
List of Indo-Aryan languages
Encyclopedia
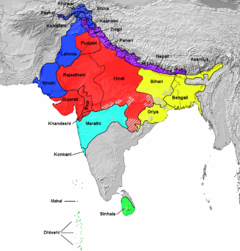
Indo-Aryan languages
The Indo-Aryan languages constitutes a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages, itself a branch of the Indo-European language family...
include some 210 (SIL
SIL International
SIL International is a U.S.-based, worldwide, Christian non-profit organization, whose main purpose is to study, develop and document languages, especially those that are lesser-known, in order to expand linguistic knowledge, promote literacy, translate the Christian Bible into local languages,...
estimate) languages and dialects spoken by many people in Asia
Asia
Asia is the world's largest and most populous continent, located primarily in the eastern and northern hemispheres. It covers 8.7% of the Earth's total surface area and with approximately 3.879 billion people, it hosts 60% of the world's current human population...
; this language family is a part of the Indo-Iranian language family.
Historical
- Old Indic (ca. 1500-300 BC)
- early Old Indic: Vedic SanskritVedic SanskritVedic Sanskrit is an old Indo-Aryan language. It is an archaic form of Sanskrit, an early descendant of Proto-Indo-Iranian. It is closely related to Avestan, the oldest preserved Iranian language...
(1500 to 500 BCE) - late Old Indic: Epic Sanskrit, Classical Sanskrit (500 to 300 BCE)
- early Old Indic: Vedic Sanskrit
- Middle Indic (ca. 300 BCE to 1500 CE)
- early phase: 3rd century BC
- Ashoka-Prakrits (3rd century BC regional dialects)
- PaliPáli- External links :* *...
(language of the Buddhist canon) - early Ardhamagadhi (language of the oldest Jain sutras)
- middle phase (200 BCE to 700 CE)
- Niya Prakrit
- Ardhamagadhi (later Jain canon)
- Dramatic PrakritDramatic PrakritDramatic Prakrits were those standard forms of Prakrit dialects that were used in dramas and other literature in medieval India. They may have once been spoken languages or were based on spoken languages, but continued to be used as literary languages long after they ceased to be spoken...
s (Maurya period)- Maharashtri Prakrit
- Magadhi PrakritMagadhi PrakritMagadhi Prakrit is of one of the three Dramatic Prakrits, the written languages of Ancient India following the decline of Pali and Sanskrit. Magadhi Prakrit was spoken in the eastern Indian subcontinent, in a region spanning what is now eastern India, Bangladesh, and Nepal. It is believed to be the...
- Sauraseni Prakrit
- Sinhala Prakrit
- hybrid Sanskrit (MahayanaMahayanaMahāyāna is one of the two main existing branches of Buddhism and a term for classification of Buddhist philosophies and practice...
canon)
- late phase: Apabhramsa (700 CE to 1500 CE)
- AbahattaAbahattaAbahatta, from Prakrit abasatta and ultimately from Sanskrit apaśabda "meaningless sound", is a stage in the evolution of the Eastern group of Indo-Aryan languages such as Bangla, Maithili, Oriya. It is also called Apabhramsa Avahatta, Apabhramsha Abahatta or Purvi Apabhramsa. Abahatta is...
(Maghadi Apabhramsa) - EluEluThe Elu language is the name given to the ancient form of the Sinhala variant of the Middle Indo-Aryan languages...
(Sinhalese Apabhramsa)
- Abahatta
- early phase: 3rd century BC
- Early Modern Indic (Mughal period, 1500 to 1800)
- early Dakkhini (Kalmitul-hakayat 1580)
- emergence of KhariboliKhariboliKhariboli , also Khari Boli, Khadiboli, Khadi Boli or simply Khari, is a Western Hindi dialect spoken mainly in the rural surroundings of Delhi, the northern areas of Western Uttar Pradesh and the southern areas of Uttarakhand in India...
(Gora-badal ki katha, 1620s) - emergence of "UrduUrduUrdu is a register of the Hindustani language that is identified with Muslims in South Asia. It belongs to the Indo-European family. Urdu is the national language and lingua franca of Pakistan. It is also widely spoken in some regions of India, where it is one of the 22 scheduled languages and an...
" at Delhi fortDelhi FortThe Red Fort is a 17th century fort complex constructed by the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan in the walled city of Old Delhi that served as the residence of the Mughal Emperors. It also served as the capital of the Mughals until 1857, when Mughal emperor Bahadur Shah Zafar was exiled by the British...
(1670s)
Contemporary languages
This classification follows Kausen (2005). The main differences from SIL are noted.(SIL includes the Nuristani languages
Nuristani languages
The Nuristani languages are one of the three groups within the Indo-Iranian language family, alongside the much larger Indo-Aryan and Iranian groups. They are spoken primarily in eastern Afghanistan...
within Indo-Aryan.)
Dardic
(The relation of this family to other Indo-Aryan languages is unclear; SIL includes it in the Northwestern zone, despite these languages having a very different grammatical structure from that of the Classical Indo-Aryan languages.)Kunar languages
- PashayiPashayi languagePashayi - also known as Pashai - is a language spoken by the Pashai people in parts of Kapisa, Laghman, Nuristan, Kunar, and Nangarhar Provinces in Northeastern Afghanistan....
- Gawar-BatiGawar-Bati languageGawar-Bati is known in Chitral as Aranduyiwar, because it is spoken in Village Arandu, which is the last village in the bottom of Chitral and is across the Kunar River from Berkot in Afghanistan. Chitral keeps a military base in Arandu to guard against an attack by Afghanistan.There are 9,000...
- Dameli
- ShumashtiShumashti languageShumashti – also known as Shumasht – is a language spoken in parts of western Pakistan and eastern Afghanistan.It belongs to the Indo-European language family, and is on the Dardic group of the Indo-Iranian branch....
- NangalamiNangalami languageNangalami, or Grangali, is a Dardic language of Afghanistan....
(includes Grangali)
Chitral languages
- KhowarKhowar languageFor the ethnic group, see under Chitrali people.Khowar , also known as Chitrali, is a Dardic language spoken by 400,000 people in Chitral in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, in the Ghizer district of Gilgit-Baltistan , and in parts of Upper Swat...
- KalashaKalasha languageThe description Kalasha language may refer to:*Kalasha-mondr, the language of the Kalasha of Chitral*Kalasha-ala, the language of the Kalasha of Nuristan...
Kohistani languages
- KalamiKalami languageKalami is a Dardic language spoken in northern Pakistan.The language is also known as Gawri or Garwi , but this name is considered pejorative by some speakers.-Classification:...
- TorwaliTorwali languageThe Torwali , or Turvali, language is spoken in Kohistan and Swat districts of the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Province of Pakistan. The language is indigenous to the Torwali people who live in scattered hamlets in the mountainous upper reaches of the Swat valley, above the Pashto-speaking town of Madyan up...
- Kalkoti
- Indus Kohistani
- Bateri
- ChilissoChilisso languageChilisso is a Dardic language in the Kohistani language group spoken by about 2,300 people in eastern Kohistan....
- Gowro
- Wotapuri-Katarqalai
- Tirahi
Shina languages
- Shina languageShina languageShina is a Dardic language spoken by a plurality of people in Gilgit-Baltistan of Pakistan and Dras in Ladakh of Indian-Administered Kashmir. The valleys in which it is spoken include Astore, Chilas, Dareil, Tangeer, Gilgit, Ghizer, and a few parts of Baltistan and Kohistan. It is also spoken in...
- Brokskad (the Shina of Baltistan and Ladakh)
- Ushojo
- DomaakiDomaaki languageDomaakí – also known as Dumaki or Domaá – is a language spoken by a few hundred people living in the Northern Areas of Pakistan.It belongs to the Indo-European language family, and can be affiliated to the Dardic group of the Indo-Iranian branch....
- Palula
- Savi
Kashmiri
- KashmiriKashmiri languageKashmiri is a language from the Dardic sub-group and it is spoken primarily in the Kashmir Valley, in Jammu and Kashmir. There are approximately 5,554,496 speakers in Jammu and Kashmir, according to the Census of 2001. Most of the 105,000 speakers or so in Pakistan are émigrés from the Kashmir...
- Poguli
Northern Zone
- Garhwali (includes Tehri)
- Kumauni
- NepaliNepali languageNepali or Nepalese is a language in the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European language family.It is the official language and de facto lingua franca of Nepal and is also spoken in Bhutan, parts of India and parts of Myanmar...
(Gurkali; includes PalpaPalpa languageThe Palpa language of Nepal is closely related to the Nepali language, and is sometimes considered a dialect of it. It has Kumauni influence, and has also been classified as a dialect of that language....
)
North-Western Zone
(included in Pahari by SIL)
- DogriDogri languageDogri is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by about five million people in Pakistan and India, chiefly in the Jammu region of Jammu and Kashmir, but also in northern Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, other parts of Jammu and Kashmir, and elsewhere. Dogri speakers are called Dogras, and the Dogri-speaking...
-KangriKangri languageKangri is a dialect spoken in northern India, predominantly in the Kangra district of Himachal Pradesh, by the people of the Kangra Valley. It is an Indo-Aryan dialect, related to Dogri and classified as one of the Western Pahari group of languages, with deep vocabulary impact from Punjabi, which... - Gaddi
- Churahi
- Bhattiyali
- Bilaspuri
- Harijan Kinnauri
- Chambeali
- Mandeali
- Mahasu Pahari
- Jaunsari
- Pangwali
Lahnda languages
Lahnda languages
The Lahnda or Western Punjabi Languages are an Indo-Aryan languages dialect continuum that are Mutually intelligible and are spoken in South Asia.According to the Ethnologue they include:...
- Potwari (also known as Mirpuri or Pothohari and usually classified as Pahari)
- HindkoHindko languageHindko , also Hindku, or Hinko, is the sixth main regional language of Pakistan. It forms a subgroup of Indo-Aryan languages spoken by Hindkowans in Pakistan and northern India, some Pashtun tribes in Pakistan, as well as by the Hindki people of Afghanistan...
- SaraikiSaraiki languageSaraiki , transliterated as Sirāikī and sometimes spelled Seraiki and Saraiki, is a standardized written language of Pakistan belonging to the Indo-Aryan languages. It is a language spoken in the heart of Pakistan...
(South Punjabi or Multani)
Sindhi languages
- SindhiSindhi languageSindhi is the language of the Sindh region of Pakistan that is spoken by the Sindhi people. In India, it is among 22 constitutionally recognized languages, where Sindhis are a sizeable minority. It is spoken by 53,410,910 people in Pakistan, according to the national government's Statistics Division...
- Jadgali
- Kachchi
Western Zone
(SIL includes these languages in the Central zone)- MewatiMewati languageMewati is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by about five million speakers in the Alwar, Bharatpur and Dholpur districts of Rajasthan, Mewat districts of Haryana, as well as parts of southern Pakistan and in Punjab. It contributed profoundly to Rajasthani literature in medieval periods.There are 9...
(of uncertain affiliation)
Rajasthani language
Rajasthani language
Rajasthani Rajasthani Rajasthani (Devanagari: , Perso-Arabic: is a language of the Indo-Aryan languages family. It is spoken by 50 million people in Rajasthan and other states of India and in some areas of Pakistan. The number of speakers may be up to 80 million worldwide...
s
- MarwariMarwari languageThe Marwari language , also variously Marvari, Marwadi, Marvadi), is spoken in the Indian state of Rajasthan. Marwari is also found in the neighboring state of Gujarat and Haryana and in Eastern Pakistan...
(includes MewariMewari languageMewari is one of the major dialects of Rajasthani language of Indo-Aryan languages family. It is spoken by about five million speakers in Rajsamand, Bhilwara, Udaipur, and Chittorgarh districts of Rajasthan state of India. It has SOV word order....
) - HarautiHarauti languageThe Harauti language is a dialect of Rajasthani language of Indo-Aryan language family. It is spoken in historical Hadoti region: Kota, Baran, Bundi and Jhalawar districts of Rajasthan and its adjacent areas of Madhya Pradesh....
- GoariaGoaria languageGoaria is a Marwari Rajasthani language spoken by some 25,000 people in Sindh Province, Pakistan. The people are predominantly Hindu, and use the Hindi language for worship.-External links:* at the Ethnologue...
- MalviMalvi languageMalvi is the language of the Malva region of India, with sixteen million speakers. Nimadi, spoken in the Nimar region of Madhya Pradesh and in Rajasthan, is its closest relative...
- NimadiNimadi languageNimadi is spoken in the Nimar region of Madhya Pradesh, which lies adjacent to Maharashtra and south of Malwa. The districts which speak Nimadi are: Barwani, East Nimar, West Nimar and parts of Dhar district. The famous writers of Nimari was Late Gaurishankar Sharma, lalitnarayan upadhyay etc...
- Gujari
- BagriBagri languageBagri is a dialect of Rajasthani language of the Indo-Aryan family. It is spoken by about five million speakers in Hanumangarh and Sriganganagar districts of Rajasthan, Sirsa and Hissar districts of Haryana, Firozepur and Muktsar districts of Punjab of India and Bahawalpur and Bahawalnagar areas...
- LambadiLambadi languageLambadi is a Rajasthani language spoken by nomadic Banjara people across India.The language is known by various other names, including Lamani, Lamadi, Lambani, Labhani, Lambara, Lavani, Lemadi, Lumadale, Labhani Muka and variants, Banjara, Banjari, Bangala, Banjori, Banjuri, Brinjari, Vanjari,...
- LoarkiLoarki languageLoarki is an Indo-Aryan language, classified as a Rajasthani language, and is spoken by 20,000 nomadic people in rural Sindh of Pakistan....
Gujarati language
Gujarati language
Gujarati is an Indo-Aryan language, and part of the greater Indo-European language family. It is derived from a language called Old Gujarati which is the ancestor language of the modern Gujarati and Rajasthani languages...
s
- Southern GujaratiGujarati languageGujarati is an Indo-Aryan language, and part of the greater Indo-European language family. It is derived from a language called Old Gujarati which is the ancestor language of the modern Gujarati and Rajasthani languages...
- Vasavi
- SourashtraSourashtra languageSourashtra or "Sourashtras" or ꢱꣃꢬꢵꢰ꣄ꢜ꣄ꢬꢵ refers to a community of people who had their original homes in Gujarat and presently settled almost in all major Towns of Tamil Nadu and are concentrated more in Madurai which is considered as their cultural Headquarters.They have also settled in...
Bhil languages
Bhil languages
The Bhil languages are a group of Western Indo-Aryan languages spoken by some 6 million Bhils in western, central, and by small numbers, even in far eastern, India...
- BhiliBhili languageBhili is a Western Indo-Aryan language spoken in west-central India, in the region east of Ahmedabad. Other names for the language include Bhagoria and Bhilboli; varieties are Wagdi and Garasia. Bhili is a member of the Bhil language family, which is related to Gujarati and the Rajasthani language...
(includes GamitGamit languageGamit is a Bhil language of Gujarat, mainly the area of Surat. It is mostly spoken by the Gamit caste; according to Ethnologue "most speakers have high school or college education". Gamti proper has most of the speakers; Mawchi Gamti of Gujarat and Maharashtra has about 80,000....
)
Khandeshi
- AhiraniAhirani languageThe Khandeshi languages form a small subgroup within the Indo-Aryan languages, wedged between the territory of Bhili and that of Marathi.It consists of Khandeshi proper , Dhanki and Ahirani which comes from Ahir caste...
(Kandeshi)
Domari-Romani
(treated as a separate group by Kausen)
- DomariDomari languageDomari is an Indo-Aryan language, spoken by the Dom people across the Middle East, mainly in Iran and Egypt, but significant numbers of speakers are also found in India where they are known as Domba....
- Romani languageRomani languageRomani or Romany, Gypsy or Gipsy is any of several languages of the Romani people. They are Indic, sometimes classified in the "Central" or "Northwestern" zone, and sometimes treated as a branch of their own....
s
Central Zone

- Eastern or Central Punjabi
- Majhi or MajhailMajhi dialectMajhi dialect is referred to as the standard dialect of Punjabi language originating from the Majha region of the Punjab...
- Malwi or MalwaiMalwa (Punjab)Malwa is a region of Punjab and parts of Haryana between the Sutlej and Yamuna rivers. This Malwa should not be confused with the Malwa Plateau region of Madhya Pradesh, Central India...
- DoabiDoabiDoabi is one of the Punjabi dialects spoken in Doab . The word "Do Aabi" means "the land between two rivers" and this dialects is spoken between the rivers of Beas and Sutlej...
- Powadhi
- Majhi or Majhail
West Central Zone (Western Hindi
Western Hindi
Western Hindi is a group of Hindi dialects that evolved out of the Apabhramsa form of Shaurseni prakrit. According to G. A. Grierson it comprises such varieties as Haryanvi or Bangaru , Brajbhakha , Bundeli Western Hindi is a group of Hindi dialects that evolved out of the Apabhramsa form of...
)
- Hindi-Urdu
- Braj Bhasa-Kanauji
- Haryanvi
- Bundeli
- Bhaya
- Sansi
- Chamari
- Ghera
- Gowli
East Central Zone (Eastern Hindi)
- AwadhiAwadhi languageAwadhi is an Indo-Aryan language, part of the Hindi-Urdu continuum. It is spoken chiefly in the Awadh region of Uttar Pradesh, although its speakers are also found in Madhya Pradesh, Delhi and Nepal. Furthermore, the Fiji Hindi dialect spoken by Indo-Fijians is considered a variant of Awadhi,...
(includes Fijian Hindi) - Bagheli
- ChhattisgarhiChhattisgarhi languageChhattisgarhi is the official language in the Indian state of Chhattisgarh and has approximately 17.5 million speakers. It is an East Central Indo-Iranian language with heavy presence of vocabulary and linguistic features from Munda and Dravidian languages...
Eastern Zone (Magadhan)
These languages derive from Magadhi PrakritMagadhi Prakrit
Magadhi Prakrit is of one of the three Dramatic Prakrits, the written languages of Ancient India following the decline of Pali and Sanskrit. Magadhi Prakrit was spoken in the eastern Indian subcontinent, in a region spanning what is now eastern India, Bangladesh, and Nepal. It is believed to be the...
through Ardhamagadhi ("Half-Magadhi").
Assamese–Bengali languages
- Assamese (Ôxômiya)Assamese languageAssamese is the easternmost Indo-Aryan language. It is used mainly in the state of Assam in North-East India. It is also the official language of Assam. It is also spoken in parts of Arunachal Pradesh and other northeast Indian states. Nagamese, an Assamese-based Creole language is widely used in...
- Bengali (Bangla)Bengali languageBengali or Bangla is an eastern Indo-Aryan language. It is native to the region of eastern South Asia known as Bengal, which comprises present day Bangladesh, the Indian state of West Bengal, and parts of the Indian states of Tripura and Assam. It is written with the Bengali script...
(includes Mal PahariaMal Paharia languageMal Paharia, is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by about 60,000 of 111,000 ethnic Mal Paharia in the states of Jharkhand and West Bengal in India and possibly in Bangladesh. There is a positive attitude amongst speakers of the language, and the language health is considered vigorous. Nonetheless,...
) - Bishnupriya Manipuri (Imar Thar)Bishnupriya Manipuri languageThe Bishnupriya or Bishnupriya Manipuri is an Indo-Aryan language spoken in parts of the Indian states of Assam, Tripura, Manipur and others, as well as in Bangladesh, Burma, and other countries.-History and development:...
- ChakmaChakma languageChakma language is an Indo-European language spoken by the Chakma people. Its better-known closest relatives are Bengali, Assamese, Chittagonian, Bishnupriya Manipuri, Tanchangya, Rohingya and Sylheti. It is spoken by nearly 310,000 people in southeast Bangladesh near Chittagong City, and another...
- ChittagonianChittagonian languageChittagonian is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by the people of Chittagong in Bangladesh and in much of the southeast of the country. It is closely related to Bangla, but is normally considered by linguists to be a separate language rather than a dialect of Bangla. It is estimated to have 14...
- HajongHajong languageHajong is an Indo-Aryan language with Tibeto-Burman roots spoken by more than 175,000 ethnic Hajong in the states of Assam, Meghalaya, Arunachal Pradesh and West Bengal in India and the Mymensingh District in Bangladesh. It is written in the Assamese script, and it is being supplanted by the...
- Kharia TharKharia Thar languageKharia Thar is an Indic language spoken by the Hill Kharia culture of India....
- Rajbangsi
- RohingyaRohingya languageRohingya is a language spoken by the Rohingya people of Arakan , Burma . It is smiliar to the Chittagonian language spoken in the neighboring southeastern Chittagong Division of Bangladesh...
- SylhetiSylheti languageSylheti is the language of Sylhet, which is also known as the Surma Valley and is located in the north-eastern region of Bangladesh, and also spoken in parts of the Northeast Indian states of Assam and Tripura...
- TanchangyaTanchangya languageTanchangya is an Indo-European language of Indo-Iranian sub-family, part of the Southeastern Bengali–Assamese branch of Eastern Indo-Aryan language group. Tanchangya is spoken by Tanchangya people. It is closely related to Chakma language, Bengali, Chittagonian, Assamese, Sylheti, Bishnupriya...
Bihari languages
Bihari languages
Bihari is a name given to the western group of Eastern Indic languages, spoken in Bihar and neighboring states in India. Angika, Bajjika, Bhojpuri, Magahi, and Maithili are spoken in Nepal as well. The Angika, Bajjika, Bhojpuri, Magahi and Maithili speaking population form more than 21% of Nepalese...
- AngikaAngika languageAngika is an Indo-Iranian language of the Anga region of India, a 58,000 km² area approx. that falls within the states of Bihar, Jharkhand and West Bengal....
- BhojpuriBhojpuri languageBhojpuri is a language spoken in parts of north-central and eastern India. It is spoken in the western part of state of Bihar, the northwestern part of Jharkhand, and the Purvanchal region of Uttar Pradesh , as well as adjoining parts of the Nepal Terai. Bhojpuri is also spoken in Guyana,...
(includes Caribbean Hindustani) - MaithiliMaithili languageMaithili language is spoken in the eastern region of India and South-eastern region of Nepal. The native speakers of Maithili reside in Bihar, Jharkhand,parts of West Bengal and South-east Nepal...
- Magahi
- MajhiMajhi languageMajhi is a language spoken in parts of Nepal and Sikkim. Total population: 22,087.-External links:*...
- MusasaMusasa languageMusasa is one of the eastern Indian Bihari languages.-See also:* List of Indo-European languages* List of Indo-Aryan languages...
- Oraon Sadri
- SadriSadri languageSadri is a branch of Prakrit language and is regarded as a sister language of Oriya, Bengali and Angika. It is spoken in the Indian states of Jharkhand, Orissa and the north of West Bengal, and in Bangladesh....
Oriya languages
- Oriya (Oŗia)Oriya languageOriya , officially Odia from November, 2011, is an Indian language, belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European language family. It is mainly spoken in the Indian states of Orissa and West Bengal...
- Adivasi Oriya
- HalbiHalbi languageHalbi is an Eastern zone Indo-Aryan language of the Oriya subgroup, spoken by about 500,000 individuals across the central part of India. It is considered a dilect of Oriya language by linguist.It uses SOV word order , makes strong use of affixes, and places adjectives before nouns...
Tharu
- TharuTharu languageTharu is an Eastern zone Indo-Aryan language, or cluster of languages, spoken by the Tharu people. Not all Tharu speak distinct languages, but the languages of those who do may be divided as follows,...
(several languages)
Southern Zone languages
- Marathi
- Dakhini
- Konkani
- Nawayathi
Insular Indic
The insular languages are spoken in the islands of Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka, officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka is a country off the southern coast of the Indian subcontinent. Known until 1972 as Ceylon , Sri Lanka is an island surrounded by the Indian Ocean, the Gulf of Mannar and the Palk Strait, and lies in the vicinity of India and the...
and Maldives
Maldives
The Maldives , , officially Republic of Maldives , also referred to as the Maldive Islands, is an island nation in the Indian Ocean formed by a double chain of twenty-six atolls oriented north-south off India's Lakshadweep islands, between Minicoy Island and...
along with the island of Minicoy
Minicoy
Minicoy, locally known as Maliku is a census town in the Indian union territory of Lakshadweep and was formerly a part of Maldive Islands.-Etymology:...
.
The insular languages share several characteristics which set them apart significantly from their continental sister languages. (SIL makes them a separate branch of Indo-Aryan.) However, Sinhala and Dhivehi
Dhivehi language
Maldivian is an Indo-Aryan language predominantly spoken by about 350,000 people in the Maldives where it is the national language. It is also the first language of nearly 10,000 people in the island of Minicoy in the Union territory of Lakshadweep, India where the Mahl dialect of the Maldivian...
are no longer mutually intelligible.
- DhivehiDhivehi languageMaldivian is an Indo-Aryan language predominantly spoken by about 350,000 people in the Maldives where it is the national language. It is also the first language of nearly 10,000 people in the island of Minicoy in the Union territory of Lakshadweep, India where the Mahl dialect of the Maldivian...
- Sinhala
- VeddaVedda languageThe Vedda language is the language of the indigenous Vedda people of Sri Lanka. But communities, such as Coast Veddas and Anuradhapura Veddas, that do not strictly identify themselves as Veddas also use the Vedda language in part for communication during hunting and or for religious chants,...
Unclassified
The following languages have not been classified within the Indo-Aryan family.- Dhanwar Rai
- Tippera
- Kanjari
- Od
- Usui
- Vaagri Booli
- Darai
- Kumhali
- Chinali
See also
- Nuristani languagesNuristani languagesThe Nuristani languages are one of the three groups within the Indo-Iranian language family, alongside the much larger Indo-Aryan and Iranian groups. They are spoken primarily in eastern Afghanistan...
- Varieties of Hindi
- Proto-Indo-Iranian
- List of languages of India

