
History of the Hebrew alphabet
Encyclopedia
History

Paleo-Hebrew alphabet
The Paleo-Hebrew alphabet , is an abjad offshoot of the ancient Semitic alphabet, identical to the Phoenician alphabet. At the very least it dates to the 10th century BCE...
developed alongside others in the region during the course of the late second and first millennia BCE; it is closely related to the Phoenician script
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
, which itself probably gave rise to the use of alphabetic writing in Greece
Greece
Greece , officially the Hellenic Republic , and historically Hellas or the Republic of Greece in English, is a country in southeastern Europe....
(Greek
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
). It is sometimes claimed that around the 10th century BCE
a distinct Hebrew variant, the original "Hebrew script", emerged, which was widely used in the ancient kingdoms of Israel and Judah
Kingdom of Judah
The Kingdom of Judah was a Jewish state established in the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. It is often referred to as the "Southern Kingdom" to distinguish it from the northern Kingdom of Israel....
until they fell in the 8th and 6th centuries BCE, respectively. It is not straightforward, however, to distinguish Israelite
Israelite
According to the Bible the Israelites were a Hebrew-speaking people of the Ancient Near East who inhabited the Land of Canaan during the monarchic period .The word "Israelite" derives from the Biblical Hebrew ישראל...
/Judahite scripts from others which were in use in the immediate area, most notably by the Moabites and Ammon
Ammon
Ammon , also referred to as the Ammonites and children of Ammon, was an ancient nation located east of the Jordan River, Gilead, and the Dead Sea, in present-day Jordan. The chief city of the country was Rabbah or Rabbath Ammon, site of the modern city of Amman, Jordan's capital...
ites.
Following the Babylonian exile, Jews gradually stopped using the Hebrew script, and instead adopted the "square" Aramaic script (another offshoot of the same family of scripts). This script, used for writing Hebrew, later evolved into the Jewish, or "square" script, that is still used today. Closely related scripts were in use all over the Middle East for several hundred years, but following the rise of Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
(and later, the rise of Islam
Islam
Islam . The most common are and . : Arabic pronunciation varies regionally. The first vowel ranges from ~~. The second vowel ranges from ~~~...
), they gave way to the Roman and Arabic
Arabic alphabet
The Arabic alphabet or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.-Consonants:The Arabic alphabet has...
alphabets, respectively.
The Hebrew alphabet was later adapted in order to write down the languages of the Jewish diaspora
Jewish diaspora
The Jewish diaspora is the English term used to describe the Galut גלות , or 'exile', of the Jews from the region of the Kingdom of Judah and Roman Iudaea and later emigration from wider Eretz Israel....
(Karaim
Karaim language
The Karaim language is a Turkic language with Hebrew influences, in a similar manner to Yiddish or Ladino. It is spoken by Crimean Karaites – ethnic Turkic adherents of Karaite Judaism in Crimea, Lithuania, Poland and western Ukraine...
, Judæo-Arabic, Ladino, Yiddish
Yiddish language
Yiddish is a High German language of Ashkenazi Jewish origin, spoken throughout the world. It developed as a fusion of German dialects with Hebrew, Aramaic, Slavic languages and traces of Romance languages...
, etc.), and was retained all the while in relatively unadapted form throughout the diaspora for Hebrew, which remained the language of Jewish law, scriptures and scholarship. The Hebrew alphabet was also retained as the alphabet used for writing down the Hebrew language
Hebrew language
Hebrew is a Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Culturally, is it considered by Jews and other religious groups as the language of the Jewish people, though other Jewish languages had originated among diaspora Jews, and the Hebrew language is also used by non-Jewish groups, such...
during its rebirth as an everyday modern language starting in the 18th to 19th century.
According to one Jewish tradition, however, the block script seen today in Hebrew Torah Scrolls, known as Kthav Ashurith
Ashuri alphabet
Ashuri alphabet means Assyrian alphabet and also refers to the Assyrian script which is a traditional name for the Hebrew alphabet and a term that was first used in the Mishnah to refer to either the Aramaic alphabet or the formal script used in certain Jewish ceremonial items, including Sefer...
, was the original Hebrew script carved into the Ten Commandments
Ten Commandments
The Ten Commandments, also known as the Decalogue , are a set of biblical principles relating to ethics and worship, which play a fundamental role in Judaism and most forms of Christianity. They include instructions to worship only God and to keep the Sabbath, and prohibitions against idolatry,...
. According to this opinion, the Ktav Ashurith was lost over time, as the masses used Paleo-Hebrew
Paleo-Hebrew alphabet
The Paleo-Hebrew alphabet , is an abjad offshoot of the ancient Semitic alphabet, identical to the Phoenician alphabet. At the very least it dates to the 10th century BCE...
and its cousins, known as Kthav Ivri, for day to day writing, just as Jews today use a non block script for everyday writing.
Ancestral scripts and script variants
| Symbol | | Name | | Scripts | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| | Hebrew | | Ancestral | | Related | |||||||||||||||||
| Cursive | Rashi Rashi script Rashi script is a semi-cursive typeface for the Hebrew alphabet. It is named for the author of the most famous rabbinic commentary on the Hebrew Bible and the Talmud, Rashi, and is customarily used for printing his commentaries. The typeface is based on 15th century Sephardic semi-cursive... |
Braille Hebrew braille Hebrew Braille is the system of Braille used by Hebrew readers and speakers. The International Hebrew Braille Code in wide usage throughout the world was devised in the 1930s and completed in 1944. It is based on the standard Braille system, with additional letters devised to accommodate... |
Hieroglyphic Egyptian hieroglyphs Egyptian hieroglyphs were a formal writing system used by the ancient Egyptians that combined logographic and alphabetic elements. Egyptians used cursive hieroglyphs for religious literature on papyrus and wood... base of Proto-Sinaitic (assumed) |
Proto-Semitic (reconstructed) |
Phoenician Phoenician alphabet The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia... |
Paleo-Hebrew Paleo-Hebrew alphabet The Paleo-Hebrew alphabet , is an abjad offshoot of the ancient Semitic alphabet, identical to the Phoenician alphabet. At the very least it dates to the 10th century BCE... |
Aramaic Aramaic alphabet The Aramaic alphabet is adapted from the Phoenician alphabet and became distinctive from it by the 8th century BC. The letters all represent consonants, some of which are matres lectionis, which also indicate long vowels.... |
Greek Greek alphabet The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega... |
Latin Latin alphabet The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome... |
Cyrillic Cyrillic alphabet The Cyrillic script or azbuka is an alphabetic writing system developed in the First Bulgarian Empire during the 10th century AD at the Preslav Literary School... |
Arabic Arabic alphabet The Arabic alphabet or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.-Consonants:The Arabic alphabet has... |
||||||||
| א | Alef Aleph * Aleph or Alef is the first letter of the Semitic abjads descended from Proto-Canaanite, Arabic alphabet, Phoenician alphabet, Hebrew alphabet, Syriac alphabet-People:*Aleph , an Italo disco artist and alias of Dave Rodgers... |
 |
 |
 |
|
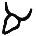 |
 |
 |
Αα | A A A is the first letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet. It is similar to the Ancient Greek letter Alpha, from which it derives.- Origins :... a |
Аа | ا | |||||||
| ב | Bet Bet (letter) Bet, Beth, Beh, or Vet is the second letter of many Semitic abjads, including Arabic alphabet , Aramaic, Hebrew , Phoenician and Syriac... , Vet Bet (letter) Bet, Beth, Beh, or Vet is the second letter of many Semitic abjads, including Arabic alphabet , Aramaic, Hebrew , Phoenician and Syriac... |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
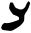 |
Ββ | B B B is the second letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet. It is used to represent a variety of bilabial sounds , most commonly a voiced bilabial plosive.-History:... b |
Бб Вв |
ﺑ ﺏ | ||||||
| ג | Gimel |  |
 |
 |
|
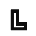 |
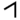 |
 |
Γγ | C C Ĉ or ĉ is a consonant in Esperanto orthography, representing the sound .Esperanto orthography uses a diacritic for all four of its postalveolar consonants, as do the Latin-based Slavic alphabets... c G G G is the seventh letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The letter 'G' was introduced in the Old Latin period as a variant of ⟨c⟩ to distinguish voiced, from voiceless, . The recorded originator of ⟨g⟩ is freedman Spurius Carvilius Ruga, the first Roman to open a fee-paying school,... g |
Гг | ﺟ ﺝ | |||||||
| ד | Dalet |  |
 |
 |
|
 |
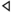 |
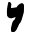 |
Δδ | D D D is the fourth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.- History :The Semitic letter Dâlet may have developed from the logogram for a fish or a door. There are various Egyptian hieroglyphs that might have inspired this. In Semitic, Ancient Greek, and Latin, the letter represented ; in the... d |
Дд | دذ | |||||||
| ה | Hei He (letter) He is the fifth letter of many Semitic alphabets, including Phoenician , Aramaic, Hebrew , Syriac and Arabic . Its sound value is a voiceless glottal fricative .... |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
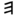 |
 |
Εε | E E E is the fifth letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet. It is the most commonly used letter in the Czech, Danish, Dutch, English, French, German, Hungarian, Latin, Norwegian, Spanish, and Swedish languages.-History:... e |
Ее Єє |
ه هـ ـهـ ـه |
|||||||
| ו | Vav Waw (letter) Waw is the sixth letter of the Northwest Semitic family of scripts, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew, Syriac, and Arabic .... |
 |
 |
 |
unknown | 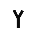 |
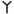 |
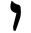 |
Υυ Ϝϝ |
F F F is the sixth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The origin of ⟨f⟩ is the Semitic letter vâv that represented a sound like or . Graphically, it originally probably depicted either a hook or a club... fU U U is the twenty-first letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The letter U ultimately comes from the Semitic letter Waw by way of the letter Y. See the letter Y for details.... uV V V is the twenty-second letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-Letter:The letter V comes from the Semitic letter Waw, as do the modern letters F, U, W, and Y. See F for details.... v W W W is the 23rd letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.In other Germanic languages, including German, its pronunciation is similar or identical to that of English V... wY Y Y is the twenty-fifth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet and represents either a vowel or a consonant in English.-Name:In Latin, Y was named Y Graeca "Greek Y". This was pronounced as I Graeca "Greek I", since Latin speakers had trouble pronouncing , which was not a native sound... y |
Ѵѵ Уу |
ﻭ | |||||||
| ז | Zayin Zayin Zayin is the seventh letter of many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician , Aramaic , Hebrew , Syriac and Perso-Arabic alphabet... |
 |
 |
 |
unknown |  |
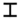 |
 |
Ζζ | Z Z Z is the twenty-sixth and final letter of the basic modern Latin alphabet.-Name and pronunciation:In most dialects of English, the letter's name is zed , reflecting its derivation from the Greek zeta but in American English, its name is zee , deriving from a late 17th century English dialectal... z |
Зз | ﺯ | |||||||
| ח | Het Khet Khet may refer to:*Khet **List of districts in Bangkok**Provinces of Cambodia*One of the Ancient Egyptian units of measurement*Heth , the eighth letter of many Semitic alphabets... |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
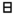 |
 |
Ηη | H H H .) is the eighth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The Semitic letter ⟨ח⟩ most likely represented the voiceless pharyngeal fricative . The form of the letter probably stood for a fence or posts.... h |
Ии | ﺣﺡ | |||||||
| ט | Tet Teth ' is the ninth letter of many Semitic abjads , including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Tet , Syriac and Arabic ; it is 9th in abjadi order and 16th in modern Arabic order.... |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
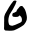 |
Θθ | ? | Ѳѳ | ﻁ | |||||||
| י | Yud Yodh Yodh is the tenth letter of many Semitic alphabets, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Yud , Syriac and Arabic... |
 |
 |
 |
|
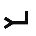 |
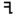 |
 |
Ιι | J J Ĵ or ĵ is a letter in Esperanto orthography representing the sound .While Esperanto orthography uses a diacritic for its four postalveolar consonants, as do the Latin-based Slavic alphabets, the base letters are Romano-Germanic... j I I I is the ninth letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:In Semitic, the letter may have originated in a hieroglyph for an arm that represented a voiced pharyngeal fricative in Egyptian, but was reassigned to by Semites, because their word for "arm" began with that sound... i |
Јј Іі |
ﻳ ﻱ | |||||||
| כ | ך | Kaf Kaph Kaph is the eleventh letter of many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Kaf , Arabic alphabet , Persian alphabet... , Khaf Kaph Kaph is the eleventh letter of many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Kaf , Arabic alphabet , Persian alphabet... |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
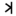 |
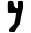 |
Κκ | K K K is the eleventh letter of the English and basic modern Latin alphabet.-History and usage:In English, the letter K usually represents the voiceless velar plosive; this sound is also transcribed by in the International Phonetic Alphabet and X-SAMPA.... k |
Кк | ﻛ ﻙ | |||
| ל | Lamed Lamedh Lamed or Lamedh is the twelfth letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Lamed and Arabic alphabet . Its sound value is .The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek Lambda , Latin L, and Cyrillic Л.-Origins:... |
 |
 |
 |
|
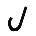 |
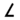 |
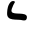 |
Λλ | L L Ł or ł, described in English as L with stroke, is a letter of the Polish, Kashubian, Sorbian, Łacinka , Łatynka , Wilamowicean, Navajo, Dene Suline, Inupiaq, Zuni, Hupa, and Dogrib alphabets, several proposed alphabets for the Venetian language, and the ISO 11940 romanization of the Thai alphabet... l |
Лл | ﻟ ﻝ | |||||||
| מ | ם | Mem |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
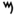 |
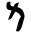 |
Μμ | Mm | Мм | ﻣ ﻡ | ||||
| נ | ן | Nun Nun (letter) Nun is the fourteenth letter of many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew and Arabic alphabet . It is the third letter in Thaana , pronounced as "noonu"... |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
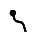 |
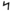 |
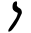 |
Νν | N N N is the fourteenth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.- History of the forms :One of the most common hieroglyphs, snake, was used in Egyptian writing to stand for a sound like English ⟨J⟩, because the Egyptian word for "snake" was djet... n |
Нн | ﻧ ﻥ | ||||
| ס | Samech Samekh Samekh or Simketh is the fifteenth letter in many Semitic alphabets, including Phoenician, Hebrew, and Aramaic, representing . The Arabic alphabet, however, uses a letter based on Phoenician šin to represent ; however, that glyph takes Samekh's place in the traditional Abjadi order of the Arabic... |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
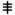 |
 |
Ξξ Χχ |
X X X is the twenty-fourth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-Uses:In mathematics, x is commonly used as the name for an independent variable or unknown value. The usage of x to represent an independent or unknown variable can be traced back to the Arabic word šay شيء = “thing,” used in Arabic... x |
Ѯѯ Хх |
? | |||||||
| ע | Ayin Ayin ' or ' is the sixteenth letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew and Arabic . It is the twenty-first letter in the new Persian alphabet... |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
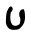 |
Οο | O O O is the fifteenth letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet.The letter was derived from the Semitic `Ayin , which represented a consonant, probably , the sound represented by the Arabic letter ع called `Ayn. This Semitic letter in its original form seems to have been inspired by a... o |
Оо | ﻋ ع غـ غ |
|||||||
| פ | ף | Pei Pe (letter) Pe is the seventeenth letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Pei and Persian, Arabic .... , Fei Pe (letter) Pe is the seventeenth letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew Pei and Persian, Arabic .... |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
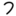 |
 |
Ππ Pi (letter) Pi is the sixteenth letter of the Greek alphabet, representing . In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 80. Letters that arose from pi include Cyrillic Pe , Coptic pi , and Gothic pairthra .The upper-case letter Π is used as a symbol for:... |
P P P is the sixteenth letter of the basic modern Latin alphabet.-Usage:In English and most other European languages, P is a voiceless bilabial plosive. Both initial and final Ps can be combined with many other discrete consonants in English words... p |
Пп | ﻓ ﻑ | |||
| צ | ץ | Tsadi |  |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
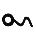 |
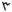 |
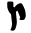 , , 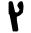 |
Ϻϻ | - | Цц Чч |
ﺻ ص ضـ ض |
||||
| ק | Kuf Qoph Qoph or Qop is the nineteenth letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Syriac, Hebrew and Arabic alphabet . Its sound value is an emphatic or . The OHED gives the letter Qoph a transliteration value of Q or a K and a final transliteration value as a ck... |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
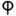 |
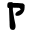 |
Ϙϙ | Q Q Q is the seventeenth letter of the basic modern Latin alphabet.- History :The Semitic sound value of Qôp was , a sound common to Semitic languages, but not found in English or most Indo-European ones... q |
Ҁҁ | ﻗ ﻕ | |||||||
| ר | Reish Resh Resh is the twentieth letter of many Semitic alphabets, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew and Arabic alphabet . Its sound value is one of a number of rhotic consonants: usually or , but also or in Hebrew.... |
 |
 |
 |
|
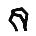 |
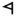 |
 |
Ρρ | R R R is the eighteenth letter of the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The original Semitic letter may have been inspired by an Egyptian hieroglyph for tp, "head". It was used for by Semites because in their language, the word for "head" was rêš . It developed into Greek Ρ and Latin R... r |
Рр | ﺭ | |||||||
| ש | Shin Shin (letter) Shin literally means "Sharp" ; It is the twenty-first letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician , Aramaic/Hebrew , and Arabic .... , Sin Shin (letter) Shin literally means "Sharp" ; It is the twenty-first letter in many Semitic abjads, including Phoenician , Aramaic/Hebrew , and Arabic .... |
 |
 |
 |
unknown | 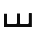 |
 |
 |
Σσς | S S S is the nineteenth letter in the ISO basic Latin alphabet.-History: Semitic Šîn represented a voiceless postalveolar fricative . Greek did not have this sound, so the Greek sigma came to represent... s |
Сс Шш |
سـ س شـ ش |
|||||||
| ת | Tav Taw Taw may refer to:* Taw , the twenty-second letter in many Semitic alphabets* Taw , the collection of all cardinal numbers* the shooter marble in a game of marbles* The River Taw in Devon, England* a method to produce white leather... |
 |
 |
 |
unknown | 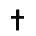 |
 |
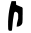 |
Ττ | T T T is the 20th letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet. It is the most commonly used consonant and the second most common letter in the English language.- History :Taw was the last letter of the Western Semitic and Hebrew alphabets... t |
Тт | ﺗ ﺕ ﺛ ﺙ |
|||||||
See also
- Cursive Hebrew
- Rashi scriptRashi scriptRashi script is a semi-cursive typeface for the Hebrew alphabet. It is named for the author of the most famous rabbinic commentary on the Hebrew Bible and the Talmud, Rashi, and is customarily used for printing his commentaries. The typeface is based on 15th century Sephardic semi-cursive...
- Proto-Sinaitic alphabetProto-Sinaitic alphabetProto-Sinaitic is a Middle Bronze Age script attested in a very small collection of inscriptions at Serabit el-Khadim in the Sinai Peninsula. Due to the extreme scarcity of Proto-Sinaitic signs, very little is known with certainty about the nature of the script...
- Phoenician alphabetPhoenician alphabetThe Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
- Paleo-Hebrew alphabetPaleo-Hebrew alphabetThe Paleo-Hebrew alphabet , is an abjad offshoot of the ancient Semitic alphabet, identical to the Phoenician alphabet. At the very least it dates to the 10th century BCE...
- Aramaic alphabetAramaic alphabetThe Aramaic alphabet is adapted from the Phoenician alphabet and became distinctive from it by the 8th century BC. The letters all represent consonants, some of which are matres lectionis, which also indicate long vowels....

