
Old Hungarian script
Encyclopedia
The Old Hungarian script (in Hungarian
known as , or , ; for short also simply "notch, score") is an alphabet
ic writing system
used by the Hungarians before the Middle Ages
. Because it is reminiscent of the runic alphabet
, the Old Hungarian script has also popularly been called "Hungarian runes" or "Hungarian runic script".
When the Kingdom of Hungary
was established in AD 1000 and Christianity was adopted, the Latin alphabet
was adopted and the script fell into disuse. In remote regions of Transylvania
, however, the script remained in marginal use by the Székely
Magyars at least into the 17th century, giving it the name székely rovásírás.
The script is adapted to the phonology of the Hungarian language
, featuring letters for phoneme
s such as cs, gy, ly, ny, ö, sz, ty, ü, zs. The modern Hungarian alphabet represents these sounds with digraphs
(letter sequences used to write a single sound) and diacritics
.
The alphabet does not contain the letters for the phonemes dz, dzs of modern Hungarian
since these are relative recent developments in the language's history. The Latin letters q, w, x and y also do not have an equivalent as these do not stand for separate phonemes in Hungarian but are only used to spell foreign words.
 The Hungarian Runes are related to the Old Turkic script, itself probably (though debatedly) deriving from Aramaic script.
The Hungarian Runes are related to the Old Turkic script, itself probably (though debatedly) deriving from Aramaic script.
Speakers of Proto-Hungarian would have come into contact with Turkic peoples during the 7th or 8th century, in the context of the Turkic expansion, as is also evidenced by numerous Turkic loanwords in Proto-Hungarian.
All the letters but one for sounds which were shared by Turkic and Ancient Hungarian can be related to their Old Turkic counterparts. Most of the missing characters were derived by script internal extensions, rather than borrowings, but a small number of characters seem to derive from Greek, such as.png) 'eF'. T
'eF'. T
The modern Hungarian term for this special script (coined in the 19th century) rovás derives from the verb róni ('to score') which is derived from old Uralic
, general Hungarian terminology describing the technique of writing (írni 'to write', betű 'letter', bicska 'knife (also: for carving letters)') derive from Turkic, which supports the theory of transmission via Turks further.
The latter inscription was found on a fragment of a quiver
made of bone. Although there have been several attempts to interpret it, the meaning of it is still unclear.
In 1000, with the coronation of Stephen I of Hungary, Hungary (previously an alliance of mostly nomadic tribes) became a Kingdom
. The Latin alphabet
was adopted as official script, however Old Hungarian continued to be used vernacularly.
The runic script was first mentioned in the 13th century Chronicle of Simon of Kéza
, where he stated that the Székely
s may use the script of the Vlachs
, possibly making a confusion between the runes and Cyrillic script (as the Romanian Cyrillic alphabet
was used to write the Romanian language till 1860–1862 and remained in occasional use until ca. 1920): "... non tamen in plano Panonie, sed cum Blackis in montibus confinii sortem habuerunt, unde Blakis commixti litteris ipsorum uti perhibentur" (="...although not on the Pannonian Plain but among the borderland mountains along with the Vlachs [where] they mixed up with them and so allegedly they use their letters"). The earliest surviving copy of the actual alphabet was found is an incunabulum
from 1483, found at the library of the castle of Nikolsburg, now Mikulov
in Moravia
, hand-written onto the endpaper
of the printed book. This alphabet lists 35 letters and 15 ligatures with Latin transcriptions.
in several areas during this period.
In Royal Hungary
, Old Hungarian script was used less, although there are relics from this territory, too.
There is another copy – similar to the Nikolsburg Alphabet – of the Old Hungarian alphabet, dated 1609. The inscription from Énlaka, dated 1668, is an example of the "folk art use".
There are a number of inscriptions ranging from the 17th to the early 19th centuries, including examples from Kibéd
, Csejd, Makfalva
, Szokolma, Marosvásárhely, Csíkrákos
, Mezőkeresztes
, Nagybánya
, Torda
, Felsőszemeréd http://www.felvidek.ma/modules.php?name=News&file=article&sid=7929, Kecskemét
and Kiskunhalas
.
After 1850, with the spread of modern education and education in Latin orthography, Hungarian runic writing was all but extinguished.
/Baroque
scholarship, in 1598 by János Telegdi in his primer, "Rudimenta Priscae Hunnorum Linguae", where he presents his understanding of the script. It also contains Hungarian texts written with runes, for example, the Lord's Prayer
.
In the 19th century scholars began to research the rules and the other features of the Old Hungarian script. From this time the name rovásírás began to enter popular consciousness in Hungary, and script historians in other countries began to use the terms "Old Hungarian", "Altungarisch", and so on. Because the Old Hungarian script had been replaced by Latin, linguistic researchers in the 20th century had to reconstruct the alphabet from historic sources. Gyula Sebestyén, ethnographer, folklorist
and Gyula (Julius) Németh
, philologist, linguist, turcologist did the lion's share of this work. Sebestyén's publications, Rovás és rovásírás (Runes and runic writing, Budapest
, 1909) and A magyar rovásírás hiteles emlékei (The authentic relics of Hungarian runic writing, Budapest
, 1915) contain valuable information on the topic.
, particularly in the United States and Canada.
Old Hungarian has seen other usages in the modern period, sometimes in association with or referencing Hungarian neopaganism, similar to the way in which Norse neopagans
have taken up the Germanic runes
, and Celtic neopagans
have taken up Ogham
script for various purposes. The use of the script sometimes has a political undertone, as they can be found from time to time in graffiti with a variety of content.
Some of the findings include:
To gather information about the transliteration's pronunciation, see Hungarian alphabet
.

The Hungarian runes also include some non-alphabetical runes which are not ligatures but separate signs. These are called . Further research is needed to define their origin and traditional usage. Some examples:

which can be called "runiform".
Within the Carpathian Basin some of these scripts, which do constitute Old Hungarian, are e.g. the relic from Homokmégy
(of which a Scythian reading has been proposed), needle-box from Szarvas
(with Hungarian readings proposed), and most prominently the inscriptions of the Treasure of Nagyszentmiklós
, a precious golden hoard of unknown origin (various Hungarian, Turkic and Greek readings proposed).
While the Szarvas and the Nagyszentmiklós inscriptions share the same script, the Homokmégy finding is written in another.
Due to the polysemy of rovás, rovásírás which can be understood, and is also used, as 'runiform script', but is also commonly used as 'Old Hungarian Script', these scripts are often confused, and relics of the latter ones are often found cited among the OHS findings.
Quite confusingly, the numerals are often referred to as integral part of the script. The counting system existed independently of the Old Hungarian Script, it is probably of different origin.
style (alternating direction right to left and then left to right).
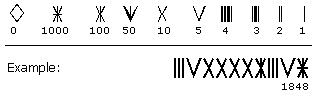 The numbers are almost the same as the Roman, Etruscan
The numbers are almost the same as the Roman, Etruscan
, and Chuvash numerals
. Numbers of livestock were carved on tally sticks and the sticks were then cut in two lengthwise to avoid later disputes.

Text from Csikszentmárton, 1501.
Runes originally written as ligatures are underlined.
Interpretation in old Hungarian
: "ÚRNaK SZÜLeTéSéTÜL FOGVÁN ÍRNaK eZeRÖTSZÁZeGY eSZTeNDŐBE MÁTYáS
JÁNOS eSTYTáN KOVÁCS CSINÁLTáK MÁTYáSMeSTeR GeRGeLYMeSTeRCSINÁLTÁK
G IJ A aS I LY LY LT A" (The letters actually written in the runic text are written with uppercase in the transcription.)
Interpretation in modern Hungarian: "(Ezt) az Úr születése utáni 1501. évben írták. Mátyás, János, István kovácsok csinálták. Mátyás mester (és) Gergely mester csinálták [uninterpretable]"
English
translation: "(This) was written in the 1501st year of our Lord. The smiths Matthias, John (and) Stephen did (this). Master Matthias (and) Master Gergely did [uninterpretable]"
range U+10C80..10CFF. A number of proposals for encoding the script, which differed in some regards from one another, were taken into consideration when the assignment was made:
A set of closely related 8-bit code pages exist. These are mapped to the Latin script with extensions. After installing one of them and applying their formatting to the document – because of the lack of capital letters – rovás characters could be entered in the following way: those letters which are unique letters in today's Hungarian orthography are virtually lowercase ones, and can be written by simply pressing the specific key; and since the modern digraphs equal to separate rovás letters, they were encoded as 'uppercase' letters, i.e. in the space originally restricted for capitals. Thus, typing a lowercase g will produce the rovas character for the sound marked with Latin script g, but entering an uppercase G will amount to a rovás sign equivalent to a digraph gy in Latin-based Hungarian orthography.
Hungarian language
Hungarian is a Uralic language, part of the Ugric group. With some 14 million speakers, it is one of the most widely spoken non-Indo-European languages in Europe....
known as , or , ; for short also simply "notch, score") is an alphabet
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letters—basic written symbols or graphemes—each of which represents a phoneme in a spoken language, either as it exists now or as it was in the past. There are other systems, such as logographies, in which each character represents a word, morpheme, or semantic...
ic writing system
Writing system
A writing system is a symbolic system used to represent elements or statements expressible in language.-General properties:Writing systems are distinguished from other possible symbolic communication systems in that the reader must usually understand something of the associated spoken language to...
used by the Hungarians before the Middle Ages
Middle Ages
The Middle Ages is a periodization of European history from the 5th century to the 15th century. The Middle Ages follows the fall of the Western Roman Empire in 476 and precedes the Early Modern Era. It is the middle period of a three-period division of Western history: Classic, Medieval and Modern...
. Because it is reminiscent of the runic alphabet
Runic alphabet
The runic alphabets are a set of related alphabets using letters known as runes to write various Germanic languages before the adoption of the Latin alphabet and for specialized purposes thereafter...
, the Old Hungarian script has also popularly been called "Hungarian runes" or "Hungarian runic script".
When the Kingdom of Hungary
Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary comprised present-day Hungary, Slovakia and Croatia , Transylvania , Carpatho Ruthenia , Vojvodina , Burgenland , and other smaller territories surrounding present-day Hungary's borders...
was established in AD 1000 and Christianity was adopted, the Latin alphabet
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
was adopted and the script fell into disuse. In remote regions of Transylvania
Transylvania
Transylvania is a historical region in the central part of Romania. Bounded on the east and south by the Carpathian mountain range, historical Transylvania extended in the west to the Apuseni Mountains; however, the term sometimes encompasses not only Transylvania proper, but also the historical...
, however, the script remained in marginal use by the Székely
Székely
The Székelys or Székely , sometimes also referred to as Szeklers , are a subgroup of the Hungarian people living mostly in the Székely Land, an ethno-cultural region in eastern Transylvania, Romania...
Magyars at least into the 17th century, giving it the name székely rovásírás.
The script is adapted to the phonology of the Hungarian language
Hungarian language
Hungarian is a Uralic language, part of the Ugric group. With some 14 million speakers, it is one of the most widely spoken non-Indo-European languages in Europe....
, featuring letters for phoneme
Phoneme
In a language or dialect, a phoneme is the smallest segmental unit of sound employed to form meaningful contrasts between utterances....
s such as cs, gy, ly, ny, ö, sz, ty, ü, zs. The modern Hungarian alphabet represents these sounds with digraphs
Digraph (orthography)
A digraph or digram is a pair of characters used to write one phoneme or a sequence of phonemes that does not correspond to the normal values of the two characters combined...
(letter sequences used to write a single sound) and diacritics
Diacritics
diacritics is a quarterly academic journal established in 1971 at Cornell University and published by the Johns Hopkins University Press. Articles serve to review recent literature in the field of literary criticism, and have covered topics in gender studies, political theory, psychoanalysis, queer...
.
The alphabet does not contain the letters for the phonemes dz, dzs of modern Hungarian
Hungarian language
Hungarian is a Uralic language, part of the Ugric group. With some 14 million speakers, it is one of the most widely spoken non-Indo-European languages in Europe....
since these are relative recent developments in the language's history. The Latin letters q, w, x and y also do not have an equivalent as these do not stand for separate phonemes in Hungarian but are only used to spell foreign words.
Origins

Speakers of Proto-Hungarian would have come into contact with Turkic peoples during the 7th or 8th century, in the context of the Turkic expansion, as is also evidenced by numerous Turkic loanwords in Proto-Hungarian.
All the letters but one for sounds which were shared by Turkic and Ancient Hungarian can be related to their Old Turkic counterparts. Most of the missing characters were derived by script internal extensions, rather than borrowings, but a small number of characters seem to derive from Greek, such as
.png)
The modern Hungarian term for this special script (coined in the 19th century) rovás derives from the verb róni ('to score') which is derived from old Uralic
Uralic languages
The Uralic languages constitute a language family of some three dozen languages spoken by approximately 25 million people. The healthiest Uralic languages in terms of the number of native speakers are Hungarian, Finnish, Estonian, Mari and Udmurt...
, general Hungarian terminology describing the technique of writing (írni 'to write', betű 'letter', bicska 'knife (also: for carving letters)') derive from Turkic, which supports the theory of transmission via Turks further.
Medieval Hungary
Epigraphic evidence for the use of the Old Hungarian script in medieval Hungary dates to the 10th century, for example, from HomokmégyHomokmégy
Homokmégy is a village and municipality in Bács-Kiskun county, in the Southern Great Plain region of southern Hungary.-Village history:Őrjeg raised from one-time branch of river Danube as a boundary of eastern land created a closed area, which probably is the same as 'Big island' written by...
The latter inscription was found on a fragment of a quiver
Quiver
A quiver is a container for arrows. Quivers have been traditionally made of leather, bark, wood, furs and other natural materials; modern quivers are often made of metal and plastic....
made of bone. Although there have been several attempts to interpret it, the meaning of it is still unclear.
In 1000, with the coronation of Stephen I of Hungary, Hungary (previously an alliance of mostly nomadic tribes) became a Kingdom
Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary comprised present-day Hungary, Slovakia and Croatia , Transylvania , Carpatho Ruthenia , Vojvodina , Burgenland , and other smaller territories surrounding present-day Hungary's borders...
. The Latin alphabet
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
was adopted as official script, however Old Hungarian continued to be used vernacularly.
The runic script was first mentioned in the 13th century Chronicle of Simon of Kéza
Simon of Kéza
Simon of Kéza was the most famous Hungarian chronicler in the 13th century. He was a priest in the royal court of king Ladislaus IV of Hungary....
, where he stated that the Székely
Székely
The Székelys or Székely , sometimes also referred to as Szeklers , are a subgroup of the Hungarian people living mostly in the Székely Land, an ethno-cultural region in eastern Transylvania, Romania...
s may use the script of the Vlachs
Vlachs
Vlach is a blanket term covering several modern Latin peoples descending from the Latinised population in Central, Eastern and Southeastern Europe. English variations on the name include: Walla, Wlachs, Wallachs, Vlahs, Olahs or Ulahs...
, possibly making a confusion between the runes and Cyrillic script (as the Romanian Cyrillic alphabet
Romanian Cyrillic alphabet
The Romanian Cyrillic alphabet was used to write the Romanian language before 1860–1862, when it was officially replaced by a Latin-based Romanian alphabet. Cyrillic remained in occasional use until circa 1920...
was used to write the Romanian language till 1860–1862 and remained in occasional use until ca. 1920): "... non tamen in plano Panonie, sed cum Blackis in montibus confinii sortem habuerunt, unde Blakis commixti litteris ipsorum uti perhibentur" (="...although not on the Pannonian Plain but among the borderland mountains along with the Vlachs [where] they mixed up with them and so allegedly they use their letters"). The earliest surviving copy of the actual alphabet was found is an incunabulum
Incunabulum
Incunable, or sometimes incunabulum is a book, pamphlet, or broadside, that was printed — not handwritten — before the year 1501 in Europe...
from 1483, found at the library of the castle of Nikolsburg, now Mikulov
Mikulov
Mikulov is a town in the South Moravian Region of the Czech Republic with a population of 7,608 . It is located directly on the border with Lower Austria. Mikulov is located at the edge of a hilly area and the three Nové Mlýny reservoirs...
in Moravia
Moravia
Moravia is a historical region in Central Europe in the east of the Czech Republic, and one of the former Czech lands, together with Bohemia and Silesia. It takes its name from the Morava River which rises in the northwest of the region...
, hand-written onto the endpaper
Endpaper
The endpapers or end-papers of a book are the leaves of paper before the title page and after the text. Booksellers sometimes refer to the front end paper as FEP....
of the printed book. This alphabet lists 35 letters and 15 ligatures with Latin transcriptions.
Early Modern period
The Old Hungarian script became part of folk artFolk art
Folk art encompasses art produced from an indigenous culture or by peasants or other laboring tradespeople. In contrast to fine art, folk art is primarily utilitarian and decorative rather than purely aesthetic....
in several areas during this period.
In Royal Hungary
Royal Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary between 1538 and 1867 was part of the lands of the Habsburg Monarchy, while outside the Holy Roman Empire.After Battle of Mohács, the country was ruled by two crowned kings . They divided the kingdom in 1538...
, Old Hungarian script was used less, although there are relics from this territory, too.
There is another copy – similar to the Nikolsburg Alphabet – of the Old Hungarian alphabet, dated 1609. The inscription from Énlaka, dated 1668, is an example of the "folk art use".
There are a number of inscriptions ranging from the 17th to the early 19th centuries, including examples from Kibéd
Chibed
Chibed is a commune in Mureş County, Romania, composed of a single village, Chibed. It lies in the Székely Land, an ethno-cultural region in eastern Transylvania...
, Csejd, Makfalva
Ghindari
Ghindari is a commune in Mureş County, Romania. It lies in the Székely Land, an ethno-cultural region in eastern Transylvania.- Component villages :The commune is composed of five villages:...
, Szokolma, Marosvásárhely, Csíkrákos
Racu
Racu is a commune in Harghita County, Romania. It lies in the Székely Land, an ethno-cultural region in eastern Transylvania.- Component villages :The commune is composed of two villages:- History :...
, Mezőkeresztes
Mezokeresztes
Mezőkeresztes is a town in Borsod-Abaúj-Zemplén county, Northern Hungary near Mezőkövesd and Eger.-Location: south from county seat Miskolc. Can be reached by car on highway M3. The train station Mezőkeresztes–Mezőnyárád is away from the town itself, towards Mezőnyárád.-History:The area around it...
, Nagybánya
Baia Mare
Baia Mare is a municipality in northwestern Romania and the capital of Maramureş County. The city is situated about 600 kilometres from Bucharest, the capital of Romania, 70 kilometres from the border with Hungary and 50 kilometres from the border with Ukraine...
, Torda
Turda
Turda is a city and Municipality in Cluj County, Romania, situated on the Arieş River.- Ancient times :The city was founded by Dacians under the name Patavissa or Potaissa...
, Felsőszemeréd http://www.felvidek.ma/modules.php?name=News&file=article&sid=7929, Kecskemét
Kecskemét
Kecskemét is a city in the central part of Hungary. It is the 8th largest city of the country, and the county seat of Bács-Kiskun.Kecskemét lies halfway between the capital Budapest and the country's third-largest city, Szeged, 86 kilometres from both of them and almost equal distance from the two...
and Kiskunhalas
Kiskunhalas
- Railroad :The city is an important railway junction. It crosses the Budapest-Subotica-Belgrade railway line. The Kiskunfélegyháza railway ends in Kiskunhalas.- Name :...
.
After 1850, with the spread of modern education and education in Latin orthography, Hungarian runic writing was all but extinguished.
Scholarly discussion
Hungarian script was first described in late HumanistRenaissance humanism
Renaissance humanism was an activity of cultural and educational reform engaged by scholars, writers, and civic leaders who are today known as Renaissance humanists. It developed during the fourteenth and the beginning of the fifteenth centuries, and was a response to the challenge of Mediæval...
/Baroque
Baroque
The Baroque is a period and the style that used exaggerated motion and clear, easily interpreted detail to produce drama, tension, exuberance, and grandeur in sculpture, painting, literature, dance, and music...
scholarship, in 1598 by János Telegdi in his primer, "Rudimenta Priscae Hunnorum Linguae", where he presents his understanding of the script. It also contains Hungarian texts written with runes, for example, the Lord's Prayer
Lord's Prayer
The Lord's Prayer is a central prayer in Christianity. In the New Testament of the Christian Bible, it appears in two forms: in the Gospel of Matthew as part of the discourse on ostentation in the Sermon on the Mount, and in the Gospel of Luke, which records Jesus being approached by "one of his...
.
In the 19th century scholars began to research the rules and the other features of the Old Hungarian script. From this time the name rovásírás began to enter popular consciousness in Hungary, and script historians in other countries began to use the terms "Old Hungarian", "Altungarisch", and so on. Because the Old Hungarian script had been replaced by Latin, linguistic researchers in the 20th century had to reconstruct the alphabet from historic sources. Gyula Sebestyén, ethnographer, folklorist
Folkloristics
Folkloristics is the formal academic study of folklore. The term derives from a nineteenth century German designation of folkloristik to distinguish between folklore as the content and folkloristics as its study, much as language is distinguished from linguistics...
and Gyula (Julius) Németh
Gyula Németh
Gyula Németh is a retired Hungarian high jumper.He finished fourteenth at the 1983 European Indoor Championships, and eighth at the 1988 European Indoor Championships. He became Hungarian high jump champion in 1986 and 1989....
, philologist, linguist, turcologist did the lion's share of this work. Sebestyén's publications, Rovás és rovásírás (Runes and runic writing, Budapest
Budapest
Budapest is the capital of Hungary. As the largest city of Hungary, it is the country's principal political, cultural, commercial, industrial, and transportation centre. In 2011, Budapest had 1,733,685 inhabitants, down from its 1989 peak of 2,113,645 due to suburbanization. The Budapest Commuter...
, 1909) and A magyar rovásírás hiteles emlékei (The authentic relics of Hungarian runic writing, Budapest
Budapest
Budapest is the capital of Hungary. As the largest city of Hungary, it is the country's principal political, cultural, commercial, industrial, and transportation centre. In 2011, Budapest had 1,733,685 inhabitants, down from its 1989 peak of 2,113,645 due to suburbanization. The Budapest Commuter...
, 1915) contain valuable information on the topic.
Popular revival
Beginning with Adorján Magyar in 1915, the script has been promulgated as a means for writing modern Hungarian. These groups approached the question of representation of the vowels of modern Hungarian in different ways. Adorján Magyar made use of characters to distinguish a/á and e/é but did not distinguish the other vowels by length. A school led by Sándor Forrai from 1974 onward did also distinguish i/í, o/ó, ö/ő, u/ú, and ü/ű. The revival has become part of significant ideological nationalist subculture not only in Hungary (largely centered in Budapest), but also amongst the Hungarian diasporaHungarian diaspora
Hungarian diaspora is a term that encompasses the total ethnic Hungarian population located outside of current-day Hungary.There are two main groups of the diaspora...
, particularly in the United States and Canada.
Old Hungarian has seen other usages in the modern period, sometimes in association with or referencing Hungarian neopaganism, similar to the way in which Norse neopagans
Ásatrú
is a form of Germanic neopaganism which developed in the United States from the 1970s....
have taken up the Germanic runes
Runic alphabet
The runic alphabets are a set of related alphabets using letters known as runes to write various Germanic languages before the adoption of the Latin alphabet and for specialized purposes thereafter...
, and Celtic neopagans
Celtic Neopaganism
Celtic Neopaganism refers to Neopagan movements based on Celtic polytheism.-Types of Celtic Neopaganism:*Neo-druidism, grew out of the Celtic revival in 18th century Romanticism....
have taken up Ogham
Ogham
Ogham is an Early Medieval alphabet used primarily to write the Old Irish language, and occasionally the Brythonic language. Ogham is sometimes called the "Celtic Tree Alphabet", based on a High Medieval Bríatharogam tradition ascribing names of trees to the individual letters.There are roughly...
script for various purposes. The use of the script sometimes has a political undertone, as they can be found from time to time in graffiti with a variety of content.
Epigraphy
In the latter part of the 20th century, several new rovás and rovás-like inscriptions were found. For rovás-like see the section "Confusion" below.Some of the findings include:
- A labeled crest etched into stone from PécsPécsPécs is the fifth largest city of Hungary, located on the slopes of the Mecsek mountains in the south-west of the country, close to its border with Croatia. It is the administrative and economical centre of Baranya county...
, late 13th century (Label: aBA SZeNTjeI vaGYUNK aKI eSZTeR ANna erZSéBeT; We are the saints [nuns] of AbaAba, HungaryAba is a village in Fejér county, Hungary.In 1559 it was property of Mihály Cseszneky and Balázs Baranyai.-Sources:* Szíj Rezső: Várpalota* Fejér megyei történeti évkönyv* Hofkammerarchiv Wien*...
; who are Esther, Anna and Elizabeth.) - Runic stick calendar, around 1300, copied by Luigi Ferdinando MarsigliLuigi Ferdinando MarsigliCount Luigi Ferdinando Marsigli , was an Italian soldier and naturalist.He was born in Bologna. He was a member of an old patrician family and was educated in accordance with his rank...
in 1690. It contains several feasts and names, thus it is one of the most extensive runic records. - Nicholsburg alphabet
- Runic record in IstanbulIstanbulIstanbul , historically known as Byzantium and Constantinople , is the largest city of Turkey. Istanbul metropolitan province had 13.26 million people living in it as of December, 2010, which is 18% of Turkey's population and the 3rd largest metropolitan area in Europe after London and...
, 1515. - SzékelyderzsDârjiuDârjiu is a commune in Harghita County, Romania. It lies in the Székely Land, an ethno-cultural region in eastern Transylvania.The toponym "Székelyderzs" was first mentioned as "De ers" in a papal list of tithes taken in 1334...
: a brick with runic inscription, found in the Unitarian church - Énlaka: runic inscription, discovered by Balázs Orbán in 1864. (photo)
- Székelydálya: runic inscription, found in the Calvinist church
- The inscription from Felsőszemeréd (Horné SemerovceHorné SemerovceHorné Semerovce is a village and municipality in the Levice District in the Nitra Region of Slovakia.-Geography:The village lies at an altitude of 134 metres and covers an area of 10.09 km²...
), SlovakiaSlovakiaThe Slovak Republic is a landlocked state in Central Europe. It has a population of over five million and an area of about . Slovakia is bordered by the Czech Republic and Austria to the west, Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east and Hungary to the south...
(15th century)
Characters
The runic alphabet includes 42 letters. Some consonants have two forms, for example, aS and eS. The 'a' form should be written after vowels a, á, o, ó, u, ú, while the 'e' form after e, ë, é, i, í, ö, ő, ü, ű.To gather information about the transliteration's pronunciation, see Hungarian alphabet
Hungarian alphabet
The Hungarian alphabet is an extension of the Latin alphabet used for writing the Hungarian language.One sometimes speaks of the smaller and greater Hungarian alphabets, depending on whether or not the letters Q, W, X, Y are listed, which can only be found in foreign words and traditional...
.

The Hungarian runes also include some non-alphabetical runes which are not ligatures but separate signs. These are called . Further research is needed to define their origin and traditional usage. Some examples:

Confusion
In the region north of the Caucasus, west of the Ural mountains up to the Carpathian Basin several related, though different, yet undeciphered scripts exist. All of them feature characteristics in ductusDuctus (linguistics)
In linguistics, ductus refers to qualities and characteristics of writing or speaking instantiated in the act of speaking or the flow of writing the text...
which can be called "runiform".
Within the Carpathian Basin some of these scripts, which do constitute Old Hungarian, are e.g. the relic from Homokmégy
Homokmégy
Homokmégy is a village and municipality in Bács-Kiskun county, in the Southern Great Plain region of southern Hungary.-Village history:Őrjeg raised from one-time branch of river Danube as a boundary of eastern land created a closed area, which probably is the same as 'Big island' written by...
(of which a Scythian reading has been proposed), needle-box from Szarvas
Szarvas
----Szarvas is a town in Békés county in southeastern Hungary. The Hungarian placename Szarvas means 'deer' in English.- History :...
(with Hungarian readings proposed), and most prominently the inscriptions of the Treasure of Nagyszentmiklós
Treasure of Nagyszentmiklós
The Treasure of Nagyszentmiklós or Treasure of Sânnicolau Mare is an important hoard of twenty-three early medieval gold vessels, in total weighing 9.945 kg, found in 1799 near the town then known as Nagy Szent Miklós or Groß-Sankt-Niklaus in northern Banat The Treasure of Nagyszentmiklós or...
, a precious golden hoard of unknown origin (various Hungarian, Turkic and Greek readings proposed).
While the Szarvas and the Nagyszentmiklós inscriptions share the same script, the Homokmégy finding is written in another.
Due to the polysemy of rovás, rovásírás which can be understood, and is also used, as 'runiform script', but is also commonly used as 'Old Hungarian Script', these scripts are often confused, and relics of the latter ones are often found cited among the OHS findings.
Quite confusingly, the numerals are often referred to as integral part of the script. The counting system existed independently of the Old Hungarian Script, it is probably of different origin.
Features
Old Hungarian letters were usually written from right to left on sticks. Later, in Transylvania, they appeared on several media. Writings on walls also were right to left and not boustrophedonBoustrophedon
Boustrophedon , is a type of bi-directional text, mostly seen in ancient manuscripts and other inscriptions. Every other line of writing is flipped or reversed, with reversed letters. Rather than going left-to-right as in modern English, or right-to-left as in Arabic and Hebrew, alternate lines in...
style (alternating direction right to left and then left to right).
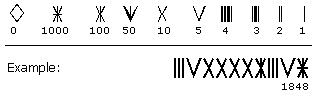
Etruscan numerals
The Etruscan numerals were used by the ancient Etruscans. The system was adapted from the Greek Attic numerals and formed the inspiration for the later Roman numerals.There is very little surviving evidence of these numerals...
, and Chuvash numerals
Chuvash numerals
Chuvash numerals is an ancient numeral system the Chuvash people used. Those numerals originate from finger numeration. They look like Roman numerals, but larger numerals stay at the right side. It was possible to carve those numerals on wood. In some cases numerals were preserved until the...
. Numbers of livestock were carved on tally sticks and the sticks were then cut in two lengthwise to avoid later disputes.
- Ligatures are common. (Note: the Hungarian runic script employed a number of ligatures. In some cases, an entire word was written with a single sign.)
- There are no lower or upper case letters, but the first letter of a proper name was often written a bit larger.
- The did not always mark vowels. The rules for vowel inclusion were as follows:
- If there are two vowels side by side, both have to be written, unless the second could be readily determined.
- The vowels have to be written if their omission created ambiguity. (Example: –
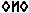 can be interpreted as –
can be interpreted as – 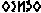 [wheel] and –
[wheel] and – 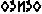 [rounded], thus the writer had to include the vowels to differentiate the intended words.)
[rounded], thus the writer had to include the vowels to differentiate the intended words.) - The vowel at the end of the word must be written.
- Sometimes, especially when writing consonant clusters, a consonant was omitted. This is however rather a phonologic process, the script reflecting the exact surface realisation.
Text example

Text from Csikszentmárton, 1501.
Runes originally written as ligatures are underlined.
Interpretation in old Hungarian
Hungarian language
Hungarian is a Uralic language, part of the Ugric group. With some 14 million speakers, it is one of the most widely spoken non-Indo-European languages in Europe....
: "ÚRNaK SZÜLeTéSéTÜL FOGVÁN ÍRNaK eZeRÖTSZÁZeGY eSZTeNDŐBE MÁTYáS
JÁNOS eSTYTáN KOVÁCS CSINÁLTáK MÁTYáSMeSTeR GeRGeLYMeSTeRCSINÁLTÁK
G IJ A aS I LY LY LT A" (The letters actually written in the runic text are written with uppercase in the transcription.)
Interpretation in modern Hungarian: "(Ezt) az Úr születése utáni 1501. évben írták. Mátyás, János, István kovácsok csinálták. Mátyás mester (és) Gergely mester csinálták [uninterpretable]"
English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
translation: "(This) was written in the 1501st year of our Lord. The smiths Matthias, John (and) Stephen did (this). Master Matthias (and) Master Gergely did [uninterpretable]"
Unicode
Old Hungarian has been provisionally assigned the UnicodeUnicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
range U+10C80..10CFF. A number of proposals for encoding the script, which differed in some regards from one another, were taken into consideration when the assignment was made:
- Hungarian Runic/Szekely-Hungarian Rovas Ad-hoc Committee: Hungarian Runic/Sekely-Hungarian Rovas Ad-hoc Report, 2011-06-08
- Gábor Hosszú: Issues of encoding the Rovas scripts, 2011-05-25
- Gábor Hosszú: Comments on encoding the Rovas scripts, 2011-05-22
- Gábor Hosszú: Revised proposal for encoding the Szekely-Hungarian Rovas script in the SMP of the UCS, 2011-05-21
- Gábor Hosszú: Notes on the Szekely-Hungarian Rovas script, 2011-05-15
- Michael EversonMichael EversonMichael Everson is a linguist, script encoder, typesetter, and font designer. His central area of expertise is with writing systems of the world, specifically in the representation of these systems in formats for computer and digital media...
& André Szabolcs Szelp: Mapping between Hungarian Runic proposals in N3697 and N4007, 2011-05-08 - Deborah Anderson: Comparison of Hungarian Runic and Szekely‐Hungarian Rovas proposals, 2011-05-07
- Deborah Anderson: Outstanding Issues on Old Hungarian/Szekler‐Hungarian Rovas/Hungarian Native Writing, 2009-04-22
- Michael EversonMichael EversonMichael Everson is a linguist, script encoder, typesetter, and font designer. His central area of expertise is with writing systems of the world, specifically in the representation of these systems in formats for computer and digital media...
: Mapping between Old Hungarian proposals in N3531, N3527, and N3526, 2008-11-02 - Michael EversonMichael EversonMichael Everson is a linguist, script encoder, typesetter, and font designer. His central area of expertise is with writing systems of the world, specifically in the representation of these systems in formats for computer and digital media...
and Szabolcs Szelp: Revised proposal for encoding the Old Hungarian script in the UCS = Javított előterjesztés a rovásírás Egyetemes Betűkészlet-beli kódolására), 2008-10-12 - Gábor Hosszú: Proposal for encoding the Szekler-Hungarian Rovas in the BMP and the SMP of the UCS, 2008-10-04
- Gábor Bakonyi: Hungarian native writing draft proposal, 2008-09-30
- Michael EversonMichael EversonMichael Everson is a linguist, script encoder, typesetter, and font designer. His central area of expertise is with writing systems of the world, specifically in the representation of these systems in formats for computer and digital media...
and Szabolcs Szelp: Preliminary proposal for encoding the Old Hungarian script in the UCS, 2008-08-04 - Michael EversonMichael EversonMichael Everson is a linguist, script encoder, typesetter, and font designer. His central area of expertise is with writing systems of the world, specifically in the representation of these systems in formats for computer and digital media...
: On encoding the Old Hungarian rovásírás in the UCS, 1998-05-02 - Michael EversonMichael EversonMichael Everson is a linguist, script encoder, typesetter, and font designer. His central area of expertise is with writing systems of the world, specifically in the representation of these systems in formats for computer and digital media...
: Draft Proposal to encode Old Hungarian in Plane 1 of ISO/IEC 10646-2, 1998-01-18 - Varga Géza: The origins of Hunnish Runic Writing
- Varga Géza: The Writing of Eden
- Varga Géza: Szekler rovas script Unicode
A set of closely related 8-bit code pages exist. These are mapped to the Latin script with extensions. After installing one of them and applying their formatting to the document – because of the lack of capital letters – rovás characters could be entered in the following way: those letters which are unique letters in today's Hungarian orthography are virtually lowercase ones, and can be written by simply pressing the specific key; and since the modern digraphs equal to separate rovás letters, they were encoded as 'uppercase' letters, i.e. in the space originally restricted for capitals. Thus, typing a lowercase g will produce the rovas character for the sound marked with Latin script g, but entering an uppercase G will amount to a rovás sign equivalent to a digraph gy in Latin-based Hungarian orthography.
Hungarian
(New Hungarian Encyclopaedia) - Akadémiai Kiadó, Budapest, 1962. (Volume 5) ISBN 963-05-2808-8- Gyula Sebestyén: , Budapest, 1915.
- István Fodor - György Diószegi - László Legeza: . (On the scent of our ancestors) - Magyar Könyvklub-Helikon Kiadó, Budapest, 1996. ISBN 963-208-400-4 (Page 82)
- Dóra Tóth-Károly Bera: Honfoglalás és őstörténet. Aquila, Budapest, 1996. ISBN 963-8276-96-7
- Kiszely István: A magyar nép õstörténete
English
- Dr. Edward D. Rockstein: "The Mystery of the Székely Runes", Epigraphic Society Occasional Papers, Vol. 19, 1990, pp. 176–183.
Latin
- J. Thelegdi: , Batavia, 1598.

