Star lifting
Encyclopedia
Star lifting is any of several hypothetical processes by which a highly advanced civilization (at least Kardashev-II
) could remove a substantial portion of a star's
matter in a controlled manner for other uses. The term appears to have been coined by David Criswell
.
Stars already lose a small flow of mass via solar wind
, coronal mass ejection
s, and other natural processes. Over the course of a star's life on the main sequence
this loss is usually negligible compared to the star's total mass; only at the end of a star's life when it becomes a red giant
or a supernova
is a large amount of material ejected. The star lifting techniques that have been proposed would operate by increasing this natural plasma
flow and manipulating it with magnetic field
s.
Stars have deep gravity well
s, so the energy required for such operations is large. For example, lifting solar material from the surface of the Sun
to infinity requires 2.1 × 1011
J
/kg
. This energy could be supplied by the star itself, collected by a Dyson sphere
; using only 10% of the Sun's total power output would allow 5.9 × 1021 kilograms of matter to be lifted per year (0.0000003% of the Sun's total mass). The Dyson sphere would need to be designed to allow the lifted material to egress through it.
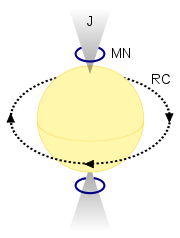 The simplest system for star lifting would increase the rate of solar wind outflow by directly heating small regions of the star's atmosphere, using any of a number of different means to deliver energy such as microwave
The simplest system for star lifting would increase the rate of solar wind outflow by directly heating small regions of the star's atmosphere, using any of a number of different means to deliver energy such as microwave
beams, laser
s, or particle beam
s – whatever proved to be most efficient for the engineers of the system. This would produce a large and sustained eruption similar to a solar flare
at the target location, feeding the solar wind.
The resulting outflow would be collected by using a ring current
around the star's equator to generate a powerful toroidal
magnetic field
with its dipole
s over the star's rotational poles. This would deflect the star's solar wind into a pair of jets aligned along its rotational axis passing through a pair of magnetic rocket nozzle
s. The magnetic nozzles would convert some of the plasma's thermal energy into outward velocity, helping to cool the outflow. The ring current required to generate this magnetic field would be generated by a ring of particle accelerator
space station
s in close orbit around the star's equator. These accelerators would be physically separate from each other but would exchange two counterdirected beams of oppositely charged ion
s with their neighbor on each side, forming a complete circuit around the star.
.
In this system the ring of particle accelerators would not be in orbit, instead depending on the outward force of the magnetic field itself for support against the star's gravity. To inject energy into the star's atmosphere the ring current would first be temporarily shut down, allowing the particle accelerator stations to begin falling freely toward the star's surface. Once the stations had developed sufficient inward velocity the ring current would be reactivated and the resulting magnetic field would be used to reverse the stations' fall. This would "squeeze" the star, propelling stellar atmosphere through the polar magnetic nozzles. The ring current would be shut down again before the ring stations achieved enough outward velocity to throw them too far away from the star, and the star's gravity would be allowed to pull them back inward to repeat the cycle.
A single set of ring stations would result in a very intermittent flow. It is possible to smooth this flow out by using multiple sets of ring stations, with each set operating in a different stage of the Huff-n-Puff cycle at any given moment so that there is always one ring "squeezing". This would also smooth out the power requirements of the system over time.
This method suffers from a number of significant complications compared to the others. Rotating the ring in this manner would require the ring stations to use powerful rocket thrust, requiring both large rocket
systems and a large amount of reaction mass. This reaction mass can be "recycled" by directing the rockets' exhausts so that it impacts the star's surface, but harvesting fresh reaction mass from the star's outflow and delivering it to the ring stations in sufficient quantity adds still more complexity to the system. Finally, the resulting jets would spiral outward from the star's equator rather than emerging straight from the poles; this could complicate harvesting it, as well as the arrangement of the Dyson sphere
powering the system.
s long, primarily composed of hydrogen
and helium
and highly diffuse by current engineering standards. The details of extracting useful materials from this stream and storing the vast quantities that would result have not been extensively explored. One possible approach is to purify useful elements from the jets using extremely large-scale mass spectrometry
, cool them by laser cooling
, and condense them on particles of dust for collection. Small artificial gas giant
planets could be constructed from excess hydrogen and helium to store it for future use.
reactions in its core. Larger stars have a larger supply of fuel, but the increased core pressure resulting from that additional mass increases the reaction rate even more; large stars have a significantly shorter lifespan than small ones. Current theories of stellar dynamics also suggest that there is very little mixing between the bulk of a star's atmosphere and the material of its core, where fusion takes place, so most of a large star's fuel will never be used naturally.
As a star's mass is reduced by star lifting its rate of nuclear fusion will decrease, reducing the amount of energy available to the star lifting process but also reducing the gravity that needs to be overcome. Theoretically, it would be possible to remove an arbitrarily large portion of a star's total mass given sufficient time. In this manner a civilization could control the rate at which its star uses fuel, optimizing the star's power output and lifespan to its needs. The hydrogen and helium extracted in the process could also be used as fusion reactor fuel. Current fusion generators (and fusion bombs) use deuterium
and tritium
. Most of a star’s mass consists of light hydrogen
and helium
. A technologically advanced civilization may develop fusion reactors capable of using ordinary hydrogen by currently unknown means. Alternatively, the material could be assembled into additional smaller stars, to improve the efficiency of its use. Theoretically all the energy of the matter lifted from a star could be harvested if it is made into small black holes, via the mechanism of Hawking Radiation
.
Kardashev scale
The Kardashev scale is a method of measuring an advanced civilization's level of technological advancement. The scale is only theoretical and in terms of an actual civilization highly speculative; however, it puts energy consumption of an entire civilization in a cosmic perspective. It was first...
) could remove a substantial portion of a star's
Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
matter in a controlled manner for other uses. The term appears to have been coined by David Criswell
David Criswell
David R. Criswell, Ph.D is currently the Director of the Institute for Space Systems Operations at the University of Houston. ISSO is the operational agent for the Houston Partnership for Space Exploration....
.
Stars already lose a small flow of mass via solar wind
Solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles ejected from the upper atmosphere of the Sun. It mostly consists of electrons and protons with energies usually between 1.5 and 10 keV. The stream of particles varies in temperature and speed over time...
, coronal mass ejection
Coronal mass ejection
A coronal mass ejection is a massive burst of solar wind, other light isotope plasma, and magnetic fields rising above the solar corona or being released into space....
s, and other natural processes. Over the course of a star's life on the main sequence
Main sequence
The main sequence is a continuous and distinctive band of stars that appears on plots of stellar color versus brightness. These color-magnitude plots are known as Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams after their co-developers, Ejnar Hertzsprung and Henry Norris Russell...
this loss is usually negligible compared to the star's total mass; only at the end of a star's life when it becomes a red giant
Red giant
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass in a late phase of stellar evolution. The outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius immense and the surface temperature low, somewhere from 5,000 K and lower...
or a supernova
Supernova
A supernova is a stellar explosion that is more energetic than a nova. It is pronounced with the plural supernovae or supernovas. Supernovae are extremely luminous and cause a burst of radiation that often briefly outshines an entire galaxy, before fading from view over several weeks or months...
is a large amount of material ejected. The star lifting techniques that have been proposed would operate by increasing this natural plasma
Plasma (physics)
In physics and chemistry, plasma is a state of matter similar to gas in which a certain portion of the particles are ionized. Heating a gas may ionize its molecules or atoms , thus turning it into a plasma, which contains charged particles: positive ions and negative electrons or ions...
flow and manipulating it with magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
s.
Stars have deep gravity well
Gravity well
A gravity well or gravitational well is a conceptual model of the gravitational field surrounding a body in space. The more massive the body the deeper and more extensive the gravity well associated with it. The Sun has a far-reaching and deep gravity well. Asteroids and small moons have much...
s, so the energy required for such operations is large. For example, lifting solar material from the surface of the Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
to infinity requires 2.1 × 1011
Scientific notation
Scientific notation is a way of writing numbers that are too large or too small to be conveniently written in standard decimal notation. Scientific notation has a number of useful properties and is commonly used in calculators and by scientists, mathematicians, doctors, and engineers.In scientific...
J
Joule
The joule ; symbol J) is a derived unit of energy or work in the International System of Units. It is equal to the energy expended in applying a force of one newton through a distance of one metre , or in passing an electric current of one ampere through a resistance of one ohm for one second...
/kg
Kilogram
The kilogram or kilogramme , also known as the kilo, is the base unit of mass in the International System of Units and is defined as being equal to the mass of the International Prototype Kilogram , which is almost exactly equal to the mass of one liter of water...
. This energy could be supplied by the star itself, collected by a Dyson sphere
Dyson sphere
A Dyson sphere is a hypothetical megastructure originally described by Freeman Dyson. Such a "sphere" would be a system of orbiting solar power satellites meant to completely encompass a star and capture most or all of its energy output...
; using only 10% of the Sun's total power output would allow 5.9 × 1021 kilograms of matter to be lifted per year (0.0000003% of the Sun's total mass). The Dyson sphere would need to be designed to allow the lifted material to egress through it.
Thermal-driven outflow

Microwave
Microwaves, a subset of radio waves, have wavelengths ranging from as long as one meter to as short as one millimeter, or equivalently, with frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz. This broad definition includes both UHF and EHF , and various sources use different boundaries...
beams, laser
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of photons. The term "laser" originated as an acronym for Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation...
s, or particle beam
Particle beam
A particle beam is a stream of charged or neutral particles which may be directed by magnets and focused by electrostatic lenses, although they may also be self-focusing ....
s – whatever proved to be most efficient for the engineers of the system. This would produce a large and sustained eruption similar to a solar flare
Solar flare
A solar flare is a sudden brightening observed over the Sun surface or the solar limb, which is interpreted as a large energy release of up to 6 × 1025 joules of energy . The flare ejects clouds of electrons, ions, and atoms through the corona into space. These clouds typically reach Earth a day...
at the target location, feeding the solar wind.
The resulting outflow would be collected by using a ring current
Ring current
A ring current is an electric current carried by charged particles trapped in a planet's magnetosphere. It is caused by the longitudinal drift of energetic particles.-Earth's ring current:...
around the star's equator to generate a powerful toroidal
Torus
In geometry, a torus is a surface of revolution generated by revolving a circle in three dimensional space about an axis coplanar with the circle...
magnetic field
Magnetic field
A magnetic field is a mathematical description of the magnetic influence of electric currents and magnetic materials. The magnetic field at any given point is specified by both a direction and a magnitude ; as such it is a vector field.Technically, a magnetic field is a pseudo vector;...
with its dipole
Dipole
In physics, there are several kinds of dipoles:*An electric dipole is a separation of positive and negative charges. The simplest example of this is a pair of electric charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign, separated by some distance. A permanent electric dipole is called an electret.*A...
s over the star's rotational poles. This would deflect the star's solar wind into a pair of jets aligned along its rotational axis passing through a pair of magnetic rocket nozzle
Nozzle
A nozzle is a device designed to control the direction or characteristics of a fluid flow as it exits an enclosed chamber or pipe via an orifice....
s. The magnetic nozzles would convert some of the plasma's thermal energy into outward velocity, helping to cool the outflow. The ring current required to generate this magnetic field would be generated by a ring of particle accelerator
Particle accelerator
A particle accelerator is a device that uses electromagnetic fields to propel charged particles to high speeds and to contain them in well-defined beams. An ordinary CRT television set is a simple form of accelerator. There are two basic types: electrostatic and oscillating field accelerators.In...
space station
Space station
A space station is a spacecraft capable of supporting a crew which is designed to remain in space for an extended period of time, and to which other spacecraft can dock. A space station is distinguished from other spacecraft used for human spaceflight by its lack of major propulsion or landing...
s in close orbit around the star's equator. These accelerators would be physically separate from each other but would exchange two counterdirected beams of oppositely charged ion
Ion
An ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
s with their neighbor on each side, forming a complete circuit around the star.
"Huff-n-Puff"
Criswell proposed a modification to the polar jet system in which the magnetic field could be used to increase solar wind outflow directly, without requiring additional heating of the star's surface. He dubbed it the "Huff-n-Puff" method, inspired from the Big Bad Wolf's threats in the fairy tale of Three Little PigsThree Little Pigs
Three Little Pigs is a fairy tale featuring anthropomorphic animals. Printed versions date back to the 1840s, but the story itself is thought to be much older...
.
In this system the ring of particle accelerators would not be in orbit, instead depending on the outward force of the magnetic field itself for support against the star's gravity. To inject energy into the star's atmosphere the ring current would first be temporarily shut down, allowing the particle accelerator stations to begin falling freely toward the star's surface. Once the stations had developed sufficient inward velocity the ring current would be reactivated and the resulting magnetic field would be used to reverse the stations' fall. This would "squeeze" the star, propelling stellar atmosphere through the polar magnetic nozzles. The ring current would be shut down again before the ring stations achieved enough outward velocity to throw them too far away from the star, and the star's gravity would be allowed to pull them back inward to repeat the cycle.
A single set of ring stations would result in a very intermittent flow. It is possible to smooth this flow out by using multiple sets of ring stations, with each set operating in a different stage of the Huff-n-Puff cycle at any given moment so that there is always one ring "squeezing". This would also smooth out the power requirements of the system over time.
Centrifugal acceleration
An alternative to the Huff-n-Puff method for using the toroidal magnetic field to increase solar wind outflow involves placing the ring stations in a polar orbit rather than an equatorial one. The two magnetic nozzles would then be located on the star's equator. To increase the rate of outflow through these two equatorial jets, the ring system would be rotated around the star at a rate significantly faster than the star's natural rotation. This would cause the stellar atmosphere swept up by the magnetic field to be flung outward.This method suffers from a number of significant complications compared to the others. Rotating the ring in this manner would require the ring stations to use powerful rocket thrust, requiring both large rocket
Rocket
A rocket is a missile, spacecraft, aircraft or other vehicle which obtains thrust from a rocket engine. In all rockets, the exhaust is formed entirely from propellants carried within the rocket before use. Rocket engines work by action and reaction...
systems and a large amount of reaction mass. This reaction mass can be "recycled" by directing the rockets' exhausts so that it impacts the star's surface, but harvesting fresh reaction mass from the star's outflow and delivering it to the ring stations in sufficient quantity adds still more complexity to the system. Finally, the resulting jets would spiral outward from the star's equator rather than emerging straight from the poles; this could complicate harvesting it, as well as the arrangement of the Dyson sphere
Dyson sphere
A Dyson sphere is a hypothetical megastructure originally described by Freeman Dyson. Such a "sphere" would be a system of orbiting solar power satellites meant to completely encompass a star and capture most or all of its energy output...
powering the system.
Harvesting lifted mass
The material lifted from a star will emerge in the form of plasma jets hundreds or thousands of astronomical unitAstronomical unit
An astronomical unit is a unit of length equal to about or approximately the mean Earth–Sun distance....
s long, primarily composed of hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
and helium
Helium
Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
and highly diffuse by current engineering standards. The details of extracting useful materials from this stream and storing the vast quantities that would result have not been extensively explored. One possible approach is to purify useful elements from the jets using extremely large-scale mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique that measures the mass-to-charge ratio of charged particles.It is used for determining masses of particles, for determining the elemental composition of a sample or molecule, and for elucidating the chemical structures of molecules, such as peptides and...
, cool them by laser cooling
Laser cooling
Laser cooling refers to the number of techniques in which atomic and molecular samples are cooled through the interaction with one or more laser light fields...
, and condense them on particles of dust for collection. Small artificial gas giant
Gas giant
A gas giant is a large planet that is not primarily composed of rock or other solid matter. There are four gas giants in the Solar System: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune...
planets could be constructed from excess hydrogen and helium to store it for future use.
Stellar husbandry
The lifespan of a star is determined by the size of its supply of nuclear "fuel" and the rate at which it uses up that fuel in fusionNuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion is the process by which two or more atomic nuclei join together, or "fuse", to form a single heavier nucleus. This is usually accompanied by the release or absorption of large quantities of energy...
reactions in its core. Larger stars have a larger supply of fuel, but the increased core pressure resulting from that additional mass increases the reaction rate even more; large stars have a significantly shorter lifespan than small ones. Current theories of stellar dynamics also suggest that there is very little mixing between the bulk of a star's atmosphere and the material of its core, where fusion takes place, so most of a large star's fuel will never be used naturally.
As a star's mass is reduced by star lifting its rate of nuclear fusion will decrease, reducing the amount of energy available to the star lifting process but also reducing the gravity that needs to be overcome. Theoretically, it would be possible to remove an arbitrarily large portion of a star's total mass given sufficient time. In this manner a civilization could control the rate at which its star uses fuel, optimizing the star's power output and lifespan to its needs. The hydrogen and helium extracted in the process could also be used as fusion reactor fuel. Current fusion generators (and fusion bombs) use deuterium
Deuterium
Deuterium, also called heavy hydrogen, is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen. It has a natural abundance in Earth's oceans of about one atom in of hydrogen . Deuterium accounts for approximately 0.0156% of all naturally occurring hydrogen in Earth's oceans, while the most common isotope ...
and tritium
Tritium
Tritium is a radioactive isotope of hydrogen. The nucleus of tritium contains one proton and two neutrons, whereas the nucleus of protium contains one proton and no neutrons...
. Most of a star’s mass consists of light hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
and helium
Helium
Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
. A technologically advanced civilization may develop fusion reactors capable of using ordinary hydrogen by currently unknown means. Alternatively, the material could be assembled into additional smaller stars, to improve the efficiency of its use. Theoretically all the energy of the matter lifted from a star could be harvested if it is made into small black holes, via the mechanism of Hawking Radiation
Hawking radiation
Hawking radiation is a thermal radiation with a black body spectrum predicted to be emitted by black holes due to quantum effects. It is named after the physicist Stephen Hawking, who provided a theoretical argument for its existence in 1974, and sometimes also after the physicist Jacob Bekenstein...
.
In fiction
- In the Star WarsStar WarsStar Wars is an American epic space opera film series created by George Lucas. The first film in the series was originally released on May 25, 1977, under the title Star Wars, by 20th Century Fox, and became a worldwide pop culture phenomenon, followed by two sequels, released at three-year...
franchise of Knights of the Old RepublicKnights of the Old RepublicThere have been a number of Knights of the Old Republic products.* Tales of the Jedi: Knights of the Old Republic, a 1990s comic book miniseries* Star Wars: Knights of the Old Republic, a role playing Star Wars video game released in 2003...
, the Star Forge is capable of star lifting. - In LexxLexxLexx is a science fantasy television series that follows the adventures of a group of mismatched individuals aboard the organic space craft Lexx. They travel through two universes and encounter planets including a parody of the Earth....
, the MantridMantridMantrid was the main antagonist of the second season of Lexx. He was played by Dieter Laser.When he was alive, he was the supreme Bio-Vizier of His Divine Shadow , until His Shadow exiled him to a barren snow-covered world...
Drones eventually became capable of star lifting simply by using their combined gravity to draw material away. - The novel Star Trek: VoyagerStar Trek: VoyagerStar Trek: Voyager is a science fiction television series set in the Star Trek universe. Set in the 24th century from the year 2371 through 2378, the series follows the adventures of the Starfleet vessel USS Voyager, which becomes stranded in the Delta Quadrant 70,000 light-years from Earth while...
– The Murdered Sun featured a reptilian race using the material from a star to sustain the opening of a wormholeWormholeIn physics, a wormhole is a hypothetical topological feature of spacetime that would be, fundamentally, a "shortcut" through spacetime. For a simple visual explanation of a wormhole, consider spacetime visualized as a two-dimensional surface. If this surface is folded along a third dimension, it...
. - In The Night's Dawn TrilogyThe Night's Dawn TrilogyBritish author Peter F. Hamilton's The Night's Dawn Trilogy consists of three science fiction novels: The Reality Dysfunction , The Neutronium Alchemist , and The Naked God...
by Peter F. HamiltonPeter F. HamiltonPeter F. Hamilton is a British author. He is best known for writing space opera. As of the publication of his tenth novel in 2004, his works had sold over two million copies worldwide.- Biography :...
, the alien species the Kiint created an arc of custom made planets around their sun from mass extracted from their star. - In The Time ShipsThe Time ShipsThe Time Ships is a 1995 science fiction novel by Stephen Baxter. A sequel to The Time Machine by H. G. Wells, it was officially authorized by the Wells estate to mark the centenary of the original's publication. It won the John W. Campbell Memorial Award and the Philip K. Dick Award in 1996, as...
by Steven Baxter, a Dyson sphereDyson sphereA Dyson sphere is a hypothetical megastructure originally described by Freeman Dyson. Such a "sphere" would be a system of orbiting solar power satellites meant to completely encompass a star and capture most or all of its energy output...
is constructed by material harvested from the sun through star-lifting. - In the web-based collaborative fictionCollaborative fictionCollaborative fiction is a form of writing by a group of authors who share creative control of a story.Collaborative fiction can occur for commercial gain, as part of education, or recreationally - many collaboratively written works have been the subject of a large degree of academic research.-...
site "Orion's ArmOrion's ArmOrion's Arm, is a multi-authored online science fiction world-building project, first established in 2000 by M. Alan Kazlev, Donna Malcolm Hirsekorn, Bernd Helfert and Anders Sandberg and further co-authored by many people since...
" the star Polaris is subject to starlifting (with image).

