.gif)
Lineage (evolution)
Encyclopedia
An evolutionary lineage is a sequence of species
, that form a line of descent, each new species the direct result of speciation from an immediate ancestral species. Lineages are subsets of the evolutionary tree of life. Lineages are often determined by the techniques of molecular systematics.
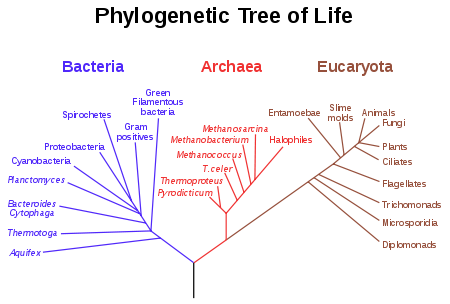 Lineages are typically visualized as subsets of a phylogenetic tree
Lineages are typically visualized as subsets of a phylogenetic tree
. For example, the tree in Figure 1 shows the separation of life into three ancient lineages: bacteria
, archaea
, and eukaryotes. Thus a lineage is a single branch of the tree. Phylogenetic trees are typically created from DNA
, RNA or protein
sequence data. Apart from this, morphological differences and similarities have been, and still are used to create phylogenetic trees. Sequences from different individuals are collected and their similarity is quantified. Mathematical procedures are used to cluster
individuals by similarity.
Just as a map is a scaled approximation of true geography
, a phylogenetic tree is an approximation of the true complete evolutionary relationships. For example, in Figure 1, the entire lineage of animals has been collapsed to a single branch of the tree. However, this is merely a limitation of rendering space. In theory, a true and complete tree for all living organisms or for any DNA
sequence could be generated.
Species
In biology, a species is one of the basic units of biological classification and a taxonomic rank. A species is often defined as a group of organisms capable of interbreeding and producing fertile offspring. While in many cases this definition is adequate, more precise or differing measures are...
, that form a line of descent, each new species the direct result of speciation from an immediate ancestral species. Lineages are subsets of the evolutionary tree of life. Lineages are often determined by the techniques of molecular systematics.
Phylogenetic representation of lineages

Phylogenetic tree
A phylogenetic tree or evolutionary tree is a branching diagram or "tree" showing the inferred evolutionary relationships among various biological species or other entities based upon similarities and differences in their physical and/or genetic characteristics...
. For example, the tree in Figure 1 shows the separation of life into three ancient lineages: bacteria
Bacteria
Bacteria are a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria have a wide range of shapes, ranging from spheres to rods and spirals...
, archaea
Archaea
The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon...
, and eukaryotes. Thus a lineage is a single branch of the tree. Phylogenetic trees are typically created from DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
, RNA or protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
sequence data. Apart from this, morphological differences and similarities have been, and still are used to create phylogenetic trees. Sequences from different individuals are collected and their similarity is quantified. Mathematical procedures are used to cluster
Data clustering
Cluster analysis or clustering is the task of assigning a set of objects into groups so that the objects in the same cluster are more similar to each other than to those in other clusters....
individuals by similarity.
Just as a map is a scaled approximation of true geography
Geography
Geography is the science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. A literal translation would be "to describe or write about the Earth". The first person to use the word "geography" was Eratosthenes...
, a phylogenetic tree is an approximation of the true complete evolutionary relationships. For example, in Figure 1, the entire lineage of animals has been collapsed to a single branch of the tree. However, this is merely a limitation of rendering space. In theory, a true and complete tree for all living organisms or for any DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
sequence could be generated.

