
Principality of Salerno
Encyclopedia
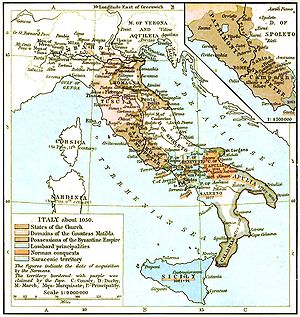
The Lombard
Lombards
The Lombards , also referred to as Longobards, were a Germanic tribe of Scandinavian origin, who from 568 to 774 ruled a Kingdom in Italy...
Principality of Salerno was a South Italian
Mezzogiorno
The Midday is a wide definition, without any administrative usage, used to indicate the southern half of the Italian state, encompassing the southern section of the continental Italian Peninsula and the two major islands of Sicily and Sardinia, in addition to a large number of minor islands...
state, centered on the port city of Salerno
Salerno
Salerno is a city and comune in Campania and is the capital of the province of the same name. It is located on the Gulf of Salerno on the Tyrrhenian Sea....
, formed in 851 out of the Principality of Benevento after a decade-long civil war.
Through its origins, it owed allegiance to the Western Emperor
Carolingian Empire
Carolingian Empire is a historiographical term which has been used to refer to the realm of the Franks under the Carolingian dynasty in the Early Middle Ages. This dynasty is seen as the founders of France and Germany, and its beginning date is based on the crowning of Charlemagne, or Charles the...
, but throughout its history it was practically independent and for brief periods even entered into the vassalage of the Byzantine Empire
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
.
Formation
In 841, the prince of Benevento, SicardSicard of Benevento
Sicard was the Prince of Benevento from 832. He was the last prince of a united Benevento which covered most of the Mezzogiorno. On his death, the principality descended into civil war which split it permanently...
, died. Immediately, his chief army officer, Radelchis
Radelchis I of Benevento
Radelchis I was the treasurer, then prince of Benevento from 839, when he assumed the throne upon the assassination of Sicard and imprisonment of Sicard's brother, Siconulf, to his death, though in his time the principality was divided.According to the Chronica S...
, seized power in Benevento and imprisoned Sicard's heir and brother, Siconulf, in Taranto
Taranto
Taranto is a coastal city in Apulia, Southern Italy. It is the capital of the Province of Taranto and is an important commercial port as well as the main Italian naval base....
. Amalfi
Amalfi
Amalfi is a town and comune in the province of Salerno, in the region of Campania, Italy, on the Gulf of Salerno, c. 35 km southeast of Naples. It lies at the mouth of a deep ravine, at the foot of Monte Cerreto , surrounded by dramatic cliffs and coastal scenery...
tan merchants rescued Siconulf from prison, and he was proclaimed prince in Salerno. A civil war erupted in the Italian Mezzogiorno
Mezzogiorno
The Midday is a wide definition, without any administrative usage, used to indicate the southern half of the Italian state, encompassing the southern section of the continental Italian Peninsula and the two major islands of Sicily and Sardinia, in addition to a large number of minor islands...
. In 847, the Emperor Lothair I
Lothair I
Lothair I or Lothar I was the Emperor of the Romans , co-ruling with his father until 840, and the King of Bavaria , Italy and Middle Francia...
had Guy I of Spoleto
Guy I of Spoleto
Guy I was the Duke of Spoleto from 842. He was the son of Lambert I of Nantes and Adelaide of Lombardy, the eldest daughter of Pepin of Italy. He travelled with his father in 834 in the entourage of Lothair I. He was given the abbey of Mettlach in Lotharingia in 840, when the Emperor Louis the...
and Sergius I of Naples
Sergius I of Naples
Sergius I was the first duke of Naples of his dynasty, often dubbed the "Sergi," which ruled over Naples for almost three centuries from his accession in 840 until the death of his namesake Sergius VII in 1137....
mediate a division of the great Lombard principality. In 849, Louis
Louis II, Holy Roman Emperor
Louis II the Younger was the King of Italy and Roman Emperor from 844, co-ruling with his father Lothair I until 855, after which he ruled alone. Louis's usual title was imperator augustus , but he used imperator Romanorum after his conquest of Bari in 871, which led to poor relations with Byzantium...
, King of Italy
King of Italy
King of Italy is a title adopted by many rulers of the Italian peninsula after the fall of the Roman Empire...
, the Radelgisi et Siginulfi principum Divisio Ducatus Beneventani divided the principality into two sections: one with its capital at Salerno and another with the original Benevento.
Salerno consisted of Taranto
Taranto
Taranto is a coastal city in Apulia, Southern Italy. It is the capital of the Province of Taranto and is an important commercial port as well as the main Italian naval base....
, Cassano
Cassano allo Ionio
Cassano allo Ionio is a small town and comune in province of Cosenza of Calabria, southern Italy, known in Roman times as Cassanum. It lies in fertile region in the concave recess of a steep mountain, 60 km NE from the town of Cosenza, 10 km W of the archaeological site of...
, Cosenza
Cosenza
Cosenza is a city in southern Italy, located at the confluence of two historic rivers: the Busento and the Crathis. The municipal population is of around 70,000; the urban area, however, counts over 260,000 inhabitants...
, Paestum
Paestum
Paestum is the classical Roman name of a major Graeco-Roman city in the Campania region of Italy. It is located in the north of Cilento, near the coast about 85 km SE of Naples in the province of Salerno, and belongs to the commune of Capaccio, officially also named...
, Conza, Potenza
Potenza
-Transportation:Potenza is a rail junction on the main line from Salerno to Taranto, managed by FS Trenitalia; it has also a connection to Altamura, served by the Ferrovie Appulo Lucane regional company...
, Sarno
Sarno
Sarno is a town and comune of Campania, Italy, in the province of Salerno, 20 km northeast from the city of Salerno and 60 km east of Naples by the main railway.-Overview:...
, Cimitile (Nola
Nola
Nola is a city and comune of Campania, southern Italy, in the province of Naples, situated in the plain between Mount Vesuvius and the Apennines...
), Capua
Capua
Capua is a city and comune in the province of Caserta, Campania, southern Italy, situated 25 km north of Naples, on the northeastern edge of the Campanian plain. Ancient Capua was situated where Santa Maria Capua Vetere is now...
, Teano
Teano
Teano is a town and comune of Campania, Italy, in the province of Caserta, 30 km north-west of that town on the main line to Rome from Naples. It stands at the south-east foot of an extinct volcano, Rocca Monfina.- Ancient times and Middle Ages:...
, and Sora
Sora, Italy
Sora is a city and comune of Lazio, Italy, in the province of Frosinone. It is built in a plain on the banks of the Liri. This part of the valley is the seat of some important manufactures, especially of paper-mills....
. It was a maritime power with numerous seaports, including Salerno itself, and controlled mostly the western half of the old duchy.
The principality did not enjoy stability in its early years. In 851, Siconulf died and his son Sico
Sico of Salerno
Sico II was the first prince of Salerno. Son and successor of Siconulf, he reigned from his father's death in 851 to his deposition in 853. He is given the ordinal "II" because he was the second Sico to rule in the south, the previous Sico being prince of Benevento.Sico was a minor when his father...
was still a child. He was deposed and replaced by his regent, Peter
Peter of Salerno
Peter was originally the tutor and guardian of the young prince of Salerno, Sico II. He held that post for two years from 851 to 853....
, in 853, and Peter was succeeded that year by his son Adhemar
Adhemar of Salerno
Adhemar was the son of Prince Peter of Salerno. He succeeded his father, an usurper, in 853.Adhemar's rule was unpopular. The counts of Capua whittled away at his princely authority and territory...
. Adhemar's stormy princeship ended violently: a revolt deposed him, and Guaifer
Guaifer of Salerno
Guaifer was the Prince of Salerno from 861. The son of Daufer the Mute and grandson of Daufer the Prophet, he was the first of the Dauferidi to sit on the Salernitan throne which his family dominated unobstructed until 977.Guaifer's sister, Adelchisa, married Sicard of Benevento and when Sicard...
, the scion of a local family of note, the Dauferidi, had him blinded and imprisoned. Guaifer succeeded him in the princely office with the support of the people.
Dauferidi
Guaifer stabilised the principality during his long reign of nineteen years. His successors reigned for similarly lengthy periods, and in a short time Salerno surpassed Benevento in greatness. During his reign, CapuaPrincipality of Capua
The Principality of Capua was a Lombard state in Southern Italy, usually de facto independent, but under the varying suzerainty of Western and Eastern Roman Empires. It was originally a gastaldate, then a county, within the principality of Salerno....
made itself independent. Salerno was still technically a vassal of the Western emperor, but it was practically independent. The prince even allied himself with the Saracens. In 880, Guaifer was removed in a precedent-setting act by his son: Guaimar I
Guaimar I of Salerno
Guaimar I was the prince of Salerno from 880, when his father entered the monastery of Monte Cassino in August. His parents were Prince Guaifer and Landelaica, daughter of Lando I of Capua...
forced him into a monastery and took up the reins of government. The chronicles of his reign describe him in despotic terms, and he does not seem to have been popular. He did reverse the alliance with the Saracens in favour of closer ties to the emperor, then Charles the Bald
Charles the Bald
Charles the Bald , Holy Roman Emperor and King of West Francia , was the youngest son of the Emperor Louis the Pious by his second wife Judith.-Struggle against his brothers:He was born on 13 June 823 in Frankfurt, when his elder...
. In 887, however, he broke with the West and paid homage to the Byzantine Emperor, receiving the title of patricius. In 900 or 901, his son, Guaimar II
Guaimar II of Salerno
Guaimar II was the Lombard prince of Salerno from 901, when his father retired to a monastery, to his death. His father was Guaimar I and his mother was Itta. He was associated with his father in the principality from 893...
, forced him into his own monastic foundation of San Massimo and began his reign.
Guaimar II raised Salerno to greatness. He was a more religious prince than his father, who had been pious by the standards of the time. He introduced the Cluniac reforms
Cluniac Reforms
The Cluniac Reforms were a series of changes within medieval monasticism of West focused on restoring the traditional monastic life, encouraging art, and caring for the poor. The movement is named for the Abbey of Cluny in Burgundy, where it started within the Benedictine order. The reforms were...
to Salerno. He was also more inclined to war with the Moslems and took part in the famous Battle of the Garigliano in 915. In this he was the ally of the Byzantines, as he was throughout his reign, with the exception of a brief period in the 920s. He increased his prestige and influence through marriage alliances with the Beneventans and Capuans, and even entered into successful schemes against the Byzantine Campania
Campania
Campania is a region in southern Italy. The region has a population of around 5.8 million people, making it the second-most-populous region of Italy; its total area of 13,590 km² makes it the most densely populated region in the country...
, where he gained much ground. Guaimar further worked to stabilise his dynasty by altering the pattern of succession. He appointed his son Gisulf I
Gisulf I of Salerno
Gisulf I was the eldest son of his father, Guaimar II, and his second wife Gaitelgrima. He was associated with his father as prince of Salerno in 943 and he succeeded him on his death in 952...
as co-prince in 943, and Gisulf succeeded in 946.
The succession was not uncontested from without. The allied forces of John III of Naples
John III of Naples
John III was the longest-reigning Duke of Naples . He was the son and successor of Marinus I.At the beginning of his reign, he warred against the Saracens and then made a treaty with them after they appeared beneath his walls in 929...
and Landulf II of Benevento
Landulf II of Benevento
Landulf II , called the Red, was the Lombard prince of Benevento and prince of Capua from 939 or 940, when his father, Landulf I, first associated him with the government, his mother was Gemma, daughter of Athanasius of Naples. He may have been associated as early as 933, when his elder brother,...
invaded, but an alliance with the Amalfi
Amalfi
Amalfi is a town and comune in the province of Salerno, in the region of Campania, Italy, on the Gulf of Salerno, c. 35 km southeast of Naples. It lies at the mouth of a deep ravine, at the foot of Monte Cerreto , surrounded by dramatic cliffs and coastal scenery...
tans saved Gisulf's reign. Gisulf like his father remained with the Greeks, even warring with the pope. He concluded a treaty with the latter and came to the defence of Pandulf Ironhead
Pandulf Ironhead
Pandulf I Ironhead was the Prince of Benevento and Capua from 943 until his death. He was made Duke of Spoleto and Camerino in 967 and succeeded as Prince of Salerno in 977 or 978...
, the prince of Benevento and Capua. Though his neighbours constantly seemed to be opposing him, the Ironhead reinstalled him after an insurrection of 974, which had been supported by his brother and the neighbouring Greek cities. Gisulf did not have any children at his death, and Salerno passed into the wider realm of the Ironhead, who bestowed it on his son Pandulf II
Pandulf II of Salerno
Pandulf II was the prince of Salerno , the second of such princes of the family of the princes of Capua. He was originally appointed heir to the childless Gisulf I of Salerno, who had been reinstated on his throne by Pandulf's father, Pandulf Ironhead. On the former's death in 977, he succeeded...
.
Foreign rule
From 978, the year of Prince Gisulf's death, to 983, when the Salernitans reinstated a dynasty of their choosing, the principality was under the rule of "foreigners": either of the Capuan princely house or the dukes of Amalfi. The Amalfitans took advantage of the Ironhead's death in 981 to seize it from Pandulf II, and Manso I of AmalfiManso I of Amalfi
Manso I was the duke of Amalfi and prince of Salerno . He was the son of Duke Sergius I and the greatest independent ruler of Amalfi, which he controlled for nearly half a century...
was made prince. He was unpopular, and a Spoletan
Spoleto
Spoleto is an ancient city in the Italian province of Perugia in east central Umbria on a foothill of the Apennines. It is S. of Trevi, N. of Terni, SE of Perugia; SE of Florence; and N of Rome.-History:...
, John, son of Lambert
John II of Salerno
John II , called the Accursed , son of Lampert of Spoleto, was the count of the palace of Salerno in 980 and acting regent for Prince Pandulf II. He was pushed out with the prince by the duke of Amalfi, Manso, in 981...
, was elected after the expulsion of the Amalfitans. Discordant relations prevailed with Amalfi until the end of the principality a century later.
Zenith and decline
John established his own dynasty, which was to usher in Salerno's final period of greatness as an independent Lombard entity. He tried to increase control of the church in his region, but failed. He followed the principle of co-regency of sons, to stabilise the succession. His son, Guaimar IIIGuaimar III of Salerno
Guaimar III was duke of Salerno from around 994 to his death. His date of death is sometimes given as 1030 or 1031, but the most reliable sources consistently indicate 1027. Under his reign, Salerno entered an era of great splendour...
, had to deal with Saracen attacks, but was aided by the Norman mercenaries
Normans
The Normans were the people who gave their name to Normandy, a region in northern France. They were descended from Norse Viking conquerors of the territory and the native population of Frankish and Gallo-Roman stock...
he had helped to recruit to the south. He moved away from Byzantium throughout his reign and supported the Lombard rebels of Melus of Bari
Melus of Bari
Melus was a Lombard nobleman from the Apulian town of Bari, whose ambition to carve for himself an autonomous territory from the Byzantine catapanate of Italy in the early 11th century inadvertently sparked the Norman presence in southern Italy.Melus and his brother-in-law Dattus rebelled in 1009...
. He also supported his neighbour, Pandulf IV of Capua
Pandulf IV of Capua
Pandulf IV was the Prince of Capua on three separate occasions.From February 1016 to 1022 he ruled in association with his cousin Pandulf II. In 1018, the Byzantine catapan Boiannes destroyed the Lombard army of Melus of Bari and his Norman allies at Cannae...
, despite the latter's unpopularity. Under Guaimar III, the Schola Medica Salernitana
Schola Medica Salernitana
The Schola Medica Salernitana was the first medieval medical school in the cosmopolitan coastal south Italian city of Salerno, which provided the most important source of medical knowledge in Western Europe at the time...
first began to flourish, and he was capable of striking Opulenta Salernitanum on his coins as a sign of the trading wealth of his city. Guaimar IV
Guaimar IV of Salerno
Guaimar IV was Prince of Salerno , Duke of Amalfi , Duke of Gaeta , and Prince of Capua in Southern Italy over the period from 1027 to 1052. He was an important figure in the final phase of Byzantine authority in the Mezzogiorno and the commencement of Norman power...
brought Salerno to its greatest heights, but it did not survive him.
He, too, used the Normans for mutual gain. He can be considered chiefly responsible for the rise of the Hautevilles in the Mezzogiorno. He opposed Pandulf of Capua, unlike his father, and he united his principality with that one for the first time since Pandulf Ironhead. In 1038, he sought the arbitration of both emperors over matters concerning Pandulf, but only the Holy Roman Emperor
Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor is a term used by historians to denote a medieval ruler who, as German King, had also received the title of "Emperor of the Romans" from the Pope...
, Conrad II
Conrad II, Holy Roman Emperor
Conrad II was Holy Roman Emperor from 1027 until his death.The son of a mid-level nobleman in Franconia, Count Henry of Speyer and Adelaide of Alsace, he inherited the titles of count of Speyer and of Worms as an infant when Henry died at age twenty...
, responded, and Salerno became fully Western in allegiance. Conrad made Guaimar a powerful prince, and he extended his authority militarily over the coastal city-states of Gaeta
Gaeta
Gaeta is a city and comune in the province of Latina, in Lazio, central Italy. Set on a promontory stretching towards the Gulf of Gaeta, it is 120 km from Rome and 80 km from Naples....
, Naples
Naples
Naples is a city in Southern Italy, situated on the country's west coast by the Gulf of Naples. Lying between two notable volcanic regions, Mount Vesuvius and the Phlegraean Fields, it is the capital of the region of Campania and of the province of Naples...
, and Amalfi. He opened up the Campania, Apulia
Apulia
Apulia is a region in Southern Italy bordering the Adriatic Sea in the east, the Ionian Sea to the southeast, and the Strait of Òtranto and Gulf of Taranto in the south. Its most southern portion, known as Salento peninsula, forms a high heel on the "boot" of Italy. The region comprises , and...
, and Calabria
Calabria
Calabria , in antiquity known as Bruttium, is a region in southern Italy, south of Naples, located at the "toe" of the Italian Peninsula. The capital city of Calabria is Catanzaro....
to conquest, but his successes were reversed by Conrad's son, Henry III
Henry III, Holy Roman Emperor
Henry III , called the Black or the Pious, was a member of the Salian Dynasty of Holy Roman Emperors...
, who in 1047 removed Guaimar from Capua and restructured the nature of his suzerain-vassal relationships to limit his power. In 1052, Guaimar was assassinated, and his son and successor, Gisulf II
Gisulf II of Salerno
Gisulf II was the last Lombard prince of Salerno ....
, showed none of his political acumen.
Under Gisulf, Salerno declined. He made useless war on Amalfi and on his Norman neighbours, finally on Robert Guiscard
Robert Guiscard
Robert d'Hauteville, known as Guiscard, Duke of Apulia and Calabria, from Latin Viscardus and Old French Viscart, often rendered the Resourceful, the Cunning, the Wily, the Fox, or the Weasel was a Norman adventurer conspicuous in the conquest of southern Italy and Sicily...
, the duke of Apulia, himself. Though Salerno remained wealthy and opulent to the end of his reign, he misused this wealth during the siege of 1077 and lost his city and his principality to the Guiscard. With Gisulf's defeat, Salerno ceased to be the capital of a large principality, and its once vast domain was completely merged into the Duchy of Apulia and Calabria, the peninsular possession of the Hauteville family. Salerno did continue as the most important city of southern Italy until the end of Hauteville rule in 1194.
The Schola Medica Salernitana
Schola Medica Salernitana
The Schola Medica Salernitana was the first medieval medical school in the cosmopolitan coastal south Italian city of Salerno, which provided the most important source of medical knowledge in Western Europe at the time...
of Guaimar III
Guaimar III of Salerno
Guaimar III was duke of Salerno from around 994 to his death. His date of death is sometimes given as 1030 or 1031, but the most reliable sources consistently indicate 1027. Under his reign, Salerno entered an era of great splendour...
survived until Napoleonic times, and it is considered the world's first university of medicine
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
.
Sources
- Chalandon, FerdinandFerdinand ChalandonFerdinand Chalandon was a French medievalist and Byzantinist.Chalandon’s work remains the most substantial study of the Normans in Italy and though the details of what he wrote a hundred years ago have in places been modified, it remains the single most important work available to historians.Being...
. Histoire de la domination normande en Italie et en Sicilie. ParisParisParis is the capital and largest city in France, situated on the river Seine, in northern France, at the heart of the Île-de-France region...
, 1907. - D'Ambrosio, A. Storia di Napoli dalle origini ad oggi. Ed. Nuova E.V. Napoli 2002
- Dizionario Biografico degli Italiani. RomeRomeRome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
, 1960–Present. - Oman, CharlesCharles OmanSir Charles William Chadwick Oman was a British military historian of the early 20th century. His reconstructions of medieval battles from the fragmentary and distorted accounts left by chroniclers were pioneering...
. The Dark Ages 476-918. Rivingtons: LondonLondonLondon is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
, 1914. - Gwatkin, H.M., Whitney, J.P. (ed) et al. The Cambridge Medieval History: Volume III. Cambridge University PressCambridge University PressCambridge University Press is the publishing business of the University of Cambridge. Granted letters patent by Henry VIII in 1534, it is the world's oldest publishing house, and the second largest university press in the world...
, 1926. - Iannizzaro, Vincenzo. Salerno. La Cinta Muraria dai Romani agli Spagnoli. Editore Elea Press. Salerno, 1999.
- Norwich, John JuliusJohn Julius NorwichJohn Julius Cooper, 2nd Viscount Norwich CVO — known as John Julius Norwich — is an English historian, travel writer and television personality.-Early life:...
. The Normans in the South 1016-1130. Longmans: LondonLondonLondon is the capital city of :England and the :United Kingdom, the largest metropolitan area in the United Kingdom, and the largest urban zone in the European Union by most measures. Located on the River Thames, London has been a major settlement for two millennia, its history going back to its...
, 1967.

