
Westerlies
Encyclopedia
The Westerlies, anti-trades, or Prevailing Westerlies, are the prevailing winds
in the middle latitudes
between 30 and 60 degrees latitude
, blowing from the high pressure area in the horse latitudes
towards the pole
s. These prevailing winds blow from the west
to the east
, and steer extratropical cyclone
s in this general manner. Tropical cyclone
s which cross the subtropical ridge
axis into the Westerlies recurve due to the increased westerly flow. The wind
s are predominantly from the southwest in the Northern Hemisphere
and from the northwest in the Southern Hemisphere
.
The Westerlies are strongest in the winter hemisphere and times when the pressure is lower over the poles, while they are weakest in the summer hemisphere and when pressures are higher over the poles. The Westerlies are particularly strong, especially in the southern hemisphere, where there is less land in the middle latitudes to cause the flow pattern to amplify, or become more north-south oriented, which slows the Westerlies down. The strongest westerly winds in the middle latitudes can come in the Roaring Forties
, between 40 and 50 degrees latitude. The Westerlies play an important role in carrying the warm, equatorial waters and winds to the western coasts of continents, especially in the southern hemisphere because of its vast oceanic expanse.
, solar heating would cause winds across the mid-latitudes to blow in a poleward direction, away from the subtropical ridge. However, the Coriolis effect
caused by the rotation of Earth causes winds to steer to the right of what would otherwise be expected across the Northern Hemisphere, and left of what would be expected in the Southern Hemisphere. This is why winds across the Northern Hemisphere tend to blow from the southwest, but they tend to be from the northwest in the Southern Hemisphere. When pressures are lower over the poles, the strength of the Westerlies increases, which has the effect of warming the mid-latitudes. This occurs when the Arctic oscillation
is positive, and during winter low pressure near the poles is stronger than it would be during the summer. When it is negative and pressures are higher over the poles, the flow is more meridional, blowing from the direction of the pole towards the equator, which brings cold air into the mid-latitudes.
Throughout the year, the Westerlies vary in strength with the polar cyclone. As the cyclone reaches its maximum intensity in winter
, the Westerlies increase in strength. As the cyclone reaches its weakest intensity in summer
, the Westerlies weaken. An example of the impact of the Westerlies is when dust plumes, originating in the Gobi desert
combine with pollutants and spread large distances downwind, or eastward, into North America
. The Westerlies can be particularly strong, especially in the Southern Hemisphere, where there is less land in the middle latitudes to cause the progression of west to east winds to slow down. In the Southern hemisphere, because of the stormy and cloudy conditions, it is usual to refer to the Westerlies as the Roaring Forties, Furious Fifties and Shrieking Sixties according to the varying degrees of latitude.
 Due to persistent winds from west to east on the poleward sides of the subtropical ridges located in the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, ocean current
Due to persistent winds from west to east on the poleward sides of the subtropical ridges located in the Atlantic and Pacific oceans, ocean current
s are driven in a similar manner in both hemispheres. The currents in the Northern Hemisphere are weaker than those in the Southern Hemisphere due to the differences in strength between the Westerlies of each hemisphere. The process of western intensification causes currents on the western boundary of an ocean basin to be stronger than those on the eastern boundary of an ocean. These western ocean currents transport warm, tropical water polewards toward the polar region
s. Ships crossing both oceans have taken advantage of the ocean currents for centuries.
The Antarctic Circumpolar Current
(ACC), or the West Wind Drift, is an ocean current
that flows from west to east around Antarctica. The ACC is the dominant circulation feature of the Southern Ocean
and, at approximately 125 Sverdrup
s, the largest ocean current. In the northern hemisphere, the Gulf Stream
, part of the North Atlantic Subtropical Gyre
, has led to the development of strong cyclone
s of all types at the base of the Westerlies, both within the atmosphere
and within the ocean
. The Kuroshio (Japanese
for "Black Tide") is a strong western boundary current in the western north Pacific Ocean
, similar to the Gulf Stream, which has also contributed to the depth of ocean storms in that region.
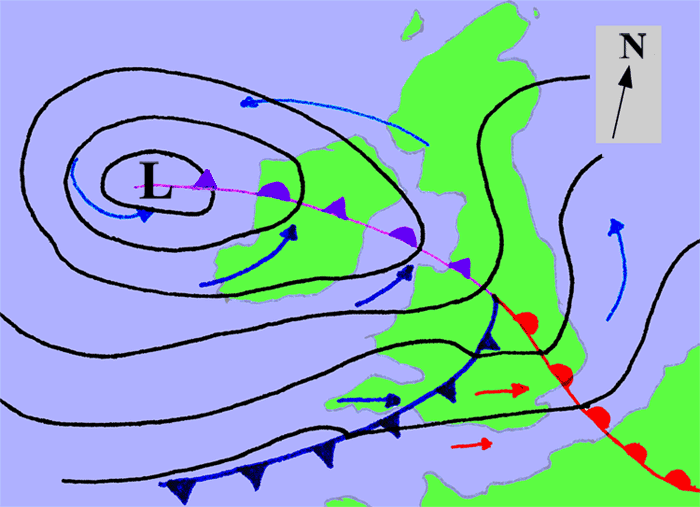
An extratropical cyclone is a synoptic scale
low pressure
weather system that has neither tropical nor polar
characteristics, being connected with fronts
and horizontal gradients in temperature
and dew point
otherwise known as "baroclinic zones".
The descriptor "extratropical" refers to the fact that this type of cyclone generally occurs outside of the tropics, in the middle latitudes of the planet, where the Westerlies steer the system generally from west to east. These systems may also be described as "mid-latitude cyclones" due to their area of formation, or "post-tropical cyclones" where extratropical transition has occurred, and are often described as "depressions" or "lows" by weather forecasters and the general public. These are the everyday phenomena which along with anti-cyclones, drive the weather over much of the Earth.
Although extratropical cyclones are almost always classified as baroclinic since they form along zones of temperature and dewpoint gradient, they can sometimes become barotropic
late in their life cycle when the temperature distribution around the cyclone becomes fairly uniform along the radius from the center of low pressure. An extratropical cyclone can transform into a subtropical storm, and from there into a tropical cyclone, if it dwells over warm waters and develops central convection, which warms its core and causes temperature and dewpoint gradients near their centers to fade.
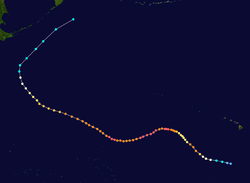 When a tropical cyclone crosses the subtropical ridge
When a tropical cyclone crosses the subtropical ridge
axis, normally through a break in the high-pressure area caused by a system traversing the Westerlies, its general track around the high-pressure area is deflected significantly by winds moving towards the general low-pressure area to its north. When the cyclone track becomes strongly poleward with an easterly component, the cyclone has begun recurvature, entering the Westerlies. A typhoon moving through the Pacific Ocean towards Asia, for example, will recurve offshore of Japan to the north, and then to the northeast, if the typhoon encounters southwesterly winds (blowing northeastward) around a low-pressure system passing over China
or Siberia
. Many tropical cyclones are eventually forced toward the northeast by extratropical cyclone
s in this manner, which move from west to east to the north of the subtropical ridge. An example of a tropical cyclone in recurvature was Typhoon Ioke
in 2006, which took a similar trajectory.
Prevailing winds
Prevailing winds are winds that blow predominantly from a single general direction over a particular point on Earth's surface. The dominant winds are the trends in direction of wind with the highest speed over a particular point on the Earth's surface. A region's prevailing and dominant winds...
in the middle latitudes
Middle latitudes
The middle latitudes are between 23°26'22" North and 66°33'39" North, and between 23°26'22" South and 66°33'39" South latitude, or, the Earth's temperate zones between the tropics and the Arctic and Antarctic. The prevailing winds in the middle latitudes are often very strong...
between 30 and 60 degrees latitude
Latitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
, blowing from the high pressure area in the horse latitudes
Horse latitudes
Horse Latitudes or Subtropical High are subtropical latitudes between 30 and 35 degrees both north and south. This region, under a ridge of high pressure called the subtropical high, is an area which receives little precipitation and has variable winds mixed with calm.The consistently warm, dry...
towards the pole
Geographical pole
A geographical pole is either of the two points—the north pole and the south pole—on the surface of a rotating planet where the axis of rotation meets the surface of the body...
s. These prevailing winds blow from the west
West
West is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.West is one of the four cardinal directions or compass points. It is the opposite of east and is perpendicular to north and south.By convention, the left side of a map is west....
to the east
East
East is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.East is one of the four cardinal directions or compass points. It is the opposite of west and is perpendicular to north and south.By convention, the right side of a map is east....
, and steer extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are a group of cyclones defined as synoptic scale low pressure weather systems that occur in the middle latitudes of the Earth having neither tropical nor polar characteristics, and are connected with fronts and...
s in this general manner. Tropical cyclone
Tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center and numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rain. Tropical cyclones strengthen when water evaporated from the ocean is released as the saturated air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor...
s which cross the subtropical ridge
Subtropical ridge
The subtropical ridge is a significant belt of high pressure situated around the latitudes of 30°N in the Northern Hemisphere and 30°S in the Southern Hemisphere. It is characterized by mostly calm winds, which acts to reduce air quality under its axis by causing fog overnight, and haze during...
axis into the Westerlies recurve due to the increased westerly flow. The wind
Wind
Wind is the flow of gases on a large scale. On Earth, wind consists of the bulk movement of air. In outer space, solar wind is the movement of gases or charged particles from the sun through space, while planetary wind is the outgassing of light chemical elements from a planet's atmosphere into space...
s are predominantly from the southwest in the Northern Hemisphere
Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
and from the northwest in the Southern Hemisphere
Southern Hemisphere
The Southern Hemisphere is the part of Earth that lies south of the equator. The word hemisphere literally means 'half ball' or "half sphere"...
.
The Westerlies are strongest in the winter hemisphere and times when the pressure is lower over the poles, while they are weakest in the summer hemisphere and when pressures are higher over the poles. The Westerlies are particularly strong, especially in the southern hemisphere, where there is less land in the middle latitudes to cause the flow pattern to amplify, or become more north-south oriented, which slows the Westerlies down. The strongest westerly winds in the middle latitudes can come in the Roaring Forties
Roaring Forties
The Roaring Forties is the name given to strong westerly winds found in the Southern Hemisphere, generally between the latitudes of 40 and 49 degrees. Air displaced from the Equator towards the South Pole, which travels close to the surface between the latitudes of 30 and 60 degrees south, combines...
, between 40 and 50 degrees latitude. The Westerlies play an important role in carrying the warm, equatorial waters and winds to the western coasts of continents, especially in the southern hemisphere because of its vast oceanic expanse.
Behavior
If the Earth were a non-rotating planetPlanet
A planet is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science,...
, solar heating would cause winds across the mid-latitudes to blow in a poleward direction, away from the subtropical ridge. However, the Coriolis effect
Coriolis effect
In physics, the Coriolis effect is a deflection of moving objects when they are viewed in a rotating reference frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the deflection is to the left of the motion of the object; in one with counter-clockwise rotation, the deflection is to the right...
caused by the rotation of Earth causes winds to steer to the right of what would otherwise be expected across the Northern Hemisphere, and left of what would be expected in the Southern Hemisphere. This is why winds across the Northern Hemisphere tend to blow from the southwest, but they tend to be from the northwest in the Southern Hemisphere. When pressures are lower over the poles, the strength of the Westerlies increases, which has the effect of warming the mid-latitudes. This occurs when the Arctic oscillation
Arctic oscillation
The Arctic oscillation or Northern Annular Mode/Northern Hemisphere Annular Mode is an index of the dominant pattern of non-seasonal sea-level pressure variations north of 20N latitude, and it is characterized by pressure anomalies of one sign in the Arctic with the opposite anomalies centered...
is positive, and during winter low pressure near the poles is stronger than it would be during the summer. When it is negative and pressures are higher over the poles, the flow is more meridional, blowing from the direction of the pole towards the equator, which brings cold air into the mid-latitudes.
Throughout the year, the Westerlies vary in strength with the polar cyclone. As the cyclone reaches its maximum intensity in winter
Winter
Winter is the coldest season of the year in temperate climates, between autumn and spring. At the winter solstice, the days are shortest and the nights are longest, with days lengthening as the season progresses after the solstice.-Meteorology:...
, the Westerlies increase in strength. As the cyclone reaches its weakest intensity in summer
Summer
Summer is the warmest of the four temperate seasons, between spring and autumn. At the summer solstice, the days are longest and the nights are shortest, with day-length decreasing as the season progresses after the solstice...
, the Westerlies weaken. An example of the impact of the Westerlies is when dust plumes, originating in the Gobi desert
Gobi Desert
The Gobi is a large desert region in Asia. It covers parts of northern and northwestern China, and of southern Mongolia. The desert basins of the Gobi are bounded by the Altai Mountains and the grasslands and steppes of Mongolia on the north, by the Hexi Corridor and Tibetan Plateau to the...
combine with pollutants and spread large distances downwind, or eastward, into North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
. The Westerlies can be particularly strong, especially in the Southern Hemisphere, where there is less land in the middle latitudes to cause the progression of west to east winds to slow down. In the Southern hemisphere, because of the stormy and cloudy conditions, it is usual to refer to the Westerlies as the Roaring Forties, Furious Fifties and Shrieking Sixties according to the varying degrees of latitude.
Impact on ocean currents

Ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of ocean water generated by the forces acting upon this mean flow, such as breaking waves, wind, Coriolis effect, cabbeling, temperature and salinity differences and tides caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun...
s are driven in a similar manner in both hemispheres. The currents in the Northern Hemisphere are weaker than those in the Southern Hemisphere due to the differences in strength between the Westerlies of each hemisphere. The process of western intensification causes currents on the western boundary of an ocean basin to be stronger than those on the eastern boundary of an ocean. These western ocean currents transport warm, tropical water polewards toward the polar region
Polar region
Earth's polar regions are the areas of the globe surrounding the poles also known as frigid zones. The North Pole and South Pole being the centers, these regions are dominated by the polar ice caps, resting respectively on the Arctic Ocean and the continent of Antarctica...
s. Ships crossing both oceans have taken advantage of the ocean currents for centuries.
The Antarctic Circumpolar Current
Antarctic Circumpolar Current
The Antarctic Circumpolar Current is an ocean current that flows from west to east around Antarctica. An alternative name for the ACC is the West Wind Drift. The ACC is the dominant circulation feature of the Southern Ocean and, at approximately 125 Sverdrups, the largest ocean current...
(ACC), or the West Wind Drift, is an ocean current
Ocean current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of ocean water generated by the forces acting upon this mean flow, such as breaking waves, wind, Coriolis effect, cabbeling, temperature and salinity differences and tides caused by the gravitational pull of the Moon and the Sun...
that flows from west to east around Antarctica. The ACC is the dominant circulation feature of the Southern Ocean
Southern Ocean
The Southern Ocean comprises the southernmost waters of the World Ocean, generally taken to be south of 60°S latitude and encircling Antarctica. It is usually regarded as the fourth-largest of the five principal oceanic divisions...
and, at approximately 125 Sverdrup
Sverdrup
The sverdrup, named in honour of the pioneering oceanographer Harald Sverdrup, is a unit of measure of volume transport. It is used almost exclusively in oceanography, to measure the transport of ocean currents. Its symbol is Sv. Note that the sverdrup is not an SI unit, and that its symbol...
s, the largest ocean current. In the northern hemisphere, the Gulf Stream
Gulf Stream
The Gulf Stream, together with its northern extension towards Europe, the North Atlantic Drift, is a powerful, warm, and swift Atlantic ocean current that originates at the tip of Florida, and follows the eastern coastlines of the United States and Newfoundland before crossing the Atlantic Ocean...
, part of the North Atlantic Subtropical Gyre
Gyre
A gyre in oceanography is any large system of rotating ocean currents, particularly those involved with large wind movements. Gyres are caused by the Coriolis Effect; planetary vorticity along with horizontal and vertical friction, which determine the circulation patterns from the wind curl...
, has led to the development of strong cyclone
Cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone is an area of closed, circular fluid motion rotating in the same direction as the Earth. This is usually characterized by inward spiraling winds that rotate anticlockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere of the Earth. Most large-scale...
s of all types at the base of the Westerlies, both within the atmosphere
Atmosphere
An atmosphere is a layer of gases that may surround a material body of sufficient mass, and that is held in place by the gravity of the body. An atmosphere may be retained for a longer duration, if the gravity is high and the atmosphere's temperature is low...
and within the ocean
Ocean
An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a principal component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas.More than half of this area is over 3,000...
. The Kuroshio (Japanese
Japanese language
is a language spoken by over 130 million people in Japan and in Japanese emigrant communities. It is a member of the Japonic language family, which has a number of proposed relationships with other languages, none of which has gained wide acceptance among historical linguists .Japanese is an...
for "Black Tide") is a strong western boundary current in the western north Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
, similar to the Gulf Stream, which has also contributed to the depth of ocean storms in that region.
Extratropical cyclones

An extratropical cyclone is a synoptic scale
Synoptic scale meteorology
The synoptic scale in meteorology is a horizontal length scale of the order of 1000 kilometres or more. This corresponds to a horizontal scale typical of mid-latitude depressions...
low pressure
Low pressure area
A low-pressure area, or "low", is a region where the atmospheric pressure at sea level is below that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence which occur in upper levels of the troposphere. The formation process of a low-pressure area is known as...
weather system that has neither tropical nor polar
Polar cyclone
Polar cyclones are low-pressure areas which strengthen in the winter and weaken in the summer...
characteristics, being connected with fronts
Surface weather analysis
Surface weather analysis is a special type of weather map that provides a view of weather elements over a geographical area at a specified time based on information from ground-based weather stations...
and horizontal gradients in temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
and dew point
Dew point
The dew point is the temperature to which a given parcel of humid air must be cooled, at constant barometric pressure, for water vapor to condense into liquid water. The condensed water is called dew when it forms on a solid surface. The dew point is a saturation temperature.The dew point is...
otherwise known as "baroclinic zones".
The descriptor "extratropical" refers to the fact that this type of cyclone generally occurs outside of the tropics, in the middle latitudes of the planet, where the Westerlies steer the system generally from west to east. These systems may also be described as "mid-latitude cyclones" due to their area of formation, or "post-tropical cyclones" where extratropical transition has occurred, and are often described as "depressions" or "lows" by weather forecasters and the general public. These are the everyday phenomena which along with anti-cyclones, drive the weather over much of the Earth.
Although extratropical cyclones are almost always classified as baroclinic since they form along zones of temperature and dewpoint gradient, they can sometimes become barotropic
Barotropic
In meteorology, a barotropic atmosphere is one in which the pressure depends only on the density and vice versa, so that isobaric surfaces are also isopycnic surfaces . The isobaric surfaces will also be isothermal surfaces, hence the geostrophic wind is independent of height...
late in their life cycle when the temperature distribution around the cyclone becomes fairly uniform along the radius from the center of low pressure. An extratropical cyclone can transform into a subtropical storm, and from there into a tropical cyclone, if it dwells over warm waters and develops central convection, which warms its core and causes temperature and dewpoint gradients near their centers to fade.
Interaction with tropical cyclones

Subtropical ridge
The subtropical ridge is a significant belt of high pressure situated around the latitudes of 30°N in the Northern Hemisphere and 30°S in the Southern Hemisphere. It is characterized by mostly calm winds, which acts to reduce air quality under its axis by causing fog overnight, and haze during...
axis, normally through a break in the high-pressure area caused by a system traversing the Westerlies, its general track around the high-pressure area is deflected significantly by winds moving towards the general low-pressure area to its north. When the cyclone track becomes strongly poleward with an easterly component, the cyclone has begun recurvature, entering the Westerlies. A typhoon moving through the Pacific Ocean towards Asia, for example, will recurve offshore of Japan to the north, and then to the northeast, if the typhoon encounters southwesterly winds (blowing northeastward) around a low-pressure system passing over China
China
Chinese civilization may refer to:* China for more general discussion of the country.* Chinese culture* Greater China, the transnational community of ethnic Chinese.* History of China* Sinosphere, the area historically affected by Chinese culture...
or Siberia
Siberia
Siberia is an extensive region constituting almost all of Northern Asia. Comprising the central and eastern portion of the Russian Federation, it was part of the Soviet Union from its beginning, as its predecessor states, the Tsardom of Russia and the Russian Empire, conquered it during the 16th...
. Many tropical cyclones are eventually forced toward the northeast by extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are a group of cyclones defined as synoptic scale low pressure weather systems that occur in the middle latitudes of the Earth having neither tropical nor polar characteristics, and are connected with fronts and...
s in this manner, which move from west to east to the north of the subtropical ridge. An example of a tropical cyclone in recurvature was Typhoon Ioke
Hurricane Ioke
Hurricane Ioke was the strongest hurricane ever recorded in the Central Pacific...
in 2006, which took a similar trajectory.

