
Peak signal-to-noise ratio
Encyclopedia
The phrase peak signal-to-noise ratio, often abbreviated PSNR, is an engineering term for the ratio between the maximum possible power of a signal and the power of corrupting noise
that affects the fidelity of its representation. Because many signals have a very wide dynamic range
, PSNR is usually expressed in terms of the logarithm
ic decibel
scale.
The PSNR is most commonly used as a measure of quality of reconstruction of lossy compression codec
s (e.g., for image compression
). The signal in this case is the original data, and the noise is the error introduced by compression. When comparing compression codecs it is used as an approximation to human perception of reconstruction quality, therefore in some cases one reconstruction may appear to be closer to the original than another, even though it has a lower PSNR (a higher PSNR would normally indicate that the reconstruction is of higher quality). One has to be extremely careful with the range of validity of this metric; it is only conclusively valid when it is used to compare results from the same codec (or codec type) and same content.
It is most easily defined via the mean squared error
(MSE) which for two m×n monochrome images I and K where one of the images is considered a noisy approximation of the other is defined as: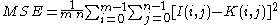
The PSNR is defined as: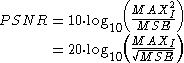
Here, MAXI is the maximum possible pixel value of the image. When the pixels are represented using 8 bits per sample, this is 255
. More generally, when samples are represented using linear PCM with B bits per sample, MAXI is 2B−1. For color image
s with three RGB values per pixel, the definition of PSNR is the same except the MSE is the sum over all squared value differences divided by image size and by three. Alternately, for color images the image is converted to a different color space
and PSNR is reported against each channel of that color space, e.g., YCbCr
or HSL.
Typical values for the PSNR in lossy image and video compression are between 30 and 50 dB
, where higher is better. Acceptable values for wireless transmission quality loss are considered to be about 20 dB to 25 dB.
When the two images are identical, the MSE will be zero. For this value the PSNR is undefined (see Division by zero
).
Noise
In common use, the word noise means any unwanted sound. In both analog and digital electronics, noise is random unwanted perturbation to a wanted signal; it is called noise as a generalisation of the acoustic noise heard when listening to a weak radio transmission with significant electrical noise...
that affects the fidelity of its representation. Because many signals have a very wide dynamic range
Dynamic range
Dynamic range, abbreviated DR or DNR, is the ratio between the largest and smallest possible values of a changeable quantity, such as in sound and light. It is measured as a ratio, or as a base-10 or base-2 logarithmic value.-Dynamic range and human perception:The human senses of sight and...
, PSNR is usually expressed in terms of the logarithm
Logarithm
The logarithm of a number is the exponent by which another fixed value, the base, has to be raised to produce that number. For example, the logarithm of 1000 to base 10 is 3, because 1000 is 10 to the power 3: More generally, if x = by, then y is the logarithm of x to base b, and is written...
ic decibel
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
scale.
The PSNR is most commonly used as a measure of quality of reconstruction of lossy compression codec
Codec
A codec is a device or computer program capable of encoding or decoding a digital data stream or signal. The word codec is a portmanteau of "compressor-decompressor" or, more commonly, "coder-decoder"...
s (e.g., for image compression
Image compression
The objective of image compression is to reduce irrelevance and redundancy of the image data in order to be able to store or transmit data in an efficient form.- Lossy and lossless compression :...
). The signal in this case is the original data, and the noise is the error introduced by compression. When comparing compression codecs it is used as an approximation to human perception of reconstruction quality, therefore in some cases one reconstruction may appear to be closer to the original than another, even though it has a lower PSNR (a higher PSNR would normally indicate that the reconstruction is of higher quality). One has to be extremely careful with the range of validity of this metric; it is only conclusively valid when it is used to compare results from the same codec (or codec type) and same content.
It is most easily defined via the mean squared error
Mean squared error
In statistics, the mean squared error of an estimator is one of many ways to quantify the difference between values implied by a kernel density estimator and the true values of the quantity being estimated. MSE is a risk function, corresponding to the expected value of the squared error loss or...
(MSE) which for two m×n monochrome images I and K where one of the images is considered a noisy approximation of the other is defined as:
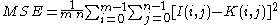
The PSNR is defined as:
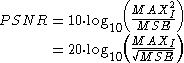
Here, MAXI is the maximum possible pixel value of the image. When the pixels are represented using 8 bits per sample, this is 255
255 (number)
255 is the natural number following 254 and preceding 256.-In mathematics:Its factorization makes it a sphenic number. Since 255 = 28 - 1, it is a Mersenne number, and the fourth such number not to be a prime number...
. More generally, when samples are represented using linear PCM with B bits per sample, MAXI is 2B−1. For color image
Color image
A color image is a digital image that includes color information for each pixel.For visually acceptable results, it is necessary to provide three samples for each pixel, which are interpreted as coordinates in some color space...
s with three RGB values per pixel, the definition of PSNR is the same except the MSE is the sum over all squared value differences divided by image size and by three. Alternately, for color images the image is converted to a different color space
Color space
A color model is an abstract mathematical model describing the way colors can be represented as tuples of numbers, typically as three or four values or color components...
and PSNR is reported against each channel of that color space, e.g., YCbCr
YCbCr
YCbCr or Y′CbCr, sometimes written or , is a family of color spaces used as a part of the color image pipeline in video and digital photography systems. Y′ is the luma component and CB and CR are the blue-difference and red-difference chroma components...
or HSL.
Typical values for the PSNR in lossy image and video compression are between 30 and 50 dB
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
, where higher is better. Acceptable values for wireless transmission quality loss are considered to be about 20 dB to 25 dB.
When the two images are identical, the MSE will be zero. For this value the PSNR is undefined (see Division by zero
Division by zero
In mathematics, division by zero is division where the divisor is zero. Such a division can be formally expressed as a / 0 where a is the dividend . Whether this expression can be assigned a well-defined value depends upon the mathematical setting...
).
See also
- Data compression ratioData compression ratioData compression ratio, also known as compression power, is a computer-science term used to quantify the reduction in data-representation size produced by a data compression algorithm...
- Mean square error
- Perceptual Evaluation of Video Quality (PEVQ)PEVQPEVQ ' is a standardized end-to-end measurement algorithm to score the picture quality of a video presentation by means of a 5-point mean opinion score...
- Signal-to-noise ratioSignal-to-noise ratioSignal-to-noise ratio is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. It is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power. A ratio higher than 1:1 indicates more signal than noise...
- Structural similarity (SSIM) index
- Subjective video qualitySubjective video qualitySubjective video quality is a subjective characteristic of video quality. It is concerned with how video is perceived by a viewer and designates his or her opinion on a particular video sequence...
- Video qualityVideo qualityVideo quality is a characteristic of a video passed through a video transmission/processing system, a formal or informal measure of perceived video degradation...

