
Weather front
Encyclopedia
A weather front is a boundary separating two masses of air
of different densities
, and is the principal cause of meteorological phenomena
. In surface weather analyses
, fronts are depicted using various colored lines and symbols, depending on the type of front. The air masses separated by a front usually differ in temperature
and humidity
.
Cold fronts may feature narrow bands of thunderstorm
s and severe weather
, and may on occasion be preceded by squall line
s or dry line
s. Warm front
s are usually preceded by stratiform precipitation
and fog
. The weather usually clears quickly after a front's passage. Some fronts produce no precipitation and little cloudiness, although there is invariably a wind shift
.
Cold fronts and occluded front
s generally move from west to east, while warm fronts move poleward
. Because of the greater density of air in their wake, cold fronts and cold occlusions move faster than warm fronts and warm occlusions. Mountain
s and warm bodies of water can slow the movement of fronts. When a front becomes stationary
, and the density contrast across the frontal boundary vanishes, the front can degenerate into a line which separates regions of differing wind velocity, known as a shearline. This is most common over the open ocean.
of different densities
, and is the principal cause of meteorological phenomena
. In surface weather analyses
, fronts are depicted using various colored lines and symbols, depending on the type of front. The air masses separated by a front usually differ in temperature
and humidity
.
Cold fronts may feature narrow bands of thunderstorm
s and severe weather
, and may on occasion be preceded by squall line
s or dry line
s. Warm front
s are usually preceded by stratiform precipitation
and fog
. The weather usually clears quickly after a front's passage. Some fronts produce no precipitation and little cloudiness, although there is invariably a wind shift
.
Cold fronts and occluded front
s generally move from west to east, while warm fronts move poleward
. Because of the greater density of air in their wake, cold fronts and cold occlusions move faster than warm fronts and warm occlusions. Mountain
s and warm bodies of water can slow the movement of fronts. When a front becomes stationary
, and the density contrast across the frontal boundary vanishes, the front can degenerate into a line which separates regions of differing wind velocity, known as a shearline. This is most common over the open ocean.
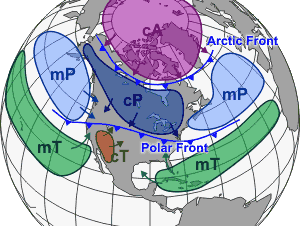 The Bergeron classification is the most widely accepted form of air mass classification. Air mass classification involves three letters. The first letter describes its moisture properties, with c used for continental air masses (dry) and m for maritime air masses (moist). The second letter describes the thermal characteristic of its source region: T for tropical, P for polar, A for arctic or Antarctic, M for monsoon, E for equatorial, and S for superior air (dry air formed by significant upward motion in the atmosphere). The third letter is used to designate the stability of the atmosphere. If the air mass is colder than the ground below it, it is labeled k. If the air mass is warmer than the ground below it, it is labeled w. Fronts separate air masses of different types or origins, and are located along troughs
The Bergeron classification is the most widely accepted form of air mass classification. Air mass classification involves three letters. The first letter describes its moisture properties, with c used for continental air masses (dry) and m for maritime air masses (moist). The second letter describes the thermal characteristic of its source region: T for tropical, P for polar, A for arctic or Antarctic, M for monsoon, E for equatorial, and S for superior air (dry air formed by significant upward motion in the atmosphere). The third letter is used to designate the stability of the atmosphere. If the air mass is colder than the ground below it, it is labeled k. If the air mass is warmer than the ground below it, it is labeled w. Fronts separate air masses of different types or origins, and are located along troughs
of lower pressure.
 A surface weather analysis is a special type of weather map
A surface weather analysis is a special type of weather map
which provides a view of weather elements over a geographical area at a specified time based on information from ground–based weather stations. Weather maps are created by plotting or tracing the values of relevant quantities such as sea-level pressure
, temperature
, and cloud cover
onto a geographical map
to help find synoptic scale
features such as weather fronts. Surface weather analyses have special symbols which show frontal systems, cloud cover, precipitation
, or other important information. For example, an H may represent high pressure, implying fair weather. An L on the other hand may represent low pressure, which frequently accompanies precipitation. Various symbols are used not just for frontal zones and other surface boundaries on weather maps, but also to depict the present weather at various locations on the weather map. In addition, areas of precipitation help determine the frontal type and location.
analysis shows up as the leading edge of the isotherm
gradient, and it normally lies within a sharp surface trough
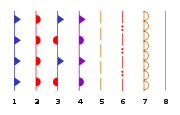
. Cold fronts can move up to twice as quickly as, and produce sharper changes in weather than, warm fronts, since cold air is denser than warm air and rapidly replaces the warm air preceding the boundary. On weather maps, the surface position of the cold front is marked with the symbol of a blue line of triangle-shaped pips pointing in the direction of travel, and it is placed at the leading edge of the cooler air mass. Cold fronts come in association with a low pressure area
. The concept of colder, dense air "wedging" under the less dense warmer air is often used to depict how air is lifted along a frontal boundary. The cold air wedging underneath warmer air creates the strongest winds just above the ground surface, a phonemena often associated with property-damaging wind gusts. This lift would then form a narrow line of showers
and thunderstorms if enough moisture
were present.
This also forces temperature differences across warm fronts to be broader in scale. Clouds ahead of the warm front are mostly strati form
, and rainfall gradually increases as the front approaches. Fog
can also occur preceding a warm frontal passage. Clearing and warming is usually rapid after frontal passage. If the warm air mass is unstable, thunderstorms may be embedded among the strati form clouds ahead of the front, and after frontal passage thundershowers may continue. On weather maps, the surface location of a warm front is marked with a red line of semicircles pointing in the direction of travel.
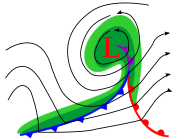 An occluded front
An occluded front
is formed when a cold front overtakes a warm front. The cold and warm fronts curve naturally poleward into the point of occlusion, which is also known as the triple point. It lies within a sharp trough, but the air mass behind the boundary can be either warm or cold. In a cold occlusion, the air mass overtaking the warm front is cooler than the cool air ahead of the warm front and plows under both air masses. In a warm occlusion, the air mass overtaking the warm front is warmer than the cold air ahead of the warm front and rides over the colder air mass while lifting the warm air.
A wide variety of weather can be found along an occluded front, with thunderstorms possible, but usually their passage is associated with a drying of the air mass. Occluded fronts are indicated on a weather map by a purple line with alternating half-circles and triangles pointing in direction of travel. Occluded fronts usually form around mature low-pressure areas.
is a non-moving (or stalled) boundary between two air masses, neither of which is strong enough to replace the other. They tend to remain essentially in the same area for extended periods of time, usually moving in waves. There is normally a broad temperature gradient
behind the boundary with more widely spaced isotherm packing.
A wide variety of weather can be found along a stationary front, but usually clouds and prolonged precipitation are found there. Stationary fronts either dissipate after several days or devolve into shear lines, but they can transform into a cold or warm front if conditions aloft change. Stationary fronts are marked on weather maps with alternating red half-circles and blue spikes pointing in opposite directions, indicating no significant movement.
When stationary fronts become smaller in scale, degenerating to a narrow zone where wind direction changes significantly over a relatively short distance, they become known as shearlines. A shearline is depicted as a line of red dots and dashes.
, which is the boundary between air masses with significant moisture differences. When the westerlies
increase on the north side of surface highs, areas of lowered pressure will form downwind of north–south oriented mountain chains, leading to the formation of a lee trough. Near the surface during daylight hours, warm moist air is denser than dry air of greater temperature, and thus the warm moist air wedges under the drier air like a cold front. At higher altitudes, the warm moist air is less dense than the dry air and the boundary slope reverses. In the vicinity of the reversal aloft, severe weather
is possible, especially when a triple point is formed with a cold front. A weaker form of the dry line seen more commonly is the lee trough, which displays weaker differences in moisture
. When moisture pools along the boundary during the warm season, it can be the focus of diurnal thunderstorms.
The dry line may occur anywhere on earth in regions intermediate between desert
areas and warm seas. The southern plains west of the Mississippi River
in the United States
are a particularly favored location. The dry line normally moves eastward during the day and westward at night. A dry line is depicted on National Weather Service
(NWS) surface analyses as an orange line with scallops facing into the moist sector. Dry lines are one of the few surface fronts where the pips indicated do not necessarily reflect the direction of motion.
 Organized areas of thunderstorm activity not only reinforce pre-existing frontal zones, but can outrun cold fronts in a pattern where the upper level jet splits apart into two streams, with the resultant Mesoscale Convective System
Organized areas of thunderstorm activity not only reinforce pre-existing frontal zones, but can outrun cold fronts in a pattern where the upper level jet splits apart into two streams, with the resultant Mesoscale Convective System
(MCS) forming at the point of the upper level split in the wind pattern running southeast into the warm sector parallel to low-level thickness lines. When the convection is strong and linear or curved, the MCS is called a squall line, with the feature placed at the leading edge of the significant wind shift and pressure rise. Even weaker and less organized areas of thunderstorms lead to locally cooler air and higher pressures, and outflow boundaries exist ahead of this type of activity, which can act as foci for additional thunderstorm activity later in the day.
These features are often depicted in the warm season across the United States on surface analyses and lie within surface troughs. If outflow boundaries or squall lines form over arid regions, a haboob
may result. Squall lines are depicted on NWS surface analyses as an alternating pattern of two red dots and a dash labelled SQLN or SQUALL LINE, while outflow boundaries are depicted as troughs with a label of OUTFLOW BNDRY.
 Fronts are the principal cause of significant weather. Convective precipitation (showers, thundershowers, and related unstable weather) is caused by air being lifted and condensing into clouds by the movement of the cold front or cold occlusion under a mass of warmer, moist air. If the temperature differences of the two air masses involved are large and the turbulence is extreme because of wind shear
Fronts are the principal cause of significant weather. Convective precipitation (showers, thundershowers, and related unstable weather) is caused by air being lifted and condensing into clouds by the movement of the cold front or cold occlusion under a mass of warmer, moist air. If the temperature differences of the two air masses involved are large and the turbulence is extreme because of wind shear
and the presence of a strong jet stream
, "roll clouds" and tornado
es may occur.
In the warm season
, lee troughs, breezes, outflow boundaries and occlusions can lead to convection if enough moisture is available. Orographic precipitation is precipitation created through the lifting action of air moving over terrain such as mountains and hills, which is most common behind cold fronts that move into mountainous areas. It may sometimes occur in advance of warm fronts moving northward to the east of mountainous terrain. However, precipitation along warm fronts is relatively steady, as in rain or drizzle. Fog, sometimes extensive and dense, often occurs in pre-warm-frontal areas. Although, not all fronts produce precipitation or even clouds because moisture must be present in the air mass which is being lifted.
, but do not move as quickly. Cold fronts and occluded fronts in the Northern Hemisphere usually travel from the northwest to southeast, while warm fronts move more poleward with time. In the Northern Hemisphere a warm front moves from southwest to northeast. In the Southern Hemisphere, the reverse is true; a cold front usually moves from southwest to northeast, and a warm front moves from northwest to southeast. Movement is largely caused by the pressure gradient force (horizontal differences in atmospheric pressure) and the Coriolis effect
, which is caused by Earth
's spinning about its axis. Frontal zones can be slowed down by geographic features like mountains and large bodies of warm water.
Air mass
In meteorology, an air mass is a volume of air defined by its temperature and water vapor content. Air masses cover many hundreds or thousands of square miles, and adopt the characteristics of the surface below them. They are classified according to latitude and their continental or maritime...
of different densities
Density
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
, and is the principal cause of meteorological phenomena
Meteorological phenomenon
A meteorological phenomenon is a weather event that can be explained by the principles of meteorology. Such events include:* Air mass* Anticyclone* Arctic cyclone* Clouds* Crow Instability* Derecho* Diamond dust* Drought* Dust devil* Dust storm...
. In surface weather analyses
Surface weather analysis
Surface weather analysis is a special type of weather map that provides a view of weather elements over a geographical area at a specified time based on information from ground-based weather stations...
, fronts are depicted using various colored lines and symbols, depending on the type of front. The air masses separated by a front usually differ in temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
and humidity
Humidity
Humidity is a term for the amount of water vapor in the air, and can refer to any one of several measurements of humidity. Formally, humid air is not "moist air" but a mixture of water vapor and other constituents of air, and humidity is defined in terms of the water content of this mixture,...
.
Cold fronts may feature narrow bands of thunderstorm
Thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm, a lightning storm, thundershower or simply a storm is a form of weather characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere known as thunder. The meteorologically assigned cloud type associated with the...
s and severe weather
Severe weather
Severe weather phenomena are weather conditions that are hazardous to human life and property.- Examples Include :Severe weather can occur under a variety of situations, but three characteristics are generally needed: a temperature or moisture boundary, moisture, and , instability in the...
, and may on occasion be preceded by squall line
Squall line
A squall line is a line of severe thunderstorms that can form along or ahead of a cold front. In the early 20th century, the term was used as a synonym for cold front. It contains heavy precipitation, hail, frequent lightning, strong straight-line winds, and possibly tornadoes and waterspouts....
s or dry line
Dry line
A dry line separates moist air from the Gulf of Mexico and dry desert air from the south-western states . The dry line is an important factor in severe weather frequency in the Great Plains of North America...
s. Warm front
Warm front
A warm front is a density discontinuity located at the leading edge of a homogeneous warm air mass, and is typically located on the equator-facing edge of an isotherm gradient...
s are usually preceded by stratiform precipitation
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation...
and fog
Fog
Fog is a collection of water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. While fog is a type of stratus cloud, the term "fog" is typically distinguished from the more generic term "cloud" in that fog is low-lying, and the moisture in the fog is often generated...
. The weather usually clears quickly after a front's passage. Some fronts produce no precipitation and little cloudiness, although there is invariably a wind shift
Wind direction
Wind direction is reported by the direction from which it originates. For example, a northerly wind blows from the north to the south. Wind direction is usually reported in cardinal directions or in azimuth degrees...
.
Cold fronts and occluded front
Occluded front
An occluded front is formed during the process of cyclogenesis when a cold front overtakes a warm front. When this occurs, the warm air is separated from the cyclone center at the Earth's surface...
s generally move from west to east, while warm fronts move poleward
Geographical pole
A geographical pole is either of the two points—the north pole and the south pole—on the surface of a rotating planet where the axis of rotation meets the surface of the body...
. Because of the greater density of air in their wake, cold fronts and cold occlusions move faster than warm fronts and warm occlusions. Mountain
Mountain
Image:Himalaya_annotated.jpg|thumb|right|The Himalayan mountain range with Mount Everestrect 58 14 160 49 Chomo Lonzorect 200 28 335 52 Makalurect 378 24 566 45 Mount Everestrect 188 581 920 656 Tibetan Plateaurect 250 406 340 427 Rong River...
s and warm bodies of water can slow the movement of fronts. When a front becomes stationary
Stationary front
A stationary front is a boundary between two different air masses, neither of which is strong enough to replace the other. On a weather map, this is shown by an inter-playing series of blue spikes pointing one direction and red domes pointing the other. They tend to remain essentially in the same...
, and the density contrast across the frontal boundary vanishes, the front can degenerate into a line which separates regions of differing wind velocity, known as a shearline. This is most common over the open ocean.
Bergeron classification of air masses
A weather front is a boundary separating two masses of airAir mass
In meteorology, an air mass is a volume of air defined by its temperature and water vapor content. Air masses cover many hundreds or thousands of square miles, and adopt the characteristics of the surface below them. They are classified according to latitude and their continental or maritime...
of different densities
Density
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
, and is the principal cause of meteorological phenomena
Meteorological phenomenon
A meteorological phenomenon is a weather event that can be explained by the principles of meteorology. Such events include:* Air mass* Anticyclone* Arctic cyclone* Clouds* Crow Instability* Derecho* Diamond dust* Drought* Dust devil* Dust storm...
. In surface weather analyses
Surface weather analysis
Surface weather analysis is a special type of weather map that provides a view of weather elements over a geographical area at a specified time based on information from ground-based weather stations...
, fronts are depicted using various colored lines and symbols, depending on the type of front. The air masses separated by a front usually differ in temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
and humidity
Humidity
Humidity is a term for the amount of water vapor in the air, and can refer to any one of several measurements of humidity. Formally, humid air is not "moist air" but a mixture of water vapor and other constituents of air, and humidity is defined in terms of the water content of this mixture,...
.
Cold fronts may feature narrow bands of thunderstorm
Thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm, a lightning storm, thundershower or simply a storm is a form of weather characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere known as thunder. The meteorologically assigned cloud type associated with the...
s and severe weather
Severe weather
Severe weather phenomena are weather conditions that are hazardous to human life and property.- Examples Include :Severe weather can occur under a variety of situations, but three characteristics are generally needed: a temperature or moisture boundary, moisture, and , instability in the...
, and may on occasion be preceded by squall line
Squall line
A squall line is a line of severe thunderstorms that can form along or ahead of a cold front. In the early 20th century, the term was used as a synonym for cold front. It contains heavy precipitation, hail, frequent lightning, strong straight-line winds, and possibly tornadoes and waterspouts....
s or dry line
Dry line
A dry line separates moist air from the Gulf of Mexico and dry desert air from the south-western states . The dry line is an important factor in severe weather frequency in the Great Plains of North America...
s. Warm front
Warm front
A warm front is a density discontinuity located at the leading edge of a homogeneous warm air mass, and is typically located on the equator-facing edge of an isotherm gradient...
s are usually preceded by stratiform precipitation
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation...
and fog
Fog
Fog is a collection of water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. While fog is a type of stratus cloud, the term "fog" is typically distinguished from the more generic term "cloud" in that fog is low-lying, and the moisture in the fog is often generated...
. The weather usually clears quickly after a front's passage. Some fronts produce no precipitation and little cloudiness, although there is invariably a wind shift
Wind direction
Wind direction is reported by the direction from which it originates. For example, a northerly wind blows from the north to the south. Wind direction is usually reported in cardinal directions or in azimuth degrees...
.
Cold fronts and occluded front
Occluded front
An occluded front is formed during the process of cyclogenesis when a cold front overtakes a warm front. When this occurs, the warm air is separated from the cyclone center at the Earth's surface...
s generally move from west to east, while warm fronts move poleward
Geographical pole
A geographical pole is either of the two points—the north pole and the south pole—on the surface of a rotating planet where the axis of rotation meets the surface of the body...
. Because of the greater density of air in their wake, cold fronts and cold occlusions move faster than warm fronts and warm occlusions. Mountain
Mountain
Image:Himalaya_annotated.jpg|thumb|right|The Himalayan mountain range with Mount Everestrect 58 14 160 49 Chomo Lonzorect 200 28 335 52 Makalurect 378 24 566 45 Mount Everestrect 188 581 920 656 Tibetan Plateaurect 250 406 340 427 Rong River...
s and warm bodies of water can slow the movement of fronts. When a front becomes stationary
Stationary front
A stationary front is a boundary between two different air masses, neither of which is strong enough to replace the other. On a weather map, this is shown by an inter-playing series of blue spikes pointing one direction and red domes pointing the other. They tend to remain essentially in the same...
, and the density contrast across the frontal boundary vanishes, the front can degenerate into a line which separates regions of differing wind velocity, known as a shearline. This is most common over the open ocean.

Trough (meteorology)
A trough is an elongated region of relatively low atmospheric pressure, often associated with fronts.Unlike fronts, there is not a universal symbol for a trough on a weather chart. The weather charts in some countries or regions mark troughs by a line. In the United States, a trough may be marked...
of lower pressure.
Surface weather analysis

Weather map
A weather map displays various meteorological features across a particular area at a particular point in time. Such maps have been in use since the mid-19th century and are used for research and weather forecasting purposes. Maps using isotherms show temperature gradients, which can help locate...
which provides a view of weather elements over a geographical area at a specified time based on information from ground–based weather stations. Weather maps are created by plotting or tracing the values of relevant quantities such as sea-level pressure
Atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure is the force per unit area exerted into a surface by the weight of air above that surface in the atmosphere of Earth . In most circumstances atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point...
, temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
, and cloud cover
Cloud cover
Cloud cover refers to the fraction of the sky obscured by clouds when observed from a particular location...
onto a geographical map
Cartography
Cartography is the study and practice of making maps. Combining science, aesthetics, and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively.The fundamental problems of traditional cartography are to:*Set the map's...
to help find synoptic scale
Synoptic scale meteorology
The synoptic scale in meteorology is a horizontal length scale of the order of 1000 kilometres or more. This corresponds to a horizontal scale typical of mid-latitude depressions...
features such as weather fronts. Surface weather analyses have special symbols which show frontal systems, cloud cover, precipitation
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation...
, or other important information. For example, an H may represent high pressure, implying fair weather. An L on the other hand may represent low pressure, which frequently accompanies precipitation. Various symbols are used not just for frontal zones and other surface boundaries on weather maps, but also to depict the present weather at various locations on the weather map. In addition, areas of precipitation help determine the frontal type and location.
Front types
There are two different words used within meteorology to describe weather around a frontal zone. The term anafront describes boundaries which show instability, meaning air rises rapidly along and over the boundary to cause significant weather changes. Katafronts are weaker, bringing smaller changes in temperature and moisture, as well as limited rainfall.Cold front
A cold front is located at the leading edge of the temperature drop off, which in an isothermContour line
A contour line of a function of two variables is a curve along which the function has a constant value. In cartography, a contour line joins points of equal elevation above a given level, such as mean sea level...
analysis shows up as the leading edge of the isotherm
Isotherm
Isotherm may refer to:* Isotherm a type of contour line that connects points of equal temperature at a given date or time on a geographic map* Isotherm in thermodynamics, a curve on a p-V diagram for an isothermal process...
gradient, and it normally lies within a sharp surface trough
Trough (meteorology)
A trough is an elongated region of relatively low atmospheric pressure, often associated with fronts.Unlike fronts, there is not a universal symbol for a trough on a weather chart. The weather charts in some countries or regions mark troughs by a line. In the United States, a trough may be marked...
. Cold fronts can move up to twice as quickly as, and produce sharper changes in weather than, warm fronts, since cold air is denser than warm air and rapidly replaces the warm air preceding the boundary. On weather maps, the surface position of the cold front is marked with the symbol of a blue line of triangle-shaped pips pointing in the direction of travel, and it is placed at the leading edge of the cooler air mass. Cold fronts come in association with a low pressure area
Low pressure area
A low-pressure area, or "low", is a region where the atmospheric pressure at sea level is below that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence which occur in upper levels of the troposphere. The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as...
. The concept of colder, dense air "wedging" under the less dense warmer air is often used to depict how air is lifted along a frontal boundary. The cold air wedging underneath warmer air creates the strongest winds just above the ground surface, a phonemena often associated with property-damaging wind gusts. This lift would then form a narrow line of showers
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation...
and thunderstorms if enough moisture
Moisture
Humidity is the amount of moisture the air can hold before it rains. Moisture refers to the presence of a liquid, especially water, often in trace amounts...
were present.
Warm front
Warm fronts are at the leading edge of a homogeneous warm air mass, which is located on the equator ward edge of the gradient in isotherms, and lie within broader troughs of low pressure than cold fronts. A warm front moves more slowly than the cold front which usually follows because cold air is denser and harder to remove from the Earth's surface.This also forces temperature differences across warm fronts to be broader in scale. Clouds ahead of the warm front are mostly strati form
Stratus cloud
A stratus cloud is a cloud belonging to a class characterized by horizontal layering with a uniform base, as opposed to convective clouds that are as tall or taller than wide . More specifically, the term stratus is used to describe flat, hazy, featureless clouds of low altitude varying in color...
, and rainfall gradually increases as the front approaches. Fog
Fog
Fog is a collection of water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. While fog is a type of stratus cloud, the term "fog" is typically distinguished from the more generic term "cloud" in that fog is low-lying, and the moisture in the fog is often generated...
can also occur preceding a warm frontal passage. Clearing and warming is usually rapid after frontal passage. If the warm air mass is unstable, thunderstorms may be embedded among the strati form clouds ahead of the front, and after frontal passage thundershowers may continue. On weather maps, the surface location of a warm front is marked with a red line of semicircles pointing in the direction of travel.
Occluded front

Occluded front
An occluded front is formed during the process of cyclogenesis when a cold front overtakes a warm front. When this occurs, the warm air is separated from the cyclone center at the Earth's surface...
is formed when a cold front overtakes a warm front. The cold and warm fronts curve naturally poleward into the point of occlusion, which is also known as the triple point. It lies within a sharp trough, but the air mass behind the boundary can be either warm or cold. In a cold occlusion, the air mass overtaking the warm front is cooler than the cool air ahead of the warm front and plows under both air masses. In a warm occlusion, the air mass overtaking the warm front is warmer than the cold air ahead of the warm front and rides over the colder air mass while lifting the warm air.
A wide variety of weather can be found along an occluded front, with thunderstorms possible, but usually their passage is associated with a drying of the air mass. Occluded fronts are indicated on a weather map by a purple line with alternating half-circles and triangles pointing in direction of travel. Occluded fronts usually form around mature low-pressure areas.
Stationary front and shearline
A stationary frontStationary front
A stationary front is a boundary between two different air masses, neither of which is strong enough to replace the other. On a weather map, this is shown by an inter-playing series of blue spikes pointing one direction and red domes pointing the other. They tend to remain essentially in the same...
is a non-moving (or stalled) boundary between two air masses, neither of which is strong enough to replace the other. They tend to remain essentially in the same area for extended periods of time, usually moving in waves. There is normally a broad temperature gradient
Temperature gradient
A temperature gradient is a physical quantity that describes in which direction and at what rate the temperature changes the most rapidly around a particular location. The temperature gradient is a dimensional quantity expressed in units of degrees per unit length...
behind the boundary with more widely spaced isotherm packing.
A wide variety of weather can be found along a stationary front, but usually clouds and prolonged precipitation are found there. Stationary fronts either dissipate after several days or devolve into shear lines, but they can transform into a cold or warm front if conditions aloft change. Stationary fronts are marked on weather maps with alternating red half-circles and blue spikes pointing in opposite directions, indicating no significant movement.
When stationary fronts become smaller in scale, degenerating to a narrow zone where wind direction changes significantly over a relatively short distance, they become known as shearlines. A shearline is depicted as a line of red dots and dashes.
Dry line
A similar phenomenon to a weather front is the dry lineDry line
A dry line separates moist air from the Gulf of Mexico and dry desert air from the south-western states . The dry line is an important factor in severe weather frequency in the Great Plains of North America...
, which is the boundary between air masses with significant moisture differences. When the westerlies
Westerlies
The Westerlies, anti-trades, or Prevailing Westerlies, are the prevailing winds in the middle latitudes between 30 and 60 degrees latitude, blowing from the high pressure area in the horse latitudes towards the poles. These prevailing winds blow from the west to the east, and steer extratropical...
increase on the north side of surface highs, areas of lowered pressure will form downwind of north–south oriented mountain chains, leading to the formation of a lee trough. Near the surface during daylight hours, warm moist air is denser than dry air of greater temperature, and thus the warm moist air wedges under the drier air like a cold front. At higher altitudes, the warm moist air is less dense than the dry air and the boundary slope reverses. In the vicinity of the reversal aloft, severe weather
Severe weather
Severe weather phenomena are weather conditions that are hazardous to human life and property.- Examples Include :Severe weather can occur under a variety of situations, but three characteristics are generally needed: a temperature or moisture boundary, moisture, and , instability in the...
is possible, especially when a triple point is formed with a cold front. A weaker form of the dry line seen more commonly is the lee trough, which displays weaker differences in moisture
Moisture
Humidity is the amount of moisture the air can hold before it rains. Moisture refers to the presence of a liquid, especially water, often in trace amounts...
. When moisture pools along the boundary during the warm season, it can be the focus of diurnal thunderstorms.
The dry line may occur anywhere on earth in regions intermediate between desert
Desert
A desert is a landscape or region that receives an extremely low amount of precipitation, less than enough to support growth of most plants. Most deserts have an average annual precipitation of less than...
areas and warm seas. The southern plains west of the Mississippi River
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the largest river system in North America. Flowing entirely in the United States, this river rises in western Minnesota and meanders slowly southwards for to the Mississippi River Delta at the Gulf of Mexico. With its many tributaries, the Mississippi's watershed drains...
in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
are a particularly favored location. The dry line normally moves eastward during the day and westward at night. A dry line is depicted on National Weather Service
National Weather Service
The National Weather Service , once known as the Weather Bureau, is one of the six scientific agencies that make up the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration of the United States government...
(NWS) surface analyses as an orange line with scallops facing into the moist sector. Dry lines are one of the few surface fronts where the pips indicated do not necessarily reflect the direction of motion.
Squall line

Mesoscale Convective System
A mesoscale convective system is a complex of thunderstorms that becomes organized on a scale larger than the individual thunderstorms but smaller than extratropical cyclones, and normally persists for several hours or more...
(MCS) forming at the point of the upper level split in the wind pattern running southeast into the warm sector parallel to low-level thickness lines. When the convection is strong and linear or curved, the MCS is called a squall line, with the feature placed at the leading edge of the significant wind shift and pressure rise. Even weaker and less organized areas of thunderstorms lead to locally cooler air and higher pressures, and outflow boundaries exist ahead of this type of activity, which can act as foci for additional thunderstorm activity later in the day.
These features are often depicted in the warm season across the United States on surface analyses and lie within surface troughs. If outflow boundaries or squall lines form over arid regions, a haboob
Haboob
A haboob is a type of intense duststorm carried on an atmospheric gravity current. Haboobs are regularly observed in arid regions throughout the world. They have been observed in the Sahara desert , as well as across the Arabian Peninsula, throughout Kuwait, and in the most arid regions of Iraq...
may result. Squall lines are depicted on NWS surface analyses as an alternating pattern of two red dots and a dash labelled SQLN or SQUALL LINE, while outflow boundaries are depicted as troughs with a label of OUTFLOW BNDRY.
Precipitation produced

Wind shear
Wind shear, sometimes referred to as windshear or wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere...
and the presence of a strong jet stream
Jet stream
Jet streams are fast flowing, narrow air currents found in the atmospheres of some planets, including Earth. The main jet streams are located near the tropopause, the transition between the troposphere and the stratosphere . The major jet streams on Earth are westerly winds...
, "roll clouds" and tornado
Tornado
A tornado is a violent, dangerous, rotating column of air that is in contact with both the surface of the earth and a cumulonimbus cloud or, in rare cases, the base of a cumulus cloud. They are often referred to as a twister or a cyclone, although the word cyclone is used in meteorology in a wider...
es may occur.
In the warm season
Season
A season is a division of the year, marked by changes in weather, ecology, and hours of daylight.Seasons result from the yearly revolution of the Earth around the Sun and the tilt of the Earth's axis relative to the plane of revolution...
, lee troughs, breezes, outflow boundaries and occlusions can lead to convection if enough moisture is available. Orographic precipitation is precipitation created through the lifting action of air moving over terrain such as mountains and hills, which is most common behind cold fronts that move into mountainous areas. It may sometimes occur in advance of warm fronts moving northward to the east of mountainous terrain. However, precipitation along warm fronts is relatively steady, as in rain or drizzle. Fog, sometimes extensive and dense, often occurs in pre-warm-frontal areas. Although, not all fronts produce precipitation or even clouds because moisture must be present in the air mass which is being lifted.
Movement
Fronts are generally guided by winds aloftWinds aloft
Winds Aloft, officially known as the Winds and Temperatures Aloft Forecast , is a forecast of specific atmospheric conditions in terms of wind and temperature at certain altitudes, typically measured in feet above mean sea level...
, but do not move as quickly. Cold fronts and occluded fronts in the Northern Hemisphere usually travel from the northwest to southeast, while warm fronts move more poleward with time. In the Northern Hemisphere a warm front moves from southwest to northeast. In the Southern Hemisphere, the reverse is true; a cold front usually moves from southwest to northeast, and a warm front moves from northwest to southeast. Movement is largely caused by the pressure gradient force (horizontal differences in atmospheric pressure) and the Coriolis effect
Coriolis effect
In physics, the Coriolis effect is a deflection of moving objects when they are viewed in a rotating reference frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the deflection is to the left of the motion of the object; in one with counter-clockwise rotation, the deflection is to the right...
, which is caused by Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
's spinning about its axis. Frontal zones can be slowed down by geographic features like mountains and large bodies of warm water.
See also
- Cyclogenesis
- Extratropical cycloneExtratropical cycloneExtratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are a group of cyclones defined as synoptic scale low pressure weather systems that occur in the middle latitudes of the Earth having neither tropical nor polar characteristics, and are connected with fronts and...
- Norwegian cyclone modelNorwegian cyclone modelThe older of the models of extratropical cyclone development is known as the Norwegian Cyclone Model, developed during and shortly after World War I within the Bergen School of Meteorology. In this theory, cyclones develop as they move up and along a frontal boundary, eventually occluding and...
- Surface weather analysisSurface weather analysisSurface weather analysis is a special type of weather map that provides a view of weather elements over a geographical area at a specified time based on information from ground-based weather stations...
- Trough (meteorology)Trough (meteorology)A trough is an elongated region of relatively low atmospheric pressure, often associated with fronts.Unlike fronts, there is not a universal symbol for a trough on a weather chart. The weather charts in some countries or regions mark troughs by a line. In the United States, a trough may be marked...

