
Breast cancer treatment
Encyclopedia
The mainstay of breast cancer treatment is surgery
when the tumor is localized, followed by chemotherapy (when indicated), radiotherapy and adjuvant hormonal therapy for ER positive tumours (with tamoxifen
or an aromatase inhibitor
). Management of breast cancer is undertaken by a multidisciplinary team based on national and international guidelines. Depending on clinical criteria (age, type of cancer, size, metastasis) patients are roughly divided to high risk and low risk cases, with each risk category following different rules for therapy. Treatment possibilities include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and immune therapy.
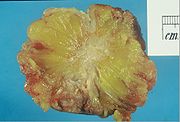 Depending on the staging and type of the tumor, just a lumpectomy
Depending on the staging and type of the tumor, just a lumpectomy
(removal of the lump only) may be all that is necessary, or removal of larger amounts of breast tissue may be necessary. Surgical removal of the entire breast is called mastectomy
.
Lumpectomy techniques are increasingly utilized for breast-conservation cancer surgery. Studies indicate that for patients with a single tumor smaller than 4cm, lumpectomy may be as effective as a mastectomy. Prior to a lumpectomy, a needle-localization
of the lesion with placement of a guidewire may be performed, sometimes by a radiologist if the area being removed was detected by mammography
or ultrasound
, and sometimes by the surgeon
if the lesion can be directly palpated.
However, mastectomy may be the preferred treatment in certain instances:
Standard practice requires the surgeon to establish that the tissue removed in the operation has margins clear of cancer, indicating that the cancer has been completely excised. If the removed tissue does not have clear margins, further operations to remove more tissue may be necessary. This may sometimes require removal of part of the pectoralis major muscle
, which is the main muscle of the anterior chest wall.
During the operation, the lymph nodes in the axilla are also considered for removal. In the past, large axillary operations took out 10 to 40 nodes to establish whether cancer had spread. This had the unfortunate side effect of frequently causing lymphedema
of the arm on the same side, as the removal of this many lymph nodes affected lymphatic drainage. More recently, the technique of sentinel lymph node
(SLN) dissection has become popular, as it requires the removal of far fewer lymph nodes, resulting in fewer side effects. The sentinel lymph node is the first node that drains the tumor, and subsequent SLN mapping can save 65-70% of patients with breast cancer from having a complete lymph node dissection for what could turn out to be a negative nodal basin. Advances in Sentinel Lymph Node mapping over the past decade have increased the accuracy of detecting Sentinel Lymph Node from 80% using blue dye alone to between 92% and 98% using combined modalities.
SLN biopsy is indicated for patients with T1 and T2 lesions (<5 cm) and carries a number of recommendations for use on patient subgroups. Recent trends continue to favor less radical axillar node resection even in the presence of some metastases in the sentinel node.
Radiation therapy involves using high-energy X-rays or gamma ray
s that target a tumor or post surgery tumor site. This radiation is very effective in killing cancer cells that may remain after surgery or recur where the tumor was removed.
Radiation therapy can be delivered by either external beam radiotherapy
or brachytherapy
(internal radiotherapy). In the case of external beam radiotherapy, X-rays are delivered from outside the body by a machine called a Linear Accelerator
or Linac. In contrast, brachytherapy involves the precise placement of radiation source(s) directly at the treatment site. Radiation therapy for breast cancer is usually performed after surgery and is an integral component of breast-conserving therapy.
Radiation therapy eliminates the microscopic cancer cells that may remain near the area where the tumor was surgically removed. The dose of radiation must be strong enough to ensure the elimination of cancer cells. However, radiation affects normal cells and cancer cells alike, causing some damage to the normal tissue around where the tumor was. Healthy tissue can repair itself, while cancer cells do not repair themselves as well as normal cells. For this reason, radiation treatments are given over an extended period, enabling the healthy tissue to heal. Treatments using external beam radiotherapy are typically given over a period of five to seven weeks, performed five days a week. Each treatment takes about 15 minutes. A newer approach, called 'accelerated partial breast irradiaton' (APBI), uses brachytherapy to deliver the radiation in a much shorter period of time. APBI deliveres radiation to only the immediate region surrounding the original tumor and can typically be completed over the course of one week.
Although radiation therapy can reduce the chance of breast cancer recurrence, it is much less effective in prolonging patient survival. According to a review of six studies by the United States' National Cancer Institute, none of them found a survival benefit for radiation therapy. Patients who are unable to have radiation therapy after lumpectomy should consult with a surgeon who understands this research and who believes that lumpectomy (or partial mastectomy) alone is a reasonable treatment option.
is usually recommended for all patients who had (lumpectomy
, quadrant-resection). Radiation therapy is usually not indicated in patients with advanced (stage IV disease) except for palliation of symptoms like bone pain, fungating lesion.
In general recommendations would include radiation:
Other factors which may influence adding adjuvant radiation therapy:
This usually involves treating the whole breast in the case of breast lumpectomy or the whole chest wall in the case of mastectomy. Lumpectomy patients with early-stage breast cancer may be eligible for a newer, shorter form of treatment called “breast brachytherapy
”. This approach allows physicians to treat only part of the breast in order to spare healthy tissue from unnecessary radiation.
Improvements in computers and treatment delivery technology have led to more complex radiotherapy treatment options. One such new technology is using IMRT (intensity modulated radiation therapy), which can change the shape and intensity of the radiation beam making "beamlets" at different points across and inside the breast. This allows for better dose distribution within the breast while minimizing dose to healthy organs such as the lung or heart. However there is yet to be a demonstrated difference in treatment outcomes (both tumor recurrence and level of side effects) for IMRT in breast cancer when compared to conventional radiotherapy treatment. In addition, conventional radiotherapy can also deliver similar dose distributions utilizing modern computer dosimetry planning and equipment. External beam radiation therapy treatments for breast cancer are typically given every day, five days a week, for five to 10 weeks.
Within the past decade, a new approach called accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI) has gained popularity. APBI is used to deliver radiation as part of breast conservation therapy. It treats only the area where the tumor was surgically removed, plus adjacent tissue. APBI reduces the length of treatment to just five days, compared to the typical six or seven weeks for whole breast irradiation.
APBI treatments can be given as brachytherapy or external beam with a linear accelerator. These treatments are usually limited to women with well-defined tumors that have not spread.
In breast brachytherapy, the radiation source is placed inside the breast, treating the cavity from the inside out. There are several different devices that deliver breast brachytherapy. Some use a single catheter and balloon to deliver the radiation. Other devices utilize multiple catheters to deliver radiation.
A study is currently underway by the National Surgical Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) to determine whether limiting radiation therapy to only the tumor site following lumpectomy is as effective as radiating the whole breast.
New technology has also allowed more precise delivery of radiotherapy in a portable fashion — for example in the operating theatre. Targeted intraoperative radiotherapy (TARGIT) is a method of delivering therapeutic radiation from within the breast using a portable X-ray generator called Intrabeam.
The TARGIT-A trial was an international randomised controlled non-inferiority phase III clinical trial led from University College London. 28 centres in 9 countries accrued 2232 patients to test whether TARGIT can replace the whole course of radiotherapy in selected patients. The TARGIT-A trial results found that the difference between the two treatments was 0.25% (95% CI -1.0 to 1.5) i.e., at most 1.5% worse or at best 1.0% better with single dose TARGIT than with standard course of several weeks of external beam radiotherapy. In the TARGIT-B trial, as the TARGIT technique is precisely aimed and given immediately after surgery, in theory it could be able provide a better boost dose to the tumor bed as suggested in phase II studies. This will be tested in a TARGIT-B trial.
After surgery, radiation and other treatments have been completed, many patients notice the affected breast seems smaller or seems to have shrunk. This is basically due to the removal of tissue during the lumpectomy operation.
The use of adjuvant radiation has significant potential effects if the patient has to later undergo breast reconstruction
surgery. Fibrosis of chest wall skin from radiation negatively affects skin elasticity and makes tissue expansion
techniques difficult. Traditionally most patients are advised to defer immediate breast reconstruction when adjuvant radiation is planned and are most often recommended surgery involving autologous tissue reconstruction rather than breast implants.
Studies suggest APBI may reduce the side effects associated with radiation therapy, because it treats only the tumor cavity and the surrounding tissue. In particular, a device that uses multiple catheters and allows modulation of the radiation dose delivered by each of these catheters has been shown to reduce harm to nearby, healthy tissue.
(drug treatment for cancer) may be used before surgery, after surgery, or instead of surgery for those cases in which surgery is considered unsuitable.
Patients with estrogen receptor positive tumors will typically receive hormonal therapy
after chemotherapy is completed. Typical hormonal treatments include:
(Herceptin) is used to block the activity of the HER2 protein in breast cancer cells, slowing their growth.
In the advanced cancer setting, trastuzumab use in combination with chemotherapy can both delay cancer growth as well as improve the recipient's survival.
More recently, several clinical trials have also confirmed that in the adjuvant setting i.e. postoperative following breast cancer surgery, the use of trastuzumab for up to one year also delays the recurrence of breast cancer and improves survival.
Other types of antibodies that are being researched to fight cancer include:
The newest targeted therapies are helping doctors to tailor increasingly effective treatments to individual patients.
Other Possible Targets Cyclin D1
http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/128357.php
Other Potential drugs PV-10 http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/127343.php, Hormone Progestin and p53 http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/137167.php
CR011-vcMMAE aka CDX-011 and Glembatumumab vedotin
.
CR011-vcMMAE is an antibody-drug conjugate
(ADC) (targeted at transmembrane glycoprotein NMB (GPNMB)) that consists of a fully human monoclonal antibody, CR011, linked to a potent cell-killing drug, monomethyl-auristatin E (MMAE). CR011-vcMMAE is currently in two Phase II trials assessing its safety and efficacy in the treatment of melanoma and for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer, and in a Phase I trial to evaluate the safety and activity of alternate dosing schedules.http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/154376.php http://meeting.ascopubs.org/cgi/content/abstract/28/15_suppl/8525 http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/173950.php
, underwent testing in a randomized clinical trial whose preliminary results were announced by the National Cancer Institute in 2005. The preliminary data indicated that bevacizumab delays disease progression for up to five months over conventional chemotherapy, but survival was no better. Genentech
, manufacturer of bevacizumab, has filed a supplemental biological application with the US FDA for approval of bevacizumab in the setting of metastatic breast cancer, on the strength of the improvement in progression-free survival.
called protein tyrosine phosphatase
1B (PTP1B), which has been implicated in the onset of breast cancer in mouse models of the disease. Elevated levels of PTP1B have also been found in diabetes and obesity
. A drug to block the activity of PTP1B is under development by Merck
, and was found to delay the development of breast tumors and prevent lung cancer
up to two months from the administration of the drug. The researchers hope to continue further research in mouse models which are also HER-2 positive (responsive to Herceptin) so that the drug could benefit a significant population of women.
and the cancer drug doxorubicin killed human cancer stem cells and non-stem cancer cells in culture. The researchers used four genetically distinct breast cancer cell lines.
In mice, pretreatment with the diabetes drug prevented the otherwise dramatic ability of human breast cancer stem cells to form tumors. In other mice where tumors were allowed to take hold for 10 days, the dual therapy also reduced tumor mass more quickly and prevented relapse for longer than doxorubicin alone. In the two months between the end of treatment and the end of the experiment, tumors regrew in mice treated with chemotherapy alone, but not in mice that had received both drugs. By itself, metformin was ineffective in treating tumors. http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/163990.php, http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/222376.php
biology have led to refinements for individualised thermochemotherapy approaches to treatments as well as interesting potential for exploiting hyperthermia in conjunction with cancer vaccine
s. MR imaging is playing an increasing role for measuring patient response to hyperthermia.
Interest in hyperthermia as a treatment
for breast cancer has led to significant advances and research activity which, in turn, has had a significant impact on treatment protocol. The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) now includes hyperthermia
in their Breast Cancer Guidelines as a treatment for recurrent cancer.
Erasmus Medical Centre in the Netherlands, is one of Europe's largest hyperthermia centres.
ThermoDox is a proprietary heat-activated liposomal encapsulation of doxorubicin
, an approved and frequently used oncology drug for the treatment of a wide range of cancers including breast cancer. ThermoDox, which is administered intravenously and in combination with local hyperthermia, has the potential to provide local tumor control and improve quality of life. Localized mild hyperthermia (39.5-42 degrees Celsius) releases the entrapped doxorubicin from the liposome. This delivery technology enables high concentrations of doxorubicin to be deposited preferentially in a targeted tumor.
study involving 32 postmenopausal patients confirming that 25g flaxseed daily intake significantly reduced cell proliferation, increased apoptosis
and reduced c-erbB2 expression of human breast cancer cells. The preliminary research into flax seeds indicates that flax can significantly change breast cancer growth and metastasis, and enhance the inhibitory effect of tamoxifen on estrogen-dependent tumors.
Dendritic cell therapy (Planned trial)
A new clinical trial is designed around the use of QI's proprietary dendritic cell therapy, which employs oncofetal antigen ("OFA") to recruit the patient's own immune system to target and attack the cancer cells with the intent to improve patient survivability and quality of life. Each patient will receive three monthly injections of the patient's own dendritic cells that have been sensitized to OFA. It is anticipated that once the sensitized cells are injected back into the patient, the patient's T-cells will locate the OFA found on the patient's cancer cells, thereby generating an immune response with the goal of killing the cancer cells and preventing further spread of the disease. http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/157912.php
Stimuvax - mostly for hormone receptor positive (phase III)
Stimuvax
is an investigational therapeutic cancer vaccine designed to induce an immune response to cancer cells that express MUC1, a glycoprotein antigen widely expressed on common cancers. MUC1 is over-expressed on many cancers such as lung cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer and colorectal cancer. Stimuvax is thought to work by stimulating the body's immune system to identify and destroy cancer cells expressing MUC1. http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/154900.php
Phase IIb study of 171 patients with inoperable stage IIIb NSCLC (lung cancer), in which Stimuvax showed a trend towards extending median overall survival from 13.3 months for patients receiving best supportive care (BSC) to 30.6 months for patients receiving Stimuvax plus BSC.2,3 Reported side effects included mild-to-moderate flu-like symptoms, gastrointestinal disturbances and mild injection-site reactions.
The objective of chemoimmunotherapy is to amplify natural pre-existing T cell responses specific for any known or unknown tumor antigen and to recruit and amplify new tumor-specific T cell responses resulting from the use of cytotoxic drugs. The direct cytolytic effect of some cytotoxic drugs, such as paclitaxel, can enhance antigen presentation by inducing tumor cell apoptosis. This mechanism of therapeutic synergy has been shown with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, or paclitaxel when given with dendritic cell - based vaccines. Until 9 years ago, it was thought that the T cell depletion caused by chemotherapy would make immunotherapy ineffective. However it has now been shown that, on the contrary, the vigorous T cell repopulation following depletion can be directed against the tumor.
IMP321 induced both a sustained increase in the number and activation of APC (monocytes and dendritic cells) and an increase in the percentage of NK and long-lived cytotoxic effector-memory CD8 T cells. Clinical benefit was observed for 90 per cent of patients with only 3 progressors at 6 months. Also, the objective tumor response rate of 50 per cent compared favorably to the 25 per cent rate reported in the historical control group. This form of chemo-immunotherapy should be applicable to many chemotherapies. http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/200182.php
of breast cancer have been proposed.
Approximately 40 percent of menopausal women experience sleep disruption, often in the form of difficulty with sleep initiation and frequent nighttime awakenings. There is a study, first to show sustained benefits in sleep quality from gabapentin, which Rochester researchers already have demonstrated alleviates hot flashes. http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/163260.php
Pregabalin is a newer version of gabapentin and is found equally effective in treating hot flashes.http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/150286.php
The tests use proprietary algorithms developed by Chronix researchers to detect, analyze and identify cancer-related fragments of circulating DNA that are released into the bloodstream by apoptotic cells. Chronix researchers consistently find that this apoptotic DNA in the serum is coming from a limited number of regions or "hotspots" on the genome specific to each cancer. According to the data presented today, DNA fragments from any one of the 29 breast cancer "hotspots" and 32 prostate cancer "hotspots" identified by Chronix researchers indicate that cancer is present. http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/191129.php
Surgery
Surgery is an ancient medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a patient to investigate and/or treat a pathological condition such as disease or injury, or to help improve bodily function or appearance.An act of performing surgery may be called a surgical...
when the tumor is localized, followed by chemotherapy (when indicated), radiotherapy and adjuvant hormonal therapy for ER positive tumours (with tamoxifen
Tamoxifen
Tamoxifen is an antagonist of the estrogen receptor in breast tissue via its active metabolite, hydroxytamoxifen. In other tissues such as the endometrium, it behaves as an agonist, hence tamoxifen may be characterized as a mixed agonist/antagonist...
or an aromatase inhibitor
Aromatase inhibitor
Aromatase inhibitors are a class of drugs used in the treatment of breast cancer and ovarian cancer in postmenopausal women. AIs may also be used off-label to treat or prevent gynaecomastia in men....
). Management of breast cancer is undertaken by a multidisciplinary team based on national and international guidelines. Depending on clinical criteria (age, type of cancer, size, metastasis) patients are roughly divided to high risk and low risk cases, with each risk category following different rules for therapy. Treatment possibilities include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and immune therapy.
Staging
A patient generally first goes through a staging process to see if s/he can benefit from local treatment. Staging makes use of clinical, imaging and pathological assessment to make a best guess by the physician. If the cancer has spread beyond the breast and the lymph nodes then it is classified as Stage 4 or metastatic cancer and requires mostly systemic treatment.Surgery

Lumpectomy
Lumpectomy is a common surgical procedure designed to remove a discrete lump, usually a benign tumor or breast cancer, from an affected man or woman's breast...
(removal of the lump only) may be all that is necessary, or removal of larger amounts of breast tissue may be necessary. Surgical removal of the entire breast is called mastectomy
Mastectomy
Mastectomy is the medical term for the surgical removal of one or both breasts, partially or completely. Mastectomy is usually done to treat breast cancer; in some cases, women and some men believed to be at high risk of breast cancer have the operation prophylactically, that is, to prevent cancer...
.
Lumpectomy techniques are increasingly utilized for breast-conservation cancer surgery. Studies indicate that for patients with a single tumor smaller than 4cm, lumpectomy may be as effective as a mastectomy. Prior to a lumpectomy, a needle-localization
Needle-localized biopsy
Needle-localized biopsy is a procedure that uses very thin needles or guide wires to mark the location of an abnormal area of tissue so it can be surgically sampled. An imaging device such as an ultrasound probe is used to place the wire in or around the abnormal area...
of the lesion with placement of a guidewire may be performed, sometimes by a radiologist if the area being removed was detected by mammography
Mammography
Mammography is the process of using low-energy-X-rays to examine the human breast and is used as a diagnostic and a screening tool....
or ultrasound
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is cyclic sound pressure with a frequency greater than the upper limit of human hearing. Ultrasound is thus not separated from "normal" sound based on differences in physical properties, only the fact that humans cannot hear it. Although this limit varies from person to person, it is...
, and sometimes by the surgeon
Surgeon
In medicine, a surgeon is a specialist in surgery. Surgery is a broad category of invasive medical treatment that involves the cutting of a body, whether human or animal, for a specific reason such as the removal of diseased tissue or to repair a tear or breakage...
if the lesion can be directly palpated.
However, mastectomy may be the preferred treatment in certain instances:
- Two or more tumors exist in different areas of the breast (a "multifocal" cancer).
- The breast has previously received radiotherapy.
- The tumor is large relative to the size of the breast.
- The patient has had sclerodermaSclerodermaSystemic sclerosis or systemic scleroderma is a systemic autoimmune disease or systemic connective tissue disease that is a subtype of scleroderma.-Skin symptoms:...
or another disease of the connective tissue, which can complicate radiotherapy. - The patient lives in an area where radiotherapy is inaccessible.
- The patient is apprehensive about the risk of local recurrence after lumpectomy.
Standard practice requires the surgeon to establish that the tissue removed in the operation has margins clear of cancer, indicating that the cancer has been completely excised. If the removed tissue does not have clear margins, further operations to remove more tissue may be necessary. This may sometimes require removal of part of the pectoralis major muscle
Pectoralis major muscle
The pectoralis major is a thick, fan-shaped muscle, situated at the chest of the body. It makes up the bulk of the chest muscles in the male and lies under the breast in the female...
, which is the main muscle of the anterior chest wall.
During the operation, the lymph nodes in the axilla are also considered for removal. In the past, large axillary operations took out 10 to 40 nodes to establish whether cancer had spread. This had the unfortunate side effect of frequently causing lymphedema
Lymphedema
Lymphedema , also known as lymphatic obstruction, is a condition of localized fluid retention and tissue swelling caused by a compromised lymphatic system....
of the arm on the same side, as the removal of this many lymph nodes affected lymphatic drainage. More recently, the technique of sentinel lymph node
Sentinel lymph node
The sentinel lymph node is the hypothetical first lymph node or group of nodes reached by metastasizing cancer cells from a primary tumor.-Physiology:...
(SLN) dissection has become popular, as it requires the removal of far fewer lymph nodes, resulting in fewer side effects. The sentinel lymph node is the first node that drains the tumor, and subsequent SLN mapping can save 65-70% of patients with breast cancer from having a complete lymph node dissection for what could turn out to be a negative nodal basin. Advances in Sentinel Lymph Node mapping over the past decade have increased the accuracy of detecting Sentinel Lymph Node from 80% using blue dye alone to between 92% and 98% using combined modalities.
SLN biopsy is indicated for patients with T1 and T2 lesions (<5 cm) and carries a number of recommendations for use on patient subgroups. Recent trends continue to favor less radical axillar node resection even in the presence of some metastases in the sentinel node.
Live tissue samples for testing
Recently live tissue samples from surgery are tested with various chemotherapy agents to derive probabilities of which ones may work better and specially the ones which would not work (Cell-death assays). The companies need the sample within 24 hours of surgical excision. This is specially useful for early stage cancers were a response for the therapy cannot be determined once the whole cancer is taken out during the surgery and the chemotherapy is given in an adjuciant setting. However, the benefits of such tests have not yet been established in clinical trials and is not mainstream.Lymphedema
Some patients develop lymphedema, as a result of axillary node dissection or of radiation treatment to the lymph nodes. Although traditional recommendations limited exercise, a new study shows that participating in a safe, structured weight-lifting routine can help women with lymphedema take control of their symptoms and reap the many rewards that resistance training has on their overall health as they begin life as a cancer survivor. It recommends that women start with a slowly progressive program, supervised by a certified fitness professional, in order to learn how to do these types of exercises properly. Women with lymphedema should also wear a well-fitting compression garment during all exercise sessions.http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/160540.phpRadiation therapy
Radiation therapy is an adjuvant treatment for most women who have undergone lumpectomy and for some women who have mastectomy surgery. In these cases the purpose of radiation is to reduce the chance that the cancer will recur.Radiation therapy involves using high-energy X-rays or gamma ray
Gamma ray
Gamma radiation, also known as gamma rays or hyphenated as gamma-rays and denoted as γ, is electromagnetic radiation of high frequency . Gamma rays are usually naturally produced on Earth by decay of high energy states in atomic nuclei...
s that target a tumor or post surgery tumor site. This radiation is very effective in killing cancer cells that may remain after surgery or recur where the tumor was removed.
Radiation therapy can be delivered by either external beam radiotherapy
External beam radiotherapy
External beam radiotherapy or teletherapy is the most common form of radiotherapy. The patient sits or lies on a couch and an external source of radiation is pointed at a particular part of the body...
or brachytherapy
Brachytherapy
Brachytherapy , also known as internal radiotherapy, sealed source radiotherapy, curietherapy or endocurietherapy, is a form of radiotherapy where a radiation source is placed inside or next to the area requiring treatment...
(internal radiotherapy). In the case of external beam radiotherapy, X-rays are delivered from outside the body by a machine called a Linear Accelerator
Linear particle accelerator
A linear particle accelerator is a type of particle accelerator that greatly increases the velocity of charged subatomic particles or ions by subjecting the charged particles to a series of oscillating electric potentials along a linear beamline; this method of particle acceleration was invented...
or Linac. In contrast, brachytherapy involves the precise placement of radiation source(s) directly at the treatment site. Radiation therapy for breast cancer is usually performed after surgery and is an integral component of breast-conserving therapy.
Radiation therapy eliminates the microscopic cancer cells that may remain near the area where the tumor was surgically removed. The dose of radiation must be strong enough to ensure the elimination of cancer cells. However, radiation affects normal cells and cancer cells alike, causing some damage to the normal tissue around where the tumor was. Healthy tissue can repair itself, while cancer cells do not repair themselves as well as normal cells. For this reason, radiation treatments are given over an extended period, enabling the healthy tissue to heal. Treatments using external beam radiotherapy are typically given over a period of five to seven weeks, performed five days a week. Each treatment takes about 15 minutes. A newer approach, called 'accelerated partial breast irradiaton' (APBI), uses brachytherapy to deliver the radiation in a much shorter period of time. APBI deliveres radiation to only the immediate region surrounding the original tumor and can typically be completed over the course of one week.
Although radiation therapy can reduce the chance of breast cancer recurrence, it is much less effective in prolonging patient survival. According to a review of six studies by the United States' National Cancer Institute, none of them found a survival benefit for radiation therapy. Patients who are unable to have radiation therapy after lumpectomy should consult with a surgeon who understands this research and who believes that lumpectomy (or partial mastectomy) alone is a reasonable treatment option.
Indications for radiation
Radiation treatment is mainly effective in reducing the risk of local relapse in the affected breast. Therefore it is recommended in most cases of breast conserving surgeries and less frequently after mastectomy. Indications for radiation treatment are constantly evolving. Patients treated in Europe have been more likely in the past to be recommended adjuvant radiation after breast cancer surgery as compared to patients in North America. Radiation therapyRadiation therapy
Radiation therapy , radiation oncology, or radiotherapy , sometimes abbreviated to XRT or DXT, is the medical use of ionizing radiation, generally as part of cancer treatment to control malignant cells.Radiation therapy is commonly applied to the cancerous tumor because of its ability to control...
is usually recommended for all patients who had (lumpectomy
Lumpectomy
Lumpectomy is a common surgical procedure designed to remove a discrete lump, usually a benign tumor or breast cancer, from an affected man or woman's breast...
, quadrant-resection). Radiation therapy is usually not indicated in patients with advanced (stage IV disease) except for palliation of symptoms like bone pain, fungating lesion.
In general recommendations would include radiation:
- As part of breast conserving therapy.
- After mastectomy for patients with higher risk of recurrence because of conditions such as a large primary tumorTumorA tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
or substantial involvement of the lymph nodeLymph nodeA lymph node is a small ball or an oval-shaped organ of the immune system, distributed widely throughout the body including the armpit and stomach/gut and linked by lymphatic vessels. Lymph nodes are garrisons of B, T, and other immune cells. Lymph nodes are found all through the body, and act as...
s.
Other factors which may influence adding adjuvant radiation therapy:
- Tumor close to or involving the margins on pathology specimen
- Multiple areas of tumor (multicentric disease)
- Microscopic invasion of lymphatic or vascular tissues
- Microcopic invasion of the skin, nipple/areola, or underlying pectoralis major muscle
- Patients with extension out of the substance of a LN
- Inadequate numbers of axillary LN sampled
Types of radiotherapy
Radiotherapy can be delivered in many ways but is most commonly produced by a linear accelerator.This usually involves treating the whole breast in the case of breast lumpectomy or the whole chest wall in the case of mastectomy. Lumpectomy patients with early-stage breast cancer may be eligible for a newer, shorter form of treatment called “breast brachytherapy
Brachytherapy
Brachytherapy , also known as internal radiotherapy, sealed source radiotherapy, curietherapy or endocurietherapy, is a form of radiotherapy where a radiation source is placed inside or next to the area requiring treatment...
”. This approach allows physicians to treat only part of the breast in order to spare healthy tissue from unnecessary radiation.
Improvements in computers and treatment delivery technology have led to more complex radiotherapy treatment options. One such new technology is using IMRT (intensity modulated radiation therapy), which can change the shape and intensity of the radiation beam making "beamlets" at different points across and inside the breast. This allows for better dose distribution within the breast while minimizing dose to healthy organs such as the lung or heart. However there is yet to be a demonstrated difference in treatment outcomes (both tumor recurrence and level of side effects) for IMRT in breast cancer when compared to conventional radiotherapy treatment. In addition, conventional radiotherapy can also deliver similar dose distributions utilizing modern computer dosimetry planning and equipment. External beam radiation therapy treatments for breast cancer are typically given every day, five days a week, for five to 10 weeks.
Within the past decade, a new approach called accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI) has gained popularity. APBI is used to deliver radiation as part of breast conservation therapy. It treats only the area where the tumor was surgically removed, plus adjacent tissue. APBI reduces the length of treatment to just five days, compared to the typical six or seven weeks for whole breast irradiation.
APBI treatments can be given as brachytherapy or external beam with a linear accelerator. These treatments are usually limited to women with well-defined tumors that have not spread.
In breast brachytherapy, the radiation source is placed inside the breast, treating the cavity from the inside out. There are several different devices that deliver breast brachytherapy. Some use a single catheter and balloon to deliver the radiation. Other devices utilize multiple catheters to deliver radiation.
A study is currently underway by the National Surgical Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP) to determine whether limiting radiation therapy to only the tumor site following lumpectomy is as effective as radiating the whole breast.
New technology has also allowed more precise delivery of radiotherapy in a portable fashion — for example in the operating theatre. Targeted intraoperative radiotherapy (TARGIT) is a method of delivering therapeutic radiation from within the breast using a portable X-ray generator called Intrabeam.
The TARGIT-A trial was an international randomised controlled non-inferiority phase III clinical trial led from University College London. 28 centres in 9 countries accrued 2232 patients to test whether TARGIT can replace the whole course of radiotherapy in selected patients. The TARGIT-A trial results found that the difference between the two treatments was 0.25% (95% CI -1.0 to 1.5) i.e., at most 1.5% worse or at best 1.0% better with single dose TARGIT than with standard course of several weeks of external beam radiotherapy. In the TARGIT-B trial, as the TARGIT technique is precisely aimed and given immediately after surgery, in theory it could be able provide a better boost dose to the tumor bed as suggested in phase II studies. This will be tested in a TARGIT-B trial.
Side effects of radiation therapy
External beam radiation therapy is a non-invasive treatment with some short term and some longer term side effects. Patients undergoing some weeks of treatment usually experience fatigue caused by the healthy tissue repairing itself and aside from this there can be no side effects at all. However many breast cancer patients develop a suntan-like change in skin color in the exact area being treated. As with a suntan, this darkening of the skin usually returns to normal in the one to two months after treatment. In some cases permanent changes in color and texture of the skin is experienced. Other side effects sometimes experienced with radiation can include:- muscle stiffness
- mild swelling
- tenderness in the area
- lymphedema
After surgery, radiation and other treatments have been completed, many patients notice the affected breast seems smaller or seems to have shrunk. This is basically due to the removal of tissue during the lumpectomy operation.
The use of adjuvant radiation has significant potential effects if the patient has to later undergo breast reconstruction
Breast reconstruction
Breast reconstruction is the rebuilding of a breast, usually in women. It involves using autologous tissue or prosthetic material to construct a natural-looking breast. Often this includes the reformation of a natural-looking areola and nipple...
surgery. Fibrosis of chest wall skin from radiation negatively affects skin elasticity and makes tissue expansion
Tissue expansion
Tissue expansion is a technique used by plastic and restorative surgeons to cause the body to grow additional skin, bone or other tissues.-Skin expansion:...
techniques difficult. Traditionally most patients are advised to defer immediate breast reconstruction when adjuvant radiation is planned and are most often recommended surgery involving autologous tissue reconstruction rather than breast implants.
Studies suggest APBI may reduce the side effects associated with radiation therapy, because it treats only the tumor cavity and the surrounding tissue. In particular, a device that uses multiple catheters and allows modulation of the radiation dose delivered by each of these catheters has been shown to reduce harm to nearby, healthy tissue.
Systemic therapy
Systemic therapy uses medications to treat cancer cells throughout the body. Any combination of systemic treatments may be used to treat breast cancer. Systemic treatments include chemotherapy, immune therapy, and hormonal therapy.Chemotherapy
ChemotherapyChemotherapy
Chemotherapy is the treatment of cancer with an antineoplastic drug or with a combination of such drugs into a standardized treatment regimen....
(drug treatment for cancer) may be used before surgery, after surgery, or instead of surgery for those cases in which surgery is considered unsuitable.
Hormonal Receptor Status
Women who have had breast cancer are at increased risk of a second primary breast cancer, compared with risk in the general population. It was also found that women whose first tumors were hormone-receptor negative, compared with those whose tumors were hormone-receptor positive, had almost twice as much risk of any second breast cancer, and a fivefold increase in risk of a second hormone-receptor negative breast cancer.Patients with estrogen receptor positive tumors will typically receive hormonal therapy
Hormonal therapy (oncology)
Hormonal therapy is one of the major modalities of medical treatment for cancer, others being cytotoxic chemotherapy and targeted therapy . It involves the manipulation of the endocrine system through exogenous administration of specific hormones, particularly steroid hormones, or drugs which...
after chemotherapy is completed. Typical hormonal treatments include:
- TamoxifenTamoxifenTamoxifen is an antagonist of the estrogen receptor in breast tissue via its active metabolite, hydroxytamoxifen. In other tissues such as the endometrium, it behaves as an agonist, hence tamoxifen may be characterized as a mixed agonist/antagonist...
is typically given to premenopausal women to inhibit the estrogen receptors.
- Aromatase inhibitors are typically given to postmenopausal women to lower the amount of estrogen in their systems.
- GnRH-analogues are used in premenopausal women for ovarian ablation or suppression.
- Estogen cycling was reported at the 31st annual San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium. About a third of the 66 participants - women with metastatic breast cancer that had developed resistance to standard estrogen-lowering therapy - a daily dose of estrogen could stop the growth of their tumors or even cause them to shrink. If study participants experienced disease progression on estrogen, they could go back to an aromatase inhibitorAromatase inhibitorAromatase inhibitors are a class of drugs used in the treatment of breast cancer and ovarian cancer in postmenopausal women. AIs may also be used off-label to treat or prevent gynaecomastia in men....
that they were previously resistant to and see a benefit - their tumors were once again inhibited by estrogen deprivation. That effect sometimes wore off after several months, but then the tumors might again be sensitive to estrogen therapy. In fact, some patients have cycled back and forth between estrogen and an aromatase inhibitor for several years. PET (positron emission tomographyPositron emission tomographyPositron emission tomography is nuclear medicine imaging technique that produces a three-dimensional image or picture of functional processes in the body. The system detects pairs of gamma rays emitted indirectly by a positron-emitting radionuclide , which is introduced into the body on a...
) scans before starting estrogen and again 24 hours later predicted those tumors which responded to estrogen therapy: the responsive tumors showed an increased glucose uptake, called a PET flare. The mechanism of action is uncertain, although estrogen reduces the amount of a tumor-promoting hormone called insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF1).
Targeted therapy
In patients whose cancer expresses an over-abundance of the HER2 protein, a monoclonal antibody known as trastuzumabTrastuzumab
Trastuzumab is a monoclonal antibody that interferes with the HER2/neu receptor.The HER receptors are proteins that are embedded in the cell membrane and communicate molecular signals from outside the cell to inside the cell, and turn genes on and off...
(Herceptin) is used to block the activity of the HER2 protein in breast cancer cells, slowing their growth.
In the advanced cancer setting, trastuzumab use in combination with chemotherapy can both delay cancer growth as well as improve the recipient's survival.
More recently, several clinical trials have also confirmed that in the adjuvant setting i.e. postoperative following breast cancer surgery, the use of trastuzumab for up to one year also delays the recurrence of breast cancer and improves survival.
Other types of antibodies that are being researched to fight cancer include:
- Angiogenesis inhibitors. These antibodies prevent the growth of new blood vessels, cutting off the supply of oxygen and nutrients to cancer cells.
- Signal transduction inhibitors. These antibodies block signals inside the cancer cell that helps the cells divide, stopping the cancer from growing.
| Target | Drug | Type | Efficacy Trial |
|---|---|---|---|
| ER/PR |
|
Aromatase inhibitor Aromatase inhibitor Aromatase inhibitors are a class of drugs used in the treatment of breast cancer and ovarian cancer in postmenopausal women. AIs may also be used off-label to treat or prevent gynaecomastia in men.... |
http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/132746.php |
|
Exemestane Exemestane is a drug used to treat breast cancer. It is a member of the class of drugs known as aromatase inhibitors. Some breast cancers require estrogen to grow. Those cancers have estrogen receptors , and are called ER-positive. They may also be called estrogen-responsive,... (Aromasin) Fulvestrant Fulvestrant, also known as ICI 182,780, is a drug treatment of hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer in postmenopausal women with disease progression following anti-estrogen therapy. It is an estrogen receptor antagonist with no agonist effects, which works both by down-regulating and... (Faslodex) |
Other | ||
| HER2 receptor protein |
Trastuzumab Trastuzumab is a monoclonal antibody that interferes with the HER2/neu receptor.The HER receptors are proteins that are embedded in the cell membrane and communicate molecular signals from outside the cell to inside the cell, and turn genes on and off... (Herceptin) http://www.medilexicon.com/drugs/herceptin.php, Pertuzumab Pertuzumab is a monoclonal antibody. The first of its class in a line of agents called "HER dimerization inhibitors". By binding to HER2, it inhibits the dimerization of HER2 with other HER receptors, which is hypothesized to result in slowed tumor growth... Neratinib Neratinib is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor under investigation for the treatment breast cancer and other solid tumours.It is in development for the treatment of early- and late-stage HER2-positive breast cancer.... (HKI-272) in Phase II http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/151895.php |
Monoclonal antibody | |
|
Lapatinib Lapatinib , used in the form of lapatinib ditosylate, is an orally active drug for breast cancer and other solid tumours. It is a dual tyrosine kinase inhibitor which interrupts the HER2 growth receptor pathway. It is used in combination therapy for HER2-positive breast cancer... (TykerB)http://www.medilexicon.com/drugs/tykerb.php |
Kinase inhibitor | ||
|
|
Vaccine | NeuVax is a HER2/neu peptide-based T-cell immunotherapy aimed at preventing disease recurrence and prolonging survival in cancer patients that have tumors expressing the HER2/neu oncoprotein. To date, clinical study results have demonstrated that NeuVax significantly reduces the rate of cancer recurrence while showing minimal side effects http://www.apthera.com/neuvax_p2_results.php | |
|
Trastuzumab emtansine Trastuzumab emtansine is an antibody-drug conjugate consisting of the antibody trastuzumab linked to the cytotoxin mertansine .... (Herceptin+DM1) http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/204095.php |
Other | ||
| HER1/ EGFR |
|
tyrosine kinase inhibitor | However, clinical studies did not find most EGFR inhibitors effective against breast cancer for a large enough proportion of patients. Some oncologists believe it may be possible to select a fraction of patients, either through genetics or the characteristics of their tumors, who have a better chance of having the drugs work http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/131480.php |
| insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) |
|
Monoclonal antibody | |
| insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor (IGF-1R) and insulin receptor Insulin receptor In molecular biology, the insulin receptor is a transmembrane receptor that is activated by insulin. It belongs to the large class of tyrosine kinase receptors.... (IR) |
|
Dual kinase inhibitor | |
| PI3K/AKT/mTOR cell survival pathway |
|
Kinase inhibitor | |
| VEGF receptor protein (involved
in forming tumor blood vessels) |
|
Monoclonal antibody |
AVADO |
|
Kinase inhibitor | ||
|
|
Other | ||
| P53 P53 p53 , is a tumor suppressor protein that in humans is encoded by the TP53 gene. p53 is crucial in multicellular organisms, where it regulates the cell cycle and, thus, functions as a tumor suppressor that is involved in preventing cancer... |
|
Vaccine | |
|
Gendicine Gendicine is a recombinant adenovirus engineered to express wildtype-p53 . This virus is designed to treat patients with tumors which have mutated p53 genes.... (from China) |
Gene therapy Gene therapy Gene therapy is the insertion, alteration, or removal of genes within an individual's cells and biological tissues to treat disease. It is a technique for correcting defective genes that are responsible for disease development... |
||
|
|
Other | ||
| PARP protein inhibitor PARP inhibitor PARP inhibitors are a group of pharmacological inhibitors of the enzyme poly ADP ribose polymerase . They are developed for multiple indications; the most important is the treatment of cancer... |
Olaparib Olaparib is a chemotherapeutic agent developed by KuDOS Pharmaceuticals and later by Astra Zeneca. It is an inhibitor of PARP, an enzyme involved in DNA repair. It acts against cancers in people with hereditary BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations, which includes many ovarian, breast and prostate cancers... (Phase I with good results) BSI 201 Iniparib is a drug that acts as an irreversible inhibitor of PARP1 and possibly other enzymes through covalent modification. It is undergoing clinical trials for treatment of some types of breast cancer.It is the first PARP inhibitor to commence phase III clinical trials... (Phase II - Clinical Benefit In 62% Of Patients With Triple-Negative) |
DNA repair blocker - kills cancer cells with a faulty BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene by preventing the repair of DNA. A cell with a BRCA fault relies on a protein called PARP to keep its DNA healthy. Olaparib, known as a 'PARP-inhibitor PARP inhibitor PARP inhibitors are a group of pharmacological inhibitors of the enzyme poly ADP ribose polymerase . They are developed for multiple indications; the most important is the treatment of cancer... ', blocks PARP, which causes the cancer cells to die. |
Olaparib - In the initial findings, Over 40% of tumours in the higher dose group reduced significantly in size, and tumours were prevented from progressing for an average of six months, while one patient's tumour disappeared completely in a heavily pre-treated set of patiens in an ongoning trail. http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/155525.php BSI-201 - Among other investigational PARP inhibitors in the industry, BSI-201 is the furthest along in clinical development in metastatic TNBC. BSI-201 is currently being evaluated for its potential to enhance the effect of chemotherapy-induced DNA damage. The clinical development of BSI-201 is supported by well documented safety profile based on studies of more than 200 patients.http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/152811.php |
| ATGR1 (ERBB2) |
|
AGTR1 is seen in 10 percent to 20 percent of breast tumors. Specifically, overexpressed only in tumors that are HER2-negative and ER-positive. AGTR1 was found to be as much as 100-fold overexpressed in some tumors. | http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/152162.php |
| eIF4E EIF4E Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E, also known as eIF4E, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the eIF4E gene.- Function :... gene |
Ribavirin Ribavirin is an anti-viral drug indicated for severe RSV infection , hepatitis C infection and other viral infections. Ribavirin is a prodrug, which when metabolised resembles purine RNA nucleotides... (a common anti-viral drug) |
eIF4E gene is dysregulated in 30 percent of cancers including breast, prostate, head and neck, colon and stomach cancer. | The trial studied patients with M4/M5 acute myeloid leukemia Acute myeloid leukemia Acute myeloid leukemia , also known as acute myelogenous leukemia, is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal white blood cells that accumulate in the bone marrow and interfere with the production of normal blood cells. AML is the most common acute... who had undergone several other treatments that had previously failed. They had striking clinical improvements with even partial and complete remissions. http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/150062.php |
| Other Targets |
Dasatinib Dasatinib, previously known as BMS-354825, is a cancer drug produced by Bristol-Myers Squibb and sold under the trade name Sprycel. Dasatinib is an oral multi- BCR/ABL and Src family tyrosine kinase inhibitor approved for use in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia after imatinib treatment... (SRC inhibitor) |
Kinase inhibitor | Drug already used to treat CML is a possible cure for a subset of breast cancer population who test positive for alpha-v beta-3 Alpha-v beta-3 αVβ3 is a type of integrin that is a receptor for vitronectin. It consists of two components, integrin alpha V and integrin beta 3 , and is expressed by platelets. Furthermore it is a receptor for phagocytosis on macrophages or dendritic cells.... .http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/163181.php |
|
|
Kinase inhibitor | Combining Herceptin and saracatinib to treat resistant tumors in mice reduced tumor volume by 90 percent in 25 days. Herceptin alone kept tumor volume about the same during the same period, while control and saracatinib alone permitted growth of more than 200 percent. http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/219008.php | |
|
Sorafenib Sorafenib , is a drug approved for the treatment of primary kidney cancer and advanced primary liver cancer .... (Nexavar) http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/165122.php |
multi-kinase inhibitor | ||
|
|
Vaccine - Stimuvax Stimuvax Stimuvax is an investigational therapeutic cancer vaccine designed to induce an immune response to cancer cells that express MUC1, a glycoprotein antigen widely expressed on common cancers. MUC1 is over-expressed on many cancers such as lung cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer and colorectal... |
||
|
Bavituximab Bavituximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody designed for the treatment of cancers and viral infections.-Mechanism of action:Bavituximab binds to phosphatidylserine which is exposed on the surface of certain atypical animal cells, including tumour cells and cells infected with any of six different... in Phase II http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/147762.php |
Other |
The newest targeted therapies are helping doctors to tailor increasingly effective treatments to individual patients.
Other Possible Targets Cyclin D1
Cyclin D1
G1/S-specific cyclin-D1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCND1 gene.Immunohistochemical staining of cyclin D1 antibodies is used to diagnose mantle cell lymphoma.-Interactions:...
http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/128357.php
Other Potential drugs PV-10 http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/127343.php, Hormone Progestin and p53 http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/137167.php
CR011-vcMMAE aka CDX-011 and Glembatumumab vedotin
Glembatumumab vedotin
Glembatumumab vedotin is an antibody-drug conjugate that targets cancer cells expressing transmembrane glycoprotein NMB ....
.
CR011-vcMMAE is an antibody-drug conjugate
Antibody-drug conjugate
Antibody-drug conjugates are a new type of targeted therapy, used for example for cancer. They consist of an antibody linked to a payload drug . Hence, they are a type of immunoconjugate and often an immunotoxin.The antibody causes the ADC to bind to the target cancer cells...
(ADC) (targeted at transmembrane glycoprotein NMB (GPNMB)) that consists of a fully human monoclonal antibody, CR011, linked to a potent cell-killing drug, monomethyl-auristatin E (MMAE). CR011-vcMMAE is currently in two Phase II trials assessing its safety and efficacy in the treatment of melanoma and for the treatment of metastatic breast cancer, and in a Phase I trial to evaluate the safety and activity of alternate dosing schedules.http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/154376.php http://meeting.ascopubs.org/cgi/content/abstract/28/15_suppl/8525 http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/173950.php
Antiangiogenic therapy
A commercially available monoclonal antibody that blocks the activation of the VEGF receptor, bevacizumabBevacizumab
Bevacizumab is a drug that blocks angiogenesis, the growth of new blood vessels. It is commonly used to treat various cancers, including colorectal, lung, breast, kidney, and glioblastomas....
, underwent testing in a randomized clinical trial whose preliminary results were announced by the National Cancer Institute in 2005. The preliminary data indicated that bevacizumab delays disease progression for up to five months over conventional chemotherapy, but survival was no better. Genentech
Genentech
Genentech Inc., or Genetic Engineering Technology, Inc., is a biotechnology corporation, founded in 1976 by venture capitalist Robert A. Swanson and biochemist Dr. Herbert Boyer. Trailing the founding of Cetus by five years, it was an important step in the evolution of the biotechnology industry...
, manufacturer of bevacizumab, has filed a supplemental biological application with the US FDA for approval of bevacizumab in the setting of metastatic breast cancer, on the strength of the improvement in progression-free survival.
Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B)
In the March 2007, edition of the scientific journal, Nature Genetics, researchers from Canada's McGill University reported that they have developed a potential drug target for treating up to 40 percent of breast cancers by blocking an enzymeEnzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
called protein tyrosine phosphatase
Protein tyrosine phosphatase
Protein tyrosine phosphatases are a group of enzymes that remove phosphate groups from phosphorylated tyrosine residues on proteins. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation is a common post-translational modification that can create novel recognition motifs for protein interactions and cellular...
1B (PTP1B), which has been implicated in the onset of breast cancer in mouse models of the disease. Elevated levels of PTP1B have also been found in diabetes and obesity
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated to the extent that it may have an adverse effect on health, leading to reduced life expectancy and/or increased health problems...
. A drug to block the activity of PTP1B is under development by Merck
Merck & Co.
Merck & Co., Inc. , also known as Merck Sharp & Dohme or MSD outside the United States and Canada, is one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. The Merck headquarters is located in Whitehouse Station, New Jersey, an unincorporated area in Readington Township...
, and was found to delay the development of breast tumors and prevent lung cancer
Lung cancer
Lung cancer is a disease characterized by uncontrolled cell growth in tissues of the lung. If left untreated, this growth can spread beyond the lung in a process called metastasis into nearby tissue and, eventually, into other parts of the body. Most cancers that start in lung, known as primary...
up to two months from the administration of the drug. The researchers hope to continue further research in mouse models which are also HER-2 positive (responsive to Herceptin) so that the drug could benefit a significant population of women.
Cholestrol drug - Ro 48-8071
It's possible that one mechanism utilized by PRIMA-1 to kill cancer cells may include shutting down cholesterol synthesis, but not certain if that's the case. What is now known is that Ro 48-8071 does stop cholesterol synthesis, and it proved to be just as effective in destroying cancer cells as PRIMA-1, without harming other normal breast cells, which is a big advantage. http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/217274.phpAntidiabetic
In experiments led by postdoctoral fellows Heather Hirsch and Dimitrios Iliopoulos, the combination of metforminMetformin
Metformin is an oral antidiabetic drug in the biguanide class. It is the first-line drug of choice for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, in particular, in overweight and obese people and those with normal kidney function. Its use in gestational diabetes has been limited by safety concerns...
and the cancer drug doxorubicin killed human cancer stem cells and non-stem cancer cells in culture. The researchers used four genetically distinct breast cancer cell lines.
In mice, pretreatment with the diabetes drug prevented the otherwise dramatic ability of human breast cancer stem cells to form tumors. In other mice where tumors were allowed to take hold for 10 days, the dual therapy also reduced tumor mass more quickly and prevented relapse for longer than doxorubicin alone. In the two months between the end of treatment and the end of the experiment, tumors regrew in mice treated with chemotherapy alone, but not in mice that had received both drugs. By itself, metformin was ineffective in treating tumors. http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/163990.php, http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/222376.php
Thermochemotherapy
Modern advancements in hyperthermiaHyperthermia
Hyperthermia is an elevated body temperature due to failed thermoregulation. Hyperthermia occurs when the body produces or absorbs more heat than it can dissipate...
biology have led to refinements for individualised thermochemotherapy approaches to treatments as well as interesting potential for exploiting hyperthermia in conjunction with cancer vaccine
Cancer vaccine
The term cancer vaccine refers to a vaccine that either prevents infections with cancer-causing viruses, treats existing cancer or prevents the development of cancer in certain high risk individuals...
s. MR imaging is playing an increasing role for measuring patient response to hyperthermia.
Interest in hyperthermia as a treatment
Hyperthermia therapy
Hyperthermia therapy is a type of medical treatment in which body tissue is exposed to slightly higher temperatures to damage and kill cancer cells or to make cancer cells more sensitive to the effects of radiation and certain anti-cancer drugs...
for breast cancer has led to significant advances and research activity which, in turn, has had a significant impact on treatment protocol. The National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) now includes hyperthermia
Hyperthermia therapy
Hyperthermia therapy is a type of medical treatment in which body tissue is exposed to slightly higher temperatures to damage and kill cancer cells or to make cancer cells more sensitive to the effects of radiation and certain anti-cancer drugs...
in their Breast Cancer Guidelines as a treatment for recurrent cancer.
Erasmus Medical Centre in the Netherlands, is one of Europe's largest hyperthermia centres.
ThermoDox is a proprietary heat-activated liposomal encapsulation of doxorubicin
Doxorubicin
Doxorubicin INN is a drug used in cancer chemotherapy. It is an anthracycline antibiotic, closely related to the natural product daunomycin, and like all anthracyclines, it works by intercalating DNA....
, an approved and frequently used oncology drug for the treatment of a wide range of cancers including breast cancer. ThermoDox, which is administered intravenously and in combination with local hyperthermia, has the potential to provide local tumor control and improve quality of life. Localized mild hyperthermia (39.5-42 degrees Celsius) releases the entrapped doxorubicin from the liposome. This delivery technology enables high concentrations of doxorubicin to be deposited preferentially in a targeted tumor.
Flax
Testing of flaxseed (the highest source of mammalian lignans) on rats led to reduction and regression of tumours. This led to a formal randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blindDouble-blind
A blind or blinded experiment is a scientific experiment where some of the people involved are prevented from knowing certain information that might lead to conscious or subconscious bias on their part, invalidating the results....
study involving 32 postmenopausal patients confirming that 25g flaxseed daily intake significantly reduced cell proliferation, increased apoptosis
Apoptosis
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
and reduced c-erbB2 expression of human breast cancer cells. The preliminary research into flax seeds indicates that flax can significantly change breast cancer growth and metastasis, and enhance the inhibitory effect of tamoxifen on estrogen-dependent tumors.
Immunotherapy
The immune system can help a body fight tumors.http://www.americanscientist.org/issues/feature/2009/1/healing-heat/1Dendritic cell therapy (Planned trial)
A new clinical trial is designed around the use of QI's proprietary dendritic cell therapy, which employs oncofetal antigen ("OFA") to recruit the patient's own immune system to target and attack the cancer cells with the intent to improve patient survivability and quality of life. Each patient will receive three monthly injections of the patient's own dendritic cells that have been sensitized to OFA. It is anticipated that once the sensitized cells are injected back into the patient, the patient's T-cells will locate the OFA found on the patient's cancer cells, thereby generating an immune response with the goal of killing the cancer cells and preventing further spread of the disease. http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/157912.php
Stimuvax - mostly for hormone receptor positive (phase III)
Stimuvax
Stimuvax
Stimuvax is an investigational therapeutic cancer vaccine designed to induce an immune response to cancer cells that express MUC1, a glycoprotein antigen widely expressed on common cancers. MUC1 is over-expressed on many cancers such as lung cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer and colorectal...
is an investigational therapeutic cancer vaccine designed to induce an immune response to cancer cells that express MUC1, a glycoprotein antigen widely expressed on common cancers. MUC1 is over-expressed on many cancers such as lung cancer, breast cancer, prostate cancer and colorectal cancer. Stimuvax is thought to work by stimulating the body's immune system to identify and destroy cancer cells expressing MUC1. http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/154900.php
Phase IIb study of 171 patients with inoperable stage IIIb NSCLC (lung cancer), in which Stimuvax showed a trend towards extending median overall survival from 13.3 months for patients receiving best supportive care (BSC) to 30.6 months for patients receiving Stimuvax plus BSC.2,3 Reported side effects included mild-to-moderate flu-like symptoms, gastrointestinal disturbances and mild injection-site reactions.
Chemoimmunotherapy
Manipulating the immune system to recognize and eradicate breast tumor cells is a highly attractive alternative approach to disease management. Active immunization offers multiple theoretical advantages over all other therapies, including low toxicity. The sustained antitumor effect due to immunological memory would obviate the requirement for prolonged, repetitive cycles of therapy.The objective of chemoimmunotherapy is to amplify natural pre-existing T cell responses specific for any known or unknown tumor antigen and to recruit and amplify new tumor-specific T cell responses resulting from the use of cytotoxic drugs. The direct cytolytic effect of some cytotoxic drugs, such as paclitaxel, can enhance antigen presentation by inducing tumor cell apoptosis. This mechanism of therapeutic synergy has been shown with cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, or paclitaxel when given with dendritic cell - based vaccines. Until 9 years ago, it was thought that the T cell depletion caused by chemotherapy would make immunotherapy ineffective. However it has now been shown that, on the contrary, the vigorous T cell repopulation following depletion can be directed against the tumor.
IMP321 induced both a sustained increase in the number and activation of APC (monocytes and dendritic cells) and an increase in the percentage of NK and long-lived cytotoxic effector-memory CD8 T cells. Clinical benefit was observed for 90 per cent of patients with only 3 progressors at 6 months. Also, the objective tumor response rate of 50 per cent compared favorably to the 25 per cent rate reported in the historical control group. This form of chemo-immunotherapy should be applicable to many chemotherapies. http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/200182.php
Thermochemotherapy
Medifocus heat treatment added to Standard of Care (SoC) chemotherapy increased the median tumor shrinkage in the thermochemotherapy arm to 88.4%, while for chemotherapy alone the median tumor shrinkage was 58.8%. For the thermo-chemotherapy treatment arm, almost 80% of breast tumors had a tumor volume reduction of 80% or more, compared to only 20% for the chemotherapy alone.http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/205491.phpAlternative treatments
A wide range of alternative non medical treatmentsAlternative medicine
Alternative medicine is any healing practice, "that does not fall within the realm of conventional medicine." It is based on historical or cultural traditions, rather than on scientific evidence....
of breast cancer have been proposed.
Gene expression profiling
Gene expression profiling of breast tumors can predict the chances of developing breast cancer again. The most useful setting for these tests is where the benefit of chemotherapy is felt to be small. In up to 10% of patients, there will be disease recurrences, but treating every patient with chemotherapy is overkill. In this setting, a high-risk score can help doctors decide whether to recommend chemotherapy.Treatment response assessment
Physical examination and conventional imaging techniques still have an important place in the evaluation of breast cancer treated by neoadjuvant chemotherapy. At this time, this morphologic evaluation is the only one recognized by the international criteria. The new functional and metabolic imaging modalities, particularly MRI and PET scan, can approach the nature of residual tumour, allow early detection of bad responders and depict multifocal tumours and metastases.
- Using PET/CT Imaging, UCLA Cancer Researchers Can Tell After A Single Cycle Of Chemotherapy Whether Drugs Are Working http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/146322.php
- MRI accurately detects residual breast tumors after radiofrequency ablation
- water diffusion MRI — a potential new biomarker of response to cancer therapy http://www.ajronline.org/cgi/content/full/188/6/1622
- CK18 biomarkers are useful for early prediction of the response to CEF therapy in breast cancer and may be useful biomarkers for clinical trials.
- 3T MRI depicted a significantly higher number of malignant tumors of the breast than mammography and sonography http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/146171.php
Blood Test
The current standard of care for metastatic disease involves the use of radiology studies such as CT scans, ultrasounds, and the like to determine whether or not patients are deriving benefit from their current therapies. An alternative is the FDA-approved CellSearch technology, looking at circulating tumor cells (CTCs) in blood collected from women in need of a new treatment regimen for metastatic breast cancer. About one tablespoon of blood was collected when the patient started the new therapy, and then again at three to four week intervals. The number of CTCs was correlated with disease response or progression as determined by standard radiology studies (e.g., CT scans) performed every nine to 12 weeks.http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/164155.phpManaging Side Effects
Drugs and radiotherapy given for cancer can cause unpleasant side effects such as nausea and vomiting, mouth sores, dermatitis, and menopausal symptoms. Around a third of patients with cancer use complementary therapies, including homeopathic medicines, to try to reduce these side effects. http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/146077.phpInsomnia
It was believed that one would find a bi-directional relationship between insomnia and pain, but instead it was found that trouble sleeping was more likely a cause, rather than a consequence, of pain in patients with cancer. An early intervention to manage sleep would overall relieve patient with side effects.http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/146317.phpApproximately 40 percent of menopausal women experience sleep disruption, often in the form of difficulty with sleep initiation and frequent nighttime awakenings. There is a study, first to show sustained benefits in sleep quality from gabapentin, which Rochester researchers already have demonstrated alleviates hot flashes. http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/163260.php
Hot Flashes
Gabapentin and many of antidepressants are commonly prescribed for treatment of hot flashes, although these agents are not specifically approved by the FDA for such use.Pregabalin is a newer version of gabapentin and is found equally effective in treating hot flashes.http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/150286.php
Reoccurrence monitoring
Chronix Biomedical has reported new data further demonstrating that its serum DNA blood tests have the potential to accurately detect early stage breast cancer and prostate cancer. Chronix's proprietary technology identifies disease-specific genetic fingerprints based on circulating DNA fragments that are released into the bloodstream by damaged and dying (apoptotic) cells.The tests use proprietary algorithms developed by Chronix researchers to detect, analyze and identify cancer-related fragments of circulating DNA that are released into the bloodstream by apoptotic cells. Chronix researchers consistently find that this apoptotic DNA in the serum is coming from a limited number of regions or "hotspots" on the genome specific to each cancer. According to the data presented today, DNA fragments from any one of the 29 breast cancer "hotspots" and 32 prostate cancer "hotspots" identified by Chronix researchers indicate that cancer is present. http://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/191129.php
Attribution
- The original version of this article incorporated text from the Wikipedia article Breast cancerBreast cancerBreast cancer is cancer originating from breast tissue, most commonly from the inner lining of milk ducts or the lobules that supply the ducts with milk. Cancers originating from ducts are known as ductal carcinomas; those originating from lobules are known as lobular carcinomas...
.
External links
- IBC treatment options on IBC Watch - is a detailed update of recently emerging treatment options.
- Breast Cancer Network of Strength -list of treatment options and possible side effects

