
Central nervous system
Encyclopedia
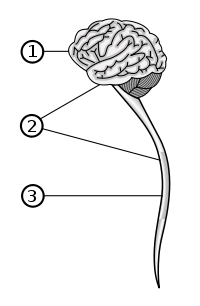
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system
that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish
. It contains the majority of the nervous system and consists of the brain
and the spinal cord
. Some classifications also include the retina
and the cranial nerves
in the CNS. Together with the peripheral nervous system
, it has a fundamental role in the control of behavior
. The CNS is contained within the dorsal cavity, with the brain
in the cranial cavity
and the spinal cord in the spinal cavity. In vertebrate
s, the brain is protected by the skull, while the spinal cord is protected by the vertebrae, and both are enclosed in the meninges
.
on the neural plate
gradually deepens as ridges on either side of the groove (the neural folds
) become elevated, and ultimately meet, transforming the groove into a closed tube
, the ectoderm
al wall of which forms the rudiment of the nervous system. This tube initially differentiates into three vesicles
(pockets): the prosencephalon
at the front, the mesencephalon
, and, between the mesencephalon and the spinal cord, the rhombencephalon
. (By six weeks in the human embryo) the prosencephalon then divides further into the telencephalon
and diencephalon
; and the rhombencephalon divides into the metencephalon
and myelencephalon
.
As the vertebrate grows, these vesicles differentiate further still. The telencephalon differentiates into, among other things, the striatum
, the hippocampus
and the neocortex
, and its cavity becomes the first and second ventricles
. Diencephalon elaborations include the subthalamus
, hypothalamus
, thalamus
and epithalamus
, and its cavity forms the third ventricle
. The tectum, pretectum
, cerebral peduncle
and other structures develop out of the mesencephalon, and its cavity grows into the mesencephalic duct (cerebral aqueduct). The metencephalon becomes, among other things, the pons
and the cerebellum
, the myelencephalon forms the medulla oblongata
, and their cavities develop into the fourth ventricle.

 Planarians, members of the phylum Platyhelminthes (flatworms), have the simplest, clearly defined delineation of a nervous system into a central nervous system (CNS) and a peripheral nervous system
Planarians, members of the phylum Platyhelminthes (flatworms), have the simplest, clearly defined delineation of a nervous system into a central nervous system (CNS) and a peripheral nervous system
(PNS).
Their primitive brain, consisting of two fused anterior ganglia, and longitudinal nerve cords form the CNS; the laterally projecting nerves form the PNS. A molecular study found that more than 95% of the 116 genes involved in the nervous system of planarians, which includes genes related to the CNS, also exist in humans. Like planarians, vertebrates have a distinct CNS and PNS, though more complex than those of planarians.
The CNS of chordate
s differs from that of other animals in being placed dorsally in the body, above the gut and notochord
/spine
. The basic pattern of the CNS is highly conserved throughout the different species of vertebrates and during evolution. The major trend that can be observed is towards a progressive telencephalisation: the telencephalon
of reptiles is only an appendix to the large olfactory bulb
, while in mammals it makes up most of the volume of the CNS. In the human brain, the telencephalon covers most of the diencephalon
and the mesencephalon
. Indeed, the allometric study of brain size among different species shows a striking continuity from rats to whales, and allows us to complete the knowledge about the evolution of the CNS obtained through cranial endocasts.
Mammal
s – which appear in the fossil record after the first fishes, amphibians, and reptiles – are the only vertebrates to possess the evolutionarily recent, outermost part of the cerebral cortex
known as the neocortex
.
The neocortex of monotremes (the duck-billed platypus
and several species of spiny anteater
s) and of marsupials (such as kangaroo
s, koala
s, opossums, wombat
s, and Tasmanian devil
s) lack the convolutions – gyri and sulci
– found in the neocortex of most placental mammals (eutherians).
Within placental mammals, the size and complexity of the neocortex increased over time. The area of the neocortex of mice is only about 1/100 that of monkeys, and that of monkeys is only about 1/10 that of humans. In addition, rats lack convolutions in their neocortex (possibly also because rats are small mammals), whereas cats have a moderate degree of convolutions, and humans have quite extensive convolutions. Extreme convolution of the neocortex is found in dolphin
s, possibly related to their complex echolocation
.
and poliomyelitis
, neurodegenerative diseases
such as Alzheimer's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
, autoimmune
and inflammatory diseases such as multiple sclerosis
or acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
, and genetic disorders such as Krabbe's disease, Huntington's disease
, or adrenoleukodystrophy
. Lastly, cancers of the central nervous system can cause severe illness and, when malignant, can have very high mortality rates.
Nervous system
The nervous system is an organ system containing a network of specialized cells called neurons that coordinate the actions of an animal and transmit signals between different parts of its body. In most animals the nervous system consists of two parts, central and peripheral. The central nervous...
that integrates the information that it receives from, and coordinates the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterian animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish
Radiata
The Radiata are the radially symmetric animals of the Eumetazoa subkingdom. The term Radiata has had various meanings in the history of classification...
. It contains the majority of the nervous system and consists of the brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
and the spinal cord
Spinal cord
The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the brain . The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system...
. Some classifications also include the retina
Retina
The vertebrate retina is a light-sensitive tissue lining the inner surface of the eye. The optics of the eye create an image of the visual world on the retina, which serves much the same function as the film in a camera. Light striking the retina initiates a cascade of chemical and electrical...
and the cranial nerves
Cranial nerves
Cranial nerves are nerves that emerge directly from the brain, in contrast to spinal nerves, which emerge from segments of the spinal cord. In humans, there are traditionally twelve pairs of cranial nerves...
in the CNS. Together with the peripheral nervous system
Peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system consists of the nerves and ganglia outside of the brain and spinal cord. The main function of the PNS is to connect the central nervous system to the limbs and organs. Unlike the CNS, the PNS is not protected by the bone of spine and skull, or by the blood–brain...
, it has a fundamental role in the control of behavior
Behavior
Behavior or behaviour refers to the actions and mannerisms made by organisms, systems, or artificial entities in conjunction with its environment, which includes the other systems or organisms around as well as the physical environment...
. The CNS is contained within the dorsal cavity, with the brain
Brain
The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,...
in the cranial cavity
Cranial cavity
The cranial cavity, or intracranial space, is the space formed inside the skull. The brain occupies the cranial cavity, which is lined by the meninges and which contains cerebrospinal fluid to cushion blows....
and the spinal cord in the spinal cavity. In vertebrate
Vertebrate
Vertebrates are animals that are members of the subphylum Vertebrata . Vertebrates are the largest group of chordates, with currently about 58,000 species described. Vertebrates include the jawless fishes, bony fishes, sharks and rays, amphibians, reptiles, mammals, and birds...
s, the brain is protected by the skull, while the spinal cord is protected by the vertebrae, and both are enclosed in the meninges
Meninges
The meninges is the system of membranes which envelopes the central nervous system. The meninges consist of three layers: the dura mater, the arachnoid mater, and the pia mater. The primary function of the meninges and of the cerebrospinal fluid is to protect the central nervous system.-Dura...
.
Development
During early development of the vertebrate embryo, a longitudinal grooveNeural groove
The neural groove is a shallow median groove between the neural folds of an embryo. The neural folds are two longitudinal ridges that are caused by a folding up of the ectoderm in front of the primitive streak of the developing embryo...
on the neural plate
Neural plate
In human embryology, formation of neural plate is the first step of neurulation. It is created by a flat thickening opposite to the primitive streak of the ectoderm.-Development:...
gradually deepens as ridges on either side of the groove (the neural folds
Neural folds
In front of the primitive streak two longitudinal ridges, caused by a folding up of the ectoderm, make their appearance, one on either side of the middle line...
) become elevated, and ultimately meet, transforming the groove into a closed tube
Neural tube
In the developing vertebrate, the neural tube is the embryo's precursor to the central nervous system, which comprises the brain and spinal cord...
, the ectoderm
Ectoderm
The "ectoderm" is one of the three primary germ cell layers in the very early embryo. The other two layers are the mesoderm and endoderm , with the ectoderm as the most exterior layer...
al wall of which forms the rudiment of the nervous system. This tube initially differentiates into three vesicles
Vesicle (biology)
A vesicle is a bubble of liquid within another liquid, a supramolecular assembly made up of many different molecules. More technically, a vesicle is a small membrane-enclosed sack that can store or transport substances. Vesicles can form naturally because of the properties of lipid membranes , or...
(pockets): the prosencephalon
Prosencephalon
In the anatomy of the brain of vertebrates, the prosencephalon is the rostral-most portion of the brain. The prosencephalon, the mesencephalon , and rhombencephalon are the three primary portions of the brain during early development of the central nervous system...
at the front, the mesencephalon
Mesencephalon
The midbrain or mesencephalon is a portion of the central nervous system associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep/wake, arousal , and temperature regulation....
, and, between the mesencephalon and the spinal cord, the rhombencephalon
Rhombencephalon
The rhombencephalon is a developmental categorization of portions of the central nervous system in vertebrates.The rhombencephalon can be subdivided in a variable number of transversal swellings called rhombomeres...
. (By six weeks in the human embryo) the prosencephalon then divides further into the telencephalon
Telencephalon
The cerebrum or telencephalon, together with the diencephalon, constitutes the forebrain. The cerebrum is the most anterior region of the vertebrate central nervous system. Telencephalon refers to the embryonic structure, from which the mature cerebrum develops...
and diencephalon
Diencephalon
The diencephalon is the region of the vertebrate neural tube which gives rise to posterior forebrain structures. In development, the forebrain develops from the prosencephalon, the most anterior vesicle of the neural tube which later forms both the diencephalon and the...
; and the rhombencephalon divides into the metencephalon
Metencephalon
The metencephalon is a developmental categorization of portions of the central nervous system. The metencephalon is composed of the pons and the cerebellum; contains a portion of the fourth ventricle; and the trigeminal nerve , abducens nerve , facial nerve , and a portion of the vestibulocochlear...
and myelencephalon
Myelencephalon
The myelencephalon is categorized as a secondary vesicle in the development of the central nervous system. The prefix "myelen" is derived from Greek for medulla...
.
As the vertebrate grows, these vesicles differentiate further still. The telencephalon differentiates into, among other things, the striatum
Striatum
The striatum, also known as the neostriatum or striate nucleus, is a subcortical part of the forebrain. It is the major input station of the basal ganglia system. The striatum, in turn, gets input from the cerebral cortex...
, the hippocampus
Hippocampus
The hippocampus is a major component of the brains of humans and other vertebrates. It belongs to the limbic system and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory and spatial navigation. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in...
and the neocortex
Neocortex
The neocortex , also called the neopallium and isocortex , is a part of the brain of mammals. It is the outer layer of the cerebral hemispheres, and made up of six layers, labelled I to VI...
, and its cavity becomes the first and second ventricles
Lateral ventricles
The lateral ventricles are part of the ventricular system of the brain. Classified as part of the telencephalon, they are the largest of the ventricles....
. Diencephalon elaborations include the subthalamus
Subthalamus
The subthalamus is a part of the diencephalon. Its major part is the subthalamic nucleus. Functionally, it also encompasses the globus pallidus, which is topographically part of the telencephalon.-Anatomy:...
, hypothalamus
Hypothalamus
The Hypothalamus is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions...
, thalamus
Thalamus
The thalamus is a midline paired symmetrical structure within the brains of vertebrates, including humans. It is situated between the cerebral cortex and midbrain, both in terms of location and neurological connections...
and epithalamus
Epithalamus
The epithalamus is a dorsal posterior segment of the diencephalon which includes the habenula, the stria medullaris and the pineal body...
, and its cavity forms the third ventricle
Third ventricle
The third ventricle is one of four connected fluid-filled cavities comprising the ventricular system within the human brain. It is a median cleft between the two thalami, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid ....
. The tectum, pretectum
Pretectum
The pretectum, also known as the pretectal area, is a region of neurons found between the thalamus and midbrain. It receives binocular sensory input from retinal ganglion cells of the eyes, and is the region responsible for maintaining the pupillary light reflex.-Outputs:The pretectum, after...
, cerebral peduncle
Cerebral peduncle
Mainly, the three common areas that give rise to the cerebral peduncles are the cortex, the spinal cord and the cerebellum. The cerebral peduncle, by most classifications, is everything in the mesencephalon except the tectum. The region includes the midbrain tegmentum, crus cerebri and pretectum...
and other structures develop out of the mesencephalon, and its cavity grows into the mesencephalic duct (cerebral aqueduct). The metencephalon becomes, among other things, the pons
Pons
The pons is a structure located on the brain stem, named after the Latin word for "bridge" or the 16th-century Italian anatomist and surgeon Costanzo Varolio . It is superior to the medulla oblongata, inferior to the midbrain, and ventral to the cerebellum. In humans and other bipeds this means it...
and the cerebellum
Cerebellum
The cerebellum is a region of the brain that plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognitive functions such as attention and language, and in regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established...
, the myelencephalon forms the medulla oblongata
Medulla oblongata
The medulla oblongata is the lower half of the brainstem. In discussions of neurology and similar contexts where no ambiguity will result, it is often referred to as simply the medulla...
, and their cavities develop into the fourth ventricle.

| Central nervous system |
Brain Brain The brain is the center of the nervous system in all vertebrate and most invertebrate animals—only a few primitive invertebrates such as sponges, jellyfish, sea squirts and starfishes do not have one. It is located in the head, usually close to primary sensory apparatus such as vision, hearing,... |
Prosencephalon Prosencephalon In the anatomy of the brain of vertebrates, the prosencephalon is the rostral-most portion of the brain. The prosencephalon, the mesencephalon , and rhombencephalon are the three primary portions of the brain during early development of the central nervous system... |
Telencephalon Telencephalon The cerebrum or telencephalon, together with the diencephalon, constitutes the forebrain. The cerebrum is the most anterior region of the vertebrate central nervous system. Telencephalon refers to the embryonic structure, from which the mature cerebrum develops... |
Rhinencephalon Rhinencephalon In animal anatomy, the rhinencephalon is a part of the brain involved with olfaction.-Components:The term rhinencephalon has been used to describe different structures at different points in time.... , Amygdala Amygdala The ' are almond-shaped groups of nuclei located deep within the medial temporal lobes of the brain in complex vertebrates, including humans. Shown in research to perform a primary role in the processing and memory of emotional reactions, the amygdalae are considered part of the limbic system.-... , Hippocampus Hippocampus The hippocampus is a major component of the brains of humans and other vertebrates. It belongs to the limbic system and plays important roles in the consolidation of information from short-term memory to long-term memory and spatial navigation. Humans and other mammals have two hippocampi, one in... , Neocortex Neocortex The neocortex , also called the neopallium and isocortex , is a part of the brain of mammals. It is the outer layer of the cerebral hemispheres, and made up of six layers, labelled I to VI... , Basal ganglia Basal ganglia The basal ganglia are a group of nuclei of varied origin in the brains of vertebrates that act as a cohesive functional unit. They are situated at the base of the forebrain and are strongly connected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus and other brain areas... , Lateral ventricles Lateral ventricles The lateral ventricles are part of the ventricular system of the brain. Classified as part of the telencephalon, they are the largest of the ventricles.... |
|
| Diencephalon Diencephalon The diencephalon is the region of the vertebrate neural tube which gives rise to posterior forebrain structures. In development, the forebrain develops from the prosencephalon, the most anterior vesicle of the neural tube which later forms both the diencephalon and the... |
Epithalamus Epithalamus The epithalamus is a dorsal posterior segment of the diencephalon which includes the habenula, the stria medullaris and the pineal body... , Thalamus Thalamus The thalamus is a midline paired symmetrical structure within the brains of vertebrates, including humans. It is situated between the cerebral cortex and midbrain, both in terms of location and neurological connections... , Hypothalamus Hypothalamus The Hypothalamus is a portion of the brain that contains a number of small nuclei with a variety of functions... , Subthalamus Subthalamus The subthalamus is a part of the diencephalon. Its major part is the subthalamic nucleus. Functionally, it also encompasses the globus pallidus, which is topographically part of the telencephalon.-Anatomy:... , Pituitary gland Pituitary gland In vertebrate anatomy the pituitary gland, or hypophysis, is an endocrine gland about the size of a pea and weighing 0.5 g , in humans. It is a protrusion off the bottom of the hypothalamus at the base of the brain, and rests in a small, bony cavity covered by a dural fold... , Pineal gland Pineal gland The pineal gland is a small endocrine gland in the vertebrate brain. It produces the serotonin derivative melatonin, a hormone that affects the modulation of wake/sleep patterns and seasonal functions... , Third ventricle Third ventricle The third ventricle is one of four connected fluid-filled cavities comprising the ventricular system within the human brain. It is a median cleft between the two thalami, and is filled with cerebrospinal fluid .... |
||||
| Brain stem Brain stem In vertebrate anatomy the brainstem is the posterior part of the brain, adjoining and structurally continuous with the spinal cord. The brain stem provides the main motor and sensory innervation to the face and neck via the cranial nerves... |
Mesencephalon Mesencephalon The midbrain or mesencephalon is a portion of the central nervous system associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep/wake, arousal , and temperature regulation.... |
Tectum, Cerebral peduncle Cerebral peduncle Mainly, the three common areas that give rise to the cerebral peduncles are the cortex, the spinal cord and the cerebellum. The cerebral peduncle, by most classifications, is everything in the mesencephalon except the tectum. The region includes the midbrain tegmentum, crus cerebri and pretectum... , Pretectum Pretectum The pretectum, also known as the pretectal area, is a region of neurons found between the thalamus and midbrain. It receives binocular sensory input from retinal ganglion cells of the eyes, and is the region responsible for maintaining the pupillary light reflex.-Outputs:The pretectum, after... , Mesencephalic duct |
|||
| Rhombencephalon Rhombencephalon The rhombencephalon is a developmental categorization of portions of the central nervous system in vertebrates.The rhombencephalon can be subdivided in a variable number of transversal swellings called rhombomeres... |
Metencephalon Metencephalon The metencephalon is a developmental categorization of portions of the central nervous system. The metencephalon is composed of the pons and the cerebellum; contains a portion of the fourth ventricle; and the trigeminal nerve , abducens nerve , facial nerve , and a portion of the vestibulocochlear... |
Pons Pons The pons is a structure located on the brain stem, named after the Latin word for "bridge" or the 16th-century Italian anatomist and surgeon Costanzo Varolio . It is superior to the medulla oblongata, inferior to the midbrain, and ventral to the cerebellum. In humans and other bipeds this means it... , Cerebellum Cerebellum The cerebellum is a region of the brain that plays an important role in motor control. It may also be involved in some cognitive functions such as attention and language, and in regulating fear and pleasure responses, but its movement-related functions are the most solidly established... |
|||
| Myelencephalon Myelencephalon The myelencephalon is categorized as a secondary vesicle in the development of the central nervous system. The prefix "myelen" is derived from Greek for medulla... |
Medulla oblongata Medulla oblongata The medulla oblongata is the lower half of the brainstem. In discussions of neurology and similar contexts where no ambiguity will result, it is often referred to as simply the medulla... |
||||
| Spinal cord Spinal cord The spinal cord is a long, thin, tubular bundle of nervous tissue and support cells that extends from the brain . The brain and spinal cord together make up the central nervous system... |
|||||
Evolution

Peripheral nervous system
The peripheral nervous system consists of the nerves and ganglia outside of the brain and spinal cord. The main function of the PNS is to connect the central nervous system to the limbs and organs. Unlike the CNS, the PNS is not protected by the bone of spine and skull, or by the blood–brain...
(PNS).
Their primitive brain, consisting of two fused anterior ganglia, and longitudinal nerve cords form the CNS; the laterally projecting nerves form the PNS. A molecular study found that more than 95% of the 116 genes involved in the nervous system of planarians, which includes genes related to the CNS, also exist in humans. Like planarians, vertebrates have a distinct CNS and PNS, though more complex than those of planarians.
The CNS of chordate
Chordate
Chordates are animals which are either vertebrates or one of several closely related invertebrates. They are united by having, for at least some period of their life cycle, a notochord, a hollow dorsal nerve cord, pharyngeal slits, an endostyle, and a post-anal tail...
s differs from that of other animals in being placed dorsally in the body, above the gut and notochord
Notochord
The notochord is a flexible, rod-shaped body found in embryos of all chordates. It is composed of cells derived from the mesoderm and defines the primitive axis of the embryo. In some chordates, it persists throughout life as the main axial support of the body, while in most vertebrates it becomes...
/spine
Vertebral column
In human anatomy, the vertebral column is a column usually consisting of 24 articulating vertebrae, and 9 fused vertebrae in the sacrum and the coccyx. It is situated in the dorsal aspect of the torso, separated by intervertebral discs...
. The basic pattern of the CNS is highly conserved throughout the different species of vertebrates and during evolution. The major trend that can be observed is towards a progressive telencephalisation: the telencephalon
Telencephalon
The cerebrum or telencephalon, together with the diencephalon, constitutes the forebrain. The cerebrum is the most anterior region of the vertebrate central nervous system. Telencephalon refers to the embryonic structure, from which the mature cerebrum develops...
of reptiles is only an appendix to the large olfactory bulb
Olfactory bulb
The olfactory bulb is a structure of the vertebrate forebrain involved in olfaction, the perception of odors.-Anatomy:In most vertebrates, the olfactory bulb is the most rostral part of the brain. In humans, however, the olfactory bulb is on the inferior side of the brain...
, while in mammals it makes up most of the volume of the CNS. In the human brain, the telencephalon covers most of the diencephalon
Diencephalon
The diencephalon is the region of the vertebrate neural tube which gives rise to posterior forebrain structures. In development, the forebrain develops from the prosencephalon, the most anterior vesicle of the neural tube which later forms both the diencephalon and the...
and the mesencephalon
Mesencephalon
The midbrain or mesencephalon is a portion of the central nervous system associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep/wake, arousal , and temperature regulation....
. Indeed, the allometric study of brain size among different species shows a striking continuity from rats to whales, and allows us to complete the knowledge about the evolution of the CNS obtained through cranial endocasts.
Mammal
Mammal
Mammals are members of a class of air-breathing vertebrate animals characterised by the possession of endothermy, hair, three middle ear bones, and mammary glands functional in mothers with young...
s – which appear in the fossil record after the first fishes, amphibians, and reptiles – are the only vertebrates to possess the evolutionarily recent, outermost part of the cerebral cortex
Cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex is a sheet of neural tissue that is outermost to the cerebrum of the mammalian brain. It plays a key role in memory, attention, perceptual awareness, thought, language, and consciousness. It is constituted of up to six horizontal layers, each of which has a different...
known as the neocortex
Neocortex
The neocortex , also called the neopallium and isocortex , is a part of the brain of mammals. It is the outer layer of the cerebral hemispheres, and made up of six layers, labelled I to VI...
.
The neocortex of monotremes (the duck-billed platypus
Platypus
The platypus is a semi-aquatic mammal endemic to eastern Australia, including Tasmania. Together with the four species of echidna, it is one of the five extant species of monotremes, the only mammals that lay eggs instead of giving birth to live young...
and several species of spiny anteater
Echidna
Echidnas , also known as spiny anteaters, belong to the family Tachyglossidae in the monotreme order of egg-laying mammals. There are four extant species, which, together with the platypus, are the only surviving members of that order and are the only extant mammals that lay eggs...
s) and of marsupials (such as kangaroo
Kangaroo
A kangaroo is a marsupial from the family Macropodidae . In common use the term is used to describe the largest species from this family, especially those of the genus Macropus, Red Kangaroo, Antilopine Kangaroo, Eastern Grey Kangaroo and Western Grey Kangaroo. Kangaroos are endemic to the country...
s, koala
Koala
The koala is an arboreal herbivorous marsupial native to Australia, and the only extant representative of the family Phascolarctidae....
s, opossums, wombat
Wombat
Wombats are Australian marsupials; they are short-legged, muscular quadrupeds, approximately in length with a short, stubby tail. They are adaptable in their habitat tolerances, and are found in forested, mountainous, and heathland areas of south-eastern Australia, including Tasmania, as well as...
s, and Tasmanian devil
Tasmanian Devil
The Tasmanian devil is a carnivorous marsupial of the family Dasyuridae, now found in the wild only on the Australian island state of Tasmania. The size of a small dog, it became the largest carnivorous marsupial in the world following the extinction of the thylacine in 1936...
s) lack the convolutions – gyri and sulci
Sulcus
Sulcus may refer to:* Sulcus , a groove, crevice or furrow in medicine, botany, and zoology* Sulcus , a long parallel groove on a planet or a moon-See also:...
– found in the neocortex of most placental mammals (eutherians).
Within placental mammals, the size and complexity of the neocortex increased over time. The area of the neocortex of mice is only about 1/100 that of monkeys, and that of monkeys is only about 1/10 that of humans. In addition, rats lack convolutions in their neocortex (possibly also because rats are small mammals), whereas cats have a moderate degree of convolutions, and humans have quite extensive convolutions. Extreme convolution of the neocortex is found in dolphin
Dolphin
Dolphins are marine mammals that are closely related to whales and porpoises. There are almost forty species of dolphin in 17 genera. They vary in size from and , up to and . They are found worldwide, mostly in the shallower seas of the continental shelves, and are carnivores, mostly eating...
s, possibly related to their complex echolocation
Animal echolocation
Echolocation, also called biosonar, is the biological sonar used by several kinds of animals.Echolocating animals emit calls out to the environment and listen to the echoes of those calls that return from various objects near them. They use these echoes to locate and identify the objects...
.
Diseases of the central nervous system
There are many central nervous system diseases, including infections of the central nervous system such as encephalitisEncephalitis
Encephalitis is an acute inflammation of the brain. Encephalitis with meningitis is known as meningoencephalitis. Symptoms include headache, fever, confusion, drowsiness, and fatigue...
and poliomyelitis
Poliomyelitis
Poliomyelitis, often called polio or infantile paralysis, is an acute viral infectious disease spread from person to person, primarily via the fecal-oral route...
, neurodegenerative diseases
Neurodegeneration
Neurodegeneration is the umbrella term for the progressive loss of structure or function of neurons, including death of neurons. Many neurodegenerative diseases including Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, and Huntington’s occur as a result of neurodegenerative processes. As research progresses, many...
such as Alzheimer's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis , also referred to as Lou Gehrig's disease, is a form of motor neuron disease caused by the degeneration of upper and lower neurons, located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord and the cortical neurons that provide their efferent input...
, autoimmune
Autoimmune disease
Autoimmune diseases arise from an overactive immune response of the body against substances and tissues normally present in the body. In other words, the body actually attacks its own cells. The immune system mistakes some part of the body as a pathogen and attacks it. This may be restricted to...
and inflammatory diseases such as multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis
Multiple sclerosis is an inflammatory disease in which the fatty myelin sheaths around the axons of the brain and spinal cord are damaged, leading to demyelination and scarring as well as a broad spectrum of signs and symptoms...
or acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis
Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis is an immune mediated disease of the brain. It usually occurs following a viral infection but may appear following vaccination, bacterial or parasitic infection, or even appear spontaneously. As it involves autoimmune demyelination, it is similar to multiple...
, and genetic disorders such as Krabbe's disease, Huntington's disease
Huntington's disease
Huntington's disease, chorea, or disorder , is a neurodegenerative genetic disorder that affects muscle coordination and leads to cognitive decline and dementia. It typically becomes noticeable in middle age. HD is the most common genetic cause of abnormal involuntary writhing movements called chorea...
, or adrenoleukodystrophy
Adrenoleukodystrophy
Adrenoleukodystrophy is a rare, inherited disorder that leads to progressive brain damage, failure of the adrenal glands and eventually death. ALD is a disease in a group of genetic disorders called leukodystrophies, whose chief feature is damage to myelin...
. Lastly, cancers of the central nervous system can cause severe illness and, when malignant, can have very high mortality rates.
See also
- Glossary of anatomical terminology, definitions and abbreviations
- Central nervous system diseaseCentral nervous system diseaseA central nervous system disease can affect either the spinal cord or brain , both part of the central nervous system. The central nervous system controls behaviors in the human body, so this can be a fatal illness.-Spinal Cord:...
- Neural developmentNeural developmentNeural development comprises the processes that generate, shape, and reshape the nervous system, from the earliest stages of embryogenesis to the final years of life. The study of neural development aims to describe the cellular basis of brain development and to address the underlying mechanisms...
- NeuroradiologyNeuroradiologyNeuroradiology is a subspecialty of radiology focusing on the diagnosis and characterization of abnormalities of the central and peripheral nervous system, spine, and head and neck. Primary imaging modalities include computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging...
External links
- Sylvius: 400+ structure neuroanatomical visual glossary
- High-Resolution Cytoarchitectural Primate Brain Atlases
- Human Brains: A Learning Tool.
- Explaining the human nervous system.
- Nervous System – Back Pain – Anatomy (info on nerve pairs).
- Textbook in Medical Physiology And Pathophysiology, many links
- Brain and Cranial Nerves, Anatomy and Physiology Lecture, Northland Community College
- Latest Research on the Brain and Central Nervous System From ScienceDaily
- The Department of Neuroscience at Wikiversity
- Overview of the Central Nervous System, Neuroscience Online (electronic neuroscience textbook)

