
Delhi Sultanate
Encyclopedia
The Delhi Sultanate is a term used to cover five short-lived, Delhi based kingdoms or sultan
ates, of Turkic
origin in medieval India
. The sultanates ruled from Delhi
between 1206 and 1526, when the last was replaced by the Mughal dynasty. The five dynasties were the Mamluk dynasty (1206–90); the Khilji dynasty
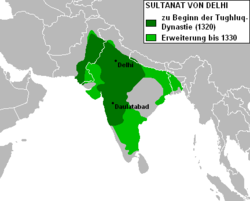
(1290–1320); the Tughlaq dynasty
(1320–1414); the Sayyid dynasty
(1414–51); and the Lodi dynasty (1451–1526).
Qutb-ud-din Aibak, a former slave (Mamluk
) of Muhammad of Ghor
, was the first sultan
of Delhi and his dynasty managed to conquer large areas of northern India. Afterwards the Khalji dynasty was also able to conquer most of central India, but both failed to unite the Indian subcontinent
. The sultanate are also noted for being one of the few states to repeatedly defeat the Mongol Empire
and thereby saving India from plundering raids and attacks.
The Sultanate ushered in a period of Indian cultural renaissance
. The resulting "Indo-Muslim" fusion of cultures left lasting syncretic monuments in architecture
, music
, literature
, religion and clothing. It is surmised that the Urdu
language (literally meaning "horde" or "camp" in various Turkic dialects) was born during this period as a result of the intermingling of the local speakers of Sanskritic Prakrit
s with immigrants speaking Persian
, Turkic
and Arabic
under the Muslim rulers. The Delhi Sultanate is the only Indo-Islamic empire to have enthroned one of the few female rulers in India, Razia Sultana
(1236–1240). In 1526 the Delhi Sultanate was absorbed by the emerging Mughal Empire
.

(d. 1206), based in Afghanistan
, had extended his state southwards at the expense of the Ghaznavids as far as Lahore
and much of the rajasthan and punjab and appointed Qutub-ud-din Aibak as governor
of this part of his realm. A slave of Cuman-Kipchak origin, he proclaimed independence after the death of his patron and ruled from Delhi. His line is therefore known as the Slave (Mamluk
) Dynasty on account of his origin. Aibak began the construction of Qutub Minar
, which was completed by Iltutmish
, his successor and son-in-law. Aibak's legitimate successor was his son Aramshah, but the nobles preferred Iltutmish, the Subedar of Badaun. Iltutmish was followed by Razia Sultana
, his daughter, who was a good administrator and the first female ruler in the Muslim world
. She was endowed with all qualities befitting a King, but she was not born of the right sex, and in the estimation of men all her virtues were worthless. Her rumored relationship with a Sidi adviser, Jamal-ud-Din Yaqut
, as he continued to rise in rank, forced her nobles to revolt against her. After Yaqut was killed and Razia imprisoned, she later wedded Altunia (the governor of Bhatinda), but she was killed by her nobles after 3 and half years. Balban succeeded her and ruled until 1286 CE. A great Emperor, he was a Sufi devotee and highly regarded their Saints; many a Sufi mystic settled in his sultanate, though only one of them rose to full ascendancy over him. Faced with revolts by conquered territories and rival families in the turmoil for succession after his death, the Mamluk dynasty came to an end in 1290.
lasted for close to a hundred years.In this period many parts of India got separated such as southern ind It produced two powerful Sultans, Muhammad-Bin Tughlaq and Firoz Shah Tughlaq. Ghias-ud-din Tughlaq (1320–1325), an efficient military commander, was the first ruler of the dynasty. He was succeeded by Jauna Khan, who took the title of Muhammad bin Tughlaq. A very powerful ruler, he shifted his capital in 1326 from Delhi to Devgiri (now known as Daulatabad). During the Qarachil expedition, he lost control over the empire and died in 1351. He was succeeded by Firoz shah Tughlaq (1351–1388) who was very successful as a reformer.
ruled Delhi Sultanate in India from 1414 to 1451. They succeeded the Tughlaq dynasty and ruled the Sultanate until they were displaced by the Lodi dynasty.
the
lodi dynasty was brought to an end by Babur
 In the first half of the 14th century, the Sultanate introduced a monetary economy
In the first half of the 14th century, the Sultanate introduced a monetary economy
in the provinces (sarkars) and districts (parganas) that had been established and founded a network of market centers, through which the traditional village economies were both exploited and stimulated to be drawn into the wider culture. State revenues remained based on a successful agriculture, which induced Sultan Muhammad bin Tughluq
(1325–51) to have village wells dug, to offer seed to the peasants, and to encourage cash crops like sugarcane
.
in the thirteenth century. However, the invasion of Timur
in 1398 significantly weakened the Delhi Sultanate. It revived briefly under the Lodis before it was conquered by the Mughal
emperor Babur
in 1526.
The last Lodi ruler, Ibrahim Lodi, was greatly disliked by his court and subjects. Upon the death of his father Sikander Lodi, he quashed a brief rebellion led by some of his nobles who wanted his younger brother Jalal Khan to be the Sultan. After seizing the throne, by having Jalal Khan murdered, he never really did succeed in pacifying his nobles. Subsequently Daulat Khan, the governor of Punjab
and Alam Khan, his uncle, sent an invitation to Babur, the ruler of Kabul
to invade Delhi
.
By way of superior generalship, vast experience in warfare, effective strategy and appropriate use of artillery, Babur
won the first Battle of Panipat (April 1526), in which Ibrahim Lodi was killed on the battlefield. Babur subsequently occupied Agra
and Delhi
and the new Mughal dynasty was to rule Delhi until 1857.
Sultan
Sultan is a title with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic language abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", and "dictatorship", derived from the masdar سلطة , meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be used as the title of certain rulers who...
ates, of Turkic
Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are peoples residing in northern, central and western Asia, southern Siberia and northwestern China and parts of eastern Europe. They speak languages belonging to the Turkic language family. They share, to varying degrees, certain cultural traits and historical backgrounds...
origin in medieval India
Medieval India
Medieval India refers to the Middle Ages i.e. 5th to 15th century AD in the Indian subcontinent, it includes:*Early Middle Ages: Middle kingdoms of India*Hoysala Empire*Kakatiya Kingdom*Delhi Sultanate*Ahom Kingdom*Reddy Kingdom...
. The sultanates ruled from Delhi
Delhi
Delhi , officially National Capital Territory of Delhi , is the largest metropolis by area and the second-largest by population in India, next to Mumbai. It is the eighth largest metropolis in the world by population with 16,753,265 inhabitants in the Territory at the 2011 Census...
between 1206 and 1526, when the last was replaced by the Mughal dynasty. The five dynasties were the Mamluk dynasty (1206–90); the Khilji dynasty
Khilji dynasty
The Khilji Sultanate was a dynasty of Turko-Afghan Khalaj origin who ruled large parts of South Asia from 1290 - 1320. They were the second dynasty to rule the Delhi Sultanate of India...
(1290–1320); the Tughlaq dynasty
Tughlaq dynasty
The Tughlaq dynasty of north India started in 1321 in Delhi when Ghazi Malik assumed the throne under the title of Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq. The Tughluqs were a Muslim family of Turkic origin...
(1320–1414); the Sayyid dynasty
Sayyid dynasty
The Sayyid dynasty ruled Delhi sultanate in India from 1414 to 1451. They succeeded the Tughlaq dynasty and ruled that sultanate until they were displaced by the Lodi dynasty.This family claimed to be Sayyids, or descendants of Prophet Muhammad...
(1414–51); and the Lodi dynasty (1451–1526).
Qutb-ud-din Aibak, a former slave (Mamluk
Mamluk
A Mamluk was a soldier of slave origin, who were predominantly Cumans/Kipchaks The "mamluk phenomenon", as David Ayalon dubbed the creation of the specific warrior...
) of Muhammad of Ghor
Muhammad of Ghor
Sultan Shahāb-ud-Din Muhammad Ghori , originally called Mu'izzuddīn Muḥammad Bin Sām , was a ruler of the Ghurid dynasty who reigned over a territory spanning present-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northern India.Shahabuddin Ghori reconquered the city of Ghazna Sultan Shahāb-ud-Din Muhammad Ghori...
, was the first sultan
Sultan
Sultan is a title with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic language abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", and "dictatorship", derived from the masdar سلطة , meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it came to be used as the title of certain rulers who...
of Delhi and his dynasty managed to conquer large areas of northern India. Afterwards the Khalji dynasty was also able to conquer most of central India, but both failed to unite the Indian subcontinent
Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent, also Indian Subcontinent, Indo-Pak Subcontinent or South Asian Subcontinent is a region of the Asian continent on the Indian tectonic plate from the Hindu Kush or Hindu Koh, Himalayas and including the Kuen Lun and Karakoram ranges, forming a land mass which extends...
. The sultanate are also noted for being one of the few states to repeatedly defeat the Mongol Empire
Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire , initially named as Greater Mongol State was a great empire during the 13th and 14th centuries...
and thereby saving India from plundering raids and attacks.
The Sultanate ushered in a period of Indian cultural renaissance
Renaissance
The Renaissance was a cultural movement that spanned roughly the 14th to the 17th century, beginning in Italy in the Late Middle Ages and later spreading to the rest of Europe. The term is also used more loosely to refer to the historical era, but since the changes of the Renaissance were not...
. The resulting "Indo-Muslim" fusion of cultures left lasting syncretic monuments in architecture
Indo-Islamic Architecture
Islamic contribution to architecture in the Indian subcontinent is far reaching and undeniable. New modes and principles of construction were developed reflecting the religious and social needs of the adherents of Islam.-Masjid and Mandir:...
, music
Ghazal
The ghazal is a poetic form consisting of rhyming couplets and a refrain, with each line sharing the same meter. A ghazal may be understood as a poetic expression of both the pain of loss or separation and the beauty of love in spite of that pain. The form is ancient, originating in 6th century...
, literature
Delhi Sultanate literature
The rise of Persian speaking people to the throne naturally resulted in the spread of the Persian language in India. It was the official language and soon literary works in the language began to appear. Initially Persian literature talked about topics which were familiar to those from Persia...
, religion and clothing. It is surmised that the Urdu
Urdu
Urdu is a register of the Hindustani language that is identified with Muslims in South Asia. It belongs to the Indo-European family. Urdu is the national language and lingua franca of Pakistan. It is also widely spoken in some regions of India, where it is one of the 22 scheduled languages and an...
language (literally meaning "horde" or "camp" in various Turkic dialects) was born during this period as a result of the intermingling of the local speakers of Sanskritic Prakrit
Prakrit
Prakrit is the name for a group of Middle Indic, Indo-Aryan languages, derived from Old Indic dialects. The word itself has a flexible definition, being defined sometimes as, "original, natural, artless, normal, ordinary, usual", or "vernacular", in contrast to the literary and religious...
s with immigrants speaking Persian
Persian language
Persian is an Iranian language within the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European languages. It is primarily spoken in Iran, Afghanistan, Tajikistan and countries which historically came under Persian influence...
, Turkic
Turkic languages
The Turkic languages constitute a language family of at least thirty five languages, spoken by Turkic peoples across a vast area from Eastern Europe and the Mediterranean to Siberia and Western China, and are considered to be part of the proposed Altaic language family.Turkic languages are spoken...
and Arabic
Arabic language
Arabic is a name applied to the descendants of the Classical Arabic language of the 6th century AD, used most prominently in the Quran, the Islamic Holy Book...
under the Muslim rulers. The Delhi Sultanate is the only Indo-Islamic empire to have enthroned one of the few female rulers in India, Razia Sultana
Razia Sultana
Razia al-Din , throne name Jalâlat ud-Dîn Raziyâ , usually referred to in history as Razia Sultan, was the Sultan of Delhi in India from 1236 to May 1240. She was of Seljuq slave ancestry and like some other Muslim princesses of the time, she was trained to lead armies and administer kingdoms if...
(1236–1240). In 1526 the Delhi Sultanate was absorbed by the emerging Mughal Empire
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
.

Mamluk (Slave) Dynasty
Muhammad of GhorMuhammad of Ghor
Sultan Shahāb-ud-Din Muhammad Ghori , originally called Mu'izzuddīn Muḥammad Bin Sām , was a ruler of the Ghurid dynasty who reigned over a territory spanning present-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northern India.Shahabuddin Ghori reconquered the city of Ghazna Sultan Shahāb-ud-Din Muhammad Ghori...
(d. 1206), based in Afghanistan
Afghanistan
Afghanistan , officially the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located in the centre of Asia, forming South Asia, Central Asia and the Middle East. With a population of about 29 million, it has an area of , making it the 42nd most populous and 41st largest nation in the world...
, had extended his state southwards at the expense of the Ghaznavids as far as Lahore
Lahore
Lahore is the capital of the Pakistani province of Punjab and the second largest city in the country. With a rich and fabulous history dating back to over a thousand years ago, Lahore is no doubt Pakistan's cultural capital. One of the most densely populated cities in the world, Lahore remains a...
and much of the rajasthan and punjab and appointed Qutub-ud-din Aibak as governor
Governor
A governor is a governing official, usually the executive of a non-sovereign level of government, ranking under the head of state...
of this part of his realm. A slave of Cuman-Kipchak origin, he proclaimed independence after the death of his patron and ruled from Delhi. His line is therefore known as the Slave (Mamluk
Mamluk
A Mamluk was a soldier of slave origin, who were predominantly Cumans/Kipchaks The "mamluk phenomenon", as David Ayalon dubbed the creation of the specific warrior...
) Dynasty on account of his origin. Aibak began the construction of Qutub Minar
Qutub Minar
Qutub Minar also Qutb Minar, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Located in Delhi, India. The Qutub Minar is constructed with red sandstone and marble, and is the tallest minaret in India, with a height of 72.5 meters , contains 379 stairs to reach the top, and the diameter of base is 14.3 meters...
, which was completed by Iltutmish
Iltutmish
Shams-ud-din Iltutmish was the third ruler of the Mamluk dynasty of Delhi of Turkic origin. He was a slave of Qutub-ud-din-Aybak and later became his son-in-law and close lieutenant. He was the Governor of Badaun when he deposed Qutub-ud-din's successor Aram Shah and acceeded to the throne of the...
, his successor and son-in-law. Aibak's legitimate successor was his son Aramshah, but the nobles preferred Iltutmish, the Subedar of Badaun. Iltutmish was followed by Razia Sultana
Razia Sultana
Razia al-Din , throne name Jalâlat ud-Dîn Raziyâ , usually referred to in history as Razia Sultan, was the Sultan of Delhi in India from 1236 to May 1240. She was of Seljuq slave ancestry and like some other Muslim princesses of the time, she was trained to lead armies and administer kingdoms if...
, his daughter, who was a good administrator and the first female ruler in the Muslim world
Muslim world
The term Muslim world has several meanings. In a religious sense, it refers to those who adhere to the teachings of Islam, referred to as Muslims. In a cultural sense, it refers to Islamic civilization, inclusive of non-Muslims living in that civilization...
. She was endowed with all qualities befitting a King, but she was not born of the right sex, and in the estimation of men all her virtues were worthless. Her rumored relationship with a Sidi adviser, Jamal-ud-Din Yaqut
Jamal-ud-Din Yaqut
Jamal-ud-Din Yaqut was an Abyssinian slave who was a close confidante of Razia Sultana, the first female monarch of the Delhi Sultanate in India and is speculated to have been her lover...
, as he continued to rise in rank, forced her nobles to revolt against her. After Yaqut was killed and Razia imprisoned, she later wedded Altunia (the governor of Bhatinda), but she was killed by her nobles after 3 and half years. Balban succeeded her and ruled until 1286 CE. A great Emperor, he was a Sufi devotee and highly regarded their Saints; many a Sufi mystic settled in his sultanate, though only one of them rose to full ascendancy over him. Faced with revolts by conquered territories and rival families in the turmoil for succession after his death, the Mamluk dynasty came to an end in 1290.
Khalji rulers of Delhi (1290-1320)
- Jalal ud din Firuz KhiljiJalal ud din Firuz KhiljiJalaluddin Firuz Khilji was the first sultan of the Khilji dynasty, who reigned from 1290 to 1296. He built his capital at Kilughari, a few miles from the city of Delhi and completed the unfinished palace and gardens of Sultan Qaiqabad.) He ruled from there for six years.-Early life and...
1290-1296 - Alauddin KhiljiAlauddin KhiljiAli Gurshap Khan better known by his titular name as Sultan Ala-ud-din Khilji was the second ruler of the Turko-Afghan Khilji dynasty in India.He was a well and capable ruler. He belonged to the Afghanized Turkic tribe of the Khiljis...
1296-1316 - Qutb ud din Mubarak ShahQutb ud din Mubarak ShahQutb-ud-din Mubarak Shah Khilji was the third and last ruler of the Khilji dynasty in Sultanate of Delhi, India. Qutb-ud-din Khilji was the son and successor of Alauddin Khilji....
1316-1320
Tughlaq
The Tughlaq dynastyTughlaq dynasty
The Tughlaq dynasty of north India started in 1321 in Delhi when Ghazi Malik assumed the throne under the title of Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq. The Tughluqs were a Muslim family of Turkic origin...
lasted for close to a hundred years.In this period many parts of India got separated such as southern ind It produced two powerful Sultans, Muhammad-Bin Tughlaq and Firoz Shah Tughlaq. Ghias-ud-din Tughlaq (1320–1325), an efficient military commander, was the first ruler of the dynasty. He was succeeded by Jauna Khan, who took the title of Muhammad bin Tughlaq. A very powerful ruler, he shifted his capital in 1326 from Delhi to Devgiri (now known as Daulatabad). During the Qarachil expedition, he lost control over the empire and died in 1351. He was succeeded by Firoz shah Tughlaq (1351–1388) who was very successful as a reformer.
Sayyid
The Sayyid dynastySayyid dynasty
The Sayyid dynasty ruled Delhi sultanate in India from 1414 to 1451. They succeeded the Tughlaq dynasty and ruled that sultanate until they were displaced by the Lodi dynasty.This family claimed to be Sayyids, or descendants of Prophet Muhammad...
ruled Delhi Sultanate in India from 1414 to 1451. They succeeded the Tughlaq dynasty and ruled the Sultanate until they were displaced by the Lodi dynasty.
the
lodi dynasty was brought to an end by Babur
Monetary system

Economic system
An economic system is the combination of the various agencies, entities that provide the economic structure that defines the social community. These agencies are joined by lines of trade and exchange along which goods, money etc. are continuously flowing. An example of such a system for a closed...
in the provinces (sarkars) and districts (parganas) that had been established and founded a network of market centers, through which the traditional village economies were both exploited and stimulated to be drawn into the wider culture. State revenues remained based on a successful agriculture, which induced Sultan Muhammad bin Tughluq
Muhammad bin Tughluq
Muhammad bin Tughluq was the Turkic Sultan of Delhi from 1325 to 1351. He was the eldest son of Ghiyas-ud-din Tughlaq.He was born in Kotla Tolay Khan in Multan. His wife was daughter of the raja of Dipalpur...
(1325–51) to have village wells dug, to offer seed to the peasants, and to encourage cash crops like sugarcane
Sugarcane
Sugarcane refers to any of six to 37 species of tall perennial grasses of the genus Saccharum . Native to the warm temperate to tropical regions of South Asia, they have stout, jointed, fibrous stalks that are rich in sugar, and measure two to six metres tall...
.
Mongol invasion and the fall of the Sultanate
Perhaps the greatest contribution of the Sultanate was its temporary success in insulating the subcontinent from the potential devastation of the Mongol invasion from Central AsiaCentral Asia
Central Asia is a core region of the Asian continent from the Caspian Sea in the west, China in the east, Afghanistan in the south, and Russia in the north...
in the thirteenth century. However, the invasion of Timur
Timur
Timur , historically known as Tamerlane in English , was a 14th-century conqueror of West, South and Central Asia, and the founder of the Timurid dynasty in Central Asia, and great-great-grandfather of Babur, the founder of the Mughal Dynasty, which survived as the Mughal Empire in India until...
in 1398 significantly weakened the Delhi Sultanate. It revived briefly under the Lodis before it was conquered by the Mughal
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire , or Mogul Empire in traditional English usage, was an imperial power from the Indian Subcontinent. The Mughal emperors were descendants of the Timurids...
emperor Babur
Babur
Babur was a Muslim conqueror from Central Asia who, following a series of setbacks, finally succeeded in laying the basis for the Mughal dynasty of South Asia. He was a direct descendant of Timur through his father, and a descendant also of Genghis Khan through his mother...
in 1526.
The last Lodi ruler, Ibrahim Lodi, was greatly disliked by his court and subjects. Upon the death of his father Sikander Lodi, he quashed a brief rebellion led by some of his nobles who wanted his younger brother Jalal Khan to be the Sultan. After seizing the throne, by having Jalal Khan murdered, he never really did succeed in pacifying his nobles. Subsequently Daulat Khan, the governor of Punjab
Punjab region
The Punjab , also spelled Panjab |water]]s"), is a geographical region straddling the border between Pakistan and India which includes Punjab province in Pakistan and the states of the Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Chandigarh and some northern parts of the National Capital Territory of Delhi...
and Alam Khan, his uncle, sent an invitation to Babur, the ruler of Kabul
Kabul
Kabul , spelt Caubul in some classic literatures, is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. It is also the capital of the Kabul Province, located in the eastern section of Afghanistan...
to invade Delhi
Delhi
Delhi , officially National Capital Territory of Delhi , is the largest metropolis by area and the second-largest by population in India, next to Mumbai. It is the eighth largest metropolis in the world by population with 16,753,265 inhabitants in the Territory at the 2011 Census...
.
By way of superior generalship, vast experience in warfare, effective strategy and appropriate use of artillery, Babur
Babur
Babur was a Muslim conqueror from Central Asia who, following a series of setbacks, finally succeeded in laying the basis for the Mughal dynasty of South Asia. He was a direct descendant of Timur through his father, and a descendant also of Genghis Khan through his mother...
won the first Battle of Panipat (April 1526), in which Ibrahim Lodi was killed on the battlefield. Babur subsequently occupied Agra
Agra
Agra a.k.a. Akbarabad is a city on the banks of the river Yamuna in the northern state of Uttar Pradesh, India, west of state capital, Lucknow and south from national capital New Delhi. With a population of 1,686,976 , it is one of the most populous cities in Uttar Pradesh and the 19th most...
and Delhi
Delhi
Delhi , officially National Capital Territory of Delhi , is the largest metropolis by area and the second-largest by population in India, next to Mumbai. It is the eighth largest metropolis in the world by population with 16,753,265 inhabitants in the Territory at the 2011 Census...
and the new Mughal dynasty was to rule Delhi until 1857.
Mamluk dynasty
- Qutb-ud-din Aibak (1206–1210), appointed Naib us Sultanat by Muhammad of GhorMuhammad of GhorSultan Shahāb-ud-Din Muhammad Ghori , originally called Mu'izzuddīn Muḥammad Bin Sām , was a ruler of the Ghurid dynasty who reigned over a territory spanning present-day Afghanistan, Pakistan and northern India.Shahabuddin Ghori reconquered the city of Ghazna Sultan Shahāb-ud-Din Muhammad Ghori...
, first Muslim Emperor of India, ruled with Delhi as capital - Aram ShahAram ShahAram Shah was the second sultan of the Mamluk Sultanate . The relationship of Aram with Qutb-ud-din Aibak is a subject of controversy. According to some, he was Aibak's son, but Minhaj-us-Siraj distinctly writes that Qutub-ud-din only had three daughters. Abul Fazl has made the "astonishing...
(1210–1211). - Shams ud din IltutmishIltutmishShams-ud-din Iltutmish was the third ruler of the Mamluk dynasty of Delhi of Turkic origin. He was a slave of Qutub-ud-din-Aybak and later became his son-in-law and close lieutenant. He was the Governor of Badaun when he deposed Qutub-ud-din's successor Aram Shah and acceeded to the throne of the...
(1211–1236), son-in-law of Qut-bud-din Aybak. - Rukn ud din FiruzRukn ud din FiruzRukn ud din Firuz was the fourth sultan of the Mamluk Sultanate , who ruled for just seven months. He was the son of Shams ud din Iltutmish and was raised to become Iltutmish's heir. However after Iltutmish's death in April 1236 he was viewed as being unfit to rule and was murdered in November 1236...
(1236), son of Iltutmish. - Raziyyat-ud-din Sultana (1236–1240), daughter of Iltutmish.
- Muiz ud din BahramMuiz ud din BahramMuiz ud din Bahram was the sixth sultan of the Mamluk Dynasty . He was the son of Shams ud din Iltutmish and brother of Razia Sultan . While his sister was in Bathinda, he declared himself king with the support of forty chiefs...
(1240–1242), son of Iltutmish. - Ala ud din MasudAla ud din MasudAla ud din Masud was the seventh sultan of the Mamluk dynasty . He was the son of Rukn ud din Firuz and the nephew of Razia Sultan . After his predecessor, Muiz ud din Bahram, was murdered by the army in 1242 after years of disorder, the chiefs chose for him to become the next ruler...
(1242–1246), son of Ruk-nud-din. - Nasir ud din MahmudNasir ud din MahmudNasir ud din Mahmud, Nasir ud din Firuz Shah was the eighth sultan of the Mamluk Sultanate . He was the youngest son of Shams ud din Iltutmish , and he succeeded Ala ud din Masud after the chiefs replaced Masud when they felt that he began to behave as a tyrant.As a ruler, Mahmud was known to be...
(1246–1266), son of Iltutmish. - Ghiyas ud din BalbanGhiyas ud din BalbanGhiyasuddin Balban was ninth sultan of the Mamluk dynasty who ruled from 1266 to 1287.-Biography:He was son of a Central Asian Turkic noble of the Ilbari tribe, but as a child he was captured by Mongols and sold as a slave at Ghazni...
(1266–1286), ex-slave, son-in-law of Sultan Nasir ud din Mahmud. - Muiz ud din QaiqabadMuiz ud din QaiqabadMuiz ud din Qaiqabad was the tenth sultan the Mamluk dynasty . He was the son of Bughra Khan as well as grandson of Ghiyas ud din Balban ....
(1286–1290), grandson of Balban and Nasir-ud-din.

Khilji dynasty
- Jalal ud din Firuz KhiljiJalal ud din Firuz KhiljiJalaluddin Firuz Khilji was the first sultan of the Khilji dynasty, who reigned from 1290 to 1296. He built his capital at Kilughari, a few miles from the city of Delhi and completed the unfinished palace and gardens of Sultan Qaiqabad.) He ruled from there for six years.-Early life and...
(1290–1296) - Alauddin KhiljiAlauddin KhiljiAli Gurshap Khan better known by his titular name as Sultan Ala-ud-din Khilji was the second ruler of the Turko-Afghan Khilji dynasty in India.He was a well and capable ruler. He belonged to the Afghanized Turkic tribe of the Khiljis...
(1296–1316) - Qutb ud din Mubarak ShahQutb ud din Mubarak ShahQutb-ud-din Mubarak Shah Khilji was the third and last ruler of the Khilji dynasty in Sultanate of Delhi, India. Qutb-ud-din Khilji was the son and successor of Alauddin Khilji....
(1316–1320)
Tughlaq dynasty
- Ghiyath al-Din TughluqGhiyath al-Din TughluqGhiyas ud-Din Tughluq , real name Ghazi Malik was the founder and first ruler of the Turkic Muslim Tughluq dynasty in India, who reigned over Sultanate of Delhi . He has been the founder of the third city of Delhi called Tughluqabad.Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq was in origin a poor Qarauna who took...
(1321–1325) - Muhammad bin TughluqMuhammad bin TughluqMuhammad bin Tughluq was the Turkic Sultan of Delhi from 1325 to 1351. He was the eldest son of Ghiyas-ud-din Tughlaq.He was born in Kotla Tolay Khan in Multan. His wife was daughter of the raja of Dipalpur...
) (1325–1351) - Mahmud Ibn MuhammadMahmud ibn MuhammadMahmud ibn Muhammad was the seventh leader of the Husainid Dynasty and the ruler of Tunisia from 1814 until his death in 1824....
(March 1351) - Firuz Shah TughluqFiruz Shah Tughluq-External links:*...
(1351–1388) - Ghiyas-ud-Din Tughluq IIGhiyas-ud-Din Tughluq IIGHIYASUDDIN TUGHLUQ DEFEATED THE LAST KHALJI RULER,GHAZI MALIK AND ESTABLISHED A NEW DYNASTY IN 1320.GHIYASUDDIN TUGHLUQ WAS AN ABLE AND BRAVE RULER.HE HAD TO FACE A NUMBER OF REFORMS WHICH HE FACED BOLDLY.HE INTRODUCED A NO OF REFORMS FOR HIS PEOPLE....
(1388–1389) - Abu Bakr Shah (1389–1390)
- Nasir ud din Muhammad Shah IIINasir ud din Muhammad Shah IIINasir ud din Muhammad Shah III was ruler of the Muslim Turkic Tughlaq dynasty.Abu Bakr became ruler of the Tughlaq Empire. However, his brother or nephew, Nasir ud din Muhammad Shah III, also desired to be ruler, and struggled against Abu Bakr over the control of the throne...
(1390–1393) - Sikander Shah I (March - April 1393)
- Nasiruddin Mahmud ShahMahmud Shah (Sultan of Bengal)Nasiruddin Mahmud Shah was a Sultan of Bengal. He was a descendant of Sultan Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah of Bengal. Nasiruddin took the title of Nasiruddin Abul Muzaffar Mahmud Shah when he ascended the power in 1435 AD...
(Sultan Mahmud II) at Delhi (1393–1394) - Nusrat Shah, grandson of Firuz Shah TughluqFiruz Shah Tughluq-External links:*...
, controlled the west from FirozabadFirozabadFirozabad is a city in India, in the state of Uttar Pradesh.The ancient name of this town was Chandwar nagar; it is said that once in reign of Akbar the great, revenue was being brought through the city. it was looted by the people who lived here...
and Nasiruddin Mahmud Shah, son of Mahmud Nasir ud din, controlled the east from Delhi (1394–1398)
Lodi dynasty
- Bahlul Lodi (1451–1489)
- Sikandar Lodi (1489–1517)
- Ibrahim Lodi (1517–26), killed by BaburBaburBabur was a Muslim conqueror from Central Asia who, following a series of setbacks, finally succeeded in laying the basis for the Mughal dynasty of South Asia. He was a direct descendant of Timur through his father, and a descendant also of Genghis Khan through his mother...
in the First Battle of Panipat on April 20, 1526.

