Battle of Kernstown I
Encyclopedia
The First Battle of Kernstown was fought on March 23, 1862, in Frederick County
and Winchester, Virginia
, the opening battle of Confederate
Maj. Gen. Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson
's campaign
through the Shenandoah Valley
during the American Civil War
.
Attempting to tie down the Union
forces in the Valley, under the overall command of Maj. Gen. Nathaniel P. Banks, Jackson received incorrect intelligence that a small detachment under Col. Nathan Kimball
was vulnerable, but it was in fact a full infantry
division
more than twice the size of Jackson's force. His initial cavalry attack was forced back and he immediately reinforced it with a small infantry brigade. With his other two brigades, Jackson sought to envelop the Union right by way of Sandy Ridge. But Col.
Erastus B. Tyler
's brigade countered this movement, and, when Kimball's brigade moved to his assistance, the Confederates were driven from the field. There was no effective Union pursuit.
Although the battle was a Confederate tactical defeat, and in fact Jackson's only defeat in the war, it represented a strategic victory for the South by preventing the Union from transferring forces from the Shenandoah Valley to reinforce the Peninsula Campaign
against the Confederate capital, Richmond
. Kernstown started Jackson on the road to being one of the most celebrated Confederate generals.
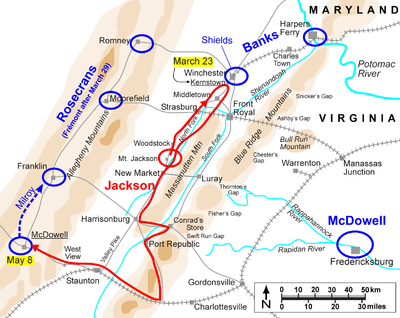
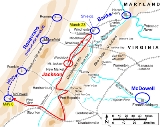
Jackson's division had been withdrawing "up" the Valley (to the higher elevations at the southwest end of the Valley) to cover the flank of Gen. Joseph E. Johnston
's army, withdrawing from the Centreville
–Manassas
area to protect Richmond. Without this protective movement, the Federal army under Banks might strike at Johnston through passes in the Blue Ridge Mountains. By March 12, 1862, Banks occupied Winchester
just after Jackson had withdrawn from the town, marching at a leisurely pace 42 miles up the Valley Pike
to Mount Jackson
. On March 21, Jackson received word that Banks was splitting his force, with two divisions (under Brig. Gens. John Sedgwick
and Alpheus S. Williams
) returning to the immediate vicinity of Washington, D.C.
, freeing up other Union troops to participate in Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan
's Peninsula Campaign against Richmond. The remaining division, under Brig. Gen. James Shields
, was stationed at Strasburg
to guard the lower (northeastern) Valley, and intelligence indicated that it was withdrawing toward Winchester. Banks made preparations to leave the Valley personally on March 23.
Jackson's orders from Johnston were to prevent Banks's force from leaving the Valley, which it appeared they were now doing. Jackson turned his men around and, in one of the more grueling forced marches of the war, moved northeast 25 miles on March 22 and another 15 to Kernstown on the morning of March 23. His cavalry, under Col. Turner Ashby
, skirmished with the Federals on March 22, during which engagement Shields was wounded with a broken arm from an artillery shell fragment. Despite his injury, Shields sent part of his division south of Winchester and one brigade marching to the north, seemingly abandoning the area, but in fact halting nearby to remain in reserve. He then turned over tactical command of his division to Col. Nathan Kimball, although throughout the battle to come, he sent numerous messages and orders to Kimball. Confederate loyalists in Winchester mistakenly informed Turner Ashby that Shields had left only four regiments and a few guns (about 3,000 men) and that these remaining troops had orders to march for Harpers Ferry in the morning. Ashby, who normally had a reputation as a reliable cavalry scout, inexplicably did not verify the civilian reports and passed them on to Jackson. Jackson marched aggressively north with his 3,000-man division, reduced from its peak as stragglers fell out of the column, unaware that he was soon to be attacking almost 9,000 men.
and arrived before the Union position at Kernstown around 11 a.m., Sunday, March 23. The devoutly religious Jackson preferred to avoid battles on the Sabbath, but throughout his Civil War career he did not hesitate when military advantage could be gained. He later wrote to his wife:
Jackson performed no personal reconnaissance before he sent Turner Ashby on a feint
against Kimball's position on the Valley Turnpike while his main force—the brigades of Col. Samuel Fulkerson and Brig. Gen. Richard B. Garnett
(the Stonewall Brigade
, Jackson's own first command)—attacked the Union artillery position on Pritchard Hill. The lead brigade under Fulkerson was repulsed, so Jackson decided to move around the Union right flank, about 2 miles west on Sandy Ridge, which appeared to be unoccupied. If this were successful, his men could move down the spine of the ridge and get into the Union rear, blocking their escape route to Winchester. Kimball countered the maneuver by moving his brigade under Col. Erastus B. Tyler
to the west, but Fulkerson's men reached a stone wall facing a clearing on the ridge before the Union men could. Jackson's aide, Sandie Pendleton, obtained a clear view from the ridge of the Union forces arrayed against them and he estimated that there were 10,000. He reported this to Jackson, who replied, "Say nothing about it. We are in for it."
Around 4 p.m, Tyler attacked Fulkerson and Garnett by using an unorthodox approach with his brigade in "close column of divisions"—a brigade front of two companies with 48 companies lined up behind them in 24 lines, in all about 75 yards wide, and 400 yards long, a formation difficult to control and lacking offensive power at the front. The Confederates were temporarily able to counter this attack with their inferior numbers by firing fierce volleys from behind the stone wall. Jackson, finally realizing the strength of the force opposing him, sent out Col. Jesse Burks's brigade, which had been held in reserve, but by the time they arrived around 6 p.m., Garnett's Stonewall Brigade had run out of ammunition and he pulled them back, leaving Fulkerson's right flank exposed. Panic set in among the Confederates, and as Burks's brigade arrived, it was caught in the fleeing mob and forced to retreat. Jackson tried in vain to rally his troops. He called out to a soldier "Where are you going, man?" The soldier replied that he was out of ammunition. "Then go back and give them the bayonet!" Jackson said. However, the soldier ignored him and kept running. Kimball organized no effective pursuit. That night, a cavalryman sat with Jackson by a campfire alongside the Valley Pike and jokingly said "It was reported that they were retreating, General, but I guess they were retreating after us." Jackson, not known for his sense of humor, replied, "I think I am satisfied, sir."
Despite the Union victory, President
Abraham Lincoln
was disturbed by Jackson's audacity and his potential threat to Washington. He sent Banks back to the Valley along with Alpheus Williams's division. He also was concerned that Jackson might move into western Virginia against Maj. Gen. John C. Frémont
, so he ordered that the division of Brig. Gen. Louis Blenker
be detached from McClellan's Army of the Potomac and sent to reinforce Frémont. Lincoln also took this opportunity to re-examine Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan
's plans for the defenses of Washington while the Peninsula Campaign was underway and decided that the forces were insufficient. He eventually ordered that the corps of Maj. Gen. Irvin McDowell
, which was moving south against Richmond in support of McClellan, remain in the vicinity of the capital. McClellan claimed that the loss of these forces prevented him from taking Richmond during his campaign. The strategic realignment of Union forces caused by Jackson's battle at Kernstown—the only battle he lost in his military career—turned out to be a strategic victory for the Confederacy. The remainder of Jackson's Valley Campaign consisted of lightning movements and five victories against superior forces organized into three Union armies, which elevated him to the position of the most famous general in the Confederacy (until this reputation was later supplanted by his superior, Gen. Robert E. Lee
).
Jackson refused to accept any responsibility for the defeat and subsequently arrested the commander of his old Stonewall Brigade
, Brig. Gen. Richard B. Garnett
, for retreating from the battlefield before permission was received. The Stonewall Brigade's withdrawal, which came after it received the bulk of the Union fire and suffered the majority of Confederate casualties, uncovered the right of Fulkerson's Brigade, forcing it to also withdraw and starting a panic. He was replaced by Brig. Gen. Charles S. Winder
. During the invasion of Maryland
in September, Robert E. Lee ordered the charges against him dropped, but Garnett suffered from the humiliation of his court-martial for over a year, until he was killed at Gettysburg during Pickett's Charge
.
A Second Battle of Kernstown occurred in the Valley Campaigns of 1864
.
Frederick County, Virginia
Frederick County is a county located in the Commonwealth of Virginia. It is included in the Winchester, Virginia-West Virginia Metropolitan Statistical Area. It was formed in 1743 by the splitting of Orange County. For ten years it was the home of George Washington. As of 2010, the population was...
and Winchester, Virginia
Winchester, Virginia
Winchester is an independent city located in the northwestern portion of the Commonwealth of Virginia in the USA. The city's population was 26,203 according to the 2010 Census...
, the opening battle of Confederate
Confederate States Army
The Confederate States Army was the army of the Confederate States of America while the Confederacy existed during the American Civil War. On February 8, 1861, delegates from the seven Deep South states which had already declared their secession from the United States of America adopted the...
Maj. Gen. Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson
Stonewall Jackson
ຄຽשת״ׇׂׂׂׂ֣|birth_place= Clarksburg, Virginia |death_place=Guinea Station, Virginia|placeofburial=Stonewall Jackson Memorial CemeteryLexington, Virginia|placeofburial_label= Place of burial|image=...
's campaign
Valley Campaign
Jackson's Valley Campaign was Confederate Maj. Gen. Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson's famous spring 1862 campaign through the Shenandoah Valley in Virginia during the American Civil War...
through the Shenandoah Valley
Shenandoah Valley
The Shenandoah Valley is both a geographic valley and cultural region of western Virginia and West Virginia in the United States. The valley is bounded to the east by the Blue Ridge Mountains, to the west by the eastern front of the Ridge-and-Valley Appalachians , to the north by the Potomac River...
during the American Civil War
American Civil War
The American Civil War was a civil war fought in the United States of America. In response to the election of Abraham Lincoln as President of the United States, 11 southern slave states declared their secession from the United States and formed the Confederate States of America ; the other 25...
.
Attempting to tie down the Union
Union Army
The Union Army was the land force that fought for the Union during the American Civil War. It was also known as the Federal Army, the U.S. Army, the Northern Army and the National Army...
forces in the Valley, under the overall command of Maj. Gen. Nathaniel P. Banks, Jackson received incorrect intelligence that a small detachment under Col. Nathan Kimball
Nathan Kimball
Nathan Kimball was a physician, politician, postmaster, and military officer, serving as a general in the Union army during the American Civil War...
was vulnerable, but it was in fact a full infantry
Infantry
Infantrymen are soldiers who are specifically trained for the role of fighting on foot to engage the enemy face to face and have historically borne the brunt of the casualties of combat in wars. As the oldest branch of combat arms, they are the backbone of armies...
division
Division (military)
A division is a large military unit or formation usually consisting of between 10,000 and 20,000 soldiers. In most armies, a division is composed of several regiments or brigades, and in turn several divisions typically make up a corps...
more than twice the size of Jackson's force. His initial cavalry attack was forced back and he immediately reinforced it with a small infantry brigade. With his other two brigades, Jackson sought to envelop the Union right by way of Sandy Ridge. But Col.
Colonel (United States)
In the United States Army, Air Force, and Marine Corps, colonel is a senior field grade military officer rank just above the rank of lieutenant colonel and just below the rank of brigadier general...
Erastus B. Tyler
Erastus B. Tyler
Erastus Bernard Tyler was an American businessman, merchant, and soldier. He was a general in the Union Army during the American Civil War and fought in many of the early battles in the Eastern Theater before being assigned command of the defenses of Baltimore, Maryland. He briefly commanded the...
's brigade countered this movement, and, when Kimball's brigade moved to his assistance, the Confederates were driven from the field. There was no effective Union pursuit.
Although the battle was a Confederate tactical defeat, and in fact Jackson's only defeat in the war, it represented a strategic victory for the South by preventing the Union from transferring forces from the Shenandoah Valley to reinforce the Peninsula Campaign
Peninsula Campaign
The Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War was a major Union operation launched in southeastern Virginia from March through July 1862, the first large-scale offensive in the Eastern Theater. The operation, commanded by Maj. Gen. George B...
against the Confederate capital, Richmond
Richmond, Virginia
Richmond is the capital of the Commonwealth of Virginia, in the United States. It is an independent city and not part of any county. Richmond is the center of the Richmond Metropolitan Statistical Area and the Greater Richmond area...
. Kernstown started Jackson on the road to being one of the most celebrated Confederate generals.
Background

Jackson's division had been withdrawing "up" the Valley (to the higher elevations at the southwest end of the Valley) to cover the flank of Gen. Joseph E. Johnston
Joseph E. Johnston
Joseph Eggleston Johnston was a career U.S. Army officer, serving with distinction in the Mexican-American War and Seminole Wars, and was also one of the most senior general officers in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War...
's army, withdrawing from the Centreville
Centreville, Virginia
Centreville is an unincorporated community in Fairfax County, Virginia, United States. Recognized by the U.S. Census Bureau as a Census Designated Place , the community population was 71,135 as of the 2010 census and is approximately west of Washington, DC.-Colonial Period:Beginning in the 1760s,...
–Manassas
Manassas, Virginia
The City of Manassas is an independent city surrounded by Prince William County and the independent city of Manassas Park in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. Its population was 37,821 as of 2010. Manassas also surrounds the county seat for Prince William County but that county...
area to protect Richmond. Without this protective movement, the Federal army under Banks might strike at Johnston through passes in the Blue Ridge Mountains. By March 12, 1862, Banks occupied Winchester
Winchester, Virginia
Winchester is an independent city located in the northwestern portion of the Commonwealth of Virginia in the USA. The city's population was 26,203 according to the 2010 Census...
just after Jackson had withdrawn from the town, marching at a leisurely pace 42 miles up the Valley Pike
Valley Pike
Valley Pike or Valley Turnpike is the traditional name given for the Indian trail and roadway which now is designated as U.S. Highway 11 in the Shenandoah Valley of Virginia....
to Mount Jackson
Mount Jackson, Virginia
Mount Jackson is a town in Shenandoah County, Virginia, United States. The population was 1,994 at the 2010 census.-Geography:Mount Jackson is located at in the southern part of Shenandoah County, Virginia at...
. On March 21, Jackson received word that Banks was splitting his force, with two divisions (under Brig. Gens. John Sedgwick
John Sedgwick
John Sedgwick was a teacher, a career military officer, and a Union Army general in the American Civil War. He was the highest ranking Union casualty in the Civil War, killed by a sniper at the Battle of Spotsylvania Court House.-Early life:Sedgwick was born in the Litchfield Hills town of...
and Alpheus S. Williams
Alpheus S. Williams
Alpheus Starkey Williams was a lawyer, judge, journalist, U.S. Congressman, and a Union general in the American Civil War.-Early life:...
) returning to the immediate vicinity of Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution....
, freeing up other Union troops to participate in Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan
George B. McClellan
George Brinton McClellan was a major general during the American Civil War. He organized the famous Army of the Potomac and served briefly as the general-in-chief of the Union Army. Early in the war, McClellan played an important role in raising a well-trained and organized army for the Union...
's Peninsula Campaign against Richmond. The remaining division, under Brig. Gen. James Shields
James Shields
James Shields was an American politician and United States Army officer who was born in Altmore, County Tyrone, Ireland. Shields, a Democrat, is the only person in United States history to serve as a U.S. Senator for three different states...
, was stationed at Strasburg
Strasburg, Virginia
Strasburg is a town in Shenandoah County, Virginia, United States, which was founded in 1761 by Peter Stover. It is the largest town, population-wise, in the county and is known for its pottery, antiques, and Civil War history...
to guard the lower (northeastern) Valley, and intelligence indicated that it was withdrawing toward Winchester. Banks made preparations to leave the Valley personally on March 23.
Jackson's orders from Johnston were to prevent Banks's force from leaving the Valley, which it appeared they were now doing. Jackson turned his men around and, in one of the more grueling forced marches of the war, moved northeast 25 miles on March 22 and another 15 to Kernstown on the morning of March 23. His cavalry, under Col. Turner Ashby
Turner Ashby
Turner Ashby, Jr. was a Confederate cavalry commander in the American Civil War. He had achieved prominence as Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson's cavalry commander, in the grade of colonel, in the Shenandoah Valley before he was killed in battle in 1862...
, skirmished with the Federals on March 22, during which engagement Shields was wounded with a broken arm from an artillery shell fragment. Despite his injury, Shields sent part of his division south of Winchester and one brigade marching to the north, seemingly abandoning the area, but in fact halting nearby to remain in reserve. He then turned over tactical command of his division to Col. Nathan Kimball, although throughout the battle to come, he sent numerous messages and orders to Kimball. Confederate loyalists in Winchester mistakenly informed Turner Ashby that Shields had left only four regiments and a few guns (about 3,000 men) and that these remaining troops had orders to march for Harpers Ferry in the morning. Ashby, who normally had a reputation as a reliable cavalry scout, inexplicably did not verify the civilian reports and passed them on to Jackson. Jackson marched aggressively north with his 3,000-man division, reduced from its peak as stragglers fell out of the column, unaware that he was soon to be attacking almost 9,000 men.
Battle
Jackson moved north from WoodstockWoodstock, Virginia
Woodstock is a town in Shenandoah County, Virginia, United States. It has a population of 5,097 according to the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Shenandoah County....
and arrived before the Union position at Kernstown around 11 a.m., Sunday, March 23. The devoutly religious Jackson preferred to avoid battles on the Sabbath, but throughout his Civil War career he did not hesitate when military advantage could be gained. He later wrote to his wife:
Jackson performed no personal reconnaissance before he sent Turner Ashby on a feint
Feint
Feint is a French term that entered English from the discipline of fencing. Feints are maneuvers designed to distract or mislead, done by giving the impression that a certain maneuver will take place, while in fact another, or even none, will...
against Kimball's position on the Valley Turnpike while his main force—the brigades of Col. Samuel Fulkerson and Brig. Gen. Richard B. Garnett
Richard B. Garnett
Richard Brooke Garnett was a career United States Army officer and a Confederate general in the American Civil War. He was killed during Pickett's Charge at the Battle of Gettysburg.-Early life:...
(the Stonewall Brigade
Stonewall Brigade
The Stonewall Brigade of the Confederate Army during the American Civil War, was a famous combat unit in United States military history. It was trained and first led by General Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson, a professor from Virginia Military Institute...
, Jackson's own first command)—attacked the Union artillery position on Pritchard Hill. The lead brigade under Fulkerson was repulsed, so Jackson decided to move around the Union right flank, about 2 miles west on Sandy Ridge, which appeared to be unoccupied. If this were successful, his men could move down the spine of the ridge and get into the Union rear, blocking their escape route to Winchester. Kimball countered the maneuver by moving his brigade under Col. Erastus B. Tyler
Erastus B. Tyler
Erastus Bernard Tyler was an American businessman, merchant, and soldier. He was a general in the Union Army during the American Civil War and fought in many of the early battles in the Eastern Theater before being assigned command of the defenses of Baltimore, Maryland. He briefly commanded the...
to the west, but Fulkerson's men reached a stone wall facing a clearing on the ridge before the Union men could. Jackson's aide, Sandie Pendleton, obtained a clear view from the ridge of the Union forces arrayed against them and he estimated that there were 10,000. He reported this to Jackson, who replied, "Say nothing about it. We are in for it."
Around 4 p.m, Tyler attacked Fulkerson and Garnett by using an unorthodox approach with his brigade in "close column of divisions"—a brigade front of two companies with 48 companies lined up behind them in 24 lines, in all about 75 yards wide, and 400 yards long, a formation difficult to control and lacking offensive power at the front. The Confederates were temporarily able to counter this attack with their inferior numbers by firing fierce volleys from behind the stone wall. Jackson, finally realizing the strength of the force opposing him, sent out Col. Jesse Burks's brigade, which had been held in reserve, but by the time they arrived around 6 p.m., Garnett's Stonewall Brigade had run out of ammunition and he pulled them back, leaving Fulkerson's right flank exposed. Panic set in among the Confederates, and as Burks's brigade arrived, it was caught in the fleeing mob and forced to retreat. Jackson tried in vain to rally his troops. He called out to a soldier "Where are you going, man?" The soldier replied that he was out of ammunition. "Then go back and give them the bayonet!" Jackson said. However, the soldier ignored him and kept running. Kimball organized no effective pursuit. That night, a cavalryman sat with Jackson by a campfire alongside the Valley Pike and jokingly said "It was reported that they were retreating, General, but I guess they were retreating after us." Jackson, not known for his sense of humor, replied, "I think I am satisfied, sir."
Aftermath
Union casualties were 590 (118 killed, 450 wounded, 22 captured or missing), Confederate 718 (80 killed, 375 wounded, 263 captured or missing).Despite the Union victory, President
President of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln
Abraham Lincoln was the 16th President of the United States, serving from March 1861 until his assassination in April 1865. He successfully led his country through a great constitutional, military and moral crisis – the American Civil War – preserving the Union, while ending slavery, and...
was disturbed by Jackson's audacity and his potential threat to Washington. He sent Banks back to the Valley along with Alpheus Williams's division. He also was concerned that Jackson might move into western Virginia against Maj. Gen. John C. Frémont
John C. Frémont
John Charles Frémont , was an American military officer, explorer, and the first candidate of the anti-slavery Republican Party for the office of President of the United States. During the 1840s, that era's penny press accorded Frémont the sobriquet The Pathfinder...
, so he ordered that the division of Brig. Gen. Louis Blenker
Louis Blenker
Louis Blenker was a German and American soldier.-Life in Germany:He was born at Worms, Germany. After being trained as a goldsmith by an uncle in Kreuznach, he was sent to a polytechnical school in Munich. Against his family's wishes, he enlisted in an Uhlan regiment which accompanied Otto to...
be detached from McClellan's Army of the Potomac and sent to reinforce Frémont. Lincoln also took this opportunity to re-examine Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan
George B. McClellan
George Brinton McClellan was a major general during the American Civil War. He organized the famous Army of the Potomac and served briefly as the general-in-chief of the Union Army. Early in the war, McClellan played an important role in raising a well-trained and organized army for the Union...
's plans for the defenses of Washington while the Peninsula Campaign was underway and decided that the forces were insufficient. He eventually ordered that the corps of Maj. Gen. Irvin McDowell
Irvin McDowell
Irvin McDowell was a career American army officer. He is best known for his defeat in the First Battle of Bull Run, the first large-scale battle of the American Civil War.-Early life:...
, which was moving south against Richmond in support of McClellan, remain in the vicinity of the capital. McClellan claimed that the loss of these forces prevented him from taking Richmond during his campaign. The strategic realignment of Union forces caused by Jackson's battle at Kernstown—the only battle he lost in his military career—turned out to be a strategic victory for the Confederacy. The remainder of Jackson's Valley Campaign consisted of lightning movements and five victories against superior forces organized into three Union armies, which elevated him to the position of the most famous general in the Confederacy (until this reputation was later supplanted by his superior, Gen. Robert E. Lee
Robert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee was a career military officer who is best known for having commanded the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia in the American Civil War....
).
Jackson refused to accept any responsibility for the defeat and subsequently arrested the commander of his old Stonewall Brigade
Stonewall Brigade
The Stonewall Brigade of the Confederate Army during the American Civil War, was a famous combat unit in United States military history. It was trained and first led by General Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson, a professor from Virginia Military Institute...
, Brig. Gen. Richard B. Garnett
Richard B. Garnett
Richard Brooke Garnett was a career United States Army officer and a Confederate general in the American Civil War. He was killed during Pickett's Charge at the Battle of Gettysburg.-Early life:...
, for retreating from the battlefield before permission was received. The Stonewall Brigade's withdrawal, which came after it received the bulk of the Union fire and suffered the majority of Confederate casualties, uncovered the right of Fulkerson's Brigade, forcing it to also withdraw and starting a panic. He was replaced by Brig. Gen. Charles S. Winder
Charles Sidney Winder
Charles Sidney Winder , was a career United States Army officer and a Confederate general officer in the American Civil War. He was killed in action during the Battle of Cedar Mountain.-Early life and career:...
. During the invasion of Maryland
Maryland Campaign
The Maryland Campaign, or the Antietam Campaign is widely considered one of the major turning points of the American Civil War. Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee's first invasion of the North was repulsed by Maj. Gen. George B...
in September, Robert E. Lee ordered the charges against him dropped, but Garnett suffered from the humiliation of his court-martial for over a year, until he was killed at Gettysburg during Pickett's Charge
Pickett's Charge
Pickett's Charge was an infantry assault ordered by Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee against Maj. Gen. George G. Meade's Union positions on Cemetery Ridge on July 3, 1863, the last day of the Battle of Gettysburg during the American Civil War. Its futility was predicted by the charge's commander,...
.
A Second Battle of Kernstown occurred in the Valley Campaigns of 1864
Valley Campaigns of 1864
The Valley Campaigns of 1864 were American Civil War operations and battles that took place in the Shenandoah Valley of Virginia from May to October 1864. Military historians divide this period into three separate campaigns, but it is useful to consider the three together and how they...
.

