
Computational systems biology
Encyclopedia
Modeling biological systems is a significant task of systems biology
and mathematical biology
.
Computational systems biology aims to develop and use efficient algorithms, data structures, visualization
and communication tools with the goal of computer modeling of biological systems. It involves the use of computer simulation
s of biological systems, like cellular
subsystems (such as the networks of metabolites
and enzyme
s which comprise metabolism
, signal transduction
pathways and gene regulatory network
s) to both analyze and visualize the complex connections of these cellular processes.
Artificial life
or virtual evolution attempts to understand evolutionary processes via the computer simulation of simple (artificial) life forms.
is a result of the interplay of the cause-and-effect among simpler, integrated parts (see biological organisation). Biological systems manifest many important examples of emergent properties in the complex interplay of components. Traditional study of biological systems requires reductive methods in which quantities of data are gathered by category, such as concentration over time in response to a certain stimulus. Computers are critical to analysis and modeling of these data. The goal is to create accurate real-time models of a system's response to environmental and internal stimuli, such as a model of a cancer cell in order to find weaknesses in its signaling pathways, or modeling of ion channel mutations to see effects on cardiomyocytes and in turn, the function of a beating heart.
A monograph on this topic summarizes an extensive amount of published research
in this area up to 1987, including subsections in the following areas: computer modeling in biology and medicine, arterial system models, neuron
models, biochemical and oscillation
networks, quantum automata, quantum computers in molecular biology
and genetics
, cancer modeling, neural nets, genetic networks, abstract relational biology, metabolic-replication systems, category theory
applications in biology and medicine, automata theory
, cellular automata, tessallation models and complete self-reproduction, chaotic systems in organism
s, relational biology and organismic theories. This published report also includes 390 references to peer-reviewed articles by a large number of authors.
and CellML
.
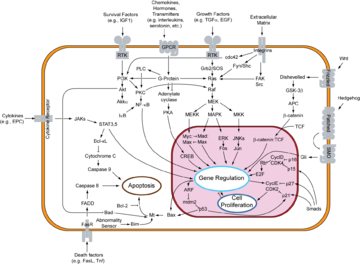
 Creating a cellular model has been a particularly challenging task of systems biology
Creating a cellular model has been a particularly challenging task of systems biology
and mathematical biology
. It involves the use of computer simulation
s of the many cellular
subsystems such as the networks of metabolites
and enzyme
s which comprise metabolism
, signal transduction
pathways and gene regulatory network
s to both analyze and visualize the complex connections of these cellular processes.
The complex network of biochemical reaction/transport processes and their spatial organization make the development of a predictive model of a living cell a grand challenge for the 21st century.
In 2006, the National Science Foundation
(NSF) put forward a grand challenge for systems biology in the 21st century to build a mathematical model of the whole cell. E-Cell Project aims "to make precise whole cell simulation at the molecular level possible". CytoSolve developed by V. A. Shiva Ayyadurai
and C. Forbes Dewey, Jr. of Department of Biological Engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
, provided a method to model the whole cell by dynamically integrating multiple molecular pathway models.
Membrane computing
is the task of modeling specifically a cell membrane
.
from its amino acid
sequence—that is, the prediction of a protein's tertiary structure
from its primary structure
. It is one of the most important goals pursued by bioinformatics
and theoretical chemistry
. Protein structure prediction
is of high importance in medicine
(for example, in drug design
) and biotechnology
(for example, in the design of novel enzymes). Every two years, the performance of current methods is assessed in the CASP
experiment.
the mammalian brain down to the molecular level. The aim of the project, founded in May 2005 by the Brain and Mind Institute of the École Polytechnique
in Lausanne
, Switzerland, is to study the brain's architectural and functional principles. The project is headed by the Institute's director, Henry Markram. Using a Blue Gene
supercomputer
running Michael Hines's NEURON software
, the simulation does not consist simply of an artificial neural network
, but involves a partially biologically realistic model of neuron
s. It is hoped by its proponents that it will eventually shed light on the nature of consciousness
.
There are a number of sub-projects, including the Cajal Blue Brain, coordinated by the Supercomputing and Visualization Center of Madrid
(CeSViMa), and others run by universities and independent laboratories in the UK, U.S., and Israel.
s to simulate growth. L-systems are very important in the field of complexity science and A-life.
A universally accepted system for describing changes in plant morphology at the cellular or modular level has yet to be devised.
The most widely implemented tree generating algorithms are described in the papers "Creation and Rendering of Realistic Trees", and Real-Time Tree Rendering
representations of ecosystem
s. Typically they simplify complex foodwebs
down to their major components or trophic level
s, and quantify these as either numbers of organism
s, biomass
or the inventory
/concentration
of some pertinent chemical element
(for instance, carbon
or a nutrient
species
such as nitrogen
or phosphorus
).
or to help manage them by vaccination
. This field tries to find parameter
s for various infectious disease
s and to use those parameters to make useful calculations about the effects of a mass vaccination
programme.
Systems biology
Systems biology is a term used to describe a number of trends in bioscience research, and a movement which draws on those trends. Proponents describe systems biology as a biology-based inter-disciplinary study field that focuses on complex interactions in biological systems, claiming that it uses...
and mathematical biology
Mathematical biology
Mathematical and theoretical biology is an interdisciplinary scientific research field with a range of applications in biology, medicine and biotechnology...
.
Computational systems biology aims to develop and use efficient algorithms, data structures, visualization
Biological data visualization
Biology Data Visualization is a branch of bioinformatics concerned with the application of computer graphics, scientific visualization, and information visualization to different areas of the life sciences. This includes visualization of sequences, genomes, alignments, phylogenies, macromolecular...
and communication tools with the goal of computer modeling of biological systems. It involves the use of computer simulation
Computer simulation
A computer simulation, a computer model, or a computational model is a computer program, or network of computers, that attempts to simulate an abstract model of a particular system...
s of biological systems, like cellular
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
subsystems (such as the networks of metabolites
Metabolic network
A metabolic network is the complete set of metabolic and physical processes that determine the physiological and biochemical properties of a cell...
and enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s which comprise metabolism
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
, signal transduction
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a cell surface receptor. In turn, this receptor alters intracellular molecules creating a response...
pathways and gene regulatory network
Gene regulatory network
A gene regulatory network or genetic regulatory network is a collection of DNA segments in a cell whichinteract with each other indirectly and with other substances in the cell, thereby governing the rates at which genes in the network are transcribed into mRNA.In general, each mRNA molecule goes...
s) to both analyze and visualize the complex connections of these cellular processes.
Artificial life
Artificial life
Artificial life is a field of study and an associated art form which examine systems related to life, its processes, and its evolution through simulations using computer models, robotics, and biochemistry. The discipline was named by Christopher Langton, an American computer scientist, in 1986...
or virtual evolution attempts to understand evolutionary processes via the computer simulation of simple (artificial) life forms.
Overview
It is understood that an unexpected emergent property of a complex systemComplex system
A complex system is a system composed of interconnected parts that as a whole exhibit one or more properties not obvious from the properties of the individual parts....
is a result of the interplay of the cause-and-effect among simpler, integrated parts (see biological organisation). Biological systems manifest many important examples of emergent properties in the complex interplay of components. Traditional study of biological systems requires reductive methods in which quantities of data are gathered by category, such as concentration over time in response to a certain stimulus. Computers are critical to analysis and modeling of these data. The goal is to create accurate real-time models of a system's response to environmental and internal stimuli, such as a model of a cancer cell in order to find weaknesses in its signaling pathways, or modeling of ion channel mutations to see effects on cardiomyocytes and in turn, the function of a beating heart.
A monograph on this topic summarizes an extensive amount of published research
in this area up to 1987, including subsections in the following areas: computer modeling in biology and medicine, arterial system models, neuron
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
models, biochemical and oscillation
Oscillation
Oscillation is the repetitive variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value or between two or more different states. Familiar examples include a swinging pendulum and AC power. The term vibration is sometimes used more narrowly to mean a mechanical oscillation but sometimes...
networks, quantum automata, quantum computers in molecular biology
Molecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that deals with the molecular basis of biological activity. This field overlaps with other areas of biology and chemistry, particularly genetics and biochemistry...
and genetics
Genetics
Genetics , a discipline of biology, is the science of genes, heredity, and variation in living organisms....
, cancer modeling, neural nets, genetic networks, abstract relational biology, metabolic-replication systems, category theory
Category theory
Category theory is an area of study in mathematics that examines in an abstract way the properties of particular mathematical concepts, by formalising them as collections of objects and arrows , where these collections satisfy certain basic conditions...
applications in biology and medicine, automata theory
Automata theory
In theoretical computer science, automata theory is the study of abstract machines and the computational problems that can be solved using these machines. These abstract machines are called automata...
, cellular automata, tessallation models and complete self-reproduction, chaotic systems in organism
Organism
In biology, an organism is any contiguous living system . In at least some form, all organisms are capable of response to stimuli, reproduction, growth and development, and maintenance of homoeostasis as a stable whole.An organism may either be unicellular or, as in the case of humans, comprise...
s, relational biology and organismic theories. This published report also includes 390 references to peer-reviewed articles by a large number of authors.
Standards
By far the most widely accepted standard format for storing and exchanging models in the field is the Systems Biology Markup Language (SBML) The SBML.org website includes a guide to many important software packages used in computational systems biology. Other markup languages with different emphases include BioPAXBioPAX
BioPAX is a RDF/OWL-basedstandard language to represent biological pathwaysat the molecular and cellular level. Its major use is to facilitate the exchange of pathway data....
and CellML
CellML
CellML is an XML based markup language for describing mathematical models. Although it could theoretically describe any mathematical model, it was originally created with the Physiome Project in mind, and hence used primarily to describe models relevant to the field of biology...
.
Cellular model



Systems biology
Systems biology is a term used to describe a number of trends in bioscience research, and a movement which draws on those trends. Proponents describe systems biology as a biology-based inter-disciplinary study field that focuses on complex interactions in biological systems, claiming that it uses...
and mathematical biology
Mathematical biology
Mathematical and theoretical biology is an interdisciplinary scientific research field with a range of applications in biology, medicine and biotechnology...
. It involves the use of computer simulation
Computer simulation
A computer simulation, a computer model, or a computational model is a computer program, or network of computers, that attempts to simulate an abstract model of a particular system...
s of the many cellular
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
subsystems such as the networks of metabolites
Metabolic network
A metabolic network is the complete set of metabolic and physical processes that determine the physiological and biochemical properties of a cell...
and enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s which comprise metabolism
Metabolism
Metabolism is the set of chemical reactions that happen in the cells of living organisms to sustain life. These processes allow organisms to grow and reproduce, maintain their structures, and respond to their environments. Metabolism is usually divided into two categories...
, signal transduction
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a cell surface receptor. In turn, this receptor alters intracellular molecules creating a response...
pathways and gene regulatory network
Gene regulatory network
A gene regulatory network or genetic regulatory network is a collection of DNA segments in a cell whichinteract with each other indirectly and with other substances in the cell, thereby governing the rates at which genes in the network are transcribed into mRNA.In general, each mRNA molecule goes...
s to both analyze and visualize the complex connections of these cellular processes.
The complex network of biochemical reaction/transport processes and their spatial organization make the development of a predictive model of a living cell a grand challenge for the 21st century.
In 2006, the National Science Foundation
National Science Foundation
The National Science Foundation is a United States government agency that supports fundamental research and education in all the non-medical fields of science and engineering. Its medical counterpart is the National Institutes of Health...
(NSF) put forward a grand challenge for systems biology in the 21st century to build a mathematical model of the whole cell. E-Cell Project aims "to make precise whole cell simulation at the molecular level possible". CytoSolve developed by V. A. Shiva Ayyadurai
Shiva Ayyadurai
V. A. Shiva Ayyadurai is an American inventor, scientist, and Faculty Lecturer in Department of Biological Engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.-Early Years & Education:...
and C. Forbes Dewey, Jr. of Department of Biological Engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology is a private research university located in Cambridge, Massachusetts. MIT has five schools and one college, containing a total of 32 academic departments, with a strong emphasis on scientific and technological education and research.Founded in 1861 in...
, provided a method to model the whole cell by dynamically integrating multiple molecular pathway models.
Membrane computing
Membrane computing
Membrane computing is an area within computer science that seeks to discover new computational models from the study of biological cells, particular of the cellular membranes. It is a sub-task of creating a cellular model....
is the task of modeling specifically a cell membrane
Cell membrane
The cell membrane or plasma membrane is a biological membrane that separates the interior of all cells from the outside environment. The cell membrane is selectively permeable to ions and organic molecules and controls the movement of substances in and out of cells. It basically protects the cell...
.
Protein folding
Protein structure prediction is the prediction of the three-dimensional structure of a proteinProtein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
from its amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
sequence—that is, the prediction of a protein's tertiary structure
Tertiary structure
In biochemistry and molecular biology, the tertiary structure of a protein or any other macromolecule is its three-dimensional structure, as defined by the atomic coordinates.-Relationship to primary structure:...
from its primary structure
Primary structure
The primary structure of peptides and proteins refers to the linear sequence of its amino acid structural units. The term "primary structure" was first coined by Linderstrøm-Lang in 1951...
. It is one of the most important goals pursued by bioinformatics
Bioinformatics
Bioinformatics is the application of computer science and information technology to the field of biology and medicine. Bioinformatics deals with algorithms, databases and information systems, web technologies, artificial intelligence and soft computing, information and computation theory, software...
and theoretical chemistry
Theoretical chemistry
Theoretical chemistry seeks to provide theories that explain chemical observations. Often, it uses mathematical and computational methods that, at times, require advanced knowledge. Quantum chemistry, the application of quantum mechanics to the understanding of valency, is a major component of...
. Protein structure prediction
Protein structure prediction
Protein structure prediction is the prediction of the three-dimensional structure of a protein from its amino acid sequence — that is, the prediction of its secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure from its primary structure. Structure prediction is fundamentally different from the inverse...
is of high importance in medicine
Medicine
Medicine is the science and art of healing. It encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention and treatment of illness....
(for example, in drug design
Drug design
Drug design, also sometimes referred to as rational drug design or structure-based drug design, is the inventive process of finding new medications based on the knowledge of the biological target...
) and biotechnology
Biotechnology
Biotechnology is a field of applied biology that involves the use of living organisms and bioprocesses in engineering, technology, medicine and other fields requiring bioproducts. Biotechnology also utilizes these products for manufacturing purpose...
(for example, in the design of novel enzymes). Every two years, the performance of current methods is assessed in the CASP
CASP
CASP, which stands for Critical Assessment of Techniques for Protein Structure Prediction, is a community-wide, worldwide experiment for protein structure prediction taking place every two years since 1994...
experiment.
Brain model
The Blue Brain Project is an attempt to create a synthetic brain by reverse-engineeringReverse engineering
Reverse engineering is the process of discovering the technological principles of a device, object, or system through analysis of its structure, function, and operation...
the mammalian brain down to the molecular level. The aim of the project, founded in May 2005 by the Brain and Mind Institute of the École Polytechnique
École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne
The École polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne is one of the two Swiss Federal Institutes of Technology and is located in Lausanne, Switzerland.The school was founded by the Swiss Federal Government with the stated mission to:...
in Lausanne
Lausanne
Lausanne is a city in Romandy, the French-speaking part of Switzerland, and is the capital of the canton of Vaud. The seat of the district of Lausanne, the city is situated on the shores of Lake Geneva . It faces the French town of Évian-les-Bains, with the Jura mountains to its north-west...
, Switzerland, is to study the brain's architectural and functional principles. The project is headed by the Institute's director, Henry Markram. Using a Blue Gene
Blue Gene
Blue Gene is a computer architecture project to produce several supercomputers, designed to reach operating speeds in the PFLOPS range, and currently reaching sustained speeds of nearly 500 TFLOPS . It is a cooperative project among IBM Blue Gene is a computer architecture project to produce...
supercomputer
Supercomputer
A supercomputer is a computer at the frontline of current processing capacity, particularly speed of calculation.Supercomputers are used for highly calculation-intensive tasks such as problems including quantum physics, weather forecasting, climate research, molecular modeling A supercomputer is a...
running Michael Hines's NEURON software
Neuron (software)
NEURON is a simulation environment for modeling individual neurons and networks of neurons.It was primarily developed by Michael Hines, John W. Moore, and Ted Carnevale at Yale and Duke....
, the simulation does not consist simply of an artificial neural network
Artificial neural network
An artificial neural network , usually called neural network , is a mathematical model or computational model that is inspired by the structure and/or functional aspects of biological neural networks. A neural network consists of an interconnected group of artificial neurons, and it processes...
, but involves a partially biologically realistic model of neuron
Neuron
A neuron is an electrically excitable cell that processes and transmits information by electrical and chemical signaling. Chemical signaling occurs via synapses, specialized connections with other cells. Neurons connect to each other to form networks. Neurons are the core components of the nervous...
s. It is hoped by its proponents that it will eventually shed light on the nature of consciousness
Consciousness
Consciousness is a term that refers to the relationship between the mind and the world with which it interacts. It has been defined as: subjectivity, awareness, the ability to experience or to feel, wakefulness, having a sense of selfhood, and the executive control system of the mind...
.
There are a number of sub-projects, including the Cajal Blue Brain, coordinated by the Supercomputing and Visualization Center of Madrid
Supercomputing and Visualization Center of Madrid
The Supercomputing and Visualization Center of Madrid also called Madrid Supercomputing and Visualization Center depends on the Computer Science Faculty of the Technical University of Madrid. This center houses Magerit, one of the most powerful supercomputers in Spain...
(CeSViMa), and others run by universities and independent laboratories in the UK, U.S., and Israel.
Model of the immune system
The last decade has seen the emergence of a growing number of simulations of the immune system.Tree model
Electronic trees (e-trees) usually use L-systemL-system
An L-system or Lindenmayer system is a parallel rewriting system, namely a variant of a formal grammar, most famously used to model the growth processes of plant development, but also able to model the morphology of a variety of organisms...
s to simulate growth. L-systems are very important in the field of complexity science and A-life.
A universally accepted system for describing changes in plant morphology at the cellular or modular level has yet to be devised.
The most widely implemented tree generating algorithms are described in the papers "Creation and Rendering of Realistic Trees", and Real-Time Tree Rendering
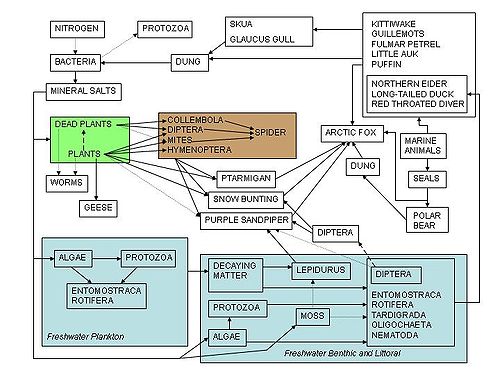
Ecological models
Ecosystem models are mathematicalMathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
representations of ecosystem
Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a biological environment consisting of all the organisms living in a particular area, as well as all the nonliving , physical components of the environment with which the organisms interact, such as air, soil, water and sunlight....
s. Typically they simplify complex foodwebs
Food web
A food web depicts feeding connections in an ecological community. Ecologists can broadly lump all life forms into one of two categories called trophic levels: 1) the autotrophs, and 2) the heterotrophs...
down to their major components or trophic level
Trophic level
The trophic level of an organism is the position it occupies in a food chain. The word trophic derives from the Greek τροφή referring to food or feeding. A food chain represents a succession of organisms that eat another organism and are, in turn, eaten themselves. The number of steps an organism...
s, and quantify these as either numbers of organism
Organism
In biology, an organism is any contiguous living system . In at least some form, all organisms are capable of response to stimuli, reproduction, growth and development, and maintenance of homoeostasis as a stable whole.An organism may either be unicellular or, as in the case of humans, comprise...
s, biomass
Biomass
Biomass, as a renewable energy source, is biological material from living, or recently living organisms. As an energy source, biomass can either be used directly, or converted into other energy products such as biofuel....
or the inventory
Inventory
Inventory means a list compiled for some formal purpose, such as the details of an estate going to probate, or the contents of a house let furnished. This remains the prime meaning in British English...
/concentration
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
of some pertinent chemical element
Chemical element
A chemical element is a pure chemical substance consisting of one type of atom distinguished by its atomic number, which is the number of protons in its nucleus. Familiar examples of elements include carbon, oxygen, aluminum, iron, copper, gold, mercury, and lead.As of November 2011, 118 elements...
(for instance, carbon
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
or a nutrient
Nutrient
A nutrient is a chemical that an organism needs to live and grow or a substance used in an organism's metabolism which must be taken in from its environment. They are used to build and repair tissues, regulate body processes and are converted to and used as energy...
species
Chemical species
Chemical species are atoms, molecules, molecular fragments, ions, etc., being subjected to a chemical process or to a measurement. Generally, a chemical species can be defined as an ensemble of chemically identical molecular entities that can explore the same set of molecular energy levels on a...
such as nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
or phosphorus
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is the chemical element that has the symbol P and atomic number 15. A multivalent nonmetal of the nitrogen group, phosphorus as a mineral is almost always present in its maximally oxidized state, as inorganic phosphate rocks...
).
Modeling of infectious disease
It is possible to model the progress of most infectious diseases mathematically to discover the likely outcome of an epidemicEpidemic
In epidemiology, an epidemic , occurs when new cases of a certain disease, in a given human population, and during a given period, substantially exceed what is expected based on recent experience...
or to help manage them by vaccination
Vaccination
Vaccination is the administration of antigenic material to stimulate the immune system of an individual to develop adaptive immunity to a disease. Vaccines can prevent or ameliorate the effects of infection by many pathogens...
. This field tries to find parameter
Parameter
Parameter from Ancient Greek παρά also “para” meaning “beside, subsidiary” and μέτρον also “metron” meaning “measure”, can be interpreted in mathematics, logic, linguistics, environmental science and other disciplines....
s for various infectious disease
Infectious disease
Infectious diseases, also known as communicable diseases, contagious diseases or transmissible diseases comprise clinically evident illness resulting from the infection, presence and growth of pathogenic biological agents in an individual host organism...
s and to use those parameters to make useful calculations about the effects of a mass vaccination
Vaccination
Vaccination is the administration of antigenic material to stimulate the immune system of an individual to develop adaptive immunity to a disease. Vaccines can prevent or ameliorate the effects of infection by many pathogens...
programme.
See also
- Biological data visualizationBiological data visualizationBiology Data Visualization is a branch of bioinformatics concerned with the application of computer graphics, scientific visualization, and information visualization to different areas of the life sciences. This includes visualization of sequences, genomes, alignments, phylogenies, macromolecular...
- Molecular modeling software
- Stochastic simulationStochastic simulationStochastic simulation algorithms and methods were initially developed to analyse chemical reactions involving large numbers of species with complex reaction kinetics. The first algorithm, the Gillespie algorithm was proposed by Dan Gillespie in 1977...
- Gillespie algorithmGillespie algorithmIn probability theory, the Gillespie algorithm generates a statistically correct trajectory of a stochastic equation. It was created by Joseph L...

