History of Mozilla Firefox
Encyclopedia
The Mozilla Firefox project was created by Dave Hyatt
and Blake Ross
as an experimental branch of the Mozilla
project. Firefox 1.0 was released on November 9, 2004. Firefox 1.5 was released on November 29, 2005. Version 2.0
was released on October 24, 2006. Firefox 3.0
was released on June 17, 2008, with Version 3.5
and Version 3.6
released on June 30, 2009 and January 21, 2010 respectively. Version 4.0 was released on March 22, 2011, Version 5.0 was released on June 21, 2011, Version 6.0 was released on August 16, 2011, Version 7.0 was released on September 27, 2011 and Version 8.0, the current release, was released on November 8, 2011.
 Hyatt, Ross, Hewitt and Chanial's browser was created to combat the perceived software bloat
Hyatt, Ross, Hewitt and Chanial's browser was created to combat the perceived software bloat
of the Mozilla Suite
(codenamed, internally referred to, and continued by the community as SeaMonkey
), which integrated features such as IRC
, mail and news, and WYSIWYG
HTML
editing into one software suite.
Firefox retains the cross-platform
nature of the original Mozilla browser, using the XUL
user interface markup language
. The use of XUL makes it possible to extend the browser's capabilities through the use of extensions and theme
s. The development and installation processes of these add-ons raised security concerns, and with the release of Firefox 0.9, the Mozilla Foundation opened a Mozilla Update website containing "approved" themes and extensions. The use of XUL sets Firefox apart from other browsers, including other projects based on Mozilla's Gecko
layout engine
and most other browsers, which use interfaces native to their respective platforms (Galeon
and Epiphany
use GTK+
; K-Meleon
uses MFC
; and Camino
uses Cocoa
). Many of these projects were started before Firefox, and probably served as inspiration.
Although the Mozilla Foundation had intended to make the Mozilla Suite obsolete and replace it with Firefox, the Foundation continued to maintain the suite until April 12, 2006 because it had many corporate users and was bundled with other software. The Mozilla community (as opposed to the Foundation) continues to release new versions of the suite, using the product name SeaMonkey
to avoid confusion with the original Mozilla Suite.
On February 5, 2004, business and IT consulting company AMS
categorized Mozilla Firefox (then known as Firebird) as a "Tier 1" ("Best of Breed") open source product, considering it technically strong and virtually risk-free.
The Phoenix name was kept until April 14, 2003, when it was changed because of a trademark
dispute with the BIOS
manufacturer, Phoenix Technologies
(which produces a BIOS-based browser called Phoenix FirstWare Connect). The new name, Firebird, met with mixed reactions, particularly as the Firebird database server
already carried the name. In response, the Mozilla Foundation stated that the browser should always bear the name Mozilla Firebird to avoid confusion with the database software. Continuing pressure from the Firebird community forced another change, and on February 9, 2004 the project was renamed Mozilla Firefox (or Firefox for short).
The name "Firefox" (a reference to the red panda
) was chosen for its similarity to "Firebird", but also for its uniqueness in the computing industry. To ensure that no further name changes would be necessary, the Mozilla Foundation began the process of registering Firefox as a trademark
with the United States Patent and Trademark Office
in December 2003. This trademark process led to a delay of several months in the release of Firefox 0.8 when the foundation discovered that Firefox had already been registered as a trademark in the UK
for Charlton Company software. The situation was resolved when the foundation was given a license to use Charlton's European trademark.
 Early Firebird and Phoenix releases of Firefox were considered to have had reasonable visual designs, but were not up to the same standards as many professionally released software packages. In October 2003, professional interface designer Steven Garrity wrote an article covering everything he considered to be wrong with Mozilla's visual identity. The page received a great deal of attention; the majority of criticism leveled at the article fell along the lines of "where's the patch?"
Early Firebird and Phoenix releases of Firefox were considered to have had reasonable visual designs, but were not up to the same standards as many professionally released software packages. In October 2003, professional interface designer Steven Garrity wrote an article covering everything he considered to be wrong with Mozilla's visual identity. The page received a great deal of attention; the majority of criticism leveled at the article fell along the lines of "where's the patch?"
Shortly afterwards, Garrity was invited by the Mozilla Foundation to head up the new visual identity team. The release of Firefox 0.8 in February 2004 saw the introduction of the new branding efforts, including new icon designs by silverorange, a group of web developers with a long-standing relationship with Mozilla, with final renderings by Jon Hicks
, who had previously worked on Camino
. The logo was later revised and updated, fixing several flaws found when it was enlarged.
The animal shown in the logo is a stylized fox, although "firefox" is considered to be a common name for the red panda
. The panda, according to Hicks, "didn't really conjure up the right imagery" and wasn't widely known. The logo was chosen to make an impression while not shouting out with overdone artwork. It had to stand out in the user's mind, be easy for others to remember, and stand out without causing too much distraction when seen among other icons.
The Firefox icon is a trademark used to designate the official Mozilla build of the Firefox software and builds of official distribution partners. For this reason, Debian
and other software distributors who distribute patched or modified versions of Firefox do not use the icon. The crash reporting service was initially closed source, but switched with version 3 from a program called Talkback to the open source BreakPad & Socorro.
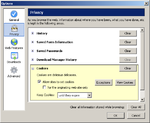 Early Firefox releases featured a preferences panel that described cookie
Early Firefox releases featured a preferences panel that described cookie
s thus: "Cookies are delicious delicacies".
The phrase was representative of the programmers' quirky sense of humor and was a reflection of the free software movement
's unconventional approach. The phrase became something of a cult legend and was even featured in an O'Reilly
computer book.
The original text was inserted by Blake Ross, one of the lead developers of Firefox, because, he said, "describing something so complicated in such a small space was quite frankly the last thing I wanted to worry about after rewriting the cookie manager".
However, in reflection of the growing acceptance and use of the Firefox browser in the Internet
mainstream, the text was later changed. It was labeled a bug
, and was "fixed" by Mike Connor to read, "Cookies are pieces of information stored by web pages on your computer. They are used to remember login information and other data." The revision was regarded as more likely to be helpful to less technically oriented computer users who were now using Firefox—representing Mozilla's desire to appeal to mainstream users.
The text became a popular in-joke
and on August 2004, the Delicious Delicacies extension, no longer maintained or updated, was released by Jesse Ruderman. The extension restored the old description of cookies, available in several languages.
As of Firefox 2.0, cookies are no longer described in the preferences window.
 On June 23, 2005, the Mozilla Foundation announced that Firefox 1.1 (which became Firefox 1.5) and other new Mozilla products would no longer support Mac OS X v10.1
On June 23, 2005, the Mozilla Foundation announced that Firefox 1.1 (which became Firefox 1.5) and other new Mozilla products would no longer support Mac OS X v10.1
, in order to improve the quality of Firefox releases on Mac OS X v10.2
and above. Mac 10.1 users could still use Firefox versions from the 1.0.x branch (e.g. Firefox 1.0.7).
 Firefox 1.5 was released on November 30, 2005. While Firefox 1.5 was originally slated to arrive later, the Mozilla foundation abandoned the 1.1 release plan after the first two 1.1 alpha builds, merging it with the feature set of 1.5, which ended up being released later than the original 1.1 date. The new version resynchronized the code base of the release builds (as opposed to nightly builds) with the core "trunk", which contained additional features not available in 1.0, as it branched
Firefox 1.5 was released on November 30, 2005. While Firefox 1.5 was originally slated to arrive later, the Mozilla foundation abandoned the 1.1 release plan after the first two 1.1 alpha builds, merging it with the feature set of 1.5, which ended up being released later than the original 1.1 date. The new version resynchronized the code base of the release builds (as opposed to nightly builds) with the core "trunk", which contained additional features not available in 1.0, as it branched
from the trunk around the 0.9 release. As such, there was a backlog of bug fixes between 0.9 and the release of 1.0, which were made available in 1.5. Version 1.5 implemented a new Mac-like options interface, the subject of much criticism from Windows and Linux users, with a "Sanitize" action to allow someone to clear their privacy-related information without manually clicking the "Clear All" button. In Firefox 1.5, a user could clear all privacy-related settings simply by exiting the browser or using a keyboard shortcut, depending on their settings. Moreover, the software update system was improved (with binary patches now possible). There were also improvements in the extension management system, with a number of new developer features.
In addition, Firefox 1.5 had preliminary SVG
1.1 support.
Alpha builds of Firefox 1.5 (1.1a1 and 1.1a2) did not carry Firefox branding; they were labeled "Deer Park" (which was Firefox 1.5's internal codename) and contained a different program icon. This was done to dissuade end-users from downloading preview versions, which are intended for developers only.
Firefox 1.5.0.12 was the final version supported on Windows 95
.
 On March 22, 2006, the first alpha version of Firefox 2 (Bon Echo Alpha 1) was released. It featured Gecko 1.8.1 for the first time.
On March 22, 2006, the first alpha version of Firefox 2 (Bon Echo Alpha 1) was released. It featured Gecko 1.8.1 for the first time.
Firefox 2 was released on October 24, 2006 and contained many new features not found in Firefox 1.5, including improved SVG and JavaScript 1.7 support, as well as UI changes.
Mozilla Firefox 2.0.0.x was the final version supported on Windows NT 4.0, 98 and Me. Mozilla Corporation announced it would not develop new versions of Firefox 2 after the 2.0.0.20 release, but continued Firefox 2 development as long as other programs, such as Thunderbird mail client
, depended on it. The final internal release was 2.0.0.22, released in late April 2009.
, Mozilla cannot offer remote control
, as volunteers are bound to the privacy policy.
 The Mozilla Foundation released Firefox 3 on June 17, 2008. The first Firefox 3 beta (under codename 'Gran Paradiso').
The Mozilla Foundation released Firefox 3 on June 17, 2008. The first Firefox 3 beta (under codename 'Gran Paradiso').
had been released several months earlier, on 19 November 2007, which was followed by several more beta releases in the Spring of 2008 culminating in the June release.
One of the major changes in Firefox 3 is the implementation of Gecko
1.9, an updated layout engine
. The new version fixes many bugs and implements new web APIs.
. It was the first version to accomplish this feat.
One minor update to Firefox 3.6, version 3.6.4 (code-named Lorentz
) is the first minor update to make non-intrusive changes other than minor stability and security fixes. It adds Out of Process Plugins (OOPP), which runs plugins in a separate process, allowing Firefox to recover from plugin crashes.
Firefox 3.6.6 lengthens the amount of time a plug-in is allowed to be unresponsive before the plug-in quits.
Firefox 3.7 (Gecko 1.9.3) Alpha 1 was released on February 10, 2010.
Alpha 2 was released on March 1, 2010, Alpha 3 on March 17, Alpha 4 on April 12, and Alpha 5 on June 16. The version number was changed to 4.0 (and Gecko's was changed to 2.0) starting with Beta 1, released on July 6, 2010. Beta 2 was released on July 27, Beta 3 on August 11, Beta 4 on August 24, Beta 5 on September 7, Beta 6 (a chemspill release) on September 14. After major delays, Beta 7 was finally released on November 10. Beta 7 was followed by Beta 8, released on December 21. Beta 9 was released on January 14, 2011, Beta 10 on January 25, Beta 11 on February 8, and Beta 12 on February 12. Firefox then moved into the RC stage. The Final Version of Firefox 4 was released on March 22, 2011.
One of the main focuses was to improve the user interface. UI overhaul mockups for the Windows version posted in the Mozilla Wiki showed numerous changes, including optional tab bar display at the top of the window, status bar
integration with the tab toolbar, as well as search bar and the reload/stop button integration with the awesomebar. A new type of tab, called an application tab, was placed in the tab bar. Similar to the Mozilla Prism
project, it allows web pages (such as Google Mail
) to become applications. The browser was given a home tab similar to new tab pages found in Internet Explorer 8
and Google Chrome
, although users were allowed to customize the button to take them to their homepage instead. The menu bar
disappeared from the mockups, and the UI used animations to manipulate tags and buttons.
The Mac OS X installer was redesigned to make installations easier. Firefox start-up windows were eliminated to make start-up quicker. Preference and add-on manager windows were redesigned to better assist users.
"Door hanger" notifications were to be added to replace "bar" notifications, which were easily spoofed by web pages.
The Gecko layout engine was improved to support more HTML5 and CSS3 features.
In addition, the Firefox Sync project was integrated into the browser to allow users to sync elements such as bookmarks, tabs, and history with either Mozilla or other third-party servers.
Even though the GUI
was changed very little, Firefox 5 features:
Immediately following the launch of Firefox 5, several software critics reviewed it. Matt Egan of PC Advisor said that there was not much new to see, and that users would have to double-check they were not still using Firefox 4, although did concede that improvements in speed and stability made an upgrade worthwhile. Gary Marshall of TechRadar.com commented that there appeared to be a version number race between different browsers and implies in his review that the changes do not merit a full version number. However, he does praise the addition of the Do Not Track button to the user interface and describes how this helps users.
Seth Rosenblatt of CNET agrees with the other two reviewers on the minor nature of the changes and praises the speed and usability improvements.
Firefox 7.0.1 was released on September 29, 2011, providing a bug-fix for a problem with add-ons that were hidden after updating.
Originally an improved tab animation for moving, reordering and detaching tabs was planned, but the new code was backed out with Beta 5 due to issues with the implementation.
builds, and Aurora, a separate nightly branch for refining code. The next scheduled date for a version shift in these channels is December 20, 2011.
Current Supported Releases
Current Test Releases
Future Releases
Future Test Releases
/American
English
, European
/Argentine Spanish
, and Chinese
in Traditional/Simplified characters, while Firefox 4.0 is available in over 80 languages.
Dave Hyatt
Dave Hyatt is an American software developer currently employed by Apple Inc. , where he is part of the development team responsible for the Safari web browser and WebKit framework. Hyatt was part of the original team that shipped the beta releases and 1.0 release of Safari...
and Blake Ross
Blake Ross
Blake Aaron Ross is an American software developer who is known for his work on the Mozilla web browser; in particular, he started the Mozilla Firefox project with Dave Hyatt, as well as the Spread Firefox project with Asa Dotzler while working as a contractor at the Mozilla Foundation...
as an experimental branch of the Mozilla
Mozilla
Mozilla is a term used in a number of ways in relation to the Mozilla.org project and the Mozilla Foundation, their defunct commercial predecessor Netscape Communications Corporation, and their related application software....
project. Firefox 1.0 was released on November 9, 2004. Firefox 1.5 was released on November 29, 2005. Version 2.0
Mozilla Firefox 2
Mozilla Firefox 2 was a version of Firefox, a web browser released on October 24, 2006 by the Mozilla Corporation.Firefox 2 uses version 1.8 of the Gecko layout engine for displaying web pages...
was released on October 24, 2006. Firefox 3.0
Mozilla Firefox 3
Mozilla Firefox 3.0 is a version of the Firefox web browser released on June 17, 2008 by the Mozilla Corporation.Firefox 3.0 uses version 1.9 of the Gecko layout engine for displaying web pages. This version fixes many bugs, improves standard compliance, and implements many new web APIs compared to...
was released on June 17, 2008, with Version 3.5
Mozilla Firefox 3.5
Mozilla Firefox 3.5 is a version of the Firefox web browser released in June 2009, adding a variety of new features to Firefox. Version 3.5 was touted as being twice as fast as 3.0...
and Version 3.6
Mozilla Firefox 3.6
Mozilla Firefox 3.6 is a version of the Firefox web browser released in January 2010. The release's main improvement over Firefox 3.5 is improved performance . It uses the Gecko 1.9.2 engine , which improves compliance with web standards...
released on June 30, 2009 and January 21, 2010 respectively. Version 4.0 was released on March 22, 2011, Version 5.0 was released on June 21, 2011, Version 6.0 was released on August 16, 2011, Version 7.0 was released on September 27, 2011 and Version 8.0, the current release, was released on November 8, 2011.
Early versions


Software bloat
Software bloat is a process whereby successive versions of a computer program include an increasing proportion of unnecessary features that are not used by end users, or generally use more system resources than necessary, while offering little or no benefit to its users.-Causes:Software developers...
of the Mozilla Suite
Mozilla Application Suite
The Mozilla Application Suite is a cross-platform integrated Internet suite. Its development was initiated by Netscape Communications Corporation, before their acquisition by AOL. It is based on the source code of Netscape Communicator...
(codenamed, internally referred to, and continued by the community as SeaMonkey
SeaMonkey
SeaMonkey is a free and open source cross-platform Internet suite. It is the continuation of the former Mozilla Application Suite, based on the same source code...
), which integrated features such as IRC
Internet Relay Chat
Internet Relay Chat is a protocol for real-time Internet text messaging or synchronous conferencing. It is mainly designed for group communication in discussion forums, called channels, but also allows one-to-one communication via private message as well as chat and data transfer, including file...
, mail and news, and WYSIWYG
WYSIWYG
WYSIWYG is an acronym for What You See Is What You Get. The term is used in computing to describe a system in which content displayed onscreen during editing appears in a form closely corresponding to its appearance when printed or displayed as a finished product...
HTML
HTML
HyperText Markup Language is the predominant markup language for web pages. HTML elements are the basic building-blocks of webpages....
editing into one software suite.
Firefox retains the cross-platform
Cross-platform
In computing, cross-platform, or multi-platform, is an attribute conferred to computer software or computing methods and concepts that are implemented and inter-operate on multiple computer platforms...
nature of the original Mozilla browser, using the XUL
XUL
In computer programming, XUL , the XML User Interface Language, is an XML user interface markup language developed by the Mozilla project. XUL operates in Mozilla cross-platform applications such as Firefox...
user interface markup language
User interface markup language
A user interface markup language is a markup language that renders and describes graphical user interfaces and controls. Many of these markup languages are dialects of XML and are dependent upon a pre-existing scripting language engine, usually a JavaScript engine, for rendering of controls and...
. The use of XUL makes it possible to extend the browser's capabilities through the use of extensions and theme
Skin (computing)
In computing, a skin is a custom graphical appearance achieved by the use of a graphical user interface that can be applied to specific software and websites to suit the purpose, topic, or tastes of different users....
s. The development and installation processes of these add-ons raised security concerns, and with the release of Firefox 0.9, the Mozilla Foundation opened a Mozilla Update website containing "approved" themes and extensions. The use of XUL sets Firefox apart from other browsers, including other projects based on Mozilla's Gecko
Gecko (layout engine)
Gecko is a free and open source layout engine used in many applications developed by Mozilla Foundation and the Mozilla Corporation , as well as in many other open source software projects....
layout engine
Web browser engine
A web browser engine, , is a software component that takes marked up content and formatting information and displays the formatted content on the screen. It "paints" on the content area of a window, which is displayed on a monitor or a printer...
and most other browsers, which use interfaces native to their respective platforms (Galeon
Galeon
Galeon is a web browser for GNOME based on Mozilla’s Gecko layout engine. Galeon’s self-declared mission was to deliver the web and only the web. Galeon was discontinued in September 2008....
and Epiphany
Epiphany (web browser)
Epiphany is an open source web browser for the GNOME desktop environment. The browser is a descendant of Galeon, and was created after developer disagreements about Galeon's growing complexity...
use GTK+
GTK+
GTK+ is a cross-platform widget toolkit for creating graphical user interfaces. It is licensed under the terms of the GNU LGPL, allowing both free and proprietary software to use it. It is one of the most popular toolkits for the X Window System, along with Qt.The name GTK+ originates from GTK;...
; K-Meleon
K-Meleon
K-Meleon is a web browser for the Microsoft Windows platform. Based on the same Gecko layout engine as Mozilla Firefox, K-Meleon uses native Windows application programming interface to create the user interface, instead of using Mozilla's cross-platform XML User Interface Language layer, and as...
uses MFC
Microsoft Foundation Class Library
The Microsoft Foundation Class Library is a library that wraps portions of the Windows API in C++ classes, including functionality that enables them to use a default application framework...
; and Camino
Camino
Camino is a free, open source, GUI-based Web browser based on Mozilla's Gecko layout engine and specifically designed for the Mac OS X operating system...
uses Cocoa
Cocoa (API)
Cocoa is Apple's native object-oriented application programming interface for the Mac OS X operating system and—along with the Cocoa Touch extension for gesture recognition and animation—for applications for the iOS operating system, used on Apple devices such as the iPhone, the iPod Touch, and...
). Many of these projects were started before Firefox, and probably served as inspiration.
Although the Mozilla Foundation had intended to make the Mozilla Suite obsolete and replace it with Firefox, the Foundation continued to maintain the suite until April 12, 2006 because it had many corporate users and was bundled with other software. The Mozilla community (as opposed to the Foundation) continues to release new versions of the suite, using the product name SeaMonkey
SeaMonkey
SeaMonkey is a free and open source cross-platform Internet suite. It is the continuation of the former Mozilla Application Suite, based on the same source code...
to avoid confusion with the original Mozilla Suite.
On February 5, 2004, business and IT consulting company AMS
American Management Systems
American Management Systems was a high technology and management consulting firm, founded in 1970 by a group of five former Defense Department officials who had worked under Robert McNamara in the Kennedy and Johnson administration...
categorized Mozilla Firefox (then known as Firebird) as a "Tier 1" ("Best of Breed") open source product, considering it technically strong and virtually risk-free.
Naming
The project which became Firefox started as an experimental branch of the Mozilla Suite called m/b (or mozilla/browser). After it had been sufficiently developed, binaries for public testing appeared in September 2002 under the name Phoenix.The Phoenix name was kept until April 14, 2003, when it was changed because of a trademark
Trademark
A trademark, trade mark, or trade-mark is a distinctive sign or indicator used by an individual, business organization, or other legal entity to identify that the products or services to consumers with which the trademark appears originate from a unique source, and to distinguish its products or...
dispute with the BIOS
BIOS
In IBM PC compatible computers, the basic input/output system , also known as the System BIOS or ROM BIOS , is a de facto standard defining a firmware interface....
manufacturer, Phoenix Technologies
Phoenix Technologies
Phoenix Technologies Ltd designs, develops and supports core system software for personal computers and other computing devices. Phoenix's products — commonly referred to as BIOS or firmware — support and enable the compatibility, connectivity, security and management of the various components and...
(which produces a BIOS-based browser called Phoenix FirstWare Connect). The new name, Firebird, met with mixed reactions, particularly as the Firebird database server
Firebird (database server)
Firebird is an open source SQL relational database management system that runs on Linux, Windows, and a variety of Unix. The database forked from Borland's open source edition of InterBase in 2000, but since Firebird 1.5 the code has been largely rewritten ....
already carried the name. In response, the Mozilla Foundation stated that the browser should always bear the name Mozilla Firebird to avoid confusion with the database software. Continuing pressure from the Firebird community forced another change, and on February 9, 2004 the project was renamed Mozilla Firefox (or Firefox for short).
The name "Firefox" (a reference to the red panda
Red Panda
The red panda , is a small arboreal mammal native to the eastern Himalayas and southwestern China. It is the only species of the genus Ailurus. Slightly larger than a domestic cat, it has reddish-brown fur, a long, shaggy tail, and a waddling gait due to its shorter front legs...
) was chosen for its similarity to "Firebird", but also for its uniqueness in the computing industry. To ensure that no further name changes would be necessary, the Mozilla Foundation began the process of registering Firefox as a trademark
Trademark
A trademark, trade mark, or trade-mark is a distinctive sign or indicator used by an individual, business organization, or other legal entity to identify that the products or services to consumers with which the trademark appears originate from a unique source, and to distinguish its products or...
with the United States Patent and Trademark Office
United States Patent and Trademark Office
The United States Patent and Trademark Office is an agency in the United States Department of Commerce that issues patents to inventors and businesses for their inventions, and trademark registration for product and intellectual property identification.The USPTO is based in Alexandria, Virginia,...
in December 2003. This trademark process led to a delay of several months in the release of Firefox 0.8 when the foundation discovered that Firefox had already been registered as a trademark in the UK
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
for Charlton Company software. The situation was resolved when the foundation was given a license to use Charlton's European trademark.
Branding and visual identity

Shortly afterwards, Garrity was invited by the Mozilla Foundation to head up the new visual identity team. The release of Firefox 0.8 in February 2004 saw the introduction of the new branding efforts, including new icon designs by silverorange, a group of web developers with a long-standing relationship with Mozilla, with final renderings by Jon Hicks
Jon Hicks (designer)
Jon Hicks is an English designer who owns his own design studio, Hicksdesign. Hicks is best known for designing the Firefox logo, and has worked on numerous other design projects.-Early life:...
, who had previously worked on Camino
Camino
Camino is a free, open source, GUI-based Web browser based on Mozilla's Gecko layout engine and specifically designed for the Mac OS X operating system...
. The logo was later revised and updated, fixing several flaws found when it was enlarged.
The animal shown in the logo is a stylized fox, although "firefox" is considered to be a common name for the red panda
Red Panda
The red panda , is a small arboreal mammal native to the eastern Himalayas and southwestern China. It is the only species of the genus Ailurus. Slightly larger than a domestic cat, it has reddish-brown fur, a long, shaggy tail, and a waddling gait due to its shorter front legs...
. The panda, according to Hicks, "didn't really conjure up the right imagery" and wasn't widely known. The logo was chosen to make an impression while not shouting out with overdone artwork. It had to stand out in the user's mind, be easy for others to remember, and stand out without causing too much distraction when seen among other icons.
The Firefox icon is a trademark used to designate the official Mozilla build of the Firefox software and builds of official distribution partners. For this reason, Debian
Debian
Debian is a computer operating system composed of software packages released as free and open source software primarily under the GNU General Public License along with other free software licenses. Debian GNU/Linux, which includes the GNU OS tools and Linux kernel, is a popular and influential...
and other software distributors who distribute patched or modified versions of Firefox do not use the icon. The crash reporting service was initially closed source, but switched with version 3 from a program called Talkback to the open source BreakPad & Socorro.
"Delicious delicacies"

HTTP cookie
A cookie, also known as an HTTP cookie, web cookie, or browser cookie, is used for an origin website to send state information to a user's browser and for the browser to return the state information to the origin site...
s thus: "Cookies are delicious delicacies".
The phrase was representative of the programmers' quirky sense of humor and was a reflection of the free software movement
Free software movement
The free software movement is a social and political movement with the goal of ensuring software users' four basic freedoms: the freedom to run their software, to study and change their software, and to redistribute copies with or without changes. The alternative terms "software libre", "open...
's unconventional approach. The phrase became something of a cult legend and was even featured in an O'Reilly
O'Reilly Media
O'Reilly Media is an American media company established by Tim O'Reilly that publishes books and Web sites and produces conferences on computer technology topics...
computer book.
The original text was inserted by Blake Ross, one of the lead developers of Firefox, because, he said, "describing something so complicated in such a small space was quite frankly the last thing I wanted to worry about after rewriting the cookie manager".
However, in reflection of the growing acceptance and use of the Firefox browser in the Internet
Internet
The Internet is a global system of interconnected computer networks that use the standard Internet protocol suite to serve billions of users worldwide...
mainstream, the text was later changed. It was labeled a bug
Software bug
A software bug is the common term used to describe an error, flaw, mistake, failure, or fault in a computer program or system that produces an incorrect or unexpected result, or causes it to behave in unintended ways. Most bugs arise from mistakes and errors made by people in either a program's...
, and was "fixed" by Mike Connor to read, "Cookies are pieces of information stored by web pages on your computer. They are used to remember login information and other data." The revision was regarded as more likely to be helpful to less technically oriented computer users who were now using Firefox—representing Mozilla's desire to appeal to mainstream users.
The text became a popular in-joke
In-joke
An in-joke, also known as an inside joke or in joke, is a joke whose humour is clear only to people who are in a particular social group, occupation, or other community of common understanding...
and on August 2004, the Delicious Delicacies extension, no longer maintained or updated, was released by Jesse Ruderman. The extension restored the old description of cookies, available in several languages.
As of Firefox 2.0, cookies are no longer described in the preferences window.
Version 1.5

Mac OS X v10.1
Mac OS X version 10.1, code named "Puma", is the second major release of Mac OS X, Apple's desktop and server operating system. It superseded Mac OS X v10.0 and preceded Mac OS X v10.2. Version 10.1 was released on 25 September 2001 as a 'free update' to version 10.0...
, in order to improve the quality of Firefox releases on Mac OS X v10.2
Mac OS X v10.2
Mac OS X version 10.2 "Jaguar" is the third major release of Mac OS X, Apple's desktop and server operating system. It superseded Mac OS X v10.1 code name Puma and preceded Mac OS X Panther...
and above. Mac 10.1 users could still use Firefox versions from the 1.0.x branch (e.g. Firefox 1.0.7).

Fork (software development)
In software engineering, a project fork happens when developers take a legal copy of source code from one software package and start independent development on it, creating a distinct piece of software...
from the trunk around the 0.9 release. As such, there was a backlog of bug fixes between 0.9 and the release of 1.0, which were made available in 1.5. Version 1.5 implemented a new Mac-like options interface, the subject of much criticism from Windows and Linux users, with a "Sanitize" action to allow someone to clear their privacy-related information without manually clicking the "Clear All" button. In Firefox 1.5, a user could clear all privacy-related settings simply by exiting the browser or using a keyboard shortcut, depending on their settings. Moreover, the software update system was improved (with binary patches now possible). There were also improvements in the extension management system, with a number of new developer features.
In addition, Firefox 1.5 had preliminary SVG
Scalable Vector Graphics
Scalable Vector Graphics is a family of specifications of an XML-based file format for describing two-dimensional vector graphics, both static and dynamic . The SVG specification is an open standard that has been under development by the World Wide Web Consortium since 1999.SVG images and their...
1.1 support.
Alpha builds of Firefox 1.5 (1.1a1 and 1.1a2) did not carry Firefox branding; they were labeled "Deer Park" (which was Firefox 1.5's internal codename) and contained a different program icon. This was done to dissuade end-users from downloading preview versions, which are intended for developers only.
Firefox 1.5.0.12 was the final version supported on Windows 95
Windows 95
Windows 95 is a consumer-oriented graphical user interface-based operating system. It was released on August 24, 1995 by Microsoft, and was a significant progression from the company's previous Windows products...
.
Version 2

Firefox 2 was released on October 24, 2006 and contained many new features not found in Firefox 1.5, including improved SVG and JavaScript 1.7 support, as well as UI changes.
Mozilla Firefox 2.0.0.x was the final version supported on Windows NT 4.0, 98 and Me. Mozilla Corporation announced it would not develop new versions of Firefox 2 after the 2.0.0.20 release, but continued Firefox 2 development as long as other programs, such as Thunderbird mail client
Mozilla Thunderbird
Mozilla Thunderbird is a free, open source, cross-platform e-mail and news client developed by the Mozilla Foundation. The project strategy is modeled after Mozilla Firefox, a project aimed at creating a web browser...
, depended on it. The final internal release was 2.0.0.22, released in late April 2009.
Firefox Live Chat
In December 2007, Mozilla launched Live Chat, a service allowing users to seek technical support from volunteers. Because Live chat is kept running by volunteers, it is only available when they are online. Support is only available in English officially, but the volunteers may also provide in other languages. Mozilla uses the open source software, Openfire and Spark with the Fastpath plugin, all by Ignite Realtime. Unlike other services by companies such as MicrosoftMicrosoft
Microsoft Corporation is an American public multinational corporation headquartered in Redmond, Washington, USA that develops, manufactures, licenses, and supports a wide range of products and services predominantly related to computing through its various product divisions...
, Mozilla cannot offer remote control
Remote desktop software
In computing, the term remote desktop refers to a software or an OS feature allowing applications, either command line programs or graphical applications, to be run remotely on a server, while being displayed locally. Remote desktop applications have varying features...
, as volunteers are bound to the privacy policy.
Version 3

had been released several months earlier, on 19 November 2007, which was followed by several more beta releases in the Spring of 2008 culminating in the June release.
One of the major changes in Firefox 3 is the implementation of Gecko
Gecko (layout engine)
Gecko is a free and open source layout engine used in many applications developed by Mozilla Foundation and the Mozilla Corporation , as well as in many other open source software projects....
1.9, an updated layout engine
Web browser engine
A web browser engine, , is a software component that takes marked up content and formatting information and displays the formatted content on the screen. It "paints" on the content area of a window, which is displayed on a monitor or a printer...
. The new version fixes many bugs and implements new web APIs.
Version 3.5
After several development releases, the final version was released on June 30, 2009. The current version is 3.5.19, released on April 28, 2011. Also, as of mid-December 2009, Firefox 3.5 was the most popular browser (when counting individual browser versions), passing Internet Explorer 7Internet Explorer 7
Windows Internet Explorer 7 is a web browser released by Microsoft in October 2006. Internet Explorer 7 is part of a long line of versions of Internet Explorer and was the first major update to the browser in more than 5 years...
. It was the first version to accomplish this feat.
Version 3.6
Version 3.6, released on January 21, 2010, uses the Gecko 1.9.2 engine and includes several interface improvements, such as "personas". This release was referred to as 3.2 before 3.1 was changed to 3.5. The codename for this version was Namoroka.One minor update to Firefox 3.6, version 3.6.4 (code-named Lorentz
Lorentz National Park
Lorentz National Park is located in the Indonesian province of Papua, formerly known as Irian Jaya . With an area of 25,056 km² , it is the largest national park in South-East Asia...
) is the first minor update to make non-intrusive changes other than minor stability and security fixes. It adds Out of Process Plugins (OOPP), which runs plugins in a separate process, allowing Firefox to recover from plugin crashes.
Firefox 3.6.6 lengthens the amount of time a plug-in is allowed to be unresponsive before the plug-in quits.
Version 4.0
Nightly builds were marked as 4.0a1pre between February and June 2008, but were renamed to 3.1a1pre afterward.Firefox 3.7 (Gecko 1.9.3) Alpha 1 was released on February 10, 2010.
Alpha 2 was released on March 1, 2010, Alpha 3 on March 17, Alpha 4 on April 12, and Alpha 5 on June 16. The version number was changed to 4.0 (and Gecko's was changed to 2.0) starting with Beta 1, released on July 6, 2010. Beta 2 was released on July 27, Beta 3 on August 11, Beta 4 on August 24, Beta 5 on September 7, Beta 6 (a chemspill release) on September 14. After major delays, Beta 7 was finally released on November 10. Beta 7 was followed by Beta 8, released on December 21. Beta 9 was released on January 14, 2011, Beta 10 on January 25, Beta 11 on February 8, and Beta 12 on February 12. Firefox then moved into the RC stage. The Final Version of Firefox 4 was released on March 22, 2011.
One of the main focuses was to improve the user interface. UI overhaul mockups for the Windows version posted in the Mozilla Wiki showed numerous changes, including optional tab bar display at the top of the window, status bar
Status bar
A status bar, similar to a status line, is an information area typically found at the bottom of windows in a graphical user interface.A status bar is sometimes divided into sections, each of which shows different information. Its job is primarily to display information about the current state of...
integration with the tab toolbar, as well as search bar and the reload/stop button integration with the awesomebar. A new type of tab, called an application tab, was placed in the tab bar. Similar to the Mozilla Prism
Mozilla Prism
Mozilla Prism is a product which integrates web applications with the desktop, allowing web applications to be launched from the desktop and configured independently of the default web browser. As of November 2010, Prism is listed as an inactive project at the Mozilla labs website.Prism is based...
project, it allows web pages (such as Google Mail
Gmail
Gmail is a free, advertising-supported email service provided by Google. Users may access Gmail as secure webmail, as well via POP3 or IMAP protocols. Gmail was launched as an invitation-only beta release on April 1, 2004 and it became available to the general public on February 7, 2007, though...
) to become applications. The browser was given a home tab similar to new tab pages found in Internet Explorer 8
Internet Explorer 8
Windows Internet Explorer 8 is a web browser developed by Microsoft in the Internet Explorer browser series. The browser was released on March 19, 2009 for Windows XP, Windows Server 2003, Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008, and Windows 7. Both 32-bit and 64-bit builds are available...
and Google Chrome
Google Chrome
Google Chrome is a web browser developed by Google that uses the WebKit layout engine. It was first released as a beta version for Microsoft Windows on September 2, 2008, and the public stable release was on December 11, 2008. The name is derived from the graphical user interface frame, or...
, although users were allowed to customize the button to take them to their homepage instead. The menu bar
Menu bar
A menu bar is a region of a screen or application interface where drop down menus are displayed. The menu bar's purpose is to supply a common housing for window- or application-specific menus which provide access to such functions as opening files, interacting with an application, or displaying...
disappeared from the mockups, and the UI used animations to manipulate tags and buttons.
The Mac OS X installer was redesigned to make installations easier. Firefox start-up windows were eliminated to make start-up quicker. Preference and add-on manager windows were redesigned to better assist users.
"Door hanger" notifications were to be added to replace "bar" notifications, which were easily spoofed by web pages.
The Gecko layout engine was improved to support more HTML5 and CSS3 features.
In addition, the Firefox Sync project was integrated into the browser to allow users to sync elements such as bookmarks, tabs, and history with either Mozilla or other third-party servers.
Rapid release development cycle
From early 2011, Mozilla initiated a rapid release development cycle, with versions planned to move through Mozilla's NIGHTLY, AURORA and BETA development channels after spending 6 weeks in each.Version 5.0
Firefox 5 was released on June 21, 2011. This was the first edition under Mozilla's rapid release development cycle, and was released only three months after Firefox 4.Even though the GUI
Graphical user interface
In computing, a graphical user interface is a type of user interface that allows users to interact with electronic devices with images rather than text commands. GUIs can be used in computers, hand-held devices such as MP3 players, portable media players or gaming devices, household appliances and...
was changed very little, Firefox 5 features:
- Better standardsWeb standardsWeb standards is a general term for the formal standards and other technical specifications that define and describe aspects of the World Wide Web. In recent years, the term has been more frequently associated with the trend of endorsing a set of standardized best practices for building web sites,...
support for HTML5, CSS3, MathMLMathMLMathematical Markup Language is an application of XML for describing mathematical notations and capturing both its structure and content. It aims at integrating mathematical formulae into World Wide Web pages and other documents...
, XHRXMLHttpRequestXMLHttpRequest is an API available in web browser scripting languages such as JavaScript. It is used to send HTTP or HTTPS requests directly to a web server and load the server response data directly back into the script. The data might be received from the server as XML text or as plain text...
and SMILSynchronized Multimedia Integration LanguageSMIL , the Synchronized Multimedia Integration Language, is a W3C recommended XML markup language for describing multimedia presentations. It defines markup for timing, layout, animations, visual transitions, and media embedding, among other things... - Better visibility for the Do not track headerDo not track headerThe do not track header is a proposed HTTP header field that would request a web application to disable their tracking of a user. The "Do Not Track" standard was created by researchers at Stanford University and is under discussion in the United States Congress and the Federal Trade Commission...
preference - Stability and securitySecuritySecurity is the degree of protection against danger, damage, loss, and crime. Security as a form of protection are structures and processes that provide or improve security as a condition. The Institute for Security and Open Methodologies in the OSSTMM 3 defines security as "a form of protection...
improvements - Better tuned HTTPHypertext Transfer ProtocolThe Hypertext Transfer Protocol is a networking protocol for distributed, collaborative, hypermedia information systems. HTTP is the foundation of data communication for the World Wide Web....
idle connection logic - Improved canvas, JavaScriptJavaScriptJavaScript is a prototype-based scripting language that is dynamic, weakly typed and has first-class functions. It is a multi-paradigm language, supporting object-oriented, imperative, and functional programming styles....
, memoryComputer memoryIn computing, memory refers to the physical devices used to store programs or data on a temporary or permanent basis for use in a computer or other digital electronic device. The term primary memory is used for the information in physical systems which are fast In computing, memory refers to the...
, and networkingComputer networkA computer network, often simply referred to as a network, is a collection of hardware components and computers interconnected by communication channels that allow sharing of resources and information....
performance - Improved spell checkingSpell checkerIn computing, a spell checker is an application program that flags words in a document that may not be spelled correctly. Spell checkers may be stand-alone capable of operating on a block of text, or as part of a larger application, such as a word processor, email client, electronic dictionary,...
for some localeLocaleIn computing, locale is a set of parameters that defines the user's language, country and any special variant preferences that the user wants to see in their user interface...
s - Improved desktop environment integration for Linux users
- Better WebGLWebGLWebGL is a software library that extends the capability of the JavaScript programming language to allow it to generate interactive 3D graphics within any compatible web browser...
security (WebGL content can no longer load cross-domain textures) - Background tabs have setTimeout and setInterval clamped to 1000 msMillisecondA millisecond is a thousandth of a second.10 milliseconds are called a centisecond....
to improve performance
Immediately following the launch of Firefox 5, several software critics reviewed it. Matt Egan of PC Advisor said that there was not much new to see, and that users would have to double-check they were not still using Firefox 4, although did concede that improvements in speed and stability made an upgrade worthwhile. Gary Marshall of TechRadar.com commented that there appeared to be a version number race between different browsers and implies in his review that the changes do not merit a full version number. However, he does praise the addition of the Do Not Track button to the user interface and describes how this helps users.
Seth Rosenblatt of CNET agrees with the other two reviewers on the minor nature of the changes and praises the speed and usability improvements.
Version 6.0
Firefox 6 was released on August 16, 2011. New features in Firefox 6.0 include:- about:permissions, a permissions manager. The user can choose what information can be shared with other sites, e.g. passwords.
- The address bar now highlights the domain of the website you are visiting.
- Streamlined the look of the site identity block
- Added support for the latest draft version of WebSockets with a prefixed API
- Added support for EventSource / server-sent events
- Added support for
window.matchMedia - Added Scratchpad, an interactive JavaScript prototyping environment
- Added a new Web Developer menu item and moved development-related items into it
- Improved usability of the Web Console
- Improved the discoverability of Firefox Sync
- Reduced browser startup time when using Panorama
- Fixed several stability issues
- Fixed several security issues
Version 7.0
Firefox 7.0 was released on September 27, 2011. New features in Firefox 7.0 include:- Drastically improved memory handling for certain use cases
- Added a new rendering backend to speed up Canvas operations on Windows systems
- Bookmark and password changes now sync almost instantly when using Firefox Sync
- The
'http://' URL prefix is now hidden by default. - Added support for text-overflow: ellipsis
- Added support for the Web Timing specification
- Enhanced support for MathML
- The WebSocket protocol has been updated from version 7 to version 8.
- Added an opt-in system for users to send performance data back to Mozilla to improve future versions of Firefox
- Fixed several stability issues
- Fixed several security issues
Firefox 7.0.1 was released on September 29, 2011, providing a bug-fix for a problem with add-ons that were hidden after updating.
Version 8.0
- Add-ons installed by third-party programs are now disabled by default
- Added a one-time add-on selection dialog to manage previously installed add-ons
- Added TwitterTwitterTwitter is an online social networking and microblogging service that enables its users to send and read text-based posts of up to 140 characters, informally known as "tweets".Twitter was created in March 2006 by Jack Dorsey and launched that July...
to the search bar - Added a preference to load tabs on demand, improving start-up time when windows are restored
- Improved performance and memory handling when using
- Added Cross-Origin Resource SharingCross-Origin Resource SharingCross-Origin Resource Sharing is a web browser technology specification, which defines ways for a web server to allow its resources be accessed by a web page from a different domain...
(CORS) support for cross-domain textures in WebGL - Added support for HTML5 context menus
- Added support for
insertAdjacentHTML - Improved CSS hyphen support for many languages
- Improved WebSocket support
- Fixed several stability issues
Originally an improved tab animation for moving, reordering and detaching tabs was planned, but the new code was backed out with Beta 5 due to issues with the implementation.
Future releases
The precursory releases of upcoming Firefox releases are named Nightly, as this is the name of the trunkTrunk (software)
In the field of software development, trunk refers to the unnamed branch of a file tree under revision control. The trunk is usually meant to be the base of a project on which development progresses. If developers are working exclusively on the trunk, it always contains the latest cutting-edge...
builds, and Aurora, a separate nightly branch for refining code. The next scheduled date for a version shift in these channels is December 20, 2011.
Expected release dates
| Version | Channel | Date |
|---|---|---|
| Firefox 9 | Beta | December 20, 2011 |
| Firefox 10 | Aurora | January 31, 2012 |
| Firefox 11 | Nightly | March 13, 2012 |
Version 9.0
The log of changes in version 9 was first published in 11 November 2011 with the first public Beta release.- Added type inferenceType inferenceType inference refers to the automatic deduction of the type of an expression in a programming language. If some, but not all, type annotations are already present it is referred to as type reconstruction....
, significantly improving JavaScript performance. - Improved theme integration for Mac OS X Lion.
- Added two finger swipe navigation for Mac OS X Lion.
- Added support for querying Do Not TrackDo not track headerThe do not track header is a proposed HTTP header field that would request a web application to disable their tracking of a user. The "Do Not Track" standard was created by researchers at Stanford University and is under discussion in the United States Congress and the Federal Trade Commission...
status via JavaScript. - Added support for the
font-stretchCSS property. - Improved support for the
text-overflowCSS property. - Improved standards support for HTML5, MathML, and CSS.
- Fixed several stability issues.
Color chart
| Colour | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Red | Former release; no longer supported |
| Pink | Former test release |
| Yellow | Former release; still supported |
| Green | Current supported release |
| Blue | Future release |
| Gold | Current test release |
| Purple | Future test release |
Current Supported Releases
- Firefox 3.6.24
- Firefox 8.0.1
Current Test Releases
- Firefox 9.0 Beta 3
- Firefox 10.0 Aurora
- Firefox 11.0 Nightly
Future Releases
- Firefox 3.6.25
- Firefox 9.0
- Firefox 10.0
- Firefox 11.0
- Firefox 12.0
Future Test Releases
- Firefox 10.0 Beta
- Firefox 11.0 Aurora
- Firefox 11.0 Beta
- Firefox 12.0 Nightly
- Firefox 12.0 Aurora
- Firefox 12.0 Beta
| Release History | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Browser name | Gecko version | Version | Codename | Release date | Significant changes |
| Phoenix | 1.2 | 0.1 | Pescadero Pescadero, California Pescadero is a census-designated place in San Mateo County, California two miles east of State Route 1 and Pescadero State Beach. The center of town, on Pescadero Creek Road, is located at latitude 37.255 and longitude 122.38028. The town is south of Half Moon Bay. The ZIP Code is 94060 and... |
September 23, 2002 | First release. Customizable toolbar, quicksearch. |
| 0.2 | Santa Cruz Santa Cruz, California Santa Cruz is the county seat and largest city of Santa Cruz County, California in the US. As of the 2010 U.S. Census, Santa Cruz had a total population of 59,946... |
October 1, 2002 | Sidebar, extension management. | ||
| 0.3 | Lucia Lucia, California Lucia is an unincorporated community in Monterey County, California. It is located east of Lopez Point, at an elevation of 354 feet . Lucia is one of the three small settlements of restaurants, and motels located along State Route 1 on the Big Sur coast... |
October 14, 2002 | Image blocking, pop-up blocking whitelist, tabbed browsing. | ||
| 1.3 | 0.4 | Oceano Oceano, California Oceano is a census-designated place in San Luis Obispo County, California, United States. The population was 7,286 at the 2010 census, up from 7,260 at the 2000 census.-Geography:Oceano is located at .... |
October 19, 2002 | Themes, pop-up blocking improvements, toolbar customization. | |
| 0.5 | Naples Naples, Long Beach, California Naples is a neighborhood of Long Beach, California, United States, built on a series of islands located in Alamitos Bay. Naples consists of three separate islands, divided by canals which open into the bay. Most of the streets on the island have Italianate names... |
December 7, 2002 | Multiple homepages, sidebar and accessibility improvements. | ||
| Firebird | 1.5 | 0.6 | Glendale Glendale, California Glendale is a city in Los Angeles County, California, United States. As of the 2010 Census, the city population is 191,719, down from 194,973 at the 2000 census. making it the third largest city in Los Angeles County and the 22nd largest city in the state of California... |
May 17, 2003 | New default theme (Qute), bookmark and privacy improvements, smooth scrolling, automatic image resizing. |
| 0.6.1 | July 28, 2003 | Bugfix release. | |||
| 0.7 | Indio Indio, California Indio is a city in Riverside County, California, United States, located in the Coachella Valley of Southern California's Colorado Desert region. It lies east of Palm Springs, east of Riverside, and east of Los Angeles. It is about north of Mexicali, Baja California on the U.S.-Mexican border... |
October 15, 2003 | Automatic scrolling, password manager, preferences panel improvements. | ||
| 0.7.1 | Three Kings Three Kings, New Zealand Three Kings refers to both a suburb of Auckland, New Zealand, and the three-peaked volcano that it is named after. Three Kings should not be confused with the Three Kings Islands, located off the northern tip of New Zealand's North Island.- Suburb :... |
October 26, 2003 | Bugfix release (Mac OS X only). | ||
| Firefox Mozilla Firefox Mozilla Firefox is a free and open source web browser descended from the Mozilla Application Suite and managed by Mozilla Corporation. , Firefox is the second most widely used browser, with approximately 25% of worldwide usage share of web browsers... |
1.6 | 0.8 | Royal Oak Royal Oak, New Zealand - to the north-east - to the east - to the south-east - to the south - to the south-west - to the west - to the north-west Epsom One Tree Hill Oranga Onehunga... |
February 9, 2004 | Windows installer, offline working, bookmarks and download manager improvements, rebranded with new logo. |
| 1.7 | 0.9 | One Tree Hill One Tree Hill, New Zealand One Tree Hill is a 182 metre volcanic peak located in Auckland, New Zealand. It is an important memorial place for both Māori and other New Zealanders... |
June 15, 2004 | New default theme (Winstripe), comprehensive data migration, new extension/theme manager, reduced download size, new help system, Linux installer, mail icon (Windows only). | |
| 0.9.1 | June 28, 2004 | Bugfix release, updated default theme. | |||
| 0.9.2 | July 8, 2004 | Vulnerability patch (Windows only). | |||
| 0.9.3 | August 4, 2004 | Vulnerability patch. | |||
| 0.10 | Firefox 1.0 Preview Release "Greenlane Greenlane Greenlane is a suburb of Auckland, New Zealand.The Greenlane shops are the main shopping centre for the suburb of Epsom and are situated at the intersection of Manukau Road and Green Lane West... " |
September 14, 2004 | Bugs with higher complexity/risk, localization impact, RSS RSS -Mathematics:* Root-sum-square, the square root of the sum of the squares of the elements of a data set* Residual sum of squares in statistics-Technology:* RSS , "Really Simple Syndication" or "Rich Site Summary", a family of web feed formats... /Atom Atom (standard) The name Atom applies to a pair of related standards. The Atom Syndication Format is an XML language used for web feeds, while the Atom Publishing Protocol is a simple HTTP-based protocol for creating and updating web resources.Web feeds allow software programs to check for updates published on a... feed support, find toolbar, plugin finder. |
||
| 0.10.1 | October 1, 2004 | Vulnerability patch. | |||
| Firefox 1 Mozilla Firefox Mozilla Firefox is a free and open source web browser descended from the Mozilla Application Suite and managed by Mozilla Corporation. , Firefox is the second most widely used browser, with approximately 25% of worldwide usage share of web browsers... |
1.0 RC1 | Firefox 1.0 Release Candidate 1 "Mission Bay Mission Bay, New Zealand Mission Bay is a suburb of Auckland city, in the North Island of New Zealand. It is located seven kilometres to the east of the city centre, on the southern shore of the Waitemata Harbour. At the census of 2001, Mission Bay was reported to have a population of 5235.The Mission Bay district has been... " |
October 27, 2004 | First Firefox release candidate. | |
| 1.0 RC2 | Firefox 1.0 Release Candidate 2 "Whangamata Whangamata The town of Whangamata is sited on the southeast coast of the Coromandel Peninsula in the North Island of New Zealand. It is located 30 kilometres north of Waihi, to the north of the western extremity of the Bay of Plenty.... " |
November 3, 2004 | Second Firefox release candidate. | ||
| 1.0 | Firefox 1.0 "Phoenix Phoenix, Arizona Phoenix is the capital, and largest city, of the U.S. state of Arizona, as well as the sixth most populated city in the United States. Phoenix is home to 1,445,632 people according to the official 2010 U.S. Census Bureau data... " |
November 9, 2004 | Official version 1.0 release. Official localized builds. | ||
| 1.0.1 | Rose & Crown | February 24, 2005 | Regular security and stability update. | ||
| 1.0.2 | March 23, 2005 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 1.0.3 | April 15, 2005 | Regular security and stability update. Installer improvements. | |||
| 1.0.4 | May 11, 2005 | Regular security and stability update. Fix to DHTML errors encountered at some web sites. | |||
| 1.0.5 | July 12, 2005 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 1.0.6 | July 19, 2005 | Off-cycle stability update. Restored API compatibility for extensions and web applications that did not work in Firefox 1.0.5. | |||
| 1.0.7 | September 20, 2005 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 1.0.8 | April 13, 2006 | Regular security and stability update. End-of-life 1.0.x product line | |||
| Firefox 1.5 | 1.8 | 1.1a1 | Deer Park Alpha 1 "Strippenkaart National Tariff System The national tariff system is a ticketing and zoning scheme for local public transport in the Netherlands. It was designed as a nationwide scheme but is being phased out and replaced by the OV-chipkaart... " |
May 31, 2005 | First Firefox 1.1 alpha release. Support for SVG Scalable Vector Graphics Scalable Vector Graphics is a family of specifications of an XML-based file format for describing two-dimensional vector graphics, both static and dynamic . The SVG specification is an open standard that has been under development by the World Wide Web Consortium since 1999.SVG images and their... and canvas. "Sanitize" privacy feature. Improvements in JavaScript 1.5 and CSS 2/3. Broken website reporter tool. |
| 1.1a2 | Deer Park Alpha 2 | July 12, 2005 | Second Firefox 1.1 alpha release. Blazing fast backwards and forwards (FastBack), drag-and-drop Drag-and-drop In computer graphical user interfaces, drag-and-drop is the action of selecting a virtual object by "grabbing" it and dragging it to a different location or onto another virtual object... tab reordering, improved pop-up blocking, error pages instead of error dialogs. |
||
| 1.5b1 | Firefox 1.5 Beta 1 | September 9, 2005 | First Firefox 1.5 beta release. New update system (binary patch). Prettier error pages, more Luna-like Winstripe theme (did not blend well with the Classic theme). | ||
| 1.5b2 | Firefox 1.5 Beta 2 | October 6, 2005 | Second Firefox 1.5 beta release. Improvements to automated update system, website rendering and performance. Several security fixes. | ||
| 1.5 RC1 | Firefox 1.5 Release Candidate 1 |
November 1, 2005 | First Firefox 1.5 release candidate. | ||
| 1.5 RC2 | Firefox 1.5 Release Candidate 2 |
November 10, 2005 | Second Firefox 1.5 release candidate. | ||
| 1.5 RC3 | Firefox 1.5 Release Candidate 3 |
November 17, 2005 | Third Firefox 1.5 release candidate. | ||
| 1.5 | Firefox 1.5 "Deer Park" |
November 29, 2005 | Official version 1.5 release. Official localized builds. Identical to 1.5 RC3. | ||
| 1.5.0.1 | February 1, 2006 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 1.5.0.2 | April 13, 2006 | Regular security and stability update. Native support for Intel-based Macintosh computers by shipping universal binary Universal binary A universal binary is, in Apple parlance, an executable file or application bundle that runs natively on either PowerPC or Intel-manufactured IA-32 or Intel 64-based Macintosh computers; it is an implementation of the concept more generally known as a fat binary.With the release of Mac OS X Snow... . |
|||
| 1.5.0.3 | May 2, 2006 | Off-cycle security update. Fix for a publicly disclosed denial of service weakness. | |||
| 1.5.0.4 | June 1, 2006 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 1.5.0.5 | July 26, 2006 | Regular security and stability update. Added changes for Frisian locale (fy-NL). | |||
| 1.5.0.6 | August 2, 2006 | Off-cycle security and stability update. Fixed an issue with playing Windows Media content introduced by previous update. | |||
| 1.5.0.7 | September 14, 2006 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 1.5.0.8 | November 7, 2006 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 1.5.0.9 | December 19, 2006 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 1.5.0.10 | February 23, 2007 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 1.5.0.11 | March 20, 2007 | Regular security and stability update. Regression fixes. | |||
| 1.5.0.12 | May 30, 2007 | Regular security and stability update. End-of-life 1.5.0.x product line | |||
| Firefox 2 | 1.8.1 | 2.0a1 | Bon Echo Alpha 1 | March 22, 2006 | First Firefox 2.0 alpha release. |
| 2.0a2 | Bon Echo Alpha 2 | May 12, 2006 | Second Firefox 2.0 alpha release. Links default to open in new tab. Close button on every tab. Inline spell checking Spell checker In computing, a spell checker is an application program that flags words in a document that may not be spelled correctly. Spell checkers may be stand-alone capable of operating on a block of text, or as part of a larger application, such as a word processor, email client, electronic dictionary,... for text boxes. Session restoration after browser crash. Search suggestion for Google and Yahoo!. New search plugin manager and add-on manager. Web feed previewing. Bookmark microsummaries. Updates to extension system. Support for Sherlock Sherlock (software) Sherlock, named after Sherlock Holmes, was a file and web search tool created by Apple Inc. for the Mac OS, introduced with Mac OS 8.5 as an extension of the Mac OS Finder's file searching capabilities. Like its predecessor, it can search for local files and file contents, which it does using the... and OpenSearch OpenSearch OpenSearch is a collection of technologies that allow publishing of search results in a format suitable for syndication and aggregation. It is a way for websites and search engines to publish search results in a standard and accessible format.... . Support for SVG text using svg:textPath. |
||
| 2.0a3 | Bon Echo Alpha 3 | May 26, 2006 | Third Firefox 2.0 alpha release. Anti-phishing Phishing Phishing is a way of attempting to acquire information such as usernames, passwords, and credit card details by masquerading as a trustworthy entity in an electronic communication. Communications purporting to be from popular social web sites, auction sites, online payment processors or IT... protection. Search suggestions appear with search history in the search box for Google and Yahoo!. Support for client-side session and persistent storage. |
||
| 2.0b1 | Firefox 2.0 Beta 1 | July 12, 2006 | First Firefox 2.0 beta release. Improved feed support. New NSIS Nullsoft Scriptable Install System Nullsoft Scriptable Install System is a script-driven Windows installation system with minimal overhead backed by Nullsoft, the creators of Winamp... -based installer. JavaScript 1.7. Enhanced security and localization support for extensions. |
||
| 2.0b2 | Firefox 2.0 Beta 2 | August 31, 2006 | Second Firefox 2.0 beta release. New Winstripe theme refresh: new navigation icons, URL bar refresh (new Go button attached to the URL bar), Search bar refresh, Tab bar refresh, Alltabs button (used to view a popup list of all tabs open). | ||
| 2.0 RC1 | Firefox 2.0 Release Candidate 1 |
September 26, 2006 | First Firefox 2.0 release candidate. | ||
| 2.0 RC2 | Firefox 2.0 Release Candidate 2 |
October 6, 2006 | Second Firefox 2.0 release candidate. | ||
| 2.0 RC3 | Firefox 2.0 Release Candidate 3 |
October 16, 2006 | Third Firefox 2.0 release candidate. | ||
| 2.0 | Firefox 2.0 "Bon Echo Bon Echo Provincial Park Bon Echo Provincial Park is a provincial park in South Central Ontario north of Kaladar, Ontario, approximately 6 km north of Cloyne.Bon Echo features several lakes, including part of Mazinaw Lake, the second-deepest lake in Ontario... " |
October 24, 2006 | Official version 2.0 release, identical to 2.0 RC3. Official localized builds. | ||
| 2.0.0.1 | December 19, 2006 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 2.0.0.2 | February 23, 2007 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 2.0.0.3 | March 20, 2007 | Regular security and stability update. Regression fixes and security fixes. | |||
| 2.0.0.4 | May 30, 2007 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 2.0.0.5 | July 17, 2007 | Security and stability update. | |||
| 2.0.0.6 | July 30, 2007 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 2.0.0.7 | September 18, 2007 | Off-cycle security update. | |||
| 2.0.0.8 | October 18, 2007 | Regular security and stability update. Mac OS X 10.5 support. | |||
| 2.0.0.9 | November 1, 2007 | Off-cycle security and stability update. | |||
| 2.0.0.10 | November 26, 2007 | Off-cycle security and stability update. | |||
| 2.0.0.11 | November 30, 2007 | Off-cycle stability update. | |||
| 2.0.0.12 | February 7, 2008 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 2.0.0.13 | March 25, 2008 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 2.0.0.14 | April 16, 2008 | Off-cycle stability update. | |||
| 2.0.0.15 | July 1, 2008 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 2.0.0.16 | July 15, 2008 | Off-cycle security update. | |||
| 2.0.0.17 | September 23, 2008 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 2.0.0.18 | November 12, 2008 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 2.0.0.19 | December 16, 2008 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 2.0.0.20 | December 18, 2008 | Off-cycle security update. End-of-life 2.0.0.x product line | |||
| Firefox 3 | 1.9 | 3.0a1 | Gran Paradiso Alpha 1 | December 8, 2006 | First Firefox 3.0 alpha release. Cairo Cairo (graphics) cairo is a software library used to provide a vector graphics-based, device-independent API for software developers. It is designed to provide primitives for 2-dimensional drawing across a number of different backends... graphics library. Cocoa Cocoa (API) Cocoa is Apple's native object-oriented application programming interface for the Mac OS X operating system and—along with the Cocoa Touch extension for gesture recognition and animation—for applications for the iOS operating system, used on Apple devices such as the iPhone, the iPod Touch, and... Widgets in OS X builds. Updated threading model. Changes to how DOM events DOM Events DOM events allow event-driven programming languages like JavaScript, JScript, ECMAScript, VBScript and Java to register various event handlers/listeners on the element nodes inside a DOM tree, e.g. HTML, XHTML, XUL and SVG documents.... are dispatched, how HTML object elements are loaded, and how web pages are painted. New SVG elements and filters, and improved SVG specification compliance. Windows 95 Windows 95 Windows 95 is a consumer-oriented graphical user interface-based operating system. It was released on August 24, 1995 by Microsoft, and was a significant progression from the company's previous Windows products... , 98 Windows 98 Windows 98 is a graphical operating system by Microsoft. It is the second major release in the Windows 9x line of operating systems. It was released to manufacturing on 15 May 1998 and to retail on 25 June 1998. Windows 98 is the successor to Windows 95. Like its predecessor, it is a hybrid... , ME Windows Me Windows Millennium Edition, or Windows Me , is a graphical operating system released on September 14, 2000 by Microsoft, and was the last operating system released in the Windows 9x series. Support for Windows Me ended on July 11, 2006.... and Mac OS X v10.2 Mac OS X v10.2 Mac OS X version 10.2 "Jaguar" is the third major release of Mac OS X, Apple's desktop and server operating system. It superseded Mac OS X v10.1 code name Puma and preceded Mac OS X Panther... no longer supported. Moving DOM nodes between documents require a call to importNode or adoptNode as per the DOM specification. |
| 3.0a2 | Gran Paradiso Alpha 2 | February 7, 2007 | Second Firefox 3.0 alpha release. Reflow refactoring (leading to Acid2 Acid2 Acid2 is a test page published and promoted by the Web Standards Project to expose web page rendering flaws in web browsers and other applications that render HTML. Named after the acid test for gold, it was developed in the spirit of Acid1, a relatively narrow test of compliance with the Cascading... test compliance) among numerous layout bug fixes. Web Apps 1.0 API for changing stylesheets support. Inline-block and inline-table values of CSS 2.1's display property implemented. XML documents can be rendered during download. Greatly improved Mac widgets support since Alpha 1. Improvements in Cairo graphics layer. Non-standard JavaScript "Script" object no longer supported. |
||
| 3.0a3 | Gran Paradiso Alpha 3 | March 23, 2007 | Third Firefox 3.0 alpha release. Support for allowing web pages to store resources in the browser's offline cache. Support for Animated PNG APNG The Animated Portable Network Graphics file format is an unofficial extension to the Portable Network Graphics specification. It allows for animated PNG files that work similarly to animated GIF files, while supporting 24-bit images and 8-bit transparency not available for GIFs... images. Support for the "HTTPOnly" cookie extension which provides enhanced cookie privacy (also backported Backporting Backporting is the action of taking a certain software modification and applying it to an older version of the software than it was initially created for. It is part of the maintenance step in a software development process.... to Firefox 2.0.0.5). Improvements to layout and scaling precision across numerous screen and printer resolutions. |
||
| 3.0a4 | Gran Paradiso Alpha 4 | April 27, 2007 | Fourth Firefox 3.0 alpha release. Adding of FUEL JavaScript library for extension developers. Rewrite of Page Info dialog. Upgrade to Cairo 1.4.2. More Cocoa regression fixes. | ||
| 3.0a5 | Gran Paradiso Alpha 5 | June 6, 2007 | Fifth Firefox 3.0 alpha release. Places (bookmark and history service based on SQLite SQLite SQLite is an ACID-compliant embedded relational database management system contained in a relatively small C programming library. The source code for SQLite is in the public domain and implements most of the SQL standard... ) used by default, but no front-end changes. Breakpad used as crash reporter on Windows and Mac OS X, superseding closed-source Talkback. Password manager rewrite. Support for Growl and native widgets within forms for Mac OS X. |
||
| 3.0a6 | Gran Paradiso Alpha 6 | July 2, 2007 | Sixth Firefox 3.0 alpha release. Upgrade of SQLite to version 3.3.17, leading to increased cookie HTTP cookie A cookie, also known as an HTTP cookie, web cookie, or browser cookie, is used for an origin website to send state information to a user's browser and for the browser to return the state information to the origin site... performance due to transition of cookie service to SQLite. Site-specific preference service, used initially for text zoom, allowing zoom setting to remain on each website. Support for native widgets within forms for Linux. New Quit dialog handles multiple windows more elegantly and allows users to save session. Autoscroll rewrite: numerous bug fixes and significant performance gain. Fixes to the use of units within the download manager. Various Places bug fixes. |
||
| 3.0a7 | Gran Paradiso Alpha 7 | August 3, 2007 | Seventh Firefox 3.0 alpha release. More APIs implemented from WHATWG Web Hypertext Application Technology Working Group The Web Hypertext Application Technology Working Group is a community of people interested in evolving HTML and related technologies. The WHATWG was founded by individuals from Apple, the Mozilla Foundation and Opera Software in 2004. Since then, the editor of the WHATWG specifications, Ian... specs, such as ability to read files from file selection fields without need to upload and cut/copy/paste events, and cross-site XMLHttpRequest XMLHttpRequest XMLHttpRequest is an API available in web browser scripting languages such as JavaScript. It is used to send HTTP or HTTPS requests directly to a web server and load the server response data directly back into the script. The data might be received from the server as XML text or as plain text... . New protocol-handling dialog. Experimental full-page zoom support, but no UI to control it. Numerous Mac OS X bug fixes, but OS X 10.3 no longer supported for Gecko 1.9. General bug fixes. |
||
| 3.0a8 | Gran Paradiso Alpha 8 | September 20, 2007 | Eighth Firefox 3.0 alpha release. New, basic UI for tagging bookmarks. Remember password prompt changed to non-modal information bar. Malware blacklist support. New UI for FTP and File protocol listings. Applications pane added to preferences. Basic support for web-based protocol handlers. | ||
| 3.0b1 | Firefox 3.0 Beta 1 | November 19, 2007 | First Firefox 3.0 beta release. | ||
| 3.0b2 | Firefox 3.0 Beta 2 | December 18, 2007 | Second Firefox 3.0 beta release. New UI improvements, including redesigned location bar, Places Organizer, Smart Bookmarks. Various stability and performance improvements. | ||
| 3.0b3 | Firefox 3.0 Beta 3 | February 12, 2008 | Third Firefox 3.0 beta release. New UI improvements, including redesigned buttons and location bar. Different default native themes for each operating system. Upgraded to SQLite 3.5.4. Various stability and performance improvements. | ||
| 3.0b4 | Firefox 3.0 Beta 4 | March 10, 2008 | Fourth Firefox 3.0 beta release. New UI improvement, including improved default themes for different operating systems. Various improvements in speed and resource usage. | ||
| 3.0b5 | Firefox 3.0 Beta 5 | April 2, 2008 | Fifth Firefox 3.0 beta release. Further improved themes to match various operating systems, JavaScript engine optimizations for speed, improved Places organizer. | ||
| 3.0 RC1 | Firefox 3.0 Release Candidate 1 |
May 16, 2008 | First Firefox 3.0 release candidate. | ||
| 3.0 RC2 | Firefox 3.0 Release Candidate 2 |
June 5, 2008 | Second Firefox 3.0 release candidate. | ||
| 3.0 RC3 | Firefox 3.0 Release Candidate 3 |
June 11, 2008 | Third Firefox 3.0 release candidate. | ||
| 3.0 | Firefox 3.0 "Gran Paradiso Gran Paradiso National Park Gran Paradiso National Park is an Italian national park in the Graian Alps, between the Aosta Valley and Piedmont regions. The park is named after Gran Paradiso mountain, which is located in the park... " |
June 17, 2008 | Official version 3.0 release. | ||
| 3.0.1 | July 16, 2008 | Security and stability update. | |||
| 3.0.2 | September 23, 2008 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.0.3 | September 26, 2008 | Bug fix for retrieving and saving passwords. | |||
| 3.0.4 | November 12, 2008 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.0.5 | December 16, 2008 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.0.6 | February 3, 2009 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.0.7 | March 4, 2009 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.0.8 | March 27, 2009 | Off-cycle security update. | |||
| 3.0.9 | April 21, 2009 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.0.10 | April 27, 2009 | Off-cycle stability update. | |||
| 3.0.11 | June 11, 2009 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.0.12 | July 21, 2009 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.0.13 | August 3, 2009 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.0.14 | September 9, 2009 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.0.15 | October 27, 2009 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.0.16 | December 15, 2009 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.0.17 | January 5, 2010 | Off-cycle stability update. | |||
| 3.0.18 | February 17, 2010 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.0.19 | March 30, 2010 | Regular security and stability update. End-of-life 3.0.x product line | |||
| Firefox 3.5 | 1.9.1 | 3.1a1 | Shiretoko Alpha 1 | July 28, 2008 | First Firefox 3.1 alpha release. Web standards improvements. Text API for the |
| 3.1a2 | Shiretoko Alpha 2 | September 5, 2008 | Second Firefox 3.1 alpha release. | ||
| 3.1b1 | Firefox 3.1 Beta 1 | October 14, 2008 | First Firefox 3.1 beta release. Web standards improvements in Gecko layout engine. Added support for CSS 2.1 and CSS 3 properties. New tab-switching shortcut that shows previews of the tab user is switching to. Improved control over Smart Location Bar using special characters to restrict your search. Support for new web technologies. | ||
| 3.1b2 | Firefox 3.1 Beta 2 | December 8, 2008 | Second Firefox 3.1 beta release. Available in 54 languages. Added new Private Browsing Mode. Added functions to facilitate clearing recent history by time as well as to remove all traces of a website. New support for web worker Web Workers Web Workers define an API for running scripts, basically JavaScript, in the background independently of any user interface scripts. This allows for long-running scripts that are not interrupted by scripts that respond to clicks or other user interactions, and allows long tasks to be executed... threads. New TraceMonkey JavaScript engine on by default for web content. Improvements to Gecko layout engine, including speculative parsing for faster content rendering. Removed new tab-switching behavior based on user feedback. Support for new web technologies. |
||
| 3.1b3 | Firefox 3.1 Beta 3 | March 12, 2009 | Third Firefox 3.1 beta release. Available in 64 languages. Improved new Private Browsing Mode. Improvements to web worker thread support. Improved performance and stability with the TraceMonkey JavaScript engine. New native JSON support. Improvements to Gecko layout engine, including speculative parsing for faster content rendering. Support for new web technologies such as | ||
| 3.5b4 | Firefox 3.5 Beta 4 | April 27, 2009 | First Firefox 3.5 beta release. Available in 70 languages. Improved tools for controlling private data, including Private Browsing Mode. Better performance and stability with new TraceMonkey JavaScript engine. Ability to provide Location Aware Browsing using web standards for geolocation. Support for native JSON, and web worker threads. Improvements to Gecko layout engine, including speculative parsing for faster content rendering. Support for new web technologies such as HTML5 | ||
| 3.5b99 | Firefox 3.5 Preview | June 8, 2009 | Preview for Firefox 3.5, pre-release candidate. | ||
| 3.5 RC1 | Firefox 3.5 Release Candidate 1 |
June 16, 2009 | First Firefox 3.5 release candidate. | ||
| 3.5 RC2 | Firefox 3.5 Release Candidate 2 |
June 19, 2009 | Second Firefox 3.5 release candidate. | ||
| 3.5 RC3 | Firefox 3.5 Release Candidate 3 |
June 24, 2009 | Third Firefox 3.5 release candidate. | ||
| 3.5 | Firefox 3.5 "Shiretoko Shiretoko National Park covers most of the Shiretoko Peninsula at the northeastern tip of the island of Hokkaidō, Japan.The word "Shiretoko" is derived form an Ainu word "sir etok", meaning "end of the Earth".... " |
June 30, 2009 | Official version 3.5 release. Identical to 3.5 RC3. | ||
| 3.5.1 | July 16, 2009 | Off-cycle security and stability update. | |||
| 3.5.2 | August 3, 2009 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.5.3 | September 9, 2009 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.5.4 | October 27, 2009 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.5.5 | November 5, 2009 | Off-cycle security and stability update. | |||
| 3.5.6 | December 15, 2009 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.5.7 | January 5, 2010 | Off-cycle stability update. | |||
| 3.5.8 | February 17, 2010 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.5.9 | March 30, 2010 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.5.10 | June 22, 2010 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.5.11 | July 20, 2010 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.5.12 | September 7, 2010 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.5.13 | September 15, 2010 | Off-cycle stability update. | |||
| 3.5.14 | October 19, 2010 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.5.15 | October 27, 2010 | Off-cycle security update. | |||
| 3.5.16 | December 9, 2010 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.5.17 | March 1, 2011 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.5.18 | March 22, 2011 | Off-cycle security update. Blacklists a few invalid HTTPS certificates. | |||
| 3.5.19 | April 28, 2011 | Regular security and stability update. End-of-life 3.5.x product line | |||
| Firefox 3.6 | 1.9.2 | 3.6a1 | Namoroka Alpha 1 | August 7, 2009 | First Firefox 3.6 alpha release. |
| 3.6b1 | Firefox 3.6 Beta 1 | October 30, 2009 | First Firefox 3.6 beta release. | ||
| 3.6b2 | Firefox 3.6 Beta 2 | November 10, 2009 | Second Firefox 3.6 beta release. | ||
| 3.6b3 | Firefox 3.6 Beta 3 | November 17, 2009 | Third Firefox 3.6 beta release. | ||
| 3.6b4 | Firefox 3.6 Beta 4 | November 26, 2009 | Fourth Firefox 3.6 beta release. | ||
| 3.6b5 | Firefox 3.6 Beta 5 | December 17, 2009 | Fifth Firefox 3.6 beta release. | ||
| 3.6 RC1 | Firefox 3.6 Release Candidate 1 |
January 8, 2010 | First Firefox 3.6 release candidate. | ||
| 3.6 RC2 | Firefox 3.6 Release Candidate 2 |
January 17, 2010 | Second Firefox 3.6 release candidate. | ||
| 3.6 | Firefox 3.6 "Namoroka Tsingy de Namoroka Strict Nature Reserve Tsingy de Namoroka Strict Nature Reserve, also known as Namoroka National Park, is a strict nature reserve located in the northwestern part of Madagascar in the Mahajanga Province, specifically, the Soalala District.- Climate and geography :... " |
January 21, 2010 | Official Firefox 3.6 release. Identical to 3.6 RC2. | ||
| 3.6.2There was no version 3.6.1. | March 22, 2010 | Security and stability update. | |||
| 3.6.3 | April 1, 2010 | Quick turn-around security update. | |||
| 3.6.3plugin1 | Firefox 3.6.3plugin1 "Lorentz Lorentz National Park Lorentz National Park is located in the Indonesian province of Papua, formerly known as Irian Jaya . With an area of 25,056 km² , it is the largest national park in South-East Asia... " |
April 8, 2010 | First Firefox "Lorentz Lorentz National Park Lorentz National Park is located in the Indonesian province of Papua, formerly known as Irian Jaya . With an area of 25,056 km² , it is the largest national park in South-East Asia... " beta, followed by 7 more Firefox 3.6.4 pre-release builds, all codenamed "Lorentz Lorentz National Park Lorentz National Park is located in the Indonesian province of Papua, formerly known as Irian Jaya . With an area of 25,056 km² , it is the largest national park in South-East Asia... ". |
||
| 3.6.4 | Firefox 3.6.4 (OOPP) "Lorentz Lorentz National Park Lorentz National Park is located in the Indonesian province of Papua, formerly known as Irian Jaya . With an area of 25,056 km² , it is the largest national park in South-East Asia... " |
June 22, 2010 | Regular security and stability update, including OOPP. | ||
| 3.6.6There was no version 3.6.5. | June 26, 2010 | Off-cycle stability update. Modified crash protection feature to increase amount of time plugins allowed to be non-responsive before being terminated. | |||
| 3.6.7 | July 20, 2010 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.6.8 | July 23, 2010 | Off-cycle stability update. | |||
| 3.6.9 | September 7, 2010 | Regular security and stability update. Also added support for X-FRAME-OPTIONS HTTP response header to help prevent clickjackingClickjacking Clickjacking is a malicious technique of tricking Web users into revealing confidential information or taking control of their computer while clicking on seemingly innocuous web pages... and removed option to enable experimental HTML5 parser via user preference html5.enable in about:config. |
|||
| 3.6.10 | September 15, 2010 | Off-cycle stability update. | |||
| 3.6.11 | October 19, 2010 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.6.12 | October 27, 2010 | Off-cycle security update. | |||
| 3.6.13 | December 9, 2010 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.6.14 | March 1, 2011 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.6.15 | March 4, 2011 | Off-cycle stability update. Fixed issue where some Java applets failed to load in Firefox 3.6.14. | |||
| 3.6.16 | March 22, 2011 | Off-cycle security update. Blacklisted several invalid HTTPS certificates. | |||
| 3.6.17 | April 28, 2011 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.6.18 | June 21, 2011 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.6.19 | July 11, 2011 | Off-cycle stability update. Turned off downloadable font support for users running Mac OS X 10.7 due to an underlying platform bug. No changes made on Windows side. | |||
| 3.6.20 | August 16, 2011 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.6.21 | August 30, 2011 | Off-cycle security update. Blacklisted a compromised HTTPS certificate. | |||
| 3.6.22 | September 6, 2011 | Off-cycle security update. | |||
| 3.6.23 | September 27, 2011 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.6.24 | November 8, 2011 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| 3.6.25 | December 20, 2011 | Regular security and stability update. | |||
| Firefox 4 | 1.9.3 | 3.7a1 | Mozilla Developer Preview 3.7 Alpha 1 | February 10, 2010 | First Firefox 3.7 alpha release. |
| 3.7a2 | Mozilla Developer Preview 3.7 Alpha 2 | March 3, 2010 | Second Firefox 3.7 alpha release. | ||
| 3.7a3 | Mozilla Developer Preview 3.7 Alpha 3 | March 17, 2010 | Third Firefox 3.7 alpha release. | ||
| 3.7a4 | Mozilla Developer Preview 3.7 Alpha 4 | April 12, 2010 | Fourth Firefox 3.7 alpha release. | ||
| 3.7a4webm | Mozilla Developer Preview 3.7 Alpha 4 WebM | May 19, 2010 | Added WebM WebM WebM is an audio-video format designed to provide a royalty-free, open video compression format for use with HTML5 video. The project's development is sponsored by Google.... video playback. |
||
| 3.7a5 | Mozilla Developer Preview 3.7 Alpha 5 | June 14, 2010 | Fifth Firefox 3.7 alpha release. First official release to include linux-x86_64 and mac-x86_64 builds and first regular release to include WebM WebM WebM is an audio-video format designed to provide a royalty-free, open video compression format for use with HTML5 video. The project's development is sponsored by Google.... video playback. |
||
| 2.0 | 4.0b1 | Firefox 4.0 Beta 1 | July 6, 2010 | First Firefox 4.0 beta release. | |
| 4.0b2 | Firefox 4.0 Beta 2 | July 27, 2010 | Second Firefox 4.0 beta release. | ||
| 4.0b3 | Firefox 4.0 Beta 3 | August 11, 2010 | Third Firefox 4.0 beta release. | ||
| 4.0b4 | Firefox 4.0 Beta 4 | August 24, 2010 | Fourth Firefox 4.0 beta release. | ||
| 4.0b5 | Firefox 4.0 Beta 5 | September 7, 2010 | Fifth Firefox 4.0 beta release. | ||
| 4.0b6 | Firefox 4.0 Beta 6 | September 14, 2010 | Sixth Firefox 4.0 beta release. | ||
| 4.0b7 | Firefox 4.0 Beta 7 | November 10, 2010 | Seventh Firefox 4.0 beta release. | ||
| 4.0b8 | Firefox 4.0 Beta 8 | December 21, 2010 | Eighth Firefox 4.0 beta release. | ||
| 4.0b9 | Firefox 4.0 Beta 9 | January 14, 2011 | Ninth Firefox 4.0 beta release. | ||
| 4.0b10 | Firefox 4.0 Beta 10 | January 25, 2011 | Tenth Firefox 4.0 beta release. | ||
| 4.0b11 | Firefox 4.0 Beta 11 | February 8, 2011 | Eleventh Firefox 4.0 beta release. | ||
| 4.0b12 | Firefox 4.0 Beta 12 | February 25, 2011 | Twelfth Firefox 4.0 beta release. | ||
| 4.0 RC1 | Firefox 4.0 Release Candidate 1 |
March 9, 2011 | First Firefox 4.0 release candidate. | ||
| 4.0 RC2 | Firefox 4.0 Release Candidate 2 |
March 18, 2011 | Second Firefox 4.0 release candidate. | ||
| 4.0 | Firefox 4.0 "Tumucumaque Tumucumaque National Park The Tumucumaque National Park is situated in northwestern Brazil inside the Amazon Rainforest state of Amapá. It’s bordered to the north by French Guyana and Suriname.... " |
March 22, 2011 | Official Firefox 4.0 release. Identical to 4.0 RC2. | ||
| 4.0.1 | Firefox 4.0.1 "Macaw Macaw Macaws are small to large, often colourful New World parrots. Of the many different Psittacidae genera, six are classified as macaws: Ara, Anodorhynchus, Cyanopsitta, Primolius, Orthopsittaca, and Diopsittaca... " |
April 28, 2011 | Regular security and stability update. End-of-life 4.0.x product line | ||
| Firefox 5 | 5.0 | 5.0a2 | Firefox 5.0 Aurora | April 13, 2011 | First Firefox 5.0 Aurora build. |
| 5.0b1 | Firefox 5.0 Beta 1 | May 4, 2011 | No official Firefox 5.0 beta release. Renamed "Aurora 5.0 Alpha 2" build to test release channel switching for users on the Aurora-Channel. |
||
| 5.0b2 | Firefox 5.0 Beta 2 | May 20, 2011 | First Firefox 5.0 Beta release. | ||
| 5.0b3 | Firefox 5.0 Beta 3 | June 1, 2011 | Second Firefox 5.0 Beta release. | ||
| 5.0b5Builds of version 5.0b4 were created, but not released. | Firefox 5.0 Beta 5 | June 9, 2011 | Third Firefox 5.0 Beta release. | ||
| 5.0b6 | Firefox 5.0 Beta 6 | June 14, 2011 | Fourth Firefox 5.0 Beta release. | ||
| 5.0b7 | Firefox 5.0 Beta 7 | June 15, 2011 | Fifth Firefox 5.0 Beta release. | ||
| 5.0 | Firefox 5.0 | June 21, 2011 | Official Firefox 5.0 release. | ||
| 5.0.1 | Firefox 5.0.1 | July 11, 2011 | Off-cycle stability update. Worked around issue in Mac OS X 10.7 that caused Firefox to crash, and issue caused by Apple's "Java for Mac OS X 10.6 Update 5" that prevented Java plugin from loading. No changes made on Windows side. End-of-life 5.0.x product line on August 16, 2011. | ||
| Firefox 6 | 6.0 | 6.0a1 | Firefox 6.0 Nightly | April 13, 2011 | First Firefox 6.0 Nightly build. |
| 6.0a2 | Firefox 6.0 Aurora | May 25, 2011 | First Firefox 6.0 Aurora build. | ||
| 6.0b1 | Firefox 6.0 Beta 1 | July 8, 2011 | First Firefox 6.0 Beta release. | ||
| 6.0b2 | Firefox 6.0 Beta 2 | July 16, 2011 | Second Firefox 6.0 Beta release. | ||
| 6.0b3 | Firefox 6.0 Beta 3 | July 26, 2011 | Third Firefox 6.0 Beta release. | ||
| 6.0b4 | Firefox 6.0 Beta 4 | August 1, 2011 | Fourth Firefox 6.0 Beta release. | ||
| 6.0b5 | Firefox 6.0 Beta 5 | August 5, 2011 | Fifth Firefox 6.0 Beta release. | ||
| 6.0 | Firefox 6.0 | August 16, 2011 | Official Firefox 6.0 release. | ||
| 6.0.1 | Firefox 6.0.1 | August 30, 2011 | Off-cycle security update. Blacklisted a compromised HTTPS certificate. | ||
| 6.0.2 | Firefox 6.0.2 | September 6, 2011 | Off-cycle security update. End-of-life 6.0.x product line on September 27, 2011. | ||
| Firefox 7 | 7.0 | 7.0a1 | Firefox 7.0 Nightly | May 25, 2011 | First Firefox 7.0 Nightly build. |
| 7.0a2 | Firefox 7.0 Aurora | July 6, 2011 | First Firefox 7.0 Aurora build. | ||
| 7.0b1 | Firefox 7.0 Beta 1 | August 18, 2011 | First Firefox 7.0 Beta release. | ||
| 7.0b2 | Firefox 7.0 Beta 2 | August 26, 2011 | Second Firefox 7.0 Beta release. | ||
| 7.0b4 Builds of version 7.0b3 were created, but not released. | Firefox 7.0 Beta 4 | September 6, 2011 | Third Firefox 7.0 Beta release. | ||
| 7.0b5 | Firefox 7.0 Beta 5 | September 9, 2011 | Fourth Firefox 7.0 Beta release. | ||
| 7.0b6 | Firefox 7.0 Beta 6 | September 19, 2011 | Fifth Firefox 7.0 Beta release. | ||
| 7.0 | Firefox 7.0 | September 27, 2011 | Official Firefox 7.0 release. | ||
| 7.0.1 | Firefox 7.0.1 | September 29, 2011 | Off-cycle stability update. Fixed a rare issue that hid one or more add-ons after a Firefox update. End-of-life 7.0.x product line on November 8, 2011. | ||
| Firefox 8 | 8.0 | 8.0a1 | Firefox 8.0 Nightly | July 6, 2011 | First Firefox 8.0 Nightly build. |
| 8.0a2 | Firefox 8.0 Aurora | August 19, 2011 | First Firefox 8.0 Aurora build. | ||
| 8.0b1 | Firefox 8.0 Beta 1 | September 29, 2011 | First Firefox 8.0 Beta release. | ||
| 8.0b2 | Firefox 8.0 Beta 2 | October 10, 2011 | Second Firefox 8.0 Beta release. | ||
| 8.0b3 | Firefox 8.0 Beta 3 | October 13, 2011 | Third Firefox 8.0 Beta release. | ||
| 8.0b4 | Firefox 8.0 Beta 4 | October 19, 2011 | Fourth Firefox 8.0 Beta release. | ||
| 8.0b5 | Firefox 8.0 Beta 5 | October 27, 2011 | Fifth Firefox 8.0 Beta release. Removed support for new tab animation due to incompatibilities with some extensions. | ||
| 8.0b6 | Firefox 8.0 Beta 6 | November 1, 2011 | Sixth Firefox 8.0 Beta release. | ||
| 8.0 | Firefox 8.0 | November 8, 2011 | Official Firefox 8.0 release. | ||
| 8.0.1 | Firefox 8.0.1 | November 21, 2011 | Off-cycle stability update. End-of-life 8.0.x product line on December 20, 2011. | ||
| Firefox 9 | 9.0 | 9.0a1 | Firefox 9.0 Nightly | August 17, 2011 | First Firefox 9.0 Nightly build. |
| 9.0a2 | Firefox 9.0 Aurora | September 28, 2011 | First Firefox 9.0 Aurora build. | ||
| 9.0b1 | Firefox 9.0 Beta 1 | November 10, 2011 | First Firefox 9.0 Beta release. | ||
| 9.0b2 | Firefox 9.0 Beta 2 | November 17, 2011 | Second Firefox 9.0 Beta release. | ||
| 9.0b3 | Firefox 9.0 Beta 3 | November 24, 2011 | Third Firefox 9.0 Beta release. | ||
| 9.0 | Firefox 9.0 | December 20, 2011 | Official Firefox 9.0 release. End-of-life 9.0 product line on January 31, 2012. | ||
| Firefox 10 | 10.0 | 10.0a1 | Firefox 10.0 Nightly | September 28, 2011 | First Firefox 10.0 Nightly build. |
| 10.0a2 | Firefox 10.0 Aurora | November 8, 2011 | First Firefox 10.0 Aurora build. | ||
| 10.0b1 | Firefox 10.0 Beta 1 | December 20, 2011 | First Firefox 10.0 Beta release. | ||
| 10.0 | Firefox 10.0 | January 31, 2012 | Official Firefox 10.0 release. | ||
| Firefox 11 | 11.0 | 11.0a1 | Firefox 11.0 Nightly | November 9, 2011 | First Firefox 11.0 Nightly build. |
| 11.0a2 | Firefox 11.0 Aurora | December 20, 2011 | First Firefox 11.0 Aurora build. | ||
| 11.0b1 | Firefox 11.0 Beta 1 | January 31, 2012 | First Firefox 11.0 Beta release. | ||
| 11.0 | Firefox 11.0 | March 13, 2012 | Official Firefox 11.0 release. | ||
| Browser name | Gecko version | Version | Codename | Release date | Significant changes |
Localizations
The number of localizations of Firefox has increased steadily. The first official release in November 2004 was distributed in 28 languages, including BritishBritish English
British English, or English , is the broad term used to distinguish the forms of the English language used in the United Kingdom from forms used elsewhere...
/American
American English
American English is a set of dialects of the English language used mostly in the United States. Approximately two-thirds of the world's native speakers of English live in the United States....
English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
, European
Peninsular Spanish
Peninsular Spanish, also known as European Spanish, refers to the varieties of the Spanish language spoken in the Iberian Peninsula, as opposed to the Spanish spoken in the Americas and in the Canary Islands....
/Argentine Spanish
Spanish language
Spanish , also known as Castilian , is a Romance language in the Ibero-Romance group that evolved from several languages and dialects in central-northern Iberia around the 9th century and gradually spread with the expansion of the Kingdom of Castile into central and southern Iberia during the...
, and Chinese
Standard Chinese
Standard Chinese, or Modern Standard Chinese, also known as Mandarin or Putonghua, is the official language of the People's Republic of China and Republic of China , and is one of the four official languages of Singapore....
in Traditional/Simplified characters, while Firefox 4.0 is available in over 80 languages.
See also
- GNU IceCatGNU IceCatGNU IceCat, formerly known as GNU IceWeasel, is a free software rebranding of the Mozilla Firefox web browser distributed by the GNU Project. It is compatible with both the GNU/Linux and Mac OS X operating systems....
- History of Free SoftwareHistory of free softwareThis is a timeline-style look at how free and open-source software has evolved and existed from its inception.The phrase "free software" refers to software that is liberally licensed, allowing the end user more freedoms than conventional-software licences. This is not to be confused with software...
- History of Mozilla Application SuiteHistory of Mozilla Application SuiteThe history of the Mozilla Application Suite began with the release of the source code of the Netscape suite as an open source project. Going through years of hard working , Mozilla 1.0 was eventually released on June 5, 2002...
- Mozilla Corporation software rebranded by the Debian project
External links
- Mozilla Firefox release notes for each version
- Indistinguishable from Jesse, Jesse Ruderman, unofficial changelogs for Firefox releases
- MozillaZine Weblogs, Where Did Firefox Come From?
- MozillaWiki, MozillaWiki - ReleaseRoadmap
- BBC News, Firefox browser for web 2.0 age

