
Upsilon
Encyclopedia
Upsilon is the 20th letter of the Greek alphabet
. In the system of Greek numerals
it has a value of 400. It is derived from the Phoenician waw
. The name of the letter is pronounced ˈipsilon in Modern Greek
, and in English ˈʌpsɨlɒn, juːpˈsaɪlən , or ˈjuːpsɨlɒn . It is occasionally called "ypsilon" (/ˈɪpsɨlɒn/) in English after its rendering in Latin, where the Greek upsilon corresponded with the letter Y
.

. This was the case at least until the year 1030AD. In Modern Greek
it is pronounced like continental i or English ee, i, and in diphthongs, [f] or [v]. In ancient Greek it occurred in both long and short versions, but this distinction has been lost in Modern Greek.
As an initial letter in Classical Greek it always carried the rough breathing (equivalent to h) as reflected in the many Greek-derived English words
, such as those that begin with hyper- and hypo-. This rough breathing was derived from an older pronunciation which used a sibilant
instead; this sibilant was not lost in Latin, giving rise to such cognates as super- (for hyper-) and sub- (for hypo-).
Upsilon participated as the second element in falling diphthongs, which have subsequently developed in various ways: for instance after alpha or epsilon it is pronounced [f] or [v].
in Latin dates back to the first century BC. It was used to transcribe loanwords from Greek, so it was not a native sound of Latin and was usually pronounced /u/ or /i/. The latter pronunciation was the most common in the Classical period and was used by most people except the educated ones. The Roman Emperor
Claudius
proposed introducing a new letter
into the Latin alphabet
to transcribe the so-called sonus medius (a short vowel before labial consonants), but in inscriptions was sometimes used for Greek upsilon instead.
The name of the letter was originally just υ (y; also called hy, hence "hyoid", meaning "y-shaped"). It changed to υ ψιλόν, (u psilon, meaning 'simple u') to distinguish it from οι, which had come to have the same [y] pronunciation. Four letters of the Latin alphabet
arose from it: V
and Y
and, much later, U
and W
. In the Cyrillic alphabet
, the letters U
(У, у) and Izhitsa
(Ѵ, ѵ) arose from it.
In some languages (most notably German
), the name upsilon, (üppsilon) is used to refer to the Latin letter Y as well as the Greek letter.
used it as an emblem of the path of virtue or vice. As the Roman writer Persius wrote in Satire III:
Lactantius
, an early Christian author (ca. 240 – ca. 320), refers to this:
Greek alphabet
The Greek alphabet is the script that has been used to write the Greek language since at least 730 BC . The alphabet in its classical and modern form consists of 24 letters ordered in sequence from alpha to omega...
. In the system of Greek numerals
Greek numerals
Greek numerals are a system of representing numbers using letters of the Greek alphabet. They are also known by the names Ionian numerals, Milesian numerals , Alexandrian numerals, or alphabetic numerals...
it has a value of 400. It is derived from the Phoenician waw
Waw (letter)
Waw is the sixth letter of the Northwest Semitic family of scripts, including Phoenician, Aramaic, Hebrew, Syriac, and Arabic ....
. The name of the letter is pronounced ˈipsilon in Modern Greek
Modern Greek
Modern Greek refers to the varieties of the Greek language spoken in the modern era. The beginning of the "modern" period of the language is often symbolically assigned to the fall of the Byzantine Empire in 1453, even though that date marks no clear linguistic boundary and many characteristic...
, and in English ˈʌpsɨlɒn, juːpˈsaɪlən , or ˈjuːpsɨlɒn . It is occasionally called "ypsilon" (/ˈɪpsɨlɒn/) in English after its rendering in Latin, where the Greek upsilon corresponded with the letter Y
Y
Y is the twenty-fifth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet and represents either a vowel or a consonant in English.-Name:In Latin, Y was named Y Graeca "Greek Y". This was pronounced as I Graeca "Greek I", since Latin speakers had trouble pronouncing , which was not a native sound...
.

Pronunciation
In early Greek and modern physics it is pronounced oo u . In Classical Greek, it was pronounced like French u or German ü, y—a sound that is not found in most dialects of EnglishEnglish language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
. This was the case at least until the year 1030AD. In Modern Greek
Modern Greek
Modern Greek refers to the varieties of the Greek language spoken in the modern era. The beginning of the "modern" period of the language is often symbolically assigned to the fall of the Byzantine Empire in 1453, even though that date marks no clear linguistic boundary and many characteristic...
it is pronounced like continental i or English ee, i, and in diphthongs, [f] or [v]. In ancient Greek it occurred in both long and short versions, but this distinction has been lost in Modern Greek.
As an initial letter in Classical Greek it always carried the rough breathing (equivalent to h) as reflected in the many Greek-derived English words
English words of Greek origin
The Greek language has contributed to the English vocabulary in three ways:#directly as an immediate donor,#indirectly through other intermediate language, as an original donor , and#modern coinages using Greek roots....
, such as those that begin with hyper- and hypo-. This rough breathing was derived from an older pronunciation which used a sibilant
Sibilant consonant
A sibilant is a manner of articulation of fricative and affricate consonants, made by directing a stream of air with the tongue towards the sharp edge of the teeth, which are held close together. Examples of sibilants are the consonants at the beginning of the English words sip, zip, ship, chip,...
instead; this sibilant was not lost in Latin, giving rise to such cognates as super- (for hyper-) and sub- (for hypo-).
Upsilon participated as the second element in falling diphthongs, which have subsequently developed in various ways: for instance after alpha or epsilon it is pronounced [f] or [v].
Correspondence with Latin Y
The usage of YY
Y is the twenty-fifth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet and represents either a vowel or a consonant in English.-Name:In Latin, Y was named Y Graeca "Greek Y". This was pronounced as I Graeca "Greek I", since Latin speakers had trouble pronouncing , which was not a native sound...
in Latin dates back to the first century BC. It was used to transcribe loanwords from Greek, so it was not a native sound of Latin and was usually pronounced /u/ or /i/. The latter pronunciation was the most common in the Classical period and was used by most people except the educated ones. The Roman Emperor
Roman Emperor
The Roman emperor was the ruler of the Roman State during the imperial period . The Romans had no single term for the office although at any given time, a given title was associated with the emperor...
Claudius
Claudius
Claudius , was Roman Emperor from 41 to 54. A member of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, he was the son of Drusus and Antonia Minor. He was born at Lugdunum in Gaul and was the first Roman Emperor to be born outside Italy...
proposed introducing a new letter
Claudian letters
The Claudian letters were developed by, and named after, the Roman Emperor Claudius . He introduced three new letters:*a reversed C to replace BS and PS, much like X stood in for CS and GS...
into the Latin alphabet
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
to transcribe the so-called sonus medius (a short vowel before labial consonants), but in inscriptions was sometimes used for Greek upsilon instead.
The name of the letter was originally just υ (y; also called hy, hence "hyoid", meaning "y-shaped"). It changed to υ ψιλόν, (u psilon, meaning 'simple u') to distinguish it from οι, which had come to have the same [y] pronunciation. Four letters of the Latin alphabet
Latin alphabet
The Latin alphabet, also called the Roman alphabet, is the most recognized alphabet used in the world today. It evolved from a western variety of the Greek alphabet called the Cumaean alphabet, which was adopted and modified by the Etruscans who ruled early Rome...
arose from it: V
V
V is the twenty-second letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-Letter:The letter V comes from the Semitic letter Waw, as do the modern letters F, U, W, and Y. See F for details....
and Y
Y
Y is the twenty-fifth letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet and represents either a vowel or a consonant in English.-Name:In Latin, Y was named Y Graeca "Greek Y". This was pronounced as I Graeca "Greek I", since Latin speakers had trouble pronouncing , which was not a native sound...
and, much later, U
U
U is the twenty-first letter and a vowel in the basic modern Latin alphabet.-History:The letter U ultimately comes from the Semitic letter Waw by way of the letter Y. See the letter Y for details....
and W
W
W is the 23rd letter in the basic modern Latin alphabet.In other Germanic languages, including German, its pronunciation is similar or identical to that of English V...
. In the Cyrillic alphabet
Cyrillic alphabet
The Cyrillic script or azbuka is an alphabetic writing system developed in the First Bulgarian Empire during the 10th century AD at the Preslav Literary School...
, the letters U
U (Cyrillic)
U is a letter of the Cyrillic alphabet. It commonly represents the close back rounded vowel , somewhat like the pronunciation of ⟨oo⟩ in "boot"...
(У, у) and Izhitsa
Izhitsa
Izhitsa is a letter of the early Cyrillic alphabet. It was used to represent ypsilon in words derived from Greek, such as . It represented the same sound /i/ as the normal letter и in Russian...
(Ѵ, ѵ) arose from it.
In some languages (most notably German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
), the name upsilon, (üppsilon) is used to refer to the Latin letter Y as well as the Greek letter.
Usage
- In particle physicsParticle physicsParticle physics is a branch of physics that studies the existence and interactions of particles that are the constituents of what is usually referred to as matter or radiation. In current understanding, particles are excitations of quantum fields and interact following their dynamics...
the capital Greek letter Υ denotes an Upsilon particleUpsilon particleThe Upsilon meson is a flavorless meson formed from a bottom quark and its antiparticle. It was discovered by the E288 collaboration, headed by Leon Lederman, at Fermilab in 1977, and was the first particle containing a bottom quark to be discovered because it is the lightest that can be produced...
. Note that the symbol should always look like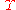 in order to avoid confusion with a Latin Y denoting the hyperchargeHyperchargeIn particle physics, the hypercharge Y of a particle is related to the strong interaction, and is distinct from the similarly named weak hypercharge, which has an analogous role in the electroweak interaction...
in order to avoid confusion with a Latin Y denoting the hyperchargeHyperchargeIn particle physics, the hypercharge Y of a particle is related to the strong interaction, and is distinct from the similarly named weak hypercharge, which has an analogous role in the electroweak interaction...
. - Automobile manufacturer LanciaLanciaLancia Automobiles S.p.A. is an Italian automobile manufacturer founded in 1906 by Vincenzo Lancia and which became part of the Fiat Group in 1969. The company has a long history of producing distinctive cars and also has a strong rally heritage. Some modern Lancias are seen as presenting a more...
has a model called the Ypsilon. See Lancia YpsilonLancia YpsilonThe Lancia Ypsilon is a supermini produced by Italian automaker Lancia since 1996. It is the replacement of the Y10, although larger and more expensive...
. - In linguisticsLinguisticsLinguistics is the scientific study of human language. Linguistics can be broadly broken into three categories or subfields of study: language form, language meaning, and language in context....
, the symbol is used to represent a labiodental approximantLabiodental approximantThe labiodental approximant is a type of consonantal sound, similar to an English double-u pronounced with the teeth and lips held in the position used to articulate the letter vee, used in some spoken languages...
.
Symbolism
Upsilon is known as Pythagoras' letter, or the Samian letter, because PythagorasPythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos was an Ionian Greek philosopher, mathematician, and founder of the religious movement called Pythagoreanism. Most of the information about Pythagoras was written down centuries after he lived, so very little reliable information is known about him...
used it as an emblem of the path of virtue or vice. As the Roman writer Persius wrote in Satire III:
-
-
- "and the letter which spreads out into Pythagorean branches has pointed out to you the steep path which rises on the right."
-
Lactantius
Lactantius
Lucius Caecilius Firmianus Lactantius was an early Christian author who became an advisor to the first Christian Roman emperor, Constantine I, guiding his religious policy as it developed, and tutor to his son.-Biography:...
, an early Christian author (ca. 240 – ca. 320), refers to this:
-
-
- "For they say that the course of human life resembles the letter Y, because every one of men, when he has reached the threshold of early youth, and has arrived at the place "where the way divides itself into two parts," is in doubt, and hesitates, and does not know to which side he should rather turn himself."
-

