |
hopper | failure | missed target | |||||
| 132524 APL | New Horizons New Horizons New Horizons is a NASA robotic spacecraft mission currently en route to the dwarf planet Pluto. It is expected to be the first spacecraft to fly by and study Pluto and its moons, Charon, Nix, Hydra and S/2011 P 1. Its estimated arrival date at the Pluto-Charon system is July 14th, 2015... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
June 2006 | distant flyby | success | en route to Pluto |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2006-001A | |
| 2867 Šteins 2867 Šteins 2867 Šteins is a small main-belt asteroid that was discovered in 1969 by N. S. Chernykh. It is named after Kārlis Šteins, a Latvian and Soviet astronomer... |
Rosetta Rosetta (spacecraft) Rosetta is a robotic spacecraft of the European Space Agency on a mission to study the comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. Rosetta consists of two main elements: the Rosetta space probe and the Philae lander. The spacecraft was launched on 2 March 2004 on an Ariane 5 rocket and will reach the comet by... |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
5 September 2008 | flyby | success | en route to comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko Comet Churyumov–Gerasimenko, officially designated 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko, is a comet with a current orbital period of 6.6 years. It is the destination of the European Space Agency's Rosetta spacecraft mission, launched on March 2, 2004.... |
 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2004-006A | |
| 21 Lutetia 21 Lutetia 21 Lutetia is a large main-belt asteroid of an unusual spectral type. It measures about 100 kilometers in diameter . It was discovered in 1852 by Hermann Goldschmidt, and is named after Lutetia, the Latin name for Paris.... |
Rosetta Rosetta (spacecraft) Rosetta is a robotic spacecraft of the European Space Agency on a mission to study the comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. Rosetta consists of two main elements: the Rosetta space probe and the Philae lander. The spacecraft was launched on 2 March 2004 on an Ariane 5 rocket and will reach the comet by... |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
11 July 2010 | flyby | success | en route to comet 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko Comet Churyumov–Gerasimenko, officially designated 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko, is a comet with a current orbital period of 6.6 years. It is the destination of the European Space Agency's Rosetta spacecraft mission, launched on March 2, 2004.... |
 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2004-006A | |
| 4 Vesta 4 Vesta Vesta, formally designated 4 Vesta, is one of the largest asteroids, with a mean diameter of about . It was discovered by Heinrich Wilhelm Olbers on March 29, 1807, and is named after the Roman virgin goddess of home and hearth, Vesta.... |
Dawn Dawn Mission Dawn is a NASA spacecraft tasked with the exploration and study of the two largest members of the asteroid belt – Vesta and the dwarf planet Ceres. The spacecraft was constructed with some European cooperation, with partners in Germany, Italy, and the Netherlands providing Dawns framing... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
16 July 2011 | orbiter | success | scheduled to continue to Ceres |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=DAWN | |
JupiterJupiterJupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet within the Solar System. It is a gas giant with mass one-thousandth that of the Sun but is two and a half times the mass of all the other planets in our Solar System combined. Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn,...
probes
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pioneer 10 Pioneer 10 Pioneer 10 is a 258-kilogram robotic space probe that completed the first interplanetary mission to Jupiter, and became the first spacecraft to achieve escape velocity from the Solar System. The project was managed by the NASA Ames Research Center and the contract for the construction of the... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
3 December 1973 | flyby | success | first probe to cross the asteroid belt; first Jupiter probe; first man-made object on an interstellar trajectory; now in the outer regions of the Solar System but no longer contactable | 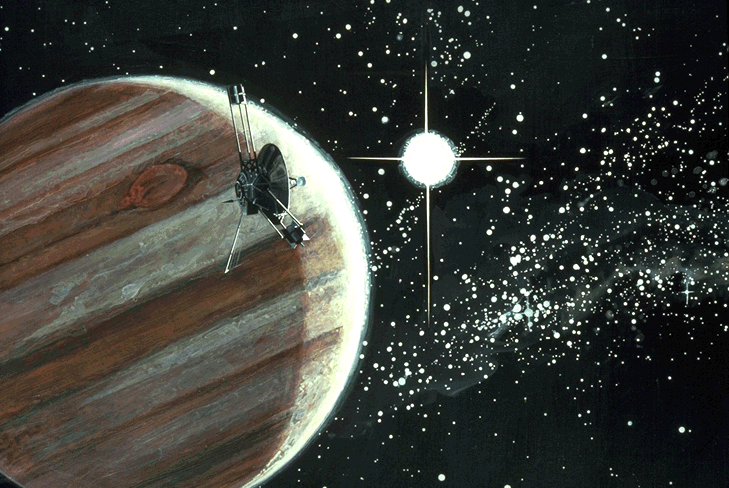 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1972-012A | |
| Pioneer 11 Pioneer 11 Pioneer 11 is a 259-kilogram robotic space probe launched by NASA on April 6, 1973 to study the asteroid belt, the environment around Jupiter and Saturn, solar wind, cosmic rays, and eventually the far reaches of the solar system and heliosphere... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
4 December 1974 | flyby | success | went on to visit Saturn |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1973-019A | |
| Voyager 1 Voyager 1 The Voyager 1 spacecraft is a 722-kilogram space probe launched by NASA in 1977, to study the outer Solar System and eventually interstellar space. Operating for as of today , the spacecraft receives routine commands and transmits data back to the Deep Space Network. At a distance of as of... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
5 March 1979 | flyby | success | went on to visit Saturn |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1977-084A | |
| Voyager 2 Voyager 2 The Voyager 2 spacecraft is a 722-kilogram space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977 to study the outer Solar System and eventually interstellar space... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
9 July 1979 | flyby | success | went on to visit Saturn, Uranus and Neptune |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1977-076A | |
| Ulysses Ulysses probe Ulysses is a decommissioned robotic space probe that was designed to study the Sun as a joint venture of NASA and the European Space Agency . The spacecraft was originally named Odysseus, because of its lengthy and indirect trajectory to near Solar distance... (first pass) |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... /  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
February 1992 | flyby | success | gravity assist en route to inclined heliocentric orbit for solar polar observations |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1990-090B | |
| Galileo Orbiter |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... /  DLR DLRGerman Aerospace Center The German Aerospace Center is the national centre for aerospace, energy and transportation research of the Federal Republic of Germany. It has multiple locations throughout Germany. Its headquarters are located in Cologne. It is engaged in a wide range of research and development projects in... |
7 December 1995 – 21 September 2003 |
orbiter | success | also flew by various of Jupiter's moons; intentionally flown into Jupiter at end of mission; first spacecraft to orbit Jupiter; first spacecraft to flyby an asteroid |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1989-084B | |
| Galileo Probe |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... /  DLR DLRGerman Aerospace Center The German Aerospace Center is the national centre for aerospace, energy and transportation research of the Federal Republic of Germany. It has multiple locations throughout Germany. Its headquarters are located in Cologne. It is engaged in a wide range of research and development projects in... |
7 December 1995 | atmospheric probe | success | first probe to enter Jupiter's atmosphere |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1989-084E | |
| Cassini |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... /  ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... /  ASI ASIItalian Space Agency The Italian Space Agency is a government agency established in 1988 to fund, regulate and coordinate space exploration activities in Italy... |
December 2000 | flyby | success | gravity assist en route to Saturn |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1997-061A | |
| Ulysses Ulysses probe Ulysses is a decommissioned robotic space probe that was designed to study the Sun as a joint venture of NASA and the European Space Agency . The spacecraft was originally named Odysseus, because of its lengthy and indirect trajectory to near Solar distance... (second pass) |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... /  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2003–04 | distant flyby | success |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1990-090B | ||
| New Horizons New Horizons New Horizons is a NASA robotic spacecraft mission currently en route to the dwarf planet Pluto. It is expected to be the first spacecraft to fly by and study Pluto and its moons, Charon, Nix, Hydra and S/2011 P 1. Its estimated arrival date at the Pluto-Charon system is July 14th, 2015... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
28 February 2007 | flyby | success | gravity assist en route to Pluto |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2006-001A | |
| Juno Juno (spacecraft) Juno is a NASA New Frontiers mission to the planet Jupiter. Juno was launched from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station on August 5, 2011. The spacecraft is to be placed in a polar orbit to study the planet's composition, gravity field, magnetic field, and polar magnetosphere... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
5 August 2011 launch |
orbiter | en route |  |
http://sse.jpl.nasa.gov/missions/profile.cfm?MCode=Juno | ||
| EJSM Europa Jupiter System Mission The Europa Jupiter System Mission – Laplace was a proposed joint NASA/ESA unmanned space mission slated to launch around 2020 for the in-depth exploration of Jupiter's moons with a focus on Europa, Ganymede and Jupiter's magnetosphere... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... /  ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
2020? | orbiters/landers | proposed | http://opfm.jpl.nasa.gov/europajupitersystemmissionejsm/ | |||
SaturnSaturnSaturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest planet in the Solar System, after Jupiter. Saturn is named after the Roman god Saturn, equated to the Greek Cronus , the Babylonian Ninurta and the Hindu Shani. Saturn's astronomical symbol represents the Roman god's sickle.Saturn,...
probes
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pioneer 11 Pioneer 11 Pioneer 11 is a 259-kilogram robotic space probe launched by NASA on April 6, 1973 to study the asteroid belt, the environment around Jupiter and Saturn, solar wind, cosmic rays, and eventually the far reaches of the solar system and heliosphere... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
1 September 1979 | flyby | success | previously visited Jupiter |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1973-019A | |
| Voyager 1 Voyager 1 The Voyager 1 spacecraft is a 722-kilogram space probe launched by NASA in 1977, to study the outer Solar System and eventually interstellar space. Operating for as of today , the spacecraft receives routine commands and transmits data back to the Deep Space Network. At a distance of as of... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
12 November 1980 | flyby | success | previously visited Jupiter |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1977-084A | |
| Voyager 2 Voyager 2 The Voyager 2 spacecraft is a 722-kilogram space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977 to study the outer Solar System and eventually interstellar space... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
5 August 1981 | flyby | success | previously visited Jupiter, went on to visit Uranus and Neptune |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1977-076A | |
| Cassini |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... /  ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... /  ASI ASIItalian Space Agency The Italian Space Agency is a government agency established in 1988 to fund, regulate and coordinate space exploration activities in Italy... |
1 July 2004 – | orbiter | success | also performed flybys of a number of Saturn's moons, and deployed the Huygens Titan lander; first spacecraft to orbit Saturn |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1997-061A | |
TitanTitan (moon)Titan , or Saturn VI, is the largest moon of Saturn, the only natural satellite known to have a dense atmosphere, and the only object other than Earth for which clear evidence of stable bodies of surface liquid has been found....
probes
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Huygens |  ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
14 January 2005 | atmospheric probe, lander | success | deployed by Cassini; first probe to land on a satellite of another planet | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1997-061C | ||
| Titan Saturn System Mission Titan Saturn System Mission Titan Saturn System Mission was a joint NASA/ESA proposal for an exploration of Saturn and its moons Titan and Enceladus, where many complex phenomena have been revealed by the recent Cassini–Huygens mission... |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... /  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
October 2029 | orbiter, montgolfière, lander | under study | ||||
UranusUranusUranus is the seventh planet from the Sun. It has the third-largest planetary radius and fourth-largest planetary mass in the Solar System. It is named after the ancient Greek deity of the sky Uranus , the father of Cronus and grandfather of Zeus...
probes
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voyager 2 Voyager 2 The Voyager 2 spacecraft is a 722-kilogram space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977 to study the outer Solar System and eventually interstellar space... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
24 January 1986 | flyby | success | previously visited Jupiter and Saturn; went on to visit Neptune |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1977-076A | |
NeptuneNeptuneNeptune is the eighth and farthest planet from the Sun in the Solar System. Named for the Roman god of the sea, it is the fourth-largest planet by diameter and the third largest by mass. Neptune is 17 times the mass of Earth and is slightly more massive than its near-twin Uranus, which is 15 times...
probes
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Voyager 2 Voyager 2 The Voyager 2 spacecraft is a 722-kilogram space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977 to study the outer Solar System and eventually interstellar space... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
25 August 1989 | flyby | success | previously visited Jupiter, Saturn and Uranus |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1977-076A | |
PlutoPlutoPluto, formal designation 134340 Pluto, is the second-most-massive known dwarf planet in the Solar System and the tenth-most-massive body observed directly orbiting the Sun...
probes
| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| New Horizons New Horizons New Horizons is a NASA robotic spacecraft mission currently en route to the dwarf planet Pluto. It is expected to be the first spacecraft to fly by and study Pluto and its moons, Charon, Nix, Hydra and S/2011 P 1. Its estimated arrival date at the Pluto-Charon system is July 14th, 2015... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2015 | flyby | en route | flybys of other Kuiper Belt Kuiper belt The Kuiper belt , sometimes called the Edgeworth–Kuiper belt, is a region of the Solar System beyond the planets extending from the orbit of Neptune to approximately 50 AU from the Sun. It is similar to the asteroid belt, although it is far larger—20 times as wide and 20 to 200 times as massive... objects may follow (targets yet to be decided) |
 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2006-001A | |
CometCometA comet is an icy small Solar System body that, when close enough to the Sun, displays a visible coma and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena are both due to the effects of solar radiation and the solar wind upon the nucleus of the comet...
probes
| Target | Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21P/Giacobini-Zinner 21P/Giacobini-Zinner Comet Giacobini–Zinner is a periodic comet in our solar system.It was discovered by Michel Giacobini from , who observed the comet in the constellation of Aquarius on December 20, 1900... |
ICE International Cometary Explorer The International Cometary Explorer spacecraft was originally known as International Sun/Earth Explorer 3 satellite, launched August 12, 1978. It was part of the ISEE international cooperative program between NASA and ESRO/ESA to study the interaction between the Earth's magnetic field and the... (formerly ISEE3) |
11 September 1985 | flyby | success | previously solar monitor ISEE3; went on to observe Halley's Comet |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1978-079A | ||
| 1P/Halley | Vega 1 Vega 1 Vega 1 is a Soviet space probe part of the Vega program. The spacecraft was a development of the earlier Venera craft... |
 SAS SASRussian Academy of Sciences The Russian Academy of Sciences consists of the national academy of Russia and a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation as well as auxiliary scientific and social units like libraries, publishers and hospitals.... |
6 March 1986 | flyby | success | minimum distance 8,890 km; previously visited Venus | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1984-125A | ||
| 1P/Halley | Suisei Suisei probe Suisei , originally known as Planet-A, was an unmanned space probe developed by the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science .... |
 ISAS ISASInstitute of Space and Astronautical Science is a Japanese national research organization of astrophysics using rockets, astronomical satellites and interplanetary probes. It is a division of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency .- History :... |
8 March 1986 | flyby | success | 151,000 km |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1985-073A | |
| 1P/Halley | Vega 2 Vega 2 Vega 2 is a Soviet space probe part of the Vega program. The spacecraft was a development of the earlier Venera craft. They were designed by Babakin Space Center and constructed as 5VK by Lavochkin at Khimki... |
 SAS SASRussian Academy of Sciences The Russian Academy of Sciences consists of the national academy of Russia and a network of scientific research institutes from across the Russian Federation as well as auxiliary scientific and social units like libraries, publishers and hospitals.... |
9 March 1986 | flyby | success | minimum distance 8,890 km; previously visited Venus | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1984-128A | ||
| 1P/Halley | Sakigake Sakigake Sakigake , pre-launch codename MS-T5, was Japan's first interplanetary spacecraft, and the first deep space probe to be launched by any country other than the USA or the Soviet Union... |
 ISAS ISASInstitute of Space and Astronautical Science is a Japanese national research organization of astrophysics using rockets, astronomical satellites and interplanetary probes. It is a division of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency .- History :... |
March 1986 | distant flyby | partial success | minimum distance 6.99 million km |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1985-001A | |
| 1P/Halley | Giotto Giotto mission Giotto was a European robotic spacecraft mission from the European Space Agency, intended to fly by and study Halley's Comet. On 13 March 1986, the mission succeeded in approaching Halley's nucleus at a distance of 596 kilometers.... |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
14 March 1986 | flyby | success | minimum distance 596 km; went on to visit comet 26P/Grigg-Skjellerup 26P/Grigg-Skjellerup Comet Grigg–Skjellerup is a periodic comet.Discovered in 1902 by John Grigg of New Zealand, and rediscovered in its next appearance in 1922 by John Francis Skjellerup, an Australian then living and working for about two decades in South Africa where he was a founder member of the Astronomical... |
 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1985-056A | |
| 1P/Halley | ICE International Cometary Explorer The International Cometary Explorer spacecraft was originally known as International Sun/Earth Explorer 3 satellite, launched August 12, 1978. It was part of the ISEE international cooperative program between NASA and ESRO/ESA to study the interaction between the Earth's magnetic field and the... (formerly ISEE3) |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
28 March 1986 | distant obser- vations |
success | minimum distance 32 million km; previously visited comet 21P/Giacobini-Zinner 21P/Giacobini-Zinner Comet Giacobini–Zinner is a periodic comet in our solar system.It was discovered by Michel Giacobini from , who observed the comet in the constellation of Aquarius on December 20, 1900... |
 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1978-079A | |
| 26P/Grigg-Skjellerup 26P/Grigg-Skjellerup Comet Grigg–Skjellerup is a periodic comet.Discovered in 1902 by John Grigg of New Zealand, and rediscovered in its next appearance in 1922 by John Francis Skjellerup, an Australian then living and working for about two decades in South Africa where he was a founder member of the Astronomical... |
Giotto Giotto mission Giotto was a European robotic spacecraft mission from the European Space Agency, intended to fly by and study Halley's Comet. On 13 March 1986, the mission succeeded in approaching Halley's nucleus at a distance of 596 kilometers.... |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
10 July 1992 | flyby | success | previously visited Halley's Comet |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1985-056A | |
| 45P/ Honda-Mrkos-Pajdusakova 45P/Honda-Mrkos-Pajdusakova 45P/Honda–Mrkos–Pajdušáková is a short-period comet discovered by Minoru Honda December 3, 1948. The comet is named after Minoru Honda, Antonín Mrkos, and Ľudmila Pajdušáková. The comet is on a elliptical orbit with a period of 5.26 years. The comet nucleus is estimated to be 0.5-1.6 kilometers in... |
Sakigake Sakigake Sakigake , pre-launch codename MS-T5, was Japan's first interplanetary spacecraft, and the first deep space probe to be launched by any country other than the USA or the Soviet Union... |
 ISAS ISASInstitute of Space and Astronautical Science is a Japanese national research organization of astrophysics using rockets, astronomical satellites and interplanetary probes. It is a division of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency .- History :... |
1996 | flyby | failure | contact lost; previously visited Halley's Comet |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1985-001A | |
| 21P/Giacobini-Zinner 21P/Giacobini-Zinner Comet Giacobini–Zinner is a periodic comet in our solar system.It was discovered by Michel Giacobini from , who observed the comet in the constellation of Aquarius on December 20, 1900... |
Sakigake Sakigake Sakigake , pre-launch codename MS-T5, was Japan's first interplanetary spacecraft, and the first deep space probe to be launched by any country other than the USA or the Soviet Union... |
 ISAS ISASInstitute of Space and Astronautical Science is a Japanese national research organization of astrophysics using rockets, astronomical satellites and interplanetary probes. It is a division of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency .- History :... |
1998 | flyby | failure | ||||
| 55P/Tempel-Tuttle 55P/Tempel-Tuttle 55P/Tempel–Tuttle is a comet that was independently discovered by Ernst Tempel on December 19, 1865 and by Horace Parnell Tuttle on January 6, 1866.It is the parent body of the Leonid meteor shower... |
Suisei Suisei probe Suisei , originally known as Planet-A, was an unmanned space probe developed by the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science .... |
 ISAS ISASInstitute of Space and Astronautical Science is a Japanese national research organization of astrophysics using rockets, astronomical satellites and interplanetary probes. It is a division of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency .- History :... |
1998 | flyby | failure | abandoned due to lack of fuel; previously visited Halley's Comet |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1985-073A | |
| 21P/Giacobini-Zinner 21P/Giacobini-Zinner Comet Giacobini–Zinner is a periodic comet in our solar system.It was discovered by Michel Giacobini from , who observed the comet in the constellation of Aquarius on December 20, 1900... |
Suisei Suisei probe Suisei , originally known as Planet-A, was an unmanned space probe developed by the Institute of Space and Astronautical Science .... |
 ISAS ISASInstitute of Space and Astronautical Science is a Japanese national research organization of astrophysics using rockets, astronomical satellites and interplanetary probes. It is a division of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency .- History :... |
1998 | flyby | failure | ||||
| 19P/Borrelly 19P/Borrelly Comet Borrelly or Borrelly's Comet is a periodic comet, which was visited by the spacecraft Deep Space 1 in 2001.- Discovery :... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
flyby | success | previously visited asteroid 9969 Braille 9969 Braille 9969 Braille is a small Mars-crossing asteroid that orbits the Sun once every 3.58 years. It was discovered in 1992 by astronomers at Palomar observatory and later named after Louis Braille, the inventor of the writing system for the blind... |
 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1998-061A | |||
| 2P/Encke | CONTOUR CONTOUR The COmet Nucleus TOUR was a NASA Discovery-class space probe that failed shortly after its July 2002 launch. It had as its primary objective close flybys of two comet nuclei with the possibility of a flyby of a third known comet or an as-yet-undiscovered comet.The two comets scheduled to be... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2003 | flyby | failure | contact lost shortly after launch |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2002-034A | |
| 81P/Wild 81P/Wild Comet 81P/Wild, also known as Wild 2 , is a comet named after Swiss astronomer Paul Wild, who discovered it in 1978 using a 40-cm Schmidt telescope at Zimmerwald.... |
Stardust Stardust (spacecraft) Stardust is a 300-kilogram robotic space probe launched by NASA on February 7, 1999 to study the asteroid 5535 Annefrank and collect samples from the coma of comet Wild 2. The primary mission was completed January 15, 2006, when the sample return capsule returned to Earth... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2 January 2004 | flyby, sample return | success | sample returned January 2006; also visited asteroid 5535 Annefrank 5535 Annefrank 5535 Annefrank is an inner main-belt asteroid, and member of the Augusta family. It was discovered by Karl Reinmuth in 1942. It is named after Anne Frank, the Dutch-Jewish diarist who died in a concentration camp... |
 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1999-003A | |
| 9P/Tempel 9P/Tempel Tempel 1 , is a periodic comet discovered by Wilhelm Tempel in 1867. It currently completes an orbit of the Sun every 5.5 years. Tempel 1 was the target of the Deep Impact space mission, which photographed a deliberate high-speed impact upon the comet in 2005... |
Deep Impact |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
July 2005 | flyby | success |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2005-001A | ||
| Impactor |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
4 July 2005 | impactor | success | |||||
| 73P/ Schwassmann-Wachmann 73P/Schwassmann-Wachmann 73P/Schwassmann–Wachmann, also known as Schwassmann–Wachmann 3, is a periodic comet in our solar system which is in the process of disintegrating. Starting the 2011 perihelion passage the primary component 73P-C was recovered on 28 November 2010 near apparent magnitude 21.3... |
CONTOUR CONTOUR The COmet Nucleus TOUR was a NASA Discovery-class space probe that failed shortly after its July 2002 launch. It had as its primary objective close flybys of two comet nuclei with the possibility of a flyby of a third known comet or an as-yet-undiscovered comet.The two comets scheduled to be... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2006 | flyby | failure | contact lost shortly after launch |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2002-034A | |
| 6P/d'Arrest 6P/d'Arrest 6P/d'Arrest is a periodic comet in our Solar System, orbiting between Mars and Jupiter. It passed 53 Gm from the Earth, about a third of the Earth-Sun distance, on August 9, 2008.... |
CONTOUR CONTOUR The COmet Nucleus TOUR was a NASA Discovery-class space probe that failed shortly after its July 2002 launch. It had as its primary objective close flybys of two comet nuclei with the possibility of a flyby of a third known comet or an as-yet-undiscovered comet.The two comets scheduled to be... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2008 | flyby | failure | contact lost shortly after launch |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2002-034A | |
| 103P/Hartley 103P/Hartley Comet Hartley 2, designated as 103P/Hartley by the Minor Planet Center, is a small periodic comet with an orbital period of 6.46 years. It was discovered by Malcolm Hartley in 1986 at the Schmidt Telescope Unit, Siding Spring Observatory, Australia... |
Deep Impact (redesignated EPOXI EPOXI EPOXI is a NASA unmanned space mission led by the University of Maryland using the existing Deep Impact vehicle to begin a new series of observations. It first investigated extrasolar planets and, on November 4, 2010, it performed a close approach to the comet 103P/Hartley... ) |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
4 November 2010 | flyby | success | mission extension (target changed from comet Boethin) |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2005-001A | |
| 9P/Tempel 9P/Tempel Tempel 1 , is a periodic comet discovered by Wilhelm Tempel in 1867. It currently completes an orbit of the Sun every 5.5 years. Tempel 1 was the target of the Deep Impact space mission, which photographed a deliberate high-speed impact upon the comet in 2005... |
Stardust Stardust (spacecraft) Stardust is a 300-kilogram robotic space probe launched by NASA on February 7, 1999 to study the asteroid 5535 Annefrank and collect samples from the coma of comet Wild 2. The primary mission was completed January 15, 2006, when the sample return capsule returned to Earth... (redesignated NExT) |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
14 February 2011 | flyby | success | mission extension |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1999-003A | |
| 67P/Churyumov- 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko Comet Churyumov–Gerasimenko, officially designated 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko, is a comet with a current orbital period of 6.6 years. It is the destination of the European Space Agency's Rosetta spacecraft mission, launched on March 2, 2004.... Gerasimenko 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko Comet Churyumov–Gerasimenko, officially designated 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko, is a comet with a current orbital period of 6.6 years. It is the destination of the European Space Agency's Rosetta spacecraft mission, launched on March 2, 2004.... |
Rosetta Rosetta (spacecraft) Rosetta is a robotic spacecraft of the European Space Agency on a mission to study the comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. Rosetta consists of two main elements: the Rosetta space probe and the Philae lander. The spacecraft was launched on 2 March 2004 on an Ariane 5 rocket and will reach the comet by... |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
2014–15 | orbiter | en route | flybys of asteroids 2867 Šteins 2867 Šteins 2867 Šteins is a small main-belt asteroid that was discovered in 1969 by N. S. Chernykh. It is named after Kārlis Šteins, a Latvian and Soviet astronomer... and 21 Lutetia 21 Lutetia 21 Lutetia is a large main-belt asteroid of an unusual spectral type. It measures about 100 kilometers in diameter . It was discovered in 1852 by Hermann Goldschmidt, and is named after Lutetia, the Latin name for Paris.... also scheduled |
 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2004-006A | |
| Philae |  ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
2014 | lander | en route | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=PHILAE | ||||
Probes leaving the Solar System
| Spacecraft | Organization | Notes | Image | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pioneer 10 Pioneer 10 Pioneer 10 is a 258-kilogram robotic space probe that completed the first interplanetary mission to Jupiter, and became the first spacecraft to achieve escape velocity from the Solar System. The project was managed by the NASA Ames Research Center and the contract for the construction of the... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
Left Jupiter in December 1973. Mission ended March 1997. Last contact January 23, 2003. Craft now presumed dead; no further contact attempts planned. |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1972-012A |
| Pioneer 11 Pioneer 11 Pioneer 11 is a 259-kilogram robotic space probe launched by NASA on April 6, 1973 to study the asteroid belt, the environment around Jupiter and Saturn, solar wind, cosmic rays, and eventually the far reaches of the solar system and heliosphere... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
Left Saturn in September 1979. Last contact September 1995. The craft's antenna cannot be manoeuvred to point to Earth, and it is not known if it is still transmitting. No further contact attempts are planned. |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1973-019A |
| Voyager 1 Voyager 1 The Voyager 1 spacecraft is a 722-kilogram space probe launched by NASA in 1977, to study the outer Solar System and eventually interstellar space. Operating for as of today , the spacecraft receives routine commands and transmits data back to the Deep Space Network. At a distance of as of... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
Left Saturn in November 1980. Still in regular contact and transmitting scientific data (as of April 2011). Contact hoped to be maintained until at least 2020. |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1977-084A |
| Voyager 2 Voyager 2 The Voyager 2 spacecraft is a 722-kilogram space probe launched by NASA on August 20, 1977 to study the outer Solar System and eventually interstellar space... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
Left Neptune in August 1989. Still in regular contact and transmitting scientific data (as of April 2011). Contact hoped to be maintained until at least 2020. |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=1977-076A |
| New Horizons New Horizons New Horizons is a NASA robotic spacecraft mission currently en route to the dwarf planet Pluto. It is expected to be the first spacecraft to fly by and study Pluto and its moons, Charon, Nix, Hydra and S/2011 P 1. Its estimated arrival date at the Pluto-Charon system is July 14th, 2015... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
Currently en route to outer Solar System. Expected to reach Pluto in July 2015. |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2006-001A |
Other probes to leave Earth orbit
For completeness, this section lists probes that have left (or will leave) Earth orbit, but are not targeted at any of the above bodies.| Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Location | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| WMAP |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
30 June 2001 (launch) – to October 2010 (end) | Sun-Earth L2 Lagrangian point The Lagrangian points are the five positions in an orbital configuration where a small object affected only by gravity can theoretically be stationary relative to two larger objects... point |
success | cosmic background radiation observations; sent to graveyard orbit Graveyard orbit A graveyard orbit, also called a supersynchronous orbit, junk orbit or disposal orbit, is an orbit significantly above synchronous orbit, where spacecraft are intentionally placed at the end of their operational life... after 9 years of use. |
 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2001-027A | |
| Spitzer Space Telescope Spitzer Space Telescope The Spitzer Space Telescope , formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility is an infrared space observatory launched in 2003... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
25 August 2003 (launch) – still active (as of December 2010) | Earth-trailing heliocentric orbit | success | infrared astronomy |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2003-038A | |
| Kepler Kepler Mission The Kepler spacecraft is an American space observatory, the space-based portion of NASA's Kepler Mission to discover Earth-like planets orbiting other stars. The spacecraft is named in honor of the 17th-century German astronomer Johannes Kepler... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
6 March 2009 (launch) | Earth-trailing heliocentric orbit | operational | search for extrasolar planet Extrasolar planet An extrasolar planet, or exoplanet, is a planet outside the Solar System. A total of such planets have been identified as of . It is now known that a substantial fraction of stars have planets, including perhaps half of all Sun-like stars... s |
 |
http://kepler.nasa.gov/ | |
| Herschel Space Observatory Herschel Space Observatory The Herschel Space Observatory is a European Space Agency space observatory sensitive to the far infrared and submillimetre wavebands. It is the largest space telescope ever launched, carrying a single mirror of in diameter.... |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
14 May 2009 (launch) | Lissajous orbit Lissajous orbit In orbital mechanics, a Lissajous orbit, , named after Jules Antoine Lissajous, is a quasi-periodic orbital trajectory that an object can follow around a Lagrangian point of a three-body system without requiring any propulsion. Lyapunov orbits around a libration point are curved paths that lie... around Sun-Earth L2 Lagrangian point The Lagrangian points are the five positions in an orbital configuration where a small object affected only by gravity can theoretically be stationary relative to two larger objects... point |
operational | study of formation and evolution of galaxies and stars |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=FIRST | |
| Planck Surveyor Planck Surveyor Planck is a space observatory of the European Space Agency and designed to observe the anisotropies of the cosmic microwave background over the entire sky, at a high sensitivity and angular resolution... |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
14 May 2009 (launch) | Lissajous orbit Lissajous orbit In orbital mechanics, a Lissajous orbit, , named after Jules Antoine Lissajous, is a quasi-periodic orbital trajectory that an object can follow around a Lagrangian point of a three-body system without requiring any propulsion. Lyapunov orbits around a libration point are curved paths that lie... around Sun-Earth L2 Lagrangian point The Lagrangian points are the five positions in an orbital configuration where a small object affected only by gravity can theoretically be stationary relative to two larger objects... point |
operational | cosmic microwave background observations |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=PLANCK | |
| IKAROS IKAROS IKAROS is a Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency experimental spacecraft. The spacecraft was launched on 21 May, 2010, aboard an H-IIA rocket, together with the Akatsuki probe and four other small spacecraft... |
 JAXA JAXAJapan Aerospace Exploration Agency The , or JAXA, is Japan's national aerospace agency. Through the merger of three previously independent organizations, JAXA was formed on October 1, 2003, as an Independent Administrative Institution administered by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology and the... |
20 May 2010 (launch) | Earth-Venus transfer heliocentric orbit | operational | solar sail Solar sail Solar sails are a form of spacecraft propulsion using the radiation pressure of light from a star or laser to push enormous ultra-thin mirrors to high speeds.... technology development / interplanetary space exploration |
http://www.jspec.jaxa.jp/e/activity/ikaros.html | ||
| Shin'en Shin'en (spacecraft) Shin'en, known before launch as UNITEC-1 or UNISEC Technology Experiment Carrier 1, is a Japanese student spacecraft which was intended to make a flyby of Venus in order to study the effects of interplanetary spaceflight on spacecraft computers. In doing so, it was intended to become the first... (UNITEC-1) |
 UNISEC UNISEC |
failure | technology development; contact lost shortly after launch | http://www.unisec.jp/unitec-1/en/top.html | ||||
| LISA Pathfinder LISA Pathfinder LISA Pathfinder is the revised name for SMART-2, a NASA/ESA space probe to be launched in June 2013. SMART stands for Small Missions for Advanced Research in Technology. The aim of the LISA Pathfinder is to test technologies needed for the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna, a joint NASA/ESA... |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
2013 (launch) | Halo orbit around Sun-Earth L1 Lagrangian point The Lagrangian points are the five positions in an orbital configuration where a small object affected only by gravity can theoretically be stationary relative to two larger objects... point |
planned | test mission for proposed LISA Laser Interferometer Space Antenna The Laser Interferometer Space Antenna is a planned space mission to detect and accurately measure gravitational waves from astronomical sources. LISA was originally conceived as a joint effort between the United States space agency NASA and the European Space Agency... gravitational wave observatory |
http://www.esa.int/esaSC/120397_index_0_m.html | ||
| James Webb Space Telescope James Webb Space Telescope The James Webb Space Telescope , previously known as Next Generation Space Telescope , is a planned next-generation space telescope, optimized for observations in the infrared. The main technical features are a large and very cold 6.5 meter diameter mirror, an observing position far from Earth,... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...  ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states...  CSA CSA |
2013 (launch) | Sun-Earth L2 Lagrangian point The Lagrangian points are the five positions in an orbital configuration where a small object affected only by gravity can theoretically be stationary relative to two larger objects... point |
planned | infrared astronomy |  |
http://www.esa.int/esaCP/SEMA3T7OY2F_index_0.html | |
Cancelled probes and missions
| Target | Spacecraft | Organization | Date | Type | Status | Notes | Image | Ref | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mercury | BepiColombo Mercury Surface Element |  ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
lander | cancelled | |||||
| Moon | LUNAR-A LUNAR-A LUNAR-A is a cancelled Japanese spacecraft project that was originally scheduled to be launched in August 2004. After many delays LUNAR-A is a cancelled Japanese spacecraft project that was originally scheduled to be launched in August 2004. After many delays LUNAR-A is a cancelled Japanese... |
 JAXA JAXA |
orbiter, penetrators | cancelled | originally scheduled for 2004, finally cancelled 2007 | http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=LUNAR-A | |||
| Mars | Mars Surveyor 2001 Lander Mars Surveyor 2001 Lander The NASA Mars Surveyor 2001 Lander was a planned Mars probe which was canceled in May 2000 in the wake of the failures of the Mars Climate Orbiter and Mars Polar Lander missions in late 1999... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2001 | lander | cancelled |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=MS2001L | ||
| Mars | NetLander NetLander For late 2007 CNES and ESA had planned to send to Mars a remote sensing orbiter and four small Netlanders. The Netlanders were to have landed in four different Mars locations.... |
 CNES CNESCNES The is the French government space agency . Established under President Charles de Gaulle in 1961, its headquarters are located in central Paris and it is under the supervision of the French Ministries of Defence and Research... /  ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
lander | cancelled | http://smsc.cnes.fr/NETLANDER/ | ||||
| Mars | Mars Telecommunications Orbiter Mars Telecommunications Orbiter The Mars Telecommunications Orbiter was a cancelled Mars mission that was originally intended to launch in 2009 and would have established an Interplanetary Internet between Earth and Mars... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2010 | orbiter | cancelled |  |
http://aerospacescholars.jsc.nasa.gov/HAS/cirr/em/8/12.cfm | ||
| Phobos | Aladdin |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
sample return | not selected | http://stardust.jpl.nasa.gov/news/news38.html | ||||
| Europa | Europa Orbiter Europa Orbiter The Europa Orbiter was a planned NASA mission to Jupiter's Moon Europa, that was cancelled in 2002. Its main objectives included determining the presence or absence of a subsurface ocean and identifying candidate sites for future lander misions.... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
orbiter | cancelled | http://sse.jpl.nasa.gov/scitech/display.cfm?ST_ID=286 | ||||
| Europa | Jupiter Icy Moons Orbiter Jupiter Icy Moons Orbiter The Jupiter Icy Moons Orbiter was a proposed spacecraft designed to explore the icy moons of Jupiter. The main target was Europa, the suspected ocean of which is one of the places where simple alien life is a possibility in our solar system... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
orbiter | cancelled |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/planetary/prop_missions.html | |||
| Ganymede | Jupiter Icy Moons Orbiter |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
orbiter | cancelled |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/planetary/prop_missions.html | |||
| Callisto | Jupiter Icy Moons Orbiter |  NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
orbiter | cancelled |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/planetary/prop_missions.html | |||
| Pluto | Pluto Fast Flyby Pluto Fast Flyby The Pluto Fast Flyby was a space mission meant to perform a flyby of the dwarf planet Pluto. This spacecraft was meant to be launched by 2000 and reach Pluto by 2010, so it could examine Pluto's atmosphere before it froze to the ground as 'snow' as Pluto moves away from the sun... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2010 | flyby | cancelled | Now known as New Horizons New Horizons New Horizons is a NASA robotic spacecraft mission currently en route to the dwarf planet Pluto. It is expected to be the first spacecraft to fly by and study Pluto and its moons, Charon, Nix, Hydra and S/2011 P 1. Its estimated arrival date at the Pluto-Charon system is July 14th, 2015... |
|||
| Pluto | Pluto Kuiper Express Pluto Kuiper Express The Pluto Kuiper Express mission was a space mission designed to fly by the Pluto-Charon system and at least one large object in the Kuiper belt beyond Pluto's orbit. Originally designated the Pluto Fast Flyby, it was scheduled to reach Pluto by 2012... |
 NASA NASANASA The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... |
2012 | flyby | cancelled | Now known as New Horizons New Horizons New Horizons is a NASA robotic spacecraft mission currently en route to the dwarf planet Pluto. It is expected to be the first spacecraft to fly by and study Pluto and its moons, Charon, Nix, Hydra and S/2011 P 1. Its estimated arrival date at the Pluto-Charon system is July 14th, 2015... |
 |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=PLUTOKE | |
| 4660 Nereus 4660 Nereus 4660 Nereus is a small asteroid. It was discovered by Eleanor F. Helin on February 28, 1982, approximately 1 month after a near pass by the Earth. It is named after Nereus, a Titan in Greek mythology.Nereus is potentially a very important asteroid... |
Hayabusa Hayabusa was an unmanned spacecraft developed by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency to return a sample of material from a small near-Earth asteroid named 25143 Itokawa to Earth for further analysis.... |
 ISAS ISASInstitute of Space and Astronautical Science is a Japanese national research organization of astrophysics using rockets, astronomical satellites and interplanetary probes. It is a division of Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency .- History :... |
sample return | cancelled | rerouted to 25143 Itokawa | _sampling.jpg) |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2003-019A | ||
| 3840 Mimistrobell 3840 Mimistrobell 3840 Mimistrobell is a main-belt asteroid discovered on October 9, 1980 by C. Shoemaker at Palomar.- External links :*... |
Rosetta Rosetta (spacecraft) Rosetta is a robotic spacecraft of the European Space Agency on a mission to study the comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. Rosetta consists of two main elements: the Rosetta space probe and the Philae lander. The spacecraft was launched on 2 March 2004 on an Ariane 5 rocket and will reach the comet by... |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
2006 | flyby | cancelled | rerouted |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2004-006A | |
| 4979 Otawara 4979 Otawara 4979 Otawara is a main-belt asteroid discovered on August 2, 1949 by K. Reinmuth at Heidelberg.- External links :*... |
Rosetta Rosetta (spacecraft) Rosetta is a robotic spacecraft of the European Space Agency on a mission to study the comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. Rosetta consists of two main elements: the Rosetta space probe and the Philae lander. The spacecraft was launched on 2 March 2004 on an Ariane 5 rocket and will reach the comet by... |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
2006 | flyby | cancelled | rerouted |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2004-006A | |
| 4660 Nereus 4660 Nereus 4660 Nereus is a small asteroid. It was discovered by Eleanor F. Helin on February 28, 1982, approximately 1 month after a near pass by the Earth. It is named after Nereus, a Titan in Greek mythology.Nereus is potentially a very important asteroid... |
Near Earth Asteroid Prospector | SpaceDev SpaceDev SpaceDev, a part of the "Space Systems Business" of Sierra Nevada Corporation, is prominent for its spaceflight and microsatellite work. It designed and built the hybrid rocket motors for Paul Allen's Tier One suborbital SpaceShipOne space program operated by Scaled Composites... |
sample return | cancelled | http://www.spacedev.com/newsite/templates/subpage3.php?pid=191&subNav=11&subSel=3 | ||||
| 46P/Wirtanen 46P/Wirtanen 46P/Wirtanen is a small short-periodic comet with a current orbital period of 5.4 years. It was the original target for close investigation by the Rosetta spacecraft, planned by the European Space Agency. It belongs to the Jupiter family of comets, all of which have aphelia between 5 and 6 AU. Its... |
Rosetta Rosetta (spacecraft) Rosetta is a robotic spacecraft of the European Space Agency on a mission to study the comet 67P/Churyumov–Gerasimenko. Rosetta consists of two main elements: the Rosetta space probe and the Philae lander. The spacecraft was launched on 2 March 2004 on an Ariane 5 rocket and will reach the comet by... |
 ESA ESAEuropean Space Agency The European Space Agency , established in 1975, is an intergovernmental organisation dedicated to the exploration of space, currently with 18 member states... |
2011 | orbiter | cancelled | rerouted to 67P/Churyumov-Gerasimenko |  |
http://nssdc.gsfc.nasa.gov/nmc/spacecraftDisplay.do?id=2004-006A | |

