History of the Hungarian language
Encyclopedia

Ugric languages
Ugric or Ugrian languages are a branch of the Uralic language family. The term derives from Yugra, a region in north-central Asia.They include three languages: Hungarian , Khanty , and Mansi language...
. It has been spoken in the region of modern-day Hungary
Hungary
Hungary , officially the Republic of Hungary , is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The...
since the Magyar invasion of Pannonia in the late 9th century.
The predecessor language of Hungarian separated from the Ob-Ugric languages, probably still during the Bronze Age
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a period characterized by the use of copper and its alloy bronze as the chief hard materials in the manufacture of some implements and weapons. Chronologically, it stands between the Stone Age and Iron Age...
. There is no attestation for a period of close to two millennia. Old Hungarian is attested fragmentarily in epigraphy in the Old Hungarian script
Old Hungarian script
The Old Hungarian script is an alphabetic writing system used by the Hungarians before the Middle Ages...
beginning in the 10th century, and isolated Hungarian words are attested in manuscript tradition from the turn of the 11th century. The oldest surviving coherent text in Old Hungarian is the Funeral Sermon and Prayer
Funeral Sermon and Prayer
The Funeral Sermon and Prayer is the oldest known and surviving contiguous Hungarian text, written by one scribal hand in the Latin script and dating to 1192-1195...
, dated to 1192.
The Old Hungarian period is by convention taken to cover Medieval Hungary, from the invasion of Pannonia in AD 896, to the collapse of the Kingdom of Hungary following the Battle of Mohács
Battle of Mohács
The Battle of Mohács was fought on August 29, 1526 near Mohács, Hungary. In the battle, forces of the Kingdom of Hungary led by King Louis II of Hungary and Bohemia were defeated by forces of the Ottoman Empire led by Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent....
of 1526. A Middle Hungarian phase is by convention taken to last from 1526 to 1772, i.e. from the first books printed in Hungarian to the Age of Enlightenment
Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment was an elite cultural movement of intellectuals in 18th century Europe that sought to mobilize the power of reason in order to reform society and advance knowledge. It promoted intellectual interchange and opposed intolerance and abuses in church and state...
, which prompted language reform
Language reform
Language reform is a type of language planning by massive change to a language. The usual tools of language reform are simplification and purification. Simplification makes the language easier to use by regularizing vocabulary and grammar...
s that resulted in the modern literary Hungarian language.
Separation from Common Uralic
The history of the Hungarian languageHungarian language
Hungarian is a Uralic language, part of the Ugric group. With some 14 million speakers, it is one of the most widely spoken non-Indo-European languages in Europe....
begins with the Uralic
Uralic languages
The Uralic languages constitute a language family of some three dozen languages spoken by approximately 25 million people. The healthiest Uralic languages in terms of the number of native speakers are Hungarian, Finnish, Estonian, Mari and Udmurt...
era, in the Neolithic
Neolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
age, when the linguistic ancestors of all Uralic languages were living together, in the area of the Ural Mountains
Ural Mountains
The Ural Mountains , or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the Ural River and northwestern Kazakhstan. Their eastern side is usually considered the natural boundary between Europe and Asia...
.
| Category | Words in Hungarian | Reconstructed words in Proto-Uralic | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fishing, water | hal 'fish', tat '(a kind of) fish', háló 'mesh', víz 'water', jó 'river', ár 'flood', láp 'fen' | *kala, *totki, *kalaw, *weti, *juka, *sarV, *loppi | See note 2 & 3. |
| Hunting, animals | ideg 'nerve', ín 'fibre', íj 'bow', nyíl 'arrow', fogoly 'partridge', nyúl 'hare', holló 'raven' | *jänti 'string', *sëxni 'vein', *joŋsi, *ńëxli, *püŋi, *ńomala, *kulaka | |
| Daily life | fő(z) 'cook', fazék 'pan', mony 'egg of a bird', fon 'spin', öv 'belt', vas 'iron' | *pexi(-ða), *pata, *muna, *puna 'braid', *wüŋä, *waśki | See note 4. |
| Family | apa 'father', fele(ség) 'wife', meny 'daughter-in-law', vő 'son-in-law', napa | *ëppi 'father-in-law', (?), *mińä, *wäŋiw, *ana-ëppi |
There are many words that are traced back to Uralic origin in Hungarian, as they occur in other Uralic languages as well and linguists have not been able to classify them as loanwords. Those that are not present in the Samoyedic languages
Samoyedic languages
The Samoyedic languages are spoken on both sides of the Ural mountains, in northernmost Eurasia, by approximately 30,000 speakers altogether....
are commonly also described as being of Finno-Ugric origin, but the existence of a definite distinction between "Uralic" and "Finno-Ugric" is disputed. (See Uralic languages#Family tree.)
As the Uralic unity disintegrated between the 4th and the 2nd millennium BC, the speakers of Samoyedic languages moved eastwards, while others, such as the Finnic
Finnic languages
The term Finnic languages often means the Baltic-Finnic languages, an undisputed branch of the Uralic languages. However, it is also commonly used to mean the Finno-Permic languages, a hypothetical intermediate branch that includes Baltic Finnic, or the more disputed Finno-Volgaic languages....
and Hungarian speakers, moved westward.
The speakers of Ugric languages were living together approximately until 1000 BC, when the ancestors of Hungarians separated from the Ob-Ugrians
Ob-Ugric languages
The Ob-Ugric languages are a hypothetical branch of the Uralic languages, specifically referring to the Khanty and Mansi languages. Both are split in numerous and highly divergent dialects...
.
Proto-Hungarian
Around 1000 BC, the linguistic ancestors of the Hungarians had moved southwestwards from their previous territories, the region west of the Ural MountainsUral Mountains
The Ural Mountains , or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western Russia, from the coast of the Arctic Ocean to the Ural River and northwestern Kazakhstan. Their eastern side is usually considered the natural boundary between Europe and Asia...
, the eastern frontier of Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
; hence the Hungarian language
Hungarian language
Hungarian is a Uralic language, part of the Ugric group. With some 14 million speakers, it is one of the most widely spoken non-Indo-European languages in Europe....
separated from its closest relatives, the Ob-Ugric languages
Ob-Ugric languages
The Ob-Ugric languages are a hypothetical branch of the Uralic languages, specifically referring to the Khanty and Mansi languages. Both are split in numerous and highly divergent dialects...
, a small group including the Mansi language
Mansi language
The Mansi language is a language of the Mansi people. It is spoken in territories of Russia along the Ob River and its tributaries, including the Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug and the Sverdlovsk Oblast...
and the Khanty language
Khanty language
Khanty or Xanty language, also known previously as the Ostyak language, is a language of the Khant peoples. It is spoken in Khanty-Mansi and Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous okrugs, as well as in Aleksandrovsky and Kargosoksky districts of Tomsk Oblast in Russia...
. The latter two languages separated only later, and their speakers were influenced by an Asian, possibly Western-Siberian tribe, as the Mansies and Khanties had moved northeast.
The Hungarians gradually changed their way of living from settled hunters to nomadic cattle-raising. Their most important animals included sheep and cattle. There are no written resources on the era, thus only a little is known about it.
After a long journey, the Hungarians had settled the coastal region of the northeastern Black Sea
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
, where they were significantly influenced by Turkic peoples
Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are peoples residing in northern, central and western Asia, southern Siberia and northwestern China and parts of eastern Europe. They speak languages belonging to the Turkic language family. They share, to varying degrees, certain cultural traits and historical backgrounds...
. With the fall of Attila's empire, the Huns
Huns
The Huns were a group of nomadic people who, appearing from east of the Volga River, migrated into Europe c. AD 370 and established the vast Hunnic Empire there. Since de Guignes linked them with the Xiongnu, who had been northern neighbours of China 300 years prior to the emergence of the Huns,...
had receded to this area, and established their new state, which also ruled over the Hungarians. Maybe a memoir of this is a Hungarian myth: the saga of Hunor and Magor
Hunor and Magor
Hunor and Magor were, according to a famous Hungarian legend, the ancestors of the Huns and the Magyars. The myth was promoted by the medieval historian Simon Kézai in his Gesta Ungarorum . Kézai's aim in providing a common ancestry for the Huns and the Magyars was to suggest historical continuum...
, who are said to be the common ancestors of the Huns and the Hungarians.
However, the Hunnish rule had not been long-lasting, as the Hungarians soon fell under Turk
Göktürks
The Göktürks or Kök Türks, were a nomadic confederation of peoples in medieval Inner Asia. Known in Chinese sources as 突厥 , the Göktürks under the leadership of Bumin Qaghan The Göktürks or Kök Türks, (Old Turkic: Türük or Kök Türük or Türük; Celestial Turks) were a nomadic confederation of...
(Göktürks) rule. The Turk Empire
Göktürks
The Göktürks or Kök Türks, were a nomadic confederation of peoples in medieval Inner Asia. Known in Chinese sources as 突厥 , the Göktürks under the leadership of Bumin Qaghan The Göktürks or Kök Türks, (Old Turkic: Türük or Kök Türük or Türük; Celestial Turks) were a nomadic confederation of...
flourished from the 6th century to the 8th century. This is very probably the time when the Hungarians were first exposed to the concept of writing
Writing
Writing is the representation of language in a textual medium through the use of a set of signs or symbols . It is distinguished from illustration, such as cave drawing and painting, and non-symbolic preservation of language via non-textual media, such as magnetic tape audio.Writing most likely...
, through the Göktürks' mediation. The latter used the Orkhon script
Orkhon script
The Old Turkic script is the alphabet used by the Göktürk and other early Turkic Khanates from at least the 7th century to record the Old Turkic language. It was later used by the Uyghur Empire...
or Turkic runic script, and reputedly the Old Hungarian script
Old Hungarian script
The Old Hungarian script is an alphabetic writing system used by the Hungarians before the Middle Ages...
(rovásírás) is a parent writing system of it.
The Hungarians call themselves Magyars . Their external name, Hungarian, derive from the Turkic word onugor, meaning "ten arrows", and referring to a tribal alliance. This name was spread by the Slavs later in Europe. The name Magyar once was the name of a Hungarian tribe, Megyer(i). It likely means "talking man" (the first syllable may show a link to the Mansi language
Mansi language
The Mansi language is a language of the Mansi people. It is spoken in territories of Russia along the Ob River and its tributaries, including the Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug and the Sverdlovsk Oblast...
, as in Mansi, mañši means 'man, Mansi').
The Hungarians also came into contact with the Khazars
Khazars
The Khazars were semi-nomadic Turkic people who established one of the largest polities of medieval Eurasia, with the capital of Atil and territory comprising much of modern-day European Russia, western Kazakhstan, eastern Ukraine, Azerbaijan, large portions of the northern Caucasus , parts of...
. After the collapse of the latter's empire, Magyars lived as an independent nation, moving westward. In 895–896, under the rulership of Prince Árpád
Árpád
Árpád was the second Grand Prince of the Hungarians . Under his rule the Hungarian people settled in the Carpathian basin. The dynasty descending from him ruled the Hungarian tribes and later the Kingdom of Hungary until 1301...
, they crossed the Carpathian Mountains
Carpathian Mountains
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians are a range of mountains forming an arc roughly long across Central and Eastern Europe, making them the second-longest mountain range in Europe...
, and settled the area of present-day Hungary
Hungary
Hungary , officially the Republic of Hungary , is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The...
. They also began to establish their own state here, namely the Principality of Hungary.
Early loanwords
There are some really early loanwords in Hungarian, which enriched the language's vocabulary, estimated to 25,000 words at the time. Here are some examples:| Origin | |
|
|---|---|---|
| Turkic Turkic languages The Turkic languages constitute a language family of at least thirty five languages, spoken by Turkic peoples across a vast area from Eastern Europe and the Mediterranean to Siberia and Western China, and are considered to be part of the proposed Altaic language family.Turkic languages are spoken... |
hattyú 'swan', szó 'word', hód 'beaver' | homok 'sand', harang 'bell', ér 'worth sth' |
| Permic Permic languages Permic languages are a branch of the Uralic language family. They are spoken in the foothills of the Ural Mountains of Russia.* Komi** Komi-Permyak** Komi-Yodzyak ** Komi-Zyryan... |
agyar 'fang', daru 'crane', hagyma 'bulb' |
In the era of the Turkic influences, Hungarians developed especially culturally: the borrowed vocabulary consist of terms referring to sophisticated dressing, and the words of a learned upper class society. The phrases of basic literacy are also of Turkic origin. A number of words related to agriculture
Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
and viticulture
Viticulture
Viticulture is the science, production and study of grapes which deals with the series of events that occur in the vineyard. When the grapes are used for winemaking, it is also known as viniculture...
have the same background.
Vowels
| Hungarian | Finnish | Translation |
|---|---|---|
| hal | kala | fish |
| kő (compare 2nd root köv-!) | kivi | stone |
| lúd | lintu | hu: goose, fi:bird |
| kéz | käsi | hand |
The phonetic system of Hungarian went through large changes in the Proto-Hungarian period. The most important change was the disappearance of the original Uralic word-ending vowels (which eroded in many descendant languages. For example Finnish
Finnish language
Finnish is the language spoken by the majority of the population in Finland Primarily for use by restaurant menus and by ethnic Finns outside Finland. It is one of the two official languages of Finland and an official minority language in Sweden. In Sweden, both standard Finnish and Meänkieli, a...
however largely preserves these sounds; see the table on the right.) However, declined forms of the nouns and inflected verbs of Uralic origin still show traces of the lost sounds: ló (horse)—lovas (rider); kő (stone)—köves. This was the process of phonetic reduction.
Possibly there had been also present a velar ï sound
Close back unrounded vowel
The close back unrounded vowel, or high back unrounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is . Typographically a turned letter m, given its relation to the sound represented by the letter u it...
as well, later replaced by a palatal i
Close front unrounded vowel
The close front unrounded vowel, or high front unrounded vowel, is a type of vowel sound, used in many spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is ....
. Today, since Hungarian has vowel harmony
Vowel harmony
Vowel harmony is a type of long-distance assimilatory phonological process involving vowels that occurs in some languages. In languages with vowel harmony, there are constraints on which vowels may be found near each other....
, some words containing the palatal sound i pick up the back suffix when conjugated or declined—instead of the front suffix, which is usual for is of other origin. Some examples: nyíl (arrow) → nyilat (accusative; instead of regular *nyilet); inni ([v inf], to drink) → ivás (drinking [n], instead of regular *ivés).
The transition from diphthongs to simple vowels had already begun in the Proto-Hungarian period.
Consonants
Stop consonant
Stop consonant
In phonetics, a plosive, also known as an occlusive or an oral stop, is a stop consonant in which the vocal tract is blocked so that all airflow ceases. The occlusion may be done with the tongue , lips , and &...
s between vowels developed to spirants, and those after a nasal consonant
Nasal consonant
A nasal consonant is a type of consonant produced with a lowered velum in the mouth, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. Examples of nasal consonants in English are and , in words such as nose and mouth.- Definition :...
became voice
Voice (phonetics)
Voice or voicing is a term used in phonetics and phonology to characterize speech sounds, with sounds described as either voiceless or voiced. The term, however, is used to refer to two separate concepts. Voicing can refer to the articulatory process in which the vocal cords vibrate...
d:
| → | f | (voiceless labiodental fricative Voiceless labiodental fricative The voiceless labiodental fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is .-Features:Features of the voiceless labiodental fricative:... ) |
initial | |
| → | β | (voiced bilabial fricative Voiced bilabial fricative -See also:* List of phonetics topics... ) |
medial | |
| t | → | z | (voiced alveolar fricative Voiced alveolar fricative The voiced alveolar fricatives are consonantal sounds. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents these sounds depends on whether a sibilant or non-sibilant fricative is being described.... ) |
medial |
| k | → | x | (voiceless velar fricative Voiceless velar fricative The voiceless velar fricative is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The sound was part of the consonant inventory of Old English and can still be found in some dialects of English, most notably in Scottish English.... ) |
in initial position in words that contain only velar vowels |
| → | ɣ | (voiced velar fricative Voiced velar fricative The voiced velar fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in various spoken languages. It is not found in English today, but did exist in Old English... ) |
medial | |
| mp | → | b | (voiced bilabial stop) | everywhere |
| nt | → | d | (voiced alveolar stop) | everywhere |
| ŋk | → | ɡ | (voiced velar stop) | everywhere |
Grammar
The language developed its interesting features, the transitive and intransitive verb conjugations. (See Hungarian grammar (verbs)Hungarian grammar (verbs)
This page is about verbs in Hungarian grammar.-Lemma or citation form:There is basically only one pattern for verb endings, with predictable variations dependent on the phonological context....
.) Marked possessive relations appeared. The accusative marker -t was developed, as well as many verb tenses.
Old Hungarian (10th to 15th centuries)
By the 10th century, the Hungarians had established a principality in present-day HungaryHungary
Hungary , officially the Republic of Hungary , is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The...
and its neighbourhood. In 1000, Vajk—the later Stephen I of Hungary—had got his crown
The Crown
The Crown is a corporation sole that in the Commonwealth realms and any provincial or state sub-divisions thereof represents the legal embodiment of governance, whether executive, legislative, or judicial...
from the Papal State, and the history of the Christian Kingdom of Hungary
Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary comprised present-day Hungary, Slovakia and Croatia , Transylvania , Carpatho Ruthenia , Vojvodina , Burgenland , and other smaller territories surrounding present-day Hungary's borders...
began.
The Latin language was made official in the country—especially in the 11th to 15th centuries, the language of literature and religion was Latin. However, Hungarian was used in certain cases; sometimes it was fitted into Latin documents, to avoid later disputes about proprietary rights.
Though, the first official document of Hungary is not in Latin, but in Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
—this is the "Charter of the nuns of Veszprémvölgy", dated to 997. The text contains some Hungarian (and also some Slavic) place names: saɣarbrien (compound formed from saɣar 'shaft' + an obsolete Turkic loanword
Loanword
A loanword is a word borrowed from a donor language and incorporated into a recipient language. By contrast, a calque or loan translation is a related concept where the meaning or idiom is borrowed rather than the lexical item itself. The word loanword is itself a calque of the German Lehnwort,...
, brien 'coalition'—today Szárberény); saːmtaɣ 'plough'; meleɡdi (from meleg 'warm' + -di dimunitive suffix); and so on.
The next most important document is the "Establishing charter of the abbey of Tihany
Tihany
Tihany is a village on the northern shore of Lake Balaton on the Tihany Peninsula . The whole peninsula is a historical district....
", dated to 1055. In the Latin text, 3 Hungarian sentences, 58 words, and 33 suffixes are present. The longest sentence is "fɛhɛːrvaːru reaː mɛnɛɣ hodu utu reaː" (original transcript: feheruuaru rea meneh hodu utu rea; modern Hungarian: "Fehérvárra
Székesfehérvár
Székesfehérvár is a city in central Hungary and is the 9th largest in the country. Located around southwest of Budapest. It is inhabited by 101,973 people , with 136,995 in the Székesfehérvár Subregion. The city is the centre of Fejér county and the regional centre of Central Transdanubia...
menő hadi útra"—the postposition "rea", meaning "onto", became the suffix "-ra/-re"—English: 'up to the military road going to Fehérvár
Székesfehérvár
Székesfehérvár is a city in central Hungary and is the 9th largest in the country. Located around southwest of Budapest. It is inhabited by 101,973 people , with 136,995 in the Székesfehérvár Subregion. The city is the centre of Fejér county and the regional centre of Central Transdanubia...
'). Today, the vellum is kept in the abbey of Pannonhalma
Pannonhalma
Pannonhalma is a town in western Hungary, in Győr-Moson-Sopron county with approximately 4,000 inhabitants. It is about from Győr. Archduke Otto Habsburg's heart is kept at the Pannonhalma Archabbey, while his body was laid at the Capuchin Crypt in the old Imperial capital of Vienna.-History:The...
.
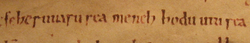

Funeral Sermon and Prayer
The Funeral Sermon and Prayer is the oldest known and surviving contiguous Hungarian text, written by one scribal hand in the Latin script and dating to 1192-1195...
", from 1192. This is the first completely Hungarian text. The document is located on the 154th page of the Codex Pray (Pray here is not English; it is a name). The sermon begins with the words "laːtjaːtuk fɛlɛim symtyxːɛl mik voɟmuk iʃaː por eʃ xomou voɟmuk"—"Do you see, my friends, what we are: truly, we are only dust and ash."
Literature in Hungarian
Hungarian literature
Hungarian literature is literature written in the Hungarian language, predominantly by Hungarians.There is a limited amount of Old Hungarian literature dating to between the late 12th and the early 16th centuries...
is counted since the previous writing. The first known Hungarian poem has the title 'Laments of Mary
Old Hungarian 'Lamentations of Mary'
The Old Hungarian Lamentations of Mary is the oldest extant Hungarian poem, copied in about 1300 into a Latin codex, similarly to the first coherent written Hungarian text , which was written down between 1192 and 1195...
'—its theme is the story of Jesus
Jesus
Jesus of Nazareth , commonly referred to as Jesus Christ or simply as Jesus or Christ, is the central figure of Christianity...
' crucifixion, from the viewpoint of Mary
Mary (mother of Jesus)
Mary , commonly referred to as "Saint Mary", "Mother Mary", the "Virgin Mary", the "Blessed Virgin Mary", or "Mary, Mother of God", was a Jewish woman of Nazareth in Galilee...
. It was denoted around 1300, but possibly it is not the first version—its text is clear, easy to understand and logical, free of latinism
Latinism
A Latinism is an idiom, structure, or word derived from or suggestive of the Latin language. For Latinistic words in English, see Latin influence in English....
s. The first verse:
volɛːk ʃirolm tudotlon ʃirolmol ʃɛpɛdik buol osuk, ɛpedɛk |
I was lament-ignorant; I am suffering from lament, I am suffering, languishing from sorrow. |
The next important relic—with a cheerless history—is the "Fragment of Königsberg", dated approximately to the 1350s. This is the remain of the first known, explicitly proven Hungarian book
Book
A book is a set or collection of written, printed, illustrated, or blank sheets, made of hot lava, paper, parchment, or other materials, usually fastened together to hinge at one side. A single sheet within a book is called a leaf or leaflet, and each side of a leaf is called a page...
. The codex had arrived at Wrocław, Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
, by the end of the century; there, because of it was not understandable to the Polish bookbinder, it was chopped and used to bind a Latin book. The other important book from the time is the Codex Jókay; a 15th century copy of the original from 1372. The codex is about the life of Francis of Assisi
Francis of Assisi
Saint Francis of Assisi was an Italian Catholic friar and preacher. He founded the men's Franciscan Order, the women’s Order of St. Clare, and the lay Third Order of Saint Francis. St...
.

Bible
The Bible refers to any one of the collections of the primary religious texts of Judaism and Christianity. There is no common version of the Bible, as the individual books , their contents and their order vary among denominations...
: this is the Hussite Bible
Hussite Bible
The Hussite Bible is the oldest known Hungarian, but also Uralic Bible translation, dated to the 1420s–1430s.-History:The Hussite Bible is the only written vestige of Hussitism in Hungary. The book – or at least the most of it – was translated by Tamás Pécsi and Bálint Újlaki...
, dated to 1430. The Bible was translated by Tamás Pécsi and Bálint Ujlaki; both were priests. They were affected by the concepts of Jan Hus
Jan Hus
Jan Hus , often referred to in English as John Hus or John Huss, was a Czech priest, philosopher, reformer, and master at Charles University in Prague...
during their university years (1399–1411) in Prague
Prague
Prague is the capital and largest city of the Czech Republic. Situated in the north-west of the country on the Vltava river, the city is home to about 1.3 million people, while its metropolitan area is estimated to have a population of over 2.3 million...
. The Inquisition
Inquisition
The Inquisition, Inquisitio Haereticae Pravitatis , was the "fight against heretics" by several institutions within the justice-system of the Roman Catholic Church. It started in the 12th century, with the introduction of torture in the persecution of heresy...
pursued these concepts, and the translation was confiscated from the translators; anyway, it became such popular that there are several authentic copies of the original.
More and more Hungarian books were written; most of them is religious. Over and above the "Laments of Mary", the other important item of Old Hungarian poetry is the "Fight of Šabac
Šabac
Šabac is a city and municipality in western Serbia, along the Sava river, in the historic region of Mačva. It is the administrative center of the Mačva District. The city has a population of 52,822 , while population of the municipality is 115,347...
". Reputedly it was denoted in the year of the battle (1476); in this, Hungarian troops led by King Matthias of Hungary had a glorious victory over the Ottoman
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
army—its issue is secular. Possibly it is a fragment of a longer poem. A quotation:
dɛ ɑz feʎːøːl mondot paːl keneʒi aːroknɑk meːʎʃeːɡeːt iɡen nezi ki ʃɑbatʃ erøːʃ voltaːt ɛlmeːlːeː honːeːɡ minemøː aːlɟuː kel mɛlːeː |
But, Pál Kinizsi Pál Kinizsi Pál Kinizsi was a Hungarian general, legendary commoner commander in the army of king Matthias Corvinus. He was Comes of Temes since 1484 and Captain General of the Lower Parts of the Kingdom of Hungary... said about the thing, who was regarding the dike's depth; who knew the powerfulness of Šabac Šabac Šabac is a city and municipality in western Serbia, along the Sava river, in the historic region of Mačva. It is the administrative center of the Mačva District. The city has a population of 52,822 , while population of the municipality is 115,347... : what sort of cannons should be brought from where. |
In the 1490s, Hungarian was spoken by about 3.2 million people; this number was fairly high at the time. The first examples of official and legal use are dated back to these years. Some personal letters and wills are known. Nevertheless, the Ottoman Empire
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman EmpireIt was usually referred to as the "Ottoman Empire", the "Turkish Empire", the "Ottoman Caliphate" or more commonly "Turkey" by its contemporaries...
put pressure on neighbouring nations, just like on Hungary—the latter was unstable at the time, due to internal lordship debates. This led to the Hungarian (led by Louis II of Hungary) loss of the Battle of Mohács
Battle of Mohács
The Battle of Mohács was fought on August 29, 1526 near Mohács, Hungary. In the battle, forces of the Kingdom of Hungary led by King Louis II of Hungary and Bohemia were defeated by forces of the Ottoman Empire led by Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent....
(1526). In 1541, Ottomans finally captured the capital, Buda
Buda
For detailed information see: History of Buda CastleBuda is the western part of the Hungarian capital Budapest on the west bank of the Danube. The name Buda takes its name from the name of Bleda the Hun ruler, whose name is also Buda in Hungarian.Buda comprises about one-third of Budapest's...
as well. The country was split up to three parts; the southern regions fell under Ottoman rule; the western parts officially remained "Kingdom of Hungary", with Habsburg kings; and the eastern area, mainly Transylvania
Transylvania
Transylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
and the Partium
Partium
Partium or Részek is the name given in Hungarian to the region located to the north and west of Transylvania.-Origin of the name:...
became independent.
Some Old Hungarian script
Old Hungarian script
The Old Hungarian script is an alphabetic writing system used by the Hungarians before the Middle Ages...
inscriptions are also known, such as the "Alphabet of Nikolsburg" (1483) and a number of deciphered and undeciphered inscriptions. Historic linguists put the end of the Old Hungarian period to 1526, as it is a such important date in Hungarian history.
Vocabulary
In this period, Hungarian developed several new words. One way this happened was through loanwordLoanword
A loanword is a word borrowed from a donor language and incorporated into a recipient language. By contrast, a calque or loan translation is a related concept where the meaning or idiom is borrowed rather than the lexical item itself. The word loanword is itself a calque of the German Lehnwort,...
s coming from languages whose speakers mediated the new concepts. On the other hand, internal word formation also took place, in which the words for new concepts were derived from earlier words.
Old Hungarian was rich—especially compared to Modern Hungarian—in derivative suffixes. Most of these suffixes are also derived from other suffixes, so they can be aligned in "suffix-bushes".
There were numerous diminutive suffixes, unknown in today's Hungarian: -d ("holmod", from "holom"—"tiny hill"); -t (it left its trace in some geographic names) -n, -ny, -m (as in kicsiny, from kicsi—very little), and so on.
Forming compounds was also a way to coin new terms.
But then again, there are several loanwords dating back to the period 896–1526. Loans were mainly acquired from Slavic languages
Slavic languages
The Slavic languages , a group of closely related languages of the Slavic peoples and a subgroup of Indo-European languages, have speakers in most of Eastern Europe, in much of the Balkans, in parts of Central Europe, and in the northern part of Asia.-Branches:Scholars traditionally divide Slavic...
(for example, kiraːʎ 'king'), German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
(e. g. hɛrtsɛɡ 'prince'), and Latin (e. g., tɛmplom 'church'). As emerges from the previous examples, these words are primarily associated with Christianity and politics. Other loans are the names of animals living outside Hungary, terms of technology, and so on.
Grammar
VerbsLike English, Modern Hungarian has two verb tenses: past and nonpast. Futurity is expressed using the auxiliary verb foɡ. However, Old Hungarian had six verb tenses: Past Narrative (Latin: praeteritum), Past Finite, Past Complex, Present, Future Simple, and Future Complex.
Past Narrative was marked using the suffixes -é, -á in transitive and -e, -a in intransitive. The tense was used to describe an array of past events originally. The verb várni 'to wait' conjugated in this tense:
| Past Narrative - várni | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Person | Type | |
| Transitive | Intransitive | ||
| Singular | 1st (I) | várám | várék |
| 2nd (You) | várád | várál | |
| 3rd (He/She) | várá | vára | |
| Plural | 1st (We) | váránk | váránk |
| 2nd (You) | várátok | várátok | |
| 3rd (They) | várák | várának | |
Future Simple was expressed using the suffix -nd. Future Complex (the present-day Future tense of the language) is conjugated in the following way:
- Infinitive + auxiliary verb 'fog'
- menni fog—he/she is going to go
-
- See also: Hungarian grammar (verbs)Hungarian grammar (verbs)This page is about verbs in Hungarian grammar.-Lemma or citation form:There is basically only one pattern for verb endings, with predictable variations dependent on the phonological context....
.
- See also: Hungarian grammar (verbs)
Middle Hungarian
The first printed Hungarian bookBook
A book is a set or collection of written, printed, illustrated, or blank sheets, made of hot lava, paper, parchment, or other materials, usually fastened together to hinge at one side. A single sheet within a book is called a leaf or leaflet, and each side of a leaf is called a page...
was published in Kraków
Kraków
Kraków also Krakow, or Cracow , is the second largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in the Lesser Poland region, the city dates back to the 7th century. Kraków has traditionally been one of the leading centres of Polish academic, cultural, and artistic life...
in 1533, by Benedek Komjáti. The work's title is Az Szent Pál levelei magyar nyelven (In original spelling: Az zenth Paal leueley magyar nyeluen), i.e. The letters of Saint Paul in the Hungarian language. In the 17th century, the language was already very similar to its present-day form, although two of the past tenses were still used. German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
, Italian
Italian language
Italian is a Romance language spoken mainly in Europe: Italy, Switzerland, San Marino, Vatican City, by minorities in Malta, Monaco, Croatia, Slovenia, France, Libya, Eritrea, and Somalia, and by immigrant communities in the Americas and Australia...
and French
French language
French is a Romance language spoken as a first language in France, the Romandy region in Switzerland, Wallonia and Brussels in Belgium, Monaco, the regions of Quebec and Acadia in Canada, and by various communities elsewhere. Second-language speakers of French are distributed throughout many parts...
loans also appeared in the language by these years. Further Turkish words were borrowed during the Ottoman occupation
Ottoman Hungary
History of Ottoman Hungary refers to the history of parts of the Ottoman Empire situated in what today is Hungary, in the period from 1541 to 1699.-History:...
of much of Hungary between 1541 and 1699.
Modern Hungarian
In the late 18th century, the language was incapable of clearly expressing scientific concepts, and several writers found the vocabulary a bit scant for literary purposes. Thus, a group of writers, most notably Ferenc KazinczyFerenc Kazinczy
Ferenc Kazinczy was a Hungarian author, the most indefatigable agent in the regeneration of the Magyar language and literature at the end of the 18th and beginning of the 19th century...
, began to compensate for these imperfections. Some words were shortened (győzedelem > győzelem, 'triumph' or 'victory'); a number of dialect
Dialect
The term dialect is used in two distinct ways, even by linguists. One usage refers to a variety of a language that is a characteristic of a particular group of the language's speakers. The term is applied most often to regional speech patterns, but a dialect may also be defined by other factors,...
al words spread nationally (e. g. cselleng 'dawdle'); extinct words were reintroduced (dísz 'décor'); a wide range of expressions were coined using the various derivative suffixes; and some other, less frequently used methods of expanding the language were utilized. This movement was called the 'language reform
Language reform
Language reform is a type of language planning by massive change to a language. The usual tools of language reform are simplification and purification. Simplification makes the language easier to use by regularizing vocabulary and grammar...
' (Hungarian: nyelvújítás), and produced more than ten thousand words, many of which are used actively today. The reforms led to the installment of Hungarian as the official language over Latin in the multiethnic country in 1844.
The 19th and 20th centuries saw further standardization of the language, and differences between the mutually already comprehensible dialects gradually lessened. In 1920, by signing the Treaty of Trianon
Treaty of Trianon
The Treaty of Trianon was the peace agreement signed in 1920, at the end of World War I, between the Allies of World War I and Hungary . The treaty greatly redefined and reduced Hungary's borders. From its borders before World War I, it lost 72% of its territory, which was reduced from to...
, Hungary lost 71% of its territories, and along with these, 33% of the ethnic Hungarian population. Today, the language is official in Hungary, and regionally also in Romania, in Slovakia
Hungarians in Slovakia
Hungarians in Slovakia are the largest ethnic minority of the country, numbering 520,528 people or 9.7% of population . They are concentrated mostly in the southern part of the country, near the border with Hungary...
, and in Serbia
Hungarians in Vojvodina
Hungarians are the second largest ethnic group in the Vojvodina province in northern Serbia. According to the 2002 census, there are 290,207 ethnic Hungarians in Vojvodina who compose 14.28% of the provincial population. The number of ethnic Hungarians in the whole of Serbia is 293,299, and their...
.
History of the Hungarian language
Old Hungarian text sample
Hungarian
Latiatuc feleym zumtuchel mic vogmuc. yſa pur eſ chomuv uogmuc. Menyi miloſtben terumteve eleve miv iſemucut adamut. eſ odutta vola neki paradiſumut hazoa. Eſ mend paradiſumben uolov gimilcictul munda neki elnie. Heon tilutoa wt ig fa gimilce tvl. Ge mundoa neki meret nu eneyc. yſa ki nopun emdul oz gimilſtwl. halalnec halalaal holz. Hadlaua choltat terumteve iſtentul. ge feledeve. Engede urdung intetvinec. eſ evec oz tiluvt gimilſtwl. es oz gimilſben halalut evec. Eſ oz gimilſnek vvl keſeruv uola vize. hug turchucat mige zocoztia vola. Num heon muga nec. ge mend w foianec halalut evec. Horogu vec iſten. eſ veteve wt ez munkaſ vilagbele. eſ levn halalnec eſ poculnec feze. eſ mend w nemenec. Kic ozvc. miv vogmuc.
English
Ye see, my brethren, with your eyes, what we are! Behold, we are dust and ashes. Through His divine grace the Lord God first made our ancestor, Adam, and gave him the Paradise of Eden for his home. And of all the fruits of Paradise, He bade him live, forbidding to him only the fruit of one tree, yet telling him, why he should not eat of it: "Lo, on the day thou eatest of this fruit, thou shalt die the death of deaths." Adam had heard of his death from his Creator-God, yet he forgot. He yielded to the Devil’s allurement, and ate of the forbidden fruit, and in that fruit he partook of death. And so bitter was the juice of that fruit, it (almost?) burst their throats. Not only for himself, but for all his race he ate death. In anger, God cast him into this world of toil, and he became the nest of death and damnation, for all his kind. Who shalt be those? We are them.
See also
- Hungarian languageHungarian languageHungarian is a Uralic language, part of the Ugric group. With some 14 million speakers, it is one of the most widely spoken non-Indo-European languages in Europe....
- Hungarian literatureHungarian literatureHungarian literature is literature written in the Hungarian language, predominantly by Hungarians.There is a limited amount of Old Hungarian literature dating to between the late 12th and the early 16th centuries...
- Funeral Sermon and PrayerFuneral Sermon and PrayerThe Funeral Sermon and Prayer is the oldest known and surviving contiguous Hungarian text, written by one scribal hand in the Latin script and dating to 1192-1195...
- Old Hungarian 'Lamentations of Mary'Old Hungarian 'Lamentations of Mary'The Old Hungarian Lamentations of Mary is the oldest extant Hungarian poem, copied in about 1300 into a Latin codex, similarly to the first coherent written Hungarian text , which was written down between 1192 and 1195...
- HungaryHungaryHungary , officially the Republic of Hungary , is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The...
- History of HungaryHistory of HungaryHungary is a country in central Europe. Its history under this name dates to the early Middle Ages, when the Pannonian Basin was colonized by the Magyars, a semi-nomadic people from what is now central-northern Russia...
Reference works
- Molnár József—Simon Györgyi: Magyar nyelvemlékek. 3rd edition, Tankönyvkiadó, Budapest, 1980.
- Dr. Inczefi Géza: A magyar nyelv fejlődéstörténete. Typescript. Tankönyvkiadó, Budapest, 1969.
- Gáspár Heltai: Száz fabvla. Heltai Press, Kolozsvár, 1566.
- A magyar középkor története. Pannonica, 2006.
- Péter Ruffy: Bujdosó nyelvemlékeink. Móra Publishing, 1977.
External links
- http://multitree.org/codes/ohu.html

