Radium in the environment
Encyclopedia
Radium in quack medicine
See the story of Eben ByersEben Byers
Eben McBurney Byers was a wealthy American socialite, athlete, and industrialist. Byers earned notoriety in the early 1930s when he died from radiation poisoning after consuming a popular patent medicine made from radium dissolved in water.-Biography:The son of industrialist Alexander Byers, Eben...
for details of one very nasty case which involved a product called Radithor
Radithor
Radithor was a patent medicine that is a well known example of radioactive quackery. It consisted of triple distilled water containing at a minimum each of the radium 226 and 228 isotopes.-History:...
which contained 1 uCi (40 MBq) of 226Ra and 1 uCi of 228Ra per bottle. Radithor was taken by mouth and as radium is a calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
mimic it has a very long biological halflife in bone
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
.
Radium in the oil/gas industry
Residues from the oilPetroleum
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
and gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
industry often contain radium
Radium
Radium is a chemical element with atomic number 88, represented by the symbol Ra. Radium is an almost pure-white alkaline earth metal, but it readily oxidizes on exposure to air, becoming black in color. All isotopes of radium are highly radioactive, with the most stable isotope being radium-226,...
and its daughters. The sulfate scale from an oil well can be very radium rich. It is the case that the water inside an oil field is often very rich in strontium
Strontium
Strontium is a chemical element with the symbol Sr and the atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white or yellowish metallic element that is highly reactive chemically. The metal turns yellow when exposed to air. It occurs naturally in the minerals celestine and...
, barium
Barium
Barium is a chemical element with the symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in Group 2, a soft silvery metallic alkaline earth metal. Barium is never found in nature in its pure form due to its reactivity with air. Its oxide is historically known as baryta but it reacts with...
and radium
Radium
Radium is a chemical element with atomic number 88, represented by the symbol Ra. Radium is an almost pure-white alkaline earth metal, but it readily oxidizes on exposure to air, becoming black in color. All isotopes of radium are highly radioactive, with the most stable isotope being radium-226,...
while seawater is very rich in sulfate
Sulfate
In inorganic chemistry, a sulfate is a salt of sulfuric acid.-Chemical properties:...
so if water from an oil well is discharged into the sea or mixed with seawater the radium is likely to be brought out of solution by the barium/strontium sulfate which acts as a carrier
Carrier
Carrier may refer to:- Science :* Carrier wave, a waveform suitable for modulation by an information-bearing signal* Charge carrier, an unbound particle carrying an electric charge* a mathematical Set over which an algebraic structure is defined...
precipitate.
Glow in the dark products (radioluminescent)
Local contamination from radium-based radioluminescentRadioluminescence
Radioluminescence is the phenomenon by which luminescence is produced in a material by the bombardment of ionizing radiation such as beta particles.-Tritium:...
paints having been improperly disposed of is not unknown. http://www.epa.gov/region02/superfund/npl/0200772c.pdf
Radon
The majority of the dose is caused by the decay of the poloniumPolonium
Polonium is a chemical element with the symbol Po and atomic number 84, discovered in 1898 by Marie Skłodowska-Curie and Pierre Curie. A rare and highly radioactive element, polonium is chemically similar to bismuth and tellurium, and it occurs in uranium ores. Polonium has been studied for...
(218Po) and lead
Lead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
(214Pb) daughters from 222Rn. It is the case that by controlling the daughters that the dose to the skin
Skin
-Dermis:The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis that consists of connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis by a basement membrane. It also harbors many Mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and heat...
and lung
Lung
The lung is the essential respiration organ in many air-breathing animals, including most tetrapods, a few fish and a few snails. In mammals and the more complex life forms, the two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart...
s can be reduced by at least 90%. This can be done by wearing a dust mask, and wearing a suit to cover the entire body. Note that exposure to smoke
Smoke
Smoke is a collection of airborne solid and liquid particulates and gases emitted when a material undergoes combustion or pyrolysis, together with the quantity of air that is entrained or otherwise mixed into the mass. It is commonly an unwanted by-product of fires , but may also be used for pest...
at the same time as radon
Radon
Radon is a chemical element with symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas, occurring naturally as the decay product of uranium or thorium. Its most stable isotope, 222Rn, has a half-life of 3.8 days...
and radon daughters will increase the harmful effect of the radon. In uranium miner
Uranium mining
Uranium mining is the process of extraction of uranium ore from the ground. The worldwide production of uranium in 2009 amounted to 50,572 tonnes, of which 27% was mined in Kazakhstan. Kazakhstan, Canada, and Australia are the top three producers and together account for 63% of world uranium...
s radon has been found to be more carcinogenic in smokers
Tobacco smoking
Tobacco smoking is the practice where tobacco is burned and the resulting smoke is inhaled. The practice may have begun as early as 5000–3000 BCE. Tobacco was introduced to Eurasia in the late 16th century where it followed common trade routes...
than in non-smokers.
Occurrence of radon
On average, there is one atom of radon in 1 x 1021 molecules of air. Radon can be found in some spring waters and hot springHot spring
A hot spring is a spring that is produced by the emergence of geothermally heated groundwater from the Earth's crust. There are geothermal hot springs in many locations all over the crust of the earth.-Definitions:...
s. The towns of Misasa
Misasa, Tottori
is a town located in Tōhaku District, Tottori, Japan. It is also home to the official treasure of Sanbutsuji and the Okayama Hospital.The name "Misasa" originates from the belief that one who stays to enjoy three mornings in the town's famous hot springs will find all of his ailments cured.As of...
, Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
, and Bad Kreuznach
Bad Kreuznach
Bad Kreuznach is the capital of the district of Bad Kreuznach, Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany. It is located on the Nahe river, a tributary of the Rhine...
, Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
boast radium-rich springs which emit radon. Unsurprisingly, Radium Springs, New Mexico
Radium Springs, New Mexico
Radium Springs is a census-designated place in Doña Ana County, New Mexico, United States. The population was 1,518 at the 2000 census. It is part of the Las Cruces Metropolitan Statistical Area.-Geography:...
does too.
Radon exhausts naturally from the ground, particularly in certain regions, especially but not only regions with granitic
Granite
Granite is a common and widely occurring type of intrusive, felsic, igneous rock. Granite usually has a medium- to coarse-grained texture. Occasionally some individual crystals are larger than the groundmass, in which case the texture is known as porphyritic. A granitic rock with a porphyritic...
soils. Not all granitic regions are prone to high emissions of radon, for instance while the rock which Aberdeen
Aberdeen
Aberdeen is Scotland's third most populous city, one of Scotland's 32 local government council areas and the United Kingdom's 25th most populous city, with an official population estimate of ....
is on is very radium rich the rock lacks the cracks required for the radon to migrate. In other nearby areas of Scotland (to the north of Aberdeen) and in Cornwall
Cornwall
Cornwall is a unitary authority and ceremonial county of England, within the United Kingdom. It is bordered to the north and west by the Celtic Sea, to the south by the English Channel, and to the east by the county of Devon, over the River Tamar. Cornwall has a population of , and covers an area of...
/Devon
Devon
Devon is a large county in southwestern England. The county is sometimes referred to as Devonshire, although the term is rarely used inside the county itself as the county has never been officially "shired", it often indicates a traditional or historical context.The county shares borders with...
the radon is very able to leave the rock.
Radon is a decay product of radium
Radium
Radium is a chemical element with atomic number 88, represented by the symbol Ra. Radium is an almost pure-white alkaline earth metal, but it readily oxidizes on exposure to air, becoming black in color. All isotopes of radium are highly radioactive, with the most stable isotope being radium-226,...
which in turn is a decay product of uranium. It is possible to get maps of average radon levels in houses, these maps assist in the planning of radon mitigation measures for homes.http://eetd.lbl.gov/IEP/high-radon/USgm.htm
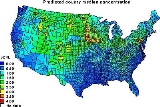
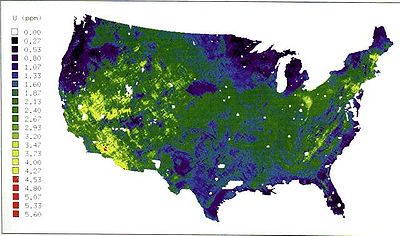
Soil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
/rock
Rock (geology)
In geology, rock or stone is a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids.The Earth's outer solid layer, the lithosphere, is made of rock. In general rocks are of three types, namely, igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic...
under a house does not always lead to a high radon level in air, a positive correlation between the uranium content of the soil and the radon level in air can be seen.
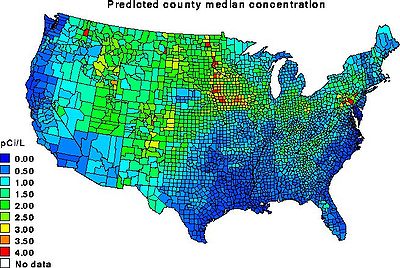
Radon in air
Radon is related to Indoor air qualityIndoor air quality
Indoor air quality is a term referring to the air quality within and around buildings and structures, especially as it relates to the health and comfort of building occupants....
as it blights many homes. (See "Radon in Houses" below.)
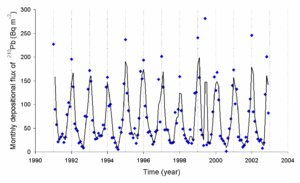
The radon (222Rn) released into the air decays to 210Pb and other radioisotopes, the levels of 210Pb
Lead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
can be measured. It is important to note that the rate of deposition of this radioisotope is very dependent on the season. Here is a graph of the deposition rate observed in Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
(M. Yamamoto et al., Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 2006, 86, 110-131).
Radon in Groundwater
Well water can be very radon rich, the use of this water inside a house is an additional route allowing radon to enter the house. The radon can enter the air and then be a source of exposure to the humans, or the water can be consumed by humans which is a different exposure route.Radon in Rainwater
Rainwater can be intensely radioactive due to high levels of radon and its decay progeny 214Bi & 214Pb, concentrations can be high enough to seriously disrupt radiation monitoring at nuclear power plants. The highest levels of radon in rainwater occurs during thunderstorms, and it is hypothesized that radon is concentrated in thunderstorms on account of the atom's positive electrical charge. Estimates of the age of rain drops have been obtained from measuring the isotopic abundance of radon's short-lived decay progeny in rainwater.Radon in the oil/gas industry
The water, oil and gas from a well often contains radonRadon
Radon is a chemical element with symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas, occurring naturally as the decay product of uranium or thorium. Its most stable isotope, 222Rn, has a half-life of 3.8 days...
. The radon decays to form solid radioisotopes which form coatings on the inside of pipework. In an oil processing plant the area of the plant where propane
Propane
Propane is a three-carbon alkane with the molecular formula , normally a gas, but compressible to a transportable liquid. A by-product of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, it is commonly used as a fuel for engines, oxy-gas torches, barbecues, portable stoves, and residential central...
is processed is often one of the more contaminated areas of the plant as radon has a similar boiling point to propane.http://www.enprotec-inc.com/Presentations/NORM.pdf
Radon in mines and caves
Because uranium minerals emit radonRadon
Radon is a chemical element with symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas, occurring naturally as the decay product of uranium or thorium. Its most stable isotope, 222Rn, has a half-life of 3.8 days...
gas, and their harmful and highly radioactive daughter products
Decay product
In nuclear physics, a decay product is the remaining nuclide left over from radioactive decay. Radioactive decay often involves a sequence of steps...
, uranium mining is considerably more dangerous than other (already dangerous) hard rock mining, requiring adequate ventilation systems if the mines are not open pit
Open-pit mining
Open-pit mining or opencast mining refers to a method of extracting rock or minerals from the earth by their removal from an open pit or borrow....
. During the 1950s, a significant number of American uranium miners were Navajo
Navajo Nation
The Navajo Nation is a semi-autonomous Native American-governed territory covering , occupying all of northeastern Arizona, the southeastern portion of Utah, and northwestern New Mexico...
Indians, as many uranium deposits were discovered on Navajo reservations
Indian reservation
An American Indian reservation is an area of land managed by a Native American tribe under the United States Department of the Interior's Bureau of Indian Affairs...
. A statistically significant subset of these miners later developed small-cell lung cancer, a type of cancer usually not associated with smoking, after exposure to uranium ore and radon
Radon
Radon is a chemical element with symbol Rn and atomic number 86. It is a radioactive, colorless, odorless, tasteless noble gas, occurring naturally as the decay product of uranium or thorium. Its most stable isotope, 222Rn, has a half-life of 3.8 days...
-222, a natural decay product of uranium.http://www.chestjournal.org/cgi/content/abstract/81/4/449 The radon, which is produced by the uranium, and not the uranium itself has been shown to be the cancer causing agent. http://www.rand.org/pubs/monograph_reports/MR1018.7/mr1018.7.chap2.html Some survivors and their descendants received compensation under the Radiation Exposure Compensation Act
Radiation Exposure Compensation Act
The United States Radiation Exposure Compensation Act is a federal statute providing for the monetary compensation of people, including atomic veterans, who contracted cancer and a number of other specified diseases as a direct result of their exposure to atmospheric nuclear testing undertaken by...
in 1990.
Currently the level of radon in the air of mines is normally controlled by law
Law
Law is a system of rules and guidelines which are enforced through social institutions to govern behavior, wherever possible. It shapes politics, economics and society in numerous ways and serves as a social mediator of relations between people. Contract law regulates everything from buying a bus...
. In a working mine, the radon level can be controlled by ventilation
Ventilation (architecture)
Ventilating is the process of "changing" or replacing air in any space to provide high indoor air quality...
, sealing off old workings and controlling the water in the mine. The level in a mine can go up when a mine is abandoned, it can reach a level which is able to cause the skin
Skin
-Dermis:The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis that consists of connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis by a basement membrane. It also harbors many Mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and heat...
to become red
Red
Red is any of a number of similar colors evoked by light consisting predominantly of the longest wavelengths of light discernible by the human eye, in the wavelength range of roughly 630–740 nm. Longer wavelengths than this are called infrared , and cannot be seen by the naked eye...
(a mild radiation burn
Radiation burn
A radiation burn is damage to the skin or other biological tissue caused by exposure to radio frequency energy or ionizing radiation.The most common type of radiation burn is a sunburn caused by UV radiation. High exposure to X-rays during diagnostic medical imaging or radiotherapy can also result...
). The radon levels in some of the mines can reach 400 to 700 kBq m−3.
A common unit of exposure of lung tissue to alpha
Alpha
Alpha is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. Alpha or ALPHA may also refer to:-Science:*Alpha , the highest ranking individuals in a community of social animals...
emitters is the Working level month (WLM), this is where the human lung
Lung
The lung is the essential respiration organ in many air-breathing animals, including most tetrapods, a few fish and a few snails. In mammals and the more complex life forms, the two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart...
s have been exposed for 170 hours (a typical month worth of work for a miner) to air which has 3.7 kBq of 222Rn (in equilibrium with its decay products). This is air which has the alpha dose rate of 1 working level (WL). It is estimated that the average person (general public
General Public
General Public were a band formed by The Beat vocalists, Dave Wakeling and Ranking Roger, and which included former members of Dexy's Midnight Runners, The Specials and The Clash...
) is subject to 0.2 WLM per year, which works out at about 15 to 20 WLM in a lifetime. According to the NRC 1 WLM is a 5 to 10 mSv lung dose (0.5 to 1.0 rem
Röntgen equivalent man
Named after Wilhelm Röntgen , the roentgen equivalent in man or rem is a unit of radiation dose equivalent...
), while the OECD consider that 1 WLM is equal to a lung dose of 5.5 mSv, the ICRP consider 1 WLM to be a 5 mSv lung dose for professional workers (and 4 mSv lung dose for the general public). Lastly the UN (UNSCEAR) consider that the exposure of the lungs to 1 Bq of 222Rn (in equilibrium with its decay products) for one year will cause a dose of 61 μSv. This overview of the working level month is based upon the book by Jiří Hála and James D. Navratil (ISBN 80-7302-053-X).
In humans a relationship between lung cancer
Lung cancer
Lung cancer is a disease characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. If left untreated, this growth can spread beyond the lung in a process called metastasis into nearby tissue and, eventually, into other parts of the body. Most cancers that start in lung, known as primary...
and radon has been shown at exist (beyond all reasonable doubt) for exposures of 100 WLM and above. By using the data from several studies it has been possible to show that an increased risk can be caused by a dose as low as 15 to 20 WLM. Sadly these studies have been difficult as the random errors in the data are very large. It is likely that the miners are also subject to other effects which can harm their lungs while at work (for example dust and diesel
Diesel exhaust
Diesel exhaust is the exhaust gas of a diesel engine....
fumes).
Radon References
A.R. Denman, J.P. Eatough, G. Gillmore and P.S. Phillips, Assessment of Health Risks To Skin and Lung Of Elevated Radon Level in Abandoned Mines, Health Physics, 2003, 85, 733.
G.K. Gillmore, P. Phillips, A. Denman, M Sperrin and G. Pearse, Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2001, 49, 281.
Radioactivity, ionizing radiation and Nuclear Energy, Jiří Hála and James D. Navratil, Chapter 8 (Radioactivity and ionizing radiation in the environment), ISBN 80-7302-053-X.
J.H. Lubin and J.D. Boice, Journal Natl. Cancer Inst., 1997, 89, 49. (Risks of indoor radon)
N.M. Hurley and J.H. Hurley, Environment International, 1986, 12, 39. (Lung cancer in uranium miners as a function of radon exposure).
Radon in houses
The danger of radon exposure in dwellings was discovered in 1984 by Stanley Watras, an employee at the Limerick nuclear power plantLimerick Nuclear Power Plant
The Limerick Generating Station in Pennsylvania is located next to the Schuylkill River in Limerick Township, Montgomery County, northwest of Philadelphia. The facility has two General Electric boiling water reactor units, cooled by natural draft cooling towers...
in Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania
The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to...
. Mr. Watras set off the radiation
Radiation
In physics, radiation is a process in which energetic particles or energetic waves travel through a medium or space. There are two distinct types of radiation; ionizing and non-ionizing...
alarms (see Geiger counter
Geiger counter
A Geiger counter, also called a Geiger–Müller counter, is a type of particle detector that measures ionizing radiation. They detect the emission of nuclear radiation: alpha particles, beta particles or gamma rays. A Geiger counter detects radiation by ionization produced in a low-pressure gas in a...
) on his way into work for two weeks straight while authorities searched for the source of the contamination
Contamination
Contamination is the presence of a minor and unwanted constituent in material, physical body, natural environment, at a workplace, etc.-Specifics:"Contamination" also has more specific meanings in science:...
. They were shocked to find that the source was astonishingly high levels of Radon in his basement
Basement
__FORCETOC__A basement is one or more floors of a building that are either completely or partially below the ground floor. Basements are typically used as a utility space for a building where such items as the furnace, water heater, breaker panel or fuse box, car park, and air-conditioning system...
and it was not related to the nuclear plant. The risks associated with living in his house were estimated to be equivalent to smoking
Tobacco smoking
Tobacco smoking is the practice where tobacco is burned and the resulting smoke is inhaled. The practice may have begun as early as 5000–3000 BCE. Tobacco was introduced to Eurasia in the late 16th century where it followed common trade routes...
135 packs of cigarette
Cigarette
A cigarette is a small roll of finely cut tobacco leaves wrapped in a cylinder of thin paper for smoking. The cigarette is ignited at one end and allowed to smoulder; its smoke is inhaled from the other end, which is held in or to the mouth and in some cases a cigarette holder may be used as well...
s every day.http://www.bradford.ac.uk/acad/envsci/radon_hotline/radonstory.htm
Depending on how houses are built and ventilated, radon may accumulate in basements and dwellings. The European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
recommends that action should be taken starting from concentrations of 400 Bq
Becquerel
The becquerel is the SI-derived unit of radioactivity. One Bq is defined as the activity of a quantity of radioactive material in which one nucleus decays per second. The Bq unit is therefore equivalent to an inverse second, s−1...
/m3 for old houses, and 200 Bq/m3 for new ones.
The National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements
National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements
The National Council on Radiation Protection and Measurements is a U.S. organization. It has a congressional charter under Title 36 of the United States Code, but this does not imply it has any sort of oversight or supervision from Congress; it is not a government entity.This text appears on the...
(NCRP) recommends action for any house with a concentration higher than 8 pCi
Curie
The curie is a unit of radioactivity, defined asThis is roughly the activity of 1 gram of the radium isotope 226Ra, a substance studied by the pioneers of radiology, Marie and Pierre Curie, for whom the unit was named. In addition to the curie, activity can be measured using an SI derived unit,...
/L (300 Bq/m³).
The United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
Environmental Protection Agency
United States Environmental Protection Agency
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency is an agency of the federal government of the United States charged with protecting human health and the environment, by writing and enforcing regulations based on laws passed by Congress...
recommends action for any house with a concentration higher than 148 Bq/m3 (given as 4 pCi
Curie
The curie is a unit of radioactivity, defined asThis is roughly the activity of 1 gram of the radium isotope 226Ra, a substance studied by the pioneers of radiology, Marie and Pierre Curie, for whom the unit was named. In addition to the curie, activity can be measured using an SI derived unit,...
/L). Nearly one in 15 homes in the U.S. has a high level of indoor radon according to their statistics. The U.S. Surgeon General and EPA recommend all homes be tested for radon. Since 1985, millions of homes have been tested for radon in the U.S.
By adding a crawl space under the ground floor, which is subject to forced ventilation the radon level in the house can be lowered.http://www.p2pays.org/ref/07/06295.pdf
Further reading
- Hala, J. and Navratil J.D., Radioactivity, Ionizing Radiation and Nuclear Energy, Konvoj, 2003. ISBN 80-7302-053-X

