
Malthusian growth model
Encyclopedia
The Malthusian growth model, sometimes called the simple exponential growth model, is essentially exponential growth
based on a constant rate of compound interest
. The model is named after the Reverend Thomas Malthus, who authored An Essay on the Principle of Population
, one of the earliest and most influential books on population
.
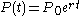
where P0 = Initial Population,
r = growth rate, sometimes also called Malthusian Parameter,
t = time.
(Does population ecology have general laws?, 2001 and Complex Population Dynamics, 2003), this model is often referred to as The Exponential Law and is widely regarded in the field of population ecology
as the first principle of population dynamics
, with Malthus as the founder.
At best, it can be described as an approximate physical law
as it is generally acknowledged that nothing can grow at a constant rate indefinitely (Cassell's Laws Of Nature, James Trefil
, 2002 - Refer 'exponential growth law'). Joel E. Cohen has stated that the simplicity of the model makes it useful for very short-term predictions and of not much use for predictions beyond 10 or 20 years (How Many People Can The Earth Support, 1995).
Antony Flew
- in his introduction to the Penguin Books
publication of Malthus' essay (1st edition) - argued a "certain limited resemblance" between Malthus' law of population to laws of Newtonian mechanics.
is a useful rule of thumb
that roughly explains the time periods involved in exponential growth
at a constant rate. For example, if growth is measured annually then a 1% growth rate results in a doubling every 70 years. At 2% doubling occurs every 35 years.
The number 70 comes from the observation that the natural log
of 2 is approximately 0.7, by multiplying this by 100 we obtain 70. To find the doubling time we divide the natural log of 2 by the growth rate. To find the time it takes to increase by a factor of 3 we would use the natural log of 3, approximately 1.1.
.
Pierre Francois Verhulst
first published his logistic growth function in 1838 after he had read Malthus' An Essay on the Principle of Population
. Benjamin Gompertz
also published work developing the Malthusian growth model further.
Exponential growth
Exponential growth occurs when the growth rate of a mathematical function is proportional to the function's current value...
based on a constant rate of compound interest
Compound interest
Compound interest arises when interest is added to the principal, so that from that moment on, the interest that has been added also itself earns interest. This addition of interest to the principal is called compounding...
. The model is named after the Reverend Thomas Malthus, who authored An Essay on the Principle of Population
An Essay on the Principle of Population
The book An Essay on the Principle of Population was first published anonymously in 1798 through J. Johnson . The author was soon identified as The Reverend Thomas Robert Malthus. While it was not the first book on population, it has been acknowledged as the most influential work of its era...
, one of the earliest and most influential books on population
Population
A population is all the organisms that both belong to the same group or species and live in the same geographical area. The area that is used to define a sexual population is such that inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with individuals...
.
Formula
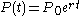
where P0 = Initial Population,
r = growth rate, sometimes also called Malthusian Parameter,
t = time.
Exponential law
As noted by Peter TurchinPeter Turchin
Peter Turchin is a Russian-American scientist, specializing in population biology and "cliodynamics" — mathematical modeling and statistical analysis of the dynamics of historical societies.- Biography :...
(Does population ecology have general laws?, 2001 and Complex Population Dynamics, 2003), this model is often referred to as The Exponential Law and is widely regarded in the field of population ecology
Population ecology
Population ecology is a sub-field of ecology that deals with the dynamics of species populations and how these populations interact with the environment. It is the study of how the population sizes of species living together in groups change over time and space....
as the first principle of population dynamics
Population dynamics
Population dynamics is the branch of life sciences that studies short-term and long-term changes in the size and age composition of populations, and the biological and environmental processes influencing those changes...
, with Malthus as the founder.
At best, it can be described as an approximate physical law
Physical law
A physical law or scientific law is "a theoretical principle deduced from particular facts, applicable to a defined group or class of phenomena, and expressible by the statement that a particular phenomenon always occurs if certain conditions be present." Physical laws are typically conclusions...
as it is generally acknowledged that nothing can grow at a constant rate indefinitely (Cassell's Laws Of Nature, James Trefil
James Trefil
James S. Trefil is an American physicist and author of more than thirty books. Much of his published work focuses on science for the general audience. Dr...
, 2002 - Refer 'exponential growth law'). Joel E. Cohen has stated that the simplicity of the model makes it useful for very short-term predictions and of not much use for predictions beyond 10 or 20 years (How Many People Can The Earth Support, 1995).
Antony Flew
Antony Flew
Antony Garrard Newton Flew was a British philosopher. Belonging to the analytic and evidentialist schools of thought, he was notable for his works on the philosophy of religion....
- in his introduction to the Penguin Books
Penguin Books
Penguin Books is a publisher founded in 1935 by Sir Allen Lane and V.K. Krishna Menon. Penguin revolutionised publishing in the 1930s through its high quality, inexpensive paperbacks, sold through Woolworths and other high street stores for sixpence. Penguin's success demonstrated that large...
publication of Malthus' essay (1st edition) - argued a "certain limited resemblance" between Malthus' law of population to laws of Newtonian mechanics.
Malthusian law
The exponential law is also sometimes referred to as The Malthusian Law (refer "Laws Of Population Ecology" by Dr. Paul Haemig, 2005).Rule of 70
The rule of 70Rule of 72
In finance, the rule of 72, the rule of 70 and the rule of 69 are methods for estimating an investment's doubling time. The rule number is divided by the interest percentage per period to obtain the approximate number of periods required for doubling...
is a useful rule of thumb
Rule of thumb
A rule of thumb is a principle with broad application that is not intended to be strictly accurate or reliable for every situation. It is an easily learned and easily applied procedure for approximately calculating or recalling some value, or for making some determination...
that roughly explains the time periods involved in exponential growth
Exponential growth
Exponential growth occurs when the growth rate of a mathematical function is proportional to the function's current value...
at a constant rate. For example, if growth is measured annually then a 1% growth rate results in a doubling every 70 years. At 2% doubling occurs every 35 years.
The number 70 comes from the observation that the natural log
Natural logarithm
The natural logarithm is the logarithm to the base e, where e is an irrational and transcendental constant approximately equal to 2.718281828...
of 2 is approximately 0.7, by multiplying this by 100 we obtain 70. To find the doubling time we divide the natural log of 2 by the growth rate. To find the time it takes to increase by a factor of 3 we would use the natural log of 3, approximately 1.1.
Logistic growth model
The Malthusian growth model is the direct ancestor of the logistic functionLogistic function
A logistic function or logistic curve is a common sigmoid curve, given its name in 1844 or 1845 by Pierre François Verhulst who studied it in relation to population growth. It can model the "S-shaped" curve of growth of some population P...
.
Pierre Francois Verhulst
Pierre François Verhulst
Pierre François Verhulst was a mathematician and a doctor in number theory from the University of Ghent in 1825...
first published his logistic growth function in 1838 after he had read Malthus' An Essay on the Principle of Population
An Essay on the Principle of Population
The book An Essay on the Principle of Population was first published anonymously in 1798 through J. Johnson . The author was soon identified as The Reverend Thomas Robert Malthus. While it was not the first book on population, it has been acknowledged as the most influential work of its era...
. Benjamin Gompertz
Benjamin Gompertz
Benjamin Gompertz was a British self educated mathematician and actuary, who became a Fellow of the Royal Society...
also published work developing the Malthusian growth model further.
See also
- Albert BartlettAlbert BartlettAlbert Allen Bartlett is an emeritus Professor of Physics at the University of Colorado at Boulder, USA. Professor Bartlett has lectured over 1,600 times since September, 1969 on Arithmetic, Population, and Energy...
- a leading proponent of the Malthusian Growth Model - Exogenous growth modelExogenous growth modelThe neoclassical growth model, also known as the Solow–Swan growth model or exogenous growth model, is a class of economic models of long-run economic growth set within the framework of neoclassical economics...
- related growth model from economicsEconomicsEconomics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"... - Exponential growthExponential growthExponential growth occurs when the growth rate of a mathematical function is proportional to the function's current value...
- Growth theory - related ideas from economicsEconomicsEconomics is the social science that analyzes the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. The term economics comes from the Ancient Greek from + , hence "rules of the house"...
- Irruptive growthIrruptive growthIrruptive growth, sometimes called Malthusian growth, is a growth pattern defined by population explosions and subsequent sharp population crashes, or diebacks...
- an extension of the Malthusian model accounting for population explosions and crashes - PopulationPopulationA population is all the organisms that both belong to the same group or species and live in the same geographical area. The area that is used to define a sexual population is such that inter-breeding is possible between any pair within the area and more probable than cross-breeding with individuals...
- Mathematical models
- Neo-malthusianism
- Logistic functionLogistic functionA logistic function or logistic curve is a common sigmoid curve, given its name in 1844 or 1845 by Pierre François Verhulst who studied it in relation to population growth. It can model the "S-shaped" curve of growth of some population P...
- Scientific laws named after peopleScientific laws named after peopleThis is a list of scientific laws named after people . For other lists of eponyms, see eponym.-See also:* Eponym* Fields of science...
- strictly speaking, no scientific law has been named after Malthus - Scientific phenomena named after peopleScientific phenomena named after peopleThis is a list of scientific phenomena and concepts named after people . For other lists of eponyms, see eponym.-A:* Abderhalden–Fauser reaction – Emil Abderhalden* Abney effect, Abney's law of additivity – William de Wiveleslie Abney...
- being mathematical, and relating to population dynamicsPopulation dynamicsPopulation dynamics is the branch of life sciences that studies short-term and long-term changes in the size and age composition of populations, and the biological and environmental processes influencing those changes...
, the Malthusian Growth Model qualifies - Malthusian catastropheMalthusian catastropheA Malthusian catastrophe was originally foreseen to be a forced return to subsistence-level conditions once population growth had outpaced agricultural production...
External links
- Malthusian Growth Model from Steve McKelvey, Department of Mathematics, Saint Olaf College, Northfield, Minnesota
- Logistic Model from Steve McKelvey, Department of Mathematics, Saint Olaf College, Northfield, Minnesota
- Laws Of Population Ecology Dr. Paul D. Haemig
- On principles, laws and theory of population ecology Professor of Entomology, Alan Berryman, Washington State University
- Mathematical Growth Models
- e the EXPONENTIAL - the Magic Number of GROWTH - Keith Tognetti, University of Wollongong, NSW, Australia
- Introduction to Social Macrodynamics Professor Andrey KorotayevAndrey KorotayevAndrey Korotayev is an anthropologist, economic historian, and sociologist, with major contributions to world-systems theory, cross-cultural studies, Near Eastern history, and mathematical modeling of social and economic macrodynamics.Education and career=Born in Moscow, Andrey Korotayev attended...
- Interesting Facts about Population Growth Mathematical Models from Jacobo Bulaevsky, Arcytech.

