Geography of Tunisia
Encyclopedia
Tunisia
is a country located in Northern Africa, bordering the Mediterranean Sea
, between Algeria
and Libya
. Its geographic coordinates are 34°00′N 9°00′E. Tunisia
occupies an area of 163,610 square kilometres, of which 8,250 are water. Tunisia borders Algeria for 965 km and Libya for 459 km.
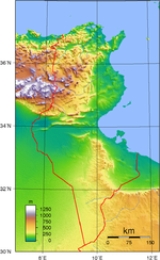
 Tunisia is situated on the Mediterranean coast of North Africa, midway between the Atlantic Ocean and the Nile Delta. It is bordered by Algeria on the west and Libya on the south east. It lies between latitudes 30° and 38°N, and longitudes 7° and 12°E. An abrupt southward turn of the Mediterranean coast in northern Tunisia gives the country two distinctive Mediterranean coasts, west-east in the north, and north-south in the east.
Tunisia is situated on the Mediterranean coast of North Africa, midway between the Atlantic Ocean and the Nile Delta. It is bordered by Algeria on the west and Libya on the south east. It lies between latitudes 30° and 38°N, and longitudes 7° and 12°E. An abrupt southward turn of the Mediterranean coast in northern Tunisia gives the country two distinctive Mediterranean coasts, west-east in the north, and north-south in the east.
Tunisia is about the size of the American state of Wisconsin. Despite its relatively small size, Tunisia has great environmental diversity due to its north-south extent. Its east-west extent is limited. Differences in Tunisia, like the rest of the Maghreb, are largely north-south environmental differences defined by sharply decreasing rainfall southward from any point. The Dorsal, the eastern extension of the Atlas Mountains, runs across Tunisia in a northeasterly direction from the Algerian border in the west to the Cape Bon peninsula in the east. North of the Dorsal is the Tell, a region characterized by low, rolling hills and plains, again an extension of mountains to the west in Algeria. In the Khroumerie, the northwestern corner of the Tunisian Tell, elevations reach 1,050 metres (3,440 ft) and snow occurs in winter.
The Sahel, a broadening coastal plain along Tunisia's eastern Mediterranean coast, is among the world's premier areas of olive cultivation. Inland from the Sahel, between the Dorsal and a range of hills south of Gafsa, are the Steppes. Much of the southern region is semi-arid and desert.
Tunisia has a coastline 1,148 kilometres (713 mi) long. In maritime terms, the country claims a contiguous zone of 24 nautical miles (44.4 km; 27.6 mi), and a territorial sea of 12 nautical miles (22.2 km; 13.8 mi).
in the north, with mild rainy winters and hot, dry summers. Temperatures in July and August can exceed even up to 40°C. Winters are mild with temperatures rarely exceeding above 20°C (exception is the south-west of the country). The south of the country is desert. The terrain in the north is mountainous, which, moving south, gives way to a hot, dry central plain
. The south is semiarid, and merges into the Sahara
. A series of salt lakes
, known as chotts or shatts, lie in an east-west line at the northern edge of the Sahara, extending from the Gulf of Gabes
into Algeria
. The lowest point is Chott el Djerid
, at -17 m, and the highest is Jebel ech Chambi
, at 1544 metres (5,066 ft).
source: Institut National de la Statistique - Tunisie
, phosphate
s, iron
ore, lead
, zinc
, salt
and arable land. 3,850 km² of land is irrigated in Tunisia. The use of land in the country is demonstrated in the following table.
Tunisia is a party to the following international agreements: Biodiversity
, Climate Change
, Desertification
, Endangered Species
, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea
, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution (MARPOL 73/78
) and Wetlands. Tunisia has signed, but not ratified the Marine Life Conservation agreement.
Tunisia, like other North African countries, has lost much of its prehistoric biodiversity
due to the ongoing expanding human population
; for example, until historic times there was a population of the endangered primate
Barbary Macaque
, Macaca sylvanus. The Monk Seal is now extirpated
from Tunisia.
, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
Tunisia
Tunisia , officially the Tunisian RepublicThe long name of Tunisia in other languages used in the country is: , is the northernmost country in Africa. It is a Maghreb country and is bordered by Algeria to the west, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Its area...
is a country located in Northern Africa, bordering the Mediterranean Sea
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean surrounded by the Mediterranean region and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Anatolia and Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant...
, between Algeria
Algeria
Algeria , officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria , also formally referred to as the Democratic and Popular Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of Northwest Africa with Algiers as its capital.In terms of land area, it is the largest country in Africa and the Arab...
and Libya
Libya
Libya is an African country in the Maghreb region of North Africa bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad and Niger to the south, and Algeria and Tunisia to the west....
. Its geographic coordinates are 34°00′N 9°00′E. Tunisia
Tunisia
Tunisia , officially the Tunisian RepublicThe long name of Tunisia in other languages used in the country is: , is the northernmost country in Africa. It is a Maghreb country and is bordered by Algeria to the west, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Its area...
occupies an area of 163,610 square kilometres, of which 8,250 are water. Tunisia borders Algeria for 965 km and Libya for 459 km.
Maritime claims
- Contiguous zone: 24 nmi (44.4 km; 27.6 mi)
- Territorial sea: 12 nmi (22.2 km; 13.8 mi)
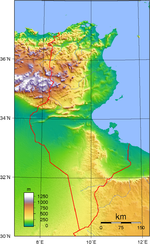
Physical geography

Tunisia is about the size of the American state of Wisconsin. Despite its relatively small size, Tunisia has great environmental diversity due to its north-south extent. Its east-west extent is limited. Differences in Tunisia, like the rest of the Maghreb, are largely north-south environmental differences defined by sharply decreasing rainfall southward from any point. The Dorsal, the eastern extension of the Atlas Mountains, runs across Tunisia in a northeasterly direction from the Algerian border in the west to the Cape Bon peninsula in the east. North of the Dorsal is the Tell, a region characterized by low, rolling hills and plains, again an extension of mountains to the west in Algeria. In the Khroumerie, the northwestern corner of the Tunisian Tell, elevations reach 1,050 metres (3,440 ft) and snow occurs in winter.
The Sahel, a broadening coastal plain along Tunisia's eastern Mediterranean coast, is among the world's premier areas of olive cultivation. Inland from the Sahel, between the Dorsal and a range of hills south of Gafsa, are the Steppes. Much of the southern region is semi-arid and desert.
Tunisia has a coastline 1,148 kilometres (713 mi) long. In maritime terms, the country claims a contiguous zone of 24 nautical miles (44.4 km; 27.6 mi), and a territorial sea of 12 nautical miles (22.2 km; 13.8 mi).
Climate
Tunisia's climate is temperateTemperate
In geography, temperate or tepid latitudes of the globe lie between the tropics and the polar circles. The changes in these regions between summer and winter are generally relatively moderate, rather than extreme hot or cold...
in the north, with mild rainy winters and hot, dry summers. Temperatures in July and August can exceed even up to 40°C. Winters are mild with temperatures rarely exceeding above 20°C (exception is the south-west of the country). The south of the country is desert. The terrain in the north is mountainous, which, moving south, gives way to a hot, dry central plain
Plain
In geography, a plain is land with relatively low relief, that is flat or gently rolling. Prairies and steppes are types of plains, and the archetype for a plain is often thought of as a grassland, but plains in their natural state may also be covered in shrublands, woodland and forest, or...
. The south is semiarid, and merges into the Sahara
Sahara
The Sahara is the world's second largest desert, after Antarctica. At over , it covers most of Northern Africa, making it almost as large as Europe or the United States. The Sahara stretches from the Red Sea, including parts of the Mediterranean coasts, to the outskirts of the Atlantic Ocean...
. A series of salt lakes
Tunisian salt lakes
The Tunisian salt lakes are a series of lakes in central Tunisia, lying south of the Atlas Mountains at the northern edge of the Sahara. The lakes include, from east to west, the Chott el Fedjedji, Chott el Djerid, and Chott el Gharsa....
, known as chotts or shatts, lie in an east-west line at the northern edge of the Sahara, extending from the Gulf of Gabes
Gulf of Gabès
The Gulf of Gabès is a gulf on Tunisia's east coast in the Mediterranean Sea, off North Africa. The gulf roughly spans the coast from modern day the town of Mahrès in Sfax Gouvernorate to Djerba...
into Algeria
Algeria
Algeria , officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria , also formally referred to as the Democratic and Popular Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of Northwest Africa with Algiers as its capital.In terms of land area, it is the largest country in Africa and the Arab...
. The lowest point is Chott el Djerid
Chott el Djerid
Chott el Djerid , also spelt Shaţţ al Jarīd, Sciott Gerid, and Shott el Jerid, is a large endorheic salt lake in southern Tunisia.-Geography:The bottom of Chott el Djerid is located between 10 and 25 meters above sea level....
, at -17 m, and the highest is Jebel ech Chambi
Jebel ech Chambi
Jebel ech Chambi is the highest mountain in Tunisia at 1544m. It stands above the city of Kasserine in western central Tunisia and is covered by a pine forest....
, at 1544 metres (5,066 ft).
Largest cities
| Cities in Tunisia | ||||
| Rank | Name | Population, 2006 | Population, 2008 | Governorate |
| 1. | Tunis Tunis Tunis is the capital of both the Tunisian Republic and the Tunis Governorate. It is Tunisia's largest city, with a population of 728,453 as of 2004; the greater metropolitan area holds some 2,412,500 inhabitants.... |
989,000 | 993,000 | Tunis Tunis Governorate Tunis Governorate the smallest and most populated of the twenty-four governorates of Tunisia. It is situated in northern Tunisia. It covers an area of and has a population of 984,000... |
| 2. | Sfax Sfax Sfax is a city in Tunisia, located southeast of Tunis. The city, founded in AD 849 on the ruins of Taparura and Thaenae, is the capital of the Sfax Governorate , and a Mediterranean port. Sfax has population of 340,000... |
881,600 | 904,900 | Sfax Sfax Governorate The Sfax Governorate is one of the governorates of Tunisia. The governorate has a population of 860,000 and an area of 7,545 km². Its capital is Sfax.The following cities and towns are located in the Sfax Governorate:* Agareb... |
| 3. | Nabeul Nabeul Nabeul is a coastal town in northeastern Tunisia, on the south coast near to the Cap Bon peninsula. It is located at around and is the capital of the Nabeul Governorate... |
714,500 | 733,500 | Nabeul Nabeul Governorate Nabeul Governorate is one of the 24 governorates of Tunisia. It is situated in north-eastern Tunisia. It covers an area of 2,788 km² and has a population of 694,000 . The capital is Nabeul.-Municipalities:... |
| 4. | Sousse Sousse Sousse is a city in Tunisia. Located 140 km south of the capital Tunis, the city has 173,047 inhabitants . Sousse is in the central-east of the country, on the Gulf of Hammamet, which is a part of the Mediterranean Sea. The name may be of Berber origin: similar names are found in Libya and in... |
568,100 | 590,400 | Sousse Sousse Governorate Sousse Governorate is one of the twenty-four governorates of Tunisia. It is situated in north-eastern Tunisia. It covers an area of 2,621 km² and has a population of 544,000... |
| 5. | Ben Arous Ben Arous Ben Arous is a coastal town in northeastern Tunisia. It is located at around and is the capital of the Ben Arous Governorate.-Information about Ben Arous:... |
531,200 | 555,700 | Ben Arous Ben Arous Governorate Ben Arous Governorate is one of the twenty-four governorates of Tunisia. It is situated in northern Tunisia. It covers an area of 761 km² and has a population of 506,000... |
| 6. | Kairouan Kairouan Kairouan , also known as Kirwan or al-Qayrawan , is the capital of the Kairouan Governorate in Tunisia. Referred to as the Islamic Cultural Capital, it is a UNESCO World Heritage site. The city was founded by the Arabs around 670... |
550,300 | 553,800 | Kairouan Kairouan Governorate Kairouan Governorate is one of the twenty-four governorates of Tunisia. It is an inland province, situated in the centre of the country. It covers an area of 6,712 km² and has a population of 546,209... |
| 7. | Bizerte Bizerte Bizerte or Benzert , is the capital city of Bizerte Governorate in Tunisia and the northernmost city in Africa. It has a population of 230,879 .-History:... |
532,900 | 538,900 | Bizerte Bizerte Governorate Bizerte Governorate is the northernmost of the 24 governorates of Tunisia. It is situated in northern Tunisia. It covers an area of 3,685 km² and has a population of 524,000 . The capital is Bizerte... |
| 8. | Monastir Monastir, Tunisia -Areas within Monastir:Monastir's north-eastern territories lead into a place called Route de la Falaise, through which you will reach its most notable suburb, Skanes, which is 6 miles from Monastir's town centre... |
475,200 | 494,900 | Monastir Monastir Governorate Monastir Governorate is one of the twenty-four governorates of Tunisia. It is situated in north-eastern Tunisia. It covers an area of 1,019 km² and has a population of 456,000... |
| 9. | Ariana Aryanah Aryanah is a coastal city in northeastern Tunisia. It is located at around . It is the capital of Ariana Governorate and the country's eighth largest city.... |
447,200 | 473,100 | Ariana Ariana Governorate Ariana Governorate is one of the twenty-four governorates of Tunisia. It is situated in northern Tunisia. It has a population of 422,000 . The capital is Aryanah.The following cities and towns are located in the Ariana Governorate:... |
| 10. | Medenine Medenine Medenine is the major town in southeastern Tunisia, south of the port of Gabès and the Island of Djerba, on the main route to Libya. It is the capital of Medenine Governorate.- Overview :... |
440,200 | 447,400 | Medenine Medenine Governorate Medenine is one of the 24 governorates of Tunisia. It is situated in south-eastern Tunisia. It covers an area of 8,588 km² and had a population of 432,503 at the 2004 census... |
source: Institut National de la Statistique - Tunisie
Natural resources
Tunisia possesses petroleumPetroleum
Petroleum or crude oil is a naturally occurring, flammable liquid consisting of a complex mixture of hydrocarbons of various molecular weights and other liquid organic compounds, that are found in geologic formations beneath the Earth's surface. Petroleum is recovered mostly through oil drilling...
, phosphate
Phosphate
A phosphate, an inorganic chemical, is a salt of phosphoric acid. In organic chemistry, a phosphate, or organophosphate, is an ester of phosphoric acid. Organic phosphates are important in biochemistry and biogeochemistry or ecology. Inorganic phosphates are mined to obtain phosphorus for use in...
s, iron
Iron
Iron is a chemical element with the symbol Fe and atomic number 26. It is a metal in the first transition series. It is the most common element forming the planet Earth as a whole, forming much of Earth's outer and inner core. It is the fourth most common element in the Earth's crust...
ore, lead
Lead
Lead is a main-group element in the carbon group with the symbol Pb and atomic number 82. Lead is a soft, malleable poor metal. It is also counted as one of the heavy metals. Metallic lead has a bluish-white color after being freshly cut, but it soon tarnishes to a dull grayish color when exposed...
, zinc
Zinc
Zinc , or spelter , is a metallic chemical element; it has the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. It is the first element in group 12 of the periodic table. Zinc is, in some respects, chemically similar to magnesium, because its ion is of similar size and its only common oxidation state is +2...
, salt
Salt
In chemistry, salts are ionic compounds that result from the neutralization reaction of an acid and a base. They are composed of cations and anions so that the product is electrically neutral...
and arable land. 3,850 km² of land is irrigated in Tunisia. The use of land in the country is demonstrated in the following table.
| Use | Percentage of Area (1993) |
|---|---|
| arable land | 19 |
| permanent crops | 13 |
| permanent pastures | 20 |
| forests and woodland | 4 |
| other | 44 |
Environment
Current environmental issues for Tunisia include:- Toxic and hazardous wasteHazardous wasteA hazardous waste is waste that poses substantial or potential threats to public health or the environment. According to the U.S. environmental laws hazardous wastes fall into two major categories: characteristic wastes and listed wastes.Characteristic hazardous wastes are materials that are known...
- disposal is ineffective and presents human health risks - Water pollutionWater pollutionWater pollution is the contamination of water bodies . Water pollution occurs when pollutants are discharged directly or indirectly into water bodies without adequate treatment to remove harmful compounds....
from raw sewage - Limited natural fresh waterFresh WaterFresh Water is the debut album by Australian rock and blues singer Alison McCallum, released in 1972. Rare for an Australian artist at the time, it came in a gatefold sleeve...
resources - DeforestationDeforestationDeforestation is the removal of a forest or stand of trees where the land is thereafter converted to a nonforest use. Examples of deforestation include conversion of forestland to farms, ranches, or urban use....
- OvergrazingOvergrazingOvergrazing occurs when plants are exposed to intensive grazing for extended periods of time, or without sufficient recovery periods. It can be caused by either livestock in poorly managed agricultural applications, or by overpopulations of native or non-native wild animals.Overgrazing reduces the...
- Soil erosion
- DesertificationDesertificationDesertification is the degradation of land in drylands. Caused by a variety of factors, such as climate change and human activities, desertification is one of the most significant global environmental problems.-Definitions:...
Tunisia is a party to the following international agreements: Biodiversity
Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the degree of variation of life forms within a given ecosystem, biome, or an entire planet. Biodiversity is a measure of the health of ecosystems. Biodiversity is in part a function of climate. In terrestrial habitats, tropical regions are typically rich whereas polar regions...
, Climate Change
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change is an international environmental treaty produced at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development , informally known as the Earth Summit, held in Rio de Janeiro from June 3 to 14, 1992...
, Desertification
Desertification
Desertification is the degradation of land in drylands. Caused by a variety of factors, such as climate change and human activities, desertification is one of the most significant global environmental problems.-Definitions:...
, Endangered Species
Endangered species
An endangered species is a population of organisms which is at risk of becoming extinct because it is either few in numbers, or threatened by changing environmental or predation parameters...
, Environmental Modification, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea
Law of the sea
Law of the sea may refer to:* United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea* Admiralty law* The Custom of the Sea...
, Marine Dumping, Nuclear Test Ban, Ozone Layer Protection, Ship Pollution (MARPOL 73/78
MARPOL 73/78
Marpol 73/78 is the International Convention for the Prevention of Pollution From Ships, 1973 as modified by the Protocol of 1978....
) and Wetlands. Tunisia has signed, but not ratified the Marine Life Conservation agreement.
Tunisia, like other North African countries, has lost much of its prehistoric biodiversity
Biodiversity
Biodiversity is the degree of variation of life forms within a given ecosystem, biome, or an entire planet. Biodiversity is a measure of the health of ecosystems. Biodiversity is in part a function of climate. In terrestrial habitats, tropical regions are typically rich whereas polar regions...
due to the ongoing expanding human population
Overpopulation
Overpopulation is a condition where an organism's numbers exceed the carrying capacity of its habitat. The term often refers to the relationship between the human population and its environment, the Earth...
; for example, until historic times there was a population of the endangered primate
Primate
A primate is a mammal of the order Primates , which contains prosimians and simians. Primates arose from ancestors that lived in the trees of tropical forests; many primate characteristics represent adaptations to life in this challenging three-dimensional environment...
Barbary Macaque
Barbary Macaque
The Barbary Macaque , or Common macaque, is a macaque with no tail. Found in the Atlas Mountains of Algeria and Morocco with a small population, of unknown origin, in Gibraltar, the Barbary Macaque is one of the best-known Old World monkey species. Besides humans, they are the only primates that...
, Macaca sylvanus. The Monk Seal is now extirpated
Local extinction
Local extinction, also known as extirpation, is the condition of a species which ceases to exist in the chosen geographic area of study, though it still exists elsewhere...
from Tunisia.
Extreme points
This is a list of the extreme points of TunisiaTunisia
Tunisia , officially the Tunisian RepublicThe long name of Tunisia in other languages used in the country is: , is the northernmost country in Africa. It is a Maghreb country and is bordered by Algeria to the west, Libya to the southeast, and the Mediterranean Sea to the north and east. Its area...
, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
- Northern-most point - Iles des Chiens, Bizerte GovernorateBizerte GovernorateBizerte Governorate is the northernmost of the 24 governorates of Tunisia. It is situated in northern Tunisia. It covers an area of 3,685 km² and has a population of 524,000 . The capital is Bizerte...
- Northern-most point (mainland) – Ras ben SakkaRas ben SakkaRas ben Sakka is the northernmost point of the African continent, located in Tunisia. It is located at 37°21' N., just 950 meters west of Cap Blanc , which is often mentioned as the northern tip of Africa, and reaching more than 30 meters further north than the latter.-References:...
(Ra's al Abyad), Bizerte GovernorateBizerte GovernorateBizerte Governorate is the northernmost of the 24 governorates of Tunisia. It is situated in northern Tunisia. It covers an area of 3,685 km² and has a population of 524,000 . The capital is Bizerte...
* - Eastern-most point – Bel Ahemer on the border with LibyaLibyaLibya is an African country in the Maghreb region of North Africa bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad and Niger to the south, and Algeria and Tunisia to the west....
, Medenine GovernorateMedenine GovernorateMedenine is one of the 24 governorates of Tunisia. It is situated in south-eastern Tunisia. It covers an area of 8,588 km² and had a population of 432,503 at the 2004 census... - Southern-most point – the tripointTripointA tripoint, or trijunction , is a geographical point at which the borders of three countries or subnational entities meet....
with AlgeriaAlgeriaAlgeria , officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria , also formally referred to as the Democratic and Popular Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of Northwest Africa with Algiers as its capital.In terms of land area, it is the largest country in Africa and the Arab...
and LibyaLibyaLibya is an African country in the Maghreb region of North Africa bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Sudan to the southeast, Chad and Niger to the south, and Algeria and Tunisia to the west....
, Tataouine GovernorateTataouine GovernorateTataouine Governorate is the southernmost of the twenty-four governorates of Tunisia, the only one to border both Algeria and Libya. It is also the largest Tunisian governorate, covering an area of 38,889 km² with a population of 143,524 , nearly tied for second least populated with Kebili ... - Western-most point - unnamed location on the border with AlgeriaAlgeriaAlgeria , officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria , also formally referred to as the Democratic and Popular Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of Northwest Africa with Algiers as its capital.In terms of land area, it is the largest country in Africa and the Arab...
due west of Nefta, Tozeur GovernorateTozeur GovernorateTozeur is one of the 24 governorates of Tunisia. It is situated in western Tunisia, bordering Algeria. It covers an area of 4,719 km² and has a population of 98,000 . The capital is Tozeur....
- *Note: this is also the northern-most point of the African continent

