
Industry Standard Architecture
Encyclopedia
Industry Standard Architecture (ISA) is a computer bus standard for IBM PC compatible
computers introduced with the IBM Personal Computer to support its Intel 8088
microprocessor
's 8-bit external data bus and extended to 16 bits for the IBM Personal Computer/AT
's Intel 80286
processor. The ISA bus was further extended for use with 32-bit processors as Extended Industry Standard Architecture
(EISA). For general desktop computer use it has been supplanted by later buses such as IBM Micro Channel
, VESA Local Bus
, Peripheral Component Interconnect
and other successors. A derivative of the AT bus structure is still used in the PC/104
bus, and internally within Super I/O
chips.
as part of the IBM PC project in 1981. It originated as an 8-bit system. The newer 16-bit standard, the IBM AT
bus, was introduced in 1984. In 1988, the Gang of Nine IBM PC compatible
manufacturers put forth the 32-bit EISA
standard and in the process retroactively renamed
the AT bus to "ISA" to avoid infringing IBM's trademark on its PC/AT computer. IBM designed the 8-bit version as a buffered interface to the external bus of the Intel 8088
(16/8 bit) CPU used in the original IBM PC and PC/XT, and the 16-bit version as an upgrade for the external bus of the Intel 80286 CPU used in the IBM AT. Therefore, the ISA bus was synchronous with the CPU clock, until sophisticated buffering methods were developed and implemented by chipsets to interface ISA to much faster CPUs.
Designed to connect peripheral cards to the motherboard
, ISA allows for bus mastering
although only the first 16 MB
of main memory are available for direct access. The 8-bit bus ran at 4.77 MHz (the clock speed of the IBM PC and IBM PC/XT's 8088 CPU), while the 16-bit bus operated at 6 or 8 MHz (because the 80286 CPUs in IBM PC/AT computers ran at 6 MHz in early models and 8 MHz in later models.) IBM RT/PC also used the 16-bit bus. It was also available on some non-IBM compatible machines such as Motorola 68k
-based Apollo
workstations, the short-lived AT&T Hobbit
and later PowerPC
based BeBox
.
 In 1987, IBM moved to replace the AT bus with their proprietary Micro Channel Architecture
In 1987, IBM moved to replace the AT bus with their proprietary Micro Channel Architecture
(MCA) in an effort to regain control of the PC architecture and the PC market. (Note the relationship between the IBM term "I/O Channel" for the AT-bus and the name "Micro Channel" for IBM's intended replacement.) MCA had many features that would later appear in PCI, the successor of ISA, but MCA was a closed standard, unlike ISA (PC-bus and AT-bus) for which IBM had released full specifications and even circuit schematics. The system was far more advanced than the AT bus, and computer manufacturers responded with the Extended Industry Standard Architecture
(EISA) and later, the VESA Local Bus
(VLB). In fact, VLB used some electronic parts originally intended for MCA because component manufacturers already were equipped to manufacture them. Both EISA and VLB were backwards-compatible expansions of the AT (ISA) bus.
Users of ISA-based machines had to know special information about the hardware they were adding to the system. While a handful of devices were essentially "plug-n-play", this was rare. Users frequently had to configure several parameters when adding a new device, such as the IRQ line, I/O address, or DMA
channel. MCA had done away with this complication, and PCI
actually incorporated many of the ideas first explored with MCA (though it was more directly descended from EISA).
This trouble with configuration eventually led to the creation of ISA PnP, a plug-n-play system that used a combination of modifications to hardware, the system BIOS
, and operating system
software to automatically manage resource allocations. This required a system with an advanced programmable interrupt controller (APIC) replacing the Intel 8259 which the PC was born with. In reality, ISA PnP can be troublesome, and did not become well-supported until the architecture was in its final days since the APIC chip was a serendipitous addition to ISA by the PCI standard, which required an APIC.
PCI slots were the first physically incompatible expansion ports to directly squeeze ISA off the motherboard
. At first, motherboards were largely ISA, including a few PCI slots. By the mid-1990s, the two slot types were roughly balanced, and ISA slots soon were in the minority of consumer systems. Microsoft
's PC 97 specification recommended that ISA slots be removed entirely, though the system architecture still required ISA to be present in some vestigial way internally to handle the floppy drive, serial port
s, etc., which was why the software compatible LPC bus was created. ISA slots remained for a few more years, and towards the turn of the century it was common to see systems with an Accelerated Graphics Port
(AGP) sitting near the central processing unit
, an array of PCI slots, and one or two ISA slots near the end. In late 2008, even floppy disk drives and serial ports were disappearing, and the extinction of vestigial ISA (by then the LPC bus) from chipsets was on the horizon.
It is also notable that PCI slots are "rotated" compared to their ISA counterparts—PCI cards were essentially inserted "upside-down," allowing ISA and PCI connectors to squeeze together on the motherboard. Only one of the two connectors can be used in each slot at a time, but this allowed for greater flexibility.
The AT Attachment
(ATA) hard disk interface is directly descended from ISA (the AT bus). ATA has its origins in hardcards that integrated a hard disk controller (HDC) — usually with an ST-506/ST-412 interface — and a hard disk drive on the same ISA adapter. This was at best awkward from a mechanical structural standpoint, as ISA slots were not designed to support such heavy devices as hard disks (and the 3.5" form-factor hard disks of the time were about twice as tall and heavy as modern drives), so the next generation of Integrated Drive Electronics drives moved both the drive and controller to a drive bay and used a ribbon cable and a very simple interface board to connect it to an ISA slot. ATA, at its essence, is basically a standardization of this arrangement, combined with a uniform command structure for software to interface with the controller on a drive. ATA has since been separated from the ISA bus, and connected directly to the local bus (usually by integration into the chipset), to be clocked much much faster than ISA could support and with much higher throughput. (Notably when ISA was introduced as the AT bus, there was no distinction between a local and extension bus, and there were no chipsets.) Still, ATA retains details which reveal its relationship to ISA. The 16-bit transfer size is the most obvious example; the signal timing, particularly in the PIO modes, is also highly correlated, and the interrupt and DMA mechanisms are clearly from ISA. (The article about ATA
has more detail about this history.)
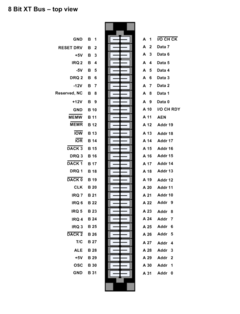
 The PC/XT-bus is an eight-bit
The PC/XT-bus is an eight-bit
ISA bus used by Intel 8086
and Intel 8088
systems in the IBM PC
and IBM PC XT in the 1980s. Among its 62 pins were demultiplexed and electrically buffered versions of the eight data and 20 address lines of the 8088 processor, along with power lines, clocks, read/write strobes, interrupt lines, etc. Power lines included -5V and +/-12 V in order to directly support pMOS
and enhancement mode nMOS
circuits such as dynamic RAMs among other things. The XT bus architecture uses a single Intel 8259
PIC
, giving eight vectorized and prioritized interrupt lines. It has four DMA
channels originally provided by the Intel 8237
, three of the DMA channels are brought out to the XT bus expansion slots; of these, two are normally already allocated to machine functions (diskette drive and hard disk controller):
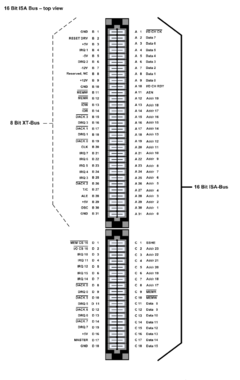
The PC/AT-bus, a 16-bit
(or 80286-) version of the PC/XT bus, was introduced with the IBM PC/AT. This bus was officially termed I/O Channel by IBM. It extends the XT-bus by adding a second shorter edge connector
in-line with the eight-bit XT-bus connector, which is unchanged, retaining compatibility with most 8-bit cards. The second connector adds four additional address lines for a total of 24, and eight additional data lines for a total of 16. It also adds new interrupt lines connected to a second 8259 PIC
(connected to one of the lines of the first) and four 16-bit DMA channels, as well as control lines to select 8 or 16 bit transfers.
The 16-bit AT bus slot originally used two standard edge connector sockets in early IBM PC/AT machines. However, with the popularity of the AT-architecture and the 16-bit ISA bus, manufacturers introduced specialized 98-pin connectors that integrated the two sockets into one unit. These can be found in almost every AT-class PC manufactured after the mid-1980s. The ISA slot connector is typically black (distinguishing it from the brown EISA connectors and white PCI connectors).
s used a separate clock generator or a clock divider which either fixed the ISA bus frequency at 4, 6 or 8 MHz or allowed the user to adjust the frequency via the BIOS
setup. When used at a higher bus frequency, some ISA cards (certain Hercules-compatible
video cards, for instance), could show significant performance improvements.
The PC/104
bus, used in industrial and embedded applications, is a derivative of the ISA bus, utilizing the same signal lines with different connectors. The LPC
bus has replaced the ISA bus as the connection to the legacy I/O devices on recent motherboards; while physically quite different, LPC looks just like ISA to software, so that the peculiarities of ISA such as the 16 MiB DMA limit (which corresponds to the full address space of the Intel 80286 CPU used in the original IBM AT) are likely to stick around for a while.
hard disks. Physically, ATA is essentially a simple subset of ISA, with 16 data bits, support for exactly one IRQ and one DMA channel, and 3 address bits plus two IDE address select ("chip select") lines, plus a few unique signal lines specific to ATA/IDE hard disks (such as the Cable Select/Spindle Sync. line.) ATA goes beyond and far outside the scope of ISA by also specifying a set of physical device registers to be implemented on every ATA (IDE) drive and accessed using the address bits and address select signals in the ATA physical interface channel; ATA also specifies a full set of protocols and device commands for controlling fixed disk drives using these registers, through which all operations of ATA hard disks are performed. A further deviation between ISA and ATA is that while the ISA bus remained locked into a single standard clock rate (for backward compatibility), the ATA interface offered many different speed modes, could select among them to match the maximum speed supported by the attached drives, and kept adding faster speeds with later versions of the ATA standard (up to 133 MB/s for ATA-6, the latest.) In most forms, ATA ran much faster than ISA.
's later XT clones. The XTA pinout was very similar to ATA, but only eight data lines and two address lines were used, and the physical device registers had completely different meanings. A few hard drives (such as the Seagate
ST351A/X) could support either type of interface, selected with a jumper.
(most non-mainframe, non-embedded) — have ISA buses allocated in virtual address space
. Embedded controller chips (southbridge
) and CPUs
themselves provide services such as temperature monitoring and voltage readings through these buses as ISA devices.
IBM PC compatible
IBM PC compatible computers are those generally similar to the original IBM PC, XT, and AT. Such computers used to be referred to as PC clones, or IBM clones since they almost exactly duplicated all the significant features of the PC architecture, facilitated by various manufacturers' ability to...
computers introduced with the IBM Personal Computer to support its Intel 8088
Intel 8088
The Intel 8088 microprocessor was a variant of the Intel 8086 and was introduced on July 1, 1979. It had an 8-bit external data bus instead of the 16-bit bus of the 8086. The 16-bit registers and the one megabyte address range were unchanged, however...
microprocessor
Microprocessor
A microprocessor incorporates the functions of a computer's central processing unit on a single integrated circuit, or at most a few integrated circuits. It is a multipurpose, programmable device that accepts digital data as input, processes it according to instructions stored in its memory, and...
's 8-bit external data bus and extended to 16 bits for the IBM Personal Computer/AT
IBM Personal Computer/AT
The IBM Personal Computer AT, more commonly known as the IBM AT and also sometimes called the PC AT or PC/AT, was IBM's second-generation PC, designed around the 6 MHz Intel 80286 microprocessor and released in 1984 as machine type 5170...
's Intel 80286
Intel 80286
The Intel 80286 , introduced on 1 February 1982, was a 16-bit x86 microprocessor with 134,000 transistors. Like its contemporary simpler cousin, the 80186, it could correctly execute most software written for the earlier Intel 8086 and 8088...
processor. The ISA bus was further extended for use with 32-bit processors as Extended Industry Standard Architecture
Extended Industry Standard Architecture
The Extended Industry Standard Architecture is a bus standard for IBM PC compatible computers...
(EISA). For general desktop computer use it has been supplanted by later buses such as IBM Micro Channel
Micro Channel architecture
Micro Channel Architecture was a proprietary 16- or 32-bit parallel computer bus introduced by IBM in 1987 which was used on PS/2 and other computers through the mid 1990s.- Background :...
, VESA Local Bus
VESA Local Bus
The VESA Local Bus was mostly used in personal computers. VESA Local Bus worked alongside the ISA bus; it acted as a high-speed conduit for memory-mapped I/O and DMA, while the ISA bus handled interrupts and port-mapped I/O.-Historical overview:In the early 1990s, the I/O bandwidth of...
, Peripheral Component Interconnect
Peripheral Component Interconnect
Conventional PCI is a computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer...
and other successors. A derivative of the AT bus structure is still used in the PC/104
PC/104
PC/104 is an embedded computer standard controlled by the which defines both a form factor and computer bus. PC/104 is intended for specialized embedded computing environments where applications depend on reliable data acquisition despite an often extreme environment...
bus, and internally within Super I/O
Super I/O
Super I/O is a class of I/O controller integrated circuits that began to be used on personal computer motherboards in the late 1980s, originally as add-in cards, later embedded on the motherboards. A super I/O chip combines interfaces for a variety of low-bandwidth devices...
chips.
History
The ISA bus was developed by a team led by Mark Dean at IBMIBM
International Business Machines Corporation or IBM is an American multinational technology and consulting corporation headquartered in Armonk, New York, United States. IBM manufactures and sells computer hardware and software, and it offers infrastructure, hosting and consulting services in areas...
as part of the IBM PC project in 1981. It originated as an 8-bit system. The newer 16-bit standard, the IBM AT
IBM Personal Computer/AT
The IBM Personal Computer AT, more commonly known as the IBM AT and also sometimes called the PC AT or PC/AT, was IBM's second-generation PC, designed around the 6 MHz Intel 80286 microprocessor and released in 1984 as machine type 5170...
bus, was introduced in 1984. In 1988, the Gang of Nine IBM PC compatible
IBM PC compatible
IBM PC compatible computers are those generally similar to the original IBM PC, XT, and AT. Such computers used to be referred to as PC clones, or IBM clones since they almost exactly duplicated all the significant features of the PC architecture, facilitated by various manufacturers' ability to...
manufacturers put forth the 32-bit EISA
Extended Industry Standard Architecture
The Extended Industry Standard Architecture is a bus standard for IBM PC compatible computers...
standard and in the process retroactively renamed
Retronym
A retronym is a type of neologism that provides a new name for an object or concept to differentiate the original form or version of it from a more recent form or version. The original name is most often augmented with an adjective to account for later developments of the object or concept itself...
the AT bus to "ISA" to avoid infringing IBM's trademark on its PC/AT computer. IBM designed the 8-bit version as a buffered interface to the external bus of the Intel 8088
Intel 8088
The Intel 8088 microprocessor was a variant of the Intel 8086 and was introduced on July 1, 1979. It had an 8-bit external data bus instead of the 16-bit bus of the 8086. The 16-bit registers and the one megabyte address range were unchanged, however...
(16/8 bit) CPU used in the original IBM PC and PC/XT, and the 16-bit version as an upgrade for the external bus of the Intel 80286 CPU used in the IBM AT. Therefore, the ISA bus was synchronous with the CPU clock, until sophisticated buffering methods were developed and implemented by chipsets to interface ISA to much faster CPUs.
Designed to connect peripheral cards to the motherboard
Motherboard
In personal computers, a motherboard is the central printed circuit board in many modern computers and holds many of the crucial components of the system, providing connectors for other peripherals. The motherboard is sometimes alternatively known as the mainboard, system board, or, on Apple...
, ISA allows for bus mastering
Bus mastering
In computing, bus mastering is a feature supported by many bus architectures that enables a device connected to the bus to initiate transactions...
although only the first 16 MB
Megabyte
The megabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information storage or transmission with two different values depending on context: bytes generally for computer memory; and one million bytes generally for computer storage. The IEEE Standards Board has decided that "Mega will mean 1 000...
of main memory are available for direct access. The 8-bit bus ran at 4.77 MHz (the clock speed of the IBM PC and IBM PC/XT's 8088 CPU), while the 16-bit bus operated at 6 or 8 MHz (because the 80286 CPUs in IBM PC/AT computers ran at 6 MHz in early models and 8 MHz in later models.) IBM RT/PC also used the 16-bit bus. It was also available on some non-IBM compatible machines such as Motorola 68k
Motorola 68020
The Motorola 68020 is a 32-bit microprocessor from Motorola, released in 1984. It is the successor to the Motorola 68010 and is succeeded by the Motorola 68030...
-based Apollo
Apollo Computer
Apollo Computer, Inc., founded 1980 in Chelmsford, Massachusetts by William Poduska and others, developed and produced Apollo/Domain workstations in the 1980s. Along with Symbolics and Sun Microsystems, Apollo was one of the first vendors of graphical workstations in the 1980s...
workstations, the short-lived AT&T Hobbit
AT&T Hobbit
The Hobbit is a microprocessor design of the early 1990s from AT&T. It developed from the company's CRISP design that was in turn developed from the C Machine experimental efforts in the late 1980s at Bell Labs. C Machine, CRISP and Hobbit were optimized for running the C programming language...
and later PowerPC
PowerPC
PowerPC is a RISC architecture created by the 1991 Apple–IBM–Motorola alliance, known as AIM...
based BeBox
BeBox
The BeBox was a short-lived dual processor personal computer, offered by Be Inc. to run the company's own operating system, BeOS. Notable aspects of the system include its CPU configuration, I/O board with "GeekPort", and "Blinkenlights" on the front bezel....
.

Micro Channel architecture
Micro Channel Architecture was a proprietary 16- or 32-bit parallel computer bus introduced by IBM in 1987 which was used on PS/2 and other computers through the mid 1990s.- Background :...
(MCA) in an effort to regain control of the PC architecture and the PC market. (Note the relationship between the IBM term "I/O Channel" for the AT-bus and the name "Micro Channel" for IBM's intended replacement.) MCA had many features that would later appear in PCI, the successor of ISA, but MCA was a closed standard, unlike ISA (PC-bus and AT-bus) for which IBM had released full specifications and even circuit schematics. The system was far more advanced than the AT bus, and computer manufacturers responded with the Extended Industry Standard Architecture
Extended Industry Standard Architecture
The Extended Industry Standard Architecture is a bus standard for IBM PC compatible computers...
(EISA) and later, the VESA Local Bus
VESA Local Bus
The VESA Local Bus was mostly used in personal computers. VESA Local Bus worked alongside the ISA bus; it acted as a high-speed conduit for memory-mapped I/O and DMA, while the ISA bus handled interrupts and port-mapped I/O.-Historical overview:In the early 1990s, the I/O bandwidth of...
(VLB). In fact, VLB used some electronic parts originally intended for MCA because component manufacturers already were equipped to manufacture them. Both EISA and VLB were backwards-compatible expansions of the AT (ISA) bus.
Users of ISA-based machines had to know special information about the hardware they were adding to the system. While a handful of devices were essentially "plug-n-play", this was rare. Users frequently had to configure several parameters when adding a new device, such as the IRQ line, I/O address, or DMA
Direct memory access
Direct memory access is a feature of modern computers that allows certain hardware subsystems within the computer to access system memory independently of the central processing unit ....
channel. MCA had done away with this complication, and PCI
Peripheral Component Interconnect
Conventional PCI is a computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer...
actually incorporated many of the ideas first explored with MCA (though it was more directly descended from EISA).
This trouble with configuration eventually led to the creation of ISA PnP, a plug-n-play system that used a combination of modifications to hardware, the system BIOS
BIOS
In IBM PC compatible computers, the basic input/output system , also known as the System BIOS or ROM BIOS , is a de facto standard defining a firmware interface....
, and operating system
Operating system
An operating system is a set of programs that manage computer hardware resources and provide common services for application software. The operating system is the most important type of system software in a computer system...
software to automatically manage resource allocations. This required a system with an advanced programmable interrupt controller (APIC) replacing the Intel 8259 which the PC was born with. In reality, ISA PnP can be troublesome, and did not become well-supported until the architecture was in its final days since the APIC chip was a serendipitous addition to ISA by the PCI standard, which required an APIC.
PCI slots were the first physically incompatible expansion ports to directly squeeze ISA off the motherboard
Motherboard
In personal computers, a motherboard is the central printed circuit board in many modern computers and holds many of the crucial components of the system, providing connectors for other peripherals. The motherboard is sometimes alternatively known as the mainboard, system board, or, on Apple...
. At first, motherboards were largely ISA, including a few PCI slots. By the mid-1990s, the two slot types were roughly balanced, and ISA slots soon were in the minority of consumer systems. Microsoft
Microsoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American public multinational corporation headquartered in Redmond, Washington, USA that develops, manufactures, licenses, and supports a wide range of products and services predominantly related to computing through its various product divisions...
's PC 97 specification recommended that ISA slots be removed entirely, though the system architecture still required ISA to be present in some vestigial way internally to handle the floppy drive, serial port
Serial port
In computing, a serial port is a serial communication physical interface through which information transfers in or out one bit at a time...
s, etc., which was why the software compatible LPC bus was created. ISA slots remained for a few more years, and towards the turn of the century it was common to see systems with an Accelerated Graphics Port
Accelerated Graphics Port
The Accelerated Graphics Port is a high-speed point-to-point channel for attaching a video card to a computer's motherboard, primarily to assist in the acceleration of 3D computer graphics. Since 2004 AGP has been progressively phased out in favor of PCI Express...
(AGP) sitting near the central processing unit
Central processing unit
The central processing unit is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. The term has been in...
, an array of PCI slots, and one or two ISA slots near the end. In late 2008, even floppy disk drives and serial ports were disappearing, and the extinction of vestigial ISA (by then the LPC bus) from chipsets was on the horizon.
It is also notable that PCI slots are "rotated" compared to their ISA counterparts—PCI cards were essentially inserted "upside-down," allowing ISA and PCI connectors to squeeze together on the motherboard. Only one of the two connectors can be used in each slot at a time, but this allowed for greater flexibility.
The AT Attachment
AT Attachment
Parallel ATA , originally ATA, is an interface standard for the connection of storage devices such as hard disks, solid-state drives, floppy drives, and optical disc drives in computers. The standard is maintained by X3/INCITS committee...
(ATA) hard disk interface is directly descended from ISA (the AT bus). ATA has its origins in hardcards that integrated a hard disk controller (HDC) — usually with an ST-506/ST-412 interface — and a hard disk drive on the same ISA adapter. This was at best awkward from a mechanical structural standpoint, as ISA slots were not designed to support such heavy devices as hard disks (and the 3.5" form-factor hard disks of the time were about twice as tall and heavy as modern drives), so the next generation of Integrated Drive Electronics drives moved both the drive and controller to a drive bay and used a ribbon cable and a very simple interface board to connect it to an ISA slot. ATA, at its essence, is basically a standardization of this arrangement, combined with a uniform command structure for software to interface with the controller on a drive. ATA has since been separated from the ISA bus, and connected directly to the local bus (usually by integration into the chipset), to be clocked much much faster than ISA could support and with much higher throughput. (Notably when ISA was introduced as the AT bus, there was no distinction between a local and extension bus, and there were no chipsets.) Still, ATA retains details which reveal its relationship to ISA. The 16-bit transfer size is the most obvious example; the signal timing, particularly in the PIO modes, is also highly correlated, and the interrupt and DMA mechanisms are clearly from ISA. (The article about ATA
AT Attachment
Parallel ATA , originally ATA, is an interface standard for the connection of storage devices such as hard disks, solid-state drives, floppy drives, and optical disc drives in computers. The standard is maintained by X3/INCITS committee...
has more detail about this history.)
ISA bus architecture


Bit
A bit is the basic unit of information in computing and telecommunications; it is the amount of information stored by a digital device or other physical system that exists in one of two possible distinct states...
ISA bus used by Intel 8086
Intel 8086
The 8086 is a 16-bit microprocessor chip designed by Intel between early 1976 and mid-1978, when it was released. The 8086 gave rise to the x86 architecture of Intel's future processors...
and Intel 8088
Intel 8088
The Intel 8088 microprocessor was a variant of the Intel 8086 and was introduced on July 1, 1979. It had an 8-bit external data bus instead of the 16-bit bus of the 8086. The 16-bit registers and the one megabyte address range were unchanged, however...
systems in the IBM PC
IBM PC
The IBM Personal Computer, commonly known as the IBM PC, is the original version and progenitor of the IBM PC compatible hardware platform. It is IBM model number 5150, and was introduced on August 12, 1981...
and IBM PC XT in the 1980s. Among its 62 pins were demultiplexed and electrically buffered versions of the eight data and 20 address lines of the 8088 processor, along with power lines, clocks, read/write strobes, interrupt lines, etc. Power lines included -5V and +/-12 V in order to directly support pMOS
PMOS logic
P-type metal-oxide-semiconductor logic uses p-type metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistors to implement logic gates and other digital circuits...
and enhancement mode nMOS
NMOS logic
N-type metal-oxide-semiconductor logic uses n-type metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistors to implement logic gates and other digital circuits...
circuits such as dynamic RAMs among other things. The XT bus architecture uses a single Intel 8259
Intel 8259
The Intel 8259 is a Programmable Interrupt Controller designed for the Intel 8085 and Intel 8086 microprocessors. The initial part was 8259, a later A suffix version was upward compatible and usable with the 8086 or 8088 processor...
PIC
Programmable Interrupt Controller
In computing, a programmable interrupt controller is a device that is used to combine several sources of interrupt onto one or more CPU lines, while allowing priority levels to be assigned to its interrupt outputs. When the device has multiple interrupt outputs to assert, it will assert them in...
, giving eight vectorized and prioritized interrupt lines. It has four DMA
Direct memory access
Direct memory access is a feature of modern computers that allows certain hardware subsystems within the computer to access system memory independently of the central processing unit ....
channels originally provided by the Intel 8237
Intel 8237
Intel 8237 is a direct memory access controller , a part of the MCS 85 microprocessor family. It was used as the DMA controller in the original IBM PC and IBM XT...
, three of the DMA channels are brought out to the XT bus expansion slots; of these, two are normally already allocated to machine functions (diskette drive and hard disk controller):
| DMA channel | Expansion | Standard function |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | No | Dynamic random-access memory refresh |
| 1 | Yes | Add-on cards |
| 2 | Yes | Floppy disk Floppy disk A floppy disk is a disk storage medium composed of a disk of thin and flexible magnetic storage medium, sealed in a rectangular plastic carrier lined with fabric that removes dust particles... controller |
| 3 | Yes | Hard disk Hard disk A hard disk drive is a non-volatile, random access digital magnetic data storage device. It features rotating rigid platters on a motor-driven spindle within a protective enclosure. Data is magnetically read from and written to the platter by read/write heads that float on a film of air above the... controller |
The PC/AT-bus, a 16-bit
Bit
A bit is the basic unit of information in computing and telecommunications; it is the amount of information stored by a digital device or other physical system that exists in one of two possible distinct states...
(or 80286-) version of the PC/XT bus, was introduced with the IBM PC/AT. This bus was officially termed I/O Channel by IBM. It extends the XT-bus by adding a second shorter edge connector
Edge connector
An edge connector is the portion of a printed circuit board consisting of traces leading to the edge of the board that are intended to plug into a matching socket. The edge connector is a money-saving device because it only requires a single discrete female connector , and they also tend to be...
in-line with the eight-bit XT-bus connector, which is unchanged, retaining compatibility with most 8-bit cards. The second connector adds four additional address lines for a total of 24, and eight additional data lines for a total of 16. It also adds new interrupt lines connected to a second 8259 PIC
Intel 8259
The Intel 8259 is a Programmable Interrupt Controller designed for the Intel 8085 and Intel 8086 microprocessors. The initial part was 8259, a later A suffix version was upward compatible and usable with the 8086 or 8088 processor...
(connected to one of the lines of the first) and four 16-bit DMA channels, as well as control lines to select 8 or 16 bit transfers.
The 16-bit AT bus slot originally used two standard edge connector sockets in early IBM PC/AT machines. However, with the popularity of the AT-architecture and the 16-bit ISA bus, manufacturers introduced specialized 98-pin connectors that integrated the two sockets into one unit. These can be found in almost every AT-class PC manufactured after the mid-1980s. The ISA slot connector is typically black (distinguishing it from the brown EISA connectors and white PCI connectors).
Number of devices
Motherboard devices have dedicated IRQs (not present in the slots). 16-bit devices can use either PC-bus or PC/AT-bus IRQs. It is therefore possible to connect up to 6 devices that use one 8-bit IRQ each, or up to 5 devices that use one 16-bit IRQ each. At the same time, up to four devices may use one 8-bit DMA channel each, while up to three devices can use one 16-bit DMA channel each.Varying bus speeds
Originally, the bus clock was synchronous with the CPU clock, resulting in varying bus clock frequencies among the many different IBM "clones" on the market (sometimes as high as 16 or 20 MHz), leading to software or electrical timing problems for certain ISA cards at bus speeds they were not designed for. Later motherboards and/or integrated chipsetChipset
A chipset, PC chipset, or chip set refers to a group of integrated circuits, or chips, that are designed to work together. They are usually marketed as a single product.- Computers :...
s used a separate clock generator or a clock divider which either fixed the ISA bus frequency at 4, 6 or 8 MHz or allowed the user to adjust the frequency via the BIOS
BIOS
In IBM PC compatible computers, the basic input/output system , also known as the System BIOS or ROM BIOS , is a de facto standard defining a firmware interface....
setup. When used at a higher bus frequency, some ISA cards (certain Hercules-compatible
Hercules Graphics Card
The Hercules Graphics Card was a computer graphics controller made by Hercules Computer Technology, Inc. which, through its popularity, became a widely supported display standard. It was common on IBM PC compatibles connected to a monochrome monitor . It supported one high resolution text mode and...
video cards, for instance), could show significant performance improvements.
8/16-bit Incompatibilities
Memory address decoding for the selection of 8 or 16-bit transfer mode was limited to 128 kB sections - A0000..BFFFF, C0000..DFFFF, E0000..FFFFF leading to problems when mixing 8 and 16-bit cards, as they could not co-exist in the same 128 kB area.Current use
ISA is still used today for specialized industrial purposes. In 2008 IEI Technologies released a modern motherboard for Intel Core 2 Duo processors which, in addition to other special I/O features, is equipped with two ISA slots. It is marketed to industrial and military users who have invested in expensive specialized ISA bus adaptors, which are not available in PCI bus versions.The PC/104
PC/104
PC/104 is an embedded computer standard controlled by the which defines both a form factor and computer bus. PC/104 is intended for specialized embedded computing environments where applications depend on reliable data acquisition despite an often extreme environment...
bus, used in industrial and embedded applications, is a derivative of the ISA bus, utilizing the same signal lines with different connectors. The LPC
Low Pin Count
The Low Pin Count bus, or LPC bus, is used on IBM-compatible personal computers to connect low-bandwidth devices to the CPU, such as the boot ROM and the "legacy" I/O devices . The "legacy" I/O devices usually include serial and parallel ports, PS/2 keyboard, PS/2 mouse, floppy disk controller...
bus has replaced the ISA bus as the connection to the legacy I/O devices on recent motherboards; while physically quite different, LPC looks just like ISA to software, so that the peculiarities of ISA such as the 16 MiB DMA limit (which corresponds to the full address space of the Intel 80286 CPU used in the original IBM AT) are likely to stick around for a while.
ATA
As explained in the History section, ISA was the basis for development of the ATA interface, used for ATA (a.k.a. IDE) and more recently Serial ATA (SATA)Serial ATA
Serial ATA is a computer bus interface for connecting host bus adapters to mass storage devices such as hard disk drives and optical drives...
hard disks. Physically, ATA is essentially a simple subset of ISA, with 16 data bits, support for exactly one IRQ and one DMA channel, and 3 address bits plus two IDE address select ("chip select") lines, plus a few unique signal lines specific to ATA/IDE hard disks (such as the Cable Select/Spindle Sync. line.) ATA goes beyond and far outside the scope of ISA by also specifying a set of physical device registers to be implemented on every ATA (IDE) drive and accessed using the address bits and address select signals in the ATA physical interface channel; ATA also specifies a full set of protocols and device commands for controlling fixed disk drives using these registers, through which all operations of ATA hard disks are performed. A further deviation between ISA and ATA is that while the ISA bus remained locked into a single standard clock rate (for backward compatibility), the ATA interface offered many different speed modes, could select among them to match the maximum speed supported by the attached drives, and kept adding faster speeds with later versions of the ATA standard (up to 133 MB/s for ATA-6, the latest.) In most forms, ATA ran much faster than ISA.
XT-IDE
Before the 16-bit ATA/IDE interface, there was an 8-bit XT-IDE (also known as XTA) interface for hard disks, though it was not nearly as popular as ATA has become, and XT-IDE hardware is now fairly hard to find (for those vintage computer enthusiasts who may look for it). Some XT-IDE adapters were available as 8-bit ISA cards, and XTA sockets were also present on the motherboards of AmstradAmstrad
Amstrad is a British electronics company, now wholly owned by BSkyB. As of 2006, Amstrad's main business is manufacturing Sky Digital interactive boxes....
's later XT clones. The XTA pinout was very similar to ATA, but only eight data lines and two address lines were used, and the physical device registers had completely different meanings. A few hard drives (such as the Seagate
Seagate Technology
Seagate Technology is one of the world's largest manufacturers of hard disk drives. Incorporated in 1978 as Shugart Technology, Seagate is currently incorporated in Dublin, Ireland and has its principal executive offices in Scotts Valley, California, United States.-1970s:On November 1, 1979...
ST351A/X) could support either type of interface, selected with a jumper.
PCMCIA
A derivation of ATA was the PCMCIA specification, merely a wire-adapter away from ATA. This then meant that Compact Flash, based on PCMCIA, were (and are) ATA compliant and can, with a very simple adapter, be used on ATA ports.Emulation by embedded chips
Although most computers do not have physical ISA buses all IBM compatible computers — x86, and x86-64X86-64
x86-64 is an extension of the x86 instruction set. It supports vastly larger virtual and physical address spaces than are possible on x86, thereby allowing programmers to conveniently work with much larger data sets. x86-64 also provides 64-bit general purpose registers and numerous other...
(most non-mainframe, non-embedded) — have ISA buses allocated in virtual address space
Virtual address space
Virtual address space is a memory mapping mechanism available in modern operating systems such as OpenVMS, UNIX, Linux, and Windows NT...
. Embedded controller chips (southbridge
Southbridge (computing)
The southbridge is one of the two chips in the core logic chipset on a personal computer motherboard, the other being the northbridge. The southbridge typically implements the slower capabilities of the motherboard in a northbridge/southbridge chipset computer architecture. In Intel chipset...
) and CPUs
Central processing unit
The central processing unit is the portion of a computer system that carries out the instructions of a computer program, to perform the basic arithmetical, logical, and input/output operations of the system. The CPU plays a role somewhat analogous to the brain in the computer. The term has been in...
themselves provide services such as temperature monitoring and voltage readings through these buses as ISA devices.
Standardization
IEEE started a standardization of the ISA bus in 1985, called the P996 specification. However, despite there even having been books published on the P996 specification, it never officially progressed past draft status.See also
- PC/104PC/104PC/104 is an embedded computer standard controlled by the which defines both a form factor and computer bus. PC/104 is intended for specialized embedded computing environments where applications depend on reliable data acquisition despite an often extreme environment...
- Embedded variant of ISA - Low Pin CountLow Pin CountThe Low Pin Count bus, or LPC bus, is used on IBM-compatible personal computers to connect low-bandwidth devices to the CPU, such as the boot ROM and the "legacy" I/O devices . The "legacy" I/O devices usually include serial and parallel ports, PS/2 keyboard, PS/2 mouse, floppy disk controller...
(LPC) - Low pin count version of ISA - Extended Industry Standard ArchitectureExtended Industry Standard ArchitectureThe Extended Industry Standard Architecture is a bus standard for IBM PC compatible computers...
(EISA) - Micro Channel architectureMicro Channel architectureMicro Channel Architecture was a proprietary 16- or 32-bit parallel computer bus introduced by IBM in 1987 which was used on PS/2 and other computers through the mid 1990s.- Background :...
(MCA) - VESA Local BusVESA Local BusThe VESA Local Bus was mostly used in personal computers. VESA Local Bus worked alongside the ISA bus; it acted as a high-speed conduit for memory-mapped I/O and DMA, while the ISA bus handled interrupts and port-mapped I/O.-Historical overview:In the early 1990s, the I/O bandwidth of...
(VLB) - Accelerated Graphics PortAccelerated Graphics PortThe Accelerated Graphics Port is a high-speed point-to-point channel for attaching a video card to a computer's motherboard, primarily to assist in the acceleration of 3D computer graphics. Since 2004 AGP has been progressively phased out in favor of PCI Express...
(AGP) - PCI-XPCI-XPCI-X, short for PCI-eXtended, is a computer bus and expansion card standard that enhances the 32-bit PCI Local Bus for higher bandwidth demanded by servers. It is a double-wide version of PCI, running at up to four times the clock speed, but is otherwise similar in electrical implementation and...
- Peripheral Component InterconnectPeripheral Component InterconnectConventional PCI is a computer bus for attaching hardware devices in a computer...
(PCI) - PCI ExpressPCI ExpressPCI Express , officially abbreviated as PCIe, is a computer expansion card standard designed to replace the older PCI, PCI-X, and AGP bus standards...
(PCI-E or PCIe) - List of computer bus interfaces
- Amiga Zorro II
- NuBusNuBusNuBus is a 32-bit parallel computer bus, originally developed at MIT as a part of the NuMachine workstation project. The first complete implementation of the NuBus and the NuMachine was done by Western Digital for their NuMachine, and for the Lisp Machines Inc. LMI-Lambda. The NuBus was later...
- Switched fabricSwitched fabricSwitched fabric, switching fabric, or just fabric, is a network topology where network nodes connect with each other via one or more network switches . The term is popular in telecommunication, Fibre Channel storage area networks and other high-speed networks, including InfiniBand...
- List of device bandwidths
- CompactPCICompactPCIA CompactPCI system is a 3U or 6U Eurocard-based industrial computer, where all boards are connected via a passive PCI backplane. The connector pin assignments are standardized by the PICMG US and PICMG Europe organizations. PICMG stands for PCI Industrial Computers Manufacturers Group...
- PC cardPC cardIn computing, PC Card is the form factor of a peripheral interface designed for laptop computers. The PC Card standard was defined and developed by the Personal Computer Memory Card International Association which itself was created by a number of computer industry companies in the United States...
- Universal Serial BusUniversal Serial BusUSB is an industry standard developed in the mid-1990s that defines the cables, connectors and protocols used in a bus for connection, communication and power supply between computers and electronic devices....
- Legacy portLegacy portA legacy port is a computer port or connector that is considered fully or partially superseded. The replacement ports usually provide the functionality of the legacy ports with higher speeds, more compact design, or plug and play and hot swap for greater ease of use; special USB adapters are often...
- BackplaneBackplaneA backplane is a group of connectors connected in parallel with each other, so that each pin of each connector is linked to the same relative pin of all the other connectors forming a computer bus. It is used as a backbone to connect several printed circuit boards together to make up a complete...

