
Green flash
Encyclopedia


Optical phenomenon
An optical phenomenon is any observable event that results from the interaction of light and matter. See also list of optical topics and optics. A mirage is an example of an optical phenomenon....
that occur shortly after sunset
Sunset
Sunset or sundown is the daily disappearance of the Sun below the horizon in the west as a result of Earth's rotation.The time of sunset is defined in astronomy as the moment the trailing edge of the Sun's disk disappears below the horizon in the west...
or before sunrise
Sunrise
Sunrise is the instant at which the upper edge of the Sun appears above the horizon in the east. Sunrise should not be confused with dawn, which is the point at which the sky begins to lighten, some time before the sun itself appears, ending twilight...
, when a green
Green
Green is a color, the perception of which is evoked by light having a spectrum dominated by energy with a wavelength of roughly 520–570 nanometres. In the subtractive color system, it is not a primary color, but is created out of a mixture of yellow and blue, or yellow and cyan; it is considered...
spot is visible, usually for no more than a second or two, above the sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
, or it may resemble a green ray shooting up from the sunset point. Green flashes are a group of phenomena stemming from different causes, and some are more common than others. Green flashes may be observed from any altitude
Altitude
Altitude or height is defined based on the context in which it is used . As a general definition, altitude is a distance measurement, usually in the vertical or "up" direction, between a reference datum and a point or object. The reference datum also often varies according to the context...
(even from an aircraft). They usually are seen at an unobstructed horizon
Horizon
The horizon is the apparent line that separates earth from sky, the line that divides all visible directions into two categories: those that intersect the Earth's surface, and those that do not. At many locations, the true horizon is obscured by trees, buildings, mountains, etc., and the resulting...
, such as over the ocean
Ocean
An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a principal component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas.More than half of this area is over 3,000...
, but are possible over cloud tops and mountain tops as well.
A green flash also may be observed in association with the Moon
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
and bright planets at the horizon, including Venus
Venus
Venus is the second planet from the Sun, orbiting it every 224.7 Earth days. The planet is named after Venus, the Roman goddess of love and beauty. After the Moon, it is the brightest natural object in the night sky, reaching an apparent magnitude of −4.6, bright enough to cast shadows...
and Jupiter
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet within the Solar System. It is a gas giant with mass one-thousandth that of the Sun but is two and a half times the mass of all the other planets in our Solar System combined. Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn,...
.
Explanation
The reason for green flash optical phenomena lies in refractionRefraction
Refraction is the change in direction of a wave due to a change in its speed. It is essentially a surface phenomenon . The phenomenon is mainly in governance to the law of conservation of energy. The proper explanation would be that due to change of medium, the phase velocity of the wave is changed...
of light
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
(as in a prism
Prism (optics)
In optics, a prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that refract light. The exact angles between the surfaces depend on the application. The traditional geometrical shape is that of a triangular prism with a triangular base and rectangular sides, and in colloquial use...
) in the atmosphere
Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention , and reducing temperature extremes between day and night...
: light moves more slowly in the lower, denser air than in the thinner air above, so sunlight rays follow paths that curve slightly, in the same direction as the curvature of the Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
. Higher frequency light (green/blue) curves more than lower frequency light (red/orange), so green/blue rays from the upper rim of the setting sun remain visible after the red rays are obstructed by the curvature of the earth.
Green flashes are enhanced by mirage
Mirage of astronomical objects
A mirage of an astronomical object is a naturally occurring optical phenomenon, in which light rays are bent to produce distorted or multiple images of an astronomical object. The mirages might be observed for such astronomical objects as the Sun, the Moon, the planets, bright stars and very...
, which increase the density gradient in the atmosphere and therefore, increase refraction. A green flash is more likely to be seen in clear air, when more of the light from the setting sun reaches the observer without being scattered. One might expect to see a blue
Blue
Blue is a colour, the perception of which is evoked by light having a spectrum dominated by energy with a wavelength of roughly 440–490 nm. It is considered one of the additive primary colours. On the HSV Colour Wheel, the complement of blue is yellow; that is, a colour corresponding to an equal...
flash, but the blue is preferentially scattered out of the line of sight, and remaining light ends up looking green.
With slight magnification
Magnification
Magnification is the process of enlarging something only in appearance, not in physical size. This enlargement is quantified by a calculated number also called "magnification"...
a green rim on the top of the solar disk
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
may be seen on most clear-day sunsets, although the flash or ray effects require a stronger layering of the atmosphere and a mirage, which serves to magnify the green for a fraction of a second to a couple of seconds.
Types
The "green flash" description relates to a group of optical phenomena, some of which are listed below:| Type | Characteristics | Conditions | Best seen from... |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inferior-mirage flash | Joule's "last glimpse"; oval, flattened below; lasts 1 or 2 seconds | Surface warmer than the overlying air | Close to sea level Sea level Mean sea level is a measure of the average height of the ocean's surface ; used as a standard in reckoning land elevation... |
| Mock-mirage flash | Indentations seem to "pinch off" a thin, pointy strip from the upper rim of the Sun; lasts 1 or 2 seconds | Atmospheric inversion layer below eye level; surface colder than air | The higher the eye, the more likely; flash is most obvious when the eye is just above the inversion. |
| Sub-duct Atmospheric duct In telecommunication, an atmospheric duct is a horizontal layer in the lower atmosphere in which the vertical refractive index gradients are such that radio signals are guided or ducted, tend to follow the curvature of the Earth, and experience less attenuation in the ducts than they would if... flash |
Large upper part of an hourglass Hourglass An hourglass measures the passage of a few minutes or an hour of time. It has two connected vertical glass bulbs allowing a regulated trickle of material from the top to the bottom. Once the top bulb is empty, it can be inverted to begin timing again. The name hourglass comes from historically... -shaped Sun turns green for up to 15 seconds; |
Observer below a strong atmospheric inversion Inversion (meteorology) In meteorology, an inversion is a deviation from the normal change of an atmospheric property with altitude. It almost always refers to a temperature inversion, i.e... |
In a narrow height interval just below a duct (can occur at any height) |
| Green ray | Green beam of light either shooting up or seen immediately after sundown; usually few degrees long, lasting several seconds | Hazy air and a bright green flash acting as a light source | Sea level |
The majority of flashes observed are inferior-mirage or mock-mirage effects, with the others constituting only 1% of reports. Some types not listed in the table above, such as the cloud
Cloud
A cloud is a visible mass of liquid droplets or frozen crystals made of water and/or various chemicals suspended in the atmosphere above the surface of a planetary body. They are also known as aerosols. Clouds in Earth's atmosphere are studied in the cloud physics branch of meteorology...
-top flash (seen as the sun sinks into a coastal fog
Fog
Fog is a collection of water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. While fog is a type of stratus cloud, the term "fog" is typically distinguished from the more generic term "cloud" in that fog is low-lying, and the moisture in the fog is often generated...
, or at distant cumulus cloud
Cumulus cloud
Cumulus clouds are a type of cloud with noticeable vertical development and clearly defined edges. Cumulus means "heap" or "pile" in Latin. They are often described as "puffy" or "cotton-like" in appearance. Cumulus clouds may appear alone, in lines, or in clusters...
s), are not understood.
Blue flashes
Very occasionally, the amount of blue light is sufficient to be visible as a "blue flash". The term should not be confused with the similar usage of blue flash referring to the blue light seen in nuclearNuclear reaction
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, a nuclear reaction is semantically considered to be the process in which two nuclei, or else a nucleus of an atom and a subatomic particle from outside the atom, collide to produce products different from the initial particles...
criticality accident
Criticality accident
A criticality accident, sometimes referred to as an excursion or a power excursion, is an accidental increase of nuclear chain reactions in a fissile material, such as enriched uranium or plutonium...
s.
Green rim

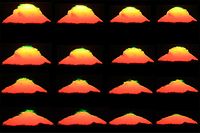
Astronomical object
Astronomical objects or celestial objects are naturally occurring physical entities, associations or structures that current science has demonstrated to exist in the observable universe. The term astronomical object is sometimes used interchangeably with astronomical body...
sets or rises in relation to the horizon, the light it emits travels through Earth's atmosphere
Atmosphere
An atmosphere is a layer of gases that may surround a material body of sufficient mass, and that is held in place by the gravity of the body. An atmosphere may be retained for a longer duration, if the gravity is high and the atmosphere's temperature is low...
, which works as a prism
Prism (optics)
In optics, a prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that refract light. The exact angles between the surfaces depend on the application. The traditional geometrical shape is that of a triangular prism with a triangular base and rectangular sides, and in colloquial use...
separating the light into different colors. The color of the upper rim of an astronomical object could go from green to blue to violet depending on the decrease in concentration of pollutants
Air pollution
Air pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or biological materials that cause harm or discomfort to humans or other living organisms, or cause damage to the natural environment or built environment, into the atmosphere....
, as they spread throughout an increasing volume of atmosphere. The lower rim of an astronomical object is always red.
A green rim is very thin, and is difficult or impossible to see with the naked eye. In usual conditions, a green rim of an astronomical object gets fainter, when an astronomical object is very low above the horizon
Horizon
The horizon is the apparent line that separates earth from sky, the line that divides all visible directions into two categories: those that intersect the Earth's surface, and those that do not. At many locations, the true horizon is obscured by trees, buildings, mountains, etc., and the resulting...
because of atmospheric reddening, but sometimes the conditions are right to see a green rim just above the horizon. The following quote describes what was probably the longest observation of a green rim, which at times could have been a green flash. It was seen on and off for 35 minutes by members of the Richard Evelyn Byrd
Richard Evelyn Byrd
Rear Admiral Richard Evelyn Byrd, Jr., USN was a naval officer who specialized in feats of exploration. He was a pioneering American aviator, polar explorer, and organizer of polar logistics...
party from the Little America exploration base in 1934:
For the explorers to have seen a green rim on and off for 35 minutes, there must have been some mirage effect present.
A green rim is present at every sunset, but it is too thin to be seen with the naked eye. Often a green rim changes to a green flash and back again during the same sunset
Sunset
Sunset or sundown is the daily disappearance of the Sun below the horizon in the west as a result of Earth's rotation.The time of sunset is defined in astronomy as the moment the trailing edge of the Sun's disk disappears below the horizon in the west...
. The best time to observe a green rim is about 10 minutes before sunset. That is too early to use any magnification
Magnification
Magnification is the process of enlarging something only in appearance, not in physical size. This enlargement is quantified by a calculated number also called "magnification"...
like binoculars
Binoculars
Binoculars, field glasses or binocular telescopes are a pair of identical or mirror-symmetrical telescopes mounted side-by-side and aligned to point accurately in the same direction, allowing the viewer to use both eyes when viewing distant objects...
or a telescope
Telescope
A telescope is an instrument that aids in the observation of remote objects by collecting electromagnetic radiation . The first known practical telescopes were invented in the Netherlands at the beginning of the 1600s , using glass lenses...
to look directly at the Sun without potential harm to the eyes. (Of course, a magnified image might be projected onto a sheet of paper for safe viewing.) When the sun gets closer to the horizon, the green rim is becoming fainter because of atmospheric reddening. According to the above, it is probably correct to conclude that although a green rim is present during every sunset, a green flash is rarer because of the required mirage
Mirage of astronomical objects
A mirage of an astronomical object is a naturally occurring optical phenomenon, in which light rays are bent to produce distorted or multiple images of an astronomical object. The mirages might be observed for such astronomical objects as the Sun, the Moon, the planets, bright stars and very...
.
See also
- Mirage of astronomical objectsMirage of astronomical objectsA mirage of an astronomical object is a naturally occurring optical phenomenon, in which light rays are bent to produce distorted or multiple images of an astronomical object. The mirages might be observed for such astronomical objects as the Sun, the Moon, the planets, bright stars and very...
- Jules VerneJules VerneJules Gabriel Verne was a French author who pioneered the science fiction genre. He is best known for his novels Twenty Thousand Leagues Under the Sea , A Journey to the Center of the Earth , and Around the World in Eighty Days...
's novel The Green RayThe Green RayThe Green Ray is a novel by the French writer Jules Verne published in 1882 and named after the optical phenomenon . It is referenced in a film of the same name by Eric Rohmer.- Plot summary :...
, 1882, which popularized the green flash - The Green Ray - a film that uses the green flash (and Verne's book) as a plot device
- David Winstanley, "Atmospheric Refraction and the Last Rays of the Setting Sun", reported at Manchester Literary & Philosophical Society Meeting, 7 October 1873
- Sir Arthur Schuster, Letter to NATURE 21 Feb. 1915 referring to his observation of the phenomenon on a voyage in the Indian Ocean in 1875
- Captain Alfred Carpenter & Captain D. Wilson-Barker, “Nature Notes for Ocean Voyagers” (London, 1915) reported on page 147
- Pirates of the Caribbean: At World's End - When the Flying Dutchman appears and disappears from the land of the dead
External links
- A Green Flash Page, Andrew T. Young's page with comprehensive explanations and simulations
- Green Flash - Atmospheric Optics, explanations and image gallery, Les Cowley's Atmospheric Optics site
- A Green Flash from Astronomy Picture of the DayAstronomy Picture of the DayAstronomy Picture of the Day is a website provided by NASA and Michigan Technological University . According to the website, "Each day a different image or photograph of our universe is featured, along with a brief explanation written by a professional astronomer."The photograph is not necessarily...
, NASANASAThe National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research... - 06/03/2010 Photograph of a green flash over the Indian Ocean

