
Lycopene
Encyclopedia
Lycopene is a bright red carotene
and carotenoid
pigment and phytochemical
found in tomato
es and other red fruits and vegetables, such as red carrot
s, watermelon
s and papaya
s (but not strawberries or cherries). Although lycopene is chemically a carotene, it has no vitamin A
activity.
In plant
s, algae
, and other photosynthetic organisms
, lycopene is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of many carotenoids, including beta carotene, responsible for yellow, orange or red pigmentation, photosynthesis, and photo-protection. Like all carotenoids, lycopene is a polyunsaturated hydrocarbon (an unsubstituted alkene
). Structurally, it is a tetraterpene
assembled from eight isoprene
units, composed entirely of carbon and hydrogen, and is insoluble in water. Lycopene's eleven conjugated double bond
s give it its deep red color and are responsible for its antioxidant
activity. Due to its strong color and non-toxicity, lycopene is a useful food coloring
(registered as E160d) and is approved for usage in the USA, Australia and New Zealand (registered as 160d) and the EU.
Lycopene is not an essential nutrient
for humans, but is commonly found in the diet, mainly from dishes prepared from tomatoes. When absorbed from the stomach, lycopene is transported in the blood by various lipoproteins and accumulates in the liver, adrenal glands, and testes.
Because preliminary research has shown an inverse correlation between consumption of tomatoes and cancer risk, lycopene has been considered a potential agent for prevention of some types of cancers, particularly prostate cancer
. However, this area of research and the relationship with prostate cancer have been deemed insufficient of evidence for health claim approval by the US Food and Drug Administration
(see below under Antioxidant properties and potential health benefits).
 Lycopene is a symmetrical tetraterpene
Lycopene is a symmetrical tetraterpene
assembled from 8 isoprene
units. It is a member of the carotenoid family of compounds, and because it consists entirely of carbon and hydrogen, is also a carotene
. Isolation procedures for lycopene were first reported in 1910, and the structure of the molecule was determined by 1931. In its natural, all-trans form, the molecule is long and straight, constrained by its system of eleven conjugated double bonds. Each double bond in this extended π electron
system reduces the energy required for electrons to transition to higher energy states, allowing the molecule to absorb visible light of progressively longer wavelengths. Lycopene absorbs all but the longest wavelengths of visible light, so it appears red.
Plants and photosynthetic bacteria naturally produce all-trans lycopene, but a total of 72 geometric isomers of the molecule are sterically possible. When exposed to light or heat, lycopene can undergo isomerization to any of a number of these cis-isomers, which have a bent rather than linear shape. Different isomers were shown to have different stabilities due to their molecular energy (highest stability: 5-cis ≥ all-trans ≥ 9-cis ≥ 13-cis > 15-cis > 7-cis > 11-cis: lowest). In the human bloodstream, various cis-isomers constitute more than 60% of the total lycopene concentration, but the biological effects of individual isomers have not been investigated.
Lycopene is insoluble in water, and can be dissolved only in organic solvents and oils. Because of its non-polarity, lycopene in food preparations will stain any sufficiently porous
material, including most plastics. While a tomato stain can be fairly easily removed from fabric (provided the stain is fresh), lycopene diffuses
into plastic, making it impossible to remove with hot water or detergent. If lycopene is oxidized (for example, by reacting with bleaches or acids), the double bonds between the carbon atoms will be broken; cleaving the molecule, breaking the conjugated double bond system, and eliminating the chromophore
.
 Carotenoids like lycopene are important pigments found in photosynthetic pigment-protein complexes in plants, photosynthetic bacteria, fungi, and algae. They are responsible for the bright colors of fruits and vegetables, perform various functions in photosynthesis, and protect photosynthetic organisms from excessive light damage. Lycopene is a key intermediate in the biosynthesis of many important carotenoids, such as beta-carotene
Carotenoids like lycopene are important pigments found in photosynthetic pigment-protein complexes in plants, photosynthetic bacteria, fungi, and algae. They are responsible for the bright colors of fruits and vegetables, perform various functions in photosynthesis, and protect photosynthetic organisms from excessive light damage. Lycopene is a key intermediate in the biosynthesis of many important carotenoids, such as beta-carotene
, and xanthophyll
s.
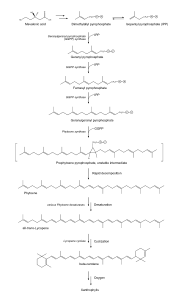
, which is converted into dimethylallyl pyrophosphate
. This is then condensed with three molecules of isopentenyl pyrophosphate
(an isomer of dimethylallyl pyrophosphate), to give the twenty carbon geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate
. Two molecules of this product are then condensed in a tail-to-tail configuration to give the forty carbon phytoene
, the first committed step in carotenoid biosynthesis. Through several desaturation steps, phytoene is converted into lycopene. The two terminal isoprene groups of lycopene can be cyclized to produce beta carotene, which can then be transformed into a wide variety of xanthophylls.
Fruit
s and vegetable
s that are high in lycopene include gac
, tomatoes, watermelon
, pink grapefruit
, pink guava
, papaya
, seabuckthorn, wolfberry
(goji, a berry relative of tomato), and rosehip. Although gac
(Momordica cochinchinensis Spreng) has the highest content of lycopene of any known fruit or vegetable, up to 70 times more than tomatoes for example, due to gac's rarity outside its native region of southeast Asia
, tomatoes and tomato-based sauces, juices, and ketchup account for more than 85% of the dietary intake of lycopene for most people. The lycopene content of tomatoes depends on species and increases as the fruit ripens.
Unlike other fruits and vegetables, where nutritional content such as vitamin C
is diminished upon cooking, processing
of tomatoes increases the concentration of bioavailable
lycopene. Lycopene in tomato paste is four times more bioavailable than in fresh tomatoes. For this reason, tomato sauce is a preferable source as opposed to raw tomatoes.
While most green leafy vegetables and other sources of lycopene are low in fats and oils, lycopene is insoluble in water and is tightly bound to vegetable fiber. Processed tomato products such as pasteurized tomato juice, soup, sauce, and ketchup contain the highest concentrations of bioavailable lycopene from tomato-based sources.
Cooking and crushing tomatoes (as in the canning
process) and serving in oil-rich dishes (such as spaghetti
sauce or pizza
) greatly increases assimilation from the digestive tract into the bloodstream. Lycopene is fat-soluble, so the oil is said to help absorption. Gac
is a notable exception, containing high concentrations of lycopene and also saturated and unsaturated fatty acids.
Lycopene may be obtained from vegetables and fruits such as the tomato, but another source of lycopene is the fungus Blakeslea trispora
. Gac
is a promising commercial source of lycopene for the purposes of extraction and purification.
The cis-lycopene from some varieties of tomato is more bioavailable.
After ingestion, lycopene is incorporated into lipid micelles in the small intestine. These micelles are formed from dietary fats and bile acids, and help to solubilize the hydrophobic lycopene and allow it to permeate the intestinal mucosal cells by a passive transport mechanism. Little is known about the liver metabolism of lycopene, but like other carotenoids, lycopene is incorporated into chylomicrons and released into the lymphatic system. In blood plasma, lycopene is eventually distributed into the very low and low density lipoprotein fractions. Lycopene is mainly distributed to fatty tissues and organs such as the adrenal glands, liver, and testes.
, being 100 times more efficient in test tube studies of singlet-oxygen quenching action than vitamin E
, which in turn has 125 times the quenching action of glutathione
(water soluble). Singlet oxygen produced during exposure to ultraviolet
light is a primary cause of skin aging
.
Given its antioxidant properties, substantial scientific and clinical research has been devoted to a possible correlation between lycopene consumption and general health. Early research suggested some amelioration of cardiovascular disease
, cancer
, diabetes, osteoporosis
, and even male infertility
.
There have been several studies produced that analyzed the anti-cancer properties of lycopene, although research has been primarily inconclusive. Evidence for lycopene’s benefit was strongest for cancers of the lung, stomach, and prostate gland. Lycopene is not modified to vitamin A in the body so it can be accessible for other benefits such as antioxidation. The absence of the beta-ionone ring structure for lycopene increases its antioxidant action. Lycopene is also the most efficient oxygen and free radical quencher and is the prime carotenoid in plasma and other tissues. Lycopene is also found in lung tissue and is valuable in protecting lymphocytes from NO2 damage found in lung cancer. Lycopene also may help decrease the impact of oxidative load from pylori infections in the stomach. The tomato-derived carotenoid lycopene may reduce risk of cancer by activating special cancer preventive enzymes such as phase II detoxification enzymes, which remove harmful carcinogens from cells and the body.
In one study of lycopene as a inhibitor of human cancer cell proliferation, it was found that unlike cancer cells, human fibroblasts were less sensitive to lycopene, and the cells gradually escaped growth inhibition over time. In addition to its inhibitory effect on basal endometrial cancer cell proliferation, lycopene also was found to suppress insulin-like growth factor-I-stimulated growth. Insulin-like growth factors are major autocrine/paracrine regulators of mammary and endometrial cancer cell growth. Therefore, lycopene interference in this major autocrine/paracrine system may open new avenues for research on the role of lycopene in the regulation of endometrial cancer and other tumors.
In different studies however, lycopene was even found to have an inhibitory effect on cataract development and several different kinds of cancer cells including breast and endometrial cancer cells, prostate carcinoma cells, and colon cancer cells.
After extensive review reported in November 2005, the United States
Food and Drug Administration
has cast significant doubt on the potential for lowering disease risk, showing no link between lycopene and prevention of prostate cancer, although it is suggestive that eating whole tomatoes does provide benefit, perhaps because as yet undiscovered compounds (other than lycopene) are the beneficial agents. The FDA review permitted a highly limited qualified claim to be used for tomatoes and tomato products which contain lycopene, as a guide that would not mislead consumers, namely:
Very limited and preliminary scientific research suggests that eating one-half to one cup of tomatoes and/or tomato sauce a week may reduce the risk of prostate cancer. FDA concludes that there is little scientific evidence supporting this claim.
The related carotenoid antioxidant, beta-carotene
, has been shown to increase the number of prostate cancer
cases in a subset of patients, although this area of research remains controversial and ongoing.
Carotene
The term carotene is used for several related unsaturated hydrocarbon substances having the formula C40Hx, which are synthesized by plants but cannot be made by animals. Carotene is an orange photosynthetic pigment important for photosynthesis. Carotenes are all coloured to the human eye...
and carotenoid
Carotenoid
Carotenoids are tetraterpenoid organic pigments that are naturally occurring in the chloroplasts and chromoplasts of plants and some other photosynthetic organisms like algae, some bacteria, and some types of fungus. Carotenoids can be synthesized fats and other basic organic metabolic building...
pigment and phytochemical
Phytochemical
Phytochemicals are biologically active chemical compounds that occur naturally in plants . Phytochemicals are the molecules responsible for the color and organoleptic properties . For example, the deep purple color of blueberries and the smell of garlic...
found in tomato
Tomato
The word "tomato" may refer to the plant or the edible, typically red, fruit which it bears. Originating in South America, the tomato was spread around the world following the Spanish colonization of the Americas, and its many varieties are now widely grown, often in greenhouses in cooler...
es and other red fruits and vegetables, such as red carrot
Carrot
The carrot is a root vegetable, usually orange in colour, though purple, red, white, and yellow varieties exist. It has a crisp texture when fresh...
s, watermelon
Watermelon
Watermelon is a vine-like flowering plant originally from southern Africa. Its fruit, which is also called watermelon, is a special kind referred to by botanists as a pepo, a berry which has a thick rind and fleshy center...
s and papaya
Papaya
The papaya , papaw, or pawpaw is the fruit of the plant Carica papaya, the sole species in the genus Carica of the plant family Caricaceae...
s (but not strawberries or cherries). Although lycopene is chemically a carotene, it has no vitamin A
Vitamin A
Vitamin A is a vitamin that is needed by the retina of the eye in the form of a specific metabolite, the light-absorbing molecule retinal, that is necessary for both low-light and color vision...
activity.
In plant
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
s, algae
Algae
Algae are a large and diverse group of simple, typically autotrophic organisms, ranging from unicellular to multicellular forms, such as the giant kelps that grow to 65 meters in length. They are photosynthetic like plants, and "simple" because their tissues are not organized into the many...
, and other photosynthetic organisms
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a chemical process that converts carbon dioxide into organic compounds, especially sugars, using the energy from sunlight. Photosynthesis occurs in plants, algae, and many species of bacteria, but not in archaea. Photosynthetic organisms are called photoautotrophs, since they can...
, lycopene is an important intermediate in the biosynthesis of many carotenoids, including beta carotene, responsible for yellow, orange or red pigmentation, photosynthesis, and photo-protection. Like all carotenoids, lycopene is a polyunsaturated hydrocarbon (an unsubstituted alkene
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond...
). Structurally, it is a tetraterpene
Terpene
Terpenes are a large and diverse class of organic compounds, produced by a variety of plants, particularly conifers, though also by some insects such as termites or swallowtail butterflies, which emit terpenes from their osmeterium. They are often strong smelling and thus may have had a protective...
assembled from eight isoprene
Isoprene
Isoprene , or 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene, is a common organic compound with the formula CH2=CCH=CH2. Under standard conditions it is a colorless liquid...
units, composed entirely of carbon and hydrogen, and is insoluble in water. Lycopene's eleven conjugated double bond
Conjugated system
In chemistry, a conjugated system is a system of connected p-orbitals with delocalized electrons in compounds with alternating single and multiple bonds, which in general may lower the overall energy of the molecule and increase stability. Lone pairs, radicals or carbenium ions may be part of the...
s give it its deep red color and are responsible for its antioxidant
Antioxidant
An antioxidant is a molecule capable of inhibiting the oxidation of other molecules. Oxidation is a chemical reaction that transfers electrons or hydrogen from a substance to an oxidizing agent. Oxidation reactions can produce free radicals. In turn, these radicals can start chain reactions. When...
activity. Due to its strong color and non-toxicity, lycopene is a useful food coloring
Food coloring
Food coloring is a substance, liquid or powder, that is added to food or drink to change its color. Food coloring is used both in commercial food production and in domestic cooking...
(registered as E160d) and is approved for usage in the USA, Australia and New Zealand (registered as 160d) and the EU.
Lycopene is not an essential nutrient
Essential nutrient
An essential nutrient is a nutrient required for normal body functioning that either cannot be synthesized by the body at all, or cannot be synthesized in amounts adequate for good health , and thus must be obtained from a dietary source...
for humans, but is commonly found in the diet, mainly from dishes prepared from tomatoes. When absorbed from the stomach, lycopene is transported in the blood by various lipoproteins and accumulates in the liver, adrenal glands, and testes.
Because preliminary research has shown an inverse correlation between consumption of tomatoes and cancer risk, lycopene has been considered a potential agent for prevention of some types of cancers, particularly prostate cancer
Prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is a form of cancer that develops in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system. Most prostate cancers are slow growing; however, there are cases of aggressive prostate cancers. The cancer cells may metastasize from the prostate to other parts of the body, particularly...
. However, this area of research and the relationship with prostate cancer have been deemed insufficient of evidence for health claim approval by the US Food and Drug Administration
Food and Drug Administration
The Food and Drug Administration is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, one of the United States federal executive departments...
(see below under Antioxidant properties and potential health benefits).
Structure and physical properties

Terpene
Terpenes are a large and diverse class of organic compounds, produced by a variety of plants, particularly conifers, though also by some insects such as termites or swallowtail butterflies, which emit terpenes from their osmeterium. They are often strong smelling and thus may have had a protective...
assembled from 8 isoprene
Isoprene
Isoprene , or 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene, is a common organic compound with the formula CH2=CCH=CH2. Under standard conditions it is a colorless liquid...
units. It is a member of the carotenoid family of compounds, and because it consists entirely of carbon and hydrogen, is also a carotene
Carotene
The term carotene is used for several related unsaturated hydrocarbon substances having the formula C40Hx, which are synthesized by plants but cannot be made by animals. Carotene is an orange photosynthetic pigment important for photosynthesis. Carotenes are all coloured to the human eye...
. Isolation procedures for lycopene were first reported in 1910, and the structure of the molecule was determined by 1931. In its natural, all-trans form, the molecule is long and straight, constrained by its system of eleven conjugated double bonds. Each double bond in this extended π electron
Pi bond
In chemistry, pi bonds are covalent chemical bonds where two lobes of one involved atomic orbital overlap two lobes of the other involved atomic orbital...
system reduces the energy required for electrons to transition to higher energy states, allowing the molecule to absorb visible light of progressively longer wavelengths. Lycopene absorbs all but the longest wavelengths of visible light, so it appears red.
Plants and photosynthetic bacteria naturally produce all-trans lycopene, but a total of 72 geometric isomers of the molecule are sterically possible. When exposed to light or heat, lycopene can undergo isomerization to any of a number of these cis-isomers, which have a bent rather than linear shape. Different isomers were shown to have different stabilities due to their molecular energy (highest stability: 5-cis ≥ all-trans ≥ 9-cis ≥ 13-cis > 15-cis > 7-cis > 11-cis: lowest). In the human bloodstream, various cis-isomers constitute more than 60% of the total lycopene concentration, but the biological effects of individual isomers have not been investigated.
Lycopene is insoluble in water, and can be dissolved only in organic solvents and oils. Because of its non-polarity, lycopene in food preparations will stain any sufficiently porous
Porosity
Porosity or void fraction is a measure of the void spaces in a material, and is a fraction of the volume of voids over the total volume, between 0–1, or as a percentage between 0–100%...
material, including most plastics. While a tomato stain can be fairly easily removed from fabric (provided the stain is fresh), lycopene diffuses
Diffusion
Molecular diffusion, often called simply diffusion, is the thermal motion of all particles at temperatures above absolute zero. The rate of this movement is a function of temperature, viscosity of the fluid and the size of the particles...
into plastic, making it impossible to remove with hot water or detergent. If lycopene is oxidized (for example, by reacting with bleaches or acids), the double bonds between the carbon atoms will be broken; cleaving the molecule, breaking the conjugated double bond system, and eliminating the chromophore
Chromophore
A chromophore is the part of a molecule responsible for its color. The color arises when a molecule absorbs certain wavelengths of visible light and transmits or reflects others. The chromophore is a region in the molecule where the energy difference between two different molecular orbitals falls...
.
Role in photosynthesis

Beta-carotene
β-Carotene is a strongly-coloured red-orange pigment abundant in plants and fruits. It is an organic compound and chemically is classified as a hydrocarbon and specifically as a terpenoid , reflecting its derivation from isoprene units...
, and xanthophyll
Xanthophyll
Xanthophylls are yellow pigments that form one of two major divisions of the carotenoid group. The name is from Greek xanthos + phyllon , due to their formation of the yellow band seen in early chromatography of leaf pigments...
s.
Biosynthesis
The unconditioned biosynthesis of lycopene in eukaryotic plants and in prokaryotic cyanobacteria is similar, as are the enzymes involved. Synthesis begins with mevalonic acidMevalonic acid
Mevalonic acid is a key organic compound in biochemistry. The anion of mevalonic acid, the predominant form in biological media, is known as mevalonate. This compound is of major pharmaceutical importance...
, which is converted into dimethylallyl pyrophosphate
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate
Dimethylallyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate product of both mevalonic acid pathway and DOXP/MEP pathway. It is an isomer of isopentenyl pyrophosphate and exists in virtually all life forms...
. This is then condensed with three molecules of isopentenyl pyrophosphate
Isopentenyl pyrophosphate
Isopentenyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate in the classical, HMG-CoA reductase pathway used by organisms in the biosynthesis of terpenes and terpenoids. IPP is formed from acetyl-CoA via mevalonic acid...
(an isomer of dimethylallyl pyrophosphate), to give the twenty carbon geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate
Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate
Geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate is an intermediate in the HMG-CoA reductase pathway used by organisms in the biosynthesis of terpenes and terpenoids. In plants it is also the precursor to carotenoids, gibberellins, tocopherols, and chlorophylls....
. Two molecules of this product are then condensed in a tail-to-tail configuration to give the forty carbon phytoene
Phytoene
Phytoene is a 40-carbon intermediate in the biosynthesis of carotenoids. The synthesis of phytoene is the committed step in the synthesis of carotenoids in plants. Phytoene is produced from two molecules of geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate by the action of the enzyme phytoene synthase...
, the first committed step in carotenoid biosynthesis. Through several desaturation steps, phytoene is converted into lycopene. The two terminal isoprene groups of lycopene can be cyclized to produce beta carotene, which can then be transformed into a wide variety of xanthophylls.
Dietary sources
| Dietary sources of lycopene | |
|---|---|
| Source | μg/g wet weight |
| Gac Gac Momordica cochinchinensis is a Southeast Asian fruit found throughout the region from Southern China to Northeastern Australia.-Etymology:It is commonly known as gac, from the Vietnamese gấc or quả gấc... |
2,000–2,300 |
| Raw tomato Tomato The word "tomato" may refer to the plant or the edible, typically red, fruit which it bears. Originating in South America, the tomato was spread around the world following the Spanish colonization of the Americas, and its many varieties are now widely grown, often in greenhouses in cooler... |
8.8–42 |
| Tomato juice | 86–100 |
| Tomato sauce | 63–131 |
| Tomato ketchup Ketchup Ketchup is a sweet-and-tangy condiment typically made from tomatoes, vinegar, sugar or high-fructose corn syrup and an assortment of... |
124 |
| Watermelon Watermelon Watermelon is a vine-like flowering plant originally from southern Africa. Its fruit, which is also called watermelon, is a special kind referred to by botanists as a pepo, a berry which has a thick rind and fleshy center... |
23–72 |
| Pink grapefruit | 3.6–34 |
| Pink guava Guava Guavas are plants in the myrtle family genus Psidium , which contains about 100 species of tropical shrubs and small trees. They are native to Mexico, Central America, and northern South America... |
54 |
| Papaya Papaya The papaya , papaw, or pawpaw is the fruit of the plant Carica papaya, the sole species in the genus Carica of the plant family Caricaceae... |
20–53 |
| Rosehip puree | 7.8 |
| Apricot Apricot The apricot, Prunus armeniaca, is a species of Prunus, classified with the plum in the subgenus Prunus. The native range is somewhat uncertain due to its extensive prehistoric cultivation.- Description :... |
< 0.1 |
Fruit
Fruit
In broad terms, a fruit is a structure of a plant that contains its seeds.The term has different meanings dependent on context. In non-technical usage, such as food preparation, fruit normally means the fleshy seed-associated structures of certain plants that are sweet and edible in the raw state,...
s and vegetable
Vegetable
The noun vegetable usually means an edible plant or part of a plant other than a sweet fruit or seed. This typically means the leaf, stem, or root of a plant....
s that are high in lycopene include gac
Gac
Momordica cochinchinensis is a Southeast Asian fruit found throughout the region from Southern China to Northeastern Australia.-Etymology:It is commonly known as gac, from the Vietnamese gấc or quả gấc...
, tomatoes, watermelon
Watermelon
Watermelon is a vine-like flowering plant originally from southern Africa. Its fruit, which is also called watermelon, is a special kind referred to by botanists as a pepo, a berry which has a thick rind and fleshy center...
, pink grapefruit
Grapefruit
The grapefruit , is a subtropical citrus tree known for its sour fruit, an 18th-century hybrid first bred in Barbados. When found, it was named the "forbidden fruit"; it has also been misidentified with the pomelo or shaddock , one of the parents of this hybrid, the other being sweet orange The...
, pink guava
Guava
Guavas are plants in the myrtle family genus Psidium , which contains about 100 species of tropical shrubs and small trees. They are native to Mexico, Central America, and northern South America...
, papaya
Papaya
The papaya , papaw, or pawpaw is the fruit of the plant Carica papaya, the sole species in the genus Carica of the plant family Caricaceae...
, seabuckthorn, wolfberry
Wolfberry
Wolfberry, commercially called goji berry, is the common name for the fruit of two very closely related species: Lycium barbarum and L. chinense , two species of boxthorn in the family Solanaceae...
(goji, a berry relative of tomato), and rosehip. Although gac
Gac
Momordica cochinchinensis is a Southeast Asian fruit found throughout the region from Southern China to Northeastern Australia.-Etymology:It is commonly known as gac, from the Vietnamese gấc or quả gấc...
(Momordica cochinchinensis Spreng) has the highest content of lycopene of any known fruit or vegetable, up to 70 times more than tomatoes for example, due to gac's rarity outside its native region of southeast Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
, tomatoes and tomato-based sauces, juices, and ketchup account for more than 85% of the dietary intake of lycopene for most people. The lycopene content of tomatoes depends on species and increases as the fruit ripens.
Unlike other fruits and vegetables, where nutritional content such as vitamin C
Vitamin C
Vitamin C or L-ascorbic acid or L-ascorbate is an essential nutrient for humans and certain other animal species. In living organisms ascorbate acts as an antioxidant by protecting the body against oxidative stress...
is diminished upon cooking, processing
Food processing
Food processing is the set of methods and techniques used to transform raw ingredients into food or to transform food into other forms for consumption by humans or animals either in the home or by the food processing industry...
of tomatoes increases the concentration of bioavailable
Bioavailability
In pharmacology, bioavailability is a subcategory of absorption and is used to describe the fraction of an administered dose of unchanged drug that reaches the systemic circulation, one of the principal pharmacokinetic properties of drugs. By definition, when a medication is administered...
lycopene. Lycopene in tomato paste is four times more bioavailable than in fresh tomatoes. For this reason, tomato sauce is a preferable source as opposed to raw tomatoes.
While most green leafy vegetables and other sources of lycopene are low in fats and oils, lycopene is insoluble in water and is tightly bound to vegetable fiber. Processed tomato products such as pasteurized tomato juice, soup, sauce, and ketchup contain the highest concentrations of bioavailable lycopene from tomato-based sources.
Cooking and crushing tomatoes (as in the canning
Canning
Canning is a method of preserving food in which the food contents are processed and sealed in an airtight container. Canning provides a typical shelf life ranging from one to five years, although under specific circumstances a freeze-dried canned product, such as canned, dried lentils, can last as...
process) and serving in oil-rich dishes (such as spaghetti
Spaghetti
Spaghetti is a long, thin, cylindrical pasta of Italian origin. Spaghetti is made of semolina or flour and water. Italian dried spaghetti is made from durum wheat semolina, but outside of Italy it may be made with other kinds of flour...
sauce or pizza
Pizza
Pizza is an oven-baked, flat, disc-shaped bread typically topped with a tomato sauce, cheese and various toppings.Originating in Italy, from the Neapolitan cuisine, the dish has become popular in many parts of the world. An establishment that makes and sells pizzas is called a "pizzeria"...
) greatly increases assimilation from the digestive tract into the bloodstream. Lycopene is fat-soluble, so the oil is said to help absorption. Gac
Gac
Momordica cochinchinensis is a Southeast Asian fruit found throughout the region from Southern China to Northeastern Australia.-Etymology:It is commonly known as gac, from the Vietnamese gấc or quả gấc...
is a notable exception, containing high concentrations of lycopene and also saturated and unsaturated fatty acids.
Lycopene may be obtained from vegetables and fruits such as the tomato, but another source of lycopene is the fungus Blakeslea trispora
Blakeslea trispora
Blakeslea trispora is a fungal plant pathogen of the genus Blakeslea.It is also a source of commercial beta carotene for dietary supplements and food additives.- External links :**...
. Gac
Gac
Momordica cochinchinensis is a Southeast Asian fruit found throughout the region from Southern China to Northeastern Australia.-Etymology:It is commonly known as gac, from the Vietnamese gấc or quả gấc...
is a promising commercial source of lycopene for the purposes of extraction and purification.
The cis-lycopene from some varieties of tomato is more bioavailable.
Pharmacokinetics
| Distribution of lycopene | |
|---|---|
| Tissue | nmol/g wet weight |
| Liver | 1.28–5.72 |
| Kidney | 0.15–0.62 |
| Adrenal | 1.9–21.6 |
| Testes | 4.34–21.4 |
| Ovary | 0.25–0.28 |
| Adipose | 0.2–1.3 |
| Lung | 0.22–0.57 |
| Colon | 0.31 |
| Breast | 0.78 |
| Skin | 0.42 |
After ingestion, lycopene is incorporated into lipid micelles in the small intestine. These micelles are formed from dietary fats and bile acids, and help to solubilize the hydrophobic lycopene and allow it to permeate the intestinal mucosal cells by a passive transport mechanism. Little is known about the liver metabolism of lycopene, but like other carotenoids, lycopene is incorporated into chylomicrons and released into the lymphatic system. In blood plasma, lycopene is eventually distributed into the very low and low density lipoprotein fractions. Lycopene is mainly distributed to fatty tissues and organs such as the adrenal glands, liver, and testes.
Adverse effects
Lycopene is non-toxic and is commonly found in the diet, but cases of excessive carotenoid intake have been reported. In a middle aged woman who had prolonged and excessive consumption of tomato juice, her skin and liver were colored orange-yellow and she had elevated levels of lycopene in her blood. After three weeks on a lycopene-free diet her skin color returned to normal. This discoloration of the skin is known as lycopenodermia and is non-toxic.Antioxidant properties and potential health benefits
Lycopene may be the most powerful carotenoid quencher of singlet oxygenSinglet oxygen
Singlet oxygen is the common name used for the diamagnetic form of molecular oxygen , which is less stable than the normal triplet oxygen. Because of its unusual properties, singlet oxygen can persist for over an hour at room temperature, depending on the environment...
, being 100 times more efficient in test tube studies of singlet-oxygen quenching action than vitamin E
Vitamin E
Vitamin E is used to refer to a group of fat-soluble compounds that include both tocopherols and tocotrienols. There are many different forms of vitamin E, of which γ-tocopherol is the most common in the North American diet. γ-Tocopherol can be found in corn oil, soybean oil, margarine and dressings...
, which in turn has 125 times the quenching action of glutathione
Glutathione
Glutathione is a tripeptide that contains an unusual peptide linkage between the amine group of cysteine and the carboxyl group of the glutamate side-chain...
(water soluble). Singlet oxygen produced during exposure to ultraviolet
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
light is a primary cause of skin aging
Human skin
The human skin is the outer covering of the body. In humans, it is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has multiple layers of ectodermal tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments and internal organs. Human skin is similar to that of most other mammals,...
.
Given its antioxidant properties, substantial scientific and clinical research has been devoted to a possible correlation between lycopene consumption and general health. Early research suggested some amelioration of cardiovascular disease
Cardiovascular disease
Heart disease or cardiovascular disease are the class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels . While the term technically refers to any disease that affects the cardiovascular system , it is usually used to refer to those related to atherosclerosis...
, cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
, diabetes, osteoporosis
Osteoporosis
Osteoporosis is a disease of bones that leads to an increased risk of fracture. In osteoporosis the bone mineral density is reduced, bone microarchitecture is deteriorating, and the amount and variety of proteins in bone is altered...
, and even male infertility
Infertility
Infertility primarily refers to the biological inability of a person to contribute to conception. Infertility may also refer to the state of a woman who is unable to carry a pregnancy to full term...
.
There have been several studies produced that analyzed the anti-cancer properties of lycopene, although research has been primarily inconclusive. Evidence for lycopene’s benefit was strongest for cancers of the lung, stomach, and prostate gland. Lycopene is not modified to vitamin A in the body so it can be accessible for other benefits such as antioxidation. The absence of the beta-ionone ring structure for lycopene increases its antioxidant action. Lycopene is also the most efficient oxygen and free radical quencher and is the prime carotenoid in plasma and other tissues. Lycopene is also found in lung tissue and is valuable in protecting lymphocytes from NO2 damage found in lung cancer. Lycopene also may help decrease the impact of oxidative load from pylori infections in the stomach. The tomato-derived carotenoid lycopene may reduce risk of cancer by activating special cancer preventive enzymes such as phase II detoxification enzymes, which remove harmful carcinogens from cells and the body.
In one study of lycopene as a inhibitor of human cancer cell proliferation, it was found that unlike cancer cells, human fibroblasts were less sensitive to lycopene, and the cells gradually escaped growth inhibition over time. In addition to its inhibitory effect on basal endometrial cancer cell proliferation, lycopene also was found to suppress insulin-like growth factor-I-stimulated growth. Insulin-like growth factors are major autocrine/paracrine regulators of mammary and endometrial cancer cell growth. Therefore, lycopene interference in this major autocrine/paracrine system may open new avenues for research on the role of lycopene in the regulation of endometrial cancer and other tumors.
In different studies however, lycopene was even found to have an inhibitory effect on cataract development and several different kinds of cancer cells including breast and endometrial cancer cells, prostate carcinoma cells, and colon cancer cells.
After extensive review reported in November 2005, the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
Food and Drug Administration
Food and Drug Administration
The Food and Drug Administration is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, one of the United States federal executive departments...
has cast significant doubt on the potential for lowering disease risk, showing no link between lycopene and prevention of prostate cancer, although it is suggestive that eating whole tomatoes does provide benefit, perhaps because as yet undiscovered compounds (other than lycopene) are the beneficial agents. The FDA review permitted a highly limited qualified claim to be used for tomatoes and tomato products which contain lycopene, as a guide that would not mislead consumers, namely:
Very limited and preliminary scientific research suggests that eating one-half to one cup of tomatoes and/or tomato sauce a week may reduce the risk of prostate cancer. FDA concludes that there is little scientific evidence supporting this claim.
The related carotenoid antioxidant, beta-carotene
Beta-carotene
β-Carotene is a strongly-coloured red-orange pigment abundant in plants and fruits. It is an organic compound and chemically is classified as a hydrocarbon and specifically as a terpenoid , reflecting its derivation from isoprene units...
, has been shown to increase the number of prostate cancer
Prostate cancer
Prostate cancer is a form of cancer that develops in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system. Most prostate cancers are slow growing; however, there are cases of aggressive prostate cancers. The cancer cells may metastasize from the prostate to other parts of the body, particularly...
cases in a subset of patients, although this area of research remains controversial and ongoing.
External links
- Phytochemicals as Nutraceuticals-Lycopene
- USDA Webpage on Lycopene Content of Gac - Fatty Acids and Carotenoids in Gac (Momordica Cochinchinensis Spreng) Fruit.
- Food Sources of Lycopene - Based on USDA (US Department of Agriculture) National Nutrient Database Release 21 (SR21).

