
JPEG 2000
Encyclopedia
JPEG 2000 is an image compression
standard and coding system. It was created by the Joint Photographic Experts Group
committee in 2000 with the intention of superseding their original discrete cosine transform
-based JPEG
standard (created in 1992) with a newly designed, wavelet
-based method. The standardized filename extension
is .jp2 for ISO
/IEC
15444-1 conforming files and .jpx for the extended part-2 specifications, published as ISO/IEC 15444-2. The registered MIME types
are defined in RFC 3745. For ISO/IEC 15444-1 it is image/jp2.
s/decoder
s that are complex and computationally demanding. Another difference, in comparison with JPEG, is in terms of visual artifacts
: JPEG 2000 produces ringing artifacts
, manifested as blur and rings near edges in the image, while JPEG produces ringing artifacts and 'blocking' artifacts, due to its 8×8 blocks.
JPEG 2000 has been published as an ISO
standard, ISO/IEC 15444. , JPEG 2000 is not widely supported in web browser
s, and hence is not generally used on the World Wide Web
.

More advantages associated with JPEG 2000 can be referred to from the Official JPEG 2000 page.
to another color space, leading to three components that are handled separately. There are two possible choices:
Image compression
The objective of image compression is to reduce irrelevance and redundancy of the image data in order to be able to store or transmit data in an efficient form.- Lossy and lossless compression :...
standard and coding system. It was created by the Joint Photographic Experts Group
Joint Photographic Experts Group
The Joint Photographic Experts Group is the joint committee between ISO/IEC JTC1 and ITU-T that created the JPEG, JPEG 2000, and JPEG XR standards. It is one of two sub-groups of ISO/IEC Joint Technical Committee 1, Subcommittee 29, Working Group 1 - titled as Coding of still pictures...
committee in 2000 with the intention of superseding their original discrete cosine transform
Discrete cosine transform
A discrete cosine transform expresses a sequence of finitely many data points in terms of a sum of cosine functions oscillating at different frequencies. DCTs are important to numerous applications in science and engineering, from lossy compression of audio and images A discrete cosine transform...
-based JPEG
JPEG
In computing, JPEG . The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image quality. JPEG typically achieves 10:1 compression with little perceptible loss in image quality....
standard (created in 1992) with a newly designed, wavelet
Wavelet
A wavelet is a wave-like oscillation with an amplitude that starts out at zero, increases, and then decreases back to zero. It can typically be visualized as a "brief oscillation" like one might see recorded by a seismograph or heart monitor. Generally, wavelets are purposefully crafted to have...
-based method. The standardized filename extension
Filename extension
A filename extension is a suffix to the name of a computer file applied to indicate the encoding of its contents or usage....
is .jp2 for ISO
International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
/IEC
International Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission is a non-profit, non-governmental international standards organization that prepares and publishes International Standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies – collectively known as "electrotechnology"...
15444-1 conforming files and .jpx for the extended part-2 specifications, published as ISO/IEC 15444-2. The registered MIME types
Internet media type
An Internet media type, originally called a MIME type after MIME and sometimes a Content-type after the name of a header in several protocols whose value is such a type, is a two-part identifier for file formats on the Internet.The identifiers were originally defined in RFC 2046 for use in email...
are defined in RFC 3745. For ISO/IEC 15444-1 it is image/jp2.
Aims of the standard
While there is a modest increase in compression performance of JPEG 2000 compared to JPEG, the main advantage offered by JPEG 2000 is the significant flexibility of the codestream. The codestream obtained after compression of an image with JPEG 2000 is scalable in nature, meaning that it can be decoded in a number of ways; for instance, by truncating the codestream at any point, one may obtain a representation of the image at a lower resolution, or signal-to-noise ratio – see scalable compression. By ordering the codestream in various ways, applications can achieve significant performance increases. However, as a consequence of this flexibility, JPEG 2000 requires encoderEncoder
An encoder is a device, circuit, transducer, software program, algorithm or person that converts information from one format or code to another, for the purposes of standardization, speed, secrecy, security, or saving space by shrinking size.-Media:...
s/decoder
Decoder
A decoder is a device which does the reverse operation of an encoder, undoing the encoding so that the original information can be retrieved. The same method used to encode is usually just reversed in order to decode...
s that are complex and computationally demanding. Another difference, in comparison with JPEG, is in terms of visual artifacts
Compression artifact
A compression artifact is a noticeable distortion of media caused by the application of lossy data compression....
: JPEG 2000 produces ringing artifacts
Ringing artifacts
In signal processing, particularly digital image processing, ringing artifacts are artifacts that appear as spurious signals near sharp transitions in a signal. Visually, they appear as bands or "ghosts" near edges; audibly, they appear as "echos" near transients, particularly sounds from...
, manifested as blur and rings near edges in the image, while JPEG produces ringing artifacts and 'blocking' artifacts, due to its 8×8 blocks.
JPEG 2000 has been published as an ISO
International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
standard, ISO/IEC 15444. , JPEG 2000 is not widely supported in web browser
Web browser
A web browser is a software application for retrieving, presenting, and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web. An information resource is identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier and may be a web page, image, video, or other piece of content...
s, and hence is not generally used on the World Wide Web
World Wide Web
The World Wide Web is a system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via the Internet...
.
Features
- Superior compression performance: at high bit rates, where artifacts become nearly imperceptible, JPEG 2000 has a small machine-measured fidelity advantage over JPEG. At lower bit rates (e.g., less than 0.25 bits/pixel for grayscale images), JPEG 2000 has a much more significant advantage over certain modes of JPEG: artifacts are less visible and there is almost no blocking. The compression gains over JPEG are attributed to the use of DWTDiscrete wavelet transformIn numerical analysis and functional analysis, a discrete wavelet transform is any wavelet transform for which the wavelets are discretely sampled...
and a more sophisticated entropy encoding scheme.

- Multiple resolution representation: JPEG 2000 decomposes the image into a multiple resolution representation in the course of its compression process. This representation can be put to use for other image presentation purposes beyond compression as such.
- Progressive transmission by pixel and resolution accuracy, commonly referred to as progressive decoding and signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) scalability: JPEG 2000 provides efficient code-stream organizations which are progressive by pixel accuracy and by image resolution (or by image size). This way, after a smaller part of the whole file has been received, the viewer can see a lower quality version of the final picture. The quality then improves progressively through downloading more data bits from the source. The 1992 JPEG standard also has a progressive transmission feature but it's rarely used.
- Lossless and lossy compression: Like Lossless JPEG, the JPEG 2000 standard provides both lossless and lossy compression in a single compression architecture. Lossless compression is provided by the use of a reversible integer wavelet transform in JPEG 2000.
- Random code-stream access and processing, also referred as Region Of InterestRegion of interestA Region of Interest, often abbreviated ROI, is a selected subset of samples within a dataset identified for a particular purpose.For example:* on a waveform , a time or frequency interval...
(ROI): JPEG 2000 code streams offer several mechanisms to support spatial random access or region of interest access at varying degrees of granularity. This way it is possible to store different parts of the same picture using different quality.
- Error resilience: Like JPEG 1992, JPEG 2000 is robust to bit errors introduced by noisy communication channels, due to the coding of data in relatively small independent blocks.
- Flexible file format: The JP2 and JPX file formats allow for handling of color-space information, metadata, and for interactivity in networked applications as developed in the JPEG Part 9 JPIP protocol.
- Side channel spatial information: it fully supports transparency and alpha planes.
More advantages associated with JPEG 2000 can be referred to from the Official JPEG 2000 page.
JPEG 2000 image coding system - Parts
The JPEG 2000 image coding system (ISO/IEC 15444) consists of following parts:| Part | Number | First public release date (First edition) | Latest public release date (edition) | Latest amendment | Identical ITU-T standard | Title | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part 1 | ISO/IEC 15444-1 | 2000 | 2004 | 2006 | T.800 | Core coding system | the basic characteristics of JPEG 2000 compression (.jp2) |
| Part 2 | ISO/IEC 15444-2 | 2004 | 2004 | 2006 | T.801 | Extensions | (.jpx, .jpf) |
| Part 3 | ISO/IEC 15444-3 | 2002 | 2007 | T.802 | Motion JPEG 2000 | (.mj2) | |
| Part 4 | ISO/IEC 15444-4 | 2002 | 2004 | T.803 | Conformance testing | ||
| Part 5 | ISO/IEC 15444-5 | 2003 | 2003 | 2003 | T.804 | Reference software | Java and C implementations |
| Part 6 | ISO/IEC 15444-6 | 2003 | 2003 | 2007 | Compound image file format | (.jpm) e.g. document imaging, for pre-press and fax-like applications | |
| Part 7 | abandoned | Guideline of minimum support function of ISO/IEC 15444-1 | (Technical Report on Minimum Support Functions) | ||||
| Part 8 | ISO/IEC 15444-8 | 2007 | 2007 | 2008 | T.807 | Secure JPEG 2000 | JPSEC (security aspects) |
| Part 9 | ISO/IEC 15444-9 | 2005 | 2005 | 2008 | T.808 | Interactivity tools, APIs and protocols | JPIP JPIP JPIP is a compression streamlining protocol that works with JPEG 2000 to produce an image using the least bandwidth required... (interactive protocols and API) |
| Part 10 | ISO/IEC 15444-10 | 2008 | 2008 | 2008 | T.809 | Extensions for three-dimensional data | JP3D (volumetric imaging) |
| Part 11 | ISO/IEC 15444-11 | 2007 | 2007 | T.810 | Wireless | JPWL (wireless applications) | |
| Part 12 | ISO/IEC 15444-12 | 2004 | 2008 | ISO base media file format ISO base media file format ISO base media file format defines a general structure for time-based multimedia files such as video and audio. It is used as the basis for other media file formats... |
|||
| Part 13 | ISO/IEC 15444-13 | 2008 | 2008 | T.812 | An entry level JPEG 2000 encoder | ||
| Part 14 | under development | XML structural representation and reference | JPXML |
Technical discussion
The aim of JPEG 2000 is not only improving compression performance over JPEG but also adding (or improving) features such as scalability and editability. JPEG 2000's improvement in compression performance relative to the original JPEG standard is actually rather modest and should not ordinarily be the primary consideration for evaluating the design. Very low and very high compression rates are supported in JPEG 2000. The ability of the design to handle a very large range of effective bit rates is one of the strengths of JPEG 2000. For example, to reduce the number of bits for a picture below a certain amount, the advisable thing to do with the first JPEG standard is to reduce the resolution of the input image before encoding it. That's unnecessary when using JPEG 2000, because JPEG 2000 already does this automatically through its multiresolution decomposition structure. The following sections describe the algorithm of JPEG 2000.Color components transformation
Initially, images have to be transformed from the RGB color spaceColor space
A color model is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers, typically as three or four values or color components...
to another color space, leading to three components that are handled separately. There are two possible choices:
- Irreversible Color Transform (ICT) uses the well known YCBCRYCbCrYCbCr or Y′CbCr, sometimes written or , is a family of color spaces used as a part of the color image pipeline in video and digital photography systems. Y′ is the luma component and CB and CR are the blue-difference and red-difference chroma components...
color space. It is called "irreversible" because it has to be implemented in floating or fix-point and causes round-off errors. - Reversible Color Transform (RCT) uses a modified YUV color space that does not introduce quantization errors, so it is fully reversible. Proper implementation of the RCT requires that numbers are rounded as specified that cannot be expressed exactly in matrix form. The transformation is:
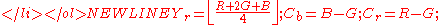
and
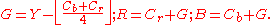
The chrominanceChrominanceChrominance is the signal used in video systems to convey the color information of the picture, separately from the accompanying luma signal . Chrominance is usually represented as two color-difference components: U = B' − Y' and V = R' − Y'...
components can be, but do not necessarily have to be, down-scaled in resolution; in fact, since the wavelet transformation already separates images into scales, downsampling is more effectively handled by dropping the finest wavelet scale. This step is called multiple component transformation in the JPEG 2000 language since its usage is not restricted to the RGB color modelRGB color modelThe RGB color model is an additive color model in which red, green, and blue light is added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors...
.
Tiling
After color transformation, the image is split into so-called tiles, rectangular regions of the image that are transformed and encoded separately. Tiles can be any size, and it is also possible to consider the whole image as one single tile. Once the size is chosen, all the tiles will have the same size (except optionally those on the right and bottom borders). Dividing the image into tiles is advantageous in that the decoder will need less memory to decode the image and it can opt to decode only selected tiles to achieve a partial decoding of the image. The disadvantage of this approach is that the quality of the picture decreases due to a lower peak signal-to-noise ratioPeak signal-to-noise ratioThe phrase peak signal-to-noise ratio, often abbreviated PSNR, is an engineering term for the ratio between the maximum possible power of a signal and the power of corrupting noise that affects the fidelity of its representation...
. Using many tiles can create a blocking effect similar to the older JPEGJPEGIn computing, JPEG . The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image quality. JPEG typically achieves 10:1 compression with little perceptible loss in image quality....
1992 standard.
Wavelet transform
These tiles are then wavelet transformed to an arbitrary depth, in contrast to JPEG 1992 which uses an 8×8 block-size discrete cosine transform Discrete cosine transformA discrete cosine transform expresses a sequence of finitely many data points in terms of a sum of cosine functions oscillating at different frequencies. DCTs are important to numerous applications in science and engineering, from lossy compression of audio and images A discrete cosine transform...
Discrete cosine transformA discrete cosine transform expresses a sequence of finitely many data points in terms of a sum of cosine functions oscillating at different frequencies. DCTs are important to numerous applications in science and engineering, from lossy compression of audio and images A discrete cosine transform...
. JPEG 2000 uses two different wavelet transforms:- irreversible: the CDFCohen-Daubechies-Feauveau waveletCohen-Daubechies-Feauveau wavelet are the historically first family of biorthogonal wavelets, which was made popular by Ingrid Daubechies. These are not the same as the orthogonal Daubechies wavelets, and also not very similar in shape and properties...
9/7 wavelet transform. It is said to be "irreversible" because it introduces quantization noise that depends on the precision of the decoder. - reversible: a rounded version of the biorthogonal CDFCohen-Daubechies-Feauveau waveletCohen-Daubechies-Feauveau wavelet are the historically first family of biorthogonal wavelets, which was made popular by Ingrid Daubechies. These are not the same as the orthogonal Daubechies wavelets, and also not very similar in shape and properties...
5/3 waveletWaveletA wavelet is a wave-like oscillation with an amplitude that starts out at zero, increases, and then decreases back to zero. It can typically be visualized as a "brief oscillation" like one might see recorded by a seismograph or heart monitor. Generally, wavelets are purposefully crafted to have...
transform. It uses only integer coefficients, so the output does not require rounding (quantization) and so it does not introduce any quantization noise. It is used in lossless coding.
The wavelet transforms are implemented by the lifting schemeLifting schemeThe lifting scheme is a technique for both designing wavelets and performing the discrete wavelet transform.Actually it is worthwhile to merge these steps and design the wavelet filters while performing the wavelet transform....
or by convolutionConvolutionIn mathematics and, in particular, functional analysis, convolution is a mathematical operation on two functions f and g, producing a third function that is typically viewed as a modified version of one of the original functions. Convolution is similar to cross-correlation...
.
Quantization
After the wavelet transform, the coefficients are scalar-quantizedQuantization (image processing)Quantization, involved in image processing, is a lossy compression technique achieved by compressing a range of values to a single quantum value. When the number of discrete symbols in a given stream is reduced, the stream becomes more compressible. For example, reducing the number of colors...
to reduce the number of bits to represent them, at the expense of quality. The output is a set of integer numbers which have to be encoded bit-by-bit. The parameter that can be changed to set the final quality is the quantization step: the greater the step, the greater is the compression and the loss of quality. With a quantization step that equals 1, no quantization is performed (it is used in lossless compression).
Coding
The result of the previous process is a collection of sub-bands which represent several approximation scales. A sub-band is a set of coefficients—real numbers which represent aspects of the image associated with a certain frequency range as well as a spatial area of the image.
The quantized sub-bands are split further into precincts, rectangular regions in the wavelet domain. They are typically selected in a way that the coefficients within them across the sub-bands form approximately spatial blocks in the (reconstructed) image domain, though this is not a requirement.
Precincts are split further into code blocks. Code blocks are located in a single sub-band and have equal sizes—except those located at the edges of the image. The encoder has to encode the bits of all quantized coefficients of a code block, starting with the most significant bits and progressing to less significant bits by a process called the EBCOT scheme. EBCOT here stands for Embedded Block Coding with Optimal Truncation. In this encoding process, each bit planeBIT planeThis article is about Natalie Jeremijenko and the Bureau of Inverse Technology's project. For the company, see Bitplane. For the digital information term, see bit plane....
of the code block gets encoded in three so-called coding passes, first encoding bits (and signs) of insignificant coefficients with significant neighbors (i.e., with 1-bits in higher bit planes), then refinement bits of significant coefficients and finally coefficients without significant neighbors. The three passes are called Significance Propagation, Magnitude Refinement and Cleanup pass, respectively.
Clearly, in lossless mode all bit planes have to be encoded by the EBCOT, and no bit planes can be dropped.
The bits selected by these coding passes then get encoded by a context-driven binary arithmetic coderArithmetic codingArithmetic coding is a form of variable-length entropy encoding used in lossless data compression. Normally, a string of characters such as the words "hello there" is represented using a fixed number of bits per character, as in the ASCII code...
, namely the binary MQ-coder. The context of a coefficient is formed by the state of its nine neighbors in the code block.
The result is a bit-stream that is split into packets where a packet groups selected passes of all code blocks from a precinct into one indivisible unit. Packets are the key to quality scalability (i.e., packets containing less significant bits can be discarded to achieve lower bit rates and higher distortion).
Packets from all sub-bands are then collected in so-called layers.
The way the packets are built up from the code-block coding passes, and thus which packets a layer will contain, is not defined by the JPEG 2000 standard, but in general a codec will try to build layers in such a way that the image quality will increase monotonically with each layer, and the image distortion will shrink from layer to layer. Thus, layers define the progression by image quality within the code stream.
The problem is now to find the optimal packet length for all code blocks which minimizes the overall distortion in a way that the generated target bitrate equals the demanded bit rate.
While the standard does not define a procedure as to how to perform this form of rate–distortion optimizationRate–distortion optimizationRate–distortion optimization is a method of improving video quality in video compression. The name refers to the optimization of the amount of distortion against the amount of data required to encode the video, the rate...
, the general outline is given in one of its many appendices: For each bit encoded by the EBCOT coder, the improvement in image quality, defined as mean square error, gets measured; this can be implemented by an easy table-lookup algorithm. Furthermore, the length of the resulting code stream gets measured. This forms for each code block a graph in the rate–distortion plane, giving image quality over bitstream length. The optimal selection for the truncation points, thus for the packet-build-up points is then given by defining critical slopes of these curves, and picking all those coding passes whose curve in the rate–distortion graph is steeper than the given critical slope. This method can be seen as a special application of the method of Lagrange multiplier which is used for optimization problems under constraints. The Lagrange multiplier, typically denoted by λ, turns out to be the critical slope, the constraint is the demanded target bitrate, and the value to optimize is the overall distortion.
Packets can be reordered almost arbitrarily in the JPEG 2000 bit-stream; this gives the encoder as well as image servers a high degree of freedom.
Already encoded images can be sent over networks with arbitrary bit rates by using a layer-progressive encoding order.
On the other hand, color components can be moved back in the bit-stream; lower resolutions (corresponding to low-frequency sub-bands) could be sent first for image previewing.
Finally, spatial browsing of large images is possible through appropriate tile and/or partition selection.
All these operations do not require any re-encoding but only byte-wise copy operations.
Performance
Compared to the previous JPEG standard, JPEG 2000 delivers a typical compression gain in the range of 20%, depending on the image characteristics. Higher-resolution images tend to benefit more, where JPEG-2000's spatial-redundancy prediction can contribute more to the compression process. In very low-bitrate applications, studies have shown JPEG 2000 to be outperformed by the intra-frame coding mode of H.264. Good applications for JPEG 2000 are large images, images with low-contrast edges — e.g., medical images.
File format and code stream
Similar to JPEG-1, JPEG 2000 defines both a file format and a code stream. Whereas the latter entirely describes the image samples, the former includes additional meta-information such as the resolution of the image or the color space that has been used to encode the image. JPEG 2000 images should — if stored as files — be boxed in the JPEG 2000 file format, where they get the .jp2 extender. The part-2 extension to JPEG 2000, i.e., ISO/IEC 15444-2, also enriches this file format by including mechanisms for animation or composition of several code streams into one single image. Images in this extended file-format use the .jpx extension.
There is no standardized extension for code-stream data because code-stream data is not to be considered to be stored in files in the first place, though when done for testing purposes, the extension .jpc or .j2k appear frequently.
Metadata
For traditional JPEG, additional metadataMetadataThe term metadata is an ambiguous term which is used for two fundamentally different concepts . Although the expression "data about data" is often used, it does not apply to both in the same way. Structural metadata, the design and specification of data structures, cannot be about data, because at...
, e.g. lighting and exposure conditions, is kept in an application marker in the ExifExchangeable image file formatExchangeable image file format is a standard that specifies the formats for images, sound, and ancillary tags used by digital cameras , scanners and other systems handling image and sound files recorded by digital cameras...
format specified by the JEITA. JPEG 2000 chooses a different route, encoding the same metadata in XMLXMLExtensible Markup Language is a set of rules for encoding documents in machine-readable form. It is defined in the XML 1.0 Specification produced by the W3C, and several other related specifications, all gratis open standards....
form. The reference between the Exif tags and the XML elements is standardized by the ISO TC42 committee in the standard 12234-1.4.
Extensible Metadata PlatformExtensible Metadata PlatformThe Adobe Extensible Metadata Platform is a standard, created by Adobe Systems Inc., for processing and storing standardized and proprietary information relating to the contents of a file....
can also be embedded in JPEG 2000.
Applications of JPEG 2000
Some markets and applications intended to be served by this standard are listed below:- Consumer applications such as multimedia devices (e.g., digital cameras, personal digital assistants, 3G mobile phones, color facsimile, printers, scanners, etc.)
- Client/server communication (e.g., the Internet, Image database, Video streaming, video server, etc.)
- Military/surveillance (e.g., HD satellite images, Motion detection, network distribution and storage, etc.)
- Medical imagery, esp. the DICOM specifications for medical data interchange.
- Remote sensingRemote sensingRemote sensing is the acquisition of information about an object or phenomenon, without making physical contact with the object. In modern usage, the term generally refers to the use of aerial sensor technologies to detect and classify objects on Earth by means of propagated signals Remote sensing...
- High-quality frame-based video recording, editing and storage.
- Live HDTV feed contribution (I-frame only video compression with low transmission latency), such as live HDTV feed of a sport event linked to the TV station studio
- Digital cinemaDigital cinemaDigital cinema refers to the use of digital technology to distribute and project motion pictures. A movie can be distributed via hard drives, optical disks or satellite and projected using a digital projector instead of a conventional film projector...
- JPEG 2000 has many design commonalities with the ICERICERICER is a wavelet-based image compression file format used by the NASA Mars Rovers. ICER has both lossy and lossless compression modes.The Mars Exploration Rovers “Spirit” and “Opportunity” both use ICER...
image compression format that is used to send images back from the MarsMarsMars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. The planet is named after the Roman god of war, Mars. It is often described as the "Red Planet", as the iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance...
rovers. - World Meteorological OrganizationWorld Meteorological OrganizationThe World Meteorological Organization is an intergovernmental organization with a membership of 189 Member States and Territories. It originated from the International Meteorological Organization , which was founded in 1873...
has built JPEG 2000 Compression into the new GRIB2 file format. The GRIB file structure is designed for global distribution of meteorological data. The implementation of JPEG 2000 compression in GRIB2 has reduced file sizes up to 80%.
Comparison with PNG
Although JPEG 2000 format supports lossless encoding, it is not intended to completely supersede today's dominant lossless image file formats.
The PNG (Portable Network Graphics) format is still more space-efficient in the case of images with many pixels of the same color, such as diagrams, and supports special compression features that JPEG 2000 does not.
Legal issues
JPEG 2000 is by itself licensed, but the contributing companies and organizations agreed that licenses for its first part—the core coding system—can be obtained free of charge from all contributors.
The JPEG committee has stated:
- It has always been a strong goal of the JPEG committee that its standards should be implementable in their baseline form without payment of royalty and license fees... The up and coming JPEG 2000 standard has been prepared along these lines, and agreement reached with over 20 large organizations holding many patents in this area to allow use of their intellectual property in connection with the standard without payment of license fees or royalties.
However, the JPEG committee has also noted that undeclared and obscure submarine patentSubmarine patentA submarine patent is a patent whose issuance and publication are intentionally delayed by the applicant for a long time, such as several years. This strategy requires a patent system where patent applications are not published. In the United States, patent applications filed before November 2000...
s may still present a hazard:
- It is of course still possible that other organizations or individuals may claim intellectual property rights that affect implementation of the standard, and any implementers are urged to carry out their own searches and investigations in this area.
Because of this statement, controversy remains in the software community concerning the legal status of the JPEG 2000 standard.
However, many Linux distributionLinux distributionA Linux distribution is a member of the family of Unix-like operating systems built on top of the Linux kernel. Such distributions are operating systems including a large collection of software applications such as word processors, spreadsheets, media players, and database applications...
s include a JPEG 2000 library.
Related standards
Several additional parts of the JPEG 2000 standard exist;
Amongst them are ISO/IEC 15444-2:2000, JPEG 2000 extensions defining the .jpx file format, featuring for example Trellis quantizationTrellis quantizationTrellis quantization is an algorithm that can improve data compression in DCT-based encoding methods. It is used to optimize residual DCT coefficients after motion estimation in lossy video compression encoders such as Xvid and x264. Trellis quantization reduces the size of some DCT coefficients...
, an extended file format and additional color spaceColor spaceA color model is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers, typically as three or four values or color components...
s, ISO/IEC 15444-4:2000, the reference testing and ISO/IEC 15444-6:2000, the compound image file format (.jpm), allowing compression of compound text/image graphics.
Extensions for secure image transfer, JPSEC (ISO/IEC 15444-8), enhanced error-correction schemes for wireless applications, JPWL (ISO/IEC 15444-11) and extensions for encoding of volumetric images, JP3D (ISO/IEC 15444-10) are also already available from the ISO.
JPIP protocol for streaming JPEG 2000 images
In 2005, a JPEG 2000 based image browsing protocol, called JPIPJPIPJPIP is a compression streamlining protocol that works with JPEG 2000 to produce an image using the least bandwidth required...
has been published as ISO/IEC 15444-9. Within this framework, only selected regions of potentially huge images have to be transmitted from an image server on the request of a client, thus reducing the required bandwidth.
JPEG 2000 data may also be streamed using the ECWP and ECWPS protocols found within the ERDAS ECWECW (file format)ECW is a proprietary wavelet compression image format optimized for aerial and satellite imagery. It was developed by Earth Resource Mapping, and is now owned by ERDAS, which is owned by Intergraph...
/JP2 SDK.
Motion JPEG 2000
Motion JPEG 2000 is defined in ISO/IEC 15444-3 and in ITU-T T.802. It specifies the use of the JPEG 2000 format for timed sequences of images (motion sequences), possibly combined with audio, and composed into an overall presentation. It also defines a file format, based on ISO base media file format (ISO 15444-12). Filename extensions for Motion JPEG 2000 video files are .mj2 and .mjp2 according to RFC 3745.
Motion JPEG 2000 (often referenced as MJ2 or MJP2) also is under consideration as a digital archival format by the Library of CongressLibrary of CongressThe Library of Congress is the research library of the United States Congress, de facto national library of the United States, and the oldest federal cultural institution in the United States. Located in three buildings in Washington, D.C., it is the largest library in the world by shelf space and...
. It is an open ISOInternational Organization for StandardizationThe International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
standard and an advanced update to MJPEGMJPEGIn multimedia, Motion JPEG is an informal name for a class of video formats where each video frame or interlaced field of a digital video sequence is separately compressed as a JPEG image...
(or MJ), which was based on the legacy JPEGJPEGIn computing, JPEG . The degree of compression can be adjusted, allowing a selectable tradeoff between storage size and image quality. JPEG typically achieves 10:1 compression with little perceptible loss in image quality....
format. Unlike common video formats, such as MPEG-4 Part 2MPEG-4 Part 2MPEG-4 Part 2, MPEG-4 Visual is a video compression technology developed by MPEG. It belongs to the MPEG-4 ISO/IEC standards. It is a discrete cosine transform compression standard, similar to previous standards such as MPEG-1 and MPEG-2...
, WMV, and H.264H.264/MPEG-4 AVCH.264/MPEG-4 Part 10 or AVC is a standard for video compression, and is currently one of the most commonly used formats for the recording, compression, and distribution of high definition video...
, MJ2 does not employ temporal or inter-frame compression. Instead, each frame is an independent entity encoded by either a lossy or lossless variant of JPEG 2000. Its physical structure does not depend on time ordering, but it does employ a separate profile to complement the data. For audio, it supports LPCMLPCMLinear pulse-code modulation is a method of encoding audio information digitally. The term also refers collectively to formats using this method of encoding...
encoding, as well as various MPEG-4 variants, as "raw" or complement data.
ISO base media file format
ISO/IEC 15444-12 is identical with ISO/IEC 14496-12 (MPEG-4 Part 12) and it defines ISO base media file formatISO base media file formatISO base media file format defines a general structure for time-based multimedia files such as video and audio. It is used as the basis for other media file formats...
. For example, Motion JPEG 2000 file format, MP4 file format or 3GP3GP3GP is a multimedia container format defined by the Third Generation Partnership Project for 3G UMTS multimedia services. It is used on 3G mobile phones but can also be played on some 2G and 4G phones....
file format are also based on this ISO base media file format.
GML JP2 Georeferencing
The Open Geospatial ConsortiumOpen Geospatial ConsortiumThe Open Geospatial Consortium , an international voluntary consensus standards organization, originated in 1994. In the OGC, more than 400 commercial, governmental, nonprofit and research organizations worldwide collaborate in a consensus process encouraging development and implementation of open...
(OGC) has defined a metadata standard for georeferencing JPEG 2000 images with embedded XMLXMLExtensible Markup Language is a set of rules for encoding documents in machine-readable form. It is defined in the XML 1.0 Specification produced by the W3C, and several other related specifications, all gratis open standards....
using the Geography Markup LanguageGeography Markup LanguageThe Geography Markup Language is the XML grammar defined by the Open Geospatial Consortium to express geographical features. GML serves as a modeling language for geographic systems as well as an open interchange format for geographic transactions on the Internet...
(GML) format: GML in JPEG 2000 for Geographic Imagery Encoding (GMLJP2), version 1.0.0, dated 2006-01-18.
JP2 and JPX files containing GMLJP2 markup can be located and displayed in the correct position on the Earth's surface by a suitable Geographic Information SystemGeographic Information SystemA geographic information system, geographical information science, or geospatial information studies is a system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage, and present all types of geographically referenced data...
(GIS), in a similar way to GeoTIFFGeoTIFFGeoTIFF is a public domain metadata standard which allows georeferencing information to be embedded within a TIFF file. The potential additional information includes map projection, coordinate systems, ellipsoids, datums, and everything else necessary to establish the exact spatial reference for...
images.
Applications
Application support for JPEG 2000 Program Basic Advanced License Read Write Read Write ACDSee ACDSeeACDSee is a shareware image organizer, viewer, and editor software for Microsoft Windows and Mac OS X 10.5 and higher developed by ACD Systems. It was originally distributed as a 16-bit application for Windows 3.0 and later supplanted by a 32-bit version for Windows 95.ACDSee displays a tree view...? ? Proprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...Adobe Photoshop Adobe PhotoshopAdobe Photoshop is a graphics editing program developed and published by Adobe Systems Incorporated.Adobe's 2003 "Creative Suite" rebranding led to Adobe Photoshop 8's renaming to Adobe Photoshop CS. Thus, Adobe Photoshop CS5 is the 12th major release of Adobe Photoshop...
Proprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...Apple iPhoto IPhotoiPhoto is a digital photograph manipulation software application developed by Apple Inc. and released with every Macintosh personal computer as part of the iLife suite of digital life management applications...Proprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...Apple Preview Preview (software)Preview is Mac OS X's application for displaying images and Portable Document Format documents. Like Mac OS X itself, it comes from NeXT's OPENSTEP operating system....Proprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...BAE Systems BAE SystemsBAE Systems plc is a British multinational defence, security and aerospace company headquartered in London, United Kingdom, that has global interests, particularly in North America through its subsidiary BAE Systems Inc. BAE is among the world's largest military contractors; in 2009 it was the...
CoMPASSProprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...Blender Blender (software)Blender is a free and open-source 3D computer graphics software product used for creating animated films, visual effects, interactive 3D applications or video games. The current release version is 2.60, and was released on October 19, 2011...GPL GNU General Public LicenseThe GNU General Public License is the most widely used free software license, originally written by Richard Stallman for the GNU Project....Corel Photo-Paint Corel PHOTO-PAINTCorel PHOTO-PAINT is a raster graphics editor developed and marketed by Corel since 1992. Corel currently markets the software for Windows operating systems, previously having marketed versions for Linux and Mac OS...Proprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...digiKam DigiKamdigiKam is an image organizer and editor using KDE Platform. It runs on most known desktop environments and window managers if the required libraries are installed. It supports all major image file formats, and can organize collections of photographs in directory-based albums, or dynamic albums by...
(KDEKDEKDE is an international free software community producing an integrated set of cross-platform applications designed to run on Linux, FreeBSD, Microsoft Windows, Solaris and Mac OS X systems...
)GPL GNU General Public LicenseThe GNU General Public License is the most widely used free software license, originally written by Richard Stallman for the GNU Project....ENVI Proprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...ERDAS IMAGINE ERDAS IMAGINEERDAS IMAGINE is a remote sensing application with raster graphics editor capabilities designed by ERDAS for geospatial applications. The latest version is 2010, version 10.1. ERDAS IMAGINE is aimed primarily at geospatial raster data processing and allows the user to prepare, display and enhance...Proprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...FastStone Image Viewer FastStone Image ViewerFastStone Image Viewer is an image viewer and organizer for Microsoft Windows, provided free of charge for personal and educational use, .- Features :Highlights:* Relatively fast HQ image/thumbnail viewing, using Lanczos resampling algorithm...Proprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...FastStone MaxView Proprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...GIMP GIMPGIMP is a free software raster graphics editor. It is primarily employed as an image retouching and editing tool and is freely available in versions tailored for most popular operating systems including Microsoft Windows, Apple Mac OS X, and Linux.In addition to detailed image retouching and...GPL GNU General Public LicenseThe GNU General Public License is the most widely used free software license, originally written by Richard Stallman for the GNU Project....GraphicConverter GraphicConverterGraphicConverter is computer software that displays and edits computer graphics files. It also converts files between different formats. For example, one can convert a GIF file to a JPEG file....Shareware SharewareThe term shareware is a proprietary software that is provided to users without payment on a trial basis and is often limited by any combination of functionality, availability, or convenience. Shareware is often offered as a download from an Internet website or as a compact disc included with a...Gwenview GwenviewGwenview is an image viewer for the KDE Software Compilation desktop environment. The current maintainer is Aurélien Gâteau. The word "Gwen" means "white" in the Breton language and is commonly used as a first name....
(KDEKDEKDE is an international free software community producing an integrated set of cross-platform applications designed to run on Linux, FreeBSD, Microsoft Windows, Solaris and Mac OS X systems...
)GPL GNU General Public LicenseThe GNU General Public License is the most widely used free software license, originally written by Richard Stallman for the GNU Project....IDL Proprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...ImageMagick ImageMagickImageMagick is an open source software suite for displaying, converting, and editing raster image files. It can read and write over 100 image file formats. ImageMagick is licensed under the Apache 2.0 license.- Features and capabilities:...ImageMagick License IrfanView IrfanViewIrfanView is a freeware/shareware image viewer for Microsoft Windows that can view, edit, and convert image files and play video/audio files. It is noted for its small size, speed, ease of use, and ability to handle a wide variety of graphic file formats, and has some image creation and painting...Proprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...KolourPaint KolourPaintKolourPaint is a free, raster graphics editor for the KDE, similar to Microsoft's Paint application before Windows 7, but has some additional features such as support for transparency....
(KDEKDEKDE is an international free software community producing an integrated set of cross-platform applications designed to run on Linux, FreeBSD, Microsoft Windows, Solaris and Mac OS X systems...
)2-clause BSD BSD licensesBSD licenses are a family of permissive free software licenses. The original license was used for the Berkeley Software Distribution , a Unix-like operating system after which it is named....Mathematica MathematicaMathematica is a computational software program used in scientific, engineering, and mathematical fields and other areas of technical computing...Proprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...Matlab MATLABMATLAB is a numerical computing environment and fourth-generation programming language. Developed by MathWorks, MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs written in other languages,...via toolbox via toolbox via toolbox via toolbox Proprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...Mozilla Firefox Mozilla FirefoxMozilla Firefox is a free and open source web browser descended from the Mozilla Application Suite and managed by Mozilla Corporation. , Firefox is the second most widely used browser, with approximately 25% of worldwide usage share of web browsers...via extension - - MPL Mozilla Public LicenseThe Mozilla Public License is a free and open source software license. Version 1.0 was developed by Mitchell Baker when she worked as a lawyer at Netscape Communications Corporation and version 1.1 at the Mozilla Foundation...
/GPLGNU General Public LicenseThe GNU General Public License is the most widely used free software license, originally written by Richard Stallman for the GNU Project....
/LGPLGNU Lesser General Public LicenseThe GNU Lesser General Public License or LGPL is a free software license published by the Free Software Foundation . It was designed as a compromise between the strong-copyleft GNU General Public License or GPL and permissive licenses such as the BSD licenses and the MIT License...Opera Opera (web browser)Opera is a web browser and Internet suite developed by Opera Software with over 200 million users worldwide. The browser handles common Internet-related tasks such as displaying web sites, sending and receiving e-mail messages, managing contacts, chatting on IRC, downloading files via BitTorrent,...via Quicktime QuickTimeQuickTime is an extensible proprietary multimedia framework developed by Apple Inc., capable of handling various formats of digital video, picture, sound, panoramic images, and interactivity. The classic version of QuickTime is available for Windows XP and later, as well as Mac OS X Leopard and...- - Proprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...Paint Shop Pro Proprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...Pixel image editor Pixel image editorPixel Image Editor is an Image editor written by the Slovak programmer Pavel Kanzelsberger. It is written with Free Pascal.-Features:...Proprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...Safari Safari (web browser)Safari is a web browser developed by Apple Inc. and included with the Mac OS X and iOS operating systems. First released as a public beta on January 7, 2003 on the company's Mac OS X operating system, it became Apple's default browser beginning with Mac OS X v10.3 "Panther". Safari is also the...- - Proprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...SilverFast SilverFastSilverFast is software for scanning and image processing, including photos, documents and slides, developed by LaserSoft Imaging.- History :...Proprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...XnView XnViewXnView is a cross-platform image viewer used for viewing, converting, organising and editing graphical & video files. It is free of charge for private, educational and non-profit organisations...
Proprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...Ziproxy ZiproxyZiproxy is a forwarding, non-caching, HTTP proxy targeted for traffic optimization.The ziproxy software is regarded as lightweight in terms of memory and processing power consumption....GPL
Libraries
Library support for JPEG 2000 Program Basic Advanced Language License Read Write Read Write ERDAS ECW JPEG2000 SDK ECW (file format)ECW is a proprietary wavelet compression image format optimized for aerial and satellite imagery. It was developed by Earth Resource Mapping, and is now owned by ERDAS, which is owned by Intergraph...C/C++ Proprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...FFmpeg FFmpegFFmpeg is a free software project that produces libraries and programs for handling multimedia data. The most notable parts of FFmpeg are libavcodec, an audio/video codec library used by several other projects, libavformat, an audio/video container mux and demux library, and the ffmpeg command line...C C (programming language)C is a general-purpose computer programming language developed between 1969 and 1973 by Dennis Ritchie at the Bell Telephone Laboratories for use with the Unix operating system....LGPL GTK+ GTK+GTK+ is a cross-platform widget toolkit for creating graphical user interfaces. It is licensed under the terms of the GNU LGPL, allowing both free and proprietary software to use it. It is one of the most popular toolkits for the X Window System, along with Qt.The name GTK+ originates from GTK;...
(from 2.14)C C (programming language)C is a general-purpose computer programming language developed between 1969 and 1973 by Dennis Ritchie at the Bell Telephone Laboratories for use with the Unix operating system....
/GTKLGPL J2K-Codec J2K-CodecJ2K-Codec is a commercial library to decode JPEG 2000 images. Version 2.0 was released on 12 April 2011.J2K-Codec supports decoding of different resolution levels and selective tile decoding...C++ C++C++ is a statically typed, free-form, multi-paradigm, compiled, general-purpose programming language. It is regarded as an intermediate-level language, as it comprises a combination of both high-level and low-level language features. It was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup starting in 1979 at Bell...Proprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...JasPer JasPerJasPer is a project to create a reference implementation of the codec specified in the JPEG-2000 Part-1 standard, . The project was started in 1997 by Image Power Inc. and the University of British Columbia...C C (programming language)C is a general-purpose computer programming language developed between 1969 and 1973 by Dennis Ritchie at the Bell Telephone Laboratories for use with the Unix operating system....MIT License MIT LicenseThe MIT License is a free software license originating at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology . It is a permissive license, meaning that it permits reuse within proprietary software provided all copies of the licensed software include a copy of the MIT License terms...
-styleKakadu Kakadu (software)Kakadu is a closed-source library to encode and decode JPEG 2000 images. It implements the ISO/IEC 15444-1 standard fully in part 1, and partly in parts 2-3. It is developed by David Taubman from University of New South Wales , Australia...C++ C++C++ is a statically typed, free-form, multi-paradigm, compiled, general-purpose programming language. It is regarded as an intermediate-level language, as it comprises a combination of both high-level and low-level language features. It was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup starting in 1979 at Bell...Proprietary Proprietary softwareProprietary software is computer software licensed under exclusive legal right of the copyright holder. The licensee is given the right to use the software under certain conditions, while restricted from other uses, such as modification, further distribution, or reverse engineering.Complementary...OpenJPEG OpenJPEGOpenJPEG is an open-source library to encode and decode JPEG 2000 images.-Support for lossless 16-bit images:Unlike JasPer, another open-source JPEG 2000 implementation, OpenJPEG fully respects the JPEG 2000 specification and can compress/decompress lossless 16-bit images.-Origin:OpenJPEG is a fork...C C (programming language)C is a general-purpose computer programming language developed between 1969 and 1973 by Dennis Ritchie at the Bell Telephone Laboratories for use with the Unix operating system....BSD BSD licensesBSD licenses are a family of permissive free software licenses. The original license was used for the Berkeley Software Distribution , a Unix-like operating system after which it is named....
See also
- Comparison of graphics file formatsComparison of graphics file formats-General:Ownership of the format and related information.-Technical details:...
- DjVuDjVuDjVu is a computer file format designed primarily to store scanned documents, especially those containing a combination of text, line drawings, and photographs. It uses technologies such as image layer separation of text and background/images, progressive loading, arithmetic coding, and lossy...
– a compression format that also uses wavelets and that is designed for use on the web. - ECWECW (file format)ECW is a proprietary wavelet compression image format optimized for aerial and satellite imagery. It was developed by Earth Resource Mapping, and is now owned by ERDAS, which is owned by Intergraph...
– a wavelet compression format that compares well to JPEG 2000. - High bit rate audio video over Internet ProtocolHigh bit rate audio video over Internet ProtocolHigh bit rate media transport formerly known as High bit rate audio video over IP , is a proposed standard for data encapsulation and forward error correction of high bit rate contribution oriented video/audio feed services, up to 3 Gbit/s over Ethernet networks. HBRMT is being developed by...
- QuickTimeQuickTimeQuickTime is an extensible proprietary multimedia framework developed by Apple Inc., capable of handling various formats of digital video, picture, sound, panoramic images, and interactivity. The classic version of QuickTime is available for Windows XP and later, as well as Mac OS X Leopard and...
– a multimedia framework, application and web browser plugin developed by Apple, capable of encoding, decoding and playing various multimedia files (including JPEG 2000 images by default). - MrSIDMrSID-External links:* from LizardTech's website...
– a wavelet compression format that compares well to JPEG 2000 - PGFProgressive Graphics FilePGF is a wavelet-based bitmapped image format that employs lossless and lossy data compression. PGF was created to improve upon and replace the JPEG format...
– a fast wavelet compression format that compares well to JPEG 2000 - JPIPJPIPJPIP is a compression streamlining protocol that works with JPEG 2000 to produce an image using the least bandwidth required...
– JPEG 2000 Interactive Protocol
External links
- RFC 3745, MIME Type Registrations for JPEG 2000 (ISO/IEC 15444)
- Official JPEG 2000 website
- All published books about JPEG 2000
JPEG 2000 comparisons: - irreversible: the CDF

