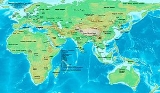
2nd century
Encyclopedia
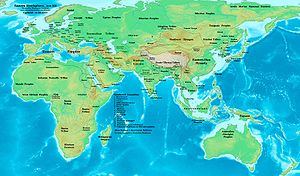
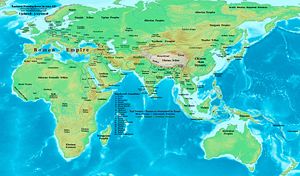
101
Year 101 was a common year starting on Friday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Traianus and Paetus...
to 200
200
Year 200 was a leap year starting on Tuesday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Severus and Victorinus...
in accordance with the Julian calendar
Julian calendar
The Julian calendar began in 45 BC as a reform of the Roman calendar by Julius Caesar. It was chosen after consultation with the astronomer Sosigenes of Alexandria and was probably designed to approximate the tropical year .The Julian calendar has a regular year of 365 days divided into 12 months...
in the Christian/Common Era
Common Era
Common Era ,abbreviated as CE, is an alternative designation for the calendar era originally introduced by Dionysius Exiguus in the 6th century, traditionally identified with Anno Domini .Dates before the year 1 CE are indicated by the usage of BCE, short for Before the Common Era Common Era...
. It is considered part of the Classical era, epoch, or historical period
History by period
Whether one can precisely define a time window as 'High Middle Ages' or 'Early Middle Ages' the title evokes an image and expectations in the reader of certain sets of characteristics—the essential essence of such labeling—a communications tool from one mind to another.Nonetheless, periods have a...
Early in the century, the Roman Empire
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
attained its greatest expansion under the emperor Trajan
Trajan
Trajan , was Roman Emperor from 98 to 117 AD. Born into a non-patrician family in the province of Hispania Baetica, in Spain Trajan rose to prominence during the reign of emperor Domitian. Serving as a legatus legionis in Hispania Tarraconensis, in Spain, in 89 Trajan supported the emperor against...
, but after his death became primarily defensive for the rest of its history. Much prosperity took place throughout the empire at this time, ruled as it were by the Five Good Emperors, a succession of just and able rulers.
This period also saw the removal of the Jews from Jerusalem during the reign of Hadrian
Hadrian
Hadrian , was Roman Emperor from 117 to 138. He is best known for building Hadrian's Wall, which marked the northern limit of Roman Britain. In Rome, he re-built the Pantheon and constructed the Temple of Venus and Roma. In addition to being emperor, Hadrian was a humanist and was philhellene in...
after Bar Kokhba's revolt
Bar Kokhba's revolt
The Bar Kokhba revolt 132–136 CE; or mered bar kokhba) against the Roman Empire, was the third major rebellion by the Jews of Judaea Province being the last of the Jewish-Roman Wars. Simon bar Kokhba, the commander of the revolt, was acclaimed as a Messiah, a heroic figure who could restore Israel...
.
The last quarter of the century saw the end of the period of peace and prosperity known as the Pax Romana
Pax Romana
Pax Romana was the long period of relative peace and minimal expansion by military force experienced by the Roman Empire in the 1st and 2nd centuries AD. Since it was established by Caesar Augustus it is sometimes called Pax Augusta...
at the death of the emperor Marcus Aurelius, last of the "Five Good Emperors", and the accession of his ineffective and deranged son Commodus
Commodus
Commodus , was Roman Emperor from 180 to 192. He also ruled as co-emperor with his father Marcus Aurelius from 177 until his father's death in 180. His name changed throughout his reign; see changes of name for earlier and later forms. His accession as emperor was the first time a son had succeeded...
.
Although the Han Dynasty
Han Dynasty
The Han Dynasty was the second imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Qin Dynasty and succeeded by the Three Kingdoms . It was founded by the rebel leader Liu Bang, known posthumously as Emperor Gaozu of Han. It was briefly interrupted by the Xin Dynasty of the former regent Wang Mang...
of China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
was firmly cemented into power and extended its imperial influence into Central Asia
Central Asia
Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north...
during the first half of the century, by the second half there was widespread corruption
History of the Han Dynasty
The Han Dynasty , founded by the peasant rebel leader Liu Bang ,From the Shang to the Sui dynasties, Chinese rulers were referred to in later records by their posthumous names, while emperors of the Tang to Yuan dynasties were referred to by their temple names, and emperors of the Ming and Qing...
and open rebellion
Yellow Turban Rebellion
The Yellow Turban Rebellion, also translated as Yellow Scarves Rebellion, was a peasant revolt that broke out in 184 AD in China during the reign of Emperor Ling of the Han Dynasty...
. This set in motion its ultimate decline, until it was overthrown in 220.
Events


- 96 – 180: Five Good Emperors of Rome: NervaNervaNerva , was Roman Emperor from 96 to 98. Nerva became Emperor at the age of sixty-five, after a lifetime of imperial service under Nero and the rulers of the Flavian dynasty. Under Nero, he was a member of the imperial entourage and played a vital part in exposing the Pisonian conspiracy of 65...
, TrajanTrajanTrajan , was Roman Emperor from 98 to 117 AD. Born into a non-patrician family in the province of Hispania Baetica, in Spain Trajan rose to prominence during the reign of emperor Domitian. Serving as a legatus legionis in Hispania Tarraconensis, in Spain, in 89 Trajan supported the emperor against...
, HadrianHadrianHadrian , was Roman Emperor from 117 to 138. He is best known for building Hadrian's Wall, which marked the northern limit of Roman Britain. In Rome, he re-built the Pantheon and constructed the Temple of Venus and Roma. In addition to being emperor, Hadrian was a humanist and was philhellene in...
, Antoninus PiusAntoninus PiusAntoninus Pius , also known as Antoninus, was Roman Emperor from 138 to 161. He was a member of the Nerva-Antonine dynasty and the Aurelii. He did not possess the sobriquet "Pius" until after his accession to the throne...
, Marcus Aurelius - The kingdomMonarchyA monarchy is a form of government in which the office of head of state is usually held until death or abdication and is often hereditary and includes a royal house. In some cases, the monarch is elected...
of Aksum emerges - 122 – 132: Hadrian's WallHadrian's WallHadrian's Wall was a defensive fortification in Roman Britain. Begun in AD 122, during the rule of emperor Hadrian, it was the first of two fortifications built across Great Britain, the second being the Antonine Wall, lesser known of the two because its physical remains are less evident today.The...
across Britain - 132 – 135: Bar Kokhba's revoltBar Kokhba's revoltThe Bar Kokhba revolt 132–136 CE; or mered bar kokhba) against the Roman Empire, was the third major rebellion by the Jews of Judaea Province being the last of the Jewish-Roman Wars. Simon bar Kokhba, the commander of the revolt, was acclaimed as a Messiah, a heroic figure who could restore Israel...
against Rome - 144: Marcion, rejected by Church of Rome, founds MarcionismMarcionismMarcionism was an Early Christian dualist belief system that originated in the teachings of Marcion of Sinope at Rome around the year 144; see also Christianity in the 2nd century....
- 167 – 175: First MarcomanniMarcomanniThe Marcomanni were a Germanic tribe, probably related to the Buri, Suebi or Suevi.-Origin:Scholars believe their name derives possibly from Proto-Germanic forms of "march" and "men"....
War - 178 – 180: Second Marcomanni War (depicted in the movie GladiatorGladiator (2000 film)Gladiator is a 2000 historical epic film directed by Ridley Scott, starring Russell Crowe, Joaquin Phoenix, Connie Nielsen, Ralf Möller, Oliver Reed, Djimon Hounsou, Derek Jacobi, John Shrapnel and Richard Harris. Crowe portrays the loyal Roman General Maximus Decimus Meridius, who is betrayed...
) - 184 – 205: the Yellow Turban RebellionYellow Turban RebellionThe Yellow Turban Rebellion, also translated as Yellow Scarves Rebellion, was a peasant revolt that broke out in 184 AD in China during the reign of Emperor Ling of the Han Dynasty...
of the Han DynastyHan DynastyThe Han Dynasty was the second imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Qin Dynasty and succeeded by the Three Kingdoms . It was founded by the rebel leader Liu Bang, known posthumously as Emperor Gaozu of Han. It was briefly interrupted by the Xin Dynasty of the former regent Wang Mang...
in China begins - Herakleitos makes The Unswept Floor, mosaic variant of a 2nd century BC2nd century BCThe 2nd century BC started the first day of 200 BC and ended the last day of 101 BC. It is considered part of the Classical era, although depending on the region being studied, other terms may be more proper .-Overview:Fresh from its victories in the Second Punic War, the...
painting by Sosos of PergamonPergamonPergamon , or Pergamum, was an ancient Greek city in modern-day Turkey, in Mysia, today located from the Aegean Sea on a promontory on the north side of the river Caicus , that became the capital of the Kingdom of Pergamon during the Hellenistic period, under the Attalid dynasty, 281–133 BC...
. It is now kept at Musei Vaticani, Museo Gregoriano Profano, ex Lateranese, RomeRomeRome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
. - Hadrian's WallHadrian's WallHadrian's Wall was a defensive fortification in Roman Britain. Begun in AD 122, during the rule of emperor Hadrian, it was the first of two fortifications built across Great Britain, the second being the Antonine Wall, lesser known of the two because its physical remains are less evident today.The...
, Great BritainGreat BritainGreat Britain or Britain is an island situated to the northwest of Continental Europe. It is the ninth largest island in the world, and the largest European island, as well as the largest of the British Isles...
, is built. - c. 2nd century-3rd century – Standing Buddha, from GandharaGandharaGandhāra , is the name of an ancient kingdom , located in northern Pakistan and eastern Afghanistan. Gandhara was located mainly in the vale of Peshawar, the Potohar plateau and on the Kabul River...
(PakistanPakistanPakistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan is a sovereign state in South Asia. It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and the Gulf of Oman in the south and is bordered by Afghanistan and Iran in the west, India in the east and China in the far northeast. In the north, Tajikistan...
), is made. Kushan period. It is now kept at Lahore MuseumLahore MuseumLahore Museum , established in 1894, is located in The Mall, Lahore, Punjab, Pakistan. Rudyard Kipling's father, John Lockwood Kipling, was one of the famous curators of the museum. Over 250,000 admissions were registered in 2005.-Attractions:...
, LahoreLahoreLahore is the capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab and the second largest city in the country. With a rich and fabulous history dating back to over a thousand years ago, Lahore is no doubt Pakistan's cultural capital. One of the most densely populated cities in the world, Lahore remains a...
.
Significant people
- Cai LunCai LunCai Lun , courtesy name Jingzhong , was a Chinese eunuch. He is traditionally regarded as the inventor of paper and the papermaking process, in forms recognizable in modern times as paper...
, the inventor of paperPaperPaper is a thin material mainly used for writing upon, printing upon, drawing or for packaging. It is produced by pressing together moist fibers, typically cellulose pulp derived from wood, rags or grasses, and drying them into flexible sheets....
and the papermakingPapermakingPapermaking is the process of making paper, a substance which is used universally today for writing and packaging.In papermaking a dilute suspension of fibres in water is drained through a screen, so that a mat of randomly interwoven fibres is laid down. Water is removed from this mat of fibres by...
process - TrajanTrajanTrajan , was Roman Emperor from 98 to 117 AD. Born into a non-patrician family in the province of Hispania Baetica, in Spain Trajan rose to prominence during the reign of emperor Domitian. Serving as a legatus legionis in Hispania Tarraconensis, in Spain, in 89 Trajan supported the emperor against...
, Roman Emperor - HadrianHadrianHadrian , was Roman Emperor from 117 to 138. He is best known for building Hadrian's Wall, which marked the northern limit of Roman Britain. In Rome, he re-built the Pantheon and constructed the Temple of Venus and Roma. In addition to being emperor, Hadrian was a humanist and was philhellene in...
, Roman Emperor - Dr AbascantusAbascantusAbascantus was a physician of Lugdunum, who probably lived in the 2nd century. He is several times mentioned by Galen, who has also preserved an antidote invented by him against the bite of serpents...
, Doctor - Marcus Aurelius, Roman Emperor
- Rabbi AkivaRabbi AkivaAkiva ben Joseph simply known as Rabbi Akiva , was a tanna of the latter part of the 1st century and the beginning of the 2nd century . He was a great authority in the matter of Jewish tradition, and one of the most central and essential contributors to the Mishnah and Midrash Halakha...
Head of all the Jewish Sages - Rabbi Yehuda haNasiJudah haNasiJudah the Prince, or Judah I, also known as Rebbi or Rabbeinu HaKadosh , was a 2nd-century CE rabbi and chief redactor and editor of the Mishnah. He was a key leader of the Jewish community during the Roman occupation of Judea . He was of the Davidic line, the royal line of King David, hence the...
Prince of the Jewish people - CommodusCommodusCommodus , was Roman Emperor from 180 to 192. He also ruled as co-emperor with his father Marcus Aurelius from 177 until his father's death in 180. His name changed throughout his reign; see changes of name for earlier and later forms. His accession as emperor was the first time a son had succeeded...
, Roman Emperor, claimed to be HerculesHerculesHercules is the Roman name for Greek demigod Heracles, son of Zeus , and the mortal Alcmene...
reincarnatedReincarnationReincarnation best describes the concept where the soul or spirit, after the death of the body, is believed to return to live in a new human body, or, in some traditions, either as a human being, animal or plant... - GalenGalenAelius Galenus or Claudius Galenus , better known as Galen of Pergamon , was a prominent Roman physician, surgeon and philosopher...
, medical writer - IgnatiusIgnatius of AntiochIgnatius of Antioch was among the Apostolic Fathers, was the third Bishop of Antioch, and was a student of John the Apostle. En route to his martyrdom in Rome, Ignatius wrote a series of letters which have been preserved as an example of very early Christian theology...
, third bishop of Antioch, author of letters - IrenaeusIrenaeusSaint Irenaeus , was Bishop of Lugdunum in Gaul, then a part of the Roman Empire . He was an early church father and apologist, and his writings were formative in the early development of Christian theology...
, second bishop of Lyon, author of Against the Heresies - JuvenalJuvenalThe Satires are a collection of satirical poems by the Latin author Juvenal written in the late 1st and early 2nd centuries AD.Juvenal is credited with sixteen known poems divided among five books; all are in the Roman genre of satire, which, at its most basic in the time of the author, comprised a...
Roman satirical poet - Montanus, Christian hereticChristian heresyChristian heresy refers to non-orthodox practices and beliefs that were deemed to be heretical by one or more of the Christian churches. In Western Christianity, the term "heresy" most commonly refers to those beliefs which were declared to be anathema by the Catholic Church prior to the schism of...
- NagarjunaNagarjunaNāgārjuna was an important Buddhist teacher and philosopher. Along with his disciple Āryadeva, he is credited with founding the Mādhyamaka school of Mahāyāna Buddhism...
, founder of MadhyamakaMadhyamakaMadhyamaka refers primarily to a Mahāyāna Buddhist school of Buddhist philosophy systematized by Nāgārjuna. Nāgārjuna may have arrived at his positions from a desire to achieve a consistent exegesis of the Buddha's doctrine as recorded in the āgamas...
Buddhism - Pliny the YoungerPliny the YoungerGaius Plinius Caecilius Secundus, born Gaius Caecilius or Gaius Caecilius Cilo , better known as Pliny the Younger, was a lawyer, author, and magistrate of Ancient Rome. Pliny's uncle, Pliny the Elder, helped raise and educate him...
- PlutarchPlutarchPlutarch then named, on his becoming a Roman citizen, Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus , c. 46 – 120 AD, was a Greek historian, biographer, essayist, and Middle Platonist known primarily for his Parallel Lives and Moralia...
, Greek historian - PolycarpPolycarpSaint Polycarp was a 2nd century Christian bishop of Smyrna. According to the Martyrdom of Polycarp, he died a martyr, bound and burned at the stake, then stabbed when the fire failed to touch him...
, bishop of SmyrnaSmyrnaSmyrna was an ancient city located at a central and strategic point on the Aegean coast of Anatolia. Thanks to its advantageous port conditions, its ease of defence and its good inland connections, Smyrna rose to prominence. The ancient city is located at two sites within modern İzmir, Turkey... - PtolemyPtolemyClaudius Ptolemy , was a Roman citizen of Egypt who wrote in Greek. He was a mathematician, astronomer, geographer, astrologer, and poet of a single epigram in the Greek Anthology. He lived in Egypt under Roman rule, and is believed to have been born in the town of Ptolemais Hermiou in the...
, Greek astronomer, astrologer and geographer - Septimius SeverusSeptimius SeverusSeptimius Severus , also known as Severus, was Roman Emperor from 193 to 211. Severus was born in Leptis Magna in the province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary succession of offices under the reigns of Marcus Aurelius and Commodus. Severus seized power after the death of...
, Roman Emperor - SuetoniusSuetoniusGaius Suetonius Tranquillus, commonly known as Suetonius , was a Roman historian belonging to the equestrian order in the early Imperial era....
, Roman historian - Valentinius, Gnostic philosopher
- Victor IPope Victor IPope Saint Victor I was Pope from 189 to 199 .Pope Victor I was the first bishop of Rome born in the Roman Province of Africa: probably he was born in Leptis Magna . He was later canonized...
, bishop of RomeRomeRome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half... - Zhang DaolingZhang DaolingZhang Ling , style name Fuhan , was an Eastern Han Dynasty Taoist hermit who founded the Way of the Celestial Masters sect of Taoism, which is also known as the Way of the Five Pecks of Rice....
, Chinese Taoist hermit - Zhang HengZhang HengZhang Heng was a Chinese astronomer, mathematician, inventor, geographer, cartographer, artist, poet, statesman, and literary scholar from Nanyang, Henan. He lived during the Eastern Han Dynasty of China. He was educated in the capital cities of Luoyang and Chang'an, and began his career as a...
, Chinese statesman, poet, inventor, astronomer, geographer, and engineer - Zhang ZhongjingZhang ZhongjingZhang Zhongjing , formal name Zhang Ji, was a Han Dynasty physician and one of the most eminent Chinese physicians during the later years of the Han Dynasty...
, one of the most famous Chinese physicians during Han DynastyHan DynastyThe Han Dynasty was the second imperial dynasty of China, preceded by the Qin Dynasty and succeeded by the Three Kingdoms . It was founded by the rebel leader Liu Bang, known posthumously as Emperor Gaozu of Han. It was briefly interrupted by the Xin Dynasty of the former regent Wang Mang...
Inventions, discoveries, introductions
- Cai LunCai LunCai Lun , courtesy name Jingzhong , was a Chinese eunuch. He is traditionally regarded as the inventor of paper and the papermaking process, in forms recognizable in modern times as paper...
of China invents paper (c. 105) - PtolemyPtolemyClaudius Ptolemy , was a Roman citizen of Egypt who wrote in Greek. He was a mathematician, astronomer, geographer, astrologer, and poet of a single epigram in the Greek Anthology. He lived in Egypt under Roman rule, and is believed to have been born in the town of Ptolemais Hermiou in the...
compiles a catalogue of all starStarA star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
s visible to the naked eye. He also compiles three of the most influential books in western history:- the AlmagestAlmagestThe Almagest is a 2nd-century mathematical and astronomical treatise on the apparent motions of the stars and planetary paths. Written in Greek by Claudius Ptolemy, a Roman era scholar of Egypt,...
which becomes the basis for western and Middle Eastern astronomy until the time of Copernicus and Kepler; - the astrological treatise, TetrabiblosTetrabiblosThe Tetrabiblos , also known under the Latin title Quadripartitum , is a text on the philosophy and practice of astrology, written in the second century AD by the Alexandrian scholar Claudius Ptolemy ....
; - and the GeographiaGeographia (Ptolemy)The Geography is Ptolemy's main work besides the Almagest...
- the Almagest
- 125125Year 125 was a common year starting on Sunday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Paullinus and Titius...
: Zhang HengZhang HengZhang Heng was a Chinese astronomer, mathematician, inventor, geographer, cartographer, artist, poet, statesman, and literary scholar from Nanyang, Henan. He lived during the Eastern Han Dynasty of China. He was educated in the capital cities of Luoyang and Chang'an, and began his career as a...
of China invents the world's first water-poweredHydraulicsHydraulics is a topic in applied science and engineering dealing with the mechanical properties of liquids. Fluid mechanics provides the theoretical foundation for hydraulics, which focuses on the engineering uses of fluid properties. In fluid power, hydraulics is used for the generation, control,...
armillary sphereArmillary sphereAn armillary sphere is a model of objects in the sky , consisting of a spherical framework of rings, centred on Earth, that represent lines of celestial longitude and latitude and other astronomically important features such as the ecliptic... - 132132Year 132 was a leap year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Serius and Sergianus...
: Zhang HengZhang HengZhang Heng was a Chinese astronomer, mathematician, inventor, geographer, cartographer, artist, poet, statesman, and literary scholar from Nanyang, Henan. He lived during the Eastern Han Dynasty of China. He was educated in the capital cities of Luoyang and Chang'an, and began his career as a...
of China invents first seismometerSeismometerSeismometers are instruments that measure motions of the ground, including those of seismic waves generated by earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and other seismic sources...
to detect the cardinal directionCardinal directionThe four cardinal directions or cardinal points are the directions of north, east, south, and west, commonly denoted by their initials: N, E, S, W. East and west are at right angles to north and south, with east being in the direction of rotation and west being directly opposite. Intermediate...
of earthquakeEarthquakeAn earthquake is the result of a sudden release of energy in the Earth's crust that creates seismic waves. The seismicity, seismism or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of earthquakes experienced over a period of time...
s

