Peptic ulcer
Encyclopedia
A peptic ulcer, also known as PUD or peptic ulcer disease, is the most common ulcer of an area of the gastrointestinal tract
that is usually acidic and thus extremely painful. It is defined as mucosal erosions equal to or greater than 0.5 cm. As many as 70–90% of such ulcers are associated with Helicobacter pylori
, a spiral-shaped bacterium that lives in the acidic environment of the stomach; however, only 40% of those cases go to a doctor. Ulcers can also be caused or worsened by drugs such as aspirin
, Plavix (clopidogrel), ibuprofen
, and other NSAIDs.
Contrary to general belief, four times as many peptic ulcers arise in the duodenum
—the first part of the small intestine
, just after the stomach—rather than in the stomach
itself. About 4% of stomach ulcers are caused by a malignant
tumor, so multiple biopsies are needed to exclude cancer. Duodenal ulcers are generally benign
.
Modified Johnson Classification of peptic ulcers:
A history of heartburn
, gastroesophageal reflux disease
(GERD) and use of certain forms of medication can raise the suspicion for peptic ulcer. Medicines associated with peptic ulcer include NSAID (non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs) that inhibit cyclooxygenase
, and most glucocorticoid
s (e.g. dexamethasone
and prednisolone
).
In patients over 45 with more than two weeks of the above symptoms, the odds for peptic ulceration are high enough to warrant rapid investigation by EGD (see below).
The timing of the symptoms in relation to the meal may differentiate between gastric and duodenal ulcers: A gastric ulcer would give epigastric pain during the meal, as gastric acid
production is increased as food enters the stomach. Symptoms of duodenal ulcers would initially be relieved by a meal, as the pyloric sphincter closes to concentrate the stomach contents, therefore acid is not reaching the duodenum. Duodenal ulcer pain would manifest mostly 2–3 hours after the meal, when the stomach begins to release digested food and acid into the duodenum
.
Also, the symptoms of peptic ulcers may vary with the location of the ulcer and the patient's age. Furthermore, typical ulcers tend to heal and recur and as a result the pain may occur for few days and weeks and then wane or disappear. Usually, child
ren and the elderly do not develop any symptoms unless complications have arisen.
Burning or gnawing feeling in the stomach area lasting between 30 minutes and 3 hours commonly accompanies ulcers. This pain can be misinterpreted as hunger
, indigestion or heartburn
. Pain is usually caused by the ulcer but it may be aggravated by the stomach acid when it comes into contact with the ulcerated area. The pain caused by peptic ulcers can be felt anywhere from the navel up to the sternum, it may last from few minutes to several hours and it may be worse when the stomach is empty. Also, sometimes the pain may flare at night and it can commonly be temporarily relieved by eating foods that buffer stomach acid or by taking anti-acid medication. However, peptic ulcer disease symptoms may be different for every sufferer.
due to Helicobacter pylori
that colonizes
the antral
mucosa . The immune system is unable to clear the infection, despite the appearance of antibodies. Thus, the bacterium can cause a chronic active gastritis
(type B gastritis), resulting in a defect in the regulation of gastrin
production by that part of the stomach, and gastrin secretion can either be increased, or as in most cases, decreased, resulting in hypo- or achlorhydria
. Gastrin
stimulates the production of gastric acid
by parietal cells and, in H. pylori colonization responses that increase gastrin, the increase in acid can contribute to the erosion of the mucosa and therefore ulcer formation.
Another major cause is the use of NSAIDs (see above). The gastric mucosa protects itself from gastric acid
with a layer of mucus, the secretion of which is stimulated by certain prostaglandins. NSAIDs block the function of cyclooxygenase
1 (cox-1), which is essential for the production of these prostaglandins. COX-2 selective anti-inflammatories (such as celecoxib
or the since withdrawn rofecoxib
) preferentially inhibit cox-2, which is less essential in the gastric mucosa, and roughly halve the risk of NSAID-related gastric ulceration. As the prevalence of H. pylori-caused ulceration declines in the Western world due to increased medical treatment, a greater proportion of ulcers will be due to increasing NSAID use among individuals with pain syndromes as well as the growth of aging populations that develop arthritis.
The incidence of duodenal ulcers has dropped significantly during the last 30 years, while the incidence of gastric ulcers has shown a small increase, mainly caused by the widespread use of NSAIDs. The drop in incidence is considered to be a cohort-phenomenon independent of the progress in treatment of the disease. The cohort-phenomenon is probably explained by improved standards of living which has lowered the incidence of H. pylori infections.
Although some studies have found correlations between smoking and ulcer formation, others have been more specific in exploring the risks involved and have found that smoking by itself may not be much of a risk factor unless associated with H. pylori infection.Kurata 1997 explains that "Data in Fig. 8 indicate that 89% of all serious upper GI disease can be accounted for by NSAIDs and H. pylori, with cigarette smoking acting as a synergistic co-factor."(14) Some suggested risk factors such as diet
, spice
consumption and blood type
, were hypothesized as ulcerogens (helping cause ulcers) until late in the 20th century, but have been shown to be of relatively minor importance in the development of peptic ulcers. Similarly, while studies have found that alcohol consumption increases risk when associated with H. pylori infection, it does not seem to independently increase risk, and even when coupled with H. pylori infection, the increase is modest in comparison to the primary risk factor.Sonnenberg in his study cautiously concludes that, among other potential factors that were found to correlate to ulcer healing, "moderate alcohol intake might [also] favor ulcer healing." (p. 1066)
Gastrinoma
s (Zollinger Ellison syndrome), rare gastrin-secreting tumors, also cause multiple and difficult-to-heal ulcers.
and head trauma, however, can lead to physiologic stress ulcer
s, which are reported in many patients who are on mechanical ventilation
.
An expert panel convened by the Academy of Behavioral Medicine Research concluded that ulcers are not purely an infectious disease
and that psychological factors do play a significant role. Researchers are examining how stress might promote H. pylori infection. For example, Helicobacter pylori thrives in an acidic environment, and stress has been demonstrated to cause the production of excess stomach acid. This was supported by a study on mice showing that both long-term water-immersion-restraint stress and H. pylori infection were independently associated with the development of peptic ulcers.
A study of peptic ulcer patients in a Thai hospital showed that chronic stress was strongly associated with an increased risk of peptic ulcer, and a combination of chronic stress and irregular mealtimes was a significant risk factor.
Confirmation of the diagnosis is made with the help of tests such as endoscopies or barium contrast x-rays. The tests are typically ordered if the symptoms do not resolve after a few weeks of treatment, or when they first appear in a person who is over age 45 or who has other symptoms such as weight loss
, because stomach cancer
can cause similar symptoms. Also, when severe ulcers resist treatment, particularly if a person has several ulcers or the ulcers are in unusual places, a doctor may suspect an underlying condition that causes the stomach to overproduce acid
.
An esophagogastroduodenoscopy
(EGD), a form of endoscopy
, also known as a gastroscopy, is carried out on patients in whom a peptic ulcer is suspected. By direct visual identification, the location and severity of an ulcer can be described. Moreover, if no ulcer is present, EGD can often provide an alternative diagnosis.
One of the reasons that blood tests are not reliable for accurate peptic ulcer diagnosis on their own is their inability to differentiate between past exposure to the bacteria and current infection. Additionally, a false negative result is possible with a blood test if the patient has recently been taking certain drugs, such as antibiotics or proton pump inhibitors.
The diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori
can be made by:
The breath test uses radioactive carbon atom to detect H. pylori. To perform this exam the patient will be asked to drink a tasteless liquid which contains the carbon as part of the substance that the bacteria breaks down. After an hour, the patient will be asked to blow into a bag that is sealed. If the patient is infected with H. pylori, the breath sample will contain radioactive carbon dioxide
. This test provides the advantage of being able to monitor the response to treatment used to kill the bacteria.
The possibility of other causes of ulcers, notably malignancy (gastric cancer) needs to be kept in mind. This is especially true in ulcers of the greater (large) curvature of the stomach
; most are also a consequence of chronic H. pylori infection.
If a peptic ulcer perforates, air will leak from the inside of the gastrointestinal tract (which always contains some air) to the peritoneal cavity (which normally never contains air). This leads to "free gas" within the peritoneal cavity. If the patient stands erect, as when having a chest X-ray, the gas will float to a position underneath the diaphragm. Therefore, gas in the peritoneal cavity, shown on an erect chest X-ray or supine lateral abdominal X-ray, is an omen of perforated peptic ulcer disease.
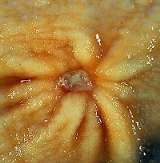
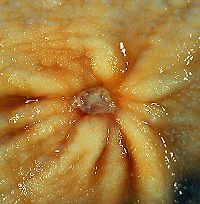 Gastric ulcers are most often localized on the lesser curvature of the stomach. The ulcer is a round to oval parietal defect ("hole"), 2 to 4 cm diameter, with a smooth base and perpendicular borders. These borders are not elevated or irregular in the acute form of peptic ulcer, regular but with elevated borders and inflammatory surrounding in the chronic form. In the ulcerative form of gastric cancer the borders are irregular. Surrounding mucosa may present radial folds, as a consequence of the parietal scarring.
Gastric ulcers are most often localized on the lesser curvature of the stomach. The ulcer is a round to oval parietal defect ("hole"), 2 to 4 cm diameter, with a smooth base and perpendicular borders. These borders are not elevated or irregular in the acute form of peptic ulcer, regular but with elevated borders and inflammatory surrounding in the chronic form. In the ulcerative form of gastric cancer the borders are irregular. Surrounding mucosa may present radial folds, as a consequence of the parietal scarring.
and muscularis propria, produced by acid-pepsin aggression. Ulcer margins are perpendicular and present chronic gastritis. During the active phase, the base of the ulcer shows 4 zones: inflammatory exudate, fibrinoid necrosis, granulation tissue and fibrous tissue. The fibrous base of the ulcer may contain vessels with thickened wall or with thrombosis.
s or H2 antagonists before EGD is undertaken. Bismuth compounds
may actually reduce or even clear organisms , though the warning labels of some bismuth subsalicylate products indicate that the product should not be used by someone with an ulcer.
Patients who are taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs) may also be prescribed a prostaglandin
analogue
(Misoprostol
) in order to help prevent peptic ulcers, which may be a side-effect
of the NSAIDs.
When H. pylori infection is present, the most effective treatments are combinations of 2 antibiotics (e.g. Clarithromycin
, Amoxicillin
, Tetracycline, Metronidazole
) and 1 proton pump inhibitor
(PPI), sometimes together with a bismuth compound. In complicated, treatment-resistant cases, 3 antibiotics (e.g. amoxicillin + clarithromycin + metronidazole) may be used together with a PPI and sometimes with bismuth compound. An effective first-line therapy for uncomplicated cases would be Amoxicillin
+ Metronidazole
+ Pantoprazole
(a PPI). In the absence of H. pylori, long-term higher dose PPIs are often used.
Treatment of H. pylori usually leads to clearing of infection, relief of symptoms and eventual healing of ulcers. Recurrence of infection can occur and retreatment may be required, if necessary with other antibiotics. Since the widespread use of PPI's in the 1990s, surgical procedures (like "highly selective vagotomy
") for uncomplicated peptic ulcers became obsolete.
Perforated peptic ulcer is a surgical emergency and requires surgical repair of the perforation. Most bleeding ulcers require endoscopy urgently to stop bleeding with cautery, injection, or clipping
.
Ranitidine
provides relief of peptic ulcers, heartburn, indigestion and excess stomach acid and prevention of these symptoms associated with excessive consumption of food and drink. Ranitidine is available over the counter from a pharmacy and works by decreasing the amount of acid the stomach produces allowing healing of ulcers. Zantac tablets contain Ranitidine 150 mg as the active ingredient which can also be bought generically.
Sucralfate
, (Carafate) has also been a successful treatment of peptic ulcers.
In Western countries the prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infections roughly matches age (i.e., 20% at age 20, 30% at age 30, 80% at age 80 etc.). Prevalence is higher in third world countries. Transmission is by food, contaminated groundwater, and through human saliva (such as from kissing or sharing food utensils).
A minority of cases of H. pylori infection will eventually lead to an ulcer and a larger proportion of people will get non-specific discomfort, abdominal pain or gastritis.
Peptic ulcer disease had a tremendous effect on morbidity and mortality until the last decades of the 20th century, when epidemiological trends started to point to an impressive fall in its incidence. The reason that the rates of peptic ulcer disease decreased is thought to be the development of new effective medication and acid suppressants and the discovery of the cause of the condition, H. pylori.
In the United States
about 4 million people have active peptic ulcers and about 350,000 new cases are diagnosed each year. Four times as many duodenal ulcers as gastric ulcers are diagnosed. Approximately 3,000 deaths per year in the United States are due to duodenal ulcer and 3,000 to gastric ulcer.
, a general practitioner
in Greece
, treated patients for peptic ulcer disease with antibiotics, beginning in 1958, long before it was commonly recognized that bacteria
were a dominant cause for the disease.
Helicobacter pylori
was rediscovered in 1982 by two Australia
n scientists, Robin Warren
and Barry J. Marshall
as a causative factor for ulcers. In their original paper, Warren and Marshall contended that most stomach ulcers and gastritis were caused by colonization with this bacterium, not by stress
or spicy food as had been assumed before.
The H. pylori
hypothesis was poorly received, so in an act of self-experimentation Marshall drank a Petri dish
containing a culture of organisms extracted from a patient and five days later developed gastritis. His symptoms disappeared after two weeks, but he took antibiotics to kill the remaining bacteria at the urging of his wife, since halitosis
is one of the symptoms of infection. This experiment was published in 1984 in the Australian Medical Journal and is among the most cited articles from the journal.
In 1997, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
, with other government agencies, academic institutions, and industry, launched a national education campaign to inform health care providers and consumers about the link between H. pylori and ulcers. This campaign reinforced the news that ulcers are a curable infection, and that health can be greatly improved and money saved by disseminating information about H. pylori.
In 2005, the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm
awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
to Dr. Marshall and his long-time collaborator Dr. Warren "for their discovery of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and its role in gastritis
and peptic ulcer disease." Professor Marshall continues research related to H. pylori and runs a molecular biology lab at UWA
in Perth, Western Australia.
Some believed that mastic gum, a tree resin extract, actively eliminates the H. pylori bacteria. However, multiple subsequent studies have found no effect of using mastic gum on reducing H. pylori levels.
Gastrointestinal tract
The human gastrointestinal tract refers to the stomach and intestine, and sometimes to all the structures from the mouth to the anus. ....
that is usually acidic and thus extremely painful. It is defined as mucosal erosions equal to or greater than 0.5 cm. As many as 70–90% of such ulcers are associated with Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori , previously named Campylobacter pyloridis, is a Gram-negative, microaerophilic bacterium found in the stomach. It was identified in 1982 by Barry Marshall and Robin Warren, who found that it was present in patients with chronic gastritis and gastric ulcers, conditions that were...
, a spiral-shaped bacterium that lives in the acidic environment of the stomach; however, only 40% of those cases go to a doctor. Ulcers can also be caused or worsened by drugs such as aspirin
Aspirin
Aspirin , also known as acetylsalicylic acid , is a salicylate drug, often used as an analgesic to relieve minor aches and pains, as an antipyretic to reduce fever, and as an anti-inflammatory medication. It was discovered by Arthur Eichengrun, a chemist with the German company Bayer...
, Plavix (clopidogrel), ibuprofen
Ibuprofen
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug used for relief of symptoms of arthritis, fever, as an analgesic , especially where there is an inflammatory component, and dysmenorrhea....
, and other NSAIDs.
Contrary to general belief, four times as many peptic ulcers arise in the duodenum
Duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine may be used instead of duodenum...
—the first part of the small intestine
Small intestine
The small intestine is the part of the gastrointestinal tract following the stomach and followed by the large intestine, and is where much of the digestion and absorption of food takes place. In invertebrates such as worms, the terms "gastrointestinal tract" and "large intestine" are often used to...
, just after the stomach—rather than in the stomach
Stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow, dilated part of the alimentary canal which functions as an important organ of the digestive tract in some animals, including vertebrates, echinoderms, insects , and molluscs. It is involved in the second phase of digestion, following mastication .The stomach is...
itself. About 4% of stomach ulcers are caused by a malignant
Malignant
Malignancy is the tendency of a medical condition, especially tumors, to become progressively worse and to potentially result in death. Malignancy in cancers is characterized by anaplasia, invasiveness, and metastasis...
tumor, so multiple biopsies are needed to exclude cancer. Duodenal ulcers are generally benign
Benign
A benign tumor is a tumor that lacks the ability to metastasize. Common examples of benign tumors include moles and uterine fibroids.The term "benign" implies a mild and nonprogressive disease. Indeed, many kinds of benign tumors are harmless to human health...
.
Classification
By Region/Location- DuodenumDuodenumThe duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine may be used instead of duodenum...
(called duodenal ulcer) - Oesophagus (called esophageal ulcer)
- StomachStomachThe stomach is a muscular, hollow, dilated part of the alimentary canal which functions as an important organ of the digestive tract in some animals, including vertebrates, echinoderms, insects , and molluscs. It is involved in the second phase of digestion, following mastication .The stomach is...
(called gastric ulcer) - Meckel's diverticulumMeckel's diverticulumA Meckel's diverticulum, a true congenital diverticulum, is a small bulge in the small intestine present at birth. It is a vestigial remnant of the omphalomesenteric duct , and is the most frequent malformation of the gastrointestinal tract...
(called Meckel's diverticulum ulcer; is very tender with palpation)
Modified Johnson Classification of peptic ulcers:
- Type I: Ulcer along the body of the stomach, most often along the lesser curve at incisura angularis along the locus minoris resistentiae.
- Type II: Ulcer in the body in combination with duodenal ulcers. Associated with acid oversecretion.
- Type III: In the pyloric channel within 3 cm of pylorus. Associated with acid oversecretion.
- Type IV: Proximal gastroesophageal ulcer
- Type V: Can occur throughout the stomach. Associated with chronic NSAID use (such as aspirin).
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of a peptic ulcer can be- abdominal painAbdominal painAbdominal pain can be one of the symptoms associated with transient disorders or serious disease. Making a definitive diagnosis of the cause of abdominal pain can be difficult, because many diseases can result in this symptom. Abdominal pain is a common problem...
, classically epigastric with severity relating to mealtimes, after around three hours of taking a meal (duodenal ulcers are classically relieved by food, while gastric ulcers are exacerbated by it); - bloatingBloatingBloating is any abnormal general swelling, or increase in diameter of the abdominal area. As a symptom, the patient feels a full and tight abdomen, which may cause abdominal pain sometimes accompanied by increased borborygmus or more seriously the total lack of borborygmus.-Symptoms:The most common...
and abdominal fullness; - waterbrash (rush of saliva after an episode of regurgitation to dilute the acid in esophagus - although this is more associated with GERDGerdIn Norse mythology, Gerðr is a jötunn, goddess, and the wife of the god Freyr. Gerðr is attested in the Poetic Edda, compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources; the Prose Edda and Heimskringla, written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson; and in the poetry of skalds...
); - nausea, and copious vomiting;
- loss of appetite and weight loss;
- hematemesisHematemesisHematemesis or haematemesis is the vomiting of blood. The source is generally the upper gastrointestinal tract. Patients can easily confuse it with hemoptysis , although the latter is more common.-Signs:...
(vomiting of blood); this can occur due to bleeding directly from a gastric ulcer, or from damage to the esophagus from severe/continuing vomiting. - melenaMelenaIn medicine, melena or melaena refers to the black, "tarry" feces that are associated with gastrointestinal hemorrhage. The black color is caused by oxidation of the iron in hemoglobin during its passage through the ileum and colon.-Melena vs...
(tarry, foul-smelling feces due to oxidized iron from hemoglobinHemoglobinHemoglobin is the iron-containing oxygen-transport metalloprotein in the red blood cells of all vertebrates, with the exception of the fish family Channichthyidae, as well as the tissues of some invertebrates...
); - rarely, an ulcer can lead to a gastric or duodenal perforationPerforationA perforation is a small hole in a thin material or web. There is usually more than one perforation in an organized fashion, where all of the holes are called a perforation...
, which leads to acute peritonitis. This is extremely painful and requires immediate surgery.
A history of heartburn
Heartburn
Heartburn, also known as pyrosis or acid indigestion is a burning sensation in the chest, just behind the breastbone or in the epigastrium...
, gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease , gastro-oesophageal reflux disease , gastric reflux disease, or acid reflux disease is chronic symptoms or mucosal damage caused by stomach acid coming up from the stomach into the esophagus...
(GERD) and use of certain forms of medication can raise the suspicion for peptic ulcer. Medicines associated with peptic ulcer include NSAID (non-steroid anti-inflammatory drugs) that inhibit cyclooxygenase
Cyclooxygenase
Cyclooxygenase is an enzyme that is responsible for formation of important biological mediators called prostanoids, including prostaglandins, prostacyclin and thromboxane. Pharmacological inhibition of COX can provide relief from the symptoms of inflammation and pain...
, and most glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoid
Glucocorticoids are a class of steroid hormones that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor , which is present in almost every vertebrate animal cell...
s (e.g. dexamethasone
Dexamethasone
Dexamethasone is a potent synthetic member of the glucocorticoid class of steroid drugs. It acts as an anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant...
and prednisolone
Prednisolone
Prednisolone is the active metabolite of prednisone, which is also used as a drug.-Uses:Prednisolone is a corticosteroid drug with predominant glucocorticoid and low mineralocorticoid activity, making it useful for the treatment of a wide range of inflammatory and auto-immune conditions such as...
).
In patients over 45 with more than two weeks of the above symptoms, the odds for peptic ulceration are high enough to warrant rapid investigation by EGD (see below).
The timing of the symptoms in relation to the meal may differentiate between gastric and duodenal ulcers: A gastric ulcer would give epigastric pain during the meal, as gastric acid
Gastric acid
Gastric acid is a digestive fluid, formed in the stomach. It has a pH of 1 to 2 and is composed of hydrochloric acid , and large quantities of potassium chloride and sodium chloride...
production is increased as food enters the stomach. Symptoms of duodenal ulcers would initially be relieved by a meal, as the pyloric sphincter closes to concentrate the stomach contents, therefore acid is not reaching the duodenum. Duodenal ulcer pain would manifest mostly 2–3 hours after the meal, when the stomach begins to release digested food and acid into the duodenum
Duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine may be used instead of duodenum...
.
Also, the symptoms of peptic ulcers may vary with the location of the ulcer and the patient's age. Furthermore, typical ulcers tend to heal and recur and as a result the pain may occur for few days and weeks and then wane or disappear. Usually, child
Child
Biologically, a child is generally a human between the stages of birth and puberty. Some vernacular definitions of a child include the fetus, as being an unborn child. The legal definition of "child" generally refers to a minor, otherwise known as a person younger than the age of majority...
ren and the elderly do not develop any symptoms unless complications have arisen.
Burning or gnawing feeling in the stomach area lasting between 30 minutes and 3 hours commonly accompanies ulcers. This pain can be misinterpreted as hunger
Hunger
Hunger is the most commonly used term to describe the social condition of people who frequently experience the physical sensation of desiring food.-Malnutrition, famine, starvation:...
, indigestion or heartburn
Heartburn
Heartburn, also known as pyrosis or acid indigestion is a burning sensation in the chest, just behind the breastbone or in the epigastrium...
. Pain is usually caused by the ulcer but it may be aggravated by the stomach acid when it comes into contact with the ulcerated area. The pain caused by peptic ulcers can be felt anywhere from the navel up to the sternum, it may last from few minutes to several hours and it may be worse when the stomach is empty. Also, sometimes the pain may flare at night and it can commonly be temporarily relieved by eating foods that buffer stomach acid or by taking anti-acid medication. However, peptic ulcer disease symptoms may be different for every sufferer.
Complications
- Gastrointestinal bleedingUpper gastrointestinal bleedingUpper gastrointestinal bleeding refers to hemorrhage in the upper gastrointestinal tract. The anatomic cut-off for upper GI bleeding is the ligament of Treitz, which connects the fourth portion of the duodenum to the diaphragm near the splenic flexure of the colon.Upper GI bleeds are considered...
is the most common complication. Sudden large bleeding can be life-threatening. It occurs when the ulcer erodes one of the blood vessels, such as the gastroduodenal artery. - Perforation (a hole in the wall) often leads to catastrophic consequences. Erosion of the gastro-intestinal wall by the ulcer leads to spillage of stomach or intestinal content into the abdominal cavity. Perforation at the anterior surface of the stomach leads to acute peritonitisPeritonitisPeritonitis is an inflammation of the peritoneum, the serous membrane that lines part of the abdominal cavity and viscera. Peritonitis may be localised or generalised, and may result from infection or from a non-infectious process.-Abdominal pain and tenderness:The main manifestations of...
, initially chemical and later bacterial peritonitis. The first sign is often sudden intense abdominal pain. Posterior wall perforation leads to bleeding due to involvement of gastroduodenal artery that lies posterior to the 1st part of duodenum. - PenetrationPenetrationPenetration may refer to:* Penetration depth of light or any electromagnetic radiation.* Penetrating trauma* Sexual penetration, a term which may mean**sexual intercourse in general or,...
is when the ulcer continues into adjacent organs such as the liver and pancreasPancreasThe pancreas is a gland organ in the digestive and endocrine system of vertebrates. It is both an endocrine gland producing several important hormones, including insulin, glucagon, and somatostatin, as well as a digestive organ, secreting pancreatic juice containing digestive enzymes that assist...
. - Scarring and swelling due to ulcers causes narrowing in the duodenum and gastric outlet obstructionGastric outlet obstructionGastric outlet obstruction is a medical condition where there is an obstruction at the level of the pylorus, which is the outlet of the stomach. Individuals with gastric outlet obstruction will often have recurrent vomiting of food that has accumulated in the stomach, but which cannot pass into...
. Patient often presents with severe vomiting. - CancerCancerCancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
is included in the differential diagnosis (elucidated by biopsyBiopsyA biopsy is a medical test involving sampling of cells or tissues for examination. It is the medical removal of tissue from a living subject to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist, and can also be analyzed chemically...
), Helicobacter pyloriHelicobacter pyloriHelicobacter pylori , previously named Campylobacter pyloridis, is a Gram-negative, microaerophilic bacterium found in the stomach. It was identified in 1982 by Barry Marshall and Robin Warren, who found that it was present in patients with chronic gastritis and gastric ulcers, conditions that were...
as the etiological factor making it 3 to 6 times more likely to develop stomach cancer from the ulcer.
Cause
A major causative factor (60% of gastric and up to 90% of duodenal ulcers) is chronic inflammationInflammation
Inflammation is part of the complex biological response of vascular tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants. Inflammation is a protective attempt by the organism to remove the injurious stimuli and to initiate the healing process...
due to Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori , previously named Campylobacter pyloridis, is a Gram-negative, microaerophilic bacterium found in the stomach. It was identified in 1982 by Barry Marshall and Robin Warren, who found that it was present in patients with chronic gastritis and gastric ulcers, conditions that were...
that colonizes
Colonisation (biology)
Colonisation is the process in biology by which a species spreads into new areas, regions, and continents. It is sometimes also referred to as immigration, but colonisation often refers to successful immigration with integration to a community, having resisted initial local extinction.One classic...
the antral
Pyloric antrum
Pyloric antrum is the initial portion of the pyloric part of the stomach. It is near the bottom of the stomach, proximal to the pyloric sphincter, which separates the stomach and the duodenum....
mucosa . The immune system is unable to clear the infection, despite the appearance of antibodies. Thus, the bacterium can cause a chronic active gastritis
Gastritis
Gastritis is an inflammation of the lining of the stomach, and has many possible causes. The main acute causes are excessive alcohol consumption or prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin or ibuprofen. Sometimes gastritis develops after major surgery, traumatic...
(type B gastritis), resulting in a defect in the regulation of gastrin
Gastrin
In humans, gastrin is a peptide hormone that stimulates secretion of gastric acid by the parietal cells of the stomach and aids in gastric motility. It is released by G cells in the antrum of the stomach, duodenum, and the pancreas...
production by that part of the stomach, and gastrin secretion can either be increased, or as in most cases, decreased, resulting in hypo- or achlorhydria
Achlorhydria
Achlorhydria or hypochlorhydria refers to states where the production of gastric acid in the stomach is absent or low, respectively. It is associated with various other medical problems.-Signs and symptoms:...
. Gastrin
Gastrin
In humans, gastrin is a peptide hormone that stimulates secretion of gastric acid by the parietal cells of the stomach and aids in gastric motility. It is released by G cells in the antrum of the stomach, duodenum, and the pancreas...
stimulates the production of gastric acid
Gastric acid
Gastric acid is a digestive fluid, formed in the stomach. It has a pH of 1 to 2 and is composed of hydrochloric acid , and large quantities of potassium chloride and sodium chloride...
by parietal cells and, in H. pylori colonization responses that increase gastrin, the increase in acid can contribute to the erosion of the mucosa and therefore ulcer formation.
Another major cause is the use of NSAIDs (see above). The gastric mucosa protects itself from gastric acid
Gastric acid
Gastric acid is a digestive fluid, formed in the stomach. It has a pH of 1 to 2 and is composed of hydrochloric acid , and large quantities of potassium chloride and sodium chloride...
with a layer of mucus, the secretion of which is stimulated by certain prostaglandins. NSAIDs block the function of cyclooxygenase
Cyclooxygenase
Cyclooxygenase is an enzyme that is responsible for formation of important biological mediators called prostanoids, including prostaglandins, prostacyclin and thromboxane. Pharmacological inhibition of COX can provide relief from the symptoms of inflammation and pain...
1 (cox-1), which is essential for the production of these prostaglandins. COX-2 selective anti-inflammatories (such as celecoxib
Celecoxib
Celecoxib INN is a sulfa non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug and selective COX-2 inhibitor used in the treatment of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, acute pain, painful menstruation and menstrual symptoms, and to reduce numbers of colon and rectum polyps in patients with familial...
or the since withdrawn rofecoxib
Rofecoxib
Rofecoxib is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug that has now been withdrawn over safety concerns. It was marketed by Merck & Co. to treat osteoarthritis, acute pain conditions, and dysmenorrhoea...
) preferentially inhibit cox-2, which is less essential in the gastric mucosa, and roughly halve the risk of NSAID-related gastric ulceration. As the prevalence of H. pylori-caused ulceration declines in the Western world due to increased medical treatment, a greater proportion of ulcers will be due to increasing NSAID use among individuals with pain syndromes as well as the growth of aging populations that develop arthritis.
The incidence of duodenal ulcers has dropped significantly during the last 30 years, while the incidence of gastric ulcers has shown a small increase, mainly caused by the widespread use of NSAIDs. The drop in incidence is considered to be a cohort-phenomenon independent of the progress in treatment of the disease. The cohort-phenomenon is probably explained by improved standards of living which has lowered the incidence of H. pylori infections.
Although some studies have found correlations between smoking and ulcer formation, others have been more specific in exploring the risks involved and have found that smoking by itself may not be much of a risk factor unless associated with H. pylori infection.Kurata 1997 explains that "Data in Fig. 8 indicate that 89% of all serious upper GI disease can be accounted for by NSAIDs and H. pylori, with cigarette smoking acting as a synergistic co-factor."(14) Some suggested risk factors such as diet
Diet (nutrition)
In nutrition, diet is the sum of food consumed by a person or other organism. Dietary habits are the habitual decisions an individual or culture makes when choosing what foods to eat. With the word diet, it is often implied the use of specific intake of nutrition for health or weight-management...
, spice
Spice
A spice is a dried seed, fruit, root, bark, or vegetative substance used in nutritionally insignificant quantities as a food additive for flavor, color, or as a preservative that kills harmful bacteria or prevents their growth. It may be used to flavour a dish or to hide other flavours...
consumption and blood type
Blood type
A blood type is a classification of blood based on the presence or absence of inherited antigenic substances on the surface of red blood cells . These antigens may be proteins, carbohydrates, glycoproteins, or glycolipids, depending on the blood group system...
, were hypothesized as ulcerogens (helping cause ulcers) until late in the 20th century, but have been shown to be of relatively minor importance in the development of peptic ulcers. Similarly, while studies have found that alcohol consumption increases risk when associated with H. pylori infection, it does not seem to independently increase risk, and even when coupled with H. pylori infection, the increase is modest in comparison to the primary risk factor.Sonnenberg in his study cautiously concludes that, among other potential factors that were found to correlate to ulcer healing, "moderate alcohol intake might [also] favor ulcer healing." (p. 1066)
Gastrinoma
Gastrinoma
A gastrinoma is a tumor in the pancreas or duodenum that secretes excess of gastrin leading to ulceration in the duodenum, stomach and the small intestine. There is hypersecretion of the HCl in the duodenum which causes the ulcers...
s (Zollinger Ellison syndrome), rare gastrin-secreting tumors, also cause multiple and difficult-to-heal ulcers.
Stress
Researchers also continue to look at stress as a possible cause, or at least complication, in the development of ulcers. There is debate as to whether psychological stress can influence the development of peptic ulcers. BurnsBurn (injury)
A burn is a type of injury to flesh caused by heat, electricity, chemicals, light, radiation or friction. Most burns affect only the skin . Rarely, deeper tissues, such as muscle, bone, and blood vessels can also be injured...
and head trauma, however, can lead to physiologic stress ulcer
Stress ulcer
Stress ulcers are single or multiple mucosal defects which can become complicated by upper gastrointestinal bleeding during the physiologic stress of serious illness...
s, which are reported in many patients who are on mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation
In medicine, mechanical ventilation is a method to mechanically assist or replace spontaneous breathing. This may involve a machine called a ventilator or the breathing may be assisted by a physician, respiratory therapist or other suitable person compressing a bag or set of bellows...
.
An expert panel convened by the Academy of Behavioral Medicine Research concluded that ulcers are not purely an infectious disease
Infectious disease
Infectious diseases, also known as communicable diseases, contagious diseases or transmissible diseases comprise clinically evident illness resulting from the infection, presence and growth of pathogenic biological agents in an individual host organism...
and that psychological factors do play a significant role. Researchers are examining how stress might promote H. pylori infection. For example, Helicobacter pylori thrives in an acidic environment, and stress has been demonstrated to cause the production of excess stomach acid. This was supported by a study on mice showing that both long-term water-immersion-restraint stress and H. pylori infection were independently associated with the development of peptic ulcers.
A study of peptic ulcer patients in a Thai hospital showed that chronic stress was strongly associated with an increased risk of peptic ulcer, and a combination of chronic stress and irregular mealtimes was a significant risk factor.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is mainly established based on the characteristic symptoms. Stomach pain is usually the first signal of a peptic ulcer. In some cases, doctors may treat ulcers without diagnosing them with specific tests and observe whether the symptoms resolve, this indicating that their primary diagnosis was accurate.Confirmation of the diagnosis is made with the help of tests such as endoscopies or barium contrast x-rays. The tests are typically ordered if the symptoms do not resolve after a few weeks of treatment, or when they first appear in a person who is over age 45 or who has other symptoms such as weight loss
Weight loss
Weight loss, in the context of medicine, health or physical fitness, is a reduction of the total body mass, due to a mean loss of fluid, body fat or adipose tissue and/or lean mass, namely bone mineral deposits, muscle, tendon and other connective tissue...
, because stomach cancer
Stomach cancer
Gastric cancer, commonly referred to as stomach cancer, can develop in any part of the stomach and may spread throughout the stomach and to other organs; particularly the esophagus, lungs, lymph nodes, and the liver...
can cause similar symptoms. Also, when severe ulcers resist treatment, particularly if a person has several ulcers or the ulcers are in unusual places, a doctor may suspect an underlying condition that causes the stomach to overproduce acid
Acid
An acid is a substance which reacts with a base. Commonly, acids can be identified as tasting sour, reacting with metals such as calcium, and bases like sodium carbonate. Aqueous acids have a pH of less than 7, where an acid of lower pH is typically stronger, and turn blue litmus paper red...
.
An esophagogastroduodenoscopy
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy
For other expansions of the initialism "OGD", see the disambiguation page.In medicine , esophagogastroduodenoscopy is a diagnostic endoscopic procedure that visualizes the upper part of the gastrointestinal tract up to the duodenum...
(EGD), a form of endoscopy
Endoscopy
Endoscopy means looking inside and typically refers to looking inside the body for medical reasons using an endoscope , an instrument used to examine the interior of a hollow organ or cavity of the body. Unlike most other medical imaging devices, endoscopes are inserted directly into the organ...
, also known as a gastroscopy, is carried out on patients in whom a peptic ulcer is suspected. By direct visual identification, the location and severity of an ulcer can be described. Moreover, if no ulcer is present, EGD can often provide an alternative diagnosis.
One of the reasons that blood tests are not reliable for accurate peptic ulcer diagnosis on their own is their inability to differentiate between past exposure to the bacteria and current infection. Additionally, a false negative result is possible with a blood test if the patient has recently been taking certain drugs, such as antibiotics or proton pump inhibitors.
The diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori , previously named Campylobacter pyloridis, is a Gram-negative, microaerophilic bacterium found in the stomach. It was identified in 1982 by Barry Marshall and Robin Warren, who found that it was present in patients with chronic gastritis and gastric ulcers, conditions that were...
can be made by:
- Urea breath testUrea breath testThe urea breath test is a rapid diagnostic procedure used to identify infections by Helicobacter pylori, a spiral bacterium implicated in gastritis, gastric ulcer, and peptic ulcer disease. It is based upon the ability of H. pylori to convert urea to ammonia and carbon dioxide...
(noninvasive and does not require EGD); - Direct culture from an EGD biopsy specimen; this is difficult to do, and can be expensive. Most labs are not set up to perform H. pylori cultures;
- Direct detection of ureaseUreaseUrease is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of urea into carbon dioxide and ammonia. The reaction occurs as follows:In 1926, James Sumner showed that urease is a protein. Urease is found in bacteria, yeast, and several higher plants. The structure of urease was first solved by P.A...
activity in a biopsy specimen by rapid urease testRapid urease testRapid urease test, also known as the CLO test , is a rapid test for diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori. The basis of the test is the ability of H. pylori to secrete the urease enzyme, which catalyzes the conversion of urea to ammonia and bicarbonate.-Process:The test is performed at the time of...
; - Measurement of antibodyAntibodyAn antibody, also known as an immunoglobulin, is a large Y-shaped protein used by the immune system to identify and neutralize foreign objects such as bacteria and viruses. The antibody recognizes a unique part of the foreign target, termed an antigen...
levels in bloodBloodBlood is a specialized bodily fluid in animals that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells....
(does not require EGD). It is still somewhat controversial whether a positive antibody without EGD is enough to warrant eradication therapy; - Stool antigenAntigenAn antigen is a foreign molecule that, when introduced into the body, triggers the production of an antibody by the immune system. The immune system will then kill or neutralize the antigen that is recognized as a foreign and potentially harmful invader. These invaders can be molecules such as...
test; - Histological examination and staining of an EGD biopsy.
The breath test uses radioactive carbon atom to detect H. pylori. To perform this exam the patient will be asked to drink a tasteless liquid which contains the carbon as part of the substance that the bacteria breaks down. After an hour, the patient will be asked to blow into a bag that is sealed. If the patient is infected with H. pylori, the breath sample will contain radioactive carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
. This test provides the advantage of being able to monitor the response to treatment used to kill the bacteria.
The possibility of other causes of ulcers, notably malignancy (gastric cancer) needs to be kept in mind. This is especially true in ulcers of the greater (large) curvature of the stomach
Stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow, dilated part of the alimentary canal which functions as an important organ of the digestive tract in some animals, including vertebrates, echinoderms, insects , and molluscs. It is involved in the second phase of digestion, following mastication .The stomach is...
; most are also a consequence of chronic H. pylori infection.
If a peptic ulcer perforates, air will leak from the inside of the gastrointestinal tract (which always contains some air) to the peritoneal cavity (which normally never contains air). This leads to "free gas" within the peritoneal cavity. If the patient stands erect, as when having a chest X-ray, the gas will float to a position underneath the diaphragm. Therefore, gas in the peritoneal cavity, shown on an erect chest X-ray or supine lateral abdominal X-ray, is an omen of perforated peptic ulcer disease.
Macroscopic appearance

Microscopic appearance
A gastric peptic ulcer is a mucosal defect which penetrates the muscularis mucosaeMuscularis mucosae
The lamina muscularis mucosae is the thin layer of smooth muscle found in most parts of the gastrointestinal tract, located outside the lamina propria mucosae and separating it from the submucosa....
and muscularis propria, produced by acid-pepsin aggression. Ulcer margins are perpendicular and present chronic gastritis. During the active phase, the base of the ulcer shows 4 zones: inflammatory exudate, fibrinoid necrosis, granulation tissue and fibrous tissue. The fibrous base of the ulcer may contain vessels with thickened wall or with thrombosis.
Treatment
Younger patients with ulcer-like symptoms are often treated with antacidAntacid
An antacid is a substance which neutralizes stomach acidity.-Mechanism of action:Antacids perform a neutralization reaction, increasing the pH to reduce acidity in the stomach. When gastric hydrochloric acid reaches the nerves in the gastrointestinal mucosa, they signal pain to the central nervous...
s or H2 antagonists before EGD is undertaken. Bismuth compounds
Bismuth subsalicylate
Bismuth subsalicylate, with a nominal chemical formula of C7H5BiO4, It is a colloidal substance obtained by hydrolysis of bismuth salicylate . The actual structure is unknown and the formulation is only approximate. Recent evidence indicates that it is composed of a bismuth oxide core structure...
may actually reduce or even clear organisms , though the warning labels of some bismuth subsalicylate products indicate that the product should not be used by someone with an ulcer.
Patients who are taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories (NSAIDs) may also be prescribed a prostaglandin
Prostaglandin
A prostaglandin is any member of a group of lipid compounds that are derived enzymatically from fatty acids and have important functions in the animal body. Every prostaglandin contains 20 carbon atoms, including a 5-carbon ring....
analogue
Analog (chemistry)
In chemistry, a structural analog , also known as chemical analog or simply analog, is a compound having a structure similar to that of another one, but differing from it in respect of a certain component. It can differ in one or more atoms, functional groups, or substructures, which are replaced...
(Misoprostol
Misoprostol
Misoprostol is a drug that is used for the prevention of non steroidal anti inflammatory drug induced gastric ulcers, for early abortion, to treat missed miscarriage, and to induce labor. The latter use is controversial in the United States. Misoprostol was invented and marketed by G.D...
) in order to help prevent peptic ulcers, which may be a side-effect
Adverse effect
In medicine, an adverse effect is a harmful and undesired effect resulting from a medication or other intervention such as surgery.An adverse effect may be termed a "side effect", when judged to be secondary to a main or therapeutic effect. If it results from an unsuitable or incorrect dosage or...
of the NSAIDs.
When H. pylori infection is present, the most effective treatments are combinations of 2 antibiotics (e.g. Clarithromycin
Clarithromycin
Clarithromycin is a macrolide antibiotic used to treat pharyngitis, tonsillitis, acute maxillary sinusitis, acute bacterial exacerbation of chronic bronchitis, pneumonia , skin and skin structure infections...
, Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin , formerly amoxycillin , and abbreviated amox, is a moderate-spectrum, bacteriolytic, β-lactam antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections caused by susceptible microorganisms. It is usually the drug of choice within the class because it is better absorbed, following oral...
, Tetracycline, Metronidazole
Metronidazole
Metronidazole is a nitroimidazole antibiotic medication used particularly for anaerobic bacteria and protozoa. Metronidazole is an antibiotic, amebicide, and antiprotozoal....
) and 1 proton pump inhibitor
Proton pump inhibitor
Proton-pump inhibitors are a group of drugs whose main action is a pronounced and long-lasting reduction of gastric acid production. They are the most potent inhibitors of acid secretion available today. The group followed and has largely superseded another group of pharmaceuticals with similar...
(PPI), sometimes together with a bismuth compound. In complicated, treatment-resistant cases, 3 antibiotics (e.g. amoxicillin + clarithromycin + metronidazole) may be used together with a PPI and sometimes with bismuth compound. An effective first-line therapy for uncomplicated cases would be Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin , formerly amoxycillin , and abbreviated amox, is a moderate-spectrum, bacteriolytic, β-lactam antibiotic used to treat bacterial infections caused by susceptible microorganisms. It is usually the drug of choice within the class because it is better absorbed, following oral...
+ Metronidazole
Metronidazole
Metronidazole is a nitroimidazole antibiotic medication used particularly for anaerobic bacteria and protozoa. Metronidazole is an antibiotic, amebicide, and antiprotozoal....
+ Pantoprazole
Pantoprazole
Pantoprazole is a proton pump inhibitor drug that inhibits gastric acid secretion.-Use:...
(a PPI). In the absence of H. pylori, long-term higher dose PPIs are often used.
Treatment of H. pylori usually leads to clearing of infection, relief of symptoms and eventual healing of ulcers. Recurrence of infection can occur and retreatment may be required, if necessary with other antibiotics. Since the widespread use of PPI's in the 1990s, surgical procedures (like "highly selective vagotomy
Vagotomy
A vagotomy is a surgical procedure that involves resection of the vagus nerve.-Applications:Truncal vagotomy is a treatment option for chronic duodenal ulcers...
") for uncomplicated peptic ulcers became obsolete.
Perforated peptic ulcer is a surgical emergency and requires surgical repair of the perforation. Most bleeding ulcers require endoscopy urgently to stop bleeding with cautery, injection, or clipping
Endoclip
An endoclip is a metallic mechanical device used in endoscopy in order to close two mucosal surfaces without the need for surgery and suturing. Its function is similar to a suture in gross surgical applications, as it is used to join together two disjointed surfaces, but, can be applied through...
.
Ranitidine
Ranitidine
Ranitidine is a histamine H2-receptor antagonist that inhibits stomach acid production. It is commonly used in treatment of peptic ulcer disease and gastroesophageal reflux disease . Ranitidine is also used alongside fexofenadine and other antihistamines for the treatment of skin conditions...
provides relief of peptic ulcers, heartburn, indigestion and excess stomach acid and prevention of these symptoms associated with excessive consumption of food and drink. Ranitidine is available over the counter from a pharmacy and works by decreasing the amount of acid the stomach produces allowing healing of ulcers. Zantac tablets contain Ranitidine 150 mg as the active ingredient which can also be bought generically.
Sucralfate
Sucralfate
Sucralfate is a cytoprotective agent, an oral gastrointestinal medication primarily indicated for the treatment of active duodenal ulcers. Brand names include Sucramal in Italy; Carafate in U.S.A.; Pepsigard, Sucral, Sucrafil, Hapifate in India; Sutra or Musin in parts of South-East Asia; Sulcrate...
, (Carafate) has also been a successful treatment of peptic ulcers.
Epidemiology
The lifetime risk for developing a peptic ulcer is approximately 10%.In Western countries the prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infections roughly matches age (i.e., 20% at age 20, 30% at age 30, 80% at age 80 etc.). Prevalence is higher in third world countries. Transmission is by food, contaminated groundwater, and through human saliva (such as from kissing or sharing food utensils).
A minority of cases of H. pylori infection will eventually lead to an ulcer and a larger proportion of people will get non-specific discomfort, abdominal pain or gastritis.
Peptic ulcer disease had a tremendous effect on morbidity and mortality until the last decades of the 20th century, when epidemiological trends started to point to an impressive fall in its incidence. The reason that the rates of peptic ulcer disease decreased is thought to be the development of new effective medication and acid suppressants and the discovery of the cause of the condition, H. pylori.
In the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
about 4 million people have active peptic ulcers and about 350,000 new cases are diagnosed each year. Four times as many duodenal ulcers as gastric ulcers are diagnosed. Approximately 3,000 deaths per year in the United States are due to duodenal ulcer and 3,000 to gastric ulcer.
History
John LykoudisJohn Lykoudis
John Lykoudis was a general practitioner in Greece who treated patients suffering from peptic ulcer disease with antibiotics long before it was commonly recognized that bacteria were a dominant cause for the disease....
, a general practitioner
General practitioner
A general practitioner is a medical practitioner who treats acute and chronic illnesses and provides preventive care and health education for all ages and both sexes. They have particular skills in treating people with multiple health issues and comorbidities...
in Greece
Greece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
, treated patients for peptic ulcer disease with antibiotics, beginning in 1958, long before it was commonly recognized that bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
were a dominant cause for the disease.
Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori , previously named Campylobacter pyloridis, is a Gram-negative, microaerophilic bacterium found in the stomach. It was identified in 1982 by Barry Marshall and Robin Warren, who found that it was present in patients with chronic gastritis and gastric ulcers, conditions that were...
was rediscovered in 1982 by two Australia
Australia
Australia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
n scientists, Robin Warren
Robin Warren
John Robin Warren AC is an Australian pathologist, Nobel Laureate and researcher who is credited with the 1979 re-discovery of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, together with Barry Marshall.- Life and career :...
and Barry J. Marshall
Barry Marshall
Barry James Marshall, AC, FRS, FAA is an Australian physician, Nobel Prize laureate in Physiology or Medicine, and Professor of Clinical Microbiology at the University of Western Australia. Marshall is well-known for proving that the bacterium Helicobacter pylori Barry James Marshall, AC, FRS, FAA...
as a causative factor for ulcers. In their original paper, Warren and Marshall contended that most stomach ulcers and gastritis were caused by colonization with this bacterium, not by stress
Stress (medicine)
Stress is a term in psychology and biology, borrowed from physics and engineering and first used in the biological context in the 1930s, which has in more recent decades become commonly used in popular parlance...
or spicy food as had been assumed before.
The H. pylori
Helicobacter pylori
Helicobacter pylori , previously named Campylobacter pyloridis, is a Gram-negative, microaerophilic bacterium found in the stomach. It was identified in 1982 by Barry Marshall and Robin Warren, who found that it was present in patients with chronic gastritis and gastric ulcers, conditions that were...
hypothesis was poorly received, so in an act of self-experimentation Marshall drank a Petri dish
Petri dish
A Petri dish is a shallow glass or plastic cylindrical lidded dish that biologists use to culture cells or small moss plants. It was named after German bacteriologist Julius Richard Petri, who invented it when working as an assistant to Robert Koch...
containing a culture of organisms extracted from a patient and five days later developed gastritis. His symptoms disappeared after two weeks, but he took antibiotics to kill the remaining bacteria at the urging of his wife, since halitosis
Halitosis
Halitosis is a term used to describe noticeably unpleasant odors exhaled in breathing. Halitosis is estimated to be the third most frequent reason for seeking dental aid, following tooth decay and periodontal disease.- General :...
is one of the symptoms of infection. This experiment was published in 1984 in the Australian Medical Journal and is among the most cited articles from the journal.
In 1997, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention are a United States federal agency under the Department of Health and Human Services headquartered in Druid Hills, unincorporated DeKalb County, Georgia, in Greater Atlanta...
, with other government agencies, academic institutions, and industry, launched a national education campaign to inform health care providers and consumers about the link between H. pylori and ulcers. This campaign reinforced the news that ulcers are a curable infection, and that health can be greatly improved and money saved by disseminating information about H. pylori.
In 2005, the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm
Karolinska Institutet
Karolinska institutet is a medical university in Solna within the Stockholm urban area, Sweden, and one of Europe's largest medical universities...
awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine administered by the Nobel Foundation, is awarded once a year for outstanding discoveries in the field of life science and medicine. It is one of five Nobel Prizes established in 1895 by Swedish chemist Alfred Nobel, the inventor of dynamite, in his will...
to Dr. Marshall and his long-time collaborator Dr. Warren "for their discovery of the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and its role in gastritis
Gastritis
Gastritis is an inflammation of the lining of the stomach, and has many possible causes. The main acute causes are excessive alcohol consumption or prolonged use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin or ibuprofen. Sometimes gastritis develops after major surgery, traumatic...
and peptic ulcer disease." Professor Marshall continues research related to H. pylori and runs a molecular biology lab at UWA
University of Western Australia
The University of Western Australia was established by an Act of the Western Australian Parliament in February 1911, and began teaching students for the first time in 1913. It is the oldest university in the state of Western Australia and the only university in the state to be a member of the...
in Perth, Western Australia.
Some believed that mastic gum, a tree resin extract, actively eliminates the H. pylori bacteria. However, multiple subsequent studies have found no effect of using mastic gum on reducing H. pylori levels.
External links
- Endoscopy Video of a deep gastric ulcer
- Gastric Ulcer Radiology and Endoscopy from MedPix

