
Cambridge Bio-Medical Campus
Encyclopedia
Cambridge Bio-Medical Campus, located at the southwest end of Hills Road
on the southern edge of Cambridge
, England
, is one of the largest centres of health science and medical research in Europe
. Managed by the University of Cambridge
, the site is funded by organisations such as Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
, the Wellcome Trust
, Cancer Research UK
, and the UK government's Medical Research Council
. It is home to Addenbrooke's Hospital
and the university's medical school
.

 Addenbrooke's Hospital
Addenbrooke's Hospital
is a large teaching hospital
, and the central focus of the campus.
, established in 1976. (See main article).
research institute funded by the UK Medical Research Council
. It was founded in Cambridge 1947 as the Unit for Research on the Molecular Structure of Biological Systems and moved to its current site at Addenbrookes Hospital in 1962. The laboratory has won nine nobel prizes and including the 1962 prize for Physiology or Medicine awarded for the discovery of the double-helix
structure of DNA
.
A new building to house the LMB is currently being constructed on the Cambridge Bio-Medical Campus site and is due for completion in 2012.
was created in 1995 to develop and apply advanced imaging methods to patients with traumatic brain injury. It is unique in being co-located with the Neurosciences Critical Care Unit of Addenbrooke's Hospital
. Since its establishment it has become an internationally leading Positron Emission Tomography
and Magnetic Resonance Imaging
centre.
and is home to four main areas of research:
The centre was officially opened by Queen Elizabeth II in February 2007.
and disease, intracellular membrane traffic, autoimmune disease
and haematopoietic stem cell biology.
Cancer Cell Unit, and the University of Cambridge "Cambridge Molecular Therapeutics Programme".
is scheduled to relocate onto the Cambridge Bio-Medical Campus in 2013.
Hills Road, Cambridge
This article is about the street. For the Sixth Form College commonly known as "Hills Road", see Hills Road Sixth Form CollegeHills Road is an arterial road in southeast Cambridge, England...
on the southern edge of Cambridge
Cambridge
The city of Cambridge is a university town and the administrative centre of the county of Cambridgeshire, England. It lies in East Anglia about north of London. Cambridge is at the heart of the high-technology centre known as Silicon Fen – a play on Silicon Valley and the fens surrounding the...
, England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
, is one of the largest centres of health science and medical research in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
. Managed by the University of Cambridge
University of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a public research university located in Cambridge, United Kingdom. It is the second-oldest university in both the United Kingdom and the English-speaking world , and the seventh-oldest globally...
, the site is funded by organisations such as Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust
The Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust is one of the United Kingdom's 79 NHS Foundation Trusts.The Trust provides healthcare for people in the Cambridge area, in southeast England...
, the Wellcome Trust
Wellcome Trust
The Wellcome Trust was established in 1936 as an independent charity funding research to improve human and animal health. With an endowment of around £13.9 billion, it is the United Kingdom's largest non-governmental source of funds for biomedical research...
, Cancer Research UK
Cancer Research UK
Cancer Research UK is a cancer research and awareness charity in the United Kingdom, formed on 4 February 2002 by the merger of The Cancer Research Campaign and the Imperial Cancer Research Fund. Its aim is to reduce the number of deaths from cancer. As the world's largest independent cancer...
, and the UK government's Medical Research Council
Medical Research Council (UK)
The Medical Research Council is a publicly-funded agency responsible for co-ordinating and funding medical research in the United Kingdom. It is one of seven Research Councils in the UK and is answerable to, although politically independent from, the Department for Business, Innovation and Skills...
. It is home to Addenbrooke's Hospital
Addenbrooke's Hospital
Addenbrooke's Hospital is an internationally renowned teaching hospital in Cambridge, England, with strong links to the University of Cambridge. It was founded in 1766 on Trumpington Street with £4,500 from the will of Dr John Addenbrooke, a fellow of St Catharine's College...
and the university's medical school
School of Clinical Medicine, University of Cambridge
The School of Clinical Medicine is the medical school of the University of Cambridge in England. According to QS World University Rankings 2010, it currently ranks as second best in the world....
.

Constituent institutes
The Cambridge Bio-Medical Campus is home to the following institutes.Addenbrooke's Hospital

Addenbrooke's Hospital
Addenbrooke's Hospital is an internationally renowned teaching hospital in Cambridge, England, with strong links to the University of Cambridge. It was founded in 1766 on Trumpington Street with £4,500 from the will of Dr John Addenbrooke, a fellow of St Catharine's College...
is a large teaching hospital
Teaching hospital
A teaching hospital is a hospital that provides clinical education and training to future and current doctors, nurses, and other health professionals, in addition to delivering medical care to patients...
, and the central focus of the campus.
The University of Cambridge School of Clinical Medicine
Cambridge University's Medical SchoolMedical school
A medical school is a tertiary educational institution—or part of such an institution—that teaches medicine. Degree programs offered at medical schools often include Doctor of Osteopathic Medicine, Bachelor/Doctor of Medicine, Doctor of Philosophy, master's degree, or other post-secondary...
, established in 1976. (See main article).
The MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology
The LMB is a molecular biologyMolecular biology
Molecular biology is the branch of biology that deals with the molecular basis of biological activity. This field overlaps with other areas of biology and chemistry, particularly genetics and biochemistry...
research institute funded by the UK Medical Research Council
Medical Research Council (UK)
The Medical Research Council is a publicly-funded agency responsible for co-ordinating and funding medical research in the United Kingdom. It is one of seven Research Councils in the UK and is answerable to, although politically independent from, the Department for Business, Innovation and Skills...
. It was founded in Cambridge 1947 as the Unit for Research on the Molecular Structure of Biological Systems and moved to its current site at Addenbrookes Hospital in 1962. The laboratory has won nine nobel prizes and including the 1962 prize for Physiology or Medicine awarded for the discovery of the double-helix
Nucleic acid double helix
In molecular biology, the term double helix refers to the structure formed by double-stranded molecules of nucleic acids such as DNA and RNA. The double helical structure of a nucleic acid complex arises as a consequence of its secondary structure, and is a fundamental component in determining its...
structure of DNA
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a nucleic acid that contains the genetic instructions used in the development and functioning of all known living organisms . The DNA segments that carry this genetic information are called genes, but other DNA sequences have structural purposes, or are involved in...
.
A new building to house the LMB is currently being constructed on the Cambridge Bio-Medical Campus site and is due for completion in 2012.
The Wolfson Brain Imaging Centre
The Wolfson Brain Imaging CentreWolfson Brain Imaging Centre
The Wolfson Brain Imaging Centre is a leading UK Biomedical Imaging Centre, located at Addenbrooke's Hospital, Cambridge, England, on the Cambridge Bio-Medical Campus at the southwestern end of Hills Road. It is a division of the Department of Clinical Neurosciences of the University of...
was created in 1995 to develop and apply advanced imaging methods to patients with traumatic brain injury. It is unique in being co-located with the Neurosciences Critical Care Unit of Addenbrooke's Hospital
Addenbrooke's Hospital
Addenbrooke's Hospital is an internationally renowned teaching hospital in Cambridge, England, with strong links to the University of Cambridge. It was founded in 1766 on Trumpington Street with £4,500 from the will of Dr John Addenbrooke, a fellow of St Catharine's College...
. Since its establishment it has become an internationally leading Positron Emission Tomography
Positron emission tomography
Positron emission tomography is nuclear medicine imaging technique that produces a three-dimensional image or picture of functional processes in the body. The system detects pairs of gamma rays emitted indirectly by a positron-emitting radionuclide , which is introduced into the body on a...
and Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
centre.
Cancer Research UK Cambridge Research Institute
The Cancer Research UK Cambridge Research Institute or "CRI" is principally funded by Cancer Research UKCancer Research UK
Cancer Research UK is a cancer research and awareness charity in the United Kingdom, formed on 4 February 2002 by the merger of The Cancer Research Campaign and the Imperial Cancer Research Fund. Its aim is to reduce the number of deaths from cancer. As the world's largest independent cancer...
and is home to four main areas of research:
- Basic research, which involves looking into the cellularCell (biology)The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
and molecular biology of cancer. - Research into molecular imagingMolecular imagingMolecular imaging originated from the field of radiopharmacology due to the need to better understand the fundamental molecular pathways inside organisms in a noninvasive manner.- Overview :...
, genomicsGenomicsGenomics is a discipline in genetics concerning the study of the genomes of organisms. The field includes intensive efforts to determine the entire DNA sequence of organisms and fine-scale genetic mapping efforts. The field also includes studies of intragenomic phenomena such as heterosis,...
, bioinformaticsBioinformaticsBioinformatics is the application of computer science and information technology to the field of biology and medicine. Bioinformatics deals with algorithms, databases and information systems, web technologies, artificial intelligence and soft computing, information and computation theory, software...
and biomolecular modeling. - Research that focuses on specific cancer sites, forming a bridge between the clinical and laboratory areas.
- Clinical investigations and trialsClinical trialClinical trials are a set of procedures in medical research and drug development that are conducted to allow safety and efficacy data to be collected for health interventions...
, including population based studies into screening and prevention.
The centre was officially opened by Queen Elizabeth II in February 2007.
The Cambridge Institute for Medical Research
The CIMR is a cross-departmental institute in the University of Cambridge, receiving funding from the Wellcome Trust. Research is focused on four main areas: misfolded proteinsProtein folding
Protein folding is the process by which a protein structure assumes its functional shape or conformation. It is the physical process by which a polypeptide folds into its characteristic and functional three-dimensional structure from random coil....
and disease, intracellular membrane traffic, autoimmune disease
Autoimmune disease
Autoimmune diseases arise from an overactive immune response of the body against substances and tissues normally present in the body. In other words, the body actually attacks its own cells. The immune system mistakes some part of the body as a pathogen and attacks it. This may be restricted to...
and haematopoietic stem cell biology.
The Hutchison/MRC Research Centre
The Hutchison/MRC Research Centre is a cancer research centre housing researchers from the University of Cambridge Department of Oncology, the MRCMedical Research Council (UK)
The Medical Research Council is a publicly-funded agency responsible for co-ordinating and funding medical research in the United Kingdom. It is one of seven Research Councils in the UK and is answerable to, although politically independent from, the Department for Business, Innovation and Skills...
Cancer Cell Unit, and the University of Cambridge "Cambridge Molecular Therapeutics Programme".
The Rosie Maternity Hospital
The Rosie Hospital is Cambridge's first purpose-built maternity hospital, opened in October 1983.MRC Mitochondrial Biology Unit
The MBU is funded by the Medical Research Council and is focused on research to understand mitochondrial process and their involvement in human diseases. It is co-located with the Cambridge Institute for Medical Research in the Wellcome Trust/MRC Building.Institute of Metabolic Science
The Institute of Metabolic Science (IMS) is dedicated to research, education, prevention and clinical care in the areas of diabetes, obesity and related metabolic and endocrine diseases.The Brain Repair Centre
Adjacent to the Institute of Public Health, Cambridge Centre for Brain Repair is a subsidiary of the University of Cambridge Department of Clinical Neurosciences. It is a research institute aiming to "understand, and eventually to alleviate and repair damage to the brain and spinal cord which results from injury or neurodegenerative disease."Institute for Public Health
The Institute for Public Health is a partnership between Cambridge University, the MRC and the NHS. It was created in 1993 to study disease in the population and to identify, evaluate and monitor public healthcare interventions.New Papworth Hospital
Papworth HospitalPapworth Hospital
Papworth Hospital is a heart and lung hospital in Cambridgeshire, England. It was home to the first successful heart transplant in the UK and one of the world's first beating-heart transplants.-History:...
is scheduled to relocate onto the Cambridge Bio-Medical Campus in 2013.
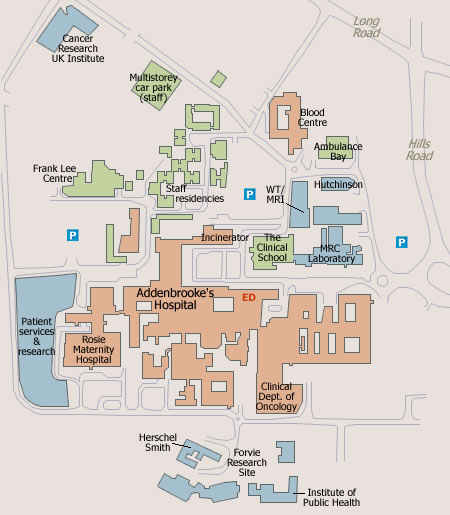
Site map
Below is a map which gives an idea of the scale of the site and the locations of the departments. Research facilities are highlighted in blue, hospital facilities in red and general facilities in green:

