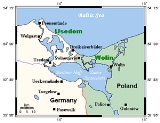
Usedom
Encyclopedia
Usedom is a Baltic Sea
island on the border between Germany
and Poland
. It is situated north of the Szczecin Lagoon estuary
of the River Oder in Pomerania
. Most of the island belongs to the German district of Vorpommern-Greifswald
in the Federal State of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, with the exception of the eastern part and the city of Świnoujście
which is in Polish West Pomeranian Voivodeship
. Its area is 445 km² (the German part 373 km²; the Polish part 72 km²).
Its population is 76,500 (the German part 31,500; the Polish part 45,000).
by the Świna
strait (or river), which is the main route connecting Szczecin Bay with the Pomeranian Bay, a part of the Baltic Sea. The strait between the island and the mainland is called Peenestrom; it is an underwater extension of the valley of the Peene
river, which flows into the westernmost part of Szczecin Bay. The island is mostly plain, partly covered by marshes.
The main town on the island is Świnoujście
, which has more inhabitants than the rest of the island. Another town, giving its name to the island, is called Usedom
. The largest municipality in the German part is Heringsdorf (from 2005 to 2006 called Dreikaiserbäder (which means "Three Emperors' Baths"). There are many popular tourist resorts on the northern coast, including the three Dreikaiserbäder cities of Ahlbeck
, Heringsdorf and Bansin
, as well as Świnoujście and Zinnowitz
.
Economic activities include agriculture, fishing, animal husbandry, food processing and timber production.
, the area was inhabited by Germanic
Rugians
, before the Polabian Slavs
moved in during the 5th, 6th and 7th centuries. Around the island, Wendish
/Scandinavian trade centres such as Vineta
/Jomsborg
and Menzlin were established. In 1128 the Pomeranian Duke
Wartislaw I was converted to Christianity
through the efforts of Otto of Bamberg
. In 1155 the Premonstratensian
s established a monastery in Grobe, generally known as Usedom Abbey
, which in 1309 was moved to the village of Pudagla
. In the meantime, a Cistercian nunnery was founded in Krummin
and soon almost the whole island was in the possession of one or the other of the ecclesiastical orders. During the Reformation
, ownership passed to the Slavic dukes of Pomerania
, who took over the island.
During the Thirty Years' War
, on June 26, 1630, the Swedish Army
under King Gustav Adolf II landed in the village of Peenemünde
, located on the Peene
river (Polish: Piana). Usedom was annexed by Sweden
after the war for almost a century, until in 1720 it was sold for 2 million thaler
s to the Prussian king Frederick William I
. In 1740 Frederick the Great developed a seaport in Swinemünde.
The small village of Peenemünde
came to prominence again during World War II
. The Luftwaffe
tested their missile
s and rocket
s, including the V-1
and V-2
in the locality. Germany used thousands of slave laborers on Usedom during World War II.
In 1945 the eastern part of the island, together with the city and port of Świnoujście
, was assigned to Poland
by the Potsdam Conference
, the German inhabitants being expelled to the west. The territory was populated with Poles who had in turn been expelled by the Soviet Union
from the Kresy
in the east.
establishments are available on both sides of the German-Polish border. In addition to the coastline, the hinterland
features nature reserves, castles, lakes and historic villages. Points of interest include:
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is a brackish mediterranean sea located in Northern Europe, from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 20°E to 26°E longitude. It is bounded by the Scandinavian Peninsula, the mainland of Europe, and the Danish islands. It drains into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, the Great Belt and...
island on the border between Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
and Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
. It is situated north of the Szczecin Lagoon estuary
Estuary
An estuary is a partly enclosed coastal body of water with one or more rivers or streams flowing into it, and with a free connection to the open sea....
of the River Oder in Pomerania
Pomerania
Pomerania is a historical region on the south shore of the Baltic Sea. Divided between Germany and Poland, it stretches roughly from the Recknitz River near Stralsund in the West, via the Oder River delta near Szczecin, to the mouth of the Vistula River near Gdańsk in the East...
. Most of the island belongs to the German district of Vorpommern-Greifswald
Vorpommern-Greifswald
Vorpommern-Greifswald is a district in the east of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is bounded by the districts Mecklenburgische Seenplatte, Vorpommern-Rügen, the Baltic Sea, Poland and the state Brandenburg...
in the Federal State of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, with the exception of the eastern part and the city of Świnoujście
Swinoujscie
Świnoujście is a city and seaport on the Baltic Sea and Szczecin Lagoon, located in the extreme north-west of Poland. It is situated mainly on the islands of Uznam and Wolin, but also occupies smaller islands, of which the largest is Karsibór island, once part of Usedom, now separated by a Piast...
which is in Polish West Pomeranian Voivodeship
West Pomeranian Voivodeship
West Pomeranian Voivodeship, , is a voivodeship in northwestern Poland. It borders on Pomeranian Voivodeship to the east, Greater Poland Voivodeship to the southeast, Lubusz Voivodeship to the south, the German federal-state of Mecklenburg-West Pomerania to the west, and the Baltic Sea to the north...
. Its area is 445 km² (the German part 373 km²; the Polish part 72 km²).
Its population is 76,500 (the German part 31,500; the Polish part 45,000).
Geography
The island is separated to the east from the neighbouring island of WolinWolin
Wolin is the name both of an island in the Baltic Sea, just off the Polish coast, and a town on that island. It is separated from the island of Usedom by the Świna river, and from mainland Pomerania by the Dziwna river...
by the Świna
Swina
The Świna is a river in Poland flowing from the Oder Lagoon to the Baltic Sea, between the islands of Usedom and Wolin. It is a part of the Oder River estuary, and carries about 75% of that river's waterflow . It has a length of about 16 km...
strait (or river), which is the main route connecting Szczecin Bay with the Pomeranian Bay, a part of the Baltic Sea. The strait between the island and the mainland is called Peenestrom; it is an underwater extension of the valley of the Peene
Peene
The Peene is a river in Germany. The Westpeene, Kleine Peene and Ostpeene flow into the Kummerower See, and from there as Peene proper to Anklam and into the Oder Lagoon....
river, which flows into the westernmost part of Szczecin Bay. The island is mostly plain, partly covered by marshes.
The main town on the island is Świnoujście
Swinoujscie
Świnoujście is a city and seaport on the Baltic Sea and Szczecin Lagoon, located in the extreme north-west of Poland. It is situated mainly on the islands of Uznam and Wolin, but also occupies smaller islands, of which the largest is Karsibór island, once part of Usedom, now separated by a Piast...
, which has more inhabitants than the rest of the island. Another town, giving its name to the island, is called Usedom
Usedom (town)
Usedom is a town in Vorpommern-Greifswald district in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is the seat of the Amt of Usedom-Süd, to which 14 other communities also belong.-Geography:...
. The largest municipality in the German part is Heringsdorf (from 2005 to 2006 called Dreikaiserbäder (which means "Three Emperors' Baths"). There are many popular tourist resorts on the northern coast, including the three Dreikaiserbäder cities of Ahlbeck
Ahlbeck
Ahlbeck is part of Heringsdorf, a seaside resort in Germany on the island of Usedom in the Baltic Sea. It is situated right next to the border of Poland and the city of Świnoujście ....
, Heringsdorf and Bansin
Bansin
Bansin forms the westernmost part of the seaside resort town of Heringsdorf in Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Germany, on the north coast of the island of Usedom, about five miles by rail northwest of Świnoujście. Bansin has, in the past, been one of the most popular resorts on the German Baltic...
, as well as Świnoujście and Zinnowitz
Zinnowitz
Zinnowitz is a spa town in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern on the northern German island of Usedom on the Baltic Sea. The town has rail connections to Wolgast and Ahlbeck.-History:...
.
Economic activities include agriculture, fishing, animal husbandry, food processing and timber production.
History
Settled since the Stone AgeStone Age
The Stone Age is a broad prehistoric period, lasting about 2.5 million years , during which humans and their predecessor species in the genus Homo, as well as the earlier partly contemporary genera Australopithecus and Paranthropus, widely used exclusively stone as their hard material in the...
, the area was inhabited by Germanic
Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples are an Indo-European ethno-linguistic group of Northern European origin, identified by their use of the Indo-European Germanic languages which diversified out of Proto-Germanic during the Pre-Roman Iron Age.Originating about 1800 BCE from the Corded Ware Culture on the North...
Rugians
Rugians
"Rugi" redirects here. For the Romanian villages by this name, see Păltiniş, Caraş-Severin and Turcineşti.The Rugii, also Rugians, Rygir, Ulmerugi, or Holmrygir were an East Germanic tribe migrated from southwest Norway to Pomerania around 100 AD, and from there to the Danube River valley...
, before the Polabian Slavs
Polabian Slavs
Polabian Slavs - is a collective term applied to a number of Lechites tribes who lived along the Elbe river, between the Baltic Sea to the north, the Saale and the Limes Saxoniae to the west, the Ore Mountains and the Western Sudetes to the south, and Poland to the east. They have also been known...
moved in during the 5th, 6th and 7th centuries. Around the island, Wendish
Wends
Wends is a historic name for West Slavs living near Germanic settlement areas. It does not refer to a homogeneous people, but to various peoples, tribes or groups depending on where and when it is used...
/Scandinavian trade centres such as Vineta
Vineta
Vineta or Wineta was a possibly legendary ancient town believed to have been on the coast of the Baltic Sea. It was commonly said to be on the present site of Wolin in Poland or of Zinnowitz on Usedom island in Germany. Today it is said to have been near Barth in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern...
/Jomsborg
Jomsborg
Jomsborg was a semi-legendary Viking stronghold at the southern coast of the Baltic Sea , that existed between the 960s and 1043. Its inhabitants are known as Jomsvikings. Jomsborg's exact location has not yet been established, though it is maintained that Jomsborg was somewhere on the islands of...
and Menzlin were established. In 1128 the Pomeranian Duke
Dukes of Pomerania
- 10th and 11th century – Dukes of the Slavic Pomeranian tribes :* 1046 mention of Zemuzil * 1113 Gallus Anonymus mentions several dukes of Pomerania: Swantibor, Gniewomir, and an unnamed duke besieged in Kołobrzeg.-Duchy of Pomerania:*1121–1135 Wartislaw I*1135–1155 Ratibor I, ancestor of the...
Wartislaw I was converted to Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
through the efforts of Otto of Bamberg
Otto of Bamberg
Saint Otto of Bamberg was a medieval German bishop and missionary who, as papal legate, converted much of Pomerania to Christianity.-Life:Otto was born into a noble family in Mistelbach, Franconia...
. In 1155 the Premonstratensian
Premonstratensian
The Order of Canons Regular of Prémontré, also known as the Premonstratensians, the Norbertines, or in Britain and Ireland as the White Canons , are a Catholic religious order of canons regular founded at Prémontré near Laon in 1120 by Saint Norbert, who later became Archbishop of Magdeburg...
s established a monastery in Grobe, generally known as Usedom Abbey
Usedom Abbey
Usedom Abbey was a medieval Premonstratensian monastery on the isle of Usedom near the town of Usedom. It was founded in Grobe and later moved to nearby Pudagla, and is thus also known as Grobe Abbey or Pudagla Abbey respectively.The abbey was founded by the Pomeranian duke Ratibor I and his...
, which in 1309 was moved to the village of Pudagla
Pudagla
Pudagla is a municipality in the Vorpommern-Greifswald district, in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. From 1307/09 until the Protestant Reformation, it was the site of Pudagla or Usedom Abbey, which moved there from Usedom . After the abbey's secularization into a ducal domain, it at times served...
. In the meantime, a Cistercian nunnery was founded in Krummin
Krummin
Krummin is a municipality in the Vorpommern-Greifswald district, in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany.-External links:*...
and soon almost the whole island was in the possession of one or the other of the ecclesiastical orders. During the Reformation
Protestant Reformation
The Protestant Reformation was a 16th-century split within Western Christianity initiated by Martin Luther, John Calvin and other early Protestants. The efforts of the self-described "reformers", who objected to the doctrines, rituals and ecclesiastical structure of the Roman Catholic Church, led...
, ownership passed to the Slavic dukes of Pomerania
Dukes of Pomerania
- 10th and 11th century – Dukes of the Slavic Pomeranian tribes :* 1046 mention of Zemuzil * 1113 Gallus Anonymus mentions several dukes of Pomerania: Swantibor, Gniewomir, and an unnamed duke besieged in Kołobrzeg.-Duchy of Pomerania:*1121–1135 Wartislaw I*1135–1155 Ratibor I, ancestor of the...
, who took over the island.
During the Thirty Years' War
Thirty Years' War
The Thirty Years' War was fought primarily in what is now Germany, and at various points involved most countries in Europe. It was one of the most destructive conflicts in European history....
, on June 26, 1630, the Swedish Army
Swedish Army
The Swedish Army is one of the oldest standing armies in the world and a branch of the Swedish Armed Forces; it is in charge of land operations. General Sverker Göranson is the Supreme Commander-in-Chief of the Army.- Organization :...
under King Gustav Adolf II landed in the village of Peenemünde
Peenemünde
The Peenemünde Army Research Center was founded in 1937 as one of five military proving grounds under the Army Weapons Office ....
, located on the Peene
Peene
The Peene is a river in Germany. The Westpeene, Kleine Peene and Ostpeene flow into the Kummerower See, and from there as Peene proper to Anklam and into the Oder Lagoon....
river (Polish: Piana). Usedom was annexed by Sweden
Sweden
Sweden , officially the Kingdom of Sweden , is a Nordic country on the Scandinavian Peninsula in Northern Europe. Sweden borders with Norway and Finland and is connected to Denmark by a bridge-tunnel across the Öresund....
after the war for almost a century, until in 1720 it was sold for 2 million thaler
Thaler
The Thaler was a silver coin used throughout Europe for almost four hundred years. Its name lives on in various currencies as the dollar or tolar. Etymologically, "Thaler" is an abbreviation of "Joachimsthaler", a coin type from the city of Joachimsthal in Bohemia, where some of the first such...
s to the Prussian king Frederick William I
Frederick William I of Prussia
Frederick William I of the House of Hohenzollern, was the King in Prussia and Elector of Brandenburg from 1713 until his death...
. In 1740 Frederick the Great developed a seaport in Swinemünde.
The small village of Peenemünde
Peenemünde
The Peenemünde Army Research Center was founded in 1937 as one of five military proving grounds under the Army Weapons Office ....
came to prominence again during World War II
World War II
World War II, or the Second World War , was a global conflict lasting from 1939 to 1945, involving most of the world's nations—including all of the great powers—eventually forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis...
. The Luftwaffe
Luftwaffe
Luftwaffe is a generic German term for an air force. It is also the official name for two of the four historic German air forces, the Wehrmacht air arm founded in 1935 and disbanded in 1946; and the current Bundeswehr air arm founded in 1956....
tested their missile
Missile
Though a missile may be any thrown or launched object, it colloquially almost always refers to a self-propelled guided weapon system.-Etymology:The word missile comes from the Latin verb mittere, meaning "to send"...
s and rocket
Rocket
A rocket is a missile, spacecraft, aircraft or other vehicle which obtains thrust from a rocket engine. In all rockets, the exhaust is formed entirely from propellants carried within the rocket before use. Rocket engines work by action and reaction...
s, including the V-1
V-1 flying bomb
The V-1 flying bomb, also known as the Buzz Bomb or Doodlebug, was an early pulse-jet-powered predecessor of the cruise missile....
and V-2
V-2 rocket
The V-2 rocket , technical name Aggregat-4 , was a ballistic missile that was developed at the beginning of the Second World War in Germany, specifically targeted at London and later Antwerp. The liquid-propellant rocket was the world's first long-range combat-ballistic missile and first known...
in the locality. Germany used thousands of slave laborers on Usedom during World War II.
In 1945 the eastern part of the island, together with the city and port of Świnoujście
Swinoujscie
Świnoujście is a city and seaport on the Baltic Sea and Szczecin Lagoon, located in the extreme north-west of Poland. It is situated mainly on the islands of Uznam and Wolin, but also occupies smaller islands, of which the largest is Karsibór island, once part of Usedom, now separated by a Piast...
, was assigned to Poland
Poland
Poland , officially the Republic of Poland , is a country in Central Europe bordered by Germany to the west; the Czech Republic and Slovakia to the south; Ukraine, Belarus and Lithuania to the east; and the Baltic Sea and Kaliningrad Oblast, a Russian exclave, to the north...
by the Potsdam Conference
Potsdam Conference
The Potsdam Conference was held at Cecilienhof, the home of Crown Prince Wilhelm Hohenzollern, in Potsdam, occupied Germany, from 16 July to 2 August 1945. Participants were the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and the United States...
, the German inhabitants being expelled to the west. The territory was populated with Poles who had in turn been expelled by the Soviet Union
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
from the Kresy
Kresy
The Polish term Kresy refers to a land considered by Poles as historical eastern provinces of their country. Today, it makes western Ukraine, western Belarus, as well as eastern Lithuania, with such major cities, as Lviv, Vilnius, and Hrodna. This territory belonged to the Polish-Lithuanian...
in the east.
Tourism
The Isle of Usedom is one of Germany's major holiday and recreation areas due to its beaches, its natural beauty and a number of elegant seaside towns such as Zinnowitz and Heringsdorf, which have been frequented by the German and international nobility as well as the general public. Many hotels and bed and breakfastBed and breakfast
A bed and breakfast is a small lodging establishment that offers overnight accommodation and breakfast, but usually does not offer other meals. Since the 1980s, the meaning of the term has also extended to include accommodations that are also known as "self-catering" establishments...
establishments are available on both sides of the German-Polish border. In addition to the coastline, the hinterland
Hinterland
The hinterland is the land or district behind a coast or the shoreline of a river. Specifically, by the doctrine of the hinterland, the word is applied to the inland region lying behind a port, claimed by the state that owns the coast. The area from which products are delivered to a port for...
features nature reserves, castles, lakes and historic villages. Points of interest include:
- Usedoms Botanischer Garten MellenthinUsedoms Botanischer Garten MellenthinThe Usedoms Botanischer Garten Mellenthin is a private botanical garden located at Chausseeberg 1, Mellenthin, Usedom, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is open daily in the warmer months; an admission fee is charged....
, a botanical gardenBotanical gardenA botanical garden The terms botanic and botanical, and garden or gardens are used more-or-less interchangeably, although the word botanic is generally reserved for the earlier, more traditional gardens. is a well-tended area displaying a wide range of plants labelled with their botanical names...

