Baltic languages
Encyclopedia
The Baltic languages are a group of related language
s belonging to the Balto-Slavic
branch of the Indo-European
language family and spoken mainly in areas extending east and southeast of the Baltic Sea
in Northern Europe
. The language group is usually divided into two sub-groups: Western Baltic, containing only extinct languages, and Eastern Baltic, containing both extinct and the two living languages in the group: Lithuanian
(including both Standard Lithuanian and Samogitian) and Latvian
(including both literary Latvian and Latgalian
). The range of Eastern Balts reached to the Ural mountains. While related, the Lithuanian, the Latvian, and particularly the Old Prussian vocabularies differ substantially from one another and are not mutually intelligible. The now-extinct Old Prussian language has been considered the most archaic of the Baltic languages. Some linguists question whether the language group is a strict genetic clade
by itself, with West Baltic, Slavic, and East Baltic all representing equally valid nodes in the Balto-Slavic branch.
(†—Extinct language)
 Speakers of modern Baltic languages are generally concentrated within the borders of Lithuania
Speakers of modern Baltic languages are generally concentrated within the borders of Lithuania
and Latvia
, and in emigrant communities in the United States
, Canada
, Australia
and states of the former Soviet Union
. Historically the languages were spoken over a larger area: West to the mouth of the Vistula
river in present-day Poland
, at least as far East as the Dniepr river in present-day Belarus
, perhaps even to Moscow
, perhaps as far south as Kiev
. Key evidence of Baltic language presence in these regions is found in hydronym
s (names of bodies of water) in the regions that are characteristically Baltic. Use of hydronyms is generally accepted to determine the extent of these cultures' influence, but not the date of such influence. Historical expansion of the usage of Slavic languages
in the South and East, and Germanic languages
in the West reduced the geographic distribution of Baltic languages to a fraction of the area which they had formerly covered.
by Martynas Mažvydas
was published in 1547 in Königsberg
, Prussia (now Kaliningrad
, Russia). Latvian appeared in a hymnal in 1530 and in a printed Catechism in 1585. One reason for the late attestation is that the Baltic peoples resisted Christianization
longer than any other Europeans, which delayed the introduction of writing and isolated their languages from outside influence.
With the establishment of a German
state in Prussia, and the eradication or flight of much of the Baltic Prussian population in the 13th century, the remaining Prussians began to be assimilated, and by the end of the 17th century, the Prussian language had become extinct.
During the years of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
(1569–1795), official documents were written in Polish
, Ruthenian
and Latin
, with Lithuanian being mostly an oral language, with small quantities of written documents.
After the Partitions of Poland
, most of the Baltic lands were under the rule of the Russian Empire
, where the native languages were sometimes prohibited from being written down, or used publicly.
.
Linguists disagree regarding the relationship of the Baltic languages to other languages in the Indo-European family. Such relationships are discerned primarily by the comparative method
, which seeks to reconstruct the chronology
of the languages' divergence from each other in phonology
and lexicon
. Language kinship is generally determined by the identification of linguistic innovations that are held in common by two languages or groups.
Several of the extinct Baltic languages have a limited or nonexistent written record, their existence being known only from the records of ancient historians and personal or place names. All of the languages in the Baltic group (including the living ones) were first written down relatively late in their probable existence as distinct languages. These two factors combined with others have obscured the history of the Baltic languages, leading to a number of theories regarding their position in the Indo-European family.
The Baltic languages show the closest relationship with the Slavic languages, and are commonly reconstructed to have passed through a common Proto-Balto-Slavic stage, during which numerous Common Balto-Slavic lexical, phonological, morphological and accentological isoglosses developed. Comparative Balto-Slavic accentology is one of the most active branches of Indo-European studies
nowadays, with numerous mysteries still waiting to be solved. Even the commonly accepted facts – such as Winter's law, identical reflexes of Proto-Indo-European syllabic sonorants or development of Balto-Slavic mobile paradigms – have many intricate problems in their formulations.
Some linguists feel that the Baltic languages do not represent a genetic node in either the Indo-European family or the Balto-Slavic group. There are virtually no non-trivial isoglosses that connect the Baltic languages to Proto-Indo-European and leave the Slavic languages aside; West and East Baltic languages seem to differ from each other as much as each of them differs from Proto-Slavic, and all major isoglosses that differentiate Slavic from Baltic that are usually mentioned are either Proto-Indo-European archaisms preserved in Baltic or later innovations in Slavic that occurred during the Common Slavic period, and not some "Common Baltic" innovations. Thus, there was most likely no "Proto-Baltic" stage, and the Baltic languages would thus represent an archaic remnant of the former Balto-Slavic dialect continuum, the last Proto-Indo-European branch to finally split, some theorize around 1500–1000 BCE. The Fatyanovo-Balanovo culture
remains, hydronyms such as the Oka river
, and Baltic loanwords in Uralic add relevant dating evidence. Examples of such Baltic loanwords into Uralic are: East Baltic Lithuanian žalgas "pole" > North Saami
čuolggu "lever", Finnish
salko "pole", or Lithuanian šaras "fodder" > Mordvinian śora "grain".
Language
Language may refer either to the specifically human capacity for acquiring and using complex systems of communication, or to a specific instance of such a system of complex communication...
s belonging to the Balto-Slavic
Balto-Slavic languages
The Balto-Slavic language group traditionally comprises Baltic and Slavic languages, belonging to the Indo-European family of languages. Baltic and Slavic languages share several linguistic traits not found in any other Indo-European branch, which points to the period of common development...
branch of the Indo-European
Indo-European languages
The Indo-European languages are a family of several hundred related languages and dialects, including most major current languages of Europe, the Iranian plateau, and South Asia and also historically predominant in Anatolia...
language family and spoken mainly in areas extending east and southeast of the Baltic Sea
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
in Northern Europe
Northern Europe
Northern Europe is the northern part or region of Europe. Northern Europe typically refers to the seven countries in the northern part of the European subcontinent which includes Denmark, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, Finland and Sweden...
. The language group is usually divided into two sub-groups: Western Baltic, containing only extinct languages, and Eastern Baltic, containing both extinct and the two living languages in the group: Lithuanian
Lithuanian language
Lithuanian is the official state language of Lithuania and is recognized as one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 2.96 million native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 170,000 abroad. Lithuanian is a Baltic language, closely related to Latvian, although they...
(including both Standard Lithuanian and Samogitian) and Latvian
Latvian language
Latvian is the official state language of Latvia. It is also sometimes referred to as Lettish. There are about 1.4 million native Latvian speakers in Latvia and about 150,000 abroad. The Latvian language has a relatively large number of non-native speakers, atypical for a small language...
(including both literary Latvian and Latgalian
Latgalian language
Latgalian language can mean one of the following:#It was a language spoken by Latgalians in a great part of the area which is now Latvia. Latgalian was a member of the Baltic group of the Indo-European language family. Historically the Latvian language is derived from Latgalian Latgalian language...
). The range of Eastern Balts reached to the Ural mountains. While related, the Lithuanian, the Latvian, and particularly the Old Prussian vocabularies differ substantially from one another and are not mutually intelligible. The now-extinct Old Prussian language has been considered the most archaic of the Baltic languages. Some linguists question whether the language group is a strict genetic clade
Genetic relationship (linguistics)
In linguistics, genetic relationship is the usual term for the relationship which exists between languages that are members of the same language family. The term genealogical relationship is sometimes used to avoid confusion with the unrelated use of the term in biological genetics...
by itself, with West Baltic, Slavic, and East Baltic all representing equally valid nodes in the Balto-Slavic branch.
Western Baltic languages †
- GalindianGalindian languageGalindian is a poorly attested extinct language, considered to be a part of the Baltic languages group. There are no extant writings in Galindian.- References :**http://www.sil.org/iso639-3/documentation.asp?id=xgl...
† - Old PrussianOld Prussian languagePrussian is an extinct Baltic language, once spoken by the inhabitants of the original territory of Prussia in an area of what later became East Prussia and eastern parts of...
† - SudovianSudovian languageSudovian is an extinct western Baltic language of Northeastern Europe. Closely related to the Old Prussian language, it was formerly spoken southwest of the Nemunas river in what is now Lithuania, east of Galindia and north of Yotvingia, and by exiles in East Prussia.-History:Sudovia and...
(Yotvingian) † - Skalvian †
Eastern Baltic languages
- LatvianLatvian languageLatvian is the official state language of Latvia. It is also sometimes referred to as Lettish. There are about 1.4 million native Latvian speakers in Latvia and about 150,000 abroad. The Latvian language has a relatively large number of non-native speakers, atypical for a small language...
(~2–2.5 million speakers, whereof ~1.39 million native speakers, 0.5–1 million ethnic Russian speakers, 0.15 million others)- LatgalianLatgalian languageLatgalian language can mean one of the following:#It was a language spoken by Latgalians in a great part of the area which is now Latvia. Latgalian was a member of the Baltic group of the Indo-European language family. Historically the Latvian language is derived from Latgalian Latgalian language...
(150 thousand speakers; usually considered a dialect of Latvian, but has its own ISO 639-3ISO 639-3ISO 639-3:2007, Codes for the representation of names of languages — Part 3: Alpha-3 code for comprehensive coverage of languages, is an international standard for language codes in the ISO 639 series. The standard describes three‐letter codes for identifying languages. It extends the ISO 639-2...
code ltg)
- Latgalian
- LithuanianLithuanian languageLithuanian is the official state language of Lithuania and is recognized as one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 2.96 million native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 170,000 abroad. Lithuanian is a Baltic language, closely related to Latvian, although they...
(~3.9 million speakers)- SamogitianSamogitian languageSamogitian is a dialect of the Lithuanian language spoken mostly in Samogitia . Attempts have been made to standardize it...
(~0.5 million speakers; usually considered a dialect of Lithuanian, but it has its own ISO 639-3ISO 639-3ISO 639-3:2007, Codes for the representation of names of languages — Part 3: Alpha-3 code for comprehensive coverage of languages, is an international standard for language codes in the ISO 639 series. The standard describes three‐letter codes for identifying languages. It extends the ISO 639-2...
code sgs)
- Samogitian
- Old CuronianCuronian languageThe Curonian language or Old Curonian is an extinct language spoken by the Curonian tribe, who lived mainly on the Courland peninsula and along the nearby Baltic shores....
† (sometimes considered Western Baltic)- New Curonian (nearly extinct; status as Eastern / Western Baltic is disputed)
- Selonian †
- SemigallianSemigallian languageSemigallian is an extinct language of the Baltic language sub-family of the Indo-European languages.It was spoken in the northern part of Lithuania and southern regions of Latvia. It is thought that it was extinct by the 16th century with the assimilation by the Latvians. Semigallian is known only...
† - Golyad'- Голядь †
(†—Extinct language)
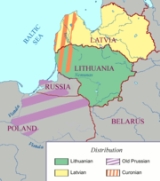
Geographic distribution

Lithuania
Lithuania , officially the Republic of Lithuania is a country in Northern Europe, the biggest of the three Baltic states. It is situated along the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea, whereby to the west lie Sweden and Denmark...
and Latvia
Latvia
Latvia , officially the Republic of Latvia , is a country in the Baltic region of Northern Europe. It is bordered to the north by Estonia , to the south by Lithuania , to the east by the Russian Federation , to the southeast by Belarus and shares maritime borders to the west with Sweden...
, and in emigrant communities in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, Canada
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
, Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
and states of the former Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
. Historically the languages were spoken over a larger area: West to the mouth of the Vistula
Vistula
The Vistula is the longest and the most important river in Poland, at 1,047 km in length. The watershed area of the Vistula is , of which lies within Poland ....
river in present-day Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
, at least as far East as the Dniepr river in present-day Belarus
Belarus
Belarus , officially the Republic of Belarus, is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe, bordered clockwise by Russia to the northeast, Ukraine to the south, Poland to the west, and Lithuania and Latvia to the northwest. Its capital is Minsk; other major cities include Brest, Grodno , Gomel ,...
, perhaps even to Moscow
Moscow
Moscow is the capital, the most populous city, and the most populous federal subject of Russia. The city is a major political, economic, cultural, scientific, religious, financial, educational, and transportation centre of Russia and the continent...
, perhaps as far south as Kiev
Kiev
Kiev or Kyiv is the capital and the largest city of Ukraine, located in the north central part of the country on the Dnieper River. The population as of the 2001 census was 2,611,300. However, higher numbers have been cited in the press....
. Key evidence of Baltic language presence in these regions is found in hydronym
Hydronym
A hydronym is a proper name of a body of water. Hydronymy is the study of hydronyms and of how bodies of water receive their names and how they are transmitted through history...
s (names of bodies of water) in the regions that are characteristically Baltic. Use of hydronyms is generally accepted to determine the extent of these cultures' influence, but not the date of such influence. Historical expansion of the usage of Slavic languages
Slavic languages
The Slavic languages , a group of closely related languages of the Slavic peoples and a subgroup of Indo-European languages, have speakers in most of Eastern Europe, in much of the Balkans, in parts of Central Europe, and in the northern part of Asia.-Branches:Scholars traditionally divide Slavic...
in the South and East, and Germanic languages
Germanic languages
The Germanic languages constitute a sub-branch of the Indo-European language family. The common ancestor of all of the languages in this branch is called Proto-Germanic , which was spoken in approximately the mid-1st millennium BC in Iron Age northern Europe...
in the West reduced the geographic distribution of Baltic languages to a fraction of the area which they had formerly covered.
Prehistory and history
Although the various Baltic tribes were mentioned by ancient historians as early as 98 B.C., the first attestation of a Baltic language was in about 1350, with the creation of the Elbing Prussian Vocabulary, a German to Prussian translation dictionary. It is also believed that Baltic languages are among the most archaic of the remaining Indo-European languages, despite their late attestation. Lithuanian was first attested in a hymnal translation in 1545; the first printed book in Lithuanian, a CatechismCatechism
A catechism , i.e. to indoctrinate) is a summary or exposition of doctrine, traditionally used in Christian religious teaching from New Testament times to the present...
by Martynas Mažvydas
Martynas Mažvydas
Martynas Mažvydas Martynas Mažvydas Martynas Mažvydas (1510 near Žemaičių Naumiestis (now in Šilutė district municipality) - May 21, 1563 in Königsberg (now Kaliningrad) was the author and the editor of the first printed book in the Lithuanian language....
was published in 1547 in Königsberg
Königsberg
Königsberg was the capital of East Prussia from the Late Middle Ages until 1945 as well as the northernmost and easternmost German city with 286,666 inhabitants . Due to the multicultural society in and around the city, there are several local names for it...
, Prussia (now Kaliningrad
Kaliningrad
Kaliningrad is a seaport and the administrative center of Kaliningrad Oblast, the Russian exclave between Poland and Lithuania on the Baltic Sea...
, Russia). Latvian appeared in a hymnal in 1530 and in a printed Catechism in 1585. One reason for the late attestation is that the Baltic peoples resisted Christianization
Northern Crusades
The Northern Crusades or Baltic Crusades were crusades undertaken by the Christian kings of Denmark and Sweden, the German Livonian and Teutonic military orders, and their allies against the pagan peoples of Northern Europe around the southern and eastern shores of the Baltic Sea...
longer than any other Europeans, which delayed the introduction of writing and isolated their languages from outside influence.
With the establishment of a German
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
state in Prussia, and the eradication or flight of much of the Baltic Prussian population in the 13th century, the remaining Prussians began to be assimilated, and by the end of the 17th century, the Prussian language had become extinct.
During the years of the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was a dualistic state of Poland and Lithuania ruled by a common monarch. It was the largest and one of the most populous countries of 16th- and 17th‑century Europe with some and a multi-ethnic population of 11 million at its peak in the early 17th century...
(1569–1795), official documents were written in Polish
Polish language
Polish is a language of the Lechitic subgroup of West Slavic languages, used throughout Poland and by Polish minorities in other countries...
, Ruthenian
Old Ruthenian language
The name Old Ruthenian language has been applied to different things.* Old East Slavic language was the language of Kievan Rus', spoken from the 9th to 14th centuries...
and Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
, with Lithuanian being mostly an oral language, with small quantities of written documents.
After the Partitions of Poland
Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland or Partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth took place in the second half of the 18th century and ended the existence of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland for 123 years...
, most of the Baltic lands were under the rule of the Russian Empire
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was a state that existed from 1721 until the Russian Revolution of 1917. It was the successor to the Tsardom of Russia and the predecessor of the Soviet Union...
, where the native languages were sometimes prohibited from being written down, or used publicly.
Relationship with other Indo-European languages
The Baltic languages are of particular interest to linguists because they retain many archaic features, which are believed to have been present in the early stages of the Proto-Indo-European languageProto-Indo-European language
The Proto-Indo-European language is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European languages, spoken by the Proto-Indo-Europeans...
.
Linguists disagree regarding the relationship of the Baltic languages to other languages in the Indo-European family. Such relationships are discerned primarily by the comparative method
Comparative method
In linguistics, the comparative method is a technique for studying the development of languages by performing a feature-by-feature comparison of two or more languages with common descent from a shared ancestor, as opposed to the method of internal reconstruction, which analyzes the internal...
, which seeks to reconstruct the chronology
Chronology
Chronology is the science of arranging events in their order of occurrence in time, such as the use of a timeline or sequence of events. It is also "the determination of the actual temporal sequence of past events".Chronology is part of periodization...
of the languages' divergence from each other in phonology
Phonology
Phonology is, broadly speaking, the subdiscipline of linguistics concerned with the sounds of language. That is, it is the systematic use of sound to encode meaning in any spoken human language, or the field of linguistics studying this use...
and lexicon
Lexicon
In linguistics, the lexicon of a language is its vocabulary, including its words and expressions. A lexicon is also a synonym of the word thesaurus. More formally, it is a language's inventory of lexemes. Coined in English 1603, the word "lexicon" derives from the Greek "λεξικόν" , neut...
. Language kinship is generally determined by the identification of linguistic innovations that are held in common by two languages or groups.
Several of the extinct Baltic languages have a limited or nonexistent written record, their existence being known only from the records of ancient historians and personal or place names. All of the languages in the Baltic group (including the living ones) were first written down relatively late in their probable existence as distinct languages. These two factors combined with others have obscured the history of the Baltic languages, leading to a number of theories regarding their position in the Indo-European family.
The Baltic languages show the closest relationship with the Slavic languages, and are commonly reconstructed to have passed through a common Proto-Balto-Slavic stage, during which numerous Common Balto-Slavic lexical, phonological, morphological and accentological isoglosses developed. Comparative Balto-Slavic accentology is one of the most active branches of Indo-European studies
Indo-European studies
Indo-European studies is a field of linguistics dealing with Indo-European languages, both current and extinct. Its goal is to amass information about the hypothetical proto-language from which all of these languages are descended, a language dubbed Proto-Indo-European , and its speakers, the...
nowadays, with numerous mysteries still waiting to be solved. Even the commonly accepted facts – such as Winter's law, identical reflexes of Proto-Indo-European syllabic sonorants or development of Balto-Slavic mobile paradigms – have many intricate problems in their formulations.
Some linguists feel that the Baltic languages do not represent a genetic node in either the Indo-European family or the Balto-Slavic group. There are virtually no non-trivial isoglosses that connect the Baltic languages to Proto-Indo-European and leave the Slavic languages aside; West and East Baltic languages seem to differ from each other as much as each of them differs from Proto-Slavic, and all major isoglosses that differentiate Slavic from Baltic that are usually mentioned are either Proto-Indo-European archaisms preserved in Baltic or later innovations in Slavic that occurred during the Common Slavic period, and not some "Common Baltic" innovations. Thus, there was most likely no "Proto-Baltic" stage, and the Baltic languages would thus represent an archaic remnant of the former Balto-Slavic dialect continuum, the last Proto-Indo-European branch to finally split, some theorize around 1500–1000 BCE. The Fatyanovo-Balanovo culture
Fatyanovo-Balanovo culture
The Fatyanovo-Balanovo culture, 3200 BC-2300 BC, is an eastern extension of the Corded Ware culture into RussiaIt runs from Lake Pskov in the west to the middle Volga in the east, with its northern reach in the valley of the upper Volga. It is really two cultures, the Fatyanovo in the west, the...
remains, hydronyms such as the Oka river
Oka River
Oka is a river in central Russia, the largest right tributary of the Volga. It flows through the regions of Oryol, Tula, Kaluga, Moscow, Ryazan, Vladimir, and Nizhny Novgorod and is navigable over a large part of its total length, as far upstream as to the town of Kaluga. Its length exceeds...
, and Baltic loanwords in Uralic add relevant dating evidence. Examples of such Baltic loanwords into Uralic are: East Baltic Lithuanian žalgas "pole" > North Saami
Saami
Saami or SAAMI can stand for:*Sami people*Sami languages*Sporting Arms and Ammunition Manufacturers' Institute...
čuolggu "lever", Finnish
Finnish language
Finnish is the language spoken by the majority of the population in Finland Primarily for use by restaurant menus and by ethnic Finns outside Finland. It is one of the two official languages of Finland and an official minority language in Sweden. In Sweden, both standard Finnish and Meänkieli, a...
salko "pole", or Lithuanian šaras "fodder" > Mordvinian śora "grain".
See also
- Historical linguisticsHistorical linguisticsHistorical linguistics is the study of language change. It has five main concerns:* to describe and account for observed changes in particular languages...
- Language families and languages
- Baltic peoples
- Balto-Slavic languagesBalto-Slavic languagesThe Balto-Slavic language group traditionally comprises Baltic and Slavic languages, belonging to the Indo-European family of languages. Baltic and Slavic languages share several linguistic traits not found in any other Indo-European branch, which points to the period of common development...
- Dacian-Baltic connection
External links
- Ethnologue Report on Baltic languages
- Baltic Online from the University of Texas at Austin

