
Introduction to genetics
Encyclopedia
Genetics is the study of genes
, and tries to explain what they are and how they work. Genes are how living organism
s inherit features from their ancestors; for example, children usually look like their parents because they have inherited their parents' genes. Genetics tries to identify which features are inherited, and explain how these features are passed from generation
to generation.
In genetics, a feature of a living thing is called a "trait". Some traits are part of an organism's physical appearance
; such as a person's eye-color, height or weight. Other sorts of traits are not easily seen and include blood types or resistance to diseases. The way our genes and environment interact to produce a trait can be complicated. For example, the chances of somebody dying of cancer
or heart disease
seems to depend on both their genes and their lifestyle.
Some traits are inherited through our genes, so tall and thin people tend to have tall and thin children; such traits which result due to inheritance alone are called genotype
s. Other traits come from interactions between our genes and the environment, so a child might inherit the tendency to be tall, but if they are poorly nourished, they will still be short; such traits which are manifested due to the combined action of inherited genes and environmental circumstances are called as phenotype
s.
Genes are made from a long molecule
called DNA
, which is copied and inherited across generations. DNA is made of simple unit
s that line up in a particular order within this large molecule. The order of these units carries genetic information, similar to how the order of letters on a page carries information. The language used by DNA is called the genetic code
, which lets organisms read the information in the genes. This information is the instructions for constructing and operating a living organism.
The information within a particular gene is not always exactly the same between one organism and another, so different copies of a gene do not always give exactly the same instructions. Each unique form of a single gene is called an allele
. As an example, one allele for the gene for hair color could instruct the body to produce a lot of pigment, producing black hair, while a different allele of the same gene might give garbled instructions that fail to produce any pigment, giving white hair. Mutation
s are random changes in genes, and can create new alleles. Mutations can also produce new traits, such as when mutations to an allele for black hair produce a new allele for white hair. This appearance of new traits is important in evolution
.
 Genes are inherited as units, with two parents dividing out copies of their genes to their offspring. You can think of this process like mixing two hands of cards, shuffling them, and then dealing them out again. Humans have two copies of each of their genes and when people reproduce they make copies of their genes and put them into eggs or sperm, but only put in one copy of each type of gene. When an egg joins with a sperm, this gives a child a complete set of genes. This child will have the same number of genes as its parents, but for any gene one of their two copies will come from their father, and one from their mother.
Genes are inherited as units, with two parents dividing out copies of their genes to their offspring. You can think of this process like mixing two hands of cards, shuffling them, and then dealing them out again. Humans have two copies of each of their genes and when people reproduce they make copies of their genes and put them into eggs or sperm, but only put in one copy of each type of gene. When an egg joins with a sperm, this gives a child a complete set of genes. This child will have the same number of genes as its parents, but for any gene one of their two copies will come from their father, and one from their mother.
The effects of this mixing depends on the types (the alleles) of the gene you are interested in. If the father has two copies for an allele for red hair, and the mother has two copies for brown hair, all their children will get the two alleles that give different instructions, one for red hair and one for brown. The hair color of these children depends on how these alleles work together. If one allele overrides the instructions from another, it is called the dominant allele, and the allele that is overridden is called the recessive allele. In the case of a daughter with alleles for both red and brown hair, brown is dominant and she ends up with brown hair.
Although the red color allele is still there in this brown-haired girl, it doesn't show. This is a difference between what you see on the surface (the traits of an organism, called its phenotype
) and the genes within the organism (its genotype
). In this example you can call the allele for brown "B" and the allele for red "b". (It is normal to write dominant alleles with capital letters and recessive ones with lower-case letters.) The brown hair daughter has the "brown hair phenotype" but her genotype is Bb, with one copy of the B allele, and one of the b allele.
Now imagine that this woman grows up and has children with a brown hair man who also has a Bb genotype. Her eggs will be a mixture of two types, one sort containing the B allele, and one sort the b allele. Similarly, her partner will produce a mix of two types of sperm containing one or the other of these two alleles. When the transmitted genes are joined up in their offspring, these children have a chance of getting either brown or red hair, since they could get a genotype of BB = brown hair, Bb = brown hair or bb = red hair. In this generation, there is therefore a chance of the recessive allele showing itself in the phenotype of the children - some of them may have red hair like their grandfather.
Many traits are inherited in a more complicated way than the example above. This can happen when there are several genes involved, each contributing a small part to the end result. Tall people tend to have tall children because their children get a package of many alleles that each contribute a bit to how much they grow. However, there are not clear groups of "short people" and "tall people", like there are groups of people with brown or red hair. This is because of the large number of genes involved; this makes the trait very variable and people are of many different heights. Despite a common misconception, the green/blue eye traits are also inherited in this complex inheritance model. Inheritance can also be complicated when the trait depends on the interaction between genetics and the environment. This is quite common, for example, if a child does not eat enough nutritious food this will not change traits like eye color, but it could stunt their growth.
s, are caused by the environment. Other diseases come from a combination of genes and the environment. Genetic disorder
s are diseases that are caused by a single allele of a gene and are inherited in families. These include Huntington's disease
, Cystic fibrosis
or Duchenne muscular dystrophy
. Cystic fibrosis, for example, is caused by mutations in a single gene called CFTR and is inherited as a recessive trait.
Other diseases are influenced by genetics, but the genes a person gets from their parents only change their risk of getting a disease. Most of these diseases are inherited in a complex way, with either multiple genes involved, or coming from both genes and the environment. As an example, the risk of breast cancer
is 50 times higher in the families most at risk, compared to the families least at risk. This variation is probably due to a large number of alleles, each changing the risk a little bit. Several of the genes have been identified, such as BRCA1
and BRCA2
, but not all of them. However, although some of the risk is genetic, the risk of this cancer is also increased by being overweight, drinking a lot of alcohol and not exercising. A woman's risk of breast cancer therefore comes from a large number of alleles interacting with her environment, so it is very hard to predict.
s in cells. Cells are the smallest independent parts of organisms: the human body contains about 100 trillion cells, while very small organisms like bacteria
are just one single cell. A cell is like a miniature and very complex factory that can make all the parts needed to produce a copy of itself, which happens when cells divide
. There is a simple division of labor in cells - genes give instructions and proteins carry out these instructions, tasks like building a new copy of a cell, or repairing damage. Each type of protein is a specialist that only does one job, so if a cell needs to do something new, it must make a new protein to do this job. Similarly, if a cell needs to do something faster or slower than before, it makes more or less of the protein responsible. Genes tell cells what to do by telling them which proteins to make and in what amounts.
 Proteins are made of a chain of 20 different types of amino acid
Proteins are made of a chain of 20 different types of amino acid
molecules. This chain folds up into a compact shape, rather like an untidy ball of string. The shape of the protein is determined by the sequence of amino acids along its chain and it is this shape that, in turn, determines what the protein will do. For example, some proteins have parts of their surface that perfectly match the shape of another molecule, allowing the protein to bind to this molecule very tightly. Other proteins are enzyme
s, which are like tiny machines that alter other molecules.
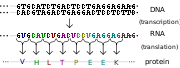
The information in DNA is held in the sequence of the repeating units along the DNA chain. These units are four types of nucleotide
s (A,T,G and C) and the sequence of nucleotides stores information in an alphabet called the genetic code
. When a gene is read by a cell the DNA sequence is copied into a very similar molecule called RNA
(this process is called transcription
). Transcription is controlled by other DNA sequences (such as promoters), which show a cell where genes are, and control how often they are copied. The RNA copy made from a gene is then fed through a structure called a ribosome
, which translates the sequence of nucleotides in the RNA into the correct sequence of amino acids and joins these amino acids together to make a complete protein chain. The new protein then folds up into its active form. The process of moving information from the language of RNA into the language of amino acids is called translation
.
 If the sequence of the nucleotides in a gene changes, the sequence of the amino acids in the protein it produces may also change - if part of a gene is deleted, the protein produced will be shorter and may not work any more. This is the reason why different alleles of a gene can have different effects in an organism. As an example, hair color depends on how much of a dark substance called melanin
If the sequence of the nucleotides in a gene changes, the sequence of the amino acids in the protein it produces may also change - if part of a gene is deleted, the protein produced will be shorter and may not work any more. This is the reason why different alleles of a gene can have different effects in an organism. As an example, hair color depends on how much of a dark substance called melanin
is put into the hair as it grows. If a person has a normal set of the genes involved in making melanin, they make all the proteins needed and they grow dark hair. However, if the alleles for a particular protein have different sequences and produce proteins that can't do their jobs, no melanin will be produced and the hair will be white. This condition is called albinism
and the person with this condition is called an albino.
. It is through a similar process that a child inherits genes from its parents, when a copy from the mother is mixed with a copy from the father.
DNA can be copied very easily and accurately because each piece of DNA can direct the creation of a new copy of its information. This is because DNA is made of two strands that pair together like the two sides of a zipper. The nucleotides are in the center, like the teeth in the zipper, and pair up to hold the two strands together. Importantly, the four different sorts of nucleotides are different shapes, so in order for the strands to close up properly, an A nucleotide must go opposite a T nucleotide, and a G opposite a C. This exact pairing is called base pairing.
When DNA is copied, the two strands of the old DNA are pulled apart by enzymes which move along each of the two single strands pairing up new nucleotide units and then zipping the strands closed. This produces two new pieces of DNA, each containing one strand from the old DNA and one newly made strand. This process isn't perfect and sometimes the proteins will make mistakes and put the wrong nucleotide into the strand they are building. This causes a change in the sequence of that gene. These changes in DNA sequence are called mutation
s. Mutations produce new alleles of genes. Sometimes these changes stop the gene from working properly, like the melanin genes discussed above. In other cases these mutations can change what the gene does or even let it do its job a little better than before. These mutations and their effects on the traits of organisms are one of the causes of evolution
.
 A population of organisms evolves when an inherited trait becomes more common or less common over time. For instance, all the mice living on an island would be a single population of mice. If over a few generations, white mice went from being rare, to being a large part of this population, then the coat color of these mice would be evolving. In terms of genetics, this is called a change in allele frequency
A population of organisms evolves when an inherited trait becomes more common or less common over time. For instance, all the mice living on an island would be a single population of mice. If over a few generations, white mice went from being rare, to being a large part of this population, then the coat color of these mice would be evolving. In terms of genetics, this is called a change in allele frequency
—such as an increase in the frequency of the allele for white fur.
Alleles become more or less common either just by chance (in a process called genetic drift
), or through natural selection
. In natural selection, if an allele makes it more likely that an organism will survive and reproduce, then over time this allele will become more common. But if an allele is harmful, natural selection will make it less common. For example, if the island was getting colder each year and was covered with snow for much of the time, then the allele for white fur would become useful for the mice, since it would make them harder to see against the snow. Fewer of the white mice would be eaten by predators, so over time white mice would out-compete mice with dark fur. White fur alleles would become more common, and dark fur alleles would become more rare.
Mutations create new alleles. These alleles have new DNA sequences and can produce proteins with new properties. So if an island was populated entirely by black mice, mutations could happen creating alleles for white fur. The combination of mutations creating new alleles at random, and natural selection picking out those which are useful, causes adaptation
. This is when organisms change in ways that help them to survive and reproduce.
works. For example, crop plants can be given a gene from an Arctic fish, so they produce an antifreeze protein
in their leaves. This can help prevent frost damage. Other genes that can be put into crops include a natural insecticide
from the bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis
. The insecticide kills insects that eat the plants, but is harmless to people. In these plants the new genes are put into the plant before it is grown, so the genes will be in every part of the plant, including its seeds. The plant's offspring will then inherit the new genes, something which has led to concern about the spread of new traits into wild plants.
The kind of technology used in genetic engineering is also being developed to treat people with genetic disorder
s in an experimental medical technique called gene therapy
. However, here the new gene is put in after the person has grown up and become ill, so any new gene will not be inherited by their children. Gene therapy works by trying to replace the allele that causes the disease with an allele that will work properly.
Gênes
Gênes is the name of a département of the First French Empire in present Italy, named after the city of Genoa. It was formed in 1805, when Napoleon Bonaparte occupied the Republic of Genoa. Its capital was Genoa, and it was divided in the arrondissements of Genoa, Bobbio, Novi Ligure, Tortona and...
, and tries to explain what they are and how they work. Genes are how living organism
Organism
In biology, an organism is any contiguous living system . In at least some form, all organisms are capable of response to stimuli, reproduction, growth and development, and maintenance of homoeostasis as a stable whole.An organism may either be unicellular or, as in the case of humans, comprise...
s inherit features from their ancestors; for example, children usually look like their parents because they have inherited their parents' genes. Genetics tries to identify which features are inherited, and explain how these features are passed from generation
Generation
Generation , also known as procreation in biological sciences, is the act of producing offspring....
to generation.
In genetics, a feature of a living thing is called a "trait". Some traits are part of an organism's physical appearance
Morphology (biology)
In biology, morphology is a branch of bioscience dealing with the study of the form and structure of organisms and their specific structural features....
; such as a person's eye-color, height or weight. Other sorts of traits are not easily seen and include blood types or resistance to diseases. The way our genes and environment interact to produce a trait can be complicated. For example, the chances of somebody dying of cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
or heart disease
Heart disease
Heart disease, cardiac disease or cardiopathy is an umbrella term for a variety of diseases affecting the heart. , it is the leading cause of death in the United States, England, Canada and Wales, accounting for 25.4% of the total deaths in the United States.-Types:-Coronary heart disease:Coronary...
seems to depend on both their genes and their lifestyle.
Some traits are inherited through our genes, so tall and thin people tend to have tall and thin children; such traits which result due to inheritance alone are called genotype
Genotype
The genotype is the genetic makeup of a cell, an organism, or an individual usually with reference to a specific character under consideration...
s. Other traits come from interactions between our genes and the environment, so a child might inherit the tendency to be tall, but if they are poorly nourished, they will still be short; such traits which are manifested due to the combined action of inherited genes and environmental circumstances are called as phenotype
Phenotype
A phenotype is an organism's observable characteristics or traits: such as its morphology, development, biochemical or physiological properties, behavior, and products of behavior...
s.
Genes are made from a long molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
called DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
, which is copied and inherited across generations. DNA is made of simple unit
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. In addition, nucleotides participate in cellular signaling , and are incorporated into important cofactors of enzymatic reactions...
s that line up in a particular order within this large molecule. The order of these units carries genetic information, similar to how the order of letters on a page carries information. The language used by DNA is called the genetic code
Genetic code
The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material is translated into proteins by living cells....
, which lets organisms read the information in the genes. This information is the instructions for constructing and operating a living organism.
The information within a particular gene is not always exactly the same between one organism and another, so different copies of a gene do not always give exactly the same instructions. Each unique form of a single gene is called an allele
Allele
An allele is one of two or more forms of a gene or a genetic locus . "Allel" is an abbreviation of allelomorph. Sometimes, different alleles can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation...
. As an example, one allele for the gene for hair color could instruct the body to produce a lot of pigment, producing black hair, while a different allele of the same gene might give garbled instructions that fail to produce any pigment, giving white hair. Mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
s are random changes in genes, and can create new alleles. Mutations can also produce new traits, such as when mutations to an allele for black hair produce a new allele for white hair. This appearance of new traits is important in evolution
Introduction to evolution
Evolution is the process of change in all forms of life over generations, and evolutionary biology is the study of how evolution occurs. The biodiversity of life evolves by means of mutations, genetic drift and natural selection....
.
Genes and inheritance


The effects of this mixing depends on the types (the alleles) of the gene you are interested in. If the father has two copies for an allele for red hair, and the mother has two copies for brown hair, all their children will get the two alleles that give different instructions, one for red hair and one for brown. The hair color of these children depends on how these alleles work together. If one allele overrides the instructions from another, it is called the dominant allele, and the allele that is overridden is called the recessive allele. In the case of a daughter with alleles for both red and brown hair, brown is dominant and she ends up with brown hair.
Although the red color allele is still there in this brown-haired girl, it doesn't show. This is a difference between what you see on the surface (the traits of an organism, called its phenotype
Phenotype
A phenotype is an organism's observable characteristics or traits: such as its morphology, development, biochemical or physiological properties, behavior, and products of behavior...
) and the genes within the organism (its genotype
Genotype
The genotype is the genetic makeup of a cell, an organism, or an individual usually with reference to a specific character under consideration...
). In this example you can call the allele for brown "B" and the allele for red "b". (It is normal to write dominant alleles with capital letters and recessive ones with lower-case letters.) The brown hair daughter has the "brown hair phenotype" but her genotype is Bb, with one copy of the B allele, and one of the b allele.
Now imagine that this woman grows up and has children with a brown hair man who also has a Bb genotype. Her eggs will be a mixture of two types, one sort containing the B allele, and one sort the b allele. Similarly, her partner will produce a mix of two types of sperm containing one or the other of these two alleles. When the transmitted genes are joined up in their offspring, these children have a chance of getting either brown or red hair, since they could get a genotype of BB = brown hair, Bb = brown hair or bb = red hair. In this generation, there is therefore a chance of the recessive allele showing itself in the phenotype of the children - some of them may have red hair like their grandfather.
Many traits are inherited in a more complicated way than the example above. This can happen when there are several genes involved, each contributing a small part to the end result. Tall people tend to have tall children because their children get a package of many alleles that each contribute a bit to how much they grow. However, there are not clear groups of "short people" and "tall people", like there are groups of people with brown or red hair. This is because of the large number of genes involved; this makes the trait very variable and people are of many different heights. Despite a common misconception, the green/blue eye traits are also inherited in this complex inheritance model. Inheritance can also be complicated when the trait depends on the interaction between genetics and the environment. This is quite common, for example, if a child does not eat enough nutritious food this will not change traits like eye color, but it could stunt their growth.
Inherited diseases
Some diseases are hereditary and run in families; others, such as infectious diseaseInfectious disease
Infectious diseases, also known as communicable diseases, contagious diseases or transmissible diseases comprise clinically evident illness resulting from the infection, presence and growth of pathogenic biological agents in an individual host organism...
s, are caused by the environment. Other diseases come from a combination of genes and the environment. Genetic disorder
Genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is an illness caused by abnormalities in genes or chromosomes, especially a condition that is present from before birth. Most genetic disorders are quite rare and affect one person in every several thousands or millions....
s are diseases that are caused by a single allele of a gene and are inherited in families. These include Huntington's disease
Huntington's disease
Huntington's disease, chorea, or disorder , is a neurodegenerative genetic disorder that affects muscle coordination and leads to cognitive decline and dementia. It typically becomes noticeable in middle age. HD is the most common genetic cause of abnormal involuntary writhing movements called chorea...
, Cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is a recessive genetic disease affecting most critically the lungs, and also the pancreas, liver, and intestine...
or Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a recessive X-linked form of muscular dystrophy, which results in muscle degeneration, difficulty walking, breathing, and death. The incidence is 1 in 3,000 boys. Females and males are affected, though females are rarely affected and are more often carriers...
. Cystic fibrosis, for example, is caused by mutations in a single gene called CFTR and is inherited as a recessive trait.
Other diseases are influenced by genetics, but the genes a person gets from their parents only change their risk of getting a disease. Most of these diseases are inherited in a complex way, with either multiple genes involved, or coming from both genes and the environment. As an example, the risk of breast cancer
Breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer originating from breast tissue, most commonly from the inner lining of milk ducts or the lobules that supply the ducts with milk. Cancers originating from ducts are known as ductal carcinomas; those originating from lobules are known as lobular carcinomas...
is 50 times higher in the families most at risk, compared to the families least at risk. This variation is probably due to a large number of alleles, each changing the risk a little bit. Several of the genes have been identified, such as BRCA1
BRCA1
BRCA1 is a human caretaker gene that produces a protein called breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein, responsible for repairing DNA. The first evidence for the existence of the gene was provided by the King laboratory at UC Berkeley in 1990...
and BRCA2
BRCA2
BRCA2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BRCA2 gene.BRCA2 orthologs have been identified in most mammals for which complete genome data are available....
, but not all of them. However, although some of the risk is genetic, the risk of this cancer is also increased by being overweight, drinking a lot of alcohol and not exercising. A woman's risk of breast cancer therefore comes from a large number of alleles interacting with her environment, so it is very hard to predict.
Genes make proteins
The function of genes is to provide the information needed to make molecules called proteinProtein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s in cells. Cells are the smallest independent parts of organisms: the human body contains about 100 trillion cells, while very small organisms like bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
are just one single cell. A cell is like a miniature and very complex factory that can make all the parts needed to produce a copy of itself, which happens when cells divide
Cell division
Cell division is the process by which a parent cell divides into two or more daughter cells . Cell division is usually a small segment of a larger cell cycle. This type of cell division in eukaryotes is known as mitosis, and leaves the daughter cell capable of dividing again. The corresponding sort...
. There is a simple division of labor in cells - genes give instructions and proteins carry out these instructions, tasks like building a new copy of a cell, or repairing damage. Each type of protein is a specialist that only does one job, so if a cell needs to do something new, it must make a new protein to do this job. Similarly, if a cell needs to do something faster or slower than before, it makes more or less of the protein responsible. Genes tell cells what to do by telling them which proteins to make and in what amounts.

Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
molecules. This chain folds up into a compact shape, rather like an untidy ball of string. The shape of the protein is determined by the sequence of amino acids along its chain and it is this shape that, in turn, determines what the protein will do. For example, some proteins have parts of their surface that perfectly match the shape of another molecule, allowing the protein to bind to this molecule very tightly. Other proteins are enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s, which are like tiny machines that alter other molecules.
The information in DNA is held in the sequence of the repeating units along the DNA chain. These units are four types of nucleotide
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are molecules that, when joined together, make up the structural units of RNA and DNA. In addition, nucleotides participate in cellular signaling , and are incorporated into important cofactors of enzymatic reactions...
s (A,T,G and C) and the sequence of nucleotides stores information in an alphabet called the genetic code
Genetic code
The genetic code is the set of rules by which information encoded in genetic material is translated into proteins by living cells....
. When a gene is read by a cell the DNA sequence is copied into a very similar molecule called RNA
RNA
Ribonucleic acid , or RNA, is one of the three major macromolecules that are essential for all known forms of life....
(this process is called transcription
Transcription (genetics)
Transcription is the process of creating a complementary RNA copy of a sequence of DNA. Both RNA and DNA are nucleic acids, which use base pairs of nucleotides as a complementary language that can be converted back and forth from DNA to RNA by the action of the correct enzymes...
). Transcription is controlled by other DNA sequences (such as promoters), which show a cell where genes are, and control how often they are copied. The RNA copy made from a gene is then fed through a structure called a ribosome
Ribosome
A ribosome is a component of cells that assembles the twenty specific amino acid molecules to form the particular protein molecule determined by the nucleotide sequence of an RNA molecule....
, which translates the sequence of nucleotides in the RNA into the correct sequence of amino acids and joins these amino acids together to make a complete protein chain. The new protein then folds up into its active form. The process of moving information from the language of RNA into the language of amino acids is called translation
Protein biosynthesis
Protein biosynthesis is the process in which cells build or manufacture proteins. The term is sometimes used to refer only to protein translation but more often it refers to a multi-step process, beginning with amino acid synthesis and transcription of nuclear DNA into messenger RNA, which is then...
.

Melanin
Melanin is a pigment that is ubiquitous in nature, being found in most organisms . In animals melanin pigments are derivatives of the amino acid tyrosine. The most common form of biological melanin is eumelanin, a brown-black polymer of dihydroxyindole carboxylic acids, and their reduced forms...
is put into the hair as it grows. If a person has a normal set of the genes involved in making melanin, they make all the proteins needed and they grow dark hair. However, if the alleles for a particular protein have different sequences and produce proteins that can't do their jobs, no melanin will be produced and the hair will be white. This condition is called albinism
Albinism
Albinism is a congenital disorder characterized by the complete or partial absence of pigment in the skin, hair and eyes due to absence or defect of an enzyme involved in the production of melanin...
and the person with this condition is called an albino.
Genes are copied
Genes are copied each time a cell divides into two new cells. The process that copies DNA is called DNA replicationDNA replication
DNA replication is a biological process that occurs in all living organisms and copies their DNA; it is the basis for biological inheritance. The process starts with one double-stranded DNA molecule and produces two identical copies of the molecule...
. It is through a similar process that a child inherits genes from its parents, when a copy from the mother is mixed with a copy from the father.
DNA can be copied very easily and accurately because each piece of DNA can direct the creation of a new copy of its information. This is because DNA is made of two strands that pair together like the two sides of a zipper. The nucleotides are in the center, like the teeth in the zipper, and pair up to hold the two strands together. Importantly, the four different sorts of nucleotides are different shapes, so in order for the strands to close up properly, an A nucleotide must go opposite a T nucleotide, and a G opposite a C. This exact pairing is called base pairing.
When DNA is copied, the two strands of the old DNA are pulled apart by enzymes which move along each of the two single strands pairing up new nucleotide units and then zipping the strands closed. This produces two new pieces of DNA, each containing one strand from the old DNA and one newly made strand. This process isn't perfect and sometimes the proteins will make mistakes and put the wrong nucleotide into the strand they are building. This causes a change in the sequence of that gene. These changes in DNA sequence are called mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
s. Mutations produce new alleles of genes. Sometimes these changes stop the gene from working properly, like the melanin genes discussed above. In other cases these mutations can change what the gene does or even let it do its job a little better than before. These mutations and their effects on the traits of organisms are one of the causes of evolution
Evolution
Evolution is any change across successive generations in the heritable characteristics of biological populations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including species, individual organisms and molecules such as DNA and proteins.Life on Earth...
.
Genes and evolution

Allele frequency
Allele frequency or Gene frequency is the proportion of all copies of a gene that is made up of a particular gene variant . In other words, it is the number of copies of a particular allele divided by the number of copies of all alleles at the genetic place in a population. It can be expressed for...
—such as an increase in the frequency of the allele for white fur.
Alleles become more or less common either just by chance (in a process called genetic drift
Genetic drift
Genetic drift or allelic drift is the change in the frequency of a gene variant in a population due to random sampling.The alleles in the offspring are a sample of those in the parents, and chance has a role in determining whether a given individual survives and reproduces...
), or through natural selection
Natural selection
Natural selection is the nonrandom process by which biologic traits become either more or less common in a population as a function of differential reproduction of their bearers. It is a key mechanism of evolution....
. In natural selection, if an allele makes it more likely that an organism will survive and reproduce, then over time this allele will become more common. But if an allele is harmful, natural selection will make it less common. For example, if the island was getting colder each year and was covered with snow for much of the time, then the allele for white fur would become useful for the mice, since it would make them harder to see against the snow. Fewer of the white mice would be eaten by predators, so over time white mice would out-compete mice with dark fur. White fur alleles would become more common, and dark fur alleles would become more rare.
Mutations create new alleles. These alleles have new DNA sequences and can produce proteins with new properties. So if an island was populated entirely by black mice, mutations could happen creating alleles for white fur. The combination of mutations creating new alleles at random, and natural selection picking out those which are useful, causes adaptation
Adaptation
An adaptation in biology is a trait with a current functional role in the life history of an organism that is maintained and evolved by means of natural selection. An adaptation refers to both the current state of being adapted and to the dynamic evolutionary process that leads to the adaptation....
. This is when organisms change in ways that help them to survive and reproduce.
Genetic engineering
Since traits come from the genes in a cell, putting a new piece of DNA into a cell can produce a new trait. This is how genetic engineeringGenetic engineering
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification, is the direct human manipulation of an organism's genome using modern DNA technology. It involves the introduction of foreign DNA or synthetic genes into the organism of interest...
works. For example, crop plants can be given a gene from an Arctic fish, so they produce an antifreeze protein
Antifreeze protein
Antifreeze proteins or ice structuring proteins refer to a class of polypeptides produced by certain vertebrates, plants, fungi and bacteria that permit their survival in subzero environments. AFPs bind to small ice crystals to inhibit growth and recrystallization of ice that would otherwise be...
in their leaves. This can help prevent frost damage. Other genes that can be put into crops include a natural insecticide
Insecticide
An insecticide is a pesticide used against insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against the eggs and larvae of insects respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and the household. The use of insecticides is believed to be one of the major factors behind...
from the bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis
Bacillus thuringiensis
Bacillus thuringiensis is a Gram-positive, soil-dwelling bacterium, commonly used as a biological pesticide; alternatively, the Cry toxin may be extracted and used as a pesticide. B...
. The insecticide kills insects that eat the plants, but is harmless to people. In these plants the new genes are put into the plant before it is grown, so the genes will be in every part of the plant, including its seeds. The plant's offspring will then inherit the new genes, something which has led to concern about the spread of new traits into wild plants.
The kind of technology used in genetic engineering is also being developed to treat people with genetic disorder
Genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is an illness caused by abnormalities in genes or chromosomes, especially a condition that is present from before birth. Most genetic disorders are quite rare and affect one person in every several thousands or millions....
s in an experimental medical technique called gene therapy
Gene therapy
Gene therapy is the insertion, alteration, or removal of genes within an individual's cells and biological tissues to treat disease. It is a technique for correcting defective genes that are responsible for disease development...
. However, here the new gene is put in after the person has grown up and become ill, so any new gene will not be inherited by their children. Gene therapy works by trying to replace the allele that causes the disease with an allele that will work properly.
See also
- Common misunderstandings of geneticsCommon misunderstandings of geneticsDuring the latter half of the 20th century, the fields of genetics and molecular biology matured greatly, significantly increasing understanding of biological heredity. As with other complex and evolving fields of knowledge, the public awareness of these advances has primarily been through the mass...
- Full genome sequencingFull genome sequencingFull genome sequencing , also known as whole genome sequencing , complete genome sequencing, or entire genome sequencing, is a laboratory process that determines the complete DNA sequence of an organism's genome at a single time...
- List of basic genetics topics
- Predictive medicinePredictive medicinePredictive medicine is a rapidly emerging field of medicine that entails predicting disease and instituting preventive measures in order to either prevent the disease altogether or significantly decrease its impact upon the patient...
Genetics
- Introduction to Genetics, University of Utah
- Introduction to Genes and Disease, NCBI open book
- Genetics glossary, A talking glossary of genetic terms.
DNA and genes
- Animated guide to cloning
- Genetics NCBI, A Science Primer
- Khan Academy on YouTube
Interactive
- What Color Eyes Would Your Children Have? Genetics of human eye color: An interactive introduction.
- Double Helix Game from the Nobel Prize website. Match CATG bases with each other, and other games.
- Transcribe and translate a gene, University of Utah
- StarGenetics software simulates mating experiments between organisms that are genetically different across a range of traits.

