
Š
Encyclopedia
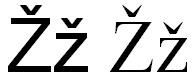
S
S is the nineteenth letter in the ISO basic Latin alphabet.-History: Semitic Šîn represented a voiceless postalveolar fricative . Greek did not have this sound, so the Greek sigma came to represent...
with caron
Caron
A caron or háček , also known as a wedge, inverted circumflex, inverted hat, is a diacritic placed over certain letters to indicate present or historical palatalization, iotation, or postalveolar pronunciation in the orthography of some Baltic, Slavic, Finno-Lappic, and other languages.It looks...
) is used in various contexts, usually denoting the voiceless postalveolar fricative
Voiceless postalveolar fricative
The voiceless palato-alveolar fricative or voiceless domed postalveolar fricative is a type of consonantal sound, used in many spoken languages, including English...
. In the International Phonetic Alphabet
International Phonetic Alphabet
The International Phonetic Alphabet "The acronym 'IPA' strictly refers [...] to the 'International Phonetic Association'. But it is now such a common practice to use the acronym also to refer to the alphabet itself that resistance seems pedantic...
this sound is denoted with , but the lowercase š is used in the Americanist phonetic notation
Americanist phonetic notation
Americanist phonetic notation is a system of phonetic notation originally developed by European and American anthropologists and language scientists for the phonetic and phonemic transcription of Native American and European languages...
, as well as in the Uralic Phonetic Alphabet
Uralic Phonetic Alphabet
The Uralic Phonetic Alphabet or Finno-Ugric transcription system is a phonetic transcription or notational system used predominantly for the transcription and reconstruction of Uralic languages...
.
For use in computer systems, Š and š are at Unicode
Unicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
codepoints U+0160 and U+0161 (Alt 352 and Alt 353 for input), respectively. In HTML code, the entities
Character entity reference
In the markup languages SGML, HTML, XHTML and XML, a character entity reference is a reference to a particular kind of named entity that has been predefined or explicitly declared in a Document Type Definition . The "replacement text" of the entity consists of a single character from the Universal...
Š and š can also be used to represent the characters.Primary usage
The symbol originates with the 15th century Czech alphabetCzech alphabet
The Czech alphabet is a version of the Latin script, used when writing Czech. Its basic principles are "one sound, one letter" and the addition of diacritical marks above letters to represent sounds alien to Latin...
as introduced by the reforms of Jan Hus
Jan Hus
Jan Hus , often referred to in English as John Hus or John Huss, was a Czech priest, philosopher, reformer, and master at Charles University in Prague...
. From there, it was adopted into the Croatian alphabet
Croatian alphabet
Gaj's Latin alphabet is a variant of the Latin script used for Croatian language. It was devised by Croatian linguist Ljudevit Gaj in 1835, based on Jan Hus's Czech alphabet....
by Ljudevit Gaj
Ljudevit Gaj
Ljudevit Gaj was a Croatian linguist, politician, journalist and writer. He was one of the central figures of the Croatian national reformation, also known as the Illyrian Movement.-Origin:...
in 1830, and other alphabets of languages, such as Bosnian
Bosnian language
Bosnian is a South Slavic language, spoken by Bosniaks. As a standardized form of the Shtokavian dialect, it is one of the three official languages of Bosnia and Herzegovina....
, Belarusian
Belarusian Latin alphabet
The Belarusian Latin alphabet or Łacinka is the common name of the several historical alphabets to render the Belarusian text in Latin script.-Use:...
, Estonian
Estonian language
Estonian is the official language of Estonia, spoken by about 1.1 million people in Estonia and tens of thousands in various émigré communities...
, Latvian
Latvian language
Latvian is the official state language of Latvia. It is also sometimes referred to as Lettish. There are about 1.4 million native Latvian speakers in Latvia and about 150,000 abroad. The Latvian language has a relatively large number of non-native speakers, atypical for a small language...
, Lithuanian
Lithuanian language
Lithuanian is the official state language of Lithuania and is recognized as one of the official languages of the European Union. There are about 2.96 million native Lithuanian speakers in Lithuania and about 170,000 abroad. Lithuanian is a Baltic language, closely related to Latvian, although they...
, Macedonian
Macedonian language
Macedonian is a South Slavic language spoken as a first language by approximately 2–3 million people principally in the region of Macedonia but also in the Macedonian diaspora...
, Montenegrin
Montenegrin language
Montenegrin is a name used for the Serbo-Croatian language as spoken by Montenegrins; it also refers to an incipient standardized form of the Shtokavian dialect of Serbo-Croatian used as the official language of Montenegro...
, Slovak
Slovak alphabet
The Slovak alphabet uses a modification of the Latin alphabet. The modifications include the four diacriticals placed above certain letters. Therefore the Slovak alphabet has 46 graphemes.- Vowels :- Consonants :Notes...
, Slovene, Serbian
Serbian language
Serbian is a form of Serbo-Croatian, a South Slavic language, spoken by Serbs in Serbia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Montenegro, Croatia and neighbouring countries....
, Karelian
Karelian alphabet
The Karelian language is spoken in Russia, mostly in the Karelian Republic and in a small region just north of Tver, though most residents there were expelled in 1939. Karelian has seen numerous proposed and adopted alphabets over the centuries, both Latin-based and Cyrillic...
, Sami
Sami languages
Sami or Saami is a general name for a group of Uralic languages spoken by the Sami people in parts of northern Finland, Norway, Sweden and extreme northwestern Russia, in Northern Europe. Sami is frequently and erroneously believed to be a single language. Several names are used for the Sami...
, Veps
Veps language
The Veps language , spoken by the Vepsians , belongs to the Finnic group of the Uralic languages...
, Sorbian
Sorbian alphabet
The Sorbian alphabet is based on the basic Latin alphabet but uses diacritics such as the acute accent and the caron, making it similar to the Czech and Polish alphabets...
and some forms of Bulgarian
Bulgarian language
Bulgarian is an Indo-European language, a member of the Slavic linguistic group.Bulgarian, along with the closely related Macedonian language, demonstrates several linguistic characteristics that set it apart from all other Slavic languages such as the elimination of case declension, the...
. Some languages in this list also use the Cyrillic script where the "š" represents the "ш" in the Latin alphabet.
Also, š occurs in Finnish
Finnish alphabet
The Finnish alphabet is based on the Latin script, and especially the Swedish alphabet. Officially it comprises 28 letters:A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I, J, K, L, M, N, O, P, Q, R, S, T, U, V, X, Y, Z, Å, Ä, Ö...
and Estonian
Estonian alphabet
The Estonian alphabet is used for writing the Estonian language and is based on the Latin alphabet, with German influence. As such, the Estonian alphabet has the letters Ä, Ö, and Ü , which represent the vowel sounds , and , respectively...
, but only in loanwords. On occasion, it is possible to replace š with sh but only when it is technically impossible to typeset the accented character.
Outside of Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is the eastern part of Europe. The term has widely disparate geopolitical, geographical, cultural and socioeconomic readings, which makes it highly context-dependent and even volatile, and there are "almost as many definitions of Eastern Europe as there are scholars of the region"...
, the "š" is also used in North American Lakota
Lakota language
Lakota is a Siouan language spoken by the Lakota people of the Sioux tribes. While generally taught and considered by speakers as a separate language, Lakota is mutually understandable with the other two languages , and is considered by most linguists one of the three major varieties of the Sioux...
, Cheyenne
Cheyenne language
The Cheyenne language is a Native American language spoken by the Cheyenne people, predominantly in present-day Montana and Oklahoma in the United States. It is part of the Algonquian language family...
and some African languages such as Northern Sotho
Northern Sotho language
Northern Sotho , also inaccurately known by the name of a major dialect, Pedi or sePedi, is one of the official languages of South Africa, and is spoken by 4,208,980 people — in the South African provinces of Gauteng,...
and Songhay
Songhay languages
The Songhay, Songhai, or Songai languages are a group of closely related languages/dialects centered on the middle stretches of the Niger River in the west African states of Mali, Niger, Benin, Burkina Faso, and Nigeria. They have been widely used as a lingua franca in that region ever since the...
.
Transliteration
The symbol is also used as the romanisation of Cyrillic ш in ISO 9ISO 9
The international standard ISO 9 establishes a system for the transliteration into Latin characters of Cyrillic characters constituting the alphabets of many Slavic and some non-Slavic languages....
and scientific transliteration
Scientific transliteration
Scientific transliteration, variously called academic, linguistic, or scholarly transliteration, is an international system for transliteration of text from the Cyrillic to the Latin alphabet...
and deployed in the Latinic writing systems of Macedonian
Romanisation of Macedonian
The Romanization of Macedonian is the transliteration of text in the Macedonian language from the Macedonian Cyrillic alphabet into the Latin alphabet. Romanization can be used for various purposes, such as rendering of proper names in foreign contexts, or for informal writing of Macedonian in...
, Bulgarian
Bulgarian language
Bulgarian is an Indo-European language, a member of the Slavic linguistic group.Bulgarian, along with the closely related Macedonian language, demonstrates several linguistic characteristics that set it apart from all other Slavic languages such as the elimination of case declension, the...
, Serbian, Belarusian, Ukrainian
Ukrainian language
Ukrainian is a language of the East Slavic subgroup of the Slavic languages. It is the official state language of Ukraine. Written Ukrainian uses a variant of the Cyrillic alphabet....
and Bashkir
Bashkir language
The Bashkir language is a Turkic language, and is the language of the Bashkirs. It is co-official with Russian in the Republic of Bashkortostan.-Speakers:...
.
In addition, the grapheme transliterates cuneiform
Cuneiform script
Cuneiform script )) is one of the earliest known forms of written expression. Emerging in Sumer around the 30th century BC, with predecessors reaching into the late 4th millennium , cuneiform writing began as a system of pictographs...
orthography of Sumerian
Sumerian language
Sumerian is the language of ancient Sumer, which was spoken in southern Mesopotamia since at least the 4th millennium BC. During the 3rd millennium BC, there developed a very intimate cultural symbiosis between the Sumerians and the Akkadians, which included widespread bilingualism...
and Akkadian
Akkadian language
Akkadian is an extinct Semitic language that was spoken in ancient Mesopotamia. The earliest attested Semitic language, it used the cuneiform writing system derived ultimately from ancient Sumerian, an unrelated language isolate...
ʃ or t͡ʃ, and (based on Akkadian orthography) the Hittite
Hittite language
Hittite is the extinct language once spoken by the Hittites, a people who created an empire centred on Hattusa in north-central Anatolia...
s phoneme, as well as the ʃ phoneme of Semitic languages
Semitic languages
The Semitic languages are a group of related languages whose living representatives are spoken by more than 270 million people across much of the Middle East, North Africa and the Horn of Africa...
, transliterating shin
Shin (letter)
Shin literally means "Sharp" ; It is the twenty-first letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician , Aramaic/Hebrew , and Arabic ....
(Phoenician

See also
- Ш, ш – Sha (Cyrillic)ShaFor other uses, see Sha .Sha is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet. It commonly represents the voiceless postalveolar fricative , like the pronunciation of ⟨sh⟩ in "sheep", or the somewhat similar voiceless retroflex fricative . It is used in every variation of the Cyrillic alphabet, for Slavic and...
- Sz (digraph)
- ŚSS is the nineteenth letter in the ISO basic Latin alphabet.-History: Semitic Šîn represented a voiceless postalveolar fricative . Greek did not have this sound, so the Greek sigma came to represent...
- ʃ – Esh (letter)Esh (letter)Esh is a character used in conjunction with the Latin Alphabet. Its lowercase form is similar to an italic long s ſ or an integral sign ∫; in 1928 the Africa Alphabet borrowed the Greek letter sigma for the uppercase form , but more recently the African reference alphabet discontinued it, using...
- CaronCaronA caron or háček , also known as a wedge, inverted circumflex, inverted hat, is a diacritic placed over certain letters to indicate present or historical palatalization, iotation, or postalveolar pronunciation in the orthography of some Baltic, Slavic, Finno-Lappic, and other languages.It looks...
- Shin (letter)Shin (letter)Shin literally means "Sharp" ; It is the twenty-first letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician , Aramaic/Hebrew , and Arabic ....
- Voiceless palato-alveolar sibilant

