Galactokinase
Encyclopedia
Galactokinase is an enzyme
that facilitates the phosphorylation
of α-D-galactose
to galactose 1-phosphate at the expense of one molecule
of ATP
. Galactokinase catalyzes the second step of the Leloir pathway
, a metabolic pathway
found in most organisms for the catabolism
of β-D-galactose to glucose 1-phosphate. First isolated from mammalian
liver
, galactokinase has been studied extensively in yeast
, archaea
, plants, and humans.
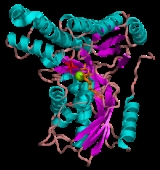
ring of ATP binds in a hydrophobic pocket located at their interface. The N-terminal domain is marked by five strands of mixed beta-sheet and five alpha-helices, and the C-terminal domain is characterized by two layers of anti-parallel beta-sheets and six alpha-helices. Galactokinase does not belong to the sugar
kinase
family, but rather to a class of ATP-dependent enzymes known as the GHMP superfamily
. GHMP is an abbreviation referring to its original members: galactokinase, homoserine kinase
, mevalonate kinase
, and phosphomevalonate kinase
. Members of the GHMP superfamily have great three-dimensional similarity despite only ten to 20% sequence identity. These enzymes contain three well-conserved motifs (I, II, and III), the second of which is involved in nucleotide binding and has the sequence Pro
-X-X-X-Gly
-Leu
-X-Ser
-Ser-Ala
.
. The enzyme cannot tolerate any C-4 modifications, but changes at the C-2 position of D-galactose do not interfere with enzyme function. Both human and rat
galactokinases are also able to successfully phosphorylate 2-deoxy-D-galactose. Galactokinase from S. cerevisiae, on the other hand, is highly specific for D-galactose and cannot phosphorylate glucose
, mannose
, arabinose
, fucose, lactose
, galactitol, or 2-deoxy-D-galactose. Moreover, the kinetic properties of galactokinase also differ across species.
residues
in human galactokinase have become understood. Asp
-186 abstracts a proton
from C1-OH of α-D-galactose, and the resulting alkoxide
nucleophile
attacks the γ-phosphorus
of ATP. A phosphate group is transferred to the sugar, and Asp-186 may be deprotonated
by water
. Nearby Arg
-37 stabilizes Asp-186 in its anionic form and has also been proven to be essential to galactokinase function in point mutation
experiments. Both the aspartic acid and arginine active site residues are highly conserved
among galactokinases.
, and UDP-galactose 4-epimerase. Galactokinase catalyzes the first committed step of galactose catabolism, forming galactose 1-phosphate.
, a rare metabolic disorder characterized by decreased ability to metabolize galactose, can be caused by a mutation in any of the three enzymes in the Leloir pathway. Galactokinase deficiency
, also known as galactosemia type II, is a recessive metabolic disorder caused by a mutation
in human galactokinase. About 20 mutations have been identified that cause galactosemia type II, the main symptom
of which is early onset cataracts. In lens
cells
of the human eye
, aldose reductase
converts galactose to galactitol. As galactose is not being catabolized to glucose due to a galactokinase mutation, galactitol accumulates. This galactitol gradient across the lens cell membrane triggers the osmotic
uptake of water, and the swelling and eventual apoptosis
of lens cells ensues.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that facilitates the phosphorylation
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation activates or deactivates many protein enzymes....
of α-D-galactose
Galactose
Galactose , sometimes abbreviated Gal, is a type of sugar that is less sweet than glucose. It is a C-4 epimer of glucose....
to galactose 1-phosphate at the expense of one molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
of ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
. Galactokinase catalyzes the second step of the Leloir pathway
Leloir pathway
The Leloir pathway is a metabolic pathway for the catabolism of D-galactose. It is named after Luis Federico Leloir.In the first step α-D-galactose is phosphorylated by a kinase to galactose 1-phosphate. Also part of this pathway is a mutarotase that facilitates the conversion of β-D-galactose to...
, a metabolic pathway
Metabolic pathway
In biochemistry, metabolic pathways are series of chemical reactions occurring within a cell. In each pathway, a principal chemical is modified by a series of chemical reactions. Enzymes catalyze these reactions, and often require dietary minerals, vitamins, and other cofactors in order to function...
found in most organisms for the catabolism
Catabolism
Catabolism is the set of metabolic pathways that break down molecules into smaller units and release energy. In catabolism, large molecules such as polysaccharides, lipids, nucleic acids and proteins are broken down into smaller units such as monosaccharides, fatty acids, nucleotides, and amino...
of β-D-galactose to glucose 1-phosphate. First isolated from mammalian
Mammal
Mammals are members of a class of air-breathing vertebrate animals characterised by the possession of endothermy, hair, three middle ear bones, and mammary glands functional in mothers with young...
liver
Liver
The liver is a vital organ present in vertebrates and some other animals. It has a wide range of functions, including detoxification, protein synthesis, and production of biochemicals necessary for digestion...
, galactokinase has been studied extensively in yeast
Yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic micro-organisms classified in the kingdom Fungi, with 1,500 species currently described estimated to be only 1% of all fungal species. Most reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by an asymmetric division process called budding...
, archaea
Archaea
The Archaea are a group of single-celled microorganisms. A single individual or species from this domain is called an archaeon...
, plants, and humans.
Structure
Galactokinase is composed of two domains separated by a large cleft. The two regions are known as the N- and C-terminal domains, and the adenineAdenine
Adenine is a nucleobase with a variety of roles in biochemistry including cellular respiration, in the form of both the energy-rich adenosine triphosphate and the cofactors nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide and flavin adenine dinucleotide , and protein synthesis, as a chemical component of DNA...
ring of ATP binds in a hydrophobic pocket located at their interface. The N-terminal domain is marked by five strands of mixed beta-sheet and five alpha-helices, and the C-terminal domain is characterized by two layers of anti-parallel beta-sheets and six alpha-helices. Galactokinase does not belong to the sugar
Carbohydrate
A carbohydrate is an organic compound with the empirical formula ; that is, consists only of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, with a hydrogen:oxygen atom ratio of 2:1 . However, there are exceptions to this. One common example would be deoxyribose, a component of DNA, which has the empirical...
kinase
Kinase
In chemistry and biochemistry, a kinase is a type of enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from high-energy donor molecules, such as ATP, to specific substrates, a process referred to as phosphorylation. Kinases are part of the larger family of phosphotransferases...
family, but rather to a class of ATP-dependent enzymes known as the GHMP superfamily
GHMP kinase family
In molecular biology, the GHMP kinase family is a family of kinase enzymes. Members of this family include homoserine kinases , galactokinases , and mevalonate kinases. These kinases make up the GHMP kinase superfamily of ATP-dependent enzymes. These enzymes are involved in the biosynthesis of...
. GHMP is an abbreviation referring to its original members: galactokinase, homoserine kinase
Homoserine kinase
In enzymology, a homoserine kinase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reactionThus, the two substrates of this enzyme are ATP and L-homoserine, whereas its two products are ADP and O-phospho-L-homoserine....
, mevalonate kinase
Mevalonate kinase
Mevalonate kinase is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the MVK gene. Mevalonate kinases are found in a wide variety of organisms from bacteria to mammals...
, and phosphomevalonate kinase
Phosphomevalonate kinase
Phosphomevalonate kinase is an enzyme in the mevalonate pathway....
. Members of the GHMP superfamily have great three-dimensional similarity despite only ten to 20% sequence identity. These enzymes contain three well-conserved motifs (I, II, and III), the second of which is involved in nucleotide binding and has the sequence Pro
Proline
Proline is an α-amino acid, one of the twenty DNA-encoded amino acids. Its codons are CCU, CCC, CCA, and CCG. It is not an essential amino acid, which means that the human body can synthesize it. It is unique among the 20 protein-forming amino acids in that the α-amino group is secondary...
-X-X-X-Gly
Glycine
Glycine is an organic compound with the formula NH2CH2COOH. Having a hydrogen substituent as its 'side chain', glycine is the smallest of the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. Its codons are GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG cf. the genetic code.Glycine is a colourless, sweet-tasting crystalline solid...
-Leu
Leucine
Leucine is a branched-chain α-amino acid with the chemical formula HO2CCHCH2CH2. Leucine is classified as a hydrophobic amino acid due to its aliphatic isobutyl side chain. It is encoded by six codons and is a major component of the subunits in ferritin, astacin and other 'buffer' proteins...
-X-Ser
Serine
Serine is an amino acid with the formula HO2CCHCH2OH. It is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. By virtue of the hydroxyl group, serine is classified as a polar amino acid.-Occurrence and biosynthesis:...
-Ser-Ala
Alanine
Alanine is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula CH3CHCOOH. The L-isomer is one of the 20 amino acids encoded by the genetic code. Its codons are GCU, GCC, GCA, and GCG. It is classified as a nonpolar amino acid...
.
Sugar Specificity
Interestingly, galactokinases across different species display a great diversity of substrate specificities. E. coli galactokinase can also phosphorylate 2-deoxy-D-galactose, 2-amino-deoxy-D-galactose, 3-deoxy-D-galactose and D-fucoseFucose
Fucose is a hexose deoxy sugar with the chemical formula C6H12O5. It is found on N-linked glycans on the mammalian, insect and plant cell surface, and is the fundamental sub-unit of the fucoidan polysaccharide...
. The enzyme cannot tolerate any C-4 modifications, but changes at the C-2 position of D-galactose do not interfere with enzyme function. Both human and rat
Rat
Rats are various medium-sized, long-tailed rodents of the superfamily Muroidea. "True rats" are members of the genus Rattus, the most important of which to humans are the black rat, Rattus rattus, and the brown rat, Rattus norvegicus...
galactokinases are also able to successfully phosphorylate 2-deoxy-D-galactose. Galactokinase from S. cerevisiae, on the other hand, is highly specific for D-galactose and cannot phosphorylate glucose
Glucose
Glucose is a simple sugar and an important carbohydrate in biology. Cells use it as the primary source of energy and a metabolic intermediate...
, mannose
Mannose
Mannose is a sugar monomer of the aldohexose series of carbohydrates. Mannose is a C-2 epimer of glucose. It is not part of human metabolism, but is a component of microbial cell walls, and is therefore a target of the immune system and also of antibiotics....
, arabinose
Arabinose
Arabinose is an aldopentose – a monosaccharide containing five carbon atoms, and including an aldehyde functional group.For biosynthetic reasons, most saccharides are almost always more abundant in nature as the "D"-form, or structurally analogous to D-glyceraldehyde.For sugars, the D/L...
, fucose, lactose
Lactose
Lactose is a disaccharide sugar that is found most notably in milk and is formed from galactose and glucose. Lactose makes up around 2~8% of milk , although the amount varies among species and individuals. It is extracted from sweet or sour whey. The name comes from or , the Latin word for milk,...
, galactitol, or 2-deoxy-D-galactose. Moreover, the kinetic properties of galactokinase also differ across species.
Mechanism
Recently, the roles of active siteActive site
In biology the active site is part of an enzyme where substrates bind and undergo a chemical reaction. The majority of enzymes are proteins but RNA enzymes called ribozymes also exist. The active site of an enzyme is usually found in a cleft or pocket that is lined by amino acid residues that...
residues
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
in human galactokinase have become understood. Asp
Aspartic acid
Aspartic acid is an α-amino acid with the chemical formula HOOCCHCH2COOH. The carboxylate anion, salt, or ester of aspartic acid is known as aspartate. The L-isomer of aspartate is one of the 20 proteinogenic amino acids, i.e., the building blocks of proteins...
-186 abstracts a proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
from C1-OH of α-D-galactose, and the resulting alkoxide
Alkoxide
An alkoxide is the conjugate base of an alcohol and therefore consists of an organic group bonded to a negatively charged oxygen atom. They can be written as RO−, where R is the organic substituent. Alkoxides are strong bases and, when R is not bulky, good nucleophiles and good ligands...
nucleophile
Nucleophile
A nucleophile is a species that donates an electron-pair to an electrophile to form a chemical bond in a reaction. All molecules or ions with a free pair of electrons can act as nucleophiles. Because nucleophiles donate electrons, they are by definition Lewis bases.Nucleophilic describes the...
attacks the γ-phosphorus
Phosphorus
Phosphorus is the chemical element that has the symbol P and atomic number 15. A multivalent nonmetal of the nitrogen group, phosphorus as a mineral is almost always present in its maximally oxidized state, as inorganic phosphate rocks...
of ATP. A phosphate group is transferred to the sugar, and Asp-186 may be deprotonated
Deprotonation
Deprotonation is the removal of a proton from a molecule, forming the conjugate base.The relative ability of a molecule to give up a proton is measured by its pKa value. A low pKa value indicates that the compound is acidic and will easily give up its proton to a base...
by water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
. Nearby Arg
Arginine
Arginine is an α-amino acid. The L-form is one of the 20 most common natural amino acids. At the level of molecular genetics, in the structure of the messenger ribonucleic acid mRNA, CGU, CGC, CGA, CGG, AGA, and AGG, are the triplets of nucleotide bases or codons that codify for arginine during...
-37 stabilizes Asp-186 in its anionic form and has also been proven to be essential to galactokinase function in point mutation
Point mutation
A point mutation, or single base substitution, is a type of mutation that causes the replacement of a single base nucleotide with another nucleotide of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. Often the term point mutation also includes insertions or deletions of a single base pair...
experiments. Both the aspartic acid and arginine active site residues are highly conserved
Conserved sequence
In biology, conserved sequences are similar or identical sequences that occur within nucleic acid sequences , protein sequences, protein structures or polymeric carbohydrates across species or within different molecules produced by the same organism...
among galactokinases.
Biological Function
The Leloir pathway catalyzes the conversion of galactose to glucose. Galactose is found in dairy products, as well as in fruits and vegetables, and can be produced endogenously in the breakdown of glycoproteins and glycolipids. Three enzymes are required in the Leloir pathway: galactokinase, galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferaseGalactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase
Galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase is an enzyme responsible for converting ingested galactose to glucose.Galactose-1-phosphate uridylyltransferase catalyzes the second step of the Leloir pathway of galactose metabolism, namely:The expression of GALT is controlled by the actions of the...
, and UDP-galactose 4-epimerase. Galactokinase catalyzes the first committed step of galactose catabolism, forming galactose 1-phosphate.
Disease Relevance
GalactosemiaGalactosemia
Galactosemia is a rare genetic metabolic disorder that affects an individual's ability to metabolize the sugar galactose properly. Although the sugar lactose can metabolize to galactose, galactosemia is not related to and should not be confused with lactose intolerance...
, a rare metabolic disorder characterized by decreased ability to metabolize galactose, can be caused by a mutation in any of the three enzymes in the Leloir pathway. Galactokinase deficiency
Galactokinase deficiency
Galactokinase deficiency, also known as Galactosemia type 2 or GALK deficiency, is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder marked by an accumulation of galactose and galactitol secondary to the decreased conversion of galactose to galactose-1-phosphate by galactokinase...
, also known as galactosemia type II, is a recessive metabolic disorder caused by a mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
in human galactokinase. About 20 mutations have been identified that cause galactosemia type II, the main symptom
Symptom
A symptom is a departure from normal function or feeling which is noticed by a patient, indicating the presence of disease or abnormality...
of which is early onset cataracts. In lens
Lens (anatomy)
The crystalline lens is a transparent, biconvex structure in the eye that, along with the cornea, helps to refract light to be focused on the retina. The lens, by changing shape, functions to change the focal distance of the eye so that it can focus on objects at various distances, thus allowing a...
cells
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
of the human eye
Eye
Eyes are organs that detect light and convert it into electro-chemical impulses in neurons. The simplest photoreceptors in conscious vision connect light to movement...
, aldose reductase
Aldose reductase
Aldose reductase is an NADPH-dependent oxidoreductase that catalyzes the reduction of a variety of aldehydes and carbonyls, including monosaccharides...
converts galactose to galactitol. As galactose is not being catabolized to glucose due to a galactokinase mutation, galactitol accumulates. This galactitol gradient across the lens cell membrane triggers the osmotic
Osmosis
Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, aiming to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides...
uptake of water, and the swelling and eventual apoptosis
Apoptosis
Apoptosis is the process of programmed cell death that may occur in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, and chromosomal DNA fragmentation...
of lens cells ensues.

