
Palestrina
Encyclopedia
Palestrina is an ancient city and comune
(municipality) with a population of about 18,000, in Lazio, c. 35 km east of Rome
. It is connected to latter by the Via Prenestina.
It is the namesake of composer Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina
.
, a range in the central Apennines
.
Palestrina borders the following municipalities: Artena
, Castel San Pietro Romano
, Cave
, Gallicano nel Lazio
, Labico
, Rocca di Cave
, Rocca Priora
, Rome
, San Cesareo
, Valmontone
, Zagarolo
.
or 7th century BC. The ancient necropolis
lay on a plateau at the foot of the hill below the ancient town. Of the objects found in the oldest graves, and supposed to date from about the 7th century BC, the cups of silver and silver-gilt and most of the gold and amber
jewelry are Phoenicia
n (possibly Carthaginian
), but the bronze
s and some of the ivory
articles seem to be of the Etruscan civilization
.
Praenestine graves from about 240 BC onwards have been found: they are surmounted by the characteristic pine-apple of local stone, containing stone coffins with rich bronze, ivory and gold ornaments beside the skeleton. From these come the famous bronze boxes (cistae) and hand mirrors with inscriptions partly in Etruscan
. Also famous is the bronze Ficoroni casket (Museo Nazionale Etrusco di Villa Giulia, Rome
), engraved with pictures of the arrival of the Argonauts
in Bithynia
and the victory of Pollux over Amycus
, found in 1738. An example of archaic Latin is the inscription on the Cista Ficoroni: "Novios Plautios Romai med fecid / Dindia Macolnia fileai dedit" ("Novios Plautios made me in Rome, Dindia Macolnia gave me to her daughter"). The caskets are unique in Italy
, but a large number of mirrors of precisely similar style have been discovered in Etruria
. Hence, although it would be reasonable to conjecture that objects with Etruscan
characteristics came from Etruria, the evidence points decisively to an Etruscan factory in or near Praeneste itself. Other imported objects in the burials show that Praeneste traded not only with Etruria
but also with the Greek east.
The origin of Praeneste was attributed by the ancients to Ulysses
, or to other fabulous characters variously called Caeculus
, Telegonus
, Erulus or Praenestus. the name derives probably from the word Praenesteus, referring to its overlooking location.
Praeneste was probably under the hegemony of Alba Longa
while that city was the head of the Latin League
. It withdrew from the league in 499 BC, according to Livy
(its earliest historical mention), and formed an alliance with Rome
. After Rome was weakened by the Gauls
of Brennus (390 BC), Praeneste switched allegiances and fought against Rome in the long struggles that culminated in the Latin War
. From 373 to 370, it was in continual war against Rome or her allies, and was defeated by Cincinnatus
.
Eventually in 354 and in 338 the Romans were victorious and Praeneste was punished by the loss of portions of its territory, becoming a city allied to Rome. As such, it furnished contingents to the Roman army, and Roman exiles were permitted to live at Praeneste, which grew prosperous. The roses of Praeneste were a byword for profusion and beauty. Præneste was situated on the Via Labicana
.
Its citizens were offered Roman citizenship
in 90 BC in the Social War, when concessions had to be made by Rome to cement necessary alliances. In Sulla's second civil war
, Gaius Marius the Younger
was blockaded in the town by the forces of Sulla (82 BC). When the city was captured, Marius slew himself, the male inhabitants were massacred in cold blood, and a military colony was settled on part of its territory. From an inscription it appears that Sulla delegated the foundation of the new colony to Marcus Terentius Varro Lucullus
, who was consul
in 73 BC. Within a decade the lands of the colonia had been assembled by a few large landowners.
It was probably after the disaster of 82 BC that the city was removed from the hillside to the lower ground at the Madonna dell'Aquila, and that the sanctuary and temple of Fortune was enlarged so as to include much of the space occupied by the ancient city.
Under the Empire the cool breezes of Praeneste made it a favorite summer resort of wealthy Romans, whose villas
studded the neighborhood, though they ridiculed the language and the rough manners of the native inhabitants. The poet Horace
ranked "cool Praeneste" with Tibur
and Baiae
as favored resorts. The emperor Augustus
stayed in Praeneste, and Tiberius
recovered there from a dangerous illness and made it a municipium
. The ruins of the villa associated with Hadrian
stand in the plain near the church of S. Maria della Villa, about three-quarters of a mile from the town. At the site was discovered the Braschi Antinous
, now in the Vatican Museums
. Marcus Aurelius, Pliny the Younger
and Symmachus
also had villas there. Inscriptions show that the inhabitants of Praeneste were fond of gladiatorial shows.

connected with the oracle
known as the Praenestine lots (sortes praenestinae). The temple was redeveloped after 82 BC as a spectacular series of terraces, exedra
s and portico
s on four levels down the hillside, linked by monumental stairs and ramps. The inspiration for this feat of unified urbanistic design lay, not in republican Rome, but in the Hellenistic monarchies of the eastern Mediterranean. Praeneste offered a foretaste of the grandiose Imperial style of the following generation.
The oldest portion of the primitive sanctuary was situated on the terrace just above the lowest one, in a grotto
in the natural rock where there was a spring that developed into a well. As the archaic shrine was elaborated from the 2nd century BC, it was given a colored mosaic
pavement representing a seascape: a temple of Poseidon
on the shore, with fish of all kinds swimming in the sea. To the east of this grotto is a large space, now open, but once very possibly roofed, and forming a two-story basilica
built against the rock on the north side, and there decorated with pilasters. To the east is an apsidal hall, often identified with the temple itself, in which was found the famous mosaic
with scenes from the Nile
, relaid in the Palazzo Barberini-Colonna in Palestrina on the uppermost terrace (now a National Museum). Under this hall is a chamber, which an inscription on its walls identified as a treasury in the 2nd century BC. In front of this temple an obelisk
was erected in the reign of Claudius
, fragments of which still exist.
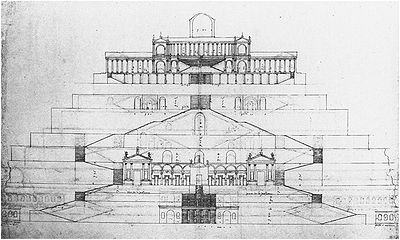 As extended under Sulla, the sanctuary of Fortune came to occupy a series of five vast terraces, which, resting on gigantic masonry substructure and connected with each other by grand staircases, rose one above the other on the hill in the form of the side of a pyramid, crowned on the highest terrace by the round temple of Fortune. This immense edifice, probably by far the largest sanctuary in Italy, must have presented a most imposing aspect, visible as it was from a great part of Latium, from Rome, and even from the sea. The ground at the foot of the lowest terrace is 1476 feet (450 m) above sea-level; here is a cistern, divided into ten large chambers, in brick-faced concrete.
As extended under Sulla, the sanctuary of Fortune came to occupy a series of five vast terraces, which, resting on gigantic masonry substructure and connected with each other by grand staircases, rose one above the other on the hill in the form of the side of a pyramid, crowned on the highest terrace by the round temple of Fortune. This immense edifice, probably by far the largest sanctuary in Italy, must have presented a most imposing aspect, visible as it was from a great part of Latium, from Rome, and even from the sea. The ground at the foot of the lowest terrace is 1476 feet (450 m) above sea-level; here is a cistern, divided into ten large chambers, in brick-faced concrete.
The goddess Fortuna here went by the name of Primigenia ("First Bearer"), she was represented suckling two babes, as in the Christian
representation of Charity
, said to be Jupiter and Juno
, and she was especially worshipped by matrons. The oracle continued to be consulted down to Christian times, until Constantine the Great, and again later Theodosius I
, forbade the practice and closed the temple.
Features of the temple influenced Roman garden design on steeply sloped sites through Antiquity and once again in Italian villa gardens from the 15th century. The monument to Victor Emmanuel II
in Rome owes a lot to the Praeneste sanctuary complex.
In 1297 the Sciarrillo di Colonna family, who had owned Praeneste (by then called Palestrina) from the eleventh century as a fief, revolted from the pope
. In the following year the town was taken by Papal forces, razed to the ground and salted
by order of Pope Boniface VIII
. In 1437 the rebuilt city was captured by the Papal general Giovanni Vitelleschi
and once more utterly destroyed at the command of Pope Eugenius IV.
It was rebuilt once more and fortified by Stefano Colonna
in 1448. It was again sacked in 1527, and occupied by the Duke of Alba, in 1556.
. It is likely the transfer was included as one of the conditions of the marriage of Taddeo Barberini
and Anna Colonna
. Thereafter, the famously nepotistic
family, headed by Maffeo Barberini (later Pope Urban VIII
), treated the comune as a principality
in its own right. Patriarchs of the Barberini family conferred, on various family members, the title of Prince of Palestrina. During the reign of Urban VIII, the title became interchangeable with that of Commander of the Papal Army (Gonfalonier of the Church
) as the Barberini family controlled the papacy and the Palestrina principality.
The Wars of Castro
ended (while Taddeo Barberini
held both titles) and members of the Barberini family (including Taddeo) fled into exile after the newly elected Pope Innocent X
launched an investigation into members of the Barberini family. Later the Barberini reconciled with the papacy when Pope Innocent X elevated Taddeo's son, Carlo Barberini
to the cardinalate and his brother Maffeo Barberini married a niece of the Pope and reclaimed the title, Prince of Palestrina.
Two members of the Barberini family were named Cardinal-Bishop of the Diocese of Palestrina
: Antonio Barberini
and Francesco Barberini (Junior)
, the son of Maffeo Barberini.
The Barberini Palace originally included the Nile mosaic of Palestrina
.
; this however brought the ancient remains of the sanctuary to light.
 The modern town of Palestrina is centered on the terraces once occupied by the massive temple of Fortuna. The town came to largely obscure the temple, whose monumental remains were revealed as a result of American bombing of German positions in World War II
The modern town of Palestrina is centered on the terraces once occupied by the massive temple of Fortuna. The town came to largely obscure the temple, whose monumental remains were revealed as a result of American bombing of German positions in World War II
. The town also contains remnants of ancient cyclopean walls.
On the summit of the hill (753 m), nearly a mile from the town, stood the ancient citadel, the site of which is now occupied by a few poor houses (Castel San Pietro) and a ruined medieval castle of the Colonna family. The view embraces the Monte Soratte, Rome, the Alban Hills
, and the Pontinian Plain as far as the sea. Considerable portions of the southern wall of the ancient citadel, built in massive cyclopean masonry consisting of limestone blocks, are still visible; and the two walls, also polygonal, which formerly united the citadel with the town, can still be traced.
 A calendar, which according to Suetonius was set up by the grammarian Marcus Verrius Flaccus in the imperial forum of Praeneste (at the Madonna dell'Aquila), was discovered in 1771 in the ruins of the church of Saint Agapitus
A calendar, which according to Suetonius was set up by the grammarian Marcus Verrius Flaccus in the imperial forum of Praeneste (at the Madonna dell'Aquila), was discovered in 1771 in the ruins of the church of Saint Agapitus
, where it had been used as building material.
The cathedral, just below the level of the temple, occupies the former civil basilica
of the town, whose facade includes a sundial
described by Varro
, traces of which may still be seen. In the modern piazza
the steps leading up to this basilica and the base of a large monument were found in 1907; evidently only part of the piazza represents the ancient forum. The cathedral has fine paintings and frescoes. In the Church of Santa Rosalia (1677) there is a noteworthy Pietà, carved in the solid rock.
The National Archeological Museum of Palestrina is housed inside the Renaissance Barberini Palace, the former baronial palace, built above the ancient temple of Fortuna. It exhibits the most important works from the ancient town of Praeneste. The famous sculpture of the Capitoline Triad
is exhibited on the first floor. The second floor is dedicated to the necropoli and sanctuaries, while the third floor contains a large polychrome mosaic depicting the flooding of the Nile (Nile mosaic of Palestrina
).
, and of the great 16th century composer Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina
. Thomas Mann
spent some time there in 1895 and, two years later, during the long harsh summer of 1897, he stayed over again, with his brother Heinrich Mann
, in a sojourn that provided the backdrop, nearly half a century later, for Adrian Leverkühn's pact with the Devil in Mann's novel Doktor Faustus
Comune
In Italy, the comune is the basic administrative division, and may be properly approximated in casual speech by the English word township or municipality.-Importance and function:...
(municipality) with a population of about 18,000, in Lazio, c. 35 km east of Rome
Rome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
. It is connected to latter by the Via Prenestina.
It is the namesake of composer Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina
Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina
Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina was an Italian Renaissance composer of sacred music and the best-known 16th-century representative of the Roman School of musical composition...
.
Geography
Palestrina is sited on a spur of the Monti PrenestiniMonti Prenestini
The Monti Prenestini is a mountain range in the Lazio sub-Apennines, in central Italy to the east of Rome. It is of limestone formation. It is bounded by the Monti Tiburtini to the north, by the Monti Ruffi to the east, and by the valley of the river Sacco to the south. The highest peak is Monte...
, a range in the central Apennines
Apennine mountains
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains or Greek oros but just as often used alone as a noun. The ancient Greeks and Romans typically but not always used "mountain" in the singular to mean one or a range; thus, "the Apennine mountain" refers to the entire chain and is translated "the Apennine...
.
Palestrina borders the following municipalities: Artena
Artena
Artena is a village and comune in the province of Rome, Italy. It is situated in the northwest of Monti Lepini, in the upper valley of the Sacco River...
, Castel San Pietro Romano
Castel San Pietro Romano
Castel San Pietro Romano is a comune in the Province of Rome in the Italian region Latium, located about 35 km east of Rome.-External links:*...
, Cave
Cave, Italy
Cave is a town and comune in the Latium region of Italy, 42 km southeast of Rome.-History:The city was mentioned first in 998 AD, and was later a fief of the Colonna family. In 1482 it was besieged by Pope Sixtus IV and obliged to surrender...
, Gallicano nel Lazio
Gallicano nel Lazio
Gallicano nel Lazio is a comune in the Province of Rome in the Italian region Latium, located about 25 km east of Rome.-External links:*...
, Labico
Labico
Labico is a comune of c. 4,500 inhabitants in the province of Rome in the Italian region Latium, located about 35 km southeast of Rome.-External links:*...
, Rocca di Cave
Rocca di Cave
Rocca di Cave is a comune in the Province of Rome in the Italian region Latium, located about 40 km east of Rome.It is home to the remains Colonna castle, which today houses a Geo-Palaeontological Museum and an astronomical observation point....
, Rocca Priora
Rocca Priora
Rocca Priora is a small town and comune in the province of Rome, Lazio, Italy. It is one of the Castelli Romani on the Alban Hills about 25 km south east of Rome, situated in the Regional Park known as the "Parco Regionale dei Castelli Romani"....
, Rome
Rome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
, San Cesareo
San Cesareo
San Cesareo is a town and comune in the province of Rome. In ancient times, it was on the Via Labicana or Via Latina, 18 miles from Rome....
, Valmontone
Valmontone
Valmontone is a comune in the Province of Rome in the Italian region Lazio, located about 45 km southeast of Rome.-Geography:...
, Zagarolo
Zagarolo
Zagarolo is a town and comune in the province of Rome, in the region of Lazio of central Italy. It has 14,620 inhabitants, a total area of 28 km2....
.
Ancient Praeneste
Early burials show that the site was already occupied in the 8th8th century BC
The 8th century BC started the first day of 800 BC and ended the last day of 701 BC.-Overview:The 8th century BC was a period of great changes in civilizations. In Egypt, the 23rd and 24th dynasties led to rule from Nubia in the 25th Dynasty...
or 7th century BC. The ancient necropolis
Necropolis
A necropolis is a large cemetery or burial ground, usually including structural tombs. The word comes from the Greek νεκρόπολις - nekropolis, literally meaning "city of the dead"...
lay on a plateau at the foot of the hill below the ancient town. Of the objects found in the oldest graves, and supposed to date from about the 7th century BC, the cups of silver and silver-gilt and most of the gold and amber
Amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin , which has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Amber is used as an ingredient in perfumes, as a healing agent in folk medicine, and as jewelry. There are five classes of amber, defined on the basis of their chemical constituents...
jewelry are Phoenicia
Phoenicia
Phoenicia , was an ancient civilization in Canaan which covered most of the western, coastal part of the Fertile Crescent. Several major Phoenician cities were built on the coastline of the Mediterranean. It was an enterprising maritime trading culture that spread across the Mediterranean from 1550...
n (possibly Carthaginian
Carthage
Carthage , implying it was a 'new Tyre') is a major urban centre that has existed for nearly 3,000 years on the Gulf of Tunis, developing from a Phoenician colony of the 1st millennium BC...
), but the bronze
Bronze
Bronze is a metal alloy consisting primarily of copper, usually with tin as the main additive. It is hard and brittle, and it was particularly significant in antiquity, so much so that the Bronze Age was named after the metal...
s and some of the ivory
Ivory
Ivory is a term for dentine, which constitutes the bulk of the teeth and tusks of animals, when used as a material for art or manufacturing. Ivory has been important since ancient times for making a range of items, from ivory carvings to false teeth, fans, dominoes, joint tubes, piano keys and...
articles seem to be of the Etruscan civilization
Etruscan civilization
Etruscan civilization is the modern English name given to a civilization of ancient Italy in the area corresponding roughly to Tuscany. The ancient Romans called its creators the Tusci or Etrusci...
.
Praenestine graves from about 240 BC onwards have been found: they are surmounted by the characteristic pine-apple of local stone, containing stone coffins with rich bronze, ivory and gold ornaments beside the skeleton. From these come the famous bronze boxes (cistae) and hand mirrors with inscriptions partly in Etruscan
Etruscan language
The Etruscan language was spoken and written by the Etruscan civilization, in what is present-day Italy, in the ancient region of Etruria and in parts of Lombardy, Veneto, and Emilia-Romagna...
. Also famous is the bronze Ficoroni casket (Museo Nazionale Etrusco di Villa Giulia, Rome
National Etruscan Museum
The National Etruscan Museum is a museum of the Etruscan civilization housed in the Villa Giulia in Rome, Italy.-History:The villa was built by the popes and remained their property until 1870 when, in the wake of the Risorgimento and the demise of the Papal States, it became the property of the...
), engraved with pictures of the arrival of the Argonauts
Argonauts
The Argonauts ) were a band of heroes in Greek mythology who, in the years before the Trojan War, accompanied Jason to Colchis in his quest to find the Golden Fleece. Their name comes from their ship, the Argo, which was named after its builder, Argus. "Argonauts", therefore, literally means...
in Bithynia
Bithynia
Bithynia was an ancient region, kingdom and Roman province in the northwest of Asia Minor, adjoining the Propontis, the Thracian Bosporus and the Euxine .-Description:...
and the victory of Pollux over Amycus
Amycus
In Greek mythology, Amycus was the son of Poseidon and Melia. He was a boxer and King of the Bebryces, a mythical people in Bithynia. Polydeuces beat him in a boxing match when the Argonauts passed through Bithynia. He was also a prominent Trojan during the Trojan War. He married Theona and had...
, found in 1738. An example of archaic Latin is the inscription on the Cista Ficoroni: "Novios Plautios Romai med fecid / Dindia Macolnia fileai dedit" ("Novios Plautios made me in Rome, Dindia Macolnia gave me to her daughter"). The caskets are unique in Italy
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
, but a large number of mirrors of precisely similar style have been discovered in Etruria
Etruria
Etruria—usually referred to in Greek and Latin source texts as Tyrrhenia—was a region of Central Italy, an area that covered part of what now are Tuscany, Latium, Emilia-Romagna, and Umbria. A particularly noteworthy work dealing with Etruscan locations is D. H...
. Hence, although it would be reasonable to conjecture that objects with Etruscan
Etruscan civilization
Etruscan civilization is the modern English name given to a civilization of ancient Italy in the area corresponding roughly to Tuscany. The ancient Romans called its creators the Tusci or Etrusci...
characteristics came from Etruria, the evidence points decisively to an Etruscan factory in or near Praeneste itself. Other imported objects in the burials show that Praeneste traded not only with Etruria
Etruria
Etruria—usually referred to in Greek and Latin source texts as Tyrrhenia—was a region of Central Italy, an area that covered part of what now are Tuscany, Latium, Emilia-Romagna, and Umbria. A particularly noteworthy work dealing with Etruscan locations is D. H...
but also with the Greek east.
The origin of Praeneste was attributed by the ancients to Ulysses
Odysseus
Odysseus or Ulysses was a legendary Greek king of Ithaca and the hero of Homer's epic poem the Odyssey. Odysseus also plays a key role in Homer's Iliad and other works in the Epic Cycle....
, or to other fabulous characters variously called Caeculus
Caeculus
In Roman mythology, Caeculus ) was a son of Vulcan, and the legendary founder of Praeneste ....
, Telegonus
Telegonus
Telegonus is the name of three different characters in Greek mythology.-Son of Odysseus:In Greek mythology, Telegonus was the youngest son of Circe and Odysseus....
, Erulus or Praenestus. the name derives probably from the word Praenesteus, referring to its overlooking location.
Praeneste was probably under the hegemony of Alba Longa
Alba Longa
Alba Longa – in Italian sources occasionally written Albalonga – was an ancient city of Latium in central Italy southeast of Rome in the Alban Hills. Founder and head of the Latin League, it was destroyed by Rome around the middle of the 7th century BC. In legend, Romulus and Remus, founders of...
while that city was the head of the Latin League
Latin league
The Latin League was a confederation of about 30 villages and tribes in the region of Latium near ancient Rome, organized for mutual defense...
. It withdrew from the league in 499 BC, according to Livy
Livy
Titus Livius — known as Livy in English — was a Roman historian who wrote a monumental history of Rome and the Roman people. Ab Urbe Condita Libri, "Chapters from the Foundation of the City," covering the period from the earliest legends of Rome well before the traditional foundation in 753 BC...
(its earliest historical mention), and formed an alliance with Rome
Rome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
. After Rome was weakened by the Gauls
Gauls
The Gauls were a Celtic people living in Gaul, the region roughly corresponding to what is now France, Belgium, Switzerland and Northern Italy, from the Iron Age through the Roman period. They mostly spoke the Continental Celtic language called Gaulish....
of Brennus (390 BC), Praeneste switched allegiances and fought against Rome in the long struggles that culminated in the Latin War
Latin War
The Latin War was a conflict between the Roman Republic and its neighbors the Latin peoples of ancient Italy. It ended in the dissolution of the Latin League, and incorporation of its territory into the Roman sphere of influence, with the Latins gaining partial rights and varying levels of...
. From 373 to 370, it was in continual war against Rome or her allies, and was defeated by Cincinnatus
Cincinnatus
Lucius Quinctius Cincinnatus was an aristocrat and political figure of the Roman Republic, serving as consul in 460 BC and Roman dictator in 458 BC and 439 BC....
.
Eventually in 354 and in 338 the Romans were victorious and Praeneste was punished by the loss of portions of its territory, becoming a city allied to Rome. As such, it furnished contingents to the Roman army, and Roman exiles were permitted to live at Praeneste, which grew prosperous. The roses of Praeneste were a byword for profusion and beauty. Præneste was situated on the Via Labicana
Via Labicana
The Via Labicana was an ancient road of Italy, leading east southeast from Rome. It seems possible that the road at first led to Tusculum, that it was then extended to Labici, and later still became a road for through traffic; it may even have superseded the Via Latina as a route to the southeast,...
.
Its citizens were offered Roman citizenship
Citizenship
Citizenship is the state of being a citizen of a particular social, political, national, or human resource community. Citizenship status, under social contract theory, carries with it both rights and responsibilities...
in 90 BC in the Social War, when concessions had to be made by Rome to cement necessary alliances. In Sulla's second civil war
Sulla's second civil war
Sulla's second civil war was one of a series of civil wars of ancient Rome. It was fought between Lucius Cornelius Sulla and Gaius Marius the younger in 82 BC.-Prelude:...
, Gaius Marius the Younger
Gaius Marius the Younger
Gaius Marius Minor, also known in English as Marius the Younger or informally "the younger Marius" , was the adopted son of Gaius Marius, who was seven times consul, and a famous military commander. Appian first describes him as the son of the great Marius, but in a subsequent passage, he is...
was blockaded in the town by the forces of Sulla (82 BC). When the city was captured, Marius slew himself, the male inhabitants were massacred in cold blood, and a military colony was settled on part of its territory. From an inscription it appears that Sulla delegated the foundation of the new colony to Marcus Terentius Varro Lucullus
Marcus Terentius Varro Lucullus
Marcus Terentius Varro Lucullus , younger brother of the more famous Lucius Licinius Lucullus, was a supporter of Lucius Cornelius Sulla and consul of ancient Rome in 73 BC. As proconsul of Macedonia in 72 BC, he defeated the Bessi in Thrace and advanced to the Danube and the west coast of the...
, who was consul
Consul
Consul was the highest elected office of the Roman Republic and an appointive office under the Empire. The title was also used in other city states and also revived in modern states, notably in the First French Republic...
in 73 BC. Within a decade the lands of the colonia had been assembled by a few large landowners.
It was probably after the disaster of 82 BC that the city was removed from the hillside to the lower ground at the Madonna dell'Aquila, and that the sanctuary and temple of Fortune was enlarged so as to include much of the space occupied by the ancient city.
Under the Empire the cool breezes of Praeneste made it a favorite summer resort of wealthy Romans, whose villas
Roman villa
A Roman villa is a villa that was built or lived in during the Roman republic and the Roman Empire. A villa was originally a Roman country house built for the upper class...
studded the neighborhood, though they ridiculed the language and the rough manners of the native inhabitants. The poet Horace
Horace
Quintus Horatius Flaccus , known in the English-speaking world as Horace, was the leading Roman lyric poet during the time of Augustus.-Life:...
ranked "cool Praeneste" with Tibur
Tivoli, Italy
Tivoli , the classical Tibur, is an ancient Italian town in Lazio, about 30 km east-north-east of Rome, at the falls of the Aniene river where it issues from the Sabine hills...
and Baiae
Baiae
Baiae , a frazione of the comune of Bacoli) in the Campania region of Italy was a Roman seaside resort on the Bay of Naples. It was said to have been named after Baius, who was supposedly buried there. Baiae was for several hundred years a fashionable resort, especially towards the end of the Roman...
as favored resorts. The emperor Augustus
Augustus
Augustus ;23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14) is considered the first emperor of the Roman Empire, which he ruled alone from 27 BC until his death in 14 AD.The dates of his rule are contemporary dates; Augustus lived under two calendars, the Roman Republican until 45 BC, and the Julian...
stayed in Praeneste, and Tiberius
Tiberius
Tiberius , was Roman Emperor from 14 AD to 37 AD. Tiberius was by birth a Claudian, son of Tiberius Claudius Nero and Livia Drusilla. His mother divorced Nero and married Augustus in 39 BC, making him a step-son of Octavian...
recovered there from a dangerous illness and made it a municipium
Municipium
Municipium , the prototype of English municipality, was the Latin term for a town or city. Etymologically the municipium was a social contract between municipes, the "duty holders," or citizens of the town. The duties, or munera, were a communal obligation assumed by the municipes in exchange for...
. The ruins of the villa associated with Hadrian
Hadrian
Hadrian , was Roman Emperor from 117 to 138. He is best known for building Hadrian's Wall, which marked the northern limit of Roman Britain. In Rome, he re-built the Pantheon and constructed the Temple of Venus and Roma. In addition to being emperor, Hadrian was a humanist and was philhellene in...
stand in the plain near the church of S. Maria della Villa, about three-quarters of a mile from the town. At the site was discovered the Braschi Antinous
Antinous
Antinoüs or Antinoös was a beautiful Bithynian youth and the favourite of the Roman emperor Hadrian...
, now in the Vatican Museums
Vatican Museums
The Vatican Museums , in Viale Vaticano in Rome, inside the Vatican City, are among the greatest museums in the world, since they display works from the immense collection built up by the Roman Catholic Church throughout the centuries, including some of the most renowned classical sculptures and...
. Marcus Aurelius, Pliny the Younger
Pliny the Younger
Gaius Plinius Caecilius Secundus, born Gaius Caecilius or Gaius Caecilius Cilo , better known as Pliny the Younger, was a lawyer, author, and magistrate of Ancient Rome. Pliny's uncle, Pliny the Elder, helped raise and educate him...
and Symmachus
Symmachus
Symmachus can refer to several different people of Roman antiquity:*Symmachus the Ebionite , was the author of one of the Greek versions of the Old Testament;*Pope Symmachus, pope from 498 to 514....
also had villas there. Inscriptions show that the inhabitants of Praeneste were fond of gladiatorial shows.

Sanctuary of Fortuna Primigenia
Praeneste was chiefly famed for its great Temple of Fortuna PrimigeniaFortuna (mythology)
Fortuna was the goddess of fortune and personification of luck in Roman religion. She might bring good luck or bad: she could be represented as veiled and blind, as in modern depictions of Justice, and came to represent life's capriciousness...
connected with the oracle
Oracle
In Classical Antiquity, an oracle was a person or agency considered to be a source of wise counsel or prophetic predictions or precognition of the future, inspired by the gods. As such it is a form of divination....
known as the Praenestine lots (sortes praenestinae). The temple was redeveloped after 82 BC as a spectacular series of terraces, exedra
Exedra
In architecture, an exedra is a semicircular recess or plinth, often crowned by a semi-dome, which is sometimes set into a building's facade. The original Greek sense was applied to a room that opened onto a stoa, ringed with curved high-backed stone benches, a suitable place for a philosophical...
s and portico
Portico
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls...
s on four levels down the hillside, linked by monumental stairs and ramps. The inspiration for this feat of unified urbanistic design lay, not in republican Rome, but in the Hellenistic monarchies of the eastern Mediterranean. Praeneste offered a foretaste of the grandiose Imperial style of the following generation.
The oldest portion of the primitive sanctuary was situated on the terrace just above the lowest one, in a grotto
Grotto
A grotto is any type of natural or artificial cave that is associated with modern, historic or prehistoric use by humans. When it is not an artificial garden feature, a grotto is often a small cave near water and often flooded or liable to flood at high tide...
in the natural rock where there was a spring that developed into a well. As the archaic shrine was elaborated from the 2nd century BC, it was given a colored mosaic
Mosaic
Mosaic is the art of creating images with an assemblage of small pieces of colored glass, stone, or other materials. It may be a technique of decorative art, an aspect of interior decoration, or of cultural and spiritual significance as in a cathedral...
pavement representing a seascape: a temple of Poseidon
Poseidon
Poseidon was the god of the sea, and, as "Earth-Shaker," of the earthquakes in Greek mythology. The name of the sea-god Nethuns in Etruscan was adopted in Latin for Neptune in Roman mythology: both were sea gods analogous to Poseidon...
on the shore, with fish of all kinds swimming in the sea. To the east of this grotto is a large space, now open, but once very possibly roofed, and forming a two-story basilica
Basilica
The Latin word basilica , was originally used to describe a Roman public building, usually located in the forum of a Roman town. Public basilicas began to appear in Hellenistic cities in the 2nd century BC.The term was also applied to buildings used for religious purposes...
built against the rock on the north side, and there decorated with pilasters. To the east is an apsidal hall, often identified with the temple itself, in which was found the famous mosaic
Nile mosaic of Palestrina
thumb|300 px|The Nile Mosaic of Palestrina.The Nile mosaic of Palestrina is a late Hellenistic floor mosaic depicting the Nile in its passage from Ethiopia to the Mediterranean...
with scenes from the Nile
Nile
The Nile is a major north-flowing river in North Africa, generally regarded as the longest river in the world. It is long. It runs through the ten countries of Sudan, South Sudan, Burundi, Rwanda, Democratic Republic of the Congo, Tanzania, Kenya, Ethiopia, Uganda and Egypt.The Nile has two major...
, relaid in the Palazzo Barberini-Colonna in Palestrina on the uppermost terrace (now a National Museum). Under this hall is a chamber, which an inscription on its walls identified as a treasury in the 2nd century BC. In front of this temple an obelisk
Obelisk
An obelisk is a tall, four-sided, narrow tapering monument which ends in a pyramid-like shape at the top, and is said to resemble a petrified ray of the sun-disk. A pair of obelisks usually stood in front of a pylon...
was erected in the reign of Claudius
Claudius
Claudius , was Roman Emperor from 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, he was the son of Drusus and Antonia Minor. He was born at Lugdunum in Gaul and was the first Roman Emperor to be born outside Italy...
, fragments of which still exist.

The goddess Fortuna here went by the name of Primigenia ("First Bearer"), she was represented suckling two babes, as in the Christian
Christian
A Christian is a person who adheres to Christianity, an Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as recorded in the Canonical gospels and the letters of the New Testament...
representation of Charity
Charity (virtue)
In Christian theology charity, or love , means an unlimited loving-kindness toward all others.The term should not be confused with the more restricted modern use of the word charity to mean benevolent giving.- Caritas: altruistic love :...
, said to be Jupiter and Juno
Juno (mythology)
Juno is an ancient Roman goddess, the protector and special counselor of the state. She is a daughter of Saturn and sister of the chief god Jupiter and the mother of Mars and Vulcan. Juno also looked after the women of Rome. Her Greek equivalent is Hera...
, and she was especially worshipped by matrons. The oracle continued to be consulted down to Christian times, until Constantine the Great, and again later Theodosius I
Theodosius I
Theodosius I , also known as Theodosius the Great, was Roman Emperor from 379 to 395. Theodosius was the last emperor to rule over both the eastern and the western halves of the Roman Empire. During his reign, the Goths secured control of Illyricum after the Gothic War, establishing their homeland...
, forbade the practice and closed the temple.
Features of the temple influenced Roman garden design on steeply sloped sites through Antiquity and once again in Italian villa gardens from the 15th century. The monument to Victor Emmanuel II
Victor Emmanuel II of Italy
Victor Emanuel II was king of Sardinia from 1849 and, on 17 March 1861, he assumed the title King of Italy to become the first king of a united Italy since the 6th century, a title he held until his death in 1878...
in Rome owes a lot to the Praeneste sanctuary complex.
Later history
The modern town is built on the ruins of the famous temple of Fortuna Primigenia. A bishop of Praeneste is first mentioned in 313.In 1297 the Sciarrillo di Colonna family, who had owned Praeneste (by then called Palestrina) from the eleventh century as a fief, revolted from the pope
Pope
The Pope is the Bishop of Rome, a position that makes him the leader of the worldwide Catholic Church . In the Catholic Church, the Pope is regarded as the successor of Saint Peter, the Apostle...
. In the following year the town was taken by Papal forces, razed to the ground and salted
Salting the earth
Salting the earth, or sowing with salt, is the ritual of spreading salt on conquered cities to symbolize a curse on its re-inhabitation. It originated as a practice in the ancient Near East and became a well-established folkloric motif in the Middle Ages.-Destroying cities:The custom of purifying...
by order of Pope Boniface VIII
Pope Boniface VIII
Pope Boniface VIII , born Benedetto Gaetani, was Pope of the Catholic Church from 1294 to 1303. Today, Boniface VIII is probably best remembered for his feuds with Dante, who placed him in the Eighth circle of Hell in his Divina Commedia, among the Simonists.- Biography :Gaetani was born in 1235 in...
. In 1437 the rebuilt city was captured by the Papal general Giovanni Vitelleschi
Giovanni Vitelleschi
Giovanni Maria Vitelleschi was an Italian cardinal and condottiere.-Biography:Vitelleschi was born in Corneto , some kilometers north to Rome. He received a military education, which he refined as apostolic protonotary under Pope Martin V...
and once more utterly destroyed at the command of Pope Eugenius IV.
It was rebuilt once more and fortified by Stefano Colonna
Colonna family
The Colonna family is an Italian noble family; it was powerful in medieval and Renaissance Rome, supplying one Pope and many other Church and political leaders...
in 1448. It was again sacked in 1527, and occupied by the Duke of Alba, in 1556.
Barberini Family
In 1630 it passed by purchase into the Barberini familyBarberini
The Barberini are a family of the Italian nobility that rose to prominence in 17th century Rome. Their influence peaked with the election of Cardinal Maffeo Barberini to the papal throne in 1623, as Pope Urban VIII...
. It is likely the transfer was included as one of the conditions of the marriage of Taddeo Barberini
Taddeo Barberini
Taddeo Barberini was an Italian nobleman of the House of Barberini who became Prince of Palestrina and Gonfalonier of the Church; commander of the Papal Army. He was a nephew of Pope Urban VIII and brother of Cardinals Francesco Barberini and Antonio Barberini...
and Anna Colonna
Anna Colonna
Anna Colonna was an Italian noblewoman of the Colonna and Barberini families and Princess of Paliano-Biography:Colonna was born in 1601; the daughter of Filippo Colonna, Prince of Paliano and Lucrezia Tomacelli, dei signori di Galatro, and was thus Princess of Paliano.On 14 October 1627, at age...
. Thereafter, the famously nepotistic
Nepotism
Nepotism is favoritism granted to relatives regardless of merit. The word nepotism is from the Latin word nepos, nepotis , from which modern Romanian nepot and Italian nipote, "nephew" or "grandchild" are also descended....
family, headed by Maffeo Barberini (later Pope Urban VIII
Pope Urban VIII
Pope Urban VIII , born Maffeo Barberini, was pope from 1623 to 1644. He was the last pope to expand the papal territory by force of arms, and was a prominent patron of the arts and reformer of Church missions...
), treated the comune as a principality
Principality
A principality is a monarchical feudatory or sovereign state, ruled or reigned over by a monarch with the title of prince or princess, or by a monarch with another title within the generic use of the term prince....
in its own right. Patriarchs of the Barberini family conferred, on various family members, the title of Prince of Palestrina. During the reign of Urban VIII, the title became interchangeable with that of Commander of the Papal Army (Gonfalonier of the Church
Gonfalonier of the Church
The Gonfalonier of the Church or Papal Gonfalonier was a military and political office of the Papal States. Originating from the use of the Papal banner during combat, the office later became largely ceremonial and political...
) as the Barberini family controlled the papacy and the Palestrina principality.
The Wars of Castro
Wars of Castro
The Wars of Castro is a term referring to a series of events in the mid-17th century revolving around the ancient city of Castro , which eventually resulted in the city's destruction on 2 September 1649...
ended (while Taddeo Barberini
Taddeo Barberini
Taddeo Barberini was an Italian nobleman of the House of Barberini who became Prince of Palestrina and Gonfalonier of the Church; commander of the Papal Army. He was a nephew of Pope Urban VIII and brother of Cardinals Francesco Barberini and Antonio Barberini...
held both titles) and members of the Barberini family (including Taddeo) fled into exile after the newly elected Pope Innocent X
Pope Innocent X
Pope Innocent X , born Giovanni Battista Pamphilj , was Pope from 1644 to 1655. Born in Rome of a family from Gubbio in Umbria who had come to Rome during the pontificate of Pope Innocent IX, he graduated from the Collegio Romano and followed a conventional cursus honorum, following his uncle...
launched an investigation into members of the Barberini family. Later the Barberini reconciled with the papacy when Pope Innocent X elevated Taddeo's son, Carlo Barberini
Carlo Barberini
thumb|Cardinal Carlo Barberini .Carlo Barberini was an Italian Catholic cardinal and member of the Barberini family. He was the grand-nephew of Maffeo Barberini and son of Taddeo Barberini .-Biography:Carlo Barberini was born 1 June 1630 in Rome...
to the cardinalate and his brother Maffeo Barberini married a niece of the Pope and reclaimed the title, Prince of Palestrina.
Two members of the Barberini family were named Cardinal-Bishop of the Diocese of Palestrina
Roman Catholic Suburbicarian Diocese of Palestrina
thumb|250 px|The Cathedral of Sant'Agapito in Palestrina.The Roman Catholic Suburbicarian Diocese of Palestrina, , is a Roman Catholic suburbicarian diocese centered on the comune of Palestrina in Italy....
: Antonio Barberini
Antonio Barberini
Antonio Barberini was an Italian Catholic cardinal, Archbishop of Reims, military leader, patron of the arts and a prominent member of the House of Barberini. As one of the cardinal-nephews of Pope Urban VIII and a supporter of France, he played a significant role at a number of the papal...
and Francesco Barberini (Junior)
Francesco Barberini (iuniore)
thumb|Francesco BarberiniFrancesco Barberini was an Italian Cardinal of the family of Pope Urban VIII and of the Princes of Palestrina.-Biography:...
, the son of Maffeo Barberini.
The Barberini Palace originally included the Nile mosaic of Palestrina
Nile mosaic of Palestrina
thumb|300 px|The Nile Mosaic of Palestrina.The Nile mosaic of Palestrina is a late Hellenistic floor mosaic depicting the Nile in its passage from Ethiopia to the Mediterranean...
.
Modern history
The centre of the city was destroyed by Allied bombings during World War IIWorld War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
; this however brought the ancient remains of the sanctuary to light.
Main sights

World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
. The town also contains remnants of ancient cyclopean walls.
On the summit of the hill (753 m), nearly a mile from the town, stood the ancient citadel, the site of which is now occupied by a few poor houses (Castel San Pietro) and a ruined medieval castle of the Colonna family. The view embraces the Monte Soratte, Rome, the Alban Hills
Alban Hills
The Alban Hills are the site of a quiescent volcanic complex in Italy, located southeast of Rome and about north of Anzio.The dominant peak is Monte Cavo. There are two small calderas which contain lakes, Lago Albano and Lake Nemi...
, and the Pontinian Plain as far as the sea. Considerable portions of the southern wall of the ancient citadel, built in massive cyclopean masonry consisting of limestone blocks, are still visible; and the two walls, also polygonal, which formerly united the citadel with the town, can still be traced.

Agapitus of Palestrina
Saint Agapitus is venerated as a Martyr saint. Agapitus may have been a member of the noble Anicia family of Palestrina. At the age of fifteen, he was beheaded on orders of the prefect Antiochus and the emperor Aurelian...
, where it had been used as building material.
The cathedral, just below the level of the temple, occupies the former civil basilica
Basilica
The Latin word basilica , was originally used to describe a Roman public building, usually located in the forum of a Roman town. Public basilicas began to appear in Hellenistic cities in the 2nd century BC.The term was also applied to buildings used for religious purposes...
of the town, whose facade includes a sundial
Sundial
A sundial is a device that measures time by the position of the Sun. In common designs such as the horizontal sundial, the sun casts a shadow from its style onto a surface marked with lines indicating the hours of the day. The style is the time-telling edge of the gnomon, often a thin rod or a...
described by Varro
Marcus Terentius Varro
Marcus Terentius Varro was an ancient Roman scholar and writer. He is sometimes called Varro Reatinus to distinguish him from his younger contemporary Varro Atacinus.-Biography:...
, traces of which may still be seen. In the modern piazza
Piazza
A piazza is a city square in Italy, Malta, along the Dalmatian coast and in surrounding regions. The term is roughly equivalent to the Spanish plaza...
the steps leading up to this basilica and the base of a large monument were found in 1907; evidently only part of the piazza represents the ancient forum. The cathedral has fine paintings and frescoes. In the Church of Santa Rosalia (1677) there is a noteworthy Pietà, carved in the solid rock.
The National Archeological Museum of Palestrina is housed inside the Renaissance Barberini Palace, the former baronial palace, built above the ancient temple of Fortuna. It exhibits the most important works from the ancient town of Praeneste. The famous sculpture of the Capitoline Triad
Capitoline Triad
In ancient Roman religion, the Capitoline Triad was a group of three supreme deities who were worshipped in an elaborate temple on Rome's Capitoline Hill, the Capitolium. Two distinct Capitoline Triads were worshipped at various times in Rome's history, both originating in ancient traditions...
is exhibited on the first floor. The second floor is dedicated to the necropoli and sanctuaries, while the third floor contains a large polychrome mosaic depicting the flooding of the Nile (Nile mosaic of Palestrina
Nile mosaic of Palestrina
thumb|300 px|The Nile Mosaic of Palestrina.The Nile mosaic of Palestrina is a late Hellenistic floor mosaic depicting the Nile in its passage from Ethiopia to the Mediterranean...
).
Culture
Praeneste was the native town of the 3rd century Roman writer AelianClaudius Aelianus
Claudius Aelianus , often seen as just Aelian, born at Praeneste, was a Roman author and teacher of rhetoric who flourished under Septimius Severus and probably outlived Elagabalus, who died in 222...
, and of the great 16th century composer Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina
Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina
Giovanni Pierluigi da Palestrina was an Italian Renaissance composer of sacred music and the best-known 16th-century representative of the Roman School of musical composition...
. Thomas Mann
Thomas Mann
Thomas Mann was a German novelist, short story writer, social critic, philanthropist, essayist, and 1929 Nobel Prize laureate, known for his series of highly symbolic and ironic epic novels and novellas, noted for their insight into the psychology of the artist and the intellectual...
spent some time there in 1895 and, two years later, during the long harsh summer of 1897, he stayed over again, with his brother Heinrich Mann
Heinrich Mann
Luiz Heinrich Mann was a German novelist who wrote works with strong social themes. His attacks on the authoritarian and increasingly militaristic nature of pre-World War II German society led to his exile in 1933.-Life and work:Born in Lübeck as the oldest child of Thomas Johann Heinrich Mann...
, in a sojourn that provided the backdrop, nearly half a century later, for Adrian Leverkühn's pact with the Devil in Mann's novel Doktor Faustus
See also
- Roman Catholic Suburbicarian Diocese of PalestrinaRoman Catholic Suburbicarian Diocese of Palestrinathumb|250 px|The Cathedral of Sant'Agapito in Palestrina.The Roman Catholic Suburbicarian Diocese of Palestrina, , is a Roman Catholic suburbicarian diocese centered on the comune of Palestrina in Italy....
- Praeneste fibulaPraeneste fibulaThe Praeneste fibula is a golden brooch bearing an inscription that was accepted nearly without question since its presentation to the public in 1887 by Wolfgang Helbig, an archaeologist, as the earliest surviving specimen of the Latin language. The origin of the fibula was not stated in the...
- Colonna
- BarberiniBarberiniThe Barberini are a family of the Italian nobility that rose to prominence in 17th century Rome. Their influence peaked with the election of Cardinal Maffeo Barberini to the papal throne in 1623, as Pope Urban VIII...

