
Colonization of Titan
Encyclopedia

Saturn
Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second largest planet in the Solar System, after Jupiter. Saturn is named after the Roman god Saturn, equated to the Greek Cronus , the Babylonian Ninurta and the Hindu Shani. Saturn's astronomical symbol represents the Roman god's sickle.Saturn,...
’s orange moon Titan
Titan (moon)
Titan , or Saturn VI, is the largest moon of Saturn, the only natural satellite known to have a dense atmosphere, and the only object other than Earth for which clear evidence of stable bodies of surface liquid has been found....
is one of several candidates for a possible future colonization of the outer solar system
Colonization of the outer solar system
Some of the moons of the outer planets of the solar system are large enough to be suitable places for colonization. Many of the larger moons contain water ice, liquid water, and organic compounds that might be useful for sustaining human life. Colonies in the outer Solar System could also serve as...
. There are many possible reasons for colonization, one of which is mining or collecting hydrocarbons which currently power much of Earth
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
's machinery.
Natural resources

Methane
Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest alkane, the principal component of natural gas, and probably the most abundant organic compound on earth. The relative abundance of methane makes it an attractive fuel...
and ethane
Ethane
Ethane is a chemical compound with chemical formula C2H6. It is the only two-carbon alkane that is an aliphatic hydrocarbon. At standard temperature and pressure, ethane is a colorless, odorless gas....
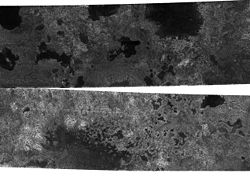
) in Titan's northern latitudes. This is the first discovery of currently-existing lakes anywhere besides Earth. The lakes range in size from about a kilometer to one which is one hundred kilometers across.
On March 13, 2007, JPL announced that it found strong evidence of sea
Sea
A sea generally refers to a large body of salt water, but the term is used in other contexts as well. Most commonly, it means a large expanse of saline water connected with an ocean, and is commonly used as a synonym for ocean...
s of methane and ethane in the northern hemisphere. At least one of these is larger than any of the Great Lakes
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes are a collection of freshwater lakes located in northeastern North America, on the Canada – United States border. Consisting of Lakes Superior, Michigan, Huron, Erie, and Ontario, they form the largest group of freshwater lakes on Earth by total surface, coming in second by volume...
in North America
North America
North America is a continent wholly within the Northern Hemisphere and almost wholly within the Western Hemisphere. It is also considered a northern subcontinent of the Americas...
.
Suitability
The JovianJupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet within the Solar System. It is a gas giant with mass one-thousandth that of the Sun but is two and a half times the mass of all the other planets in our Solar System combined. Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn,...
system is the least likely to be developed for collecting resources from a gas giant
Gas giant
A gas giant is a large planet that is not primarily composed of rock or other solid matter. There are four gas giants in the Solar System: Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune...
, because of its extraordinary radiation belt. The American aerospace engineer and author Robert Zubrin
Robert Zubrin
Robert Zubrin is an American aerospace engineer and author, best known for his advocacy of the manned exploration of Mars. He was the driving force behind Mars Direct—a proposal intended to produce significant reductions in the cost and complexity of such a mission...
identified Saturn as the most important and most valuable of the three other gas giants, because of its relative proximity, low radiation, and excellent system of moons. He also named Titan as the most important moon on which to establish a base to develop the resources of the Saturn system.
Habitability
Robert ZubrinRobert Zubrin
Robert Zubrin is an American aerospace engineer and author, best known for his advocacy of the manned exploration of Mars. He was the driving force behind Mars Direct—a proposal intended to produce significant reductions in the cost and complexity of such a mission...
has pointed out that Titan possesses an abundance of all the elements necessary to support life
Planetary habitability
Planetary habitability is the measure of a planet's or a natural satellite's potential to sustain life. Life may develop directly on a planet or satellite or be transferred to it from another body, a theoretical process known as panspermia...
, saying "In certain ways, Titan is the most hospitable extraterrestrial world within our solar system for human colonization." The atmosphere contains plentiful nitrogen
Nitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
and methane
Methane
Methane is a chemical compound with the chemical formula . It is the simplest alkane, the principal component of natural gas, and probably the most abundant organic compound on earth. The relative abundance of methane makes it an attractive fuel...
, and strong evidence indicates that liquid methane is on the surface and, liquid water
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
, and ammonia
Ammonia
Ammonia is a compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the formula . It is a colourless gas with a characteristic pungent odour. Ammonia contributes significantly to the nutritional needs of terrestrial organisms by serving as a precursor to food and fertilizers. Ammonia, either directly or...
are present under the surface and are often delivered to the surface by volcanic activity. Water can easily be used to generate breathable oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
. Nitrogen is ideal to add buffer gas
Buffer gas
A buffer gas is an inert or nonflammable gas. In the Earth's atmosphere, nitrogen acts as a buffer gas. A buffer gas adds pressure to a system and controls the speed of combustion with any oxygen present...
partial pressure to breathable air; indeed, nitrogen forms about 78% of Earth's atmosphere
Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention , and reducing temperature extremes between day and night...
. Nitrogen, methane and ammonia can all be used to produce fertilizer
Fertilizer
Fertilizer is any organic or inorganic material of natural or synthetic origin that is added to a soil to supply one or more plant nutrients essential to the growth of plants. A recent assessment found that about 40 to 60% of crop yields are attributable to commercial fertilizer use...
for growing food.
Atmosphere
Additionally, Titan has an atmospheric pressure one and a half times that of EarthEarth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
. This means that the interior air pressure of landing craft and habitats could be set equal or close to the exterior pressure, reducing the difficulty and complexity of structural engineering for landing craft and habitats compared with low or zero pressure environments such as on the Moon
Moon
The Moon is Earth's only known natural satellite,There are a number of near-Earth asteroids including 3753 Cruithne that are co-orbital with Earth: their orbits bring them close to Earth for periods of time but then alter in the long term . These are quasi-satellites and not true moons. For more...
, Mars
Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun in the Solar System. The planet is named after the Roman god of war, Mars. It is often described as the "Red Planet", as the iron oxide prevalent on its surface gives it a reddish appearance...
, or the asteroid
Asteroid
Asteroids are a class of small Solar System bodies in orbit around the Sun. They have also been called planetoids, especially the larger ones...
s. The thick atmosphere would also make radiation a non-issue, unlike on the Moon, Mars, or the asteroids. While Titan's atmosphere contains trace amounts of hydrogen cyanide, in the event of pressure suit breach, the concentration would not inflict more than a slight headache.
Gravity
Titan has a surface gravity of 0.14 gG-force
The g-force associated with an object is its acceleration relative to free-fall. This acceleration experienced by an object is due to the vector sum of non-gravitational forces acting on an object free to move. The accelerations that are not produced by gravity are termed proper accelerations, and...
, slightly less than that of the Moon. Managing long-term effects of low gravity on human health would therefore be a significant issue for long-term occupation of Titan, more so than on Mars. These effects are still an active field of study. They can include symptoms such as loss of bone density, loss of muscle density, and a weakened immune system
Immune system
An immune system is a system of biological structures and processes within an organism that protects against disease by identifying and killing pathogens and tumor cells. It detects a wide variety of agents, from viruses to parasitic worms, and needs to distinguish them from the organism's own...
. Astronaut
Astronaut
An astronaut or cosmonaut is a person trained by a human spaceflight program to command, pilot, or serve as a crew member of a spacecraft....
s in Earth orbit have remained in microgravity for up to a year and more at a time. Effective countermeasures for the negative effects of low gravity are well-established, particularly an aggressive regime of daily physical exercise or weighted clothing. The variation in the negative effects of low gravity as a function of different levels of low gravity are not known, since all research in this area is restricted to humans in zero gravity. The same goes for the potential effects of low gravity on fetal and pediatric development. It has been hypothesized that children born and raised in low gravity such as on Titan would not be well adapted for life under the higher gravity of Earth.
Temperature
The temperature on Titan is about 94 KKelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
(−179 °C, or −290.2 °F), so insulation and heat generation and management would be significant concerns. Although the air pressure at the surface is about 1.5 times that of Earth sea level, because of the colder temperature, the density of the air is about 4.5 times that of Earth sea level. This substantial density should moderate shifts in temperature over time and from one locale to another, to a fraction of the types of temperature changes familiar from the day/night cycle, the seasons, and weather on Earth. The corresponding narrow range of temperature variation further reduces the difficulties in structural engineering.
Relative thickness of the atmosphere combined with extreme cold makes additional troubles for human habitation. Unlike vacuum, the high atmospheric density makes thermoinsulation a significant engineering problem.
Flight on Titan
The very high ratio of atmospheric density to surface gravity also greatly reduces the wingspan needed for an aircraft to maintain lift, so much so that a human would be able to strap on wings and easily fly through the atmosphere.Further reading
- Stephen L. Gillett, "Titan as the Abode of Life," Analog, Vol. CXII No. 13, pp. 40–55 (1992)

