
Climate of Colombia
Encyclopedia


Geography of Colombia
The geography of Colombia is characterized by containing five main natural regions that present their own unique characteristics, from the Andes mountain range region shared with Ecuador and Venezuela; the Pacific Ocean coastal region shared with Panama and Ecuador; the Caribbean Sea coastal region...
near the Equator
Equator
An equator is the intersection of a sphere's surface with the plane perpendicular to the sphere's axis of rotation and containing the sphere's center of mass....
presenting variations within five natural regions
Natural regions of Colombia
Because of its natural structure, Colombia can be divided into six very distinct natural regions. These consist of the Andean region, covering the three branches of the Andes mountains found in Colombia; the Caribbean region, covering the area adjacent to the Caribbean sea; the Pacific region...
and depending on the altitude, temperature, humidity, winds and rainfall. Each region maintains an average temperature throughout the year only presenting variables determined by precipitation
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation...
during a rainy season caused by the Intertropical Convergence Zone
Intertropical Convergence Zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone , known by sailors as The Doldrums, is the area encircling the earth near the equator where winds originating in the northern and southern hemispheres come together....
.
Factors
Factors that specifically determine the climate of this land can be classified by geographical and atmospheric: there are 33 factors in ColombiaGeographical
The geographical factors are determined by latitudeLatitude
In geography, the latitude of a location on the Earth is the angular distance of that location south or north of the Equator. The latitude is an angle, and is usually measured in degrees . The equator has a latitude of 0°, the North pole has a latitude of 90° north , and the South pole has a...
or altitude. Colombia is crossed by the equator
Equator
An equator is the intersection of a sphere's surface with the plane perpendicular to the sphere's axis of rotation and containing the sphere's center of mass....
in its southern part, but the majority of the territory is part of the northern hemisphere
Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of a planet that is north of its equator—the word hemisphere literally means “half sphere”. It is also that half of the celestial sphere north of the celestial equator...
and within the torrid zone
Torrid Zone
Torrid Zone is a 1940 adventure film starring James Cagney, Ann Sheridan and Pat O'Brien.-Plot summary:Steve Case has to deal with trouble at his tropical fruit company's Central American banana plantation...
which is characterized for receiving direct sunlight throughout the year. A considerable area of Colombia is mountainous, mainly crossed by the Andes
Andes
The Andes is the world's longest continental mountain range. It is a continual range of highlands along the western coast of South America. This range is about long, about to wide , and of an average height of about .Along its length, the Andes is split into several ranges, which are separated...
mountain range from south to north. Altitude in this mountains counter rest the effects of the latitude characteristics producing gradual variable climates from tropical foothills and coastlines to perpetual snow peaks. In Colombia these are classified as "thermal floors" .

Andes
The Andes is the world's longest continental mountain range. It is a continual range of highlands along the western coast of South America. This range is about long, about to wide , and of an average height of about .Along its length, the Andes is split into several ranges, which are separated...
and other mountain ranges, that is the case of Lloró
Lloró
Lloró is a municipality and town in the Chocó Department, Colombia. It holds the world record for highest average annual precipitation, estimated at 523.6 inches . If accurate, that would make it the wettest place in the world. The Spanish verb llorar "to cry" can also be used as a metaphor for...
in Chocó Department
Chocó Department
Chocó is a department of Colombia known for its large Afro-Colombian population. It is in the west of the country, and is the only Colombian department to have coastlines on both the Pacific Ocean and the Atlantic Ocean. It also has all of Colombia's border with Panama. Its capital is...
which is one of the rainiest lowlands in the world. The contrary occurs with the trade winds from the northeast that also crosses Colombia penetrating without any mountainous ranges the valleys of the Magdalena
Magdalena River
The Magdalena River is the principal river of Colombia, flowing northward about through the western half of the country. It takes its name from the biblical figure Mary Magdalene. It is navigable through much of its lower reaches, in spite of the shifting sand bars at the mouth of its delta, as...
and Cauca
Cauca River
The Cauca River is a river in Colombia that lies between the Occidental and Central cordilleras. Born in southwestern Colombia near the city of Popayán, it joins the Magdalena River near Pinillos in Bolívar Department, and the combined river eventually flows out into the Caribbean Sea. It has a...
rivers, and also the trade winds from the southeast that cover the Amazon region
Amazon Region of Colombia
The Amazonía Region is a region in southern Colombia. It comprises the departments of Amazonas, Caquetá, Guainía, Guaviare, Putumayo and Vaupés, and covers an area of 403,000 km², 35% of Colombia's total territory...
only blocked by the Andes mountains. In the case of the Guajira Peninsula
Guajira Peninsula
Guajira Peninsula , is a peninsula in northern Colombia and northwestern Venezuela in the Caribbean Sea...
plains, the trade winds are unable to be stopped (despite having a low altitude range of mountains; the Serranía de Macuira
Serranía de Macuira
Serranía de Macuira is a mountain range in northern Colombia located in the municipality of Uribia, Guajira Peninsula and part of the La Guajira Department. The Serrania de Macuira stands in the middle of the La Guajira Desert at 864 meters over sea level, isolated from the mountain ranges of...
) and continue traveling inland towards Colombia's central regions, for this reason the Guajira area present a dry climate and produced the Guajira desert
La Guajira Desert
La Guajira Desert is located in the northernmost part of Colombia, north of Bogota, in the La Guajira Department, covering most of La Guajira Peninsula including Venezuelan territory. The area holds immense coal reserves, exploited in a zone known as El Cerrejon...
. For this reason the numerous mountains present in Colombia produce a varied climate and subregions.
Atmospheric
The atmospheric factors are determined by temperature, humidity and winds. The temperature is relatively average throughout the year in a same place. The tropical location of Colombia and the uniform solar radiation for being in the equator gives this country an almost constant temperature. The atmosphere varies due to the altitude in the mountains and its proximity to sea level.Humidity in Colombia is diverse and is characteristic of each region and subregion. This is produced by altitude, temperature, vegetation and water presence. The Pacific
Pacific Region of Colombia
The Pacific Region is one of the five major natural regions of the Colombian geography. The Pacific region covers the area near the Pacific Ocean in Colombia that contains certain endemic species and ecosystems accompanied by Colombian cultural influence....
, Amazon
Amazon Region of Colombia
The Amazonía Region is a region in southern Colombia. It comprises the departments of Amazonas, Caquetá, Guainía, Guaviare, Putumayo and Vaupés, and covers an area of 403,000 km², 35% of Colombia's total territory...
and Orinoquía
Orinoquía Region of Colombia
The Orinoquía Region is one of the five natural regions of Colombia. It is also known colloquially as Eastern Plains from the Spanish Llanos Orientales. The region covers most of the area of the departments of Meta, Arauca, Casanare and Vichada. The region is rich in oil and is apt for extensive...
regions are the rainiest and the lowest and dries are in the northern part of the Caribbean region, in Uribia, Guajira in the Guajira desert
La Guajira Desert
La Guajira Desert is located in the northernmost part of Colombia, north of Bogota, in the La Guajira Department, covering most of La Guajira Peninsula including Venezuelan territory. The area holds immense coal reserves, exploited in a zone known as El Cerrejon...
.

Climate zones
The diversity of climates in Colombia is characterized for having tropical rainforestTropical rainforest
A tropical rainforest is an ecosystem type that occurs roughly within the latitudes 28 degrees north or south of the equator . This ecosystem experiences high average temperatures and a significant amount of rainfall...
s, savanna
Savanna
A savanna, or savannah, is a grassland ecosystem characterized by the trees being sufficiently small or widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground to support an unbroken herbaceous layer consisting primarily of C4 grasses.Some...
s, steppe
Steppe
In physical geography, steppe is an ecoregion, in the montane grasslands and shrublands and temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biomes, characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes...
s, desert
Desert
A desert is a landscape or region that receives an extremely low amount of precipitation, less than enough to support growth of most plants. Most deserts have an average annual precipitation of less than...
s and mountain climate, this last one further subdivided into tierra caliente
Tierra caliente
Tierra caliente is a pseudo-climatalogical term used in Latin America to refer to those places within that realm which have a distinctly tropical climate...
(hot land) tierra templada
Tierra templada
Tierra templada is a pseudoclimatological term used in Latin America to refer to places within that realm which are either located in the tropics at a moderately high elevation, or are marginally outside the astronomical tropics, producing a somewhat cooler overall climate than that found in the...
(temperate land) tierra fria
Tierra fría
Tierra fría is a pseudoclimatological term used in parts of Latin America to refer to mountain locations within that cultural realm, where high elevation results in a markedly cooler climate than that encountered in the lowlands at a comparable latitude.To a climatologist, the term is inaccurate,...
(cold land), tierra helada
Tierra helada
Tierra helada is a term used in Latin America to refer to the highest places found within the Andes mountains.Tierra helada is for the Montane grasslands and shrublands, Sunis, Punas and Paramos between the Treeline and the Snow line...
(frozen land) and Páramo
Páramo
The term páramo can refer to a variety of ecosystems. Some ecologists describe the páramo broadly as “all high, tropical, montane vegetation above the continuous timberline”. A more narrow term classifies the páramo according to its regional placement - specifically located in “the northern Andes...
.
Tropical rainforest
The tropical rainforest climateTropical rainforest climate
A tropical rainforest climate, also known as an equatorial climate, is a tropical climate usually found along the equator...
is characterized by hot and high humidity climate along with heavy rainfall mostly present in the jungle
Jungle
A Jungle is an area of land in the tropics overgrown with dense vegetation.The word jungle originates from the Sanskrit word jangala which referred to uncultivated land. Although the Sanskrit word refers to "dry land", it has been suggested that an Anglo-Indian interpretation led to its...
s of the Catatumbo, the Amazon river basin
Amazon River
The Amazon of South America is the second longest river in the world and by far the largest by waterflow with an average discharge greater than the next seven largest rivers combined...
the central region of the Magdalena River
Magdalena River
The Magdalena River is the principal river of Colombia, flowing northward about through the western half of the country. It takes its name from the biblical figure Mary Magdalene. It is navigable through much of its lower reaches, in spite of the shifting sand bars at the mouth of its delta, as...
, the pacific coast
Pacific Coast
A country's Pacific coast is the part of its coast bordering the Pacific Ocean.-The Americas:Countries on the western side of the Americas have a Pacific coast as their western border.* Geography of Canada* Geography of Chile* Geography of Colombia...
, the Serrania del Perija
Serrania del Perija
The Serranía del Perijá, Cordillera de Perijá or Sierra de Perijá is a mountain range, an extension of the eastern Andean branch , in northern South America, between Colombia and Venezuela, ending further north in the Guajira Desert, a total distance of about 310 km...
and others.
Tropical savanna
The semi-humid tropical savanna climateTropical savanna climate
Tropical savanna climate or tropical wet and dry climate is a type of climate that corresponds to the Köppen climate classification categories "Aw" and '"As."...
is characterized for being between 24 and 27 °C (75.2 and 80.6 °F) with a variation in climate of two seasons; a rainy season and a dry season (produced by the trade winds from the northeast) each enduring a period of six months. Regions in Colombia with this climate characteristic are the Llanos
Llanos
The Llanos is a vast tropical grassland plain situated to the east of the Andes in Colombia and Venezuela, in northwestern South America. It is an ecoregion of the Flooded grasslands and savannas Biome....
(eastern plains), some section of the Caribbean plains near the coast, sections of the Magdalena and Cauca river valleys.
Steppe
The steppe climate is characterized for having a very few vegetation limits and minimum precipitations and can also include the desert climate for a period of 5 months of dry season. This type of weather is characteristic of the plains of BolívarBolívar Department
Bolívar is a department of Colombia. It was named after one of the original nine states of the United States of Colombia. It is located to the north of the country, extending from the coast at Cartagena near the mouth of the Magdalena River, then south along the river to a border with Antioquia.Its...
and the northern Guajira (Serranía de Macuira
Serranía de Macuira
Serranía de Macuira is a mountain range in northern Colombia located in the municipality of Uribia, Guajira Peninsula and part of the La Guajira Department. The Serrania de Macuira stands in the middle of the La Guajira Desert at 864 meters over sea level, isolated from the mountain ranges of...
), the central area of the Orinoquía region
Orinoquía Region of Colombia
The Orinoquía Region is one of the five natural regions of Colombia. It is also known colloquially as Eastern Plains from the Spanish Llanos Orientales. The region covers most of the area of the departments of Meta, Arauca, Casanare and Vichada. The region is rich in oil and is apt for extensive...
and the higher grounds of the Andes mountain range.
Tropical desert
.jpg)
The tropical desert climate
Desert climate
A desert climate , also known as an arid climate, is a climate that does not meet the criteria to be classified as a polar climate, and in which precipitation is too low to sustain any vegetation at all, or at most a very scanty scrub.An area that features this climate usually experiences less than...
in Colombia is present in the Guajira
La Guajira Desert
La Guajira Desert is located in the northernmost part of Colombia, north of Bogota, in the La Guajira Department, covering most of La Guajira Peninsula including Venezuelan territory. The area holds immense coal reserves, exploited in a zone known as El Cerrejon...
and Tatacoa desert
Tatacoa Desert
The Tatacoa Desert, the second largest arid zone in Colombia after the Guajira Peninsula, is one of the most attractive scenery Colombia occupies 330 square kilometers of land in ocher and gray brushstrokes of green cactus...
s characterized for their high temperatures and scarce precipitations. The trade winds from the northeast carry humidity from the oceans and without a mountain barrier nearby continue flowing without dropping any rainfall and eventually creating droughts.
Tropical mountain climate
Mountain climate is one of the unique features of the AndesAndes
The Andes is the world's longest continental mountain range. It is a continual range of highlands along the western coast of South America. This range is about long, about to wide , and of an average height of about .Along its length, the Andes is split into several ranges, which are separated...
, the Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta
Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta
The Sierra Nevada de Santa Marta is an isolated mountain range apart from the Andes chain that runs through Colombia. Reaching an altitude of 5,700 metres above sea level just 42 km from the Caribbean coast, the Sierra Nevada is the world's highest coastal range...
and other high altitude reliefs where climate is determined by elevation. These variations in climate depending on its altitude are called thermal floors , a classification used in some countries but with variations in the classification of each floor.
Warm climate thermal floor:
The warm thermal floor oscillate between sea level and 1000 metres (3,281 ft) above sea level with a temperature over 24 °C (75.2 °F). Climate in this step is characterized for its similarities with the equatorial and tropical plains, heavy rains and high temperatures. Temperatures can reach over 29 °C (84.2 °F) as it is the case of the Magdalena river valley, which has many areas with jungles. This thermal floor is present in the cities like Santa Marta
Santa Marta
Santa Marta is the capital city of the Colombian department of Magdalena in the Caribbean Region. It was founded in July 29, 1525 by the Spanish conqueror Rodrigo de Bastidas, which makes it the oldest remaining city in Colombia...
, Neiva, Cali
Calì
Calì, also written in English as Cali, is an Italian surname, widespread mainly in the Ionian side of Sicily.For the surname Calì is assumed the origin of the Greek word kalos , or from its Sanskrit root kali, "time."The surname refers to:...
and Cúcuta
Cúcuta
Cúcuta is a Colombian city, capital of Norte de Santander, in the northeast of the country. Due to its proximity to the Colombian-Venezuelan border, Cúcuta is an important commercial center. The city has the constitutional category of Special District. It is located at the most active...
.
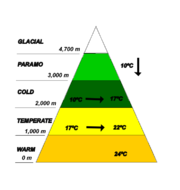
Between 1000 and 2000 m (3,280.8 and 6,561.7 ft) above sea level the temperature drops oscillating between 17 and 22 °C (62.6 and 71.6 °F) defining it as a temperate climate. Rainfall becomes variable at 1700 metres (5,577 ft) above sea level and rains between 2000 and 2500 mm (78.7 and 98.4 in) . This climate is a characteristic in the cities like Pereira
Pereira, Colombia
Pereira is the capital city of the Colombian department of Risaralda. It stands in the center of the western region of the country, located in a small valley that descends from a part of the western Andes mountain chain. Its strategic location in the coffee producing area makes the city an urban...
, Armenia
Armenia, Colombia
Armenia is the capital of Quindío, a department in Colombia. The city is located at coordinates 4.5170° north, 75.6830° west, 290 kilometers west of Bogotá. Armenia is a mid-size city located between Bogotá, Medellín and Cali, the 3 largest Colombian cities. The city's area code for phone calls is...
, Ibague
Ibagué
Ibagué is the capital of the department of Tolima in Colombia. It is situated 1,285 m above sea level, on the eastern slopes of the Cordillera Central between the Chipalo and Combeima rivers, tributaries of the Coello River...
Popayán
Popayán
Popayán is the capital of the Colombian department of Cauca. It is located in southwestern Colombia between Colombia's Western Mountain Range and Central Mountain Range...
and Medellín
Medellín
Medellín , officially the Municipio de Medellín or Municipality of Medellín, is the second largest city in Colombia. It is in the Aburrá Valley, one of the more northerly of the Andes in South America. It has a population of 2.3 million...
.
Cold climate thermal floor:
The cold climate is present between 2000 and 3000 m (6,561.7 and 9,842.5 ft) above sea level and is characterized for having Andean or cloud forest
Cloud forest
A cloud forest, also called a fog forest, is a generally tropical or subtropical evergreen montane moist forest characterized by a persistent, frequent or seasonal low-level cloud cover, usually at the canopy level. Cloud forests often exhibit an abundance of mosses covering the ground and...
s. This thermal floor is characterized for presenting an average temperature ranging between 10 and 17 °C (50 and 62.6 °F) while rainfall reaches a yearly average of 2000 mm (78.7 in). The Colombian capital city Bogotá
Bogotá
Bogotá, Distrito Capital , from 1991 to 2000 called Santa Fé de Bogotá, is the capital, and largest city, of Colombia. It is also designated by the national constitution as the capital of the department of Cundinamarca, even though the city of Bogotá now comprises an independent Capital district...
is located within this thermal floor. Other cities like San Juan de Pasto and Tunja
Tunja
Tunja is a city and municipality located in the central part of Colombia, in the region of "Alto Chicomocha". As of the 2005 Census it had 152,419 inhabitants. It is the capital of the Department of Boyacá and part of the subregion of the Central Boyacá Province. It is approximately 145 km...
are in this location.
Paramo climate thermal floor:
The Páramo
Páramo
The term páramo can refer to a variety of ecosystems. Some ecologists describe the páramo broadly as “all high, tropical, montane vegetation above the continuous timberline”. A more narrow term classifies the páramo according to its regional placement - specifically located in “the northern Andes...
climate is present between 3000 and 4000 m (9,842.5 and 13,123.4 ft) above sea level and the temperature is lower than 10 °C (50 °F) with icy winds, rare rainfall but frequent snowfall. Colombia has one of the largest páramo areas in the world; the Páramo of Sumapaz located in central Colombia, over the Andean
Andes
The Andes is the world's longest continental mountain range. It is a continual range of highlands along the western coast of South America. This range is about long, about to wide , and of an average height of about .Along its length, the Andes is split into several ranges, which are separated...
Cordillera Oriental branch. In Colombia páramos are further classified as subpáramo, páramo and superpáramo. Most of the rivers in Colombia are born here since páramos tend to hold water from precipitations and deglaciations coming from the peaks.
Glacial climate thermal floor:
The glacier
Glacier
A glacier is a large persistent body of ice that forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. At least 0.1 km² in area and 50 m thick, but often much larger, a glacier slowly deforms and flows due to stresses induced by its weight...
s in Colombia are located at 4000 metres (13,123 ft) above sea level and up and with average temperatures ranging between 10 °C (50 °F) and less. Glaciers in Colombia began retreating in the 20th century due to global warming
Global warming
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans and its projected continuation. In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades...
and are in danger of disappearing, if this occurs water supply would be scarce in the near future. Most of the glaciers are located in the Andes mountains and are inhabited by very few living species due to its sever weather.

