.gif)
Waw (letter)
Encyclopedia
Waw is the sixth letter of the Northwest Semitic family of scripts, including Phoenician
, Aramaic
, Hebrew
, Syriac
, and Arabic
("sixth" in abjadi order; it is 27th in modern Arabic order).
In most Semitic languages it represents the sound w, and in some (such as Hebrew and Arabic) also the long vowel uː, depending on context.
In Modern Hebrew
, the consonantal pronunciation is v or β, a pattern shared by certain non-Semitic languages using the Arabic alphabet such as Persian
and Urdu
.
The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek
digamma
and upsilon
, and Etruscan V
(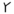 or
or  ). The latter is the source of the Latin letter F
). The latter is the source of the Latin letter F
.
Vav literally means hook/peg/spear.
Hebrew spelling:
value and phonetic
realisation:
in modern hebrew the frequency of the usage of vav, out of all the letters, is about 10.00%.
(like the English v
) in Ashkenazi, European Sephardi, and modern Israeli Hebrew
; and originally a labial-velar approximant /w/. It is still pronounced as a w by some Jews of Oriental (Arabic
speaking) origin.
In modern Israeli Hebrew, some loanword
s, the pronunciation of whose source contains w, and their derivations
, are pronounced with w, too, e.g. ואחד – /ˈwaχad/ (but: ואדי
– /ˈvadi/).
Modern Hebrew has no standardized
way to distinguish orthographically
between v and w. The pronunciation is either determined by prior knowledge or must be derived through context.
Some non standard
spellings of the sound w are sometimes found in modern Hebrew texts, such as word-initial double-vav, e.g. וואללה – /ˈwala/ (word-medial double-vav is both standard and common for both w and v, see table above) or, rarely, vav with a geresh
, e.g. ו׳יליאם – /ˈwiljam/.
for an 'o' vowel, in which case it is known as a holam male, which in pointed text is marked as vav with a dot above it. It is pronounced o̞ (phonemically transcribed more simply as /o/).
This vowel is sometimes also denoted without the vav, as just the dot placed above and to the left of the letter it points, and is called then holam haser. Some inadequate typefaces don't support the distinction between the holam male, "", /o/, and a consonantal vav pointed with a holam haser, "", /vo/ (compare holam male in "", /maˈtsot/, to consonantal vav with holam haser in "" /mitsˈvot/). To correctly display a consonantal vav with holam haser, the typeface must either support the combined character "" (HTML Entity (decimal) ) or the Unicode Character 'HEBREW POINT HOLAM HASER FOR VAV' (U+05BA, HTML Entity (decimal) ֺ), e.g. "".
Shuruk and vav with a dagesh look identical ("") and are only distinguishable through the fact that in text with nikud, vav with a dagesh will normally be attributed a vocal point in addition, e.g. (/ʃuk/), "a market", (the "" denotes a shuruk) as opposed to (/ʃiˈvek/), "to market" (the "" denotes a vav with dagesh and is additionally pointed with a zeire, "", denoting /e/). In the word (/ʃiˈvuk/), "marketting", the first ("") denotes a vav with dagesh, the second a shuruk, being the vowel attributed to the first.
represents the number six, and when used at the beginning of Hebrew years
, it means 6000 (i.e. ותשנד in numbers
would be the date
6754.)
(Note: Older Hebrew did not have "tense" in a temporal sense, "perfect," and "imperfect" instead denoting aspect of completed or continuing action. Modern Hebrew verbal tenses have developed closer to their Indo-European counterparts, mostly having a temporal quality rather than denoting aspect. As a rule, Modern Hebrew does not use the "Vav Consecutive" form.)
In the Syriac alphabet, the sixth letter is ܘ — Waw ܘܐܘ, it is pronounced as a [w]. When used as a mater lectionis, a Waw with a dot above the letter is an [o] vowel, and a Waw with a dot under the letter is an [u] vowel. It's alphabetic-numeral is 6.
Wāw is used to represent three distinct phonetic features:
As a vowel, wāw can serve as the carrier of a hamza: .
Wāw serves several functions in the Modern Standard Arabic. Perhaps foremost among them is that it is the primary conjunction
in Arabic, equivalent to "and"; it is usually prefix
ed to other conjunctions, such as ولكن wa-lakin, meaning "but". Another function is the "oath
", by preceding a noun of great significantly valued by the speaker. It is often literally translatable to "By..." or "I swear to...", and is often used in the Qur'an
in this way, and also in the generally fixed construction والله wallah ("By Allah
!" or "I swear to God!").
Phoenician alphabet
The Phoenician alphabet, called by convention the Proto-Canaanite alphabet for inscriptions older than around 1050 BC, was a non-pictographic consonantal alphabet, or abjad. It was used for the writing of Phoenician, a Northern Semitic language, used by the civilization of Phoenicia...
, Aramaic
Aramaic alphabet
The Aramaic alphabet is adapted from the Phoenician alphabet and became distinctive from it by the 8th century BC. The letters all represent consonants, some of which are matres lectionis, which also indicate long vowels....
, Hebrew
Hebrew alphabet
The Hebrew alphabet , known variously by scholars as the Jewish script, square script, block script, or more historically, the Assyrian script, is used in the writing of the Hebrew language, as well as other Jewish languages, most notably Yiddish, Ladino, and Judeo-Arabic. There have been two...
, Syriac
Syriac alphabet
The Syriac alphabet is a writing system primarily used to write the Syriac language from around the 2nd century BC . It is one of the Semitic abjads directly descending from the Aramaic alphabet and shares similarities with the Phoenician, Hebrew, Arabic, and the traditional Mongolian alphabets.-...
, and Arabic
Arabic alphabet
The Arabic alphabet or Arabic abjad is the Arabic script as it is codified for writing the Arabic language. It is written from right to left, in a cursive style, and includes 28 letters. Because letters usually stand for consonants, it is classified as an abjad.-Consonants:The Arabic alphabet has...
("sixth" in abjadi order; it is 27th in modern Arabic order).
In most Semitic languages it represents the sound w, and in some (such as Hebrew and Arabic) also the long vowel uː, depending on context.
In Modern Hebrew
Modern Hebrew
Modern Hebrew , also known as Israeli Hebrew or Modern Israeli Hebrew, is the language spoken in Israel and in some Jewish communities worldwide, from the early 20th century to the present....
, the consonantal pronunciation is v or β, a pattern shared by certain non-Semitic languages using the Arabic alphabet such as Persian
Persian language
Persian is an Iranian language within the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages. It is primarily spoken in Iran, Afghanistan, Tajikistan and countries which historically came under Persian influence...
and Urdu
Urdu
Urdu is a register of the Hindustani language that is identified with Muslims in South Asia. It belongs to the Indo-European family. Urdu is the national language and lingua franca of Pakistan. It is also widely spoken in some regions of India, where it is one of the 22 scheduled languages and an...
.
The Phoenician letter gave rise to the Greek
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
digamma
Digamma
Digamma is an archaic letter of the Greek alphabet which originally stood for the sound /w/ and later remained in use only as a numeral symbol for the number "6"...
and upsilon
Upsilon
Upsilon is the 20th letter of the Greek alphabet. In the system of Greek numerals it has a value of 400. It is derived from the Phoenician waw. The name of the letter is pronounced in Modern Greek, and in English , , or...
, and Etruscan V
V
V is the twenty-second letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-Letter:The letter V comes from the Semitic letter Waw, as do the modern letters F, U, W, and Y. See F for details....
(
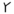

F
F is the sixth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The origin of ⟨f⟩ is the Semitic letter vâv that represented a sound like or . Graphically, it originally probably depicted either a hook or a club...
.
Vav literally means hook/peg/spear.
Hebrew Waw
| Orthographic Orthography The orthography of a language specifies a standardized way of using a specific writing system to write the language. Where more than one writing system is used for a language, for example Kurdish, Uyghur, Serbian or Inuktitut, there can be more than one orthography... variants |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Various Print Fonts | Cursive Hebrew |
Rashi Script Rashi script Rashi script is a semi-cursive typeface for the Hebrew alphabet. It is named for the author of the most famous rabbinic commentary on the Hebrew Bible and the Talmud, Rashi, and is customarily used for printing his commentaries. The typeface is based on 15th century Sephardic semi-cursive... |
||
| Serif | Sans-serif Sans-serif In typography, a sans-serif, sans serif or san serif typeface is one that does not have the small projecting features called "serifs" at the end of strokes. The term comes from the French word sans, meaning "without".... | Monospaced | ||
| ו | ו | ו |  |
 |
Hebrew spelling:
Pronunciation in Modern Hebrew
Waw has three orthographic variants, each with a different phonemicPhoneme
In a language or dialect, a phoneme is the smallest segmental unit of sound employed to form meaningful contrasts between utterances....
value and phonetic
Phonetics
Phonetics is a branch of linguistics that comprises the study of the sounds of human speech, or—in the case of sign languages—the equivalent aspects of sign. It is concerned with the physical properties of speech sounds or signs : their physiological production, acoustic properties, auditory...
realisation:
| Variant (with Niqqud) | without Niqqud Ktiv male Ktiv hasar niqqud , are the rules for writing Hebrew without vowel pointers , often replacing them with matres lectionis . To avoid confusion, consonantal ו and י are doubled in the middle of words... | Name | Phonemic Phoneme In a language or dialect, a phoneme is the smallest segmental unit of sound employed to form meaningful contrasts between utterances.... Value | Phonetic Phonetics Phonetics is a branch of linguistics that comprises the study of the sounds of human speech, or—in the case of sign languages—the equivalent aspects of sign. It is concerned with the physical properties of speech sounds or signs : their physiological production, acoustic properties, auditory... Realisation | English example |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
ו |
as initial letter:ו |
Consonantal Waw (Hebrew: Waw Itsurit ו׳ עיצורית) |
/v/ | v | vote |
| as middle letter:וו | |||||
| as final letter:ו or יו | |||||
וּ |
ו |
Vav Shruka ([väv ʃruˈkä] / ו׳ שרוקה) or Shuruq ([ʃuˈruk] / שׁוּרוּק) |
/u/ | u | glue |
וֹ |
ו |
Vav Chaluma ([väv χäluˈmä] / ו׳ חלומה) or Holam Male ([χo̞ˈläm maˈle̞] / חוֹלָם מָלֵא) |
/o/ | o̞ | no, noh |
in modern hebrew the frequency of the usage of vav, out of all the letters, is about 10.00%.
Vav as consonant
Consonantal vav (ו) generally represents a voiced labiodental fricativeVoiced labiodental fricative
The voiced labiodental fricative is a type of consonantal sound used in some spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is v....
(like the English v
V
V is the twenty-second letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-Letter:The letter V comes from the Semitic letter Waw, as do the modern letters F, U, W, and Y. See F for details....
) in Ashkenazi, European Sephardi, and modern Israeli Hebrew
Hebrew language
Hebrew is a Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Culturally, is it considered by Jews and other religious groups as the language of the Jewish people, though other Jewish languages had originated among diaspora Jews, and the Hebrew language is also used by non-Jewish groups, such...
; and originally a labial-velar approximant /w/. It is still pronounced as a w by some Jews of Oriental (Arabic
Arabic language
Arabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book...
speaking) origin.
In modern Israeli Hebrew, some loanword
Loanword
A loanword is a word borrowed from a donor language and incorporated into a recipient language. By contrast, a calque or loan translation is a related concept where the meaning or idiom is borrowed rather than the lexical item itself. The word loanword is itself a calque of the German Lehnwort,...
s, the pronunciation of whose source contains w, and their derivations
Derivation (linguistics)
In linguistics, derivation is the process of forming a new word on the basis of an existing word, e.g. happi-ness and un-happy from happy, or determination from determine...
, are pronounced with w, too, e.g. ואחד – /ˈwaχad/ (but: ואדי
Wadi
Wadi is the Arabic term traditionally referring to a valley. In some cases, it may refer to a dry riverbed that contains water only during times of heavy rain or simply an intermittent stream.-Variant names:...
– /ˈvadi/).
Modern Hebrew has no standardized
Standard language
A standard language is a language variety used by a group of people in their public discourse. Alternatively, varieties become standard by undergoing a process of standardization, during which it is organized for description in grammars and dictionaries and encoded in such reference works...
way to distinguish orthographically
Orthography
The orthography of a language specifies a standardized way of using a specific writing system to write the language. Where more than one writing system is used for a language, for example Kurdish, Uyghur, Serbian or Inuktitut, there can be more than one orthography...
between v and w. The pronunciation is either determined by prior knowledge or must be derived through context.
Some non standard
Linguistic prescription
In linguistics, prescription denotes normative practices on such aspects of language use as spelling, grammar, pronunciation, and syntax. It includes judgments on what usages are socially proper and politically correct...
spellings of the sound w are sometimes found in modern Hebrew texts, such as word-initial double-vav, e.g. וואללה – /ˈwala/ (word-medial double-vav is both standard and common for both w and v, see table above) or, rarely, vav with a geresh
Geresh
Geresh is a sign in Hebrew writing. It has two meanings.#An apostrophe-like sign placed after a letter :...
, e.g. ו׳יליאם – /ˈwiljam/.
Vav with a dot on top
Vav can be used as a mater lectionisMater lectionis
In the spelling of Hebrew and some other Semitic languages, matres lectionis , refers to the use of certain consonants to indicate a vowel. The letters that do this in Hebrew are aleph, he, waw and yod...
for an 'o' vowel, in which case it is known as a holam male, which in pointed text is marked as vav with a dot above it. It is pronounced o̞ (phonemically transcribed more simply as /o/).
This vowel is sometimes also denoted without the vav, as just the dot placed above and to the left of the letter it points, and is called then holam haser. Some inadequate typefaces don't support the distinction between the holam male, "", /o/, and a consonantal vav pointed with a holam haser, "", /vo/ (compare holam male in "", /maˈtsot/, to consonantal vav with holam haser in "" /mitsˈvot/). To correctly display a consonantal vav with holam haser, the typeface must either support the combined character "" (HTML Entity (decimal) ) or the Unicode Character 'HEBREW POINT HOLAM HASER FOR VAV' (U+05BA, HTML Entity (decimal) ֺ), e.g. "".
Vav with a dot in the middle
Vav can also be used as a mater lectionis for u, in which case it is known as a shuruk, and in text with niqqud is marked with a dot in the middle (on the left side).Shuruk and vav with a dagesh look identical ("") and are only distinguishable through the fact that in text with nikud, vav with a dagesh will normally be attributed a vocal point in addition, e.g. (/ʃuk/), "a market", (the "" denotes a shuruk) as opposed to (/ʃiˈvek/), "to market" (the "" denotes a vav with dagesh and is additionally pointed with a zeire, "", denoting /e/). In the word (/ʃiˈvuk/), "marketting", the first ("") denotes a vav with dagesh, the second a shuruk, being the vowel attributed to the first.
Numerical value
Vav in gematriaGematria
Gematria or gimatria is a system of assigning numerical value to a word or phrase, in the belief that words or phrases with identical numerical values bear some relation to each other, or bear some relation to the number itself as it may apply to a person's age, the calendar year, or the like...
represents the number six, and when used at the beginning of Hebrew years
Hebrew calendar
The Hebrew calendar , or Jewish calendar, is a lunisolar calendar used today predominantly for Jewish religious observances. It determines the dates for Jewish holidays and the appropriate public reading of Torah portions, yahrzeits , and daily Psalm reading, among many ceremonial uses...
, it means 6000 (i.e. ותשנד in numbers
Arabic numerals
Arabic numerals or Hindu numerals or Hindu-Arabic numerals or Indo-Arabic numerals are the ten digits . They are descended from the Hindu-Arabic numeral system developed by Indian mathematicians, in which a sequence of digits such as "975" is read as a numeral...
would be the date
Calendar date
A date in a calendar is a reference to a particular day represented within a calendar system. The calendar date allows the specific day to be identified. The number of days between two dates may be calculated. For example, "24 " is ten days after "14 " in the Gregorian calendar. The date of a...
6754.)
Words written as waw
Vav at the beginning of the word has several possible meanings:- Vav ConjunctiveWaw-conjunctiveA conjunctive waw or vav conjunctive is the use of Hebrew vav as a conjunction to join two parts of speech. It is distinct from waw-consecutive which is a verb construction.-Conjunction of two nouns:...
(Vav Hachibur, literally "the Vav of Connection" -- chibur means "joining, or bringing together") is a vav connecting two words or parts of a sentence; it is a grammatical conjunctionGrammatical conjunctionIn grammar, a conjunction is a part of speech that connects two words, sentences, phrases or clauses together. A discourse connective is a conjunction joining sentences. This definition may overlap with that of other parts of speech, so what constitutes a "conjunction" must be defined for each...
meaning 'and' , cognate to the Arabic. This is the most common usage. - Vav ConsecutiveWaw-consecutiveThe Waw-consecutive or Vav-consecutive is a grammatical construction in Classical Hebrew. It involves prefixing a verb form with the letter waw in order to change its aspect.-Waw-conjunctive and waw-consecutive:...
(Vav Hahipuch, literally "the Vav of Reversal" -- hipuch means "inversion"), mainly biblical, commonly mistaken for the previous type of vav; it indicates consequence of actions and reverses the tense of the verb following it:- when placed in front of a verb in the imperfect tense, it changes the verb to the perfect tense. For example, yomar means 'he will say' and vayomar means 'he said';
- when placed in front of a verb in the perfect, it changes the verb to the imperfect tense. For example, ahavtah means 'you loved', and ve'ahavtah means 'you will love'.
(Note: Older Hebrew did not have "tense" in a temporal sense, "perfect," and "imperfect" instead denoting aspect of completed or continuing action. Modern Hebrew verbal tenses have developed closer to their Indo-European counterparts, mostly having a temporal quality rather than denoting aspect. As a rule, Modern Hebrew does not use the "Vav Consecutive" form.)
Syriac Waw
| Waw |
|---|
| Madnḫaya Waw |
| Serṭo Waw |
| Esṭrangela Waw |
In the Syriac alphabet, the sixth letter is ܘ — Waw ܘܐܘ, it is pronounced as a [w]. When used as a mater lectionis, a Waw with a dot above the letter is an [o] vowel, and a Waw with a dot under the letter is an [u] vowel. It's alphabetic-numeral is 6.
Arabic wāw
The letter و is named واو wāw (wɑːw), and is written is several ways depending in its position in the word:Wāw is used to represent three distinct phonetic features:
- A consonant, pronounced as a voiced labial-velar approximantVoiced labial-velar approximantThe voiced labiovelar approximant is a type of consonantal sound, used in certain spoken languages, including English. It is the sound denoted by the letter "w" in the English alphabet; likewise, the symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is , and the equivalent...
/w/, which is the case whenever it is at the beginnings of words, but normally occurs also in the middle or end. - A longVowel lengthIn linguistics, vowel length is the perceived duration of a vowel sound. Often the chroneme, or the "longness", acts like a consonant, and may etymologically be one, such as in Australian English. While not distinctive in most dialects of English, vowel length is an important phonemic factor in...
/uː/. The preceding consonant could either have no diacritic or a short-wāw-vowel mark, damma, to aid in the pronunciation by hinting to the following long vowel. - A diphthongDiphthongA diphthong , also known as a gliding vowel, refers to two adjacent vowel sounds occurring within the same syllable. Technically, a diphthong is a vowel with two different targets: That is, the tongue moves during the pronunciation of the vowel...
, /aw/. In this case it has no diacritic, but could be marked with a sukun in some traditions. The preceding consonant could either have no diacritic or have sign, hinting to the first vowel /a/ in the diphthong. In some dialectsVarieties of ArabicThe Arabic language is a Semitic language characterized by a wide number of linguistic varieties within its five regional forms. The largest divisions occur between the spoken languages of different regions. The Arabic of North Africa, for example, is often incomprehensible to an Arabic speaker...
, the diphthong may be reduced to the long monophthongMonophthongA monophthong is a pure vowel sound, one whose articulation at both beginning and end is relatively fixed, and which does not glide up or down towards a new position of articulation....
/oː/. It is also commonly used for the latter phoneme to transcribe names or loanwordLoanwordA loanword is a word borrowed from a donor language and incorporated into a recipient language. By contrast, a calque or loan translation is a related concept where the meaning or idiom is borrowed rather than the lexical item itself. The word loanword is itself a calque of the German Lehnwort,...
s.
As a vowel, wāw can serve as the carrier of a hamza: .
Wāw serves several functions in the Modern Standard Arabic. Perhaps foremost among them is that it is the primary conjunction
Grammatical conjunction
In grammar, a conjunction is a part of speech that connects two words, sentences, phrases or clauses together. A discourse connective is a conjunction joining sentences. This definition may overlap with that of other parts of speech, so what constitutes a "conjunction" must be defined for each...
in Arabic, equivalent to "and"; it is usually prefix
Prefix
A prefix is an affix which is placed before the root of a word. Particularly in the study of languages,a prefix is also called a preformative, because it alters the form of the words to which it is affixed.Examples of prefixes:...
ed to other conjunctions, such as ولكن wa-lakin, meaning "but". Another function is the "oath
Oath
An oath is either a statement of fact or a promise calling upon something or someone that the oath maker considers sacred, usually God, as a witness to the binding nature of the promise or the truth of the statement of fact. To swear is to take an oath, to make a solemn vow...
", by preceding a noun of great significantly valued by the speaker. It is often literally translatable to "By..." or "I swear to...", and is often used in the Qur'an
Qur'an
The Quran , also transliterated Qur'an, Koran, Alcoran, Qur’ān, Coran, Kuran, and al-Qur’ān, is the central religious text of Islam, which Muslims consider the verbatim word of God . It is regarded widely as the finest piece of literature in the Arabic language...
in this way, and also in the generally fixed construction والله wallah ("By Allah
Allah
Allah is a word for God used in the context of Islam. In Arabic, the word means simply "God". It is used primarily by Muslims and Bahá'ís, and often, albeit not exclusively, used by Arabic-speaking Eastern Catholic Christians, Maltese Roman Catholics, Eastern Orthodox Christians, Mizrahi Jews and...
!" or "I swear to God!").

