
Aliphatic compound
Encyclopedia
Organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, composition, reactions, and preparation of carbon-based compounds, hydrocarbons, and their derivatives...
, aliphatic compounds (icon; G. aleiphar, fat, oil) are acyclic or cyclic
Cyclic compound
In chemistry, a cyclic compound is a compound in which a series of atoms is connected to form a loop or ring.While the vast majority of cyclic compounds are organic, a few inorganic substances form cyclic compounds as well, including sulfur, silanes, phosphanes, phosphoric acid, and triboric acid. ...
, non-aromatic
Aromaticity
In organic chemistry, Aromaticity is a chemical property in which a conjugated ring of unsaturated bonds, lone pairs, or empty orbitals exhibit a stabilization stronger than would be expected by the stabilization of conjugation alone. The earliest use of the term was in an article by August...
carbon compounds.
Thus, aliphatic compounds are opposite to aromatic compounds.
Structure
In aliphatic compounds, carbon atoms can be joined together in straight chains, branched chains, or non-aromatic rings (in which case they are called alicyclicAlicyclic compound
An alicyclic compound is an organic compound that is both aliphatic and cyclic. They contain one or more all-carbon rings which may be either saturated or unsaturated, but do not have aromatic character...
). Aliphatic compounds can be saturated
Saturation (chemistry)
In chemistry, saturation has six different meanings, all based on reaching a maximum capacity...
, joined by single bonds (alkanes), or unsaturated, with double bonds (alkenes) or triple bonds (alkynes). Besides hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
, other elements can be bound to the carbon chain, the most common being oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
, nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
, sulphur, and chlorine
Chlorine
Chlorine is the chemical element with atomic number 17 and symbol Cl. It is the second lightest halogen, found in the periodic table in group 17. The element forms diatomic molecules under standard conditions, called dichlorine...
.
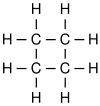
The simplest aliphatic compound is methane
Methane
Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest alkane, the principal component of natural gas, and probably the most abundant organic compound on earth. The relative abundance of methane makes it an attractive fuel...
(C
Carbon
Carbon is the chemical element with symbol C and atomic number 6. As a member of group 14 on the periodic table, it is nonmetallic and tetravalent—making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds...
H
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
4). Aliphatics include alkanes (e.g. paraffin
Paraffin
In chemistry, paraffin is a term that can be used synonymously with "alkane", indicating hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n+2. Paraffin wax refers to a mixture of alkanes that falls within the 20 ≤ n ≤ 40 range; they are found in the solid state at room temperature and begin to enter the...
hydrocarbon
Hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons from which one hydrogen atom has been removed are functional groups, called hydrocarbyls....
s), alkene
Alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing at least one carbon-to-carbon double bond...
s (e.g. ethylene
Ethylene
Ethylene is a gaseous organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest alkene . Because it contains a carbon-carbon double bond, ethylene is classified as an unsaturated hydrocarbon. Ethylene is widely used in industry and is also a plant hormone...
) and alkyne
Alkyne
Alkynes are hydrocarbons that have a triple bond between two carbon atoms, with the formula CnH2n-2. Alkynes are traditionally known as acetylenes, although the name acetylene also refers specifically to C2H2, known formally as ethyne using IUPAC nomenclature...
s (e.g. acetylene
Acetylene
Acetylene is the chemical compound with the formula C2H2. It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution.As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because...
). Fatty acid
Fatty acid
In chemistry, especially biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with a long unbranched aliphatic tail , which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have a chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are usually derived from...
s consist of an unbranched aliphatic tail attached to a carboxyl group.
Properties
Most aliphatic compounds are flammable, allowing the use of hydrocarbons as fuel, such as methaneMethane
Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest alkane, the principal component of natural gas, and probably the most abundant organic compound on earth. The relative abundance of methane makes it an attractive fuel...
in Bunsen burners and as Liquified Natural Gas (LNG), and acetylene
Acetylene
Acetylene is the chemical compound with the formula C2H2. It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution.As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because...
in welding.
Examples for aliphatic compounds
The most important group of aliphatic compounds are:- n-, Iso- and Cyclo-Alkanes (Saturated Hydrocarbons)
- n-, Iso- and Cyclo-Alkenes and -Alkynes (Unsaturated Hydrocarbons).
Important examples of low-molecular aliphatic compounds can be found in the list below (sorted by the number of carbon-atoms):
| Formula | Name | CAS-Number | Structural Formula | Chemical Classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|
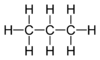
| CH4 | Methane Methane Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest alkane, the principal component of natural gas, and probably the most abundant organic compound on earth. The relative abundance of methane makes it an attractive fuel... |
74-82-8 | 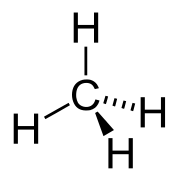 |
Alkane |
| C2H2 | Ethyne Acetylene Acetylene is the chemical compound with the formula C2H2. It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is unstable in pure form and thus is usually handled as a solution.As an alkyne, acetylene is unsaturated because... |
74-86-2 | Alkyne | |
| C2H4 | Ethene | 74-85-1 | Alkene | |
| C2H6 | Ethane Ethane Ethane is a chemical compound with chemical formula C2H6. It is the only two-carbon alkane that is an aliphatic hydrocarbon. At standard temperature and pressure, ethane is a colorless, odorless gas.... |
74-84-0 | Alkane | |
| C3H4 | Propyne | 74-99-7 | Alkyne | |
| C3H6 | Propene | - | Alkene | |
| C3H8 | Propane Propane Propane is a three-carbon alkane with the molecular formula , normally a gas, but compressible to a transportable liquid. A by-product of natural gas processing and petroleum refining, it is commonly used as a fuel for engines, oxy-gas torches, barbecues, portable stoves, and residential central... |
- |  |
Alkane |
| C4H6 | 1,2-Butadiene | 590-19-2 | Diene | |
| C4H6 | 1-Butyne | - | Alkyne | |
| C4H8 | Butene | - | e.g. | Alkene |
| C4H10 | Butane Butane Butane is a gas with the formula C4H10 that is an alkane with four carbon atoms. The term may refer to any of two structural isomers, or to a mixture of them: in the IUPAC nomenclature, however, butane refers only to the unbranched n-butane isomer; the other one being called "methylpropane" or... |
- | Alkane | |
| C6H10 | Cyclohexene Cyclohexene Cyclohexene is a hydrocarbon with the formula C6H10. This cycloalkene is a colorless liquid with a sharp smell. It is an intermediate in various industrial processes... |
110-83-8 | Cycloalkene | |
| C5H12 | n-pentane | 109-66-0 | Alkane | |
| C7H14 | Cycloheptane Cycloheptane Cycloheptane is a cycloalkane with the molecular formula C7H14. Cycloheptane is used as a nonpolar solvent for the chemical industry and as an intermediate in the manufacture of chemicals and pharmaceutical drugs. It may be derived by Clemmensen reduction from cycloheptanone. Cycloheptane vapour is... |
291-64-5 | Cycloalkane | |
| C7H14 | Methylcyclohexane Methylcyclohexane Methylcyclohexane is a colourless liquid with a faint benzene-like odour. Its molecular formula is C7H14. Methylcyclohexane is used in organic synthesis and as a solvent for cellulose ethers. It is a component of jet fuel and is also a component of correction fluids.-Structure:Monosubstituted... |
108-87-2 | Cyclohexane | |
| C8H8 | Cubane Cubane Cubane is a synthetic hydrocarbon molecule that consists of eight carbon atoms arranged at the corners of a cube, with one hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom. A solid crystalline substance, cubane is one of the Platonic hydrocarbons. It was first synthesized in 1964 by Philip Eaton, a... |
277-10-1 | 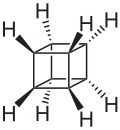 |
Cyclobutane |
| C9H20 | Nonane Nonane Nonane is a linear alkane hydrocarbon with the chemical formula C9H20.Nonane has 35 structural isomers. Tripropylene is a mixture of three specific isomers of nonane.Its substituent form is nonyl. Its cycloalkane counterpart is cyclononane, .... |
111-84-2 | Alkane | |
| C10H12 | Dicyclopentadiene Dicyclopentadiene Dicyclopentadiene, abbreviated DCPD, is a chemical compound with formula C10H12. At room temperature, it is a white crystalline solid with a camphor-like odor. Its energy density is 10,975 Wh/l.... |
77-73-6 | Diene, Cycloalkene | |
| C10H16 | Phellandrene Phellandrene Phellandrene is the name for a pair of organic compounds that have a similar molecular structure and similar chemical properties. α-Phellandrene and β-phellandrene are cyclic monoterpenes and are double-bond isomers. In α-phellandrene, both double bonds are endocyclic and in β-phellandrene, one... |
99-83-2 | 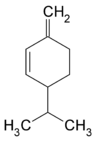 |
Terpene, Diene Cycloalkene |
| C10H16 | α-Terpinene | 99-86-5 | Terpene, Cycloalkene, Diene | |
| C10H16 | Limonene Limonene Limonene is a colourless liquid hydrocarbon classified as a cyclic terpene. The more common D isomer possesses a strong smell of oranges. It is used in chemical synthesis as a precursor to carvone and as a renewably-based solvent in cleaning products.... |
5989-27-5 | Terpene, Diene, Cycloalkene | |
| C11H24 | Undecane Undecane Undecane is a liquid alkane hydrocarbon with the chemical formula CH39CH3. It is used as a mild sex attractant for various types of moths and cockroaches, and an alert signal for a variety of ants. It has 159 isomers.... |
1120-21-4 | Alkane | |
| C30H50 | Squalene Squalene Squalene is a natural organic compound originally obtained for commercial purposes primarily from shark liver oil, though plant sources are used as well, including amaranth seed, rice bran, wheat germ, and olives. All plants and animals produce squalene, including humans... |
111-02-4 | 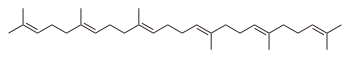 |
Terpene, Polyene |
| C2nH4n | Polyethylene Polyethylene Polyethylene or polythene is the most widely used plastic, with an annual production of approximately 80 million metric tons... |
9002-88-4 | Alkane |
Aliphatic acids
Aliphatic acids are the acids of nonaromatic hydrocarbons, such as aceticAcetic acid
Acetic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula CH3CO2H . It is a colourless liquid that when undiluted is also called glacial acetic acid. Acetic acid is the main component of vinegar , and has a distinctive sour taste and pungent smell...
, propionic
Propionic acid
Propanoic acid is a naturally occurring carboxylic acid with chemical formula CH3CH2COOH. It is a clear liquid with a pungent odor...
, and butyric acid
Butyric acid
Butyric acid , also known under the systematic name butanoic acid, is a carboxylic acid with the structural formula CH3CH2CH2-COOH. Salts and esters of butyric acid are known as butyrates or butanoates...
s.

