Volcanism of Northern Canada
Encyclopedia
Volcanism of Northern Canada has led to the formation of hundreds of volcanic areas and extensive lava formations across Northern Canada
, indicating volcanism played a major role in shaping its surface. The region's different volcano and lava types originate from different tectonic
settings and types of volcanic eruptions
, ranging from passive lava eruptions
to violent explosive eruption
s. Northern Canada has a record of very large volumes of magmatic rock called large igneous province
s. They are represented by deep-level plumbing systems consisting of giant dike swarm
s, sill
provinces and layered intrusion
s.
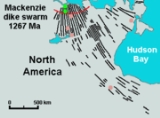
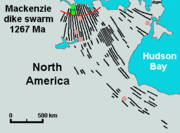 Vast volumes of basaltic lava covered Northern Canada in the form of a flood basalt
Vast volumes of basaltic lava covered Northern Canada in the form of a flood basalt
event 1,267 million years ago that engulfed the landscape near the Coppermine River
southwest of Coronation Gulf
in the Canadian Arctic. This volcanic activity built an extensive lava plateau
and large igneous province
with an area of 170000 km² (65,637 sq mi) representing a volume of lavas of at least 500000 km³ (119,956 cu mi). With an area of 170000 km² (65,637 sq mi) and a volume of 500000 km³ (119,956 cu mi), it is larger than the Columbia River Basalt Group
in the United States
and comparable in size to the Deccan Traps
in west-central India
, making it one of the largest flood basalt events ever to appear on the North American continent, as well as on Earth. This massive eruptive event was associated with the Mackenzie magmatic event, that included the coeval, layered, mafic-ultramafic Muskox intrusion
and the enormous Mackenzie dike swarm
that diverges from the Coppermine River Group flood basalt
s. The maximum thickness of the flood basalts are 4.7 km (3 mi) and consist of 150 lava flows, each 4 m (13 ft) to 100 m (328 ft) thick. These flood basalt lava flows were erupted during a single event that lasted less than five million years. Analysis of the chemical composition of the lavas gives important clues about the origin and dynamics of the flood basalt volcanism. The lowermost lavas were produced by melting in the garnet stability field below the surface at a depth of more than 90 km (56 mi) in a mantle plume
environment beneath the North American lithosphere
. As the mantle plume intruded rocks of the Canadian Shield, it created an upwelling zone of molten rock known as the Mackenzie hotspot
. Upper lavas were partly contaminated with crustal rocks as magmas from the mantle plume passed through the lower and upper crust.
During the Early Jurassic
period 196 million years ago, the New England or Great Meteor hotspot
existed in the Rankin Inlet area of southern Nunavut along the northwestern coast of Hudson Bay
, producing kimberlite magmas. This marks the first appearance of the New England hotspot, as well as the oldest kimberlite eruption throughout the New England or Great Meteor hotspot track
, which extends southeastwards across Canada and enters the northern Atlantic Ocean
where the New England hotspot is presently located.
 The Sverdrup Basin Magmatic Province
The Sverdrup Basin Magmatic Province
of northern Nunavut forms a large igneous province 95 to 92 million years old in the Canadian Arctic. Part of the larger High Arctic Large Igneous Province
, it consists of two volcanic formations called the Ellesmere Island Volcanics
and Strand Fiord Formation
. In the Strand Fiord Formation, flood basalt lavas reach a thickness of at least 1 km (0.621372736649807 mi). Flood basalts of the Sverdrup Basin Magmatic Province are similar to terrestrial flood basalts associated with breakup of continents, indicating the Sverdrup Basin Magmatic Province formed as a result of rifting of the Arctic Ocean
and when the large underwater Alpha Ridge
was still geologically active.
Widespread basalt volcanism occurred between 60.9 and 61.3 million years ago in the northern Labrador Sea
, Davis Strait
and in southern Baffin Bay
on the eastern coast of Nunavut during the Paleocene
period when North America and Greenland were being separated from tectonic movements. This resulted from seafloor spreading
where new ocean seafloor
was being created from rising magma. Scientific studies have indicated nearly 80% of the magma was erupted in one million years or less. The source for this volcanic activity was the Iceland plume
along with its surface expression, the Iceland hotspot
. This volcanic activity formed part of a large igneous province that is presently sunken beneath the northern Labrador Sea. Another period of volcanic activity began in the same region about 55 million years ago during the Eocene period when the north-south trending Mid-Atlantic Ridge
began to form under the northern Atlantic Ocean east of Greenland. The cause of this volcanism might be related to partial melting
from movement of a transform fault
system extending from Labrador Sea to the south and Baffin Bay to the north. Although the region was carried away from the Iceland plume by going plate motion over millions of years, the source of the partial melting for the final period of volcanic activity may have been remnants of still anomalously hot Iceland plume magma which were left stranded beneath the North American lithosphere in the Paleocene period. Most diatreme
s in the Northwest Territories were formed by volcanic eruptions between 45 and 75 million years ago during the Eocene
and Late Cretaceous
periods.
The Yukon portion of the northwest trending Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province
includes the youngest volcanoes in Northern Canada. The Fort Selkirk Volcanic Field
in central Yukon consists of valley-filling basalt lava flows and cinder cones. Ne Ch'e Ddhawa
, a cinder cone 2 km (1 mi) to the connection of the Yukon
and Pelly
rivers formed between 0.8 and one million years ago when this area lied beneath the vast Cordilleran Ice Sheet
. The youngest volcano, Volcano Mountain
just north of the junction of the Yukon and Pelly rivers, formed in past 10,000 years (Holocene), producing lava flows that remain unvegetated and appear to be only a few hundred years old. However, dating of sediments in a lake impounded by the lava flows indicated that the youngest lava flows could not be younger than mid-Holocene and could be early Holocene or older. Therefore the most recent activity in the Fort Selkirk volcanic field is unknown. The lava flows from Volcano Mountain are unusual because they originate much deeper in the Earth's mantle
than the more common basaltic lava flows found throughout the Yukon and are very uncommon in the geological record. This lava, known as olivine
nephelinite
, is also unusual because it contains small, angular to rounded fragments of rock called nodules
.
. This volcanic belt
lies largely in the U.S. state
of Alaska
, but extends across the Alaska-Yukon border into southwestern Yukon where it contains scattered remnants of subaerial lavas and pyroclastic rocks which are preserved along the entire eastern fringe of the ice covered Saint Elias Mountains
. The Wrangell Volcanic Belt formed as a result of arc volcanism related to subduction of the Pacific Plate
under the northern portion of the North American Plate. Over large areas extrusive rocks lie in flat undisturbed piles on a Tertiary surface of moderate relief. Locally, however, strata of the same age have been affected by a late pulse of tectonism, during which they were faulted, contorted into tight symmetrical folds, or overridden by pre-Tertiary basement rocks along southwesterly dipping thrust faults. Considerable recent uplift, accompanied by rapid erosion, has reduced once vast areas of upper Tertiary volcanic rocks to small isolated remnants. Although no eruptions have occurred in the Yukon portion of the Wrangell Belt for the past five million years, two large (VEI-6
) explosive eruptions from Mount Churchill
24 km (15 mi) west of the Alaska-Yukon border, created the White River Ash
deposit. This volcanic ash deposit is estimated 1,890 and 1,250 years old, covering more than 340000 km² (131,274.7 sq mi) of northwestern Canada and adjacent eastern Alaska. Unproven legends from indigenous people
in the area indicate the final eruption from Mount Churchill 1,250 years ago disrupted food supplies and forced them to move further south.
Northern Canada
Northern Canada, colloquially the North, is the vast northernmost region of Canada variously defined by geography and politics. Politically, the term refers to the three territories of Canada: Yukon, Northwest Territories, and Nunavut...
, indicating volcanism played a major role in shaping its surface. The region's different volcano and lava types originate from different tectonic
Tectonics
Tectonics is a field of study within geology concerned generally with the structures within the lithosphere of the Earth and particularly with the forces and movements that have operated in a region to create these structures.Tectonics is concerned with the orogenies and tectonic development of...
settings and types of volcanic eruptions
Types of volcanic eruptions
During a volcanic eruption, lava, tephra , and various gases are expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure. Several types of volcanic eruptions have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are often named after famous volcanoes where that type of behavior has been observed...
, ranging from passive lava eruptions
Effusive eruption
An effusive eruption is a volcanic eruption characterized by the outpouring of lava onto the ground...
to violent explosive eruption
Explosive eruption
An explosive eruption is a volcanic term to describe a violent, explosive type of eruption. Mount St. Helens in 1980 was an example. Such an eruption is driven by gas accumulating under great pressure. Driven by hot rising magma, it interacts with ground water until the pressure increases to the...
s. Northern Canada has a record of very large volumes of magmatic rock called large igneous province
Large igneous province
A Large Igneous Province is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks—intrusive, extrusive, or both—in the earth's crust...
s. They are represented by deep-level plumbing systems consisting of giant dike swarm
Dike swarm
A dike swarm or dyke swarm is a large geological structure consisting of a major group of parallel, linear, or radially oriented dikes intruded within continental crust. They consist of several to hundreds of dikes emplaced more or less contemporaneously during a single intrusive event and are...
s, sill
Sill (geology)
In geology, a sill is a tabular sheet intrusion that has intruded between older layers of sedimentary rock, beds of volcanic lava or tuff, or even along the direction of foliation in metamorphic rock. The term sill is synonymous with concordant intrusive sheet...
provinces and layered intrusion
Intrusion
An intrusion is liquid rock that forms under Earth's surface. Magma from under the surface is slowly pushed up from deep within the earth into any cracks or spaces it can find, sometimes pushing existing country rock out of the way, a process that can take millions of years. As the rock slowly...
s.
Plume and rift complexes

Flood basalt
A flood basalt or trap basalt is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that coats large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Flood basalts have occurred on continental scales in prehistory, creating great plateaus and mountain ranges...
event 1,267 million years ago that engulfed the landscape near the Coppermine River
Coppermine River
The Coppermine River is a river in the North Slave and Kitikmeot regions of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut in Canada. It is long. It rises in Lac de Gras, a small lake near Great Slave Lake and flows generally north to Coronation Gulf, an arm of the Arctic Ocean...
southwest of Coronation Gulf
Coronation Gulf
Coronation Gulf lies between Victoria Island and mainland Nunavut in Canada. To the northwest it connects with Dolphin and Union Strait and thence the Beaufort Sea and Arctic Ocean; to the northeast it connects with Dease Strait and thence Queen Maud Gulf. To the southeast lies Bathurst...
in the Canadian Arctic. This volcanic activity built an extensive lava plateau
Volcanic plateau
A volcanic plateau is a plateau produced by volcanic activity. There are two main types: lava plateaus and pyroclastic plateaus.-Lava plateau:...
and large igneous province
Large igneous province
A Large Igneous Province is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks—intrusive, extrusive, or both—in the earth's crust...
with an area of 170000 km² (65,637 sq mi) representing a volume of lavas of at least 500000 km³ (119,956 cu mi). With an area of 170000 km² (65,637 sq mi) and a volume of 500000 km³ (119,956 cu mi), it is larger than the Columbia River Basalt Group
Columbia River Basalt Group
The Columbia River Basalt Group is a large igneous province that lies across parts of the Western United States. It is found in the U.S. states of Washington, Oregon, Idaho, Nevada, and California...
in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
and comparable in size to the Deccan Traps
Deccan Traps
The Deccan Traps are a large igneous province located on the Deccan Plateau of west-central India and one of the largest volcanic features on Earth. They consist of multiple layers of solidified flood basalt that together are more than thick and cover an area of and a volume of...
in west-central India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
, making it one of the largest flood basalt events ever to appear on the North American continent, as well as on Earth. This massive eruptive event was associated with the Mackenzie magmatic event, that included the coeval, layered, mafic-ultramafic Muskox intrusion
Muskox intrusion
The Muskox intrusion is a layered intrusion in Nunavut, Canada. It is located northeast of Great Bear Lake and south of Kugluktuk on Coronation Gulf...
and the enormous Mackenzie dike swarm
Mackenzie dike swarm
The Mackenzie dike swarm, also called the Mackenzie dikes, form a large igneous province in the western Canadian Shield of Canada. It is part of the larger Mackenzie Large Igneous Province and is one of more than three dozen dike swarms in various parts of the Canadian Shield...
that diverges from the Coppermine River Group flood basalt
Flood basalt
A flood basalt or trap basalt is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that coats large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Flood basalts have occurred on continental scales in prehistory, creating great plateaus and mountain ranges...
s. The maximum thickness of the flood basalts are 4.7 km (3 mi) and consist of 150 lava flows, each 4 m (13 ft) to 100 m (328 ft) thick. These flood basalt lava flows were erupted during a single event that lasted less than five million years. Analysis of the chemical composition of the lavas gives important clues about the origin and dynamics of the flood basalt volcanism. The lowermost lavas were produced by melting in the garnet stability field below the surface at a depth of more than 90 km (56 mi) in a mantle plume
Mantle plume
A mantle plume is a hypothetical thermal diapir of abnormally hot rock that nucleates at the core-mantle boundary and rises through the Earth's mantle. Such plumes were invoked in 1971 to explain volcanic regions that were not thought to be explicable by the then-new theory of plate tectonics. Some...
environment beneath the North American lithosphere
Lithosphere
The lithosphere is the rigid outermost shell of a rocky planet. On Earth, it comprises the crust and the portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of thousands of years or greater.- Earth's lithosphere :...
. As the mantle plume intruded rocks of the Canadian Shield, it created an upwelling zone of molten rock known as the Mackenzie hotspot
Mackenzie hotspot
The Mackenzie hotspot was a volcanic hotspot that existed about 1,267 million years ago across Canada from the Northwest Territories and Nunavut. It is responsible for the creation of the Mackenzie Large Igneous Province, which contains the largest dike swarm on Earth...
. Upper lavas were partly contaminated with crustal rocks as magmas from the mantle plume passed through the lower and upper crust.
During the Early Jurassic
Early Jurassic
The Early Jurassic epoch is the earliest of three epochs of the Jurassic period...
period 196 million years ago, the New England or Great Meteor hotspot
New England hotspot
The New England hotspot, also referred to as the Great Meteor hotspot, is a long-lived volcanic hotspot in the Atlantic Ocean. The hotspot's most recent eruptive center is the Great Meteor Seamount, and it probably created a short line of mid to late-Tertiary age seamounts on the African Plate but...
existed in the Rankin Inlet area of southern Nunavut along the northwestern coast of Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay
Hudson Bay , sometimes called Hudson's Bay, is a large body of saltwater in northeastern Canada. It drains a very large area, about , that includes parts of Ontario, Quebec, Saskatchewan, Alberta, most of Manitoba, southeastern Nunavut, as well as parts of North Dakota, South Dakota, Minnesota,...
, producing kimberlite magmas. This marks the first appearance of the New England hotspot, as well as the oldest kimberlite eruption throughout the New England or Great Meteor hotspot track
Great Meteor hotspot track
The Great Meteor hotspot track, also referred to as the New England hotspot track, is a vast hotspot track in the Northern Hemisphere, stretching over from Nunavut in Northern Canada to the northern Atlantic Ocean...
, which extends southeastwards across Canada and enters the northern Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
where the New England hotspot is presently located.

Sverdrup Basin Magmatic Province
The Sverdrup Basin Magmatic Province is a large igneous province located on Axel Heiberg Island and Ellesmere Island, Nunavut, Canada near the rifted margin of the Arctic Ocean at the end of Alpha Ridge....
of northern Nunavut forms a large igneous province 95 to 92 million years old in the Canadian Arctic. Part of the larger High Arctic Large Igneous Province
High Arctic Large Igneous Province
The High Arctic Large Igneous Province is a major Late Cretaceous large igneous province located in the Arctic. It includes the Ellesmere Island Volcanics, Strand Fiord Formation, Alpha Ridge, Franz Josef Land and Svalbard.-See also:...
, it consists of two volcanic formations called the Ellesmere Island Volcanics
Ellesmere Island Volcanics
The Ellesmere Island Volcanics are a Late Cretaceous volcanic group of volcanoes and lava flows in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of northern Ellesmere Island, Nunavut, Canada.Ellesmere Island Volcanics are part of the Arctic Cordillera...
and Strand Fiord Formation
Strand Fiord Formation
The Strand Fiord Formation is a Late Cretaceous volcanic component, located on northwestern and west-central Axel Heiberg Island, Nunavut, Canada. The formation contains flood basalts which are found on western Axel Heiberg Island at Dragon Cliffs tall....
. In the Strand Fiord Formation, flood basalt lavas reach a thickness of at least 1 km (0.621372736649807 mi). Flood basalts of the Sverdrup Basin Magmatic Province are similar to terrestrial flood basalts associated with breakup of continents, indicating the Sverdrup Basin Magmatic Province formed as a result of rifting of the Arctic Ocean
Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean, located in the Northern Hemisphere and mostly in the Arctic north polar region, is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceanic divisions...
and when the large underwater Alpha Ridge
Alpha Ridge
The Alpha Ridge is a major volcanic ridge under the Arctic Ocean between the Canada Basin and the Lomonosov Ridge. It was active during the formation of the Amerasian Basin. It was discovered in 1963. The highest elevation is about 2.7 km over the ocean floor. It is 200 to 450 km wide...
was still geologically active.
Widespread basalt volcanism occurred between 60.9 and 61.3 million years ago in the northern Labrador Sea
Labrador Sea
The Labrador Sea is an arm of the North Atlantic Ocean between the Labrador Peninsula and Greenland. The sea is flanked by continental shelves to the southwest, northwest, and northeast. It connects to the north with Baffin Bay through the Davis Strait...
, Davis Strait
Davis Strait
Davis Strait is a northern arm of the Labrador Sea. It lies between mid-western Greenland and Nunavut, Canada's Baffin Island. The strait was named for the English explorer John Davis , who explored the area while seeking a Northwest Passage....
and in southern Baffin Bay
Baffin Bay
Baffin Bay , located between Baffin Island and the southwest coast of Greenland, is a marginal sea of the North Atlantic Ocean. It is connected to the Atlantic via Davis Strait and the Labrador Sea...
on the eastern coast of Nunavut during the Paleocene
Paleocene
The Paleocene or Palaeocene, the "early recent", is a geologic epoch that lasted from about . It is the first epoch of the Palaeogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era...
period when North America and Greenland were being separated from tectonic movements. This resulted from seafloor spreading
Seafloor spreading
Seafloor spreading is a process that occurs at mid-ocean ridges, where new oceanic crust is formed through volcanic activity and then gradually moves away from the ridge. Seafloor spreading helps explain continental drift in the theory of plate tectonics....
where new ocean seafloor
Oceanic crust
Oceanic crust is the part of Earth's lithosphere that surfaces in the ocean basins. Oceanic crust is primarily composed of mafic rocks, or sima, which is rich in iron and magnesium...
was being created from rising magma. Scientific studies have indicated nearly 80% of the magma was erupted in one million years or less. The source for this volcanic activity was the Iceland plume
Iceland plume
The Iceland Plume is a postulated upwelling of anomalously hot rock in the Earth's mantle beneath Iceland. Its origin is thought to lie deep in the mantle, perhaps at the boundary between the core and the mantle at ca. 2880 km depth. Opinions differ as to whether seismic studies have imaged...
along with its surface expression, the Iceland hotspot
Iceland hotspot
The Iceland hotspot is a hotspot which is partly responsible for the high volcanic activity which has formed the island of Iceland.-Description:...
. This volcanic activity formed part of a large igneous province that is presently sunken beneath the northern Labrador Sea. Another period of volcanic activity began in the same region about 55 million years ago during the Eocene period when the north-south trending Mid-Atlantic Ridge
Mid-Atlantic Ridge
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a mid-ocean ridge, a divergent tectonic plate boundary located along the floor of the Atlantic Ocean, and part of the longest mountain range in the world. It separates the Eurasian Plate and North American Plate in the North Atlantic, and the African Plate from the South...
began to form under the northern Atlantic Ocean east of Greenland. The cause of this volcanism might be related to partial melting
Partial melting
Partial melting occurs when only a portion of a solid is melted. For mixed substances, such as a rock containing several different minerals or a mineral that displays solid solution, this melt can be different from the bulk composition of the solid....
from movement of a transform fault
Transform fault
A transform fault or transform boundary, also known as conservative plate boundary since these faults neither create nor destroy lithosphere, is a type of fault whose relative motion is predominantly horizontal in either sinistral or dextral direction. Furthermore, transform faults end abruptly...
system extending from Labrador Sea to the south and Baffin Bay to the north. Although the region was carried away from the Iceland plume by going plate motion over millions of years, the source of the partial melting for the final period of volcanic activity may have been remnants of still anomalously hot Iceland plume magma which were left stranded beneath the North American lithosphere in the Paleocene period. Most diatreme
Diatreme
A diatreme is a breccia-filled volcanic pipe that was formed by a gaseous explosion. Diatremes often breach the surface and produce a tuff cone, a filled relatively shallow crater known as a maar, or other volcanic pipes.- Word origin :...
s in the Northwest Territories were formed by volcanic eruptions between 45 and 75 million years ago during the Eocene
Eocene
The Eocene Epoch, lasting from about 56 to 34 million years ago , is a major division of the geologic timescale and the second epoch of the Paleogene Period in the Cenozoic Era. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Palaeocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the...
and Late Cretaceous
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous period is divided in the geologic timescale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous series...
periods.
The Yukon portion of the northwest trending Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province
Northern Cordilleran volcanic province
The Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province , formerly known as the Stikine Volcanic Belt, is a geologic province defined by the occurrence of Miocene to Holocene volcanoes in the Pacific Northwest of North America...
includes the youngest volcanoes in Northern Canada. The Fort Selkirk Volcanic Field
Fort Selkirk Volcanic Field
The Fort Selkirk volcanic field is a monogenetic volcanic field in the Northern Cordilleran Volcanic Province, Yukon Territory, Canada. It is the northernmost Holocene age volcanic field in Canada, located close to the connection of the Yukon and Pelly rivers. The youngest eruptions within the...
in central Yukon consists of valley-filling basalt lava flows and cinder cones. Ne Ch'e Ddhawa
Ne Ch'e Ddhawa
Ne Ch'e Ddhawa is a cinder cone, located 7 km upstream from Fort Selkirk in the Fort Selkirk Volcanic Field, Yukon, Canada. The volcano erupted subglacially during the late Pleistocene, erupting hyaloclastite tuffs, breccias, and pillow breccias.-See also:*Volcanism of Canada*List of Northern...
, a cinder cone 2 km (1 mi) to the connection of the Yukon
Yukon River
The Yukon River is a major watercourse of northwestern North America. The source of the river is located in British Columbia, Canada. The next portion lies in, and gives its name to Yukon Territory. The lower half of the river lies in the U.S. state of Alaska. The river is long and empties into...
and Pelly
Pelly River
The Pelly River is a river in Canada, and is a headstream of the Yukon River. The river originates west of the Mackenzie Mountains and flows 530 km long through the south central Yukon. The Pelly has two main tributaries, the Ross and Macmillan rivers.The river was named by Robert Campbell in...
rivers formed between 0.8 and one million years ago when this area lied beneath the vast Cordilleran Ice Sheet
Cordilleran Ice Sheet
The Cordilleran ice sheet was a major ice sheet that covered, during glacial periods of the Quaternary, a large area of North America. This included the following areas:*Western Montana*The Idaho Panhandle...
. The youngest volcano, Volcano Mountain
Volcano Mountain
Volcano Mountain is an active cinder cone in central Yukon Territory, Canada, located a short distance north of Fort Selkirk, near the confluence of the Pelly and Yukon Rivers...
just north of the junction of the Yukon and Pelly rivers, formed in past 10,000 years (Holocene), producing lava flows that remain unvegetated and appear to be only a few hundred years old. However, dating of sediments in a lake impounded by the lava flows indicated that the youngest lava flows could not be younger than mid-Holocene and could be early Holocene or older. Therefore the most recent activity in the Fort Selkirk volcanic field is unknown. The lava flows from Volcano Mountain are unusual because they originate much deeper in the Earth's mantle
Mantle (geology)
The mantle is a part of a terrestrial planet or other rocky body large enough to have differentiation by density. The interior of the Earth, similar to the other terrestrial planets, is chemically divided into layers. The mantle is a highly viscous layer between the crust and the outer core....
than the more common basaltic lava flows found throughout the Yukon and are very uncommon in the geological record. This lava, known as olivine
Olivine
The mineral olivine is a magnesium iron silicate with the formula 2SiO4. It is a common mineral in the Earth's subsurface but weathers quickly on the surface....
nephelinite
Nephelinite
Nephelinite is a fine-grained or aphanitic igneous rock made up almost entirely of nepheline and clinopyroxene . If olivine is present, the rock may be classified as an olivine nephelinite. Nephelinite is dark in color and may resemble basalt in hand specimen...
, is also unusual because it contains small, angular to rounded fragments of rock called nodules
Nodule (geology)
A nodule in petrology or mineralogy is a secondary structure, generally spherical or irregularly rounded in shape. Nodules are typically solid replacement bodies of chert or iron oxides formed during diagenesis of a sedimentary rock...
.
Subduction complexes
More recent volcanic activity has created a northwest trending line of volcanic rocks called the Wrangell Volcanic BeltWrangell Volcanic Belt
The Wrangell Volcanic Field is a volcanic field stretching from eastern Alaska in the United States to the southwestern Yukon Territory in Canada. The field includes the four highest volcanoes in the United States, Mount Bona, Mount Blackburn, Mount Sanford, and Mount Churchill, all of which...
. This volcanic belt
Volcanic belt
A volcanic belt is a large volcanically active region. Other terms are used for smaller areas of activity, such as volcanic fields. Volcanic belts are found above zones of unusually high temperature where magma is created by partial melting of solid material in the Earth's crust and upper mantle....
lies largely in the U.S. state
U.S. state
A U.S. state is any one of the 50 federated states of the United States of America that share sovereignty with the federal government. Because of this shared sovereignty, an American is a citizen both of the federal entity and of his or her state of domicile. Four states use the official title of...
of Alaska
Alaska
Alaska is the largest state in the United States by area. It is situated in the northwest extremity of the North American continent, with Canada to the east, the Arctic Ocean to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the west and south, with Russia further west across the Bering Strait...
, but extends across the Alaska-Yukon border into southwestern Yukon where it contains scattered remnants of subaerial lavas and pyroclastic rocks which are preserved along the entire eastern fringe of the ice covered Saint Elias Mountains
Saint Elias Mountains
The Saint Elias Mountains are a subgroup of the Pacific Coast Ranges, located in southeastern Alaska in the United States, southwestern Yukon and the very far northwestern part of British Columbia in Canada. The range spans Wrangell-St. Elias National Park and Preserve in the USA and Kluane...
. The Wrangell Volcanic Belt formed as a result of arc volcanism related to subduction of the Pacific Plate
Pacific Plate
The Pacific Plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At 103 million square kilometres, it is the largest tectonic plate....
under the northern portion of the North American Plate. Over large areas extrusive rocks lie in flat undisturbed piles on a Tertiary surface of moderate relief. Locally, however, strata of the same age have been affected by a late pulse of tectonism, during which they were faulted, contorted into tight symmetrical folds, or overridden by pre-Tertiary basement rocks along southwesterly dipping thrust faults. Considerable recent uplift, accompanied by rapid erosion, has reduced once vast areas of upper Tertiary volcanic rocks to small isolated remnants. Although no eruptions have occurred in the Yukon portion of the Wrangell Belt for the past five million years, two large (VEI-6
Volcanic Explosivity Index
The Volcanic Explosivity Index was devised by Chris Newhall of the U.S. Geological Survey and Stephen Self at the University of Hawaii in 1982 to provide a relative measure of the explosiveness of volcanic eruptions....
) explosive eruptions from Mount Churchill
Mount Churchill
Mount Churchill is a volcano in the Saint Elias Mountains and the Wrangell Volcanic Field of eastern Alaska. Churchill and its higher neighbor Mount Bona about to the southwest are both large ice-covered stratovolcanoes, with Churchill being the fourth highest volcano in the United States and the...
24 km (15 mi) west of the Alaska-Yukon border, created the White River Ash
White River Ash
The White River Ash is a 2,000 year old ash deposit. It was formed by two large explosive eruptions from the stratovolcano of Mount Churchill that blanketed of Yukon and Northwest Territories, Canada and the U.S. state of Alaska with ash.-See also:...
deposit. This volcanic ash deposit is estimated 1,890 and 1,250 years old, covering more than 340000 km² (131,274.7 sq mi) of northwestern Canada and adjacent eastern Alaska. Unproven legends from indigenous people
Indigenous peoples of the Americas
The indigenous peoples of the Americas are the pre-Columbian inhabitants of North and South America, their descendants and other ethnic groups who are identified with those peoples. Indigenous peoples are known in Canada as Aboriginal peoples, and in the United States as Native Americans...
in the area indicate the final eruption from Mount Churchill 1,250 years ago disrupted food supplies and forced them to move further south.
See also
- Great Bear Magmatic ZoneGreat Bear Magmatic ZoneThe Great Bear Magmatic Zone is a linear belt of Proterozoic magmatic rocks in the northwestern Canadian Shield of the Northwest Territories. It is wide and long, extending from Great Slave Lake in the south to Great Bear Lake in the northwest...
- Volcanism of Canada
- Volcanism of Western CanadaVolcanism of Western CanadaVolcanism of Western Canada produces lava flows, lava plateaus, lava domes, cinder cones, stratovolcanoes, shield volcanoes, submarine volcanoes, calderas, diatremes and maars, along with examples of more less common volcanic forms such as tuyas and subglacial mounds.-Volcanic belts:*Anahim...
- Volcanism of Eastern CanadaVolcanism of Eastern CanadaVolcanism of Eastern Canada has led to the formation of hundreds of volcanic areas and extensive lava formations, indicating volcanism played a major role in shaping its surface. The region's different volcano and lava types originate from different tectonic settings and types of volcanic...
- List of volcanoes in Canada

