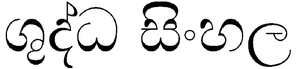Sinhala alphabet
Encyclopedia
The Sinhala alphabet is an abugida
used in Sri Lanka
to write the official language
Sinhala and also sometimes the liturgical languages Pali
and Sanskrit
. Being a member of the Brahmic family
of scripts, the Sinhala script can trace its ancestry back more than 2000 years.
Sinhala is often considered two alphabets, or an alphabet within an alphabet, due to the presence of two sets of letters. The core set, known as the (Pure Sinhala, ශුද්ධ සිංහල) or ( alphabet එළු හෝඩිය), can represent all native phoneme
s. In order to render Sanskrit and Pali words, an extended set, the (Mixed Sinhala, මිශ්ර සිංහල), is available.
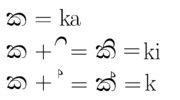 The alphabet is written from left to right. The Sinhala writing system
The alphabet is written from left to right. The Sinhala writing system
can be called an abugida
, as each consonant
has an inherent vowel
(/a/), which can be changed with the different vowel signs (see image on left).
Most of the Sinhala letters are curlicue
s; straight lines are almost completely absent from the alphabet. This is because Sinhala used to be written on dried palm leaves
, which would split along the veins on writing straight lines. This was undesirable, and therefore, the round shapes were preferred.
The core set of letters forms the alphabet (Pure Sinhala, ශුද්ධ සිංහල), which is a subset of the alphabet (Mixed Sinhala, මිශ්ර සිංහල). This "pure" alphabet contains all the graphemes necessary to write (classical Sinhala) as described in the classical grammar (1300 AD). This is the reason why this set is also called ( එළු හෝඩිය).
The definition of the two sets is thus a historic one. Out of pure coincidence, the phoneme inventory of present day colloquial Sinhala is such that yet again the śuddha alphabet suffices as a good representation of the sounds.
All native phoneme
s of the Sinhala spoken today can be represented in , while in order to render special Sanskrit and Pali sounds, one can fall back on . This is most notably necessary for the graphemes for the Middle Indic phonemes that the Sinhalese language lost during its history, such as aspirates.
Sinhalese had special symbols to represent numerals, which were in use until the beginning of the [19th] century.
This system is now superseded by Arabic numerals.
Neither the Sinhala numerals
nor U+0DF4 ෴ Sinhala punctuation kunddaliya is in general use today. The kunddaliya was formerly used as a full stop; it is included for scholarly use. The Sinhala numerals are not presently encoded.
. and is founded in the southern branch of this family
, sharing a lineage
with scripts such as Malayalam
, and Tamil
.
The Brahmi
writing system was originally used in inscriptions, the oldest ones in Sri Lanka dating from the 6th century BCE on pottery
, with lithic inscriptions dating from the 2nd century BC By the 9th century CE, literature
written in Sinhala script had emerged and the script began to be used in other contexts. For instance, the Buddhist literature
of the Theravada
-Buddhists
of Sri Lanka, written in Pali
, used the Sinhala alphabet.
Today, the alphabet is used by approximately 16,000,000 people
to write the Sinhalese language in very diverse contexts, such as newspapers, TV commercials, government announcements, graffiti
, and schoolbook
s.
Sinhala is the main language written in this alphabet, but rare instances of Sri Lanka Malay written in this script are recorded.
While a phoneme can be represented by more than one grapheme, each grapheme can be pronounced in only one way. This means that the actual pronunciation
of a word is always clear from its orthographic form.
s, 2 fricatives, 2 affricates, 2 nasal
s, 2 liquids
and 2 glide
s. Additionally, there are the two graphemes for the retroflex sounds /ɭ/ and /ɳ/, which are not phonemic in modern Sinhala, but which still form part of the set. These are shaded in the table.
The voiceless affricate (ච [t͡ʃa]) is not included in the śuddha set by purists since it does not occur in the main text of the . The does use it in examples though, so this sound did exist in . In any case, it is needed for the representation of modern Sinhala.
The basic shapes of these consonants carry an inherent /a/ unless this is replaced by another vowel or removed by the hal kirīma.
.svg.png) Vowels come in two shapes: independent and diacritic. The independent shape is used when a vowel does not follow a consonant, e.g. at the beginning of a word. The diacritic shape is used when a vowel follows a consonant. Depending on the vowel, the diacritic can attach at several places. The diacritic for
Vowels come in two shapes: independent and diacritic. The independent shape is used when a vowel does not follow a consonant, e.g. at the beginning of a word. The diacritic shape is used when a vowel follows a consonant. Depending on the vowel, the diacritic can attach at several places. The diacritic for precedes. finally is marked by the combination of preceding and following <ā>.
While are regular, the diacritic for
s resemble their plain counterparts. is made up by the left half of ⟨m⟩ and the right half of ⟨b⟩, while the other three are just like the grapheme for the stop with a little stroke attached to their left. Vowel diacritics attach in the same way as they would to the corresponding plain stop.
 The Anusvara
The Anusvara
(often called binduva 'zero' ) is represented by one small circle ං (unicode 0D82), and the Visarga
(technically part of the miśra alphabet) by two ඃ (unicode 0D83). The inherent vowel can be removed by a special diacritic, the hal kirīma(්), which varies in shape according to the consonant it attaches to. Both are represented in the image on the right side. The first one is the most common one, while the second one is used for letters ending at the top left corner.
of śuddha. It adds letters for aspirates, retroflexes and sibilants, which are not phonemic in today's Sinhala, but which are necessary to represent non-native words, like loanword
s from Sanskrit
, Pali or English
. The use of the extra letters is mainly a question of prestige. From a purely phonemic point of view, there is no benefit in using them, and they can be replaced by a (sequence of) śuddha letters as follows: For the miśra aspirates, the replacement is the plain
śuddha counterpart, for the miśra retroflex liquids
the corresponding śuddha coronal
liquid, for the sibilants, inscribed in the cup.
There are six additional vocalic diacritics in the miśra alphabet. The two diphthong
s are quite common, while the "syllabic" is much rarer, and the "syllabic" is all but obsolete. The latter are almost exclusively found in loanwords from Sanskrit.
The miśra can be also be written with śuddha ⟨r⟩+⟨u⟩ or ⟨u⟩+⟨r⟩, which corresponds to the actual pronunciation
. The miśra syllabic is obsolete, but can be rendered by śuddha ⟨l⟩+⟨i⟩. Miśra ⟨au⟩ is rendered as śuddha ⟨awu⟩, miśra ⟨ai⟩ as śuddha ⟨ayi⟩.
Note that the transliteration of both and is . This is not very problematic as the second one is extremely scarce.
or bee for the letter
a is added for easier pronunciation: the name for the letter ක් is akyanna. Another naming convention is to use al- before a letter with suppressed vowel, thus alkayanna.
Since the extra miśra letters are phonetically not distinguishable from the śuddha letters, proceeding in the same way would lead to confusion. Names of miśra letters are normally made up of the names of two śuddha letters pronounced as one word. The first one indicates the sound, the second one the shape. For example, the aspirated ඛ (kh) is called bayanu kayanna. kayanna indicates the sound, while bayanu indicates the shape: ඛ (kh) is similar in shape to බ (b) (bayunu = like bayanna).
Another method is to qualify the miśra aspirates by mahāprāna (ඛ: mahāprāna kayanna) and the miśra retroflexes by mūrdhaja (ළ: mūrdhaja layanna).
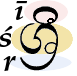 Certain combinations of graphemes trigger special ligatures. Special signs exist for an ර (r) following a consonant (inverted arch underneath), a ර (r) preceding a consonant (loop above) and a ය (y) following a consonant (half a ය on the right).
Certain combinations of graphemes trigger special ligatures. Special signs exist for an ර (r) following a consonant (inverted arch underneath), a ර (r) preceding a consonant (loop above) and a ය (y) following a consonant (half a ය on the right).
Furthermore, very frequent combinations are often written in one stroke, like ddh, kv or kś. If this is the case, the first consonant is not marked with a hal kirīma.
 The image on the left shows she glyph
The image on the left shows she glyph
for śrī, which is composed of the letter ś with the vowel ī marked above and a ligature indicating the r below. The image on the right shows ligatures of ද(d)+ය(y) and ක(k)+ෂි (ṣi) on the Political science course advertisement.
, and thus shares many similarities with other members of the family, such as the Tamil script
and Devanāgarī
. As a general example, /a/ is the inherent vowel in all three scripts. Other similarities include the diacritic for, which resembles a doubled in all three scripts (Sinhala e:ෙ, ai:ෛ; Tamil e:ெ, ai:ை, Devanāgarī pe:पे, pai:पै). The combination of the diacritics for and <ā> yields in all three scripts:
The diacritic for is composed of preceding and following <ḷ> in Sinhala (ෞ) and Tamil (ௌ).
can be done in analogy to Devanāgarī transliteration
.
A problem is the transliteration of /ඇ/, not found in Devanāgarī. This is <ä> in the German
tradition of Wilhelm Geiger
, and <æ> in the Anglophone tradition (e.g. James Gair
).
Layman's transliterations in Sri Lanka normally follow neither of these. Vowels are transliterated according to English spelling equivalences, which can yield a variety of spellings for a number of phonemes. /iː/ for instance can be, , ,
A transliteration pattern peculiar to Sinhala, and facilitated by the absence of phonemic aspirates, is the use of for the voiceless dental stop, and the use of for the voiceless retroflex stop.
This is presumably because the retroflex stop /ʈ/ is perceived the same as the English alveolar stop /t/, and the Sinhala dental stop /t̪/ is equated with the English voiceless dental fricative
/θ/. Dental and retroflex voiced stops are alway rendered as, though, presumably because is not found as a representation of ð in English orthography.
Standard in September, 1999 with the release of version 3.0.
The Unicode block for Sinhala is U+0D80–U+0DFF. Grey areas indicate non-assigned code points.
This character allocation has been adopted in Sri Lanka as the Standard SLS1134.
 Generally speaking, Sinhala support is less developed than support for Devanāgarī for instance. A recurring problem is the rendering of diacritics which precede the consonant and diacritic signs which come in different shapes, like the one for
Generally speaking, Sinhala support is less developed than support for Devanāgarī for instance. A recurring problem is the rendering of diacritics which precede the consonant and diacritic signs which come in different shapes, like the one for
Sinhala does not come built in with Windows XP
, unlike Tamil
and Hindi
. However, all versions of Windows Vista
come with Sinhala support by default, and do not require external font
s to be installed to read Sinhalese script.
For OS X, Sinhala font and keyboard support can be found at http://web.nickshanks.com/typography/ and at http://www.xenotypetech.com/osxSinhala.html
For Linux
, the scim
input method selector allows to use Sinhala script in applications like terminals
or web browser
s.

Abugida
An abugida , also called an alphasyllabary, is a segmental writing system in which consonant–vowel sequences are written as a unit: each unit is based on a consonant letter, and vowel notation is obligatory but secondary...
used in Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka is a country off the southern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Known until 1972 as Ceylon , Sri Lanka is an island surrounded by the Indian Ocean, the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait, and lies in the vicinity of India and the...
to write the official language
Official language
An official language is a language that is given a special legal status in a particular country, state, or other jurisdiction. Typically a nation's official language will be the one used in that nation's courts, parliament and administration. However, official status can also be used to give a...
Sinhala and also sometimes the liturgical languages Pali
Páli
- External links :* *...
and Sanskrit
Sanskrit
Sanskrit , is a historical Indo-Aryan language and the primary liturgical language of Hinduism, Jainism and Buddhism.Buddhism: besides Pali, see Buddhist Hybrid Sanskrit Today, it is listed as one of the 22 scheduled languages of India and is an official language of the state of Uttarakhand...
. Being a member of the Brahmic family
Brahmic family
The Brahmic or Indic scripts are a family of abugida writing systems. They are used throughout South Asia , Southeast Asia, and parts of Central and East Asia, and are descended from the Brāhmī script of the ancient Indian subcontinent...
of scripts, the Sinhala script can trace its ancestry back more than 2000 years.
Sinhala is often considered two alphabets, or an alphabet within an alphabet, due to the presence of two sets of letters. The core set, known as the (Pure Sinhala, ශුද්ධ සිංහල) or ( alphabet එළු හෝඩිය), can represent all native phoneme
Phoneme
In a language or dialect, a phoneme is the smallest segmental unit of sound employed to form meaningful contrasts between utterances....
s. In order to render Sanskrit and Pali words, an extended set, the (Mixed Sinhala, මිශ්ර සිංහල), is available.
Characteristics
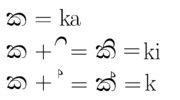
Writing system
A writing system is a symbolic system used to represent elements or statements expressible in language.-General properties:Writing systems are distinguished from other possible symbolic communication systems in that the reader must usually understand something of the associated spoken language to...
can be called an abugida
Abugida
An abugida , also called an alphasyllabary, is a segmental writing system in which consonant–vowel sequences are written as a unit: each unit is based on a consonant letter, and vowel notation is obligatory but secondary...
, as each consonant
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are , pronounced with the lips; , pronounced with the front of the tongue; , pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced in the throat; and ,...
has an inherent vowel
Inherent vowel
An inherent vowel is part of an abugida script. It is the vowel sound which is used with each unmarked or basic consonant symbol....
(/a/), which can be changed with the different vowel signs (see image on left).
Most of the Sinhala letters are curlicue
Curlicue
A curlicue, or alternatively curlycue, in the visual arts, is a fancy twist, or curl, composed usually from a series of concentric circles...
s; straight lines are almost completely absent from the alphabet. This is because Sinhala used to be written on dried palm leaves
Palm leaf manuscript
Palm leaf manuscripts are manuscripts made out of dried palm leaves. They served as the paper of the ancient world in parts of Asia as far back as the fifteenth century BCE. and possibly much earlier. They were used to record actual and mythical narratives in South Asia and in South East Asia...
, which would split along the veins on writing straight lines. This was undesirable, and therefore, the round shapes were preferred.
The core set of letters forms the alphabet (Pure Sinhala, ශුද්ධ සිංහල), which is a subset of the alphabet (Mixed Sinhala, මිශ්ර සිංහල). This "pure" alphabet contains all the graphemes necessary to write (classical Sinhala) as described in the classical grammar (1300 AD). This is the reason why this set is also called ( එළු හෝඩිය).
The definition of the two sets is thus a historic one. Out of pure coincidence, the phoneme inventory of present day colloquial Sinhala is such that yet again the śuddha alphabet suffices as a good representation of the sounds.
All native phoneme
Phoneme
In a language or dialect, a phoneme is the smallest segmental unit of sound employed to form meaningful contrasts between utterances....
s of the Sinhala spoken today can be represented in , while in order to render special Sanskrit and Pali sounds, one can fall back on . This is most notably necessary for the graphemes for the Middle Indic phonemes that the Sinhalese language lost during its history, such as aspirates.
Sinhalese had special symbols to represent numerals, which were in use until the beginning of the [19th] century.
This system is now superseded by Arabic numerals.
Neither the Sinhala numerals
Sinhala numerals
Sinhala belongs to the Indo-European language family with its roots deeply associated with Indo-Aryan sub family to which the languages such as Persian and Hindi belong [Histroy1]...
nor U+0DF4 ෴ Sinhala punctuation kunddaliya is in general use today. The kunddaliya was formerly used as a full stop; it is included for scholarly use. The Sinhala numerals are not presently encoded.
History and usage
The Sinhala script originated as an offshoot from BrahmiBrāhmī script
Brāhmī is the modern name given to the oldest members of the Brahmic family of scripts. The best-known Brāhmī inscriptions are the rock-cut edicts of Ashoka in north-central India, dated to the 3rd century BCE. These are traditionally considered to be early known examples of Brāhmī writing...
. and is founded in the southern branch of this family
Brahmic family
The Brahmic or Indic scripts are a family of abugida writing systems. They are used throughout South Asia , Southeast Asia, and parts of Central and East Asia, and are descended from the Brāhmī script of the ancient Indian subcontinent...
, sharing a lineage
Lineage (evolution)
An evolutionary lineage is a sequence of species, that form a line of descent, each new species the direct result of speciation from an immediate ancestral species. Lineages are subsets of the evolutionary tree of life. Lineages are often determined by the techniques of molecular systematics.-...
with scripts such as Malayalam
Malayalam script
The Malayalam script is a Brahmic script used commonly to write the Malayalam language—which is the principal language of the Indian state of Kerala, spoken by 36 million people in the world. Like many other Indic scripts, it is an abugida, or a writing system that is partially “alphabetic” and...
, and Tamil
Tamil script
The Tamil script is a script that is used to write the Tamil language as well as other minority languages such as Badaga, Irulas, and Paniya...
.
The Brahmi
Brāhmī script
Brāhmī is the modern name given to the oldest members of the Brahmic family of scripts. The best-known Brāhmī inscriptions are the rock-cut edicts of Ashoka in north-central India, dated to the 3rd century BCE. These are traditionally considered to be early known examples of Brāhmī writing...
writing system was originally used in inscriptions, the oldest ones in Sri Lanka dating from the 6th century BCE on pottery
Pottery
Pottery is the material from which the potteryware is made, of which major types include earthenware, stoneware and porcelain. The place where such wares are made is also called a pottery . Pottery also refers to the art or craft of the potter or the manufacture of pottery...
, with lithic inscriptions dating from the 2nd century BC By the 9th century CE, literature
Literature
Literature is the art of written works, and is not bound to published sources...
written in Sinhala script had emerged and the script began to be used in other contexts. For instance, the Buddhist literature
Pāli Canon
The Pāli Canon is the standard collection of scriptures in the Theravada Buddhist tradition, as preserved in the Pāli language. It is the only completely surviving early Buddhist canon, and one of the first to be written down...
of the Theravada
Theravada
Theravada ; literally, "the Teaching of the Elders" or "the Ancient Teaching", is the oldest surviving Buddhist school. It was founded in India...
-Buddhists
Buddhism
Buddhism is a religion and philosophy encompassing a variety of traditions, beliefs and practices, largely based on teachings attributed to Siddhartha Gautama, commonly known as the Buddha . The Buddha lived and taught in the northeastern Indian subcontinent some time between the 6th and 4th...
of Sri Lanka, written in Pali
Páli
- External links :* *...
, used the Sinhala alphabet.
Today, the alphabet is used by approximately 16,000,000 people
Demographics of Sri Lanka
This article is about the demographic features of the population of Sri Lanka, including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population....
to write the Sinhalese language in very diverse contexts, such as newspapers, TV commercials, government announcements, graffiti
Graffiti
Graffiti is the name for images or lettering scratched, scrawled, painted or marked in any manner on property....
, and schoolbook
Education in Sri Lanka
Education in Sri Lanka has a long history which dates back two millennia and the Constitution of Sri Lanka provide for education as a fundamental right. The Sri Lanka's population has a literacy rate of 92%, higher than that expected for a third world country; it has the highest literacy rate in...
s.
Sinhala is the main language written in this alphabet, but rare instances of Sri Lanka Malay written in this script are recorded.

Relations between orthography and phonology
Most phonemes of the Sinhalese language can be represented by a śuddha letter or by a miśra letter, but normally only one of them is considered correct. This one-to-many mapping of phonemes onto graphemes is a frequent source of misspellings.While a phoneme can be represented by more than one grapheme, each grapheme can be pronounced in only one way. This means that the actual pronunciation
Pronunciation
Pronunciation refers to the way a word or a language is spoken, or the manner in which someone utters a word. If one is said to have "correct pronunciation", then it refers to both within a particular dialect....
of a word is always clear from its orthographic form.
Śuddha graphemes
The śuddha graphemes are the mainstay of the Sinhala alphabet and are used on an everyday-basis. Every sequence of sounds of the Sinhalese language of today can be represented by these graphemes. Additionally, the śuddha set comprises graphemes for retroflex and , which are no longer phonemic in modern Sinhala. These two letters were needed for the representation of , but are now obsolete from a purely phonemic view. However, words which historically contain these two phonemes are still often written with the graphemes representing the retroflex sounds.Consonants
The śuddha alphabet comprises 8 stopStop consonant
In phonetics, a plosive, also known as an occlusive or an oral stop, is a stop consonant in which the vocal tract is blocked so that all airflow ceases. The occlusion may be done with the tongue , lips , and &...
s, 2 fricatives, 2 affricates, 2 nasal
Nasal consonant
A nasal consonant is a type of consonant produced with a lowered velum in the mouth, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. Examples of nasal consonants in English are and , in words such as nose and mouth.- Definition :...
s, 2 liquids
Liquid consonant
In phonetics, liquids or liquid consonants are a class of consonants consisting of lateral consonants together with rhotics.-Description:...
and 2 glide
Semivowel
In phonetics and phonology, a semivowel is a sound, such as English or , that is phonetically similar to a vowel sound but functions as the syllable boundary rather than as the nucleus of a syllable.-Classification:...
s. Additionally, there are the two graphemes for the retroflex sounds /ɭ/ and /ɳ/, which are not phonemic in modern Sinhala, but which still form part of the set. These are shaded in the table.
The voiceless affricate (ච [t͡ʃa]) is not included in the śuddha set by purists since it does not occur in the main text of the . The does use it in examples though, so this sound did exist in . In any case, it is needed for the representation of modern Sinhala.
The basic shapes of these consonants carry an inherent /a/ unless this is replaced by another vowel or removed by the hal kirīma.
| colspan="12" | |
|||||||||||
| Stops Stop consonant In phonetics, a plosive, also known as an occlusive or an oral stop, is a stop consonant in which the vocal tract is blocked so that all airflow ceases. The occlusion may be done with the tongue , lips , and &... |
|||||||||||
| voiceless | voiced | ||||||||||
| unicode Unicode Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems... |
translit. Transliteration Transliteration is a subset of the science of hermeneutics. It is a form of translation, and is the practice of converting a text from one script into another... |
IPA | unicode | translit. | IPA | ||||||
| velar Velar consonant Velars are consonants articulated with the back part of the tongue against the soft palate, the back part of the roof of the mouth, known also as the velum).... |
ක | 0D9A | ka | [ka] | ග | 0D9C | ga | [ɡa] | velar Velar consonant Velars are consonants articulated with the back part of the tongue against the soft palate, the back part of the roof of the mouth, known also as the velum).... |
||
| retroflex | ට | 0DA7 | [ʈa] | ඩ | 0DA9 | [ɖa] | retroflex | ||||
| dental | ත | 0DAD | ta | [ta] | ද | 0DAF | da | [da] | dental | ||
| labial Labial consonant Labial consonants are consonants in which one or both lips are the active articulator. This precludes linguolabials, in which the tip of the tongue reaches for the posterior side of the upper lip and which are considered coronals... |
ප | 0DB4 | pa | [pa] | බ | 0DB6 | ba | [ba] | labial Labial consonant Labial consonants are consonants in which one or both lips are the active articulator. This precludes linguolabials, in which the tip of the tongue reaches for the posterior side of the upper lip and which are considered coronals... |
||
| Other graphemes | |||||||||||
| unicode | translit. | IPA | unicode | translit. | IPA | ||||||
| fricatives | ස | 0DC3 | sa | [sa] | හ | 0DC4 | ha | [ha] | fricatives | ||
| affricates | (ච) | (0DA0) | (ca) | ([t͡ʃa]) | ජ | 0DA2 | ja | [d͡ʒa] | affricates | ||
| nasal Nasal consonant A nasal consonant is a type of consonant produced with a lowered velum in the mouth, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. Examples of nasal consonants in English are and , in words such as nose and mouth.- Definition :... s |
ම | 0DB8 | ma | [ma] | න | 0DB1 | na | [na] | nasal Nasal consonant A nasal consonant is a type of consonant produced with a lowered velum in the mouth, allowing air to escape freely through the nose. Examples of nasal consonants in English are and , in words such as nose and mouth.- Definition :... s |
||
| liquid Liquid consonant In phonetics, liquids or liquid consonants are a class of consonants consisting of lateral consonants together with rhotics.-Description:... |
ල | 0DBD | la | [la] | ර | 0DBB | ra | [ra] | liquid Liquid consonant In phonetics, liquids or liquid consonants are a class of consonants consisting of lateral consonants together with rhotics.-Description:... |
||
| glide Semivowel In phonetics and phonology, a semivowel is a sound, such as English or , that is phonetically similar to a vowel sound but functions as the syllable boundary rather than as the nucleus of a syllable.-Classification:... |
ව | 0DC0 | va | [ʋa] | ය | 0DBA | ya | [ja] | glide Semivowel In phonetics and phonology, a semivowel is a sound, such as English or , that is phonetically similar to a vowel sound but functions as the syllable boundary rather than as the nucleus of a syllable.-Classification:... |
||
| retroflex | ණ | 0DAB | [na] | ළ | 0DC5 | [la] | retroflex | ||||
| Display this table as an image | |||||||||||
Vowels
.svg.png)
While
| colspan="24" | |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vowels | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| short | long | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| independent | diacritic | independent | diacritic | ||||||||||||||||||||
| අ | 0D85 | a | [a] | inherent | a | [a, ə] | ආ | 0D86 | ā | [aː] | ා | 0DCF | ā | [aː] | |||||||||
| එ | 0D91 | e | [e] | ෙ | 0DD9 | e | [e] | ඒ | 0D92 | ē | [eː] | ේ | 0DDA | ē | [eː] | ||||||||
| ඉ | 0D89 | i | [i] | ි | 0DD2 | i | [i] | ඊ | 0D8A | ī | [iː] | ී | 0DD3 | ī | [iː] | ||||||||
| ඔ | 0D94 | o | [o] | ො | 0DDC | o | [o] | ඕ | 0D95 | ō | [oː] | ෝ | 0DDD | ō | [oː] | ||||||||
| උ | 0D8B | u | [u] | ු | 0DD4 | u | [u] | ඌ | 0D8C | ū | [uː] | ූ | 0DD6 | ū | [uː] | ||||||||
| ඇ | 0D87 | æ/ä | [æ] | ැ | 0DD0 | æ | [æ] | ඈ | 0D88 | [æː] | ෑ | 0DD1 | [æː] | ||||||||||
| Display this table as an image | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Prenasalized consonants
The prenasalized consonantPrenasalized consonant
Prenasalized consonants are phonetic sequences of a nasal and an obstruent that behave phonologically like single consonants. The reasons for considering these sequences to be single consonants is in their behavior, not in their actual composition...
s resemble their plain counterparts. is made up by the left half of ⟨m⟩ and the right half of ⟨b⟩, while the other three are just like the grapheme for the stop with a little stroke attached to their left. Vowel diacritics attach in the same way as they would to the corresponding plain stop.
| colspan="9" | |
||||||||
| Prenasalized consonants | ||||||||
| nasal | obstruent | prenasalized consonant |
unicode | translit. | IPA | |||
| velar | ඞ | ග | ඟ | 0D9F | [ⁿɡa] | velar | ||
| retroflex | ණ | ඩ | ඬ | 0DAC | [ⁿɖa] | retroflex | ||
| dental | න | ද | ඳ | 0DB3 | [ⁿda] | dental | ||
| labial | ම | බ | ඹ | 0DB9 | [ᵐba] | labial | ||
| Display this table as an image | ||||||||
Non-vocalic diacritics

Anusvara
Anusvara is the diacritic used to mark a type of nasalization used in a number of Indic languages. Depending on the location of the anusvara in the word and the language within which it is used, its exact pronunciation can vary greatly....
(often called binduva 'zero' ) is represented by one small circle ං (unicode 0D82), and the Visarga
Visarga
Visarga is a Sanskrit word meaning "sending forth, discharge". In Sanskrit phonology , is the name of a phone, , written as IAST , Harvard-Kyoto , Devanagari . Visarga is an allophone of and in pausa...
(technically part of the miśra alphabet) by two ඃ (unicode 0D83). The inherent vowel can be removed by a special diacritic, the hal kirīma(්), which varies in shape according to the consonant it attaches to. Both are represented in the image on the right side. The first one is the most common one, while the second one is used for letters ending at the top left corner.
Miśra set
The miśra alphabet is a supersetSuperSet
SuperSet Software was a group founded by friends and former Eyring Research Institute co-workers Drew Major, Dale Neibaur, Kyle Powell and later joined by Mark Hurst...
of śuddha. It adds letters for aspirates, retroflexes and sibilants, which are not phonemic in today's Sinhala, but which are necessary to represent non-native words, like loanword
Loanword
A loanword is a word borrowed from a donor language and incorporated into a recipient language. By contrast, a calque or loan translation is a related concept where the meaning or idiom is borrowed rather than the lexical item itself. The word loanword is itself a calque of the German Lehnwort,...
s from Sanskrit
Tatsama
Tatsama are Sanskrit loanwords in modern Indic languages like Bengali, Marathi, Hindi, Gujarati, Sinhala and Central Dravidian language Telugu. They belong to a higher and more erudite register than common words. That register can be compared to the use of words of Greek origin in English Tatsama...
, Pali or English
Sinhalese words of English Origin
Sinhala is the mother tongue of the Sinhalese people, who make up the largest ethnic group in Sri Lanka, numbering about 15 million. Sinhala is also spoken by other ethnic groups in Sri Lanka, totalling about 3 million. It belongs to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages...
. The use of the extra letters is mainly a question of prestige. From a purely phonemic point of view, there is no benefit in using them, and they can be replaced by a (sequence of) śuddha letters as follows: For the miśra aspirates, the replacement is the plain
Tenuis consonant
In linguistics, a tenuis consonant is a stop or affricate which is unvoiced, unaspirated, and unglottalized. That is, it has a "plain" phonation like , with a voice onset time close to zero, as in Spanish p, t, ch, k, or as in English p, t, k after s .In transcription, tenuis consonants are not...
śuddha counterpart, for the miśra retroflex liquids
Liquid consonant
In phonetics, liquids or liquid consonants are a class of consonants consisting of lateral consonants together with rhotics.-Description:...
the corresponding śuddha coronal
Coronal consonant
Coronal consonants are consonants articulated with the flexible front part of the tongue. Only the coronal consonants can be divided into apical , laminal , domed , or subapical , as well as a few rarer orientations, because only the front of the tongue has such...
liquid, for the sibilants,
| colspan="12" | |
|||||||||||
| Extra miśra stops | |||||||||||
| voiceless | voiced | ||||||||||
| unicode | translit. | IPA | unicode | translit. | IPA | ||||||
| velar | ඛ | 0D9B | kha | [ka] | ඝ | 0D9D | gha | [ɡa] | velar | ||
| retroflex | ඨ | 0DA8 | [ʈa] | ඪ | 0DAA | [ɖa] | retroflex | ||||
| dental | ථ | 0DAE | tha | [ta] | ධ | 0DB0 | dha | [da] | dental | ||
| labial | ඵ | 0DB5 | pha | [pa] | භ | 0DB7 | bha | [ba] | labial | ||
| Other additional miśra graphemes | |||||||||||
| unicode | translit. | IPA | unicode | translit. | IPA | ||||||
| sibilants | ශ | 0DC1 | śa | [sa] | ෂ | 0DC2 | [sa] | sibilants | |||
| aspirate affricates | ඡ | 0DA1 | cha | [t͡ʃa] | ඣ | 0DA3 | jha | [d͡ʒa] | aspirate affricates | ||
| nasals | ඤ | 0DA4 | ña | [ɲa] | ඥ | 0DA5 | gna | [ɡna] | nasals | ||
| other | ඞ | 0D9E | [ŋa] | ෆ | 0DC6 | fa | [fa, ɸa, pa] | other | |||
| other | ඦ | 0DA6 | [nd͡ʒa] | fප | n/a | fa | [fa, ɸa, pa] | other | |||
| Display this table as an image | |||||||||||
There are six additional vocalic diacritics in the miśra alphabet. The two diphthong
Diphthong
A diphthong , also known as a gliding vowel, refers to two adjacent vowel sounds occurring within the same syllable. Technically, a diphthong is a vowel with two different targets: That is, the tongue moves during the pronunciation of the vowel...
s are quite common, while the "syllabic" is much rarer, and the "syllabic" is all but obsolete. The latter are almost exclusively found in loanwords from Sanskrit.
The miśra can be also be written with śuddha ⟨r⟩+⟨u⟩ or ⟨u⟩+⟨r⟩, which corresponds to the actual pronunciation
Pronunciation
Pronunciation refers to the way a word or a language is spoken, or the manner in which someone utters a word. If one is said to have "correct pronunciation", then it refers to both within a particular dialect....
. The miśra syllabic is obsolete, but can be rendered by śuddha ⟨l⟩+⟨i⟩. Miśra ⟨au⟩ is rendered as śuddha ⟨awu⟩, miśra ⟨ai⟩ as śuddha ⟨ayi⟩.
| colspan="24" | |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vocalic diacritics | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| independent | diacritic | independent | diacritic | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| diphthong Diphthong A diphthong , also known as a gliding vowel, refers to two adjacent vowel sounds occurring within the same syllable. Technically, a diphthong is a vowel with two different targets: That is, the tongue moves during the pronunciation of the vowel... s |
ඓ | 0D93 | ai | [ai] | ෛ | 0DDB | ai | [ai] | ඖ | 0D96 | au | [au] | ෞ | 0DDE | au | [au] | diphthongs | |||||||||
| syllabic r Syllabic consonant A syllabic consonant is a consonant which either forms a syllable on its own, or is the nucleus of a syllable. The diacritic for this in the International Phonetic Alphabet is the under-stroke, ⟨⟩... |
ඍ | 0D8D | [ur] | ෘ | 0DD8 | [ru, ur] | ඎ | 0D8E | [ruː] | ෲ | 0DF2 | [ruː, uːr] | syllabic r | |||||||||||||
| syllabic l Syllabic consonant A syllabic consonant is a consonant which either forms a syllable on its own, or is the nucleus of a syllable. The diacritic for this in the International Phonetic Alphabet is the under-stroke, ⟨⟩... |
ඏ | 0D8F | [li] | ෟ | 0DDF | [li] | ඐ | 0D90 | [liː] | ෳ | 0DF3 | [liː] | syllabic l | |||||||||||||
| Display this table as an image | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Note that the transliteration of both and is . This is not very problematic as the second one is extremely scarce.
Names of the graphemes
The letters of the English alphabet have more or less arbitrary names, e.g. em for the letterEpenthesis
In phonology, epenthesis is the addition of one or more sounds to a word, especially to the interior of a word. Epenthesis may be divided into two types: excrescence, for the addition of a consonant, and anaptyxis for the addition of a vowel....
a is added for easier pronunciation: the name for the letter ක් is akyanna. Another naming convention is to use al- before a letter with suppressed vowel, thus alkayanna.
Since the extra miśra letters are phonetically not distinguishable from the śuddha letters, proceeding in the same way would lead to confusion. Names of miśra letters are normally made up of the names of two śuddha letters pronounced as one word. The first one indicates the sound, the second one the shape. For example, the aspirated ඛ (kh) is called bayanu kayanna. kayanna indicates the sound, while bayanu indicates the shape: ඛ (kh) is similar in shape to බ (b) (bayunu = like bayanna).
Another method is to qualify the miśra aspirates by mahāprāna (ඛ: mahāprāna kayanna) and the miśra retroflexes by mūrdhaja (ළ: mūrdhaja layanna).
Ligatures

Furthermore, very frequent combinations are often written in one stroke, like ddh, kv or kś. If this is the case, the first consonant is not marked with a hal kirīma.

Glyph
A glyph is an element of writing: an individual mark on a written medium that contributes to the meaning of what is written. A glyph is made up of one or more graphemes....
for śrī, which is composed of the letter ś with the vowel ī marked above and a ligature indicating the r below. The image on the right shows ligatures of ද(d)+ය(y) and ක(k)+ෂි (ṣi) on the Political science course advertisement.
Similarities to other scripts
Sinhala is one of the Brahmic scriptsBrahmic family
The Brahmic or Indic scripts are a family of abugida writing systems. They are used throughout South Asia , Southeast Asia, and parts of Central and East Asia, and are descended from the Brāhmī script of the ancient Indian subcontinent...
, and thus shares many similarities with other members of the family, such as the Tamil script
Tamil script
The Tamil script is a script that is used to write the Tamil language as well as other minority languages such as Badaga, Irulas, and Paniya...
and Devanāgarī
Devanagari
Devanagari |deva]]" and "nāgarī" ), also called Nagari , is an abugida alphabet of India and Nepal...
. As a general example, /a/ is the inherent vowel in all three scripts. Other similarities include the diacritic for
- Sinhala e: ෙ, Sinhala ā: ා, Sinhala o: ො
- Tamil e:ெ, Tamil ā: ா, Tamil o: ொ
- Devanāgarī e: ` ,Devanāgarī ā: ा, Devanāgarī o: ो
The diacritic for
Sinhala transliteration
Sinhala transliterationTransliteration
Transliteration is a subset of the science of hermeneutics. It is a form of translation, and is the practice of converting a text from one script into another...
can be done in analogy to Devanāgarī transliteration
Devanagari transliteration
There are several methods of transliteration from Devanāgarī to the Roman script, which is a process also known as Romanization in the Indian subcontinent...
.
A problem is the transliteration of /ඇ/, not found in Devanāgarī. This is <ä> in the German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
tradition of Wilhelm Geiger
Wilhelm Geiger
Wilhelm Ludwig Geiger was a German Orientalist, in the fields of Indian and Iranian languages. He was known as a specialist in Pali, Sinhala language and the Dhivehi language of the Maldives.-Life:...
, and <æ> in the Anglophone tradition (e.g. James Gair
James Gair
James W. Gair is a linguist in South Asian linguistics. He is a specialist in Sinhala, as well as in Pali, Tamil and Dhivehi. He teaches in the Department of Modern Languages and Linguistics of Cornell University .-Works:...
).
Layman's transliterations in Sri Lanka normally follow neither of these. Vowels are transliterated according to English spelling equivalences, which can yield a variety of spellings for a number of phonemes. /iː/ for instance can be
A transliteration pattern peculiar to Sinhala, and facilitated by the absence of phonemic aspirates, is the use of
This is presumably because the retroflex stop /ʈ/ is perceived the same as the English alveolar stop /t/, and the Sinhala dental stop /t̪/ is equated with the English voiceless dental fricative
Voiceless dental fricative
The voiceless dental non-sibilant fricative is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. It is familiar to English speakers as the 'th' in thing. Though rather rare as a phoneme in the world's inventory of languages, it is encountered in some of the most widespread and influential...
/θ/. Dental and retroflex voiced stops are alway rendered as
Unicode
Sinhala script was added to the UnicodeUnicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
Standard in September, 1999 with the release of version 3.0.
The Unicode block for Sinhala is U+0D80–U+0DFF. Grey areas indicate non-assigned code points.
This character allocation has been adopted in Sri Lanka as the Standard SLS1134.
Computer support

Sinhala does not come built in with Windows XP
Windows XP
Windows XP is an operating system produced by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops and media centers. First released to computer manufacturers on August 24, 2001, it is the second most popular version of Windows, based on installed user base...
, unlike Tamil
Tamil language
Tamil is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by Tamil people of the Indian subcontinent. It has official status in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu and in the Indian union territory of Pondicherry. Tamil is also an official language of Sri Lanka and Singapore...
and Hindi
Hindi
Standard Hindi, or more precisely Modern Standard Hindi, also known as Manak Hindi , High Hindi, Nagari Hindi, and Literary Hindi, is a standardized and sanskritized register of the Hindustani language derived from the Khariboli dialect of Delhi...
. However, all versions of Windows Vista
Windows Vista
Windows Vista is an operating system released in several variations developed by Microsoft for use on personal computers, including home and business desktops, laptops, tablet PCs, and media center PCs...
come with Sinhala support by default, and do not require external font
Font
In typography, a font is traditionally defined as a quantity of sorts composing a complete character set of a single size and style of a particular typeface...
s to be installed to read Sinhalese script.
For OS X, Sinhala font and keyboard support can be found at http://web.nickshanks.com/typography/ and at http://www.xenotypetech.com/osxSinhala.html
For Linux
Linux
Linux is a Unix-like computer operating system assembled under the model of free and open source software development and distribution. The defining component of any Linux system is the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released October 5, 1991 by Linus Torvalds...
, the scim
SCIM
The Smart Common Input Method platform is an input method platform containing support for more than thirty languages for POSIX-style operating systems including Linux and BSD....
input method selector allows to use Sinhala script in applications like terminals
Computer terminal
A computer terminal is an electronic or electromechanical hardware device that is used for entering data into, and displaying data from, a computer or a computing system...
or web browser
Web browser
A web browser is a software application for retrieving, presenting, and traversing information resources on the World Wide Web. An information resource is identified by a Uniform Resource Identifier and may be a web page, image, video, or other piece of content...
s.
- History of Sinhala SoftwareHistory of Sinhala SoftwareSinhala language software for computers have been present since the late 1980s but no standard character representation system was put in place which resulted in proprietary character representation systems and fonts...
Online resources
- Sinhala guide of the Sinhalese Wikipedia (in English)
- Online Sinhala Unicode Writer
- Sinhala Unicode Support Group
- Online Unicode Converter
See also
- Sinhala numeralsSinhala numeralsSinhala belongs to the Indo-European language family with its roots deeply associated with Indo-Aryan sub family to which the languages such as Persian and Hindi belong [Histroy1]...
- Dutch loanwords in Sinhala
- English loanwords in Sinhala
- Portuguese loanwords in Sinhala
- Tamil loanwords in Sinhala
External links
- Sinhala Unicode Character Code Chart
- Complete table of consonant-diacritic-combinations
- Complete table of consonant-diacritic-combinations as text
- Sinhala page at Omniglot
- Transliteration Add-on for Firefox (Tamil script to Sinhala script
- Sinhala Accepted As One Of The World’s Most Creative Alphabets
Image list for readers with font problems
The source of this article is wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. The text of this article is licensed under the GFDL.