Sentinel lymph node
Encyclopedia
The sentinel lymph node is the hypothetical first lymph node
or group of nodes reached by metastasizing
cancer
cell
s from a primary tumor
.
is directional. In layperson language, some cancers spread in a predictable fashion from where the cancer started. In these cases, if the cancer spreads it will spread first to lymph nodes (lymph glands) close to the tumor before it spreads to other parts of the body. The concept of sentinel lymph node surgery is to see if the cancer has spread to the very first lymph node (called the "sentinel lymph node"). If the sentinel lymph node does not contain cancer, then there is a high likelihood that the cancer has not spread to any other area of the body.
of certain types of cancer to see if they have spread to any lymph nodes, since lymph node metastasis is one of the most important prognostic signs
. It can also guide the surgeon to the appropriate therapy.
.jpg)
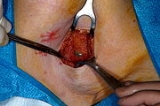
 To perform a sentinel lymph node biopsy
To perform a sentinel lymph node biopsy
, the physician performs a lymphoscintigraphy, wherein a low-activity radioactive substance
is injected near the tumor. The injected substance, Filtered Sulfur Colloid, is tagged with the radionuclide Technetium-99m
. The injection protocols differ by doctor but the most common is a 500 μCi dose divided among 5 tuberculin syringes with 1/2 inch, 24 gauge needles. The sulphur colloid is slightly acidic and causes minor stinging. A gentle massage of the injection sites spreads the sulphur colloid, relieving the pain and speeding up the lymph uptake. Scintigraphic imaging is usually started within 5 minutes of injection and the node appears from 5 min to 1 hour. This is usually done several hours before the actual biopsy. About 15 minutes before the biopsy the physician injects a blue dye in the same manner. Then, during the biopsy, the physician visually inspects the lymph nodes for staining and uses a Gamma Probe
or a Geiger counter
to assess which lymph nodes have taken up the radionuclide. One or several nodes may take up the dye and radioactive tracer, and these nodes are designated the sentinel lymph nodes. The surgeon then removes these lymph nodes and sends them to a pathologist for rapid examination under a microscope
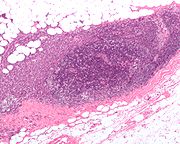
to look for the presence of cancer.
A frozen section procedure
is commonly employed (which takes less than 20 minutes), so if neoplasia is detected in the lymph node a further lymph node dissection
may be performed. With malignant melanoma, many pathologists eschew frozen sections for more accurate "permanent" specimen preparation due to the increased instances of false-negative with melanocytic staining.
, a common complication of this procedure. Increased attention on the node(s) identified to most likely contain metastasis is also more likely to detect micro-metastasis and result in staging and treatment changes. The main uses are in breast cancer
and malignant melanoma surgery
, although it has been used in other tumor types (colon cancer) with a degree of success.
.
Lymph node
A lymph node is a small ball or an oval-shaped organ of the immune system, distributed widely throughout the body including the armpit and stomach/gut and linked by lymphatic vessels. Lymph nodes are garrisons of B, T, and other immune cells. Lymph nodes are found all through the body, and act as...
or group of nodes reached by metastasizing
Metastasis
Metastasis, or metastatic disease , is the spread of a disease from one organ or part to another non-adjacent organ or part. It was previously thought that only malignant tumor cells and infections have the capacity to metastasize; however, this is being reconsidered due to new research...
cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
cell
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
s from a primary tumor
Tumor
A tumor or tumour is commonly used as a synonym for a neoplasm that appears enlarged in size. Tumor is not synonymous with cancer...
.
Physiology
The spread of some forms of cancer usually follows an orderly progression, spreading first to regional lymph nodes, then the next echelon of lymph nodes, and so on, since the flow of lymphLymph
Lymph is considered a part of the interstitial fluid, the fluid which lies in the interstices of all body tissues. Interstitial fluid becomes lymph when it enters a lymph capillary...
is directional. In layperson language, some cancers spread in a predictable fashion from where the cancer started. In these cases, if the cancer spreads it will spread first to lymph nodes (lymph glands) close to the tumor before it spreads to other parts of the body. The concept of sentinel lymph node surgery is to see if the cancer has spread to the very first lymph node (called the "sentinel lymph node"). If the sentinel lymph node does not contain cancer, then there is a high likelihood that the cancer has not spread to any other area of the body.
Uses
The concept of the sentinel lymph node is important because of the advent of the sentinel lymph node biopsy technique, also known as a sentinel node procedure. This technique is used in the stagingCancer staging
The stage of a cancer is a description of the extent the cancer has spread. The stage often takes into account the size of a tumor, how deeply it has penetrated, whether it has invaded adjacent organs, how many lymph nodes it has metastasized to , and whether it has spread to distant organs...
of certain types of cancer to see if they have spread to any lymph nodes, since lymph node metastasis is one of the most important prognostic signs
Prognosis
Prognosis is a medical term to describe the likely outcome of an illness.When applied to large statistical populations, prognostic estimates can be very accurate: for example the statement "45% of patients with severe septic shock will die within 28 days" can be made with some confidence, because...
. It can also guide the surgeon to the appropriate therapy.
.jpg)

Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test involving sampling of cells or tissues for examination. It is the medical removal of tissue from a living subject to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist, and can also be analyzed chemically...
, the physician performs a lymphoscintigraphy, wherein a low-activity radioactive substance
Radionuclide
A radionuclide is an atom with an unstable nucleus, which is a nucleus characterized by excess energy available to be imparted either to a newly created radiation particle within the nucleus or to an atomic electron. The radionuclide, in this process, undergoes radioactive decay, and emits gamma...
is injected near the tumor. The injected substance, Filtered Sulfur Colloid, is tagged with the radionuclide Technetium-99m
Technetium-99m
Technetium-99m is a metastable nuclear isomer of technetium-99, symbolized as 99mTc. The "m" indicates that this is a metastable nuclear isomer, i.e., that its half-life of 6 hours is considerably longer than most nuclear isomers that undergo gamma decay...
. The injection protocols differ by doctor but the most common is a 500 μCi dose divided among 5 tuberculin syringes with 1/2 inch, 24 gauge needles. The sulphur colloid is slightly acidic and causes minor stinging. A gentle massage of the injection sites spreads the sulphur colloid, relieving the pain and speeding up the lymph uptake. Scintigraphic imaging is usually started within 5 minutes of injection and the node appears from 5 min to 1 hour. This is usually done several hours before the actual biopsy. About 15 minutes before the biopsy the physician injects a blue dye in the same manner. Then, during the biopsy, the physician visually inspects the lymph nodes for staining and uses a Gamma Probe
Gamma Probe
A gamma probe is a handheld device used with a Geiger-Muller tube or scintillation counter, for intraoperative use following interstitial injection of a radionuclide, to locate regional lymph nodes by their radioactivity...
or a Geiger counter
Geiger counter
A Geiger counter, also called a Geiger–Müller counter, is a type of particle detector that measures ionizing radiation. They detect the emission of nuclear radiation: alpha particles, beta particles or gamma rays. A Geiger counter detects radiation by ionization produced in a low-pressure gas in a...
to assess which lymph nodes have taken up the radionuclide. One or several nodes may take up the dye and radioactive tracer, and these nodes are designated the sentinel lymph nodes. The surgeon then removes these lymph nodes and sends them to a pathologist for rapid examination under a microscope
Microscope
A microscope is an instrument used to see objects that are too small for the naked eye. The science of investigating small objects using such an instrument is called microscopy...
to look for the presence of cancer.
A frozen section procedure
Frozen section procedure
The frozen section procedure is a pathological laboratory procedure to perform rapid microscopic analysis of a specimen. It is used most often in oncological surgery. The technical name for this procedure is cryosection....
is commonly employed (which takes less than 20 minutes), so if neoplasia is detected in the lymph node a further lymph node dissection
Lymph node dissection
Lymph node dissection, also lymphadenectomy is a surgical procedure in which the lymph nodes are removed and examined to see whether they contain cancer. For a regional lymph node dissection, some of the lymph nodes in the tumor area are removed; for a radical lymph node dissection, most or all of...
may be performed. With malignant melanoma, many pathologists eschew frozen sections for more accurate "permanent" specimen preparation due to the increased instances of false-negative with melanocytic staining.
Advantages
There are various advantages to the sentinel node procedure. First and foremost, it decreases unnecessary lymph node dissections where this is not necessary, thereby reducing the risk of lymphedemaLymphedema
Lymphedema , also known as lymphatic obstruction, is a condition of localized fluid retention and tissue swelling caused by a compromised lymphatic system....
, a common complication of this procedure. Increased attention on the node(s) identified to most likely contain metastasis is also more likely to detect micro-metastasis and result in staging and treatment changes. The main uses are in breast cancer
Breast cancer
Breast cancer is cancer originating from breast tissue, most commonly from the inner lining of milk ducts or the lobules that supply the ducts with milk. Cancers originating from ducts are known as ductal carcinomas; those originating from lobules are known as lobular carcinomas...
and malignant melanoma surgery
Surgery
Surgery is an ancient medical specialty that uses operative manual and instrumental techniques on a patient to investigate and/or treat a pathological condition such as disease or injury, or to help improve bodily function or appearance.An act of performing surgery may be called a surgical...
, although it has been used in other tumor types (colon cancer) with a degree of success.
Disadvantages
However, the technique is not without drawbacks, particularly when used for melanoma patients. This technique only has therapeutic value in patients with positive nodes. Failure to detect cancer cells in the sentinel node can lead to a false negative result - there may still be cancerous cells in the lymph node basin. In addition, there is no compelling evidence that patients who have a full lymph node dissection as a result of a positive sentinel lymph node result have improved survival compared to those who do not have a full dissection until later in their disease, when the lymph nodes can be felt by a physician. Such patients may be having an unnecessary full dissection, with the attendant risk of lymphedemaLymphedema
Lymphedema , also known as lymphatic obstruction, is a condition of localized fluid retention and tissue swelling caused by a compromised lymphatic system....
.

