
267
Encyclopedia
Common year starting on Tuesday
This is the calendar for any common year starting on Tuesday, January 1 . Examples: Gregorian years 1985, 1991, 2002, 2013 and 2019or Julian year 1919 .MillenniumCenturyGregorian Year2nd Millennium:...
(link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar
Julian calendar
The Julian calendar began in 45 BC as a reform of the Roman calendar by Julius Caesar. It was chosen after consultation with the astronomer Sosigenes of Alexandria and was probably designed to approximate the tropical year .The Julian calendar has a regular year of 365 days divided into 12 months...
. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Paternus and Arcesilaus (or, less frequently, year 1020 Ab urbe condita
Ab urbe condita
Ab urbe condita is Latin for "from the founding of the City ", traditionally set in 753 BC. AUC is a year-numbering system used by some ancient Roman historians to identify particular Roman years...
). The denomination 267 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini
Anno Domini
and Before Christ are designations used to label or number years used with the Julian and Gregorian calendars....
calendar era
Calendar era
A calendar era is the year numbering system used by a calendar. For example, the Gregorian calendar numbers its years in the Western Christian era . The instant, date, or year from which time is marked is called the epoch of the era...
became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Roman Empire
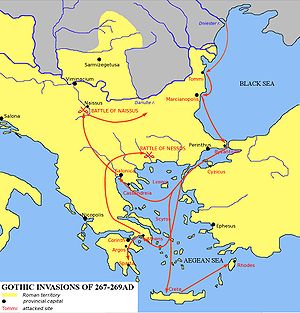
- First Gothic invasion: The GothsGothsThe Goths were an East Germanic tribe of Scandinavian origin whose two branches, the Visigoths and the Ostrogoths, played an important role in the fall of the Roman Empire and the emergence of Medieval Europe....
, originally from ScandinaviaScandinaviaScandinavia is a cultural, historical and ethno-linguistic region in northern Europe that includes the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden, characterized by their common ethno-cultural heritage and language. Modern Norway and Sweden proper are situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula,...
, with the SarmatiansSarmatiansThe Iron Age Sarmatians were an Iranian people in Classical Antiquity, flourishing from about the 5th century BC to the 4th century AD....
(from modern IranIranIran , officially the Islamic Republic of Iran , is a country in Southern and Western Asia. The name "Iran" has been in use natively since the Sassanian era and came into use internationally in 1935, before which the country was known to the Western world as Persia...
), invade the BalkansBalkansThe Balkans is a geopolitical and cultural region of southeastern Europe...
and GreeceGreeceGreece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
. They ravage MoesiaMoesiaMoesia was an ancient region and later Roman province situated in the Balkans, along the south bank of the Danube River. It included territories of modern-day Southern Serbia , Northern Republic of Macedonia, Northern Bulgaria, Romanian Dobrudja, Southern Moldova, and Budjak .-History:In ancient...
and ThraceThraceThrace is a historical and geographic area in southeast Europe. As a geographical concept, Thrace designates a region bounded by the Balkan Mountains on the north, Rhodope Mountains and the Aegean Sea on the south, and by the Black Sea and the Sea of Marmara on the east...
. - The HeruliHeruliThe Heruli were an East Germanic tribe who are famous for their naval exploits. Migrating from Northern Europe to the Black Sea in the third century They were part of the...
invade the Black SeaBlack SeaThe Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
coast, they unsuccessfully attack ByzantiumByzantiumByzantium was an ancient Greek city, founded by Greek colonists from Megara in 667 BC and named after their king Byzas . The name Byzantium is a Latinization of the original name Byzantion...
and CyzicusCyzicusCyzicus was an ancient town of Mysia in Anatolia in the current Balıkesir Province of Turkey. It was located on the shoreward side of the present Kapıdağ Peninsula , a tombolo which is said to have originally been an island in the Sea of Marmara only to be connected to the mainland in historic...
. The Romano-ByzantineRoman NavyThe Roman Navy comprised the naval forces of the Ancient Roman state. Although the navy was instrumental in the Roman conquest of the Mediterranean basin, it never enjoyed the prestige of the Roman legions...
fleet defeats the Herulian fleet (500 ships) but allows them to excape into the Aegean SeaAegean SeaThe Aegean Sea[p] is an elongated embayment of the Mediterranean Sea located between the southern Balkan and Anatolian peninsulas, i.e., between the mainlands of Greece and Turkey. In the north, it is connected to the Marmara Sea and Black Sea by the Dardanelles and Bosporus...
, where they raid the islands of LemnosLemnosLemnos is an island of Greece in the northern part of the Aegean Sea. Administratively the island forms a separate municipality within the Lemnos peripheral unit, which is part of the North Aegean Periphery. The principal town of the island and seat of the municipality is Myrina...
and SkyrosSkyrosSkyros is an island in Greece, the southernmost of the Sporades, an archipelago in the Aegean Sea. Around the 2nd millennium BC and slightly later, the island was known as The Island of the Magnetes where the Magnetes used to live and later Pelasgia and Dolopia and later Skyros...
. - The Goths sack several cities of southern Greece including AthensAthensAthens , is the capital and largest city of Greece. Athens dominates the Attica region and is one of the world's oldest cities, as its recorded history spans around 3,400 years. Classical Athens was a powerful city-state...
, Corinth, ArgosArgosArgos is a city and a former municipality in Argolis, Peloponnese, Greece. Since the 2011 local government reform it is part of the municipality Argos-Mykines, of which it is a municipal unit. It is 11 kilometres from Nafplion, which was its historic harbour...
and SpartaSpartaSparta or Lacedaemon, was a prominent city-state in ancient Greece, situated on the banks of the River Eurotas in Laconia, in south-eastern Peloponnese. It emerged as a political entity around the 10th century BC, when the invading Dorians subjugated the local, non-Dorian population. From c...
. An Athenian militia force (2,000 men) under the historian DexippusDexippusPublius Herennius Dexippus , Greek historian, statesman and general, was an hereditary priest of the Eleusinian family of the Kerykes, and held the offices of archon basileus and eponymous in Athens....
, pushed the invaders to the north where they are intercepted by the Roman armyRoman armyThe Roman army is the generic term for the terrestrial armed forces deployed by the kingdom of Rome , the Roman Republic , the Roman Empire and its successor, the Byzantine empire...
under emperor GallienusGallienusGallienus was Roman Emperor with his father Valerian from 253 to 260, and alone from 260 to 268. He took control of the Empire at a time when it was undergoing great crisis...
. He wins an important victory near the Nestos River, on the boundary between MacedoniaMacedonia (Greece)Macedonia is a geographical and historical region of Greece in Southern Europe. Macedonia is the largest and second most populous Greek region...
and Thrace. - AureolusAureolusFor the Frankish ruler of Aragon, see Aureolus of Aragon.Manius Acilius Aureolus was a Roman military commander and would-be usurper. He was one of the so-called Thirty Tyrants who populated the reign of the Emperor Gallienus...
, charged with defending ItalyItalyItaly , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
, defeats VictorinusVictorinusMarcus Piavonius Victorinus was emperor of the secessionist Gallic Empire from 269 to 271, following the brief reign of Marius. He was murdered by a jealous husband whose wife he tried to seduce.-Reign:...
(co-emperor of GaulGaulGaul was a region of Western Europe during the Iron Age and Roman era, encompassing present day France, Luxembourg and Belgium, most of Switzerland, the western part of Northern Italy, as well as the parts of the Netherlands and Germany on the left bank of the Rhine. The Gauls were the speakers of...
), is proclaimed emperor by his troops, and begins his march on RomeAncient RomeAncient Rome was a thriving civilization that grew on the Italian Peninsula as early as the 8th century BC. Located along the Mediterranean Sea and centered on the city of Rome, it expanded to one of the largest empires in the ancient world....
.
Near East
- King OdaenathusOdaenathusLucius Septimius Odaenathus, Odenathus or Odenatus , the Latinized form of the Syriac Odainath, was a ruler of Palmyra, Syria and later of the short lived Palmyrene Empire, in the second half of the 3rd century, who succeeded in recovering the Roman East from the Persians and restoring it to the...
of PalmyraPalmyraPalmyra was an ancient city in Syria. In the age of antiquity, it was an important city of central Syria, located in an oasis 215 km northeast of Damascus and 180 km southwest of the Euphrates at Deir ez-Zor. It had long been a vital caravan city for travellers crossing the Syrian desert...
makes plans for a campaign in CappadociaCappadociaCappadocia is a historical region in Central Anatolia, largely in Nevşehir Province.In the time of Herodotus, the Cappadocians were reported as occupying the whole region from Mount Taurus to the vicinity of the Euxine...
against the Goths. He is assassinatedAssassinationTo carry out an assassination is "to murder by a sudden and/or secret attack, often for political reasons." Alternatively, assassination may be defined as "the act of deliberately killing someone, especially a public figure, usually for hire or for political reasons."An assassination may be...
along with his eldest son, evidently on orders from emperor GallienusGallienusGallienus was Roman Emperor with his father Valerian from 253 to 260, and alone from 260 to 268. He took control of the Empire at a time when it was undergoing great crisis...
. His wife ZenobiaZenobiaZenobia was a 3rd-century Queen of the Palmyrene Empire in Roman Syria. She led a famous revolt against the Roman Empire. The second wife of King Septimius Odaenathus, Zenobia became queen of the Palmyrene Empire following Odaenathus' death in 267...
succeeds him, and rules with her young son VaballathusVaballathusLucius Iulius Aurelius Septimius Vabalathus Athenodorus was a king of the Palmyrene Empire. Vabalathus is the Latinized form of his name in the Arabic language, Wahb Allat or gift of the Goddess...
the Palmyrene EmpirePalmyrene EmpireThe Palmyrene Empire was a splinter empire, that broke off of the Roman Empire during the Crisis of the Third Century. It encompassed the Roman provinces of Syria Palaestina, Egypt and large parts of Asia Minor....
.

