Outline of Latvia
Encyclopedia
Baltic region
The terms Baltic region, Baltic Rim countries, and Baltic Rim refer to slightly different combinations of countries in the general area surrounding the Baltic Sea.- Etymology :...
of Northern Europe
Northern Europe
Northern Europe is the northern part or region of Europe. Northern Europe typically refers to the seven countries in the northern part of the European subcontinent which includes Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Finland and Sweden...
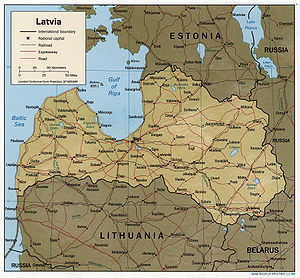
. Latvia is bordered to the north by Estonia
Estonia
Estonia , officially the Republic of Estonia , is a state in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by the Gulf of Finland, to the west by the Baltic Sea, to the south by Latvia , and to the east by Lake Peipsi and the Russian Federation . Across the Baltic Sea lies...
(343 km), to the south by Lithuania
Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
(588 km), and to the east both by Belarus
Belarus
Belarus , officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered clockwise by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno , Gomel ,...
(141 km) and the Russian Federation
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
(276 km). Across the Baltic Sea
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
to the west lies Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
. The territory of Latvia covers 64,589 km² and is influenced by a temperate seasonal climate.
The Latvians
Latvians
Latvians or Letts are the indigenous Baltic people of Latvia.-History:Latvians occasionally refer to themselves by the ancient name of Latvji, which may have originated from the word Latve which is a name of the river that presumably flowed through what is now eastern Latvia...
are a Baltic people closely related to the Lithuanians
Lithuanians
Lithuanians are the Baltic ethnic group native to Lithuania, where they number around 2,765,600 people. Another million or more make up the Lithuanian diaspora, largely found in countries such as the United States, Brazil, Canada, Colombia, Russia, United Kingdom and Ireland. Their native language...
, with the Latvian language
Latvian language
Latvian is the official state language of Latvia. It is also sometimes referred to as Lettish. There are about 1.4 million native Latvian speakers in Latvia and about 150,000 abroad. The Latvian language has a relatively large number of non-native speakers, atypical for a small language...
sharing many similarities to Lithuanian
Lithuanian language
Lithuanian is the official state language of Lithuania and is recognized as one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 2.96 million native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 170,000 abroad. Lithuanian is a Baltic language, closely related to Latvian, although they...
. Today the Latvians and Lithuanians are the only surviving members of the Baltic peoples and Baltic languages
Baltic languages
The Baltic languages are a group of related languages belonging to the Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European language family and spoken mainly in areas extending east and southeast of the Baltic Sea in Northern Europe...
of the Indo-European
Indo-European
Indo-European may refer to:* Indo-European languages** Aryan race, a 19th century and early 20th century term for those peoples who are the native speakers of Indo-European languages...
family. The modern name of Latvia is thought to originate from the ancient Latvian
Latvian
Latvian may refer to:* Something of, from, or related to Latvia, a country in Northern Europe in the Baltic region.* A member of the Latvian people . For more information, see Demographics of Latvia and Culture of Latvia. For specific persons, see List of Latvians.* The Latvian language...
name Latvji
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
, which may have originated from the word Latve which is a name of the river that presumably flowed through what is now eastern Latvia.
Latvia is a democratic parliamentary republic
Parliamentary republic
A parliamentary republic or parliamentary constitutional republic is a type of republic which operates under a parliamentary system of government - meaning a system with no clear-cut separation of powers between the executive and legislative branches. There are a number of variations of...
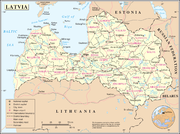
and is divided into 26 districts
Districts of Latvia
||Before July 1, 2009 Latvia was divided into 26 districts and 7 cities , indicated with asterisks:...
. The capital and largest city is Riga
Riga
Riga is the capital and largest city of Latvia. With 702,891 inhabitants Riga is the largest city of the Baltic states, one of the largest cities in Northern Europe and home to more than one third of Latvia's population. The city is an important seaport and a major industrial, commercial,...
. Latvia has been a member of the United Nations
United Nations
The United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
since 17 September 1991, of the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
since 1 May 2004 and of NATO since 29 March 2004.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to Latvia:
General reference
- Pronunciation: ˈlætviə
- Common English country name: LatviaLatviaLatvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
- Official English country name: The Republic of Latvia
- Common endonym(s): Latvija
- Official endonym(s): Latvija
- Adjectival(s): LatvianLatvianLatvian may refer to:* Something of, from, or related to Latvia, a country in Northern Europe in the Baltic region.* A member of the Latvian people . For more information, see Demographics of Latvia and Culture of Latvia. For specific persons, see List of Latvians.* The Latvian language...
- Demonym(s): Latvian
- EtymologyEtymologyEtymology is the study of the history of words, their origins, and how their form and meaning have changed over time.For languages with a long written history, etymologists make use of texts in these languages and texts about the languages to gather knowledge about how words were used during...
: Name of Latvia - International rankings of LatviaInternational rankings of Latvia-International rankings:...
- ISO country codes: LV, LVA, 428
- ISO region codes: See ISO 3166-2:LVISO 3166-2:LVISO 3166-2:LV is the entry for Latvia in ISO 3166-2, part of the ISO 3166 standard published by the International Organization for Standardization , which defines codes for the names of the principal subdivisions of all countries coded in ISO 3166-1.Currently for Latvia, ISO 3166-2 codes are...
- InternetInternetThe Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
country code top-level domainCountry code top-level domainA country code top-level domain is an Internet top-level domain generally used or reserved for a country, a sovereign state, or a dependent territory....
: .lv.lv.lv is the Internet country code top-level domain for Latvia.Registration is permitted at the second level, and this is the form of registration currently encouraged by the registry; however, registrations are also accepted at the third level beneath a number of subdomains:* .com.lv - commercial...
Geography of Latvia
- Latvia is: a country
- Location:
- Northern HemisphereNorthern HemisphereThe Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
and Eastern HemisphereEastern HemisphereThe Eastern Hemisphere, also Eastern hemisphere or eastern hemisphere, is a geographical term for the half of the Earth that is east of the Prime Meridian and west of 180° longitude. It is also used to refer to Europe, Asia, Africa, and Australasia, vis-à-vis the Western Hemisphere, which includes... - EurasiaEurasiaEurasia is a continent or supercontinent comprising the traditional continents of Europe and Asia ; covering about 52,990,000 km2 or about 10.6% of the Earth's surface located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres...
- EuropeEuropeEurope is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
- Northern EuropeNorthern EuropeNorthern Europe is the northern part or region of Europe. Northern Europe typically refers to the seven countries in the northern part of the European subcontinent which includes Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Finland and Sweden...
- Eastern EuropeEastern EuropeEastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
- Northern Europe
- Europe
- Time zoneTime zoneA time zone is a region on Earth that has a uniform standard time for legal, commercial, and social purposes. In order for the same clock time to always correspond to the same portion of the day as the Earth rotates , different places on the Earth need to have different clock times...
: Eastern European TimeEastern European TimeEastern European Time is one of the names of UTC+02:00 time zone, 2 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. It is used in some European countries that also use Eastern European Summer Time as a summer daylight saving time.- Usage :...
(UTC+02), Eastern European Summer TimeEastern European Summer TimeEastern European Summer Time is one of the names of UTC+3 time zone, 3 hours ahead of Coordinated Universal Time. It is used as a summer daylight saving time in some European, North African, and Middle Eastern countries...
(UTC+03) - Extreme points of LatviaExtreme points of LatviaThis is a list of the extreme points of Latvia: the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.- See also :* Extreme points of Europe* Extreme points of Earth* Geography of Latvia...
- High: GaizinkalnsGaizinkalnsGaiziņkalns, at 312 m above sea level, constitutes the highest point in Latvia. It is situated a short distance to the west of the town of Madona, central Vidzeme....
312 m (1,024 ft) - Low: Baltic SeaBaltic SeaThe Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
0 m
- High: Gaizinkalns
- Land boundaries: 1,382 km
- Northern Hemisphere
-
 Lithuania 576 km
Lithuania 576 km Estonia 343 km
Estonia 343 km Russia 292 km
Russia 292 km Belarus 171 km
Belarus 171 km
- Coastline: Baltic SeaBaltic SeaThe Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
498 km - Population of Latvia: 2,268,000 (May 1, 2008) - 140th most populous country
- Area of Latvia: 64,589 km2
- Atlas of Latvia
- Coastline: Baltic Sea
Environment of Latvia

- Climate of Latvia
- Environmental issues in Latvia
- Ecoregions in Latvia
- Renewable energy in Latvia
- Geology of Latvia
- Protected areas of Latvia
- Biosphere reserves in Latvia
- National parks of Latvia
- Wildlife of Latvia
- Flora of Latvia
- Fauna of Latvia
- Birds of Latvia
- Mammals of Latvia
Natural geographic features of Latvia
- Rivers of Latvia
- World Heritage Sites in Latvia
Administrative divisions of Latvia
- Regions of LatviaRegions of LatviaCultural regions of Latvia are several areas within Latvia formally recognised as distinct from the rest of the country. While some of these regions are seen purely as culturally distinct, others have historically been parts of different countries and have been used to divide the country for...
- Districts of LatviaDistricts of Latvia||Before July 1, 2009 Latvia was divided into 26 districts and 7 cities , indicated with asterisks:...
- Subdivisions of LatviaSubdivisions of LatviaThe districts of Latvia are divided into 77 cities , 10 amalgamated municipalities , 24 rural territories and 475 parishes .For the new administrative divisions from 1 July 2009, see Administrative divisions of Latvia.- Aizkraukle District :* Aiviekste Parish...
- Subdivisions of Latvia
- Districts of Latvia
Regions of Latvia
(current article is actually about the provinces of Latvia. The new Latvian regions were developed in accordance with EU-standardisation)
Municipalities of Latvia
- Capital of Latvia: Riga
- List of cities in Latvia
Government and politics of Latvia
- Main article: Government of LatviaGovernment of LatviaThe Government of Latvia is the central government of the Republic of Latvia. The Constitution of Latvia outlines the nation as a parliamentary republic represented by a unicameral parliament and the Cabinet of Ministers of the Republic of Latvia, which form the executive branch of the Government...
and Politics of LatviaPolitics of LatviaThe politics of Latvia takes place in a framework of a parliamentary representative democratic republic, whereby the Prime Minister is the head of government, and of a multi-party system. The President holds a primarily ceremonial role as Head of State. Executive power is exercised by the government...
- Form of governmentForm of governmentA form of government, or form of state governance, refers to the set of political institutions by which a government of a state is organized. Synonyms include "regime type" and "system of government".-Empirical and conceptual problems:...
: - Capital of Latvia: Riga
- Elections in LatviaElections in LatviaElections in Latvia gives information on election and election results in Latvia.Latvia elects on national level a legislature. The Saeima has 100 members, elected for a four year term by proportional representation with a 5% threshold. An unmodified Sainte-Laguë method is used to allocate seats....
- (specific elections)
- Political parties in Latvia
- Political scandals of Latvia
- Taxation in Latvia
Executive branch of the government of Latvia
- Head of stateHead of StateA head of state is the individual that serves as the chief public representative of a monarchy, republic, federation, commonwealth or other kind of state. His or her role generally includes legitimizing the state and exercising the political powers, functions, and duties granted to the head of...
: President of Latvia, Valdis ZatlersValdis ZatlersValdis Zatlers is a Latvian politician and former physician who served as the seventh president of Latvia from 2007 to 2011. He won the Latvian presidential election of 31 May 2007... - Head of governmentHead of governmentHead of government is the chief officer of the executive branch of a government, often presiding over a cabinet. In a parliamentary system, the head of government is often styled prime minister, chief minister, premier, etc...
: Prime Minister of LatviaPrime Minister of LatviaThe Prime Minister of Latvia is the most powerful member of the Government of the Republic of Latvia, and presides over the Latvian Cabinet of Ministers...
, Valdis DombrovskisValdis DombrovskisValdis Dombrovskis is the Prime Minister of Latvia. He previously served as Latvia's Minister of Finance and as a Member of the European Parliament for the New Era Party.-Education and science career:... - Cabinet of Latvia
Legislative branch of the government of Latvia
- Parliament of Latvia (unicameral)
Judicial branch of the government of Latvia
- Supreme Court of Latvia
Foreign relations of Latvia
- Diplomatic missions in Latvia
- Diplomatic missions of LatviaDiplomatic missions of LatviaThis is a list of diplomatic missions of Latvia, excluding honorary consulates. Latvia has a modest network of embassies and consulates around the world.-Europe:** Vienna ** Baku ** Minsk ** Vitebsk...
International organization membership
The Republic of Latvia is a member of:- Australia GroupAustralia GroupThe Australia Group is an informal group of countries established in 1985 to help member countries to identify those of their exports which need to be controlled so as not to contribute to the spread of chemical and biological weapons .The group, initially consisting of 15 members, held its first...
- Baltic AssemblyBaltic AssemblyThe Baltic Assembly is an international organisation which aims to promote co-operation between the parliaments of the Republics of Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania. It attempts to find a common position in relation to many international issues, including economic, political and cultural issues...
(BA) - Bank for International SettlementsBank for International SettlementsThe Bank for International Settlements is an intergovernmental organization of central banks which "fosters international monetary and financial cooperation and serves as a bank for central banks." It is not accountable to any national government...
(BIS) - Council of EuropeCouncil of EuropeThe Council of Europe is an international organisation promoting co-operation between all countries of Europe in the areas of legal standards, human rights, democratic development, the rule of law and cultural co-operation...
(CE) - Council of the Baltic Sea StatesCouncil of the Baltic Sea StatesThe Council of the Baltic Sea States is an overall political forum for regional intergovernmental cooperation which addresses the five priority areas of the environment, economic development, energy, education and culture, civil security and human dimension, including trafficking in human...
(CBSS) - Euro-Atlantic Partnership CouncilEuro-Atlantic Partnership CouncilThe Euro-Atlantic Partnership Council , a NATO institution, is a multilateral forum created to improve relations between NATO and non-NATO countries in Europe and those parts of Asia on the European periphery. The member states meet to cooperate and consult on a range of political and security issues...
(EAPC) - European Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentEuropean Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentFounded in 1991, the European Bank for Reconstruction and Development uses the tools of investment to help build market economies and democracies in 30 countries from central Europe to central Asia. Its mission was to support the formerly communist countries in the process of establishing their...
(EBRD) - European Investment BankEuropean Investment BankThe European Investment Bank is the European Union's long-term lending institution established in 1958 under the Treaty of Rome. A policy-driven bank, the EIB supports the EU’s priority objectives, especially European integration and the development of economically weak regions...
(EIB) - European UnionEuropean UnionThe European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
(EU) - Food and Agriculture OrganizationFood and Agriculture OrganizationThe Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations is a specialised agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger. Serving both developed and developing countries, FAO acts as a neutral forum where all nations meet as equals to negotiate agreements and...
(FAO) - International Atomic Energy AgencyInternational Atomic Energy AgencyThe International Atomic Energy Agency is an international organization that seeks to promote the peaceful use of nuclear energy, and to inhibit its use for any military purpose, including nuclear weapons. The IAEA was established as an autonomous organization on 29 July 1957...
(IAEA) - International Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentInternational Bank for Reconstruction and DevelopmentThe International Bank for Reconstruction and Development is one of five institutions that compose the World Bank Group. The IBRD is an international organization whose original mission was to finance the reconstruction of nations devastated by World War II. Now, its mission has expanded to fight...
(IBRD) - International Civil Aviation OrganizationInternational Civil Aviation OrganizationThe International Civil Aviation Organization , pronounced , , is a specialized agency of the United Nations. It codifies the principles and techniques of international air navigation and fosters the planning and development of international air transport to ensure safe and orderly growth...
(ICAO) - International Criminal CourtInternational Criminal CourtThe International Criminal Court is a permanent tribunal to prosecute individuals for genocide, crimes against humanity, war crimes, and the crime of aggression .It came into being on 1 July 2002—the date its founding treaty, the Rome Statute of the...
(ICCt) - International Criminal Police Organization (Interpol)
- International Development AssociationInternational Development AssociationThe International Development Association , is the part of the World Bank that helps the world’s poorest countries. It complements the World Bank's other lending arm — the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development — which serves middle-income countries with capital investment and...
(IDA) - International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent SocietiesInternational Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent SocietiesThe International Federation of Red Cross and Red Crescent Societies is a humanitarian institution that is part of the International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement along with the ICRC and 186 distinct National Societies...
(IFRCS) - International Finance CorporationInternational Finance CorporationThe International Finance Corporation promotes sustainable private sector investment in developing countries.IFC is a member of the World Bank Group and is headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States....
(IFC) - International Hydrographic OrganizationInternational Hydrographic OrganizationThe International Hydrographic Organization is the inter-governmental organisation representing the hydrographic community. It enjoys observer status at the UN and is the recognised competent authority on hydrographic surveying and nautical charting...
(IHO) - International Labour OrganizationInternational Labour OrganizationThe International Labour Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that deals with labour issues pertaining to international labour standards. Its headquarters are in Geneva, Switzerland. Its secretariat — the people who are employed by it throughout the world — is known as the...
(ILO) - International Maritime OrganizationInternational Maritime OrganizationThe International Maritime Organization , formerly known as the Inter-Governmental Maritime Consultative Organization , was established in Geneva in 1948, and came into force ten years later, meeting for the first time in 1959...
(IMO) - International Mobile Satellite OrganizationInternational Mobile Satellite OrganizationThe International Mobile Satellite Organization is the intergovernmental organization that oversees certain public satellite safety and security communication services provided via the Inmarsat satellites...
(IMSO) - International Monetary FundInternational Monetary FundThe International Monetary Fund is an organization of 187 countries, working to foster global monetary cooperation, secure financial stability, facilitate international trade, promote high employment and sustainable economic growth, and reduce poverty around the world...
(IMF) - International Olympic CommitteeInternational Olympic CommitteeThe International Olympic Committee is an international corporation based in Lausanne, Switzerland, created by Pierre de Coubertin on 23 June 1894 with Demetrios Vikelas as its first president...
(IOC) - International Organization for MigrationInternational Organization for MigrationThe International Organization for Migration is an intergovernmental organization. It was initially established in 1951 as the Intergovernmental Committee for European Migration to help resettle people displaced by World War II....
(IOM) - International Organization for StandardizationInternational Organization for StandardizationThe International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
(ISO) (correspondent)
- International Red Cross and Red Crescent MovementInternational Red Cross and Red Crescent MovementThe International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is an international humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide which was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, and to prevent and alleviate human...
(ICRM) - International Telecommunication UnionInternational Telecommunication UnionThe International Telecommunication Union is the specialized agency of the United Nations which is responsible for information and communication technologies...
(ITU) - International Trade Union ConfederationInternational Trade Union ConfederationThe International Trade Union Confederation is the world's largest trade union federation. It was formed on November 1, 2006 out of the merger of the International Confederation of Free Trade Unions and the World Confederation of Labour...
(ITUC) - Inter-Parliamentary Union (IPU)
- Multilateral Investment Guarantee AgencyMultilateral Investment Guarantee AgencyThe Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency is a member organization of the World Bank Group that offers political risk insurance. It was established to promote foreign direct investment into developing countries. MIGA was founded in 1988 with a capital base of $1 billion and is headquartered in...
(MIGA) - Nordic Investment BankNordic Investment BankThe Nordic Investment Bank is an international financial institution founded in the mid-1970s by the five Nordic countries: Denmark, Finland, Iceland, Norway and Sweden. In 2005, Estonia, Latvia and Lithuania became members of the Bank. NIB’s headquarters are located in Helsinki, Finland...
(NIB) - North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO)
- Nuclear Suppliers GroupNuclear Suppliers GroupNuclear Suppliers Group is a multinational body concerned with reducing nuclear proliferation by controlling the export and re-transfer of materials that may be applicable to nuclear weapon development and by improving safeguards and protection on existing materials.- History :It was founded in...
(NSG) - Organisation internationale de la Francophonie (OIF) (observer)
- Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE)
- Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW)
- Organization of American StatesOrganization of American StatesThe Organization of American States is a regional international organization, headquartered in Washington, D.C., United States...
(OAS) (observer) - Permanent Court of ArbitrationPermanent Court of ArbitrationThe Permanent Court of Arbitration , is an international organization based in The Hague in the Netherlands.-History:The court was established in 1899 as one of the acts of the first Hague Peace Conference, which makes it the oldest institution for international dispute resolution.The creation of...
(PCA) - Schengen Convention
- United NationsUnited NationsThe United Nations is an international organization whose stated aims are facilitating cooperation in international law, international security, economic development, social progress, human rights, and achievement of world peace...
(UN) - United Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentUnited Nations Conference on Trade and DevelopmentThe United Nations Conference on Trade and Development was established in 1964 as a permanent intergovernmental body. It is the principal organ of the United Nations General Assembly dealing with trade, investment, and development issues....
(UNCTAD) - United Nations Educational, Scientific, and Cultural Organization (UNESCO)
- Universal Postal UnionUniversal Postal UnionThe Universal Postal Union is an international organization that coordinates postal policies among member nations, in addition to the worldwide postal system. The UPU contains four bodies consisting of the Congress, the Council of Administration , the Postal Operations Council and the...
(UPU) - Western European UnionWestern European UnionThe Western European Union was an international organisation tasked with implementing the Modified Treaty of Brussels , an amended version of the original 1948 Treaty of Brussels...
(WEU) (associate partner) - World Customs OrganizationWorld Customs OrganizationThe World Customs Organization is an intergovernmental organization headquartered in Brussels, Belgium. With its worldwide membership, the WCO is recognized as the voice of the global customs community...
(WCO) - World Federation of Trade UnionsWorld Federation of Trade UnionsThe World Federation of Trade Unions was established in 1945 to replace the International Federation of Trade Unions. Its mission was to bring together trade unions across the world in a single international organization, much like the United Nations...
(WFTU) - World Health OrganizationWorld Health OrganizationThe World Health Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations that acts as a coordinating authority on international public health. Established on 7 April 1948, with headquarters in Geneva, Switzerland, the agency inherited the mandate and resources of its predecessor, the Health...
(WHO) - World Intellectual Property OrganizationWorld Intellectual Property OrganizationThe World Intellectual Property Organization is one of the 17 specialized agencies of the United Nations. WIPO was created in 1967 "to encourage creative activity, to promote the protection of intellectual property throughout the world"....
(WIPO) - World Meteorological OrganizationWorld Meteorological OrganizationThe World Meteorological Organization is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 189 Member States and Territories. It originated from the International Meteorological Organization , which was founded in 1873...
(WMO) - World Tourism OrganizationWorld Tourism OrganizationThe World Tourism Organization , based in Madrid, Spain, is a United Nations agency dealing with questions relating to tourism. It compiles the World Tourism rankings. The World Tourism Organization is a significant global body, concerned with the collection and collation of statistical information...
(UNWTO) - World Trade OrganizationWorld Trade OrganizationThe World Trade Organization is an organization that intends to supervise and liberalize international trade. The organization officially commenced on January 1, 1995 under the Marrakech Agreement, replacing the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade , which commenced in 1948...
(WTO)
Law and order in Latvia
- Capital punishment in LatviaCapital punishment in LatviaLatvia was the last country of the European Union to retain capital punishment for murder, however only during wartime.Latvia regained independence in 1991 after fall of the Soviet Union. Subsequently the death penalty in civilian cases was reserved for murder and the only method of executions, as...
- Constitution of LatviaConstitution of LatviaThe Constitution of Latvia is the fundamental law of the Republic of Latvia. It was adopted by, as it states itself, the people of Latvia, in a freely elected Constitutional Assembly, on 15 February 1922 and came into force on 7 November 1922. It was influenced by ideas of the Weimar Constitution...
- Crime in Latvia
- Human rights in LatviaHuman rights in LatviaHuman rights in Latvia are generally respected by the government, according to the US Department of State and Freedom House. Latvia is ranked above-average among the world's sovereign states in democracy, press freedom, privacy and human development...
- Latvian citizenship lawLatvian citizenship lawright|200pxThe Latvian nationality law is based on the Citizenship Law of 1994 . It is primarily based on jus sanguinis...
- LGBT rights in Latvia
- Freedom of religion in Latvia
- Latvian citizenship law
- Law enforcement in LatviaLaw enforcement in LatviaLaw enforcement in Latvia is under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of the Interior, which is composed of the State Police, Security Police and State Border Guard branches.In 2003, the State Police consisted of 8,222 officers..-External links:***...
Military of Latvia
- Command
- Commander-in-chiefCommander-in-ChiefA commander-in-chief is the commander of a nation's military forces or significant element of those forces. In the latter case, the force element may be defined as those forces within a particular region or those forces which are associated by function. As a practical term it refers to the military...
:- Ministry of Defence of LatviaMinistry of Defence (Latvia)The Ministry of Defence of the Republic of Latvia is the Latvian government ministry in charge of the formation and implementation of national security and defence policy, and for the overall management and control of related subordinate agencies...
- Ministry of Defence of Latvia
- Commander-in-chief
- Forces
- Army of Latvia
- Navy of Latvia
- Air Force of Latvia
- Special forces of Latvia
- Military history of Latvia
- Military ranks of Latvia
History of Latvia
- Main article: History of LatviaHistory of LatviaThe History of Latvia began when the area which is today Latvia was settled following the end of the last glacial period, around 9000 BC. Ancient Baltic peoples appeared during the second millennium BC and four distinct tribal realms in Latvia's territories were identifiable towards the end of the...
, Timeline of the history of Latvia, and Current events of Latvia
- Economic history of Latvia
- Military history of Latvia
Culture of Latvia
- Architecture of Latvia
- Cuisine of LatviaCuisine of LatviaLatvian cuisine typically consists of agricultural products, with meat featuring in most main meal dishes. Fish is commonly consumed due to Latvia's location on the east coast of the Baltic Sea....
- Ethnic minorities in Latvia
- Festivals in Latvia
- Humor in Latvia
- Languages of Latvia
- Media in Latvia
- National symbols of Latvia
- Coat of arms of LatviaCoat of arms of LatviaThe Latvian national coat of arms was formed after the proclamation of an independent Republic of Latvia on November 18, 1918, and was officially adopted on June 16, 1921. It was especially created for its independent statehood...
- Flag of LatviaFlag of LatviaThe national flag of Latvia was used by independent Latvia from 1918 until the country was occupied by the Soviet Union in 1940. Its use was suppressed during Soviet rule. After regaining its independence, Latvia re-adopted on February 27, 1990 the same red-white-red flag.Though officially adopted...
- National anthem of Latvia
- Coat of arms of Latvia
- People of Latvia
- Prostitution in Latvia
- Public holidays in LatviaPublic holidays in LatviaThis is a list of holidays in Latvia.-References:*, the Latvian Institute*...
- Records of Latvia
- Religion in LatviaReligion in LatviaThe main religion traditionally practised in Latvia is Christianity, with no single church predominating: most Latvian Christians follow Latvian Orthodoxy, Lutheranism or Roman Catholicism. In addition, a large proportion of the country claim to practise no religion.Latvia was one of the last...
- Buddhism in Latvia
- Christianity in Latvia
- Roman Catholicism in LatviaRoman Catholicism in LatviaThe Roman Catholic Church of Latvia is part of the worldwide Roman Catholic Church, under the spiritual leadership of the Pope and curia in Rome.There are around 430,235 Catholics — around 17% of the total population.-History:...
- Latvian Orthodox ChurchLatvian Orthodox ChurchThe Latvian Orthodox Church is a self-governing Eastern Orthodox Church under the jurisdiction of the Patriarchate of Moscow. The primate of the church carries the title of Metropolitan of Riga and all Latvia...
- Roman Catholicism in Latvia
- Hinduism in LatviaHinduism in LatviaHinduism in Latvia is a minor religion, spread mainly by ISKCON and Brahma Kumaris.ISKCON started in Latvia in the early eighties. As of April 2006, 11 congregations of Hare Krishna ISKCON are registered in Latvia. In 2005, Hare Krishna gave its membership figures as 127 to the Justice Ministry...
- Islam in LatviaIslam in LatviaThe presence of Muslims in Latvia was first recorded in the early 19th century. The Muslims had mainly Tatar and Turkic backgrounds, and most had been brought to Latvia against their will. These included Turkish prisoners of war from the Crimean War and the Russo-Turkish War of 1877...
- Judaism in Latvia
- Sikhism in Latvia
- World Heritage Sites in Latvia
Art in Latvia
- Art in Latvia
- Cinema of LatviaCinema of LatviaCinema of Latvia dates back to 1910 when the first short films were made.. The first cinematic screening in Riga took place on May 28, 1896. By 1914 all major cities in Latvia had cinemas where newsreels, documentaries and mostly foreign made short films were screened.Two years after cinema was...
- Literature of Latvia
- Music of LatviaMusic of LatviaTraditional Latvian music is often set to traditional poetry called dainas, featuring pre-Christian themes and legends, drone vocal styles and Baltic zithers.-Dainas:...
- Television in Latvia
- Theatre in Latvia
Sports in Latvia
- Football in LatviaFootball in LatviaFootball is not Latvia's national sport, however, in recent years it has gained popularity. The national team have achieved some notable results in recent years. The most remarkable of which was the participation in the Euro 2004 in Portugal after having beaten Turkey in the play-off...
- Ice Hockey in Latvia
- Basketball in Latvia
- Athletics in Latvia
- Tennis in Latvia
- Cycling in Latvia
- Floorball in Latvia
- Latvia at the OlympicsLatvia at the OlympicsLatvia first participated at the Olympic Games in 1924. After the nation was occupied by the Soviet Union in 1940, Latvian athletes competed for the Soviet Union at the Olympics between 1952 and 1988...
Economy and infrastructure of Latvia
- Economic rank, by nominal GDP (2007): 82nd (eighty-second)
- Agriculture in LatviaAgriculture in LatviaIn 1990, Latvia had 2,567,000 hectares of agricultural land—32 percent less than in 1935. More than 1 million hectares of agricultural land, much of it abandoned, were converted to forest under Soviet rule...
- Banking in Latvia
- National Bank of Latvia
- Communications in LatviaCommunications in Latvia- Telephones :Telephones - main lines in use:around 644,000 .Telephones - mobile cellular:over 2,217,000 Telephone system:...
- Internet in LatviaInternet in LatviaThe Internet in Latvia began to experience significant growth in 1999, as the consolidation of regional Internet providers began to drive down prices for dial-up access. By 2000, there were 75,000 Internet users and about a dozen e-commerce shops in Latvia. The average salary for a web programmer...
- Internet in Latvia
- Companies of Latvia
- Currency of LatviaCurrencyIn economics, currency refers to a generally accepted medium of exchange. These are usually the coins and banknotes of a particular government, which comprise the physical aspects of a nation's money supply...
: LatsLatvian latsThe lats is the currency of Latvia. It is abbreviated as Ls. The lats is sub-divided into 100 santīmi ....
- ISO 4217ISO 4217ISO 4217 is a standard published by the International Standards Organization, which delineates currency designators, country codes , and references to minor units in three tables:* Table A.1 – Current currency & funds code list...
: LVL
- ISO 4217
- Economic history of Latvia
- Energy in LatviaEnergy in LatviaEnergy in Latvia describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in the Republic of Latvia. Energy policy of Latvia will describe the politics of Latvia related to energy more in detail....
- Energy policy of Latvia
- Oil industry in Latvia
- Mining in Latvia
- Tourism in Latvia
- Transport in LatviaTransport in Latvia- Railways : total:2,347 kmRussian gauge:2,314 km gauge narrow gauge:33 km gauge - Rail links with adjacent countries :* Russia - yes* Lithuania - yes* Belarus - yes* Estonia - yes- Highways :...
- Riga Stock ExchangeRiga Stock ExchangeThe Riga Stock Exchange now "NASDAQ OMX Riga" is the sole stock exchange operating in Riga, Latvia. It is owned by NASDAQ OMX, which also operates exchanges in the USA, Denmark, Sweden, Finland, Iceland, Armenia, Lithuania, and Estonia...
- Latvian Real EstateLatvian Real EstateSince the year 2000 Latvia has had one of the highest growth rates in Europe. In 2006, annual GDP growth was 11.9% and inflation was 6.2%. Unemployment was 8.5% — almost unchanged compared to the previous two years. However, it has recently dropped to 6.1%, partly due to active economic...
(needs fixing)
Infrastructure of Latvia
-
- Telephone numbers in LatviaTelephone numbers in LatviaThe Latvian numbering plan is a closed telephone numbering plan. Subscribers' numbers are all a standard length of 8 digits and are used for all calls, even in the same area...
- Telephone numbers in Latvia
- Energy in LatviaEnergy in LatviaEnergy in Latvia describes energy and electricity production, consumption and import in the Republic of Latvia. Energy policy of Latvia will describe the politics of Latvia related to energy more in detail....
- Health care in Latvia
- Transportation in Latvia
- Airports in Latvia
- Rail transport in LatviaRail transport in LatviaRail transport in Latvia is done on Russian gauge. The main railway company is Latvijas dzelzceļš.Historically Latvia had lot of different rail gauges, most notably standard gauge and narrow gauge.- Rail links with adjacent countries :...
- Roads in Latvia
- Water supply and sanitation in Latvia
See also
- Index of Latvia-related articles
- List of international rankings
- List of Latvia-related topics
- Member state of the European UnionMember State of the European UnionA member state of the European Union is a state that is party to treaties of the European Union and has thereby undertaken the privileges and obligations that EU membership entails. Unlike membership of an international organisation, being an EU member state places a country under binding laws in...
- Member state of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization
- Member state of the United Nations
- Outline of Europe
- Outline of geographyOutline of geographyThe following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to geography:Geography – science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth.- Geography is :...
External links
- The President of Latvia
- National Statistics Agency — Statistical information on economical, demographic, social, and environmental phenomena and processes of Latvia
- Latvia from The World FactbookThe World FactbookThe World Factbook is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency of the United States with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official paper copy version is available from the National Technical Information Service and the Government Printing Office...
- Virtual World of Latvia (Latvian Institute)
- The Latvian Institute — Publications on Latvian society, economy, culture and history

