
Writing system
Encyclopedia
A writing system is a symbolic system
Symbolic system
In the fields of anthropology, sociology, and psychology, symbolic system refers to a system of interconnected symbolic meanings. In particular, the field focuses on the dynamic relationships between various symbols within different task or theoretical contexts...
used to represent elements or statements expressible in language
Language
Language may refer either to the specifically human capacity for acquiring and using complex systems of communication, or to a specific instance of such a system of complex communication...
.
General properties
Writing systems are distinguished from other possible symbolic communicationSymbolic communication
Symbolic communication is exchange of messages that change a priori expectation of events. Examples of this are modern communication technology as also exchange of information amongst animals....
systems in that the reader must usually understand something of the associated spoken language
Spoken language
Spoken language is a form of human communication in which words derived from a large vocabulary together with a diverse variety of names are uttered through or with the mouth. All words are made up from a limited set of vowels and consonants. The spoken words they make are stringed into...
to comprehend the text. In contrast, other possible symbolic systems such as information sign
Information sign
An information sign is a very legibly printed and very noticeable placard that informs people of the purpose of an object, or gives them instruction on the use of something. An example is a traffic sign such as a stop sign....
s, painting
Painting
Painting is the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a surface . The application of the medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush but other objects can be used. In art, the term painting describes both the act and the result of the action. However, painting is...
, map
Map
A map is a visual representation of an area—a symbolic depiction highlighting relationships between elements of that space such as objects, regions, and themes....
s and mathematics
Mathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
often do not require prior knowledge of a spoken language.
Every human community possesses language, which many regard as an innate and defining condition of mankind. However, the development of writing systems, and the process by which they have supplanted traditional oral
Orality
Orality is thought and verbal expression in societies where the technologies of literacy are unfamiliar to most of the population. The study of orality is closely allied to the study of oral tradition...
systems of communication has been sporadic, uneven and slow. Once established, writing systems generally change more slowly than their spoken counterparts. Thus, they often preserve features and expressions which are no longer current in the spoken language. The great benefit of writing systems is their ability to maintain a persistent record of information
Information
Information in its most restricted technical sense is a message or collection of messages that consists of an ordered sequence of symbols, or it is the meaning that can be interpreted from such a message or collection of messages. Information can be recorded or transmitted. It can be recorded as...
expressed in a language, which can be retrieved independently of the initial act of formulation
Formulation
Formulation may refer to:* Clinical formulation* Formulations * Formulation science* Pharmaceutical formulation:** Galenic formulation* Pesticide formulation...
.
All writing systems require:
- at least one set of defined base elements or symbolSymbolA symbol is something which represents an idea, a physical entity or a process but is distinct from it. The purpose of a symbol is to communicate meaning. For example, a red octagon may be a symbol for "STOP". On a map, a picture of a tent might represent a campsite. Numerals are symbols for...
s, individually termed characters and collectively called a script; - at least one set of rules and conventions (orthographyOrthographyThe orthography of a language specifies a standardized way of using a specific writing system to write the language. Where more than one writing system is used for a language, for example Kurdish, Uyghur, Serbian or Inuktitut, there can be more than one orthography...
) understood and shared by a community, which arbitrarily assigns meaning to the base elements (graphemes), their ordering and relations to one another; - at least one language (generally spokenSpoken languageSpoken language is a form of human communication in which words derived from a large vocabulary together with a diverse variety of names are uttered through or with the mouth. All words are made up from a limited set of vowels and consonants. The spoken words they make are stringed into...
) whose constructions are represented and able to be recalled by the interpretation of these elements and rules; - some physical means of distinctly representing the symbols by application to a permanent or semi-permanent mediumMedium- Communication :* Medium , storage and/or transmission tools used to store and deliver information or data* Transmission medium, in physics and telecommunications, any material substance which can propagate waves or energy...
, so they may be interpreted (usually visually, but tactile systems have also been devised).
Basic terminology

The generic term text refers to an individual product of a writing system. The act of composing a text may be referred to as writing
Writing
Writing is the representation of language in a textual medium through the use of a set of signs or symbols . It is distinguished from illustration, such as cave drawing and painting, and non-symbolic preservation of language via non-textual media, such as magnetic tape audio.Writing most likely...
, and the act of interpreting the text as reading. Likewise, orthography
Orthography
The orthography of a language specifies a standardized way of using a specific writing system to write the language. Where more than one writing system is used for a language, for example Kurdish, Uyghur, Serbian or Inuktitut, there can be more than one orthography...
refers to the method and rules of observed writing structure (literal meaning, "correct writing"), and particularly for alphabet
Alphabet
An alphabet is a standard set of letters—basic written symbols or graphemes—each of which represents a phoneme in a spoken language, either as it exists now or as it was in the past. There are other systems, such as logographies, in which each character represents a word, morpheme, or semantic...
ic systems, includes the concept of spelling
Spelling
Spelling is the writing of one or more words with letters and diacritics. In addition, the term often, but not always, means an accepted standard spelling or the process of naming the letters...
.
A grapheme is the technical term coined to refer to the specific base or atomic units of a given writing system. Graphemes are the minimally significant elements which taken together comprise the set of "building blocks" out of which texts of a given writing system may be constructed, along with rules of correspondence and use. The concept is similar to that of the phoneme
Phoneme
In a language or dialect, a phoneme is the smallest segmental unit of sound employed to form meaningful contrasts between utterances....
used in the study of spoken languages. For example, in the Latin
Latin
Latin is an Italic language originally spoken in Latium and Ancient Rome. It, along with most European languages, is a descendant of the ancient Proto-Indo-European language. Although it is considered a dead language, a number of scholars and members of the Christian clergy speak it fluently, and...
-based writing system of standard contemporary English, examples of graphemes include the majuscule and minuscule forms of the twenty-six letters of the alphabet (corresponding to various phonemes), marks of punctuation
Punctuation
Punctuation marks are symbols that indicate the structure and organization of written language, as well as intonation and pauses to be observed when reading aloud.In written English, punctuation is vital to disambiguate the meaning of sentences...
(mostly non-phonemic), and a few other symbols such as those for numerals (logograms for numbers).
Note that an individual grapheme may be represented in a wide variety of ways, where each variation is visually distinct in some regard, but all are interpreted as representing the "same" grapheme. These individual variations are known as allographs of a grapheme (compare with the term allophone
Allophone
In phonology, an allophone is one of a set of multiple possible spoken sounds used to pronounce a single phoneme. For example, and are allophones for the phoneme in the English language...
used in linguistic study). For example, the minuscule letter a has different allographs when written as a cursive
Cursive
Cursive, also known as joined-up writing, joint writing, or running writing, is any style of handwriting in which the symbols of the language are written in a simplified and/or flowing manner, generally for the purpose of making writing easier or faster...
, block, or typed
Typeface
In typography, a typeface is the artistic representation or interpretation of characters; it is the way the type looks. Each type is designed and there are thousands of different typefaces in existence, with new ones being developed constantly....
letter. The selection between different allographs may be influenced by the medium used, the writing instrument
Writing implement
A writing implement or writing instrument is an object used to produce writing. Most of these items can be also used for other functions such as painting, drawing and technical drawing, but writing instruments generally have the unique requirement to create a smooth, controllable line.Another...
, the stylistic choice of the writer and the largely unconscious features of an individual's handwriting
Handwriting
Handwriting is a person's particular & individual style of writing with pen or pencil, which contrasts with "Hand" which is an impersonal and formalised writing style in several historical varieties...
.
The terms glyph
Glyph
A glyph is an element of writing: an individual mark on a written medium that contributes to the meaning of what is written. A glyph is made up of one or more graphemes....
, sign
Sign (linguistics)
There are many models of the linguistic sign . A classic model is the one by the Swiss linguist Ferdinand de Saussure. According to him, language is made up of signs and every sign has two sides : the signifier , the "shape" of a word, its phonic component, i.e...
and character are sometimes used to refer to a grapheme. Common usage varies from discipline to discipline; compare cuneiform sign
Cuneiform script
Cuneiform script )) is one of the earliest known forms of written expression. Emerging in Sumer around the 30th century BC, with predecessors reaching into the late 4th millennium , cuneiform writing began as a system of pictographs...
, Maya glyph
Maya script
The Maya script, also known as Maya glyphs or Maya hieroglyphs, is the writing system of the pre-Columbian Maya civilization of Mesoamerica, presently the only Mesoamerican writing system that has been substantially deciphered...
, Chinese character
Chinese character
Chinese characters are logograms used in the writing of Chinese and Japanese , less frequently Korean , formerly Vietnamese , or other languages...
. The glyphs of most writing systems are made up of lines (or strokes) and are therefore called linear, but there are glyphs in non-linear writing systems made up of other types of marks, such as Cuneiform and Braille
Braille
The Braille system is a method that is widely used by blind people to read and write, and was the first digital form of writing.Braille was devised in 1825 by Louis Braille, a blind Frenchman. Each Braille character, or cell, is made up of six dot positions, arranged in a rectangle containing two...
.
Writing systems are conceptual system
Conceptual system
A conceptual system is a system that is composed of non-physical objects, i.e. ideas or concepts. In this context a system is taken to mean "an interrelated, interworking set of objects".- Overview :...
s, as are the languages to which they refer. Writing systems may be regarded as complete according to the extent to which they are able to represent all that may be expressed in the spoken language.
History of writing systems

Ideogram
An ideogram or ideograph is a graphic symbol that represents an idea or concept. Some ideograms are comprehensible only by familiarity with prior convention; others convey their meaning through pictorial resemblance to a physical object, and thus may also be referred to as pictograms.Examples of...
and/or early mnemonic
Mnemonic
A mnemonic , or mnemonic device, is any learning technique that aids memory. To improve long term memory, mnemonic systems are used to make memorization easier. Commonly encountered mnemonics are often verbal, such as a very short poem or a special word used to help a person remember something,...
symbols. The best known examples are:
- Jiahu symbolsJiahu symbolsJiahu symbols refer to the 16 distinct markings on prehistoric artifacts found in Jiahu, a neolithic Peiligang culture site found in Henan, China, and excavated in 1999 C.E...
, carved on tortoiseTortoiseTortoises are a family of land-dwelling reptiles of the order of turtles . Like their marine cousins, the sea turtles, tortoises are shielded from predators by a shell. The top part of the shell is the carapace, the underside is the plastron, and the two are connected by the bridge. The tortoise...
shells in JiahuJiahuJiahu was the site of a Neolithic Yellow River settlement based in the central plains of ancient China, modern Wuyang, Henan Province. Archaeologists consider the site to be one of the earliest examples of the Peiligang culture. Settled from 7000 to 5800 BC, the site was later flooded and abandoned...
, ca. 6600 BC - Vinča signs (Tărtăria tabletsTartaria tabletsThe Tărtăria tablets are three tablets, known since the late 19th century excavation at the Neolithic site of Turdaş in Transylvania Romania, by Zsófia Torma, which date to around 5300 BC...
), ca. 5300 BC - Early Indus scriptIndus scriptThe term Indus script refers to short strings of symbols associated with the Indus Valley Civilization, in use during the Early Harappan and Mature Harappan period, between the 35th and 20th centuries BC. In spite of many attempts at decipherments and claims, it is as yet undeciphered...
, ca. 3500 BC
The invention of the first writing systems is roughly contemporary with the beginning of the Bronze Age
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a period characterized by the use of copper and its alloy bronze as the chief hard materials in the manufacture of some implements and weapons. Chronologically, it stands between the Stone Age and Iron Age...
in the late Neolithic
Neolithic
The Neolithic Age, Era, or Period, or New Stone Age, was a period in the development of human technology, beginning about 9500 BC in some parts of the Middle East, and later in other parts of the world. It is traditionally considered as the last part of the Stone Age...
of the late 4th millennium BC
4th millennium BC
The 4th millennium BC saw major changes in human culture. It marked the beginning of the Bronze Age and of writing.The city states of Sumer and the kingdom of Egypt were established and grew to prominence. Agriculture spread widely across Eurasia...
. The Sumerian
Sumerian language
Sumerian is the language of ancient Sumer, which was spoken in southern Mesopotamia since at least the 4th millennium BC. During the 3rd millennium BC, there developed a very intimate cultural symbiosis between the Sumerians and the Akkadians, which included widespread bilingualism...
archaic cuneiform script and the Egyptian hieroglyphs
Egyptian hieroglyphs
Egyptian hieroglyphs were a formal writing system used by the ancient Egyptians that combined logographic and alphabetic elements. Egyptians used cursive hieroglyphs for religious literature on papyrus and wood...
are generally considered the earliest writing systems, both emerging out of their ancestral proto-literate symbol systems from 3400–3200 BC with earliest coherent texts from about 2600 BC
26th century BC
The 26th century BC is a century which lasted from the year 2600 BC to 2501 BC .-Events:*c. 2900 BC – 2334 BC: Mesopotamian wars of the Early Dynastic period continue....
. It is generally agreed that Sumerian writing was an independent invention; however, it is debated whether Egyptian writing was developed completely independently of Sumerian, or was a case of cultural diffusion
Cultural diffusion
In cultural anthropology and cultural geography, cultural diffusion, as first conceptualized by Alfred L. Kroeber in his influential 1940 paper Stimulus Diffusion, or trans-cultural diffusion in later reformulations, is the spread of cultural items—such as ideas, styles, religions, technologies,...
.
A similar debate exists for the Chinese script, which developed around 1200 BC.
The pre-Columbian
Pre-Columbian
The pre-Columbian era incorporates all period subdivisions in the history and prehistory of the Americas before the appearance of significant European influences on the American continents, spanning the time of the original settlement in the Upper Paleolithic period to European colonization during...
Mesoamerican writing systems
Mesoamerican writing systems
Mesoamerica, like India, Mesopotamia, China, and Egypt, is one of the few places in the world where writing has developed independently. Mesoamerican scripts deciphered to date are logosyllabic, combining the use of logograms with a syllabary, and they are often called hieroglyphic scripts...
(including among others Olmec
Olmec
The Olmec were the first major Pre-Columbian civilization in Mexico. They lived in the tropical lowlands of south-central Mexico, in the modern-day states of Veracruz and Tabasco....
and Maya script
Maya script
The Maya script, also known as Maya glyphs or Maya hieroglyphs, is the writing system of the pre-Columbian Maya civilization of Mesoamerica, presently the only Mesoamerican writing system that has been substantially deciphered...
s) are generally believed to have had independent origins.
It is thought that the first consonantal alphabetic writing appeared before 2000 BC, as a representation of language developed by Semitic
Semitic
In linguistics and ethnology, Semitic was first used to refer to a language family of largely Middle Eastern origin, now called the Semitic languages...
tribes in the Sinai-peninsula (see History of the alphabet
History of the alphabet
The origins of the alphabet are unknown, but there are several theories as to how it developed. One popular proposal — the Proto-Sinaitic theory — is that the history of the alphabet began in Ancient Egypt, more than a millennium into the history of writing...
). Most other alphabets in the world today either descended from this one innovation, many via the Phoenician alphabet
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
, or were directly inspired by its design.
The first true alphabet is the Greek script
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
which consistently represents vowel
Vowel
In phonetics, a vowel is a sound in spoken language, such as English ah! or oh! , pronounced with an open vocal tract so that there is no build-up of air pressure at any point above the glottis. This contrasts with consonants, such as English sh! , where there is a constriction or closure at some...
s since 800 BC. The Latin alphabet
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
, a direct descendant, is by far the most common writing system in use.
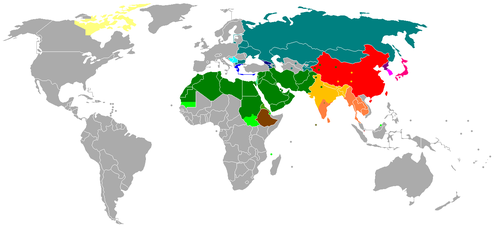
Functional classification of writing systems

- pictographic script
- ideographic script
- analytic transitional script
- phonetic script
- alphabetic script
as too simplistic, often considering the categories to be incomparable.
Hill split writing into three major categories of linguistic analysis, one of which covers discourses and is not usually considered writing proper:
- discourse system
- iconic discourse system, e.g. Amerindian
- conventional discourse system, e.g. QuipuQuipuQuipus or khipus were recording devices used in the Inca Empire and its predecessor societies in the Andean region. A quipu usually consisted of colored, spun, and plied thread or strings from llama or alpaca hair. It could also be made of cotton cords...
- morphemic writing system, e.g. Egyptian, SumerianCuneiformCuneiform can refer to:*Cuneiform script, an ancient writing system originating in Mesopotamia in the 4th millennium BC*Cuneiform , three bones in the human foot*Cuneiform Records, a music record label...
, Maya, ChineseSinogramSinogram can mean,* a Chinese character even when used in a different language, such as Japanese , Korean or Vietnamese* a tetragram which follows the graphic conventions of Chinese characters, e.g... - phonemic writing system
- partial phonemic writing system, e.g. Egyptian, Hebrew, Arabic
- poly-phonemic writing system, e.g. Linear BLinear BLinear B is a syllabic script that was used for writing Mycenaean Greek, an early form of Greek. It pre-dated the Greek alphabet by several centuries and seems to have died out with the fall of Mycenaean civilization...
, KanaKanaKana are the syllabic Japanese scripts, as opposed to the logographic Chinese characters known in Japan as kanji and the Roman alphabet known as rōmaji...
, Cherokee - mono-phonemic writing system
- phonemic writing system, e.g. Ancient Greek, Old English
- morpho-phonemic writing system, e.g. German, Modern English
DeFrancis, criticizing Sampson’s introduction of semasiographic writing and featural alphabets stresses the phonographic quality of writing proper
- pictures
- nonwriting
- writing
- rebusRebusA rebus is an allusional device that uses pictures to represent words or parts of words. It was a favourite form of heraldic expression used in the Middle Ages to denote surnames, for example in its basic form 3 salmon fish to denote the name "Salmon"...
- syllabic systems
- pure syllabic, e.g. Linear B, Yi, Kana, Cherokee
- morpho-syllabic, e.g. Sumerian, Chinese, Mayan
- consonantal
- morpho-consonantal, e.g. Egyptian
- pure consonantal, e.g. Phoenician
- alphabetic
- pure phonemic, e.g. Greek
- morpho-phonemic, e.g. English
- syllabic systems
- rebus
Faber categorizes phonographic writing by two levels, linearity and coding:
- logographic, e.g. ChineseSinogramSinogram can mean,* a Chinese character even when used in a different language, such as Japanese , Korean or Vietnamese* a tetragram which follows the graphic conventions of Chinese characters, e.g...
, Ancient Egyptian - phonographic
- syllabically linear
- syllabically coded, e.g. KanaKanaKana are the syllabic Japanese scripts, as opposed to the logographic Chinese characters known in Japan as kanji and the Roman alphabet known as rōmaji...
, Akkadian - segmentally coded, e.g. Hebrew, Syriac, Arabic, Ethiopian, Amharic, DevanagariDevanagariDevanagari |deva]]" and "nāgarī" ), also called Nagari , is an abugida alphabet of India and Nepal...
- syllabically coded, e.g. Kana
- segmentally linear
- complete (alphabet), e.g. Greco-LatinLatin alphabetThe Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
, Cyrillic - defective, e.g. Ugaritic, Phoenician, Aramaic, Old South ArabianOld South ArabianOld South Arabian is the term used to describe four extinct, closely related languages spoken in the far southern portion of the Arabian Peninsula. There were a number of other Sayhadic languages , of which very little evidence survived, however...
, Old Hebrew
- complete (alphabet), e.g. Greco-Latin
- syllabically linear
| Type | Each symbol represents | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Logographic Logogram A logogram, or logograph, is a grapheme which represents a word or a morpheme . This stands in contrast to phonograms, which represent phonemes or combinations of phonemes, and determinatives, which mark semantic categories.Logograms are often commonly known also as "ideograms"... |
morpheme Morpheme In linguistics, a morpheme is the smallest semantically meaningful unit in a language. The field of study dedicated to morphemes is called morphology. A morpheme is not identical to a word, and the principal difference between the two is that a morpheme may or may not stand alone, whereas a word,... |
Chinese character Chinese character Chinese characters are logograms used in the writing of Chinese and Japanese , less frequently Korean , formerly Vietnamese , or other languages... s |
| Syllabic Syllabary A syllabary is a set of written symbols that represent syllables, which make up words. In a syllabary, there is no systematic similarity between the symbols which represent syllables with the same consonant or vowel... |
syllable Syllable A syllable is a unit of organization for a sequence of speech sounds. For example, the word water is composed of two syllables: wa and ter. A syllable is typically made up of a syllable nucleus with optional initial and final margins .Syllables are often considered the phonological "building... or mora Mora (linguistics) Mora is a unit in phonology that determines syllable weight, which in some languages determines stress or timing. As with many technical linguistic terms, the definition of a mora varies. Perhaps the most succinct working definition was provided by the American linguist James D... |
Japanese kana Kana Kana are the syllabic Japanese scripts, as opposed to the logographic Chinese characters known in Japan as kanji and the Roman alphabet known as rōmaji... |
| Alphabet Alphabet An alphabet is a standard set of letters—basic written symbols or graphemes—each of which represents a phoneme in a spoken language, either as it exists now or as it was in the past. There are other systems, such as logographies, in which each character represents a word, morpheme, or semantic... ic |
phoneme Phoneme In a language or dialect, a phoneme is the smallest segmental unit of sound employed to form meaningful contrasts between utterances.... (consonant or vowel) |
Latin alphabet Latin alphabet The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome... |
| Abugida Abugida An abugida , also called an alphasyllabary, is a segmental writing system in which consonant–vowel sequences are written as a unit: each unit is based on a consonant letter, and vowel notation is obligatory but secondary... |
phoneme (consonant+vowel) | Indian Devanāgarī Devanagari Devanagari |deva]]" and "nāgarī" ), also called Nagari , is an abugida alphabet of India and Nepal... |
| Abjad Abjad An abjad is a type of writing system in which each symbol always or usually stands for a consonant; the reader must supply the appropriate vowel.... |
phoneme (consonant) | Arabic alphabet Arabic alphabet The Arabic alphabet or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.-Consonants:The Arabic alphabet has... |
| Featural Featural alphabet A featural alphabet is an alphabet wherein the shapes of the letters are not arbitrary, but encode phonological features of the phonemes they represent. The term featural was introduced by Geoffrey Sampson to describe Hangul and Pitman Shorthand... |
phonetic feature | Korean hangul Hangul Hangul,Pronounced or ; Korean: 한글 Hangeul/Han'gŭl or 조선글 Chosŏn'gŭl/Joseongeul the Korean alphabet, is the native alphabet of the Korean language. It is a separate script from Hanja, the logographic Chinese characters which are also sometimes used to write Korean... |
Logographic writing systems


Chinese character
Chinese characters are logograms used in the writing of Chinese and Japanese , less frequently Korean , formerly Vietnamese , or other languages...
s are classified as logograms.
As each character represents a single word (or, more precisely, a morpheme
Morpheme
In linguistics, a morpheme is the smallest semantically meaningful unit in a language. The field of study dedicated to morphemes is called morphology. A morpheme is not identical to a word, and the principal difference between the two is that a morpheme may or may not stand alone, whereas a word,...
), many logograms are required to write all the words of language. The vast array of logograms and the memorization of what they mean are the major disadvantage of the logographic systems over alphabetic systems. However, since the meaning is inherent to the symbol, the same logographic system can theoretically be used to represent different languages. In practice, this is only true for closely related languages, like the Chinese language
Chinese language
The Chinese language is a language or language family consisting of varieties which are mutually intelligible to varying degrees. Originally the indigenous languages spoken by the Han Chinese in China, it forms one of the branches of Sino-Tibetan family of languages...
s, as syntactical constraints reduce the portability of a given logographic system. Japanese
Japanese language
is a language spoken by over 130 million people in Japan and in Japanese emigrant communities. It is a member of the Japonic language family, which has a number of proposed relationships with other languages, none of which has gained wide acceptance among historical linguists .Japanese is an...
uses Chinese logograms
Kanji
Kanji are the adopted logographic Chinese characters hanzi that are used in the modern Japanese writing system along with hiragana , katakana , Indo Arabic numerals, and the occasional use of the Latin alphabet...
extensively in its writing systems, with most of the symbols carrying the same or similar meanings. However, the semantics, and especially the grammar, are different enough that a long Chinese text is not readily understandable to a Japanese reader without any knowledge of basic Chinese grammar
Chinese grammar
Standard Chinese shares a similar system of grammar with the many language varieties or dialects of the Chinese language, different from those employed by other language families, and comparable to the similar features found within the Slavic languages or Semitic languages...
, though short and concise phrases such as those on signs and newspaper headlines are much easier to comprehend.
While most languages do not use wholly logographic writing systems many languages use some logograms. A good example of modern western logograms are the Hindu-Arabic numerals — everyone who uses those symbols understands what 1 means whether he or she calls it one, eins, uno, yi, ichi, ehad or jedan. Other western logograms include the ampersand
Ampersand
An ampersand is a logogram representing the conjunction word "and". The symbol is a ligature of the letters in et, Latin for "and".-Etymology:...
&, used for and, the at sign
At sign
The at sign , also called the ampersat, apetail, arroba, atmark, at symbol, commercial at or monkey tail, is formally an abbreviation of the accounting and commercial invoice term "at the rate of"...
@, used in many contexts for at, the percent sign
Percent sign
The percent sign is the symbol used to indicate a percentage .Related signs include the permille sign ‰ and the permyriad sign , which indicate that a number is divided by one thousand or ten thousand respectively...
% and the many signs representing units of currency ($
Dollar sign
The dollar or peso sign is a symbol primarily used to indicate the various peso and dollar units of currency around the world.- Origin :...
, ¢, €
Euro sign
The euro sign is the currency sign used for the euro, the official currency of the Eurozone in the European Union . The design was presented to the public by the European Commission on 12 December 1996. The international three-letter code for the euro is EUR...
, £
Pound sign
The pound sign is the symbol for the pound sterling—the currency of the United Kingdom . The same symbol is used for similarly named currencies in some other countries and territories, such as the Irish pound, Gibraltar pound, Australian pound and the Italian lira...
, ¥ and so on.)
Logograms are sometimes called ideogram
Ideogram
An ideogram or ideograph is a graphic symbol that represents an idea or concept. Some ideograms are comprehensible only by familiarity with prior convention; others convey their meaning through pictorial resemblance to a physical object, and thus may also be referred to as pictograms.Examples of...
s, a word that refers to symbols which graphically represent abstract ideas, but linguists avoid this use, as Chinese characters are often semantic
Semantics
Semantics is the study of meaning. It focuses on the relation between signifiers, such as words, phrases, signs and symbols, and what they stand for, their denotata....
–phonetic compounds, symbols which include an element that represents the meaning and a phonetic complement
Phonetic complement
A phonetic complement is a phonetic symbol used to disambiguate word characters that have multiple readings, in mixed logographic-phonetic scripts such as Egyptian hieroglyphs, Akkadian cuneiform, Japanese, and Mayan...
element that represents the pronunciation. Some nonlinguists distinguish between lexigraphy and ideography, where symbols in lexigraphies represent words and symbols in ideographies represent words or morphemes.
The most important (and, to a degree, the only surviving) modern logographic writing system is the Chinese one, whose characters are or were used, with varying degrees of modification, in Chinese, Japanese, Korean, Vietnamese, and other east Asian languages
East Asian languages
East Asian languages describe two notional groupings of languages in East and Southeast Asia:* Languages which have been greatly influenced by Classical Chinese and the Chinese writing system, in particular Chinese, Japanese, Korean, and Vietnamese .* The larger grouping of languages includes the...
. Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
ian hieroglyphs and the Mayan writing system are also systems with certain logographic features, although they have marked phonetic features as well and are no longer in current use.
Syllabic writing systems
As logographic writing systems use a single symbol for an entire word, a syllabary is a set of written symbols that represent (or approximate) syllableSyllable
A syllable is a unit of organization for a sequence of speech sounds. For example, the word water is composed of two syllables: wa and ter. A syllable is typically made up of a syllable nucleus with optional initial and final margins .Syllables are often considered the phonological "building...
s, which make up word
Word
In language, a word is the smallest free form that may be uttered in isolation with semantic or pragmatic content . This contrasts with a morpheme, which is the smallest unit of meaning but will not necessarily stand on its own...
s. A symbol in a syllabary typically represents a consonant
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are , pronounced with the lips; , pronounced with the front of the tongue; , pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced in the throat; and ,...
sound followed by a vowel
Vowel
In phonetics, a vowel is a sound in spoken language, such as English ah! or oh! , pronounced with an open vocal tract so that there is no build-up of air pressure at any point above the glottis. This contrasts with consonants, such as English sh! , where there is a constriction or closure at some...
sound, or just a vowel alone.
In a "true syllabary", there is no systematic graphic similarity between phonetically related characters (though some do have graphic similarity for the vowels). That is, the characters for /ke/, /ka/ and /ko/ have no similarity to indicate their common "k" sound (voiceless velar plosive). More recent creations such as the Cree syllabary embody a system of varying signs, which can best be seen when arranging the syllabogram set in an onset
Onset
Onset may refer to:*Onset , the beginning of a musical note or sound*Interonset interval, a term in music*Syllable onset, a term in phonetics and phonology*Onset, Massachusetts, village in the United States...
–coda
Syllable coda
In phonology, a syllable coda comprises the consonant sounds of a syllable that follow the nucleus, which is usually a vowel. The combination of a nucleus and a coda is called a rime. Some syllables consist only of a nucleus with no coda...
or onset–rime
Rime
Rime is a coating of ice:*Hard rime, white ice that forms when water droplets in fog freeze to the outer surfaces of objects, such as trees*Soft rime, similar to hard rime, but feathery and milky in appearance...
table.
Another type of writing system with systematic syllabic linear symbols, the abugidas, is discussed below.
Syllabaries are best suited to languages with relatively simple syllable structure, such as Japanese. The English language
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
, on the other hand, allows complex syllable structures, with a relatively large inventory of vowel
Vowel
In phonetics, a vowel is a sound in spoken language, such as English ah! or oh! , pronounced with an open vocal tract so that there is no build-up of air pressure at any point above the glottis. This contrasts with consonants, such as English sh! , where there is a constriction or closure at some...
s and complex consonant cluster
Consonant cluster
In linguistics, a consonant cluster is a group of consonants which have no intervening vowel. In English, for example, the groups and are consonant clusters in the word splits....
s, making it cumbersome to write English words with a syllabary. To write English using a syllabary, every possible syllable in English would have to have a separate symbol, and whereas the number of possible syllables in Japanese is no more than about fifty to sixty, in English there are many thousands.
However, syllabaries with much larger inventories do exist. The Yi script
Yi script
The Yi script, also historically known as Cuan Wen or Wei Shu , is used to write the Yi languages.-Classical Yi:Classical Yi is a syllabic logographic system that was reputedly devised during the Tang dynasty by someone called Aki...
, for example, contains 756 different symbols (or 1,164, if symbols with a particular tone diacritic are counted as separate syllables, as in Unicode
Unicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
). The Chinese script, when used to write Middle Chinese
Middle Chinese
Middle Chinese , also called Ancient Chinese by the linguist Bernhard Karlgren, refers to the Chinese language spoken during Southern and Northern Dynasties and the Sui, Tang, and Song dynasties...
and the modern Chinese languages, also represents syllables, and includes separate glyphs for nearly all of the many thousand syllables in Middle Chinese
Middle Chinese
Middle Chinese , also called Ancient Chinese by the linguist Bernhard Karlgren, refers to the Chinese language spoken during Southern and Northern Dynasties and the Sui, Tang, and Song dynasties...
; however, because it primarily represents morpheme
Morpheme
In linguistics, a morpheme is the smallest semantically meaningful unit in a language. The field of study dedicated to morphemes is called morphology. A morpheme is not identical to a word, and the principal difference between the two is that a morpheme may or may not stand alone, whereas a word,...
s, and includes different characters to represent homophonous morphemes with different meanings, it is normally considered a logographic script rather than a syllabary.
Other languages that use true syllabaries include Mycenae
Mycenae
Mycenae is an archaeological site in Greece, located about 90 km south-west of Athens, in the north-eastern Peloponnese. Argos is 11 km to the south; Corinth, 48 km to the north...
an Greek
Greek language
Greek is an independent branch of the Indo-European family of languages. Native to the southern Balkans, it has the longest documented history of any Indo-European language, spanning 34 centuries of written records. Its writing system has been the Greek alphabet for the majority of its history;...
(Linear B
Linear B
Linear B is a syllabic script that was used for writing Mycenaean Greek, an early form of Greek. It pre-dated the Greek alphabet by several centuries and seems to have died out with the fall of Mycenaean civilization...
) and Native American languages such as Cherokee
Cherokee language
Cherokee is an Iroquoian language spoken by the Cherokee people which uses a unique syllabary writing system. It is the only Southern Iroquoian language that remains spoken. Cherokee is a polysynthetic language.-North American etymology:...
. Several languages of the Ancient Near East
Ancient Near East
The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia , ancient Egypt, ancient Iran The ancient Near East was the home of early civilizations within a region roughly corresponding to the modern Middle East: Mesopotamia...
used forms of cuneiform, which is a syllabary with some non-syllabic elements.
Segmental writing systems: Alphabets
An alphabet is a small set of letters — basic written symbols — each of which roughly represents or represented historically a phonemePhoneme
In a language or dialect, a phoneme is the smallest segmental unit of sound employed to form meaningful contrasts between utterances....
of a spoken language
Language
Language may refer either to the specifically human capacity for acquiring and using complex systems of communication, or to a specific instance of such a system of complex communication...
. The word alphabet is derived from alpha
Alpha (letter)
Alpha is the first letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 1. It was derived from the Phoenician letter Aleph...
and beta
Beta (letter)
Beta is the second letter of the Greek alphabet. In Ancient Greek, beta represented the voiced bilabial plosive . In Modern Greek, it represents the voiced labiodental fricative ....
, the first two symbols of the Greek alphabet
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
.
Consonantal writing systems: Abjads
The first type of alphabet that was developed was the abjad. An abjad is an alphabetic writing system where there is one symbol per consonant. Abjads differ from other alphabets in that they have characters only for consonantConsonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are , pronounced with the lips; , pronounced with the front of the tongue; , pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced in the throat; and ,...
al sounds. Vowels are not usually marked in abjads.
All known abjads (except maybe Tifinagh
Tifinagh
Tifinagh is a series of abjad and alphabetic scripts used by some Berber peoples, notably the Tuareg, to write their language.A modern derivate of the traditional script, known as Neo-Tifinagh, was introduced in the 20th century...
) belong to the Semitic family of scripts, and derive from the original Northern Linear Abjad
Middle Bronze Age alphabets
Proto-Sinaitic is a Middle Bronze Age script attested in a very small collection of inscriptions at Serabit el-Khadim in the Sinai Peninsula. Due to the extreme scarcity of Proto-Sinaitic signs, very little is known with certainty about the nature of the script...
. The reason for this is that Semitic languages
Semitic languages
The Semitic languages are a group of related languages whose living representatives are spoken by more than 270 million people across much of the Middle East, North Africa and the Horn of Africa...
and the related Berber languages
Berber languages
The Berber languages are a family of languages indigenous to North Africa, spoken from Siwa Oasis in Egypt to Morocco , and south to the countries of the Sahara Desert...
have a morphemic structure
Morphology (linguistics)
In linguistics, morphology is the identification, analysis and description, in a language, of the structure of morphemes and other linguistic units, such as words, affixes, parts of speech, intonation/stress, or implied context...
which makes the denotation of vowel
Vowel
In phonetics, a vowel is a sound in spoken language, such as English ah! or oh! , pronounced with an open vocal tract so that there is no build-up of air pressure at any point above the glottis. This contrasts with consonants, such as English sh! , where there is a constriction or closure at some...
s redundant in most cases.
Some abjads (such as Arabic and Hebrew) have markings for vowels as well, but use them only in special contexts, such as for teaching. Many scripts derived from abjads have been extended with vowel symbols to become full alphabets, the most famous case being the derivation of the Greek alphabet
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
from the Phoenician abjad. This has mostly happened when the script was adapted to a non-Semitic language.
The term abjad takes its name from the old order of the Arabic alphabet
Arabic alphabet
The Arabic alphabet or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.-Consonants:The Arabic alphabet has...
's consonant
Consonant
In articulatory phonetics, a consonant is a speech sound that is articulated with complete or partial closure of the vocal tract. Examples are , pronounced with the lips; , pronounced with the front of the tongue; , pronounced with the back of the tongue; , pronounced in the throat; and ,...
s 'alif, bā', jīm, dāl, though the word may have earlier roots in Phoenician
Phoenician languages
Phoenician was a language originally spoken in the coastal region then called "Canaan" in Phoenician, Arabic, Hebrew, and Aramaic, "Phoenicia" in Greek and Latin, and "Pūt" in Ancient Egyptian. Phoenician is a Semitic language of the Canaanite subgroup; its closest living relative is Hebrew, to...
or Ugaritic.
Abjad is still the word for alphabet in Arabic
Arabic language
Arabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book...
, Malay and Indonesian
Indonesian language
Indonesian is the official language of Indonesia. Indonesian is a normative form of the Riau Islands dialect of Malay, an Austronesian language which has been used as a lingua franca in the Indonesian archipelago for centuries....
.
Inherent-vowel writing systems: Abugidas
An abugida is an alphabetic writing system whose basic signs denote consonants with an inherent vowelInherent vowel
An inherent vowel is part of an abugida script. It is the vowel sound which is used with each unmarked or basic consonant symbol....
and where consistent modifications of the basic sign indicate other following vowels than the inherent one.
Thus, in an abugida there may or may not be a sign for "k" with no vowel, but also one for "ka" (if "a" is the inherent vowel), and "ke" is written by modifying the "ka" sign in a way that is consistent with how one would modify "la" to get "le". In many abugidas the modification is the addition of a vowel sign, but other possibilities are imaginable (and used), such as rotation of the basic sign, addition of diacritical marks
Diacritic
A diacritic is a glyph added to a letter, or basic glyph. The term derives from the Greek διακριτικός . Diacritic is both an adjective and a noun, whereas diacritical is only an adjective. Some diacritical marks, such as the acute and grave are often called accents...
and so on.
The contrast with "true syllabaries
Syllabary
A syllabary is a set of written symbols that represent syllables, which make up words. In a syllabary, there is no systematic similarity between the symbols which represent syllables with the same consonant or vowel...
" is that the latter have one distinct symbol per possible syllable, and the signs for each syllable have no systematic graphic similarity. The graphic similarity of most abugidas comes from the fact that they are derived from abjads, and the consonants make up the symbols with the inherent vowel and the new vowel symbols are markings added on to the base symbol.

Canadian Aboriginal Syllabics
Canadian Aboriginal syllabic writing, or simply syllabics, is a family of abugidas used to write a number of Aboriginal Canadian languages of the Algonquian, Inuit, and Athabaskan language families....
can be considered abugidas, although they are rarely thought of in those terms. The largest single group of abugidas is the Brahmic family
Brahmic family
The Brahmic or Indic scripts are a family of abugida writing systems. They are used throughout South Asia , Southeast Asia, and parts of Central and East Asia, and are descended from the Brāhmī script of the ancient Indian subcontinent...
of scripts, however, which includes nearly all the scripts used in India
India
India , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
and Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia
Southeast Asia, South-East Asia, South East Asia or Southeastern Asia is a subregion of Asia, consisting of the countries that are geographically south of China, east of India, west of New Guinea and north of Australia. The region lies on the intersection of geological plates, with heavy seismic...
.
The name abugida is derived from the first four characters of an order of the Ge'ez script used in some contexts. It was borrowed from Ethiopian languages as a linguistic term by Peter T. Daniels
Peter T. Daniels
Peter T. Daniels is a scholar of writing systems, specializing in typology. He was co-editor of the book The World's Writing Systems , and he introduced the terms abjad and abugida as modern linguistic terms...
.
Featural writing systems
A featural script represents finer detail than an alphabet. Here symbols do not represent whole phonemes, but rather the elements (features) that make up the phonemes, such as voicingVoice (phonetics)
Voice or voicing is a term used in phonetics and phonology to characterize speech sounds, with sounds described as either voiceless or voiced. The term, however, is used to refer to two separate concepts. Voicing can refer to the articulatory process in which the vocal cords vibrate...
or its place of articulation
Place of articulation
In articulatory phonetics, the place of articulation of a consonant is the point of contact where an obstruction occurs in the vocal tract between an articulatory gesture, an active articulator , and a passive location...
. Theoretically, each feature could be written with a separate letter; and abjads or abugidas, or indeed syllabaries, could be featural, but the only prominent system of this sort is Korean
Korean language
Korean is the official language of the country Korea, in both South and North. It is also one of the two official languages in the Yanbian Korean Autonomous Prefecture in People's Republic of China. There are about 78 million Korean speakers worldwide. In the 15th century, a national writing...
hangul
Hangul
Hangul,Pronounced or ; Korean: 한글 Hangeul/Han'gŭl or 조선글 Chosŏn'gŭl/Joseongeul the Korean alphabet, is the native alphabet of the Korean language. It is a separate script from Hanja, the logographic Chinese characters which are also sometimes used to write Korean...
. In hangul, the featural symbols are combined into alphabetic letters, and these letters are in turn joined into syllabic blocks, so that the system combines three levels of phonological representation.
Many scholars, e.g. DeFrancis, reject this class or at least labeling hangul as such.
The Korean script is a conscious script creation by literate experts, which Daniels calls a “sophisticated grammatogeny”. These include stenographies and constructed script
Constructed script
A constructed script is a new writing system specifically created by an individual or group, rather than having evolved as part of a language or culture like a natural script...
s of hobbyists and fiction writers (such as Tengwar
Tengwar
The Tengwar are an artificial script created by J. R. R. Tolkien. In his fictional universe of Middle-earth, the tengwar were invented by the Elf Fëanor, and used first to write the Elven tongues: Quenya, Telerin, and also Valarin. Later a great number of languages of Middle-earth were written...
), many of which feature advanced graphic designs corresponding to phonologic properties. The basic unit of writing in these systems can map to anything from phones to words. It has been shown that even the roman script has sub-character “features”.
Ambiguous writing systems
Most writing systems are not purely one type. The English writing system, for example, includes numerals and other logograms such as #, $, and &, and the phonemic letter clusters are a complex match to sound. As mentioned above, all logographic systems have phonetic components as well, whether along the lines of a syllabary, such as Chinese ("logo-syllabic"), or an abjad, as in Egyptian ("logo-consonantal").Some scripts, however, are truly ambiguous. The semi-syllabaries
Semi-syllabary
A semi-syllabary is a writing system that behaves partly as an alphabet and partly as a syllabary. The term has traditionally been extended to abugidas, but for the purposes of this article it will be restricted to scripts where some letters are alphabetic and others are syllabic.-Iberian...
of ancient Spain were syllabic for plosives such as p, t, k, but alphabetic for other consonants. In some versions, vowels were written redundantly after syllabic letters, conforming to an alphabetic orthography. Old Persian cuneiform was similar. Of 23 consonants (including null), seven were fully syllabic, thirteen were purely alphabetic, and for the other three, there was one letter for /Cu/ and another for both /Ca/ and /Ci/. However, all vowels were written overtly regardless; as in the Brahmic abugidas, the /Ca/ letter was used for a bare consonant.
The zhuyin phonetic glossing script for Chinese divides syllables in two or three, but into onset, medial, and rime
Syllable rime
In the study of phonology in linguistics, the rime or rhyme of a syllable consists of a nucleus and an optional coda. It is the part of the syllable used in poetic rhyme, and the part that is lengthened or stressed when a person elongates or stresses a word in speech.The rime is usually the...
rather than consonant and vowel. Pahawh Hmong
Pahawh Hmong
Pahawh Hmong is an indigenous semi-syllabic script, invented in 1959, to write the Hmong language.-Form:Pahawh is written left to right...
is similar, but can be considered to divide syllables into either onset-rime or consonant-vowel (all consonant clusters and diphthongs are written with single letters); as the latter, it is equivalent to an abugida but with the roles of consonant and vowel reversed. Other scripts are intermediate between the categories of alphabet, abjad and abugida, so there may be disagreement on how they should be classified.
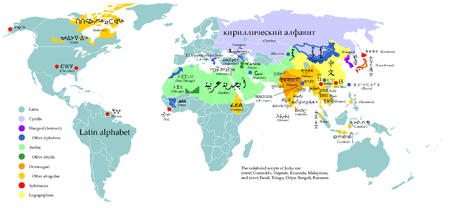
Graphic classification of writing systems
Perhaps the primary graphic distinction made in classifications is that of linearity. Linear writing systems are those in which the characters are composed of lines, such as the Latin alphabetLatin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
and Chinese character
Chinese character
Chinese characters are logograms used in the writing of Chinese and Japanese , less frequently Korean , formerly Vietnamese , or other languages...
s. Chinese characters are considered linear whether they're written with a ball-point pen or a calligraphic brush, or cast in bronze. Similarly, Egyptian hieroglyphs
Egyptian hieroglyphs
Egyptian hieroglyphs were a formal writing system used by the ancient Egyptians that combined logographic and alphabetic elements. Egyptians used cursive hieroglyphs for religious literature on papyrus and wood...
and Maya glyphs
Maya script
The Maya script, also known as Maya glyphs or Maya hieroglyphs, is the writing system of the pre-Columbian Maya civilization of Mesoamerica, presently the only Mesoamerican writing system that has been substantially deciphered...
were often painted in linear outline form, but in formal situations they were carved in bas-relief. The earliest examples of writing are linear: the Sumerian script
Cuneiform script
Cuneiform script )) is one of the earliest known forms of written expression. Emerging in Sumer around the 30th century BC, with predecessors reaching into the late 4th millennium , cuneiform writing began as a system of pictographs...
of c. 3300 BC was linear, though its cuneiform
Cuneiform
Cuneiform can refer to:*Cuneiform script, an ancient writing system originating in Mesopotamia in the 4th millennium BC*Cuneiform , three bones in the human foot*Cuneiform Records, a music record label...
descendants were not. Non-linear systems, on the other hand, such as braille
Braille
The Braille system is a method that is widely used by blind people to read and write, and was the first digital form of writing.Braille was devised in 1825 by Louis Braille, a blind Frenchman. Each Braille character, or cell, is made up of six dot positions, arranged in a rectangle containing two...
, are not composed of lines, no matter which instrument is used to write them.
Cuneiform was probably the earliest non-linear writing. Its glyphs were formed by pressing the end of a reed stylus into moist clay, not by tracing lines in the clay with the stylus as had been done previously. The result was a radical transformation of the appearance of the script.
Braille is a non-linear adaptation of the Latin alphabet that completely abandoned the Latin forms. The letters are composed of raised bumps on the writing substrate
Substrate (printing)
Substrate is a term used in converting process such as printing and Lamination or coating as a more general term to describe the base material onto which e.g. images will be printed and to be laminated as per the packing specification required for the product...
, which can be leather (Louis Braille
Louis Braille
Louis Braille was the inventor of braille, a system of reading and writing used by people who are blind or visually impaired...
's original material), stiff paper, plastic or metal.
There are also transient non-linear adaptations of the Latin alphabet, including Morse code
Morse code
Morse code is a method of transmitting textual information as a series of on-off tones, lights, or clicks that can be directly understood by a skilled listener or observer without special equipment...
, the manual alphabets of various sign language
Sign language
A sign language is a language which, instead of acoustically conveyed sound patterns, uses visually transmitted sign patterns to convey meaning—simultaneously combining hand shapes, orientation and movement of the hands, arms or body, and facial expressions to fluidly express a speaker's...
s, and semaphore
Semaphore
A semaphore telegraph, optical telegraph, shutter telegraph chain, Chappe telegraph, or Napoleonic semaphore is a system of conveying information by means of visual signals, using towers with pivoting shutters, also known as blades or paddles. Information is encoded by the position of the...
, in which flags
Flag semaphore
Semaphore Flags is the system for conveying information at a distance by means of visual signals with hand-held flags, rods, disks, paddles, or occasionally bare or gloved hands. Information is encoded by the position of the flags; it is read when the flag is in a fixed position...
or bars are positioned at prescribed angles. However, if "writing" is defined as a potentially permanent means of recording information, then these systems do not qualify as writing at all, since the symbols disappear as soon as they are used.
Directionality
Scripts are also graphically characterized by the direction in which they are written. Egyptian hieroglyphs were written in either horizontal direction, with the animal and human glyphs turned to face the beginning of the line. The early alphabet could be written in multiple directions, horizontally (left-to-right or right-to-left) or vertically (up or down). It was commonly written boustrophedonBoustrophedon
Boustrophedon , is a type of bi-directional text, mostly seen in ancient manuscripts and other inscriptions. Every other line of writing is flipped or reversed, with reversed letters. Rather than going left-to-right as in modern English, or right-to-left as in Arabic and Hebrew, alternate lines in...
ically: starting in one (horizontal) direction, then turning at the end of the line and reversing direction.
The Greek alphabet
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
and its successors settled on a left-to-right pattern, from the top to the bottom of the page. Other scripts, such as Arabic
Arabic alphabet
The Arabic alphabet or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.-Consonants:The Arabic alphabet has...
and Hebrew
Hebrew language
Hebrew is a Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Culturally, is it considered by Jews and other religious groups as the language of the Jewish people, though other Jewish languages had originated among diaspora Jews, and the Hebrew language is also used by non-Jewish groups, such...
, came to be written right-to-left. Scripts that incorporate Chinese characters have traditionally been written vertically (top-to-bottom), from the right to the left of the page, but nowadays are frequently written left-to-right, top-to-bottom, due to Western
Western culture
Western culture, sometimes equated with Western civilization or European civilization, refers to cultures of European origin and is used very broadly to refer to a heritage of social norms, ethical values, traditional customs, religious beliefs, political systems, and specific artifacts and...
influence, a growing need to accommodate terms in the Roman alphabet, and technical limitations in popular electronic document
Electronic document
An electronic document is any electronic media content that are intended to be used in either an electronic form or as printed output....
formats. The Uighur alphabet and its descendants are unique in being the only scripts written top-to-bottom, left-to-right; this direction originated from an ancestral Semitic direction by rotating the page 90° counter-clockwise to conform to the appearance of vertical Chinese writing. Several scripts used in the Philippines
Languages of the Philippines
In the Philippines, there are between 120 and 175 languages, depending on the method of classification. Four languages no longer have any known speakers. Almost all the Philippine languages belong to the Austronesian language family...
and Indonesia
Indonesia
Indonesia , officially the Republic of Indonesia , is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is an archipelago comprising approximately 13,000 islands. It has 33 provinces with over 238 million people, and is the world's fourth most populous country. Indonesia is a republic, with an...
, such as Hanunó'o
Hanunó'o script
Hanunó’o is one of the indigenous scripts of the Philippines and is used by the Mangyan people of southern Mindoro to write the Hanunó’o language. It is an abugida descended from the Indic scripts, closely related to Baybayin, and is famous for being written vertical but written upward, rather than...
, are traditionally written with lines moving away from the writer, from bottom to top, but are read horizontally left to right.
Writing systems on computers
In computers and telecommunication systems, writing systems are generally not codified as such, but graphemes and other grapheme-like units that are required for text processing are represented by "characterCharacter (computing)
In computer and machine-based telecommunications terminology, a character is a unit of information that roughly corresponds to a grapheme, grapheme-like unit, or symbol, such as in an alphabet or syllabary in the written form of a natural language....
s" that typically manifest in encoded
Character encoding
A character encoding system consists of a code that pairs each character from a given repertoire with something else, such as a sequence of natural numbers, octets or electrical pulses, in order to facilitate the transmission of data through telecommunication networks or storage of text in...
form. There are many different character encoding standards and related technologies, such as ISO/IEC 8859-1
ISO/IEC 8859-1
ISO/IEC 8859-1:1998, Information technology — 8-bit single-byte coded graphic character sets — Part 1: Latin alphabet No. 1, is part of the ISO/IEC 8859 series of ASCII-based standard character encodings, first edition published in 1987. It is informally referred to as Latin-1. It is generally...
(a character repertoire and encoding scheme oriented toward the Latin script), CJK (Chinese, Japanese, Korean) and bi-directional text
Bi-directional text
Bi-directional text is text containing text in both text directionalities, both right-to-left and left-to-right . It generally involves text containing different types of alphabets, but may also refer to boustrophedon, which is changing text directionality in each row.Some writing systems of the...
. Today, many such standards are re-defined in a collective standard, the ISO
International Organization for Standardization
The International Organization for Standardization , widely known as ISO, is an international standard-setting body composed of representatives from various national standards organizations. Founded on February 23, 1947, the organization promulgates worldwide proprietary, industrial and commercial...
/IEC
International Electrotechnical Commission
The International Electrotechnical Commission is a non-profit, non-governmental international standards organization that prepares and publishes International Standards for all electrical, electronic and related technologies – collectively known as "electrotechnology"...
10646 "Universal Character Set
Universal Character Set
The Universal Character Set , defined by the International Standard ISO/IEC 10646, Information technology — Universal multiple-octet coded character set , is a standard set of characters upon which many character encodings are based...
", and a parallel, closely related expanded work, The Unicode Standard. Both are generally encompassed by the term Unicode
Unicode
Unicode is a computing industry standard for the consistent encoding, representation and handling of text expressed in most of the world's writing systems...
. In Unicode, each character, in every language's writing system, is (simplifying slightly) given a unique identification number, known as its code point. Computer operating system
Operating system
An operating system is a set of programs that manage computer hardware resources and provide common services for application software. The operating system is the most important type of system software in a computer system...
s use code points to look up characters in the font
Typeface
In typography, a typeface is the artistic representation or interpretation of characters; it is the way the type looks. Each type is designed and there are thousands of different typefaces in existence, with new ones being developed constantly....
file, so the characters can be displayed on the page or screen.
A keyboard
Computer keyboard
In computing, a keyboard is a typewriter-style keyboard, which uses an arrangement of buttons or keys, to act as mechanical levers or electronic switches...
is the device most commonly used for writing via computer. Each key is associated with a standard code which the keyboard sends to the computer when it is pressed. By using a combination of alphabetic keys with modifier key
Modifier key
In computing, a modifier key is a special key on a computer keyboard that modifies the normal action of another key when the two are pressed in combination....
s such as Ctrl
Control key
In computing, a Control key is a modifier key which, when pressed in conjunction with another key, will perform a special operation ; similar to the Shift key, the Control key rarely performs any function when pressed by itself...
, Alt
Alt key
The Alt key on a computer keyboard is used to change the function of other pressed keys. Thus, the Alt key is a modifier key, used in a similar fashion to the Shift key. For example, simply pressing "A" will type the letter a, but if you hold down either Alt key while pressing A, the computer...
, Shift
Shift key
The shift key is a modifier key on a keyboard, used to type capital letters and other alternate "upper" characters. There are typically two shift keys, on the left and right sides of the row below the home row...
and AltGr
AltGr key
AltGr is a modifier key found on many computer keyboards and primarily used to type characters that are unusual for the locale of the keyboard layout, such as currency symbols and accented letters...
, various character codes are generated and sent to the CPU. The operating system
Operating system
An operating system is a set of programs that manage computer hardware resources and provide common services for application software. The operating system is the most important type of system software in a computer system...
intercepts and converts those signals to the appropriate characters based on the keyboard layout
Keyboard layout
A keyboard layout is any specific mechanical, visual, or functional arrangement of the keys, legends, or key–meaning associations of a computer, typewriter, or other typographic keyboard....
and input method
Input method editor
An input method is an operating system component or program that allows any data, such as keyboard strokes or mouse movements, to be received as input. In this way users can enter characters and symbols not found on their input devices...
, and then delivers those converted codes and characters to the running application software
Application software
Application software, also known as an application or an "app", is computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks. Examples include enterprise software, accounting software, office suites, graphics software and media players. Many application programs deal principally with...
, which in turn looks up the appropriate glyph
Glyph
A glyph is an element of writing: an individual mark on a written medium that contributes to the meaning of what is written. A glyph is made up of one or more graphemes....
in the currently used font file, and requests the operating system to draw these on the screen
Computer display
A monitor or display is an electronic visual display for computers. The monitor comprises the display device, circuitry, and an enclosure...
.
See also
- History of writingHistory of writingThe history of writing records the development of expressing language by letters or other marks. In the history of how systems of representation of language through graphic means have evolved in different human civilizations, more complete writing systems were preceded by proto-writing, systems of...
- Artificial script
- Asemic writingAsemic writingAsemic writing is a wordless open semantic form of writing. The word asemic means "having no specific semantic content". With the nonspecificity of asemic writing there comes a vacuum of meaning which is left for the reader to fill in and interpret. All of this is similar to the way one would...
- CalligraphyCalligraphyCalligraphy is a type of visual art. It is often called the art of fancy lettering . A contemporary definition of calligraphic practice is "the art of giving form to signs in an expressive, harmonious and skillful manner"...
- DigraphiaDigraphiaIn sociolinguistics, digraphia refers to the use of more than one writing system for the same language. Some scholars differentiate between synchronic digraphia with the coexistence of two or more writing systems for the same language and diachronic digraphia with the replacement of one writing...
- DyslexiaDyslexiaDyslexia is a very broad term defining a learning disability that impairs a person's fluency or comprehension accuracy in being able to read, and which can manifest itself as a difficulty with phonological awareness, phonological decoding, orthographic coding, auditory short-term memory, or rapid...
- FontFontIn typography, a font is traditionally defined as a quantity of sorts composing a complete character set of a single size and style of a particular typeface...
- Formal languageFormal languageA formal language is a set of words—that is, finite strings of letters, symbols, or tokens that are defined in the language. The set from which these letters are taken is the alphabet over which the language is defined. A formal language is often defined by means of a formal grammar...
- History of writing numbers
- ISO 15924ISO 15924ISO 15924, Codes for the representation of names of scripts, defines two sets of codes for a number of writing systems . Each script is given both a four-letter code and a numeric one....
— codes for the representation of names of scripts - List of inventors of writing systems
- List of writing systems
- Lower case
- Majuscule
- Nü ShuNü ShuNüshu , is a syllabic script, a simplification of Chinese characters that was used exclusively among women in Jiangyong County in Hunan province of southern China.-Language:...
- Official scriptOfficial scriptAn official script is a writing system that is specifically designated to be official in the constitutions or other applicable laws of countries, states, and other jurisdictions. Akin to an official language, an official script is much rarer. It is used primarily where an official language is in...
- OrthographyOrthographyThe orthography of a language specifies a standardized way of using a specific writing system to write the language. Where more than one writing system is used for a language, for example Kurdish, Uyghur, Serbian or Inuktitut, there can be more than one orthography...
- PasigraphyPasigraphyA pasigraphy is a writing system where each written symbol represents a concept rather than a word or sound or series of sounds in a spoken language. The aim is to be intelligible to persons of all languages...
- PenmanshipPenmanshipPenmanship is the technique of writing with the hand using a writing instrument. The various generic and formal historical styles of writing are called hands, whilst an individual personal style of penmanship is referred to as handwriting....
- ShorthandShorthandShorthand is an abbreviated symbolic writing method that increases speed or brevity of writing as compared to a normal method of writing a language. The process of writing in shorthand is called stenography, from the Greek stenos and graphē or graphie...
- SpellingSpellingSpelling is the writing of one or more words with letters and diacritics. In addition, the term often, but not always, means an accepted standard spelling or the process of naming the letters...
- TransliterationTransliterationTransliteration is a subset of the science of hermeneutics. It is a form of translation, and is the practice of converting a text from one script into another...
- Written languageWritten languageA written language is the representation of a language by means of a writing system. Written language is an invention in that it must be taught to children, who will instinctively learn or create spoken or gestural languages....
External links
- Writing Systems Research Free first issue of a journal devoted to research on writing systems
- Arch Chinese (Traditional & Simplified) Chinese character writing animations and native speaker pronunciations
- decodeunicode Unicode Wiki with all 98,884 Unicode 5.0 characters as gifs in three sizes
- African writing systems
- Omniglot A concise guide to the writing systems and languages of the world. Ultraweb.hu - főoldal
- Ancient Scripts Introduction to different writing systems
- Michael EversonMichael EversonMichael Everson is a linguist, script encoder, typesetter, and font designer. His central area of expertise is with writing systems of the world, specifically in the representation of these systems in formats for computer and digital media...
's Alphabets of Europe - The Unicode Consortium
- Elian script a writing system that combines the linearity of spelling with the free-form aspects of drawing. Written of the World

