1911 Atlantic hurricane season
Encyclopedia
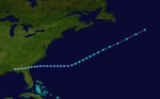
The 1911 Atlantic hurricane season was relatively inactive, with only six known tropical cyclones forming in the Atlantic during the summer and fall. There were three suspected tropical depressions, including one that began the season in February and one that ended the season when it dissipated in December. Three storms intensified into hurricanes, two of which attained Category 2 status on the modern-day Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Scale. Storm data is largely based on the Atlantic hurricane database
, which underwent a thorough revision for the period between 1911 and 1914 in 2005.
Most of the cyclones directly impacted land. A westward-moving hurricane killed 17 people and severely damaged Charleston, South Carolina
, and the surrounding area in late August. A couple of weeks earlier, the Pensacola, Florida
, area suffered from a storm in the Gulf of Mexico
that produced winds of 80 mph (128.7 km/h) over land. The fourth storm of the season struck the coast of Nicaragua
, killing 10 and causing extensive damage.
hurricane database (HURDAT) officially recognizes six tropical cyclones from the 1911 season. Only three attained hurricane status, with winds of 75 mph (120.7 km/h) or greater. The third hurricane of the season was the most intense storm, with a minimum central air pressure of 972 mbar (28.7 inHg). A week after its dissipation, another hurricane formed with wind speeds that matched the previous storm, but with unknown air pressure. Three weak tropical depressions developed and remained below tropical storm force; the first formed in February and the third in December. The first storm to reach tropical storm intensity developed on August 4, and the final tropical storm of the year dissipated on October 31.
The early 1900s lacked modern forecasting and documentation. The hurricane database from these years is sometimes found to be incomplete or incorrect, and new storms are continually being added as part of the ongoing Atlantic hurricane reanalysis
. The period from 1911 through 1914 was reanalyzed in 2005. Two previously unknown tropical cyclones were identified using records including historical weather maps and ship reports, and information on the known storms was amended and corrected. These storms are referred to simply by their number in chronological order, since tropical cyclones in the Atlantic Ocean were not given official names until much later.
and closed circulation center, the first tropical cyclone of the 1911 season formed on August 4 over southern Alabama
in the United States
. At only tropical depression strength, it tracked eastward and emerged into the Atlantic Ocean
the next day. Several days later, while located near Bermuda
, the depression became a tropical storm and turned northeastward. The storm lasted several more days until dissipating on August 11. The storm produced heavy rainfall on the Bermuda, but no gale-force winds were reported. The storm was unknown until the 2005 Atlantic hurricane database revision recognized it as a tropical storm.
and drifted westward. Early the next day it intensified into a tropical storm and began accelerating toward the northwest. As it approached the U.S. Gulf Coast, the cyclone attained maximum sustained winds estimated at 80 mph (130 km/h), corresponding to Category 1 status on the modern-day Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Scale. Pushing ashore near the Alabama–Florida border, it weakened over land and curved toward the west. On August 12, the storm drifted over Louisiana
and Texas
, where it produced heavy rainfall.
During the evening of August 11, 1911, winds blew at up to 80 mph (128.7 km/h) at Pensacola, Florida
, where pressure dropped to 29.73 inHg (1,006.8 mbar). A lull in the storm accompanied the nearby passage of its eye
before conditions once again deteriorated. Total rainfall from the storm amounted to 4.48 in (113.8 mm). The winds brought down telephone and telegraph wires, cutting off communication to outside areas for 24 hours. The city also suffered power failures on the night of August 11. Shipping suffered heavy losses, with many barges blown aground. The hurricane dispersed "immense quantities" of lumber being stored along the coast. An unspecified number of deaths were caused by the hurricane, and despite the damage, an August 1911 issue of the Monthly Weather Review
described the storm's effects as lighter than expected, estimating total damage in Pensacola at $12,000 (1911 USD, $280,000 2011 USD). Mobile, Alabama
, recorded 35 mph (56.3 km/h) winds and no damage.
, on August 28; upon making landfall, the hurricane rapidly degenerated. It deteriorated into a tropical depression on August 29 and persisted over land until dissipating a couple of days later.
The hurricane, relatively small in size, caused widespread damage between Savannah and Charleston, South Carolina
. Savannah itself received only minor damage, although the storm's center passed close by. Along the coast of Georgia
, torrential rainfall caused numerous washouts on railroads. Crops, livestock and roads in the area suffered heavy damage. At Charleston, winds were estimated at 106 mph (170.6 km/h) after an anemometer
, last reporting 94 mph (151.3 km/h), failed, and 4.9 in (124.5 mm) of precipitation fell over three days.
The storm raged for more than 36 hours, causing severe damage; the winds unroofed hundreds of buildings, demolished many houses and had an extensive impact on power and telephone services. Tides 10.6 ft (3.2 m) above normal left a "confused mass of wrecked vessels and damaged wharfs", according to a local forecaster in Charleston, while six navy torpedo boats were ripped from their moorings and blown ashore. In total, 17 people were killed in the hurricane, and property damage in Charleston was estimated at $1 million (1911 USD, $ USD).
on September 3 and moved westward, attaining tropical storm status about a day later. The storm slowed and curved toward the southwest, nearing the northern coast of Colombia
before pulling away from land and strengthening into a hurricane. It further intensified to Category 2 status before striking Nicaragua
on September 10. Quickly weakening to a tropical storm, the cyclone continued westward across Central America
and briefly entered the eastern Pacific Ocean
. It dissipated shortly thereafter. In the town of Corinto
, a report indicated the deaths of 10 people and 50 additional injuries. About 250 houses were destroyed, leaving approximately $2 million (1911 USD, $ USD) in damage. Data on this storm is extremely scarce; as such, only minor revisions could be made to its chronology in the hurricane database.
status according to the modern classification scheme. On September 15, the storm formed over the central Atlantic and initially moved westward. It gradually intensified as it turned northwestward, and on September 19 it transitioned into an extratropical cyclone
southeast of New England
. The system was subsequently absorbed by a more powerful frontal boundary approaching from the northwest.
in the Caribbean Sea
in late October. The disturbance was the precursor to a tropical depression which developed over the southern Bahamas and headed west-southwestward across Cuba
, where, at Havana, winds blew from the southeast at 44 mph (70.8 km/h). It became a tropical storm on October 27 and drifted southwestward. Near the eastern tip of the Yucatán Peninsula
, the storm turned sharply northward. An area of high pressure
over the United States
prevented the cyclone from turning eastward toward Florida, and it continued into the Gulf of Mexico
. However, on October 31, the storm curved eastward and moved ashore over northern Florida. The storm decreased in intensity as it passed into the Atlantic. The storm's circulation center remained poorly defined throughout its course. It was long believed to have developed south of Cuba, although a reevaluation of ship data indicated the depression had actually formed east of the island. On October 26, the Weather Bureau hoisted hurricane warnings along the east coast of Florida from Key West
to West Palm Beach
, and on the west coast up to Tampa
.
of low pressure in the open Atlantic and progressed westward. Although a ship dubiously reported winds of over 50 mph (80.5 km/h) in association with the system, a lack of supporting evidence precludes its designation as a tropical storm. The cyclone dissipated by February 21. The second depression evolved from an extratropical cyclone
in mid- to late May, becoming a tropical cyclone on May 22 northeast of Bermuda. It persisted for three days as it meandered around the same general area before being absorbed by another non-tropical storm. The modern-day documentation of this system was also hindered by a lack of data. On December 11, the third tropical depression formed near the Turks and Caicos Islands
. It progressed westward and was situated just north of eastern Cuba the next day. The system began to weaken on December 13 and dissipated shortly thereafter.
HURDAT
The North Atlantic hurricane database, or HURDAT, is the database for all tropical cyclones in the Atlantic Ocean, Gulf of Mexico and Caribbean Sea, since 1851.-History:...
, which underwent a thorough revision for the period between 1911 and 1914 in 2005.
Most of the cyclones directly impacted land. A westward-moving hurricane killed 17 people and severely damaged Charleston, South Carolina
Charleston, South Carolina
Charleston is the second largest city in the U.S. state of South Carolina. It was made the county seat of Charleston County in 1901 when Charleston County was founded. The city's original name was Charles Towne in 1670, and it moved to its present location from a location on the west bank of the...
, and the surrounding area in late August. A couple of weeks earlier, the Pensacola, Florida
Pensacola, Florida
Pensacola is the westernmost city in the Florida Panhandle and the county seat of Escambia County, Florida, United States of America. As of the 2000 census, the city had a total population of 56,255 and as of 2009, the estimated population was 53,752...
, area suffered from a storm in the Gulf of Mexico
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a partially landlocked ocean basin largely surrounded by the North American continent and the island of Cuba. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by Mexico, and on the southeast by Cuba. In...
that produced winds of 80 mph (128.7 km/h) over land. The fourth storm of the season struck the coast of Nicaragua
Nicaragua
Nicaragua is the largest country in the Central American American isthmus, bordered by Honduras to the north and Costa Rica to the south. The country is situated between 11 and 14 degrees north of the Equator in the Northern Hemisphere, which places it entirely within the tropics. The Pacific Ocean...
, killing 10 and causing extensive damage.
Season summary
The AtlanticAtlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
hurricane database (HURDAT) officially recognizes six tropical cyclones from the 1911 season. Only three attained hurricane status, with winds of 75 mph (120.7 km/h) or greater. The third hurricane of the season was the most intense storm, with a minimum central air pressure of 972 mbar (28.7 inHg). A week after its dissipation, another hurricane formed with wind speeds that matched the previous storm, but with unknown air pressure. Three weak tropical depressions developed and remained below tropical storm force; the first formed in February and the third in December. The first storm to reach tropical storm intensity developed on August 4, and the final tropical storm of the year dissipated on October 31.
The early 1900s lacked modern forecasting and documentation. The hurricane database from these years is sometimes found to be incomplete or incorrect, and new storms are continually being added as part of the ongoing Atlantic hurricane reanalysis
Atlantic hurricane reanalysis
Atlantic hurricane reanalysis is an ongoing project within the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration which seeks to correct and add new information about past Atlantic tropical cyclones...
. The period from 1911 through 1914 was reanalyzed in 2005. Two previously unknown tropical cyclones were identified using records including historical weather maps and ship reports, and information on the known storms was amended and corrected. These storms are referred to simply by their number in chronological order, since tropical cyclones in the Atlantic Ocean were not given official names until much later.
Tropical Storm One
Identified by its lack of associated frontal boundariesWeather front
A weather front is a boundary separating two masses of air of different densities, and is the principal cause of meteorological phenomena. In surface weather analyses, fronts are depicted using various colored lines and symbols, depending on the type of front...
and closed circulation center, the first tropical cyclone of the 1911 season formed on August 4 over southern Alabama
Alabama
Alabama is a state located in the southeastern region of the United States. It is bordered by Tennessee to the north, Georgia to the east, Florida and the Gulf of Mexico to the south, and Mississippi to the west. Alabama ranks 30th in total land area and ranks second in the size of its inland...
in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
. At only tropical depression strength, it tracked eastward and emerged into the Atlantic Ocean
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's oceanic divisions. With a total area of about , it covers approximately 20% of the Earth's surface and about 26% of its water surface area...
the next day. Several days later, while located near Bermuda
Bermuda
Bermuda is a British overseas territory in the North Atlantic Ocean. Located off the east coast of the United States, its nearest landmass is Cape Hatteras, North Carolina, about to the west-northwest. It is about south of Halifax, Nova Scotia, Canada, and northeast of Miami, Florida...
, the depression became a tropical storm and turned northeastward. The storm lasted several more days until dissipating on August 11. The storm produced heavy rainfall on the Bermuda, but no gale-force winds were reported. The storm was unknown until the 2005 Atlantic hurricane database revision recognized it as a tropical storm.
Hurricane Two
On August 8, a tropical depression formed off the southwest coast of FloridaFlorida
Florida is a state in the southeastern United States, located on the nation's Atlantic and Gulf coasts. It is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the north by Alabama and Georgia and to the east by the Atlantic Ocean. With a population of 18,801,310 as measured by the 2010 census, it...
and drifted westward. Early the next day it intensified into a tropical storm and began accelerating toward the northwest. As it approached the U.S. Gulf Coast, the cyclone attained maximum sustained winds estimated at 80 mph (130 km/h), corresponding to Category 1 status on the modern-day Saffir–Simpson Hurricane Scale. Pushing ashore near the Alabama–Florida border, it weakened over land and curved toward the west. On August 12, the storm drifted over Louisiana
Louisiana
Louisiana is a state located in the southern region of the United States of America. Its capital is Baton Rouge and largest city is New Orleans. Louisiana is the only state in the U.S. with political subdivisions termed parishes, which are local governments equivalent to counties...
and Texas
Texas
Texas is the second largest U.S. state by both area and population, and the largest state by area in the contiguous United States.The name, based on the Caddo word "Tejas" meaning "friends" or "allies", was applied by the Spanish to the Caddo themselves and to the region of their settlement in...
, where it produced heavy rainfall.
During the evening of August 11, 1911, winds blew at up to 80 mph (128.7 km/h) at Pensacola, Florida
Pensacola, Florida
Pensacola is the westernmost city in the Florida Panhandle and the county seat of Escambia County, Florida, United States of America. As of the 2000 census, the city had a total population of 56,255 and as of 2009, the estimated population was 53,752...
, where pressure dropped to 29.73 inHg (1,006.8 mbar). A lull in the storm accompanied the nearby passage of its eye
Eye (cyclone)
The eye is a region of mostly calm weather found at the center of strong tropical cyclones. The eye of a storm is a roughly circular area and typically 30–65 km in diameter. It is surrounded by the eyewall, a ring of towering thunderstorms where the second most severe weather of a cyclone...
before conditions once again deteriorated. Total rainfall from the storm amounted to 4.48 in (113.8 mm). The winds brought down telephone and telegraph wires, cutting off communication to outside areas for 24 hours. The city also suffered power failures on the night of August 11. Shipping suffered heavy losses, with many barges blown aground. The hurricane dispersed "immense quantities" of lumber being stored along the coast. An unspecified number of deaths were caused by the hurricane, and despite the damage, an August 1911 issue of the Monthly Weather Review
Monthly Weather Review
The Monthly Weather Review is a scientific journal published by the American Meteorological Society.Topics covered by the journal include research related to analysis and prediction of observed and modeled circulations of the atmosphere, including technique development, data assimilation, model...
described the storm's effects as lighter than expected, estimating total damage in Pensacola at $12,000 (1911 USD, $280,000 2011 USD). Mobile, Alabama
Mobile, Alabama
Mobile is the third most populous city in the Southern US state of Alabama and is the county seat of Mobile County. It is located on the Mobile River and the central Gulf Coast of the United States. The population within the city limits was 195,111 during the 2010 census. It is the largest...
, recorded 35 mph (56.3 km/h) winds and no damage.
Hurricane Three
Over a week after the dissipation of the previous hurricane, the third storm of the season developed on August 23 and slowly tracked west-northwestward. After attaining hurricane status, the storm turned more towards the northwest, and several days later reached its peak wind speeds of 100 mph (155 km/h); a barometric pressure of 972 mbar (hPa) was reported. The center passed inland a few miles south of Savannah, GeorgiaSavannah, Georgia
Savannah is the largest city and the county seat of Chatham County, in the U.S. state of Georgia. Established in 1733, the city of Savannah was the colonial capital of the Province of Georgia and later the first state capital of Georgia. Today Savannah is an industrial center and an important...
, on August 28; upon making landfall, the hurricane rapidly degenerated. It deteriorated into a tropical depression on August 29 and persisted over land until dissipating a couple of days later.
The hurricane, relatively small in size, caused widespread damage between Savannah and Charleston, South Carolina
Charleston, South Carolina
Charleston is the second largest city in the U.S. state of South Carolina. It was made the county seat of Charleston County in 1901 when Charleston County was founded. The city's original name was Charles Towne in 1670, and it moved to its present location from a location on the west bank of the...
. Savannah itself received only minor damage, although the storm's center passed close by. Along the coast of Georgia
Georgia (U.S. state)
Georgia is a state located in the southeastern United States. It was established in 1732, the last of the original Thirteen Colonies. The state is named after King George II of Great Britain. Georgia was the fourth state to ratify the United States Constitution, on January 2, 1788...
, torrential rainfall caused numerous washouts on railroads. Crops, livestock and roads in the area suffered heavy damage. At Charleston, winds were estimated at 106 mph (170.6 km/h) after an anemometer
Anemometer
An anemometer is a device for measuring wind speed, and is a common weather station instrument. The term is derived from the Greek word anemos, meaning wind, and is used to describe any airspeed measurement instrument used in meteorology or aerodynamics...
, last reporting 94 mph (151.3 km/h), failed, and 4.9 in (124.5 mm) of precipitation fell over three days.
The storm raged for more than 36 hours, causing severe damage; the winds unroofed hundreds of buildings, demolished many houses and had an extensive impact on power and telephone services. Tides 10.6 ft (3.2 m) above normal left a "confused mass of wrecked vessels and damaged wharfs", according to a local forecaster in Charleston, while six navy torpedo boats were ripped from their moorings and blown ashore. In total, 17 people were killed in the hurricane, and property damage in Charleston was estimated at $1 million (1911 USD, $ USD).
Hurricane Four
The next storm formed well to the east of the Lesser AntillesLesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles are a long, partly volcanic island arc in the Western Hemisphere. Most of its islands form the eastern boundary of the Caribbean Sea with the Atlantic Ocean, with the remainder located in the southern Caribbean just north of South America...
on September 3 and moved westward, attaining tropical storm status about a day later. The storm slowed and curved toward the southwest, nearing the northern coast of Colombia
Colombia
Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia , is a unitary constitutional republic comprising thirty-two departments. The country is located in northwestern South America, bordered to the east by Venezuela and Brazil; to the south by Ecuador and Peru; to the north by the Caribbean Sea; to the...
before pulling away from land and strengthening into a hurricane. It further intensified to Category 2 status before striking Nicaragua
Nicaragua
Nicaragua is the largest country in the Central American American isthmus, bordered by Honduras to the north and Costa Rica to the south. The country is situated between 11 and 14 degrees north of the Equator in the Northern Hemisphere, which places it entirely within the tropics. The Pacific Ocean...
on September 10. Quickly weakening to a tropical storm, the cyclone continued westward across Central America
Central America
Central America is the central geographic region of the Americas. It is the southernmost, isthmian portion of the North American continent, which connects with South America on the southeast. When considered part of the unified continental model, it is considered a subcontinent...
and briefly entered the eastern Pacific Ocean
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest of the Earth's oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic in the north to the Southern Ocean in the south, bounded by Asia and Australia in the west, and the Americas in the east.At 165.2 million square kilometres in area, this largest division of the World...
. It dissipated shortly thereafter. In the town of Corinto
Corinto, Nicaragua
Corinto is a town of 17,000 on the northwest Pacific coast of Nicaragua in the province of Chinandega. The municipality was founded in 1863 and was named in honour of the Greek city of Corinth.- Economy :...
, a report indicated the deaths of 10 people and 50 additional injuries. About 250 houses were destroyed, leaving approximately $2 million (1911 USD, $ USD) in damage. Data on this storm is extremely scarce; as such, only minor revisions could be made to its chronology in the hurricane database.
Tropical Storm Five
The fifth official tropical cyclone of the year was also previously unknown until contemporary reassessments. It exhibited some hybrid characteristics, and may have qualified for subtropical cycloneSubtropical cyclone
A subtropical cyclone is a weather system that has some characteristics of a tropical and an extratropical cyclone. As early as the 1950s, meteorologists were unclear whether they should be characterized as tropical or extratropical cyclones. They were officially recognized by the National...
status according to the modern classification scheme. On September 15, the storm formed over the central Atlantic and initially moved westward. It gradually intensified as it turned northwestward, and on September 19 it transitioned into an extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are a group of cyclones defined as synoptic scale low pressure weather systems that occur in the middle latitudes of the Earth having neither tropical nor polar characteristics, and are connected with fronts and...
southeast of New England
New England
New England is a region in the northeastern corner of the United States consisting of the six states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut...
. The system was subsequently absorbed by a more powerful frontal boundary approaching from the northwest.
Tropical Storm Six
The final storm was first observed as a disturbance near Puerto RicoPuerto Rico
Puerto Rico , officially the Commonwealth of Puerto Rico , is an unincorporated territory of the United States, located in the northeastern Caribbean, east of the Dominican Republic and west of both the United States Virgin Islands and the British Virgin Islands.Puerto Rico comprises an...
in the Caribbean Sea
Caribbean Sea
The Caribbean Sea is a sea of the Atlantic Ocean located in the tropics of the Western hemisphere. It is bounded by Mexico and Central America to the west and southwest, to the north by the Greater Antilles, and to the east by the Lesser Antilles....
in late October. The disturbance was the precursor to a tropical depression which developed over the southern Bahamas and headed west-southwestward across Cuba
Cuba
The Republic of Cuba is an island nation in the Caribbean. The nation of Cuba consists of the main island of Cuba, the Isla de la Juventud, and several archipelagos. Havana is the largest city in Cuba and the country's capital. Santiago de Cuba is the second largest city...
, where, at Havana, winds blew from the southeast at 44 mph (70.8 km/h). It became a tropical storm on October 27 and drifted southwestward. Near the eastern tip of the Yucatán Peninsula
Yucatán Peninsula
The Yucatán Peninsula, in southeastern Mexico, separates the Caribbean Sea from the Gulf of Mexico, with the northern coastline on the Yucatán Channel...
, the storm turned sharply northward. An area of high pressure
High pressure area
A high-pressure area is a region where the atmospheric pressure at the surface of the planet is greater than its surrounding environment. Winds within high-pressure areas flow outward due to the higher density air near their center and friction with land...
over the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
prevented the cyclone from turning eastward toward Florida, and it continued into the Gulf of Mexico
Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico is a partially landlocked ocean basin largely surrounded by the North American continent and the island of Cuba. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States, on the southwest and south by Mexico, and on the southeast by Cuba. In...
. However, on October 31, the storm curved eastward and moved ashore over northern Florida. The storm decreased in intensity as it passed into the Atlantic. The storm's circulation center remained poorly defined throughout its course. It was long believed to have developed south of Cuba, although a reevaluation of ship data indicated the depression had actually formed east of the island. On October 26, the Weather Bureau hoisted hurricane warnings along the east coast of Florida from Key West
Key West, Florida
Key West is a city in Monroe County, Florida, United States. The city encompasses the island of Key West, the part of Stock Island north of U.S. 1 , Sigsbee Park , Fleming Key , and Sunset Key...
to West Palm Beach
West Palm Beach, Florida
West Palm Beach, is a city located on the Atlantic coast in southeastern Florida and is the most populous city in and county seat of Palm Beach County, the third most populous county in Florida with a 2010 population of 1,320,134. The city is also the oldest incorporated municipality in South Florida...
, and on the west coast up to Tampa
Tampa, Florida
Tampa is a city in the U.S. state of Florida. It serves as the county seat for Hillsborough County. Tampa is located on the west coast of Florida. The population of Tampa in 2010 was 335,709....
.
Tropical depressions
In addition to the six officially recognized tropical storms and hurricanes, three tropical depressions in the 1911 season have been identified. The first developed in February from a troughTrough (meteorology)
A trough is an elongated region of relatively low atmospheric pressure, often associated with fronts.Unlike fronts, there is not a universal symbol for a trough on a weather chart. The weather charts in some countries or regions mark troughs by a line. In the United States, a trough may be marked...
of low pressure in the open Atlantic and progressed westward. Although a ship dubiously reported winds of over 50 mph (80.5 km/h) in association with the system, a lack of supporting evidence precludes its designation as a tropical storm. The cyclone dissipated by February 21. The second depression evolved from an extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclone
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are a group of cyclones defined as synoptic scale low pressure weather systems that occur in the middle latitudes of the Earth having neither tropical nor polar characteristics, and are connected with fronts and...
in mid- to late May, becoming a tropical cyclone on May 22 northeast of Bermuda. It persisted for three days as it meandered around the same general area before being absorbed by another non-tropical storm. The modern-day documentation of this system was also hindered by a lack of data. On December 11, the third tropical depression formed near the Turks and Caicos Islands
Turks and Caicos Islands
The Turks and Caicos Islands are a British Overseas Territory and overseas territory of the European Union consisting of two groups of tropical islands in the Caribbean, the larger Caicos Islands and the smaller Turks Islands, known for tourism and as an offshore financial centre.The Turks and...
. It progressed westward and was situated just north of eastern Cuba the next day. The system began to weaken on December 13 and dissipated shortly thereafter.
See also
- List of tropical cyclones
- List of Atlantic hurricane seasons

